Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diet-Induced Weight Loss and Vascular Endothelium
2.1. Endothelial Function in DIWL
2.2. Circulating Biomarkers in DIWL
3. Surgery-Induced Weight Loss and Endothelial Function
3.1. Endothelial Function in SIWL
3.2. Circulating Biomarkers in SIWL
4. Mediators Linking Weight Loss and Vascular Endothelium
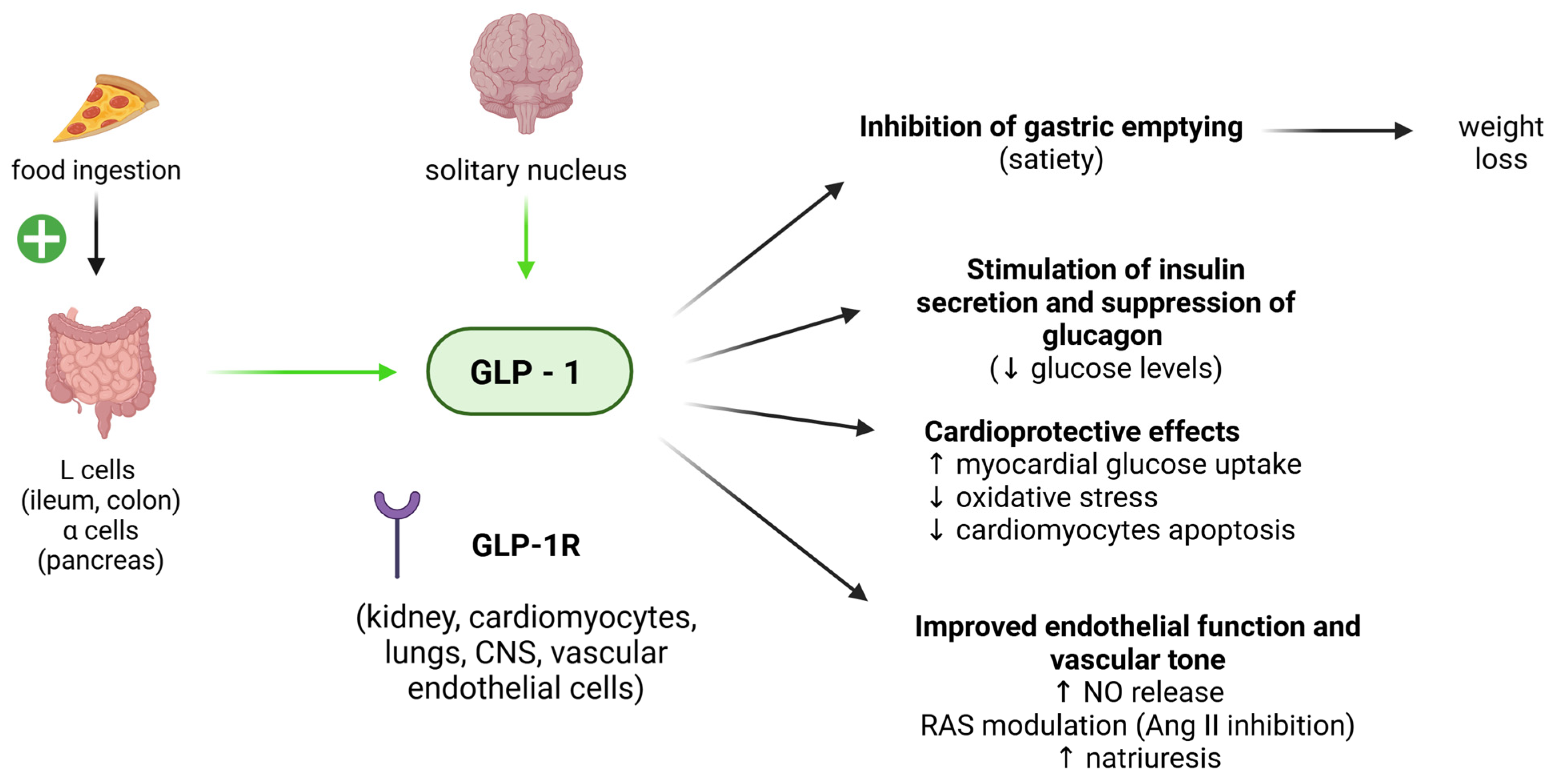
4.1. GLP-1
4.2. Ghrelin
4.3. Adiponectin
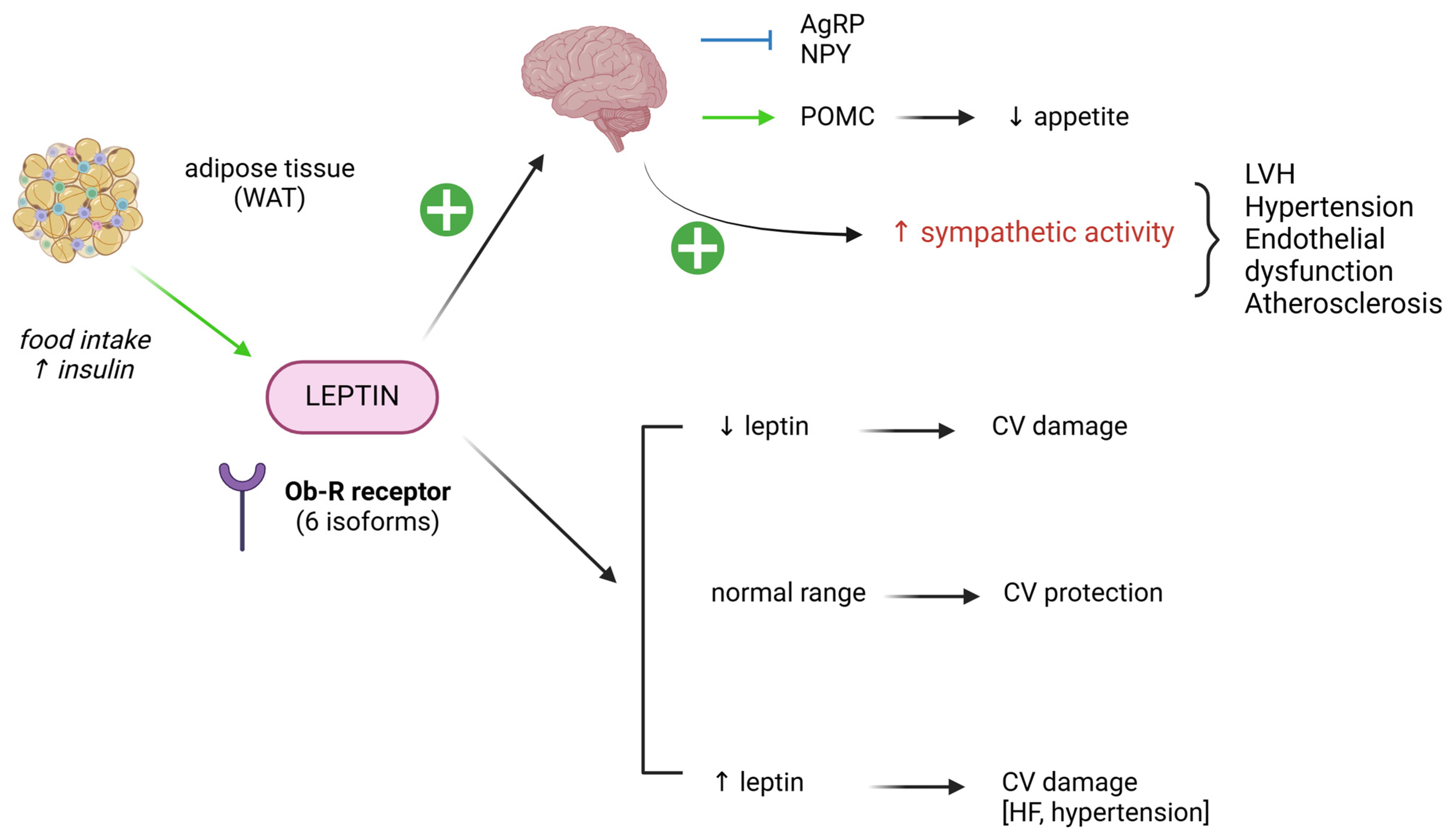
4.4. Leptin
4.5. Glucose
5. Conclusions and Gaps in Evidence
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suwala, S.; Junik, R. Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference as Predictors of Above-Average Increased Cardiovascular Risk Assessed by the SCORE2 and SCORE2-OP Calculators and the Proposition of New Optimal Cut-Off Values: Cross-Sectional Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdeva, O.; Borodkina, D.; Uchasova, E.; Dyleva, Y.; Barbarash, O. Localization of fat depots and cardiovascular risk. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Neeland, I.J.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; Cuevas, A.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Waist circumference as a vital sign in clinical practice: A Consensus Statement from the IAS and ICCR Working Group on Visceral Obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, Z.J.; Bleich, S.N.; Cradock, A.L.; Barrett, J.L.; Giles, C.M.; Flax, C.; Long, M.W.; Gortmaker, S.L. Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, M.; Hill, M.A.; Cohen, P.; Sowers, J.R. Obesity, Adipose Tissue and Vascular Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillana, N.; Astudillo-Guerrero, C.; D’Espessailles, A.; Cruz, G. White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Qian, M.; Kyler, K.; Xu, J. Adipose Tissue-Endothelial Cell Interactions in Obesity-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 681581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucka, S.; Miodonska, M.; Jakubiak, G.K.; Starzak, M.; Cieslar, G.; Stanek, A. Endothelial Function Assessment by Flow-Mediated Dilation Method: A Valuable Tool in the Evaluation of the Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinacci, M.; Krahn, T.; Dinh, W.; Volk, H.D.; Dungen, H.D.; Wagner, J.; Konen, T.; von Ahsen, O. Circulating endothelial cells as biomarker for cardiovascular diseases. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.Y.; Teo, A.; Yeo, T.W. Overview of the Assessment of Endothelial Function in Humans. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 542567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallogly, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Hung, J.D.; Brittan, M.; Skinner, E.M.; Mitchell, A.J.; Medine, C.; Luque, N.; Zodda, E.; Cascante, M.; et al. Generation of a Novel In Vitro Model to Study Endothelial Dysfunction from Atherothrombotic Specimens. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2021, 35, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Peltonen, M.; Jacobson, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Karason, K.; Wedel, H.; Ahlin, S.; Anveden, A.; Bengtsson, C.; Bergmark, G.; et al. Bariatric surgery and long-term cardiovascular events. JAMA 2012, 307, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Wahab, R.; le Roux, C.W. A review of the evidence on cardiovascular outcomes from obesity treatment. Obes. Pillars 2023, 7, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Veldhuisen, S.L.; Gorter, T.M.; van Woerden, G.; de Boer, R.A.; Rienstra, M.; Hazebroek, E.J.; van Veldhuisen, D. Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 1955–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, K.; Rashid, A.M.; Memon, U.A.A.; Fatima, S.S.; Javaid, S.S.; Shahid, O.; Zehri, F.; Obaid, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Almas, T.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and its Effect on Endothelial Function: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Aros, F.; Gòmez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Hao, Q.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Li, X.Z.; Yuan, Z.M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, S.L.; Liu, P.M. Low-Carbohydrate Diet Score and Coronary Artery Calcium Progression: Results from the CARDIA Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovski, E.; Zurbau, A.; Vuksan, V. Carbohydrates and endothelial function: Is a low-carbohydrate diet or a low-glycemic index diet favourable for vascular health? Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E.; Weigle, D.S.; Frayo, R.S.; Breen, P.A.; Ma, M.K.; Dellinger, E.P.; Purnell, J.Q. Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitakari, M.; Ilvonen, T.; Ahotupa, M.; Lehtimaki, T.; Harmoinen, A.; Suominen, P.; Elo, J.; Hartiala, J.; Raitakari, O. Weight reduction with very-low-caloric diet and endothelial function in overweight adults: Role of plasma glucose. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Koelman, L.; Rodrigues, C.E. Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: A systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bussel, B.C.; Henry, R.M.; Ferreira, I.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.; van der Kallen, C.J.; Twisk, J.W.; Feskens, E.J.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D. A healthy diet is associated with less endothelial dysfunction and less low-grade inflammation over a 7-year period in adults at risk of cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Song, Z.; Yao, X.; Xiao, Q.; Fu, H.; Tang, L. Exercise interventions for the effect of endothelial function in hypertensive patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2024, 26, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhen, K.; Ren, S.; Lv, Y.; Yu, L. Effect of continuous aerobic exercise on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1043108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ras, R.T.; Streppel, M.T.; Draijer, R.; Zock, P.L. Flow-mediated dilation and cardiovascular risk prediction: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, P.J.; Zeegers, M.P.; Mensink, R.P. Weight loss improves fasting flow-mediated vasodilation in adults: A meta-analysis of intervention studies. Atherosclerosis 2015, 239, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; Kusters, Y.H.; Houben, A.J.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Mensink, R.P. Diet-induced weight loss improves not only cardiometabolic risk markers but also markers of vascular function: A randomized controlled trial in abdominally obese men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Ahmid, Z.; Ashor, A.W.; Shannon, O.; Stephan, B.C.M.; Siervo, M. Effects of dietary-based weight loss interventions on biomarkers of endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 77, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Biomarkers of endothelial activation and dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, D.C.; Varner, S.E.; Nerem, R.M.; Medford, R.M.; Alexander, R.W. Oscillatory shear stress stimulates adhesion molecule expression in cultured human endothelium. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, J.J.; Chen, L.J.; Lee, C.I.; Lee, P.L.; Lee, D.Y.; Tsai, M.C.; Lin, C.W.; Usami, S.; Chien, S. Mechanisms of induction of endothelial cell E-selectin expression by smooth muscle cells and its inhibition by shear stress. Blood 2007, 110, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Gatt, A.; Liu, J. E-selectin in vascular pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1401399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichmann, A.; Simons, M. VEGF signaling inside vascular endothelial cells and beyond. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratliff, J.C.; Mutungi, G.; Puglisi, M.J.; Volek, J.S.; Fernandez, M.L. Eggs modulate the inflammatory response to carbohydrate restricted diets in overweight men. Nutr. Metab. 2008, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, E.L.; Rissanen, A.; Bruun, J.M.; Skogstrand, K.; Tonstad, S.; Hougaard, D.M.; Richelsen, B. Weight loss larger than 10% is needed for general improvement of levels of circulating adiponectin and markers of inflammation in obese subjects: A 3-year weight loss study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilbronn, L.K.; Noakes, M.; Clifton, P.M. Energy restriction and weight loss on very-low-fat diets reduce C-reactive protein concentrations in obese, healthy women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 968–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, N.; Vita, J.A.; McDonnell, M.; Forse, A.R.; Istfan, N.; Stoeckl, M.; Lipinska, I.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Apovian, C.M. Effect of medical and surgical weight loss on endothelial vasomotor function in obese patients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamialahmadi, T.; Alidadi, M.; Atkin, S.L.; Kroh, M.; Almahmeed, W.; Moallem, S.A.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Rodriguez, J.H.; Santos, R.D.; Ruscica, M.; et al. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Flow-Mediated Vasodilation as a Measure of Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Shikora, S.A.; Aarts, E.; Aminian, A.; Angrisani, L.; Cohen, R.V.; De Luca, M.; Faria, S.L.; Goodpaster, K.P.S.; Haddad, A.; et al. 2022 American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders (IFSO) Indications for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Zese, M.; Bandini, G.; Zappa, M.A.; Bardi, U.; Carbonelli, M.G.; Carrano, F.M.; Casella, G.; Chianelli, M.; Chiappetta, S.; et al. SICOB Italian clinical practice guidelines for the surgical treatment of obesity and associated diseases using GRADE methodology on bariatric and metabolic surgery. Updates Surg. 2024. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13304-024-01996-z (accessed on 27 January 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kane, M.; Parretti, H.M.; Pinkney, J.; Welbourn, R.; Hughes, C.A.; Mok, J.; Walker, N.; Thomas, D.; Devin, J.; Coulman, K.D.; et al. British Obesity and Metabolic Surgery Society Guidelines on perioperative and postoperative biochemical monitoring and micronutrient replacement for patients undergoing bariatric surgery-2020 update. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brethauer, S.A.; Heneghan, H.M.; Eldar, S.; Gatmaitan, P.; Huang, H.; Kashyap, S.; Gornik, H.L.; Kirwan, J.P.; Schauer, P.R. Early effects of gastric bypass on endothelial function, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk in obese patients. Surg. Endosc. 2011, 25, 2650–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, G.A.; Peraza, J.; Bravo, S.; Toplosky, L.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Morton, J.M. One year improvements in cardiovascular risk factors: A comparative trial of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs. adjustable gastric banding. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syn, N.L.; Cummings, D.E.; Wang, L.Z.; Lin, D.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Loh, M.; Koh, Z.J.; Chew, C.A.; Loo, Y.E.; Tai, B.B.; et al. Association of metabolic-bariatric surgery with long-term survival in adults with and without diabetes: A one-stage meta-analysis of matched cohort and prospective controlled studies with 174 772 participants. Lancet 2021, 397, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, M.N.; Guidone, C.; Cefalo, C.; Capaldo, B.; Riccardi, G.; Mingrone, G. Effects of bariatric surgery on markers of subclinical atherosclerosis and endothelial function: A meta-analysis of literature studies. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerla, R.; Tarzia, P.; Sestito, A.; Di Monaco, A.; Infusino, F.; Matera, D.; Greco, F.; Tacchino, R.M.; Lanza, G.A.; Crea, F. Effect of bariatric surgery on peripheral flow-mediated dilation and coronary microvascular function. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 22, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.D.; Joy, G.; Knott, K.D.; Augusto, J.B.; Lau, C.; Bhuva, A.N.; Seraphim, A.; Evain, T.; Brown, L.A.E.; Chowdhary, A.; et al. The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Coronary Microvascular Function Assessed Using Automated Quantitative Perfusion CMR. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2024, 17, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigornia, S.J.; Mott, M.M.; Hess, D.T.; Apovian, C.M.; McDonnell, M.E.; Duess, M.A.; Kluge, M.A.; Fiscale, A.J.; Vita, J.A.; Gokce, N. Long-term successful weight loss improves vascular endothelial function in severely obese individuals. Obesity 2010, 18, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Largani, M.; Nojomi, M.; Aghili, R.; Otaghvar, H.A.; Tanha, K.; Seyedi, S.H.S.; Mottaghi, A. Evaluation of all Types of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery and its Consequences: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 651–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi, J.; Alizadeh, S. Effect of Surgically Induced Weight Loss on Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 3549–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popko, K.; Gorska, E.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Plywaczewski, R.; Stoklosa, A.; Gorecka, D.; Pyrzak, B.; Demkow, U. Proinflammatory cytokines Il-6 and TNF-alpha and the development of inflammation in obese subjects. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010, 15 (Suppl. S2), 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbau, V.; Bruna, M.; Canelles, E.; Guaita, M.; Mulas, C.; Bases, C.; Celma, I.; Puche, J.; Marcaida, G.; Oviedo, M.; et al. A prospective study on inflammatory parameters in obese patients after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.R. Inflammatory markers and bariatric surgery: A meta-analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askarpour, M.; Khani, D.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaedi, E.; Alizadeh, S. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Serum Inflammatory Factors of Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2631–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolberg, C.R.; Mundbjerg, L.H.; Funch-Jensen, P.; Gram, B.; Bladbjerg, E.M.; Juhl, C.B. Effects of gastric bypass surgery followed by supervised physical training on inflammation and endothelial function: A randomized controlled trial. Atherosclerosis 2018, 273, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1409–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, A.R.; DeYoung, M.B.; Lowe, C.; Parkes, D.G. GLP-1 receptor activated insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells: Mechanism and glucose dependence. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M.; Morgan, L.M.; Tredger, J.A.; Deacon, S.; Wright, J.; Marks, V. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36)amide and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide secretion in response to nutrient ingestion in man: Acute post-prandial and 24-h secretion patterns. J. Endocrinol. 1993, 138, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, M.E.; Malkova, D. Altered gut and adipose tissue hormones in overweight and obese individuals: Cause or consequence? Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhatbegovic, L.; Mrsic, D.; Macic-Dzankovic, A. The benefits of GLP1 receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2023, 4, 1293926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyar, G.; Umudum, F.Z.; Akbas, N. Changes in ghrelin, GLP-1, and PYY levels after diet and exercise in obese individuals. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2024, 70, e20230263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdich, C.; Toubro, S.; Buemann, B.; Lysgard Madsen, J.; Juul Holst, J.; Astrup, A. The role of postprandial releases of insulin and incretin hormones in meal-induced satiety—Effect of obesity and weight reduction. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, J.; Ryberg, M.; Mellberg, C.; Andersson, T.; Chorell, E.; Lindahl, B.; Larsson, C.; Holst, J.J.; Olsson, T. Postprandial levels of GLP-1, GIP and glucagon after 2 years of weight loss with a Paleolithic diet: A randomised controlled trial in healthy obese women. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumithran, P.; Prendergast, L.A.; Delbridge, E.; Purcell, K.; Shulkes, A.; Kriketos, A.; Proietto, J. Long-term persistence of hormonal adaptations to weight loss. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, T.C.; Jocken, J.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S. Decreased glucagon-like peptide 1 release after weight loss in overweight/obese subjects. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, P.F.; Jensen, F.K.; Holst, J.J.; Haugaard, S.B.; Nilas, L.; Madsbad, S. The effect of a very low calorie diet on insulin sensitivity, beta cell function, insulin clearance, incretin hormone secretion, androgen levels and body composition in obese young women. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukan, M.I.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Holst, J.J.; Martins, C. Plasma concentration of gastrointestinal hormones and subjective appetite ratings after diet or bariatric surgery: 1-year results from the DISGAP study. Int. J. Obes. 2024. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41366-024-01658-5 (accessed on 27 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- Calik Basaran, N.; Dotan, I.; Dicker, D. Post metabolic bariatric surgery weight regain: The importance of GLP-1 levels. Int. J. Obes. 2024. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38225284/ (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Elias, K.; Webb, D.L.; Diaz Tartera, H.O.; Hellstrom, P.M.; Sundbom, M. Impact of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch on glucose homeostasis and gut hormones and their correlations with appetite. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, M.; Machineni, S.; Olivan, B.; Teixeira, J.; McGinty, J.J.; Bawa, B.; Koshy, N.; Colarusso, A.; Laferrère, B. Superior appetite hormone profile after equivalent weight loss by gastric bypass compared to gastric banding. Obesity 2010, 18, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, C.W.; Welbourn, R.; Werling, M.; Osborne, A.; Kokkinos, A.; Laurenius, A.; Lönroth, H.; Fändriks, L.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; et al. Gut hormones as mediators of appetite and weight loss after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirksen, C.; Jorgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Moller, K.N.; Kielgast, U.; Jacobsen, S.H.; Clausen, T.R.; Worm, D.; Hartmann, B.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Damgaard, M.; et al. Gut hormones, early dumping and resting energy expenditure in patients with good and poor weight loss response after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osto, E.; Doytcheva, P.; Corteville, C.; Bueter, M.; Dorig, C.; Stivala, S.; Buhmann, H.; Colin, S.; Rohrer, L.; Hasballa, R.; et al. Rapid and body weight-independent improvement of endothelial and high-density lipoprotein function after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: Role of glucagon-like peptide-1. Circulation 2015, 131, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiroa, D.; Imbernon, M.; Gallego, R.; Senra, A.; Herranz, D.; Villarroya, F.; Serrano, M.; Fernø, J.; Salvador, J.; Escalada, J.; et al. GLP-1 agonism stimulates brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and browning through hypothalamic AMPK. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3346–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, S.; Wang, Y.; Parlevliet, E.T.; Boon, M.R.; Edelschaap, D.; Snaterse, G.; Pijl, H.; Romijn, J.A.; Rensen, P.C.N. Central GLP-1 receptor signalling accelerates plasma clearance of triacylglycerol and glucose by activating brown adipose tissue in mice. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, L.G.M.; Nahon, K.J.; Bracke, K.F.M.; van den Broek, D.; Smit, R.; Sardjoe Mishre, A.S.D.; Koorneef, L.L.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Burakiewicz, J.; Kan, H.E.; et al. Twelve weeks of exenatide treatment increases [(18)F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by brown adipose tissue without affecting oxidative resting energy expenditure in nondiabetic males. Metabolism 2020, 106, 154167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Sawaguchi, A.; Mondal, M.S.; Suganuma, T.; Matsukura, S.; Kangawa, K.; Nakazato, M. Ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing acylated peptide, is synthesized in a distinct endocrine cell type in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats and humans. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4255–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamegai, J.; Tamura, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ishii, S.; Sugihara, H.; Wakabayashi, I. Central effect of ghrelin, an endogenous growth hormone secretagogue, on hypothalamic peptide gene expression. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 4797–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Prigeon, R.L.; Davis, H.W.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Kahn, S.E.; Cummings, D.E.; Tschöp, M.H.; D’Alessio, D. Ghrelin suppresses glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and deteriorates glucose tolerance in healthy humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katugampola, S.D.; Pallikaros, Z.; Davenport, A.P. [125I-His(9)]-ghrelin, a novel radioligand for localizing GHS orphan receptors in human and rat tissue: Up-regulation of receptors with athersclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaya, N.; Kojima, M.; Uematsu, M.; Yamagishi, M.; Hosoda, H.; Oya, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Kangawa, K. Hemodynamic and hormonal effects of human ghrelin in healthy volunteers. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 280, R1483–R1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, E.T.; Andersen, N.H.; Hansen, T.K.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Moller, N.; Sorensen, K.E.; Sloth, E.; Jorgensen, J.O. Cardiovascular effects of intravenous ghrelin infusion in healthy young men. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H3020–H3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Schinzari, F.; Iantorno, M.; Rizza, S.; Melina, D.; Lauro, D.; Cardillo, C. Ghrelin improves endothelial function in patients with metabolic syndrome. Circulation 2005, 112, 2986–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, L.H.; Hage, C.; Pironti, G.; Thorvaldsen, T.; Ljung-Faxen, U.; Zabarovskaja, S.; Shahgaldi, K.; Webb, D.L.; Hellström, P.M.; Anderssonn, D.C.; et al. Acyl ghrelin improves cardiac function in heart failure and increases fractional shortening in cardiomyocytes without calcium mobilization. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2009–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Furuta, H.; Doi, A.; Ariyasu, H.; Kawashima, H.; Wakasaki, H.; Nishi, M.; Sasaki, H.; Akamizu, T. Des-acyl ghrelin protects microvascular endothelial cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through sirtuin 1 signaling pathway. Metabolism 2014, 63, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.G.; Gavrila, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Gunnlaugsson, S.; Stoll, L.L.; McCormick, M.L.; Sigmund, C.D.; Tang, C.; Weintraub, N.L. Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 2004, 109, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauna, C.; Meyler, F.M.; Janssen, J.A.; Delhanty, P.J.; Abribat, T.; van Koetsveld, P.; Hofland, L.J.; Broglio, F.; Ghigo, E.; van der Lely, A.J. Administration of acylated ghrelin reduces insulin sensitivity, whereas the combination of acylated plus unacylated ghrelin strongly improves insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lear, P.V.; Iglesias, M.J.; Feijoo-Bandin, S.; Rodriguez-Penas, D.; Mosquera-Leal, A.; Garcia-Rua, V.; Gualillo, O.; Ghè, C.; Arnoletti, E.; Muccioli, G.; et al. Des-acyl ghrelin has specific binding sites and different metabolic effects from ghrelin in cardiomyocytes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3286–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterli, R.; Wolnerhanssen, B.; Peters, T.; Devaux, N.; Kern, B.; Christoffel-Courtin, C.; Drewe, J.; von Flüe, M.; Beglinger, C. Improvement in glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: Comparison of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A prospective randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, S.N.; Vagenas, K.; Kalfarentzos, F.; Alexandrides, T.K. Weight loss, appetite suppression, and changes in fasting and postprandial ghrelin and peptide-YY levels after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy: A prospective, double blind study. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Te, C.; Koshy, S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Laferrere, B. Does ghrelin really matter after bariatric surgery? Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2006, 2, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Walsh, K.; Kumada, M.; Abe, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Selective suppression of endothelial cell apoptosis by the high molecular weight form of adiponectin. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kihara, S.; Shimomura, I. Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Funahashi, T.; Arita, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Matsuda, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iwahashi, H.; Kuriyama, H.; Ouchi, N.; Maeda, K.; et al. Plasma concentrations of a novel, adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in type 2 diabetic patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin--journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Shimomura, I.; Matsukawa, Y.; Kumada, M.; Takahashi, M.; Matsuda, M.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Kawamoto, T.; Sumitsuji, S.; et al. Association of adiponectin mutation with type 2 diabetes: A candidate gene for the insulin resistance syndrome. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2325–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Ura, N.; Higashiura, K.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, M.; Moniwa, N.; Yoshida, D.; Shimamoto, K. Blockade of the renin-angiotensin system increases adiponectin concentrations in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 42, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.W.; Watts, G.F.; Barrett, P.H.; Rye, K.A.; Chan, D.C. Effect of weight loss on LDL and HDL kinetics in the metabolic syndrome: Associations with changes in plasma retinol-binding protein-4 and adiponectin levels. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2945–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summer, S.S.; Brehm, B.J.; Benoit, S.C.; D’Alessio, D.A. Adiponectin changes in relation to the macronutrient composition of a weight-loss diet. Obesity 2011, 19, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia de la Torre, N.; Rubio, M.A.; Bordiu, E.; Cabrerizo, L.; Aparicio, E.; Hernandez, C.; Sànchez-Pernaute, A.; Dìez-Valladares, L.; Torres, A.J.; Puente, M.; et al. Effects of weight loss after bariatric surgery for morbid obesity on vascular endothelial growth factor-A, adipocytokines, and insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4276–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Martin, J.M.; Balsa, J.A.; Aracil, E.; Insenser, M.; Priego, P.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Botella-Carretero, J.I. Circulating adiponectin increases in obese women after sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass driving beneficial metabolic changes but with no relationship with carotid intima-media thickness. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37 Pt A, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Hatao, F.; Imamura, K.; Takanishi, K.; Tsujino, M. Early Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Obesity-Related Cytokines and Bile Acid Metabolism in Morbidly Obese Japanese Patients. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotidis, E.V.; Koliakos, G.; Papavramidis, T.S.; Papavramidis, S.T. The effect of biliopancreatic diversion with pylorus-preserving sleeve gastrectomy and duodenal switch on fasting serum ghrelin, leptin and adiponectin levels: Is there a hormonal contribution to the weight-reducing effect of this procedure? Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adami, G.F.; Gradaschi, R.; Andraghetti, G.; Scopinaro, N.; Cordera, R. Serum Leptin and Adiponectin Concentration in Type 2 Diabetes Patients in the Short and Long Term Following Biliopancreatic Diversion. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Asakawa, A.; Amitani, H.; Inui, A. Stimulation of leptin secretion by insulin. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16 (Suppl. S3), S543–S548. [Google Scholar]
- Stepien, M.; Stepien, A.; Wlazel, R.N.; Paradowski, M.; Rizzo, M.; Banach, M.; Rysz, J. Predictors of insulin resistance in patients with obesity: A pilot study. Angiology 2014, 65, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, A.; Bochenek, M.L.; Schutz, E.; Gogiraju, R.; Munzel, T.; Schafer, K. Selective Deletion of Leptin Signaling in Endothelial Cells Enhances Neointima Formation and Phenocopies the Vascular Effects of Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1683–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilarino-Garcia, T.; Polonio-Gonzalez, M.L.; Perez-Perez, A.; Ribalta, J.; Arrieta, F.; Aguilar, M.; Obaya, J.C.; Gimeno-Orna, J.A.; Iglesias, P.; Navarro, J.; et al. Role of Leptin in Obesity, Cardiovascular Disease, and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellott, E.; Faulkner, J.L. Mechanisms of leptin-induced endothelial dysfunction. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2023, 32, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, M.; Hossein Sakhaei, M.; Kheradmand, S.; Symonds, M.E.; Rosenkranz, S.K. The impact of exercise and dietary interventions on circulating leptin and adiponectin in individuals who are overweight and those with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, O.; Luca, F.; Grunebaum, L.; Jesel, L.; Meyer, N.; Desprez, D.; Robert, S.; Dignat-George, F.; Toti, F.; Simon, C.; et al. Short-term very low-calorie diet in obese females improves the haemostatic balance through the reduction of leptin levels, PAI-1 concentrations and a diminished release of platelet and leukocyte-derived microparticles. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Herrera, K.; Florio, A.A.; Moore, M.; Marrero, A.; Tamez, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Mattei, J. The Leptin System and Diet: A Mini Review of the Current Evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 749050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Hama, S.; Liu, Y.; Siahmansur, T.; Schofield, J.; Syed, A.A.; France, M.; Pemberton, P.; Adam, S.; Hong, J.H.; et al. Effect of Roux-en-Y Bariatric Surgery on Lipoproteins, Insulin Resistance, and Systemic and Vascular Inflammation in Obesity and Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, G.; Lima, M.M.O.; Felici, A.C.; Pareja, J.C.; Vasques, A.C.J.; Novaes, F.S.; Rodovalho, S.; Hirsch, F.F.P.; Matos-Souza, J.R.; Chaim, E.A.; et al. Early Regression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness after Bariatric Surgery and Its Relation to Serum Leptin Reduction. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejka, A.; Jankiewicz-Wika, J.; Kolomecki, K.; Cywinski, J.; Piestrzeniewicz, K.; Swietoslawski, J.; Stępień, H.; Komorowski, J. Long-term impact of vertical banded gastroplasty (VBG) on plasma concentration of leptin, soluble leptin receptor, ghrelin, omentin-1, obestatin, and retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) in patients with severe obesity. Cytokine 2013, 64, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafey, M.F.; Fang, C.E.H.; Ioana, I.; Griffin, H.; Hynes, M.; O’Brien, T.; McAnena, O.; O’Shea, P.; Collins, C.; Davenport, C.; et al. The leptin to adiponectin ratio (LAR) is reduced by sleeve gastrectomy in adults with severe obesity: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Xiong, W.; Li, G.; He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, N.; Ikejiofor, C.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Leptin Reduction as a Required Component for Weight Loss. Diabetes 2024, 73, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicent, D.; Ilany, J.; Kondo, T.; Naruse, K.; Fisher, S.J.; Kisanuki, Y.Y.; Bursell, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; King, G.L.; Kahn, C.R. The role of endothelial insulin signaling in the regulation of vascular tone and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.J., Jr.; Racette, S.B.; Coggan, A.R.; Stein, R.I.; McCue, L.M.; Gropler, R.J.; Peterson, L.R. Weight Loss Affects Intramyocardial Glucose Metabolism in Obese Humans. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, e009241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Kang, C.W.; Wang, E.K.; Nam, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, K.H.; Lee, E.J.; Cho, A.; Kur, C.R. Altered Glucose Metabolism and Glucose Transporters in Systemic Organs After Bariatric Surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 937394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; Aller, R. Effect of two different dietary fatty acid profiles and variant rs266729 in ADIPOQ on weight loss and adiponectin concentrations. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2020, 67, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luis, D.A.; Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; Gomez Hoyos, E.; Lopez Gomez, J.J.; Ortola, A.; Aller, R. Role of the variant in adiponectin gene rs266729 on weight loss and cardiovascular risk factors after a hypocaloric diet with the Mediterranean pattern. Nutrition 2019, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiezzi, M.; Vieceli Dalla Sega, F.; Gentileschi, P.; Campanelli, M.; Benavoli, D.; Tremoli, E. Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020381
Tiezzi M, Vieceli Dalla Sega F, Gentileschi P, Campanelli M, Benavoli D, Tremoli E. Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020381
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiezzi, Margherita, Francesco Vieceli Dalla Sega, Paolo Gentileschi, Michela Campanelli, Domenico Benavoli, and Elena Tremoli. 2025. "Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020381
APA StyleTiezzi, M., Vieceli Dalla Sega, F., Gentileschi, P., Campanelli, M., Benavoli, D., & Tremoli, E. (2025). Effects of Weight Loss on Endothelium and Vascular Homeostasis: Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Biomedicines, 13(2), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020381





