Lyophilized Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEVs) Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Maintain Efficacy to Promote Healing in Neuronal Injuries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. sEV Isolation and Size Characterization
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
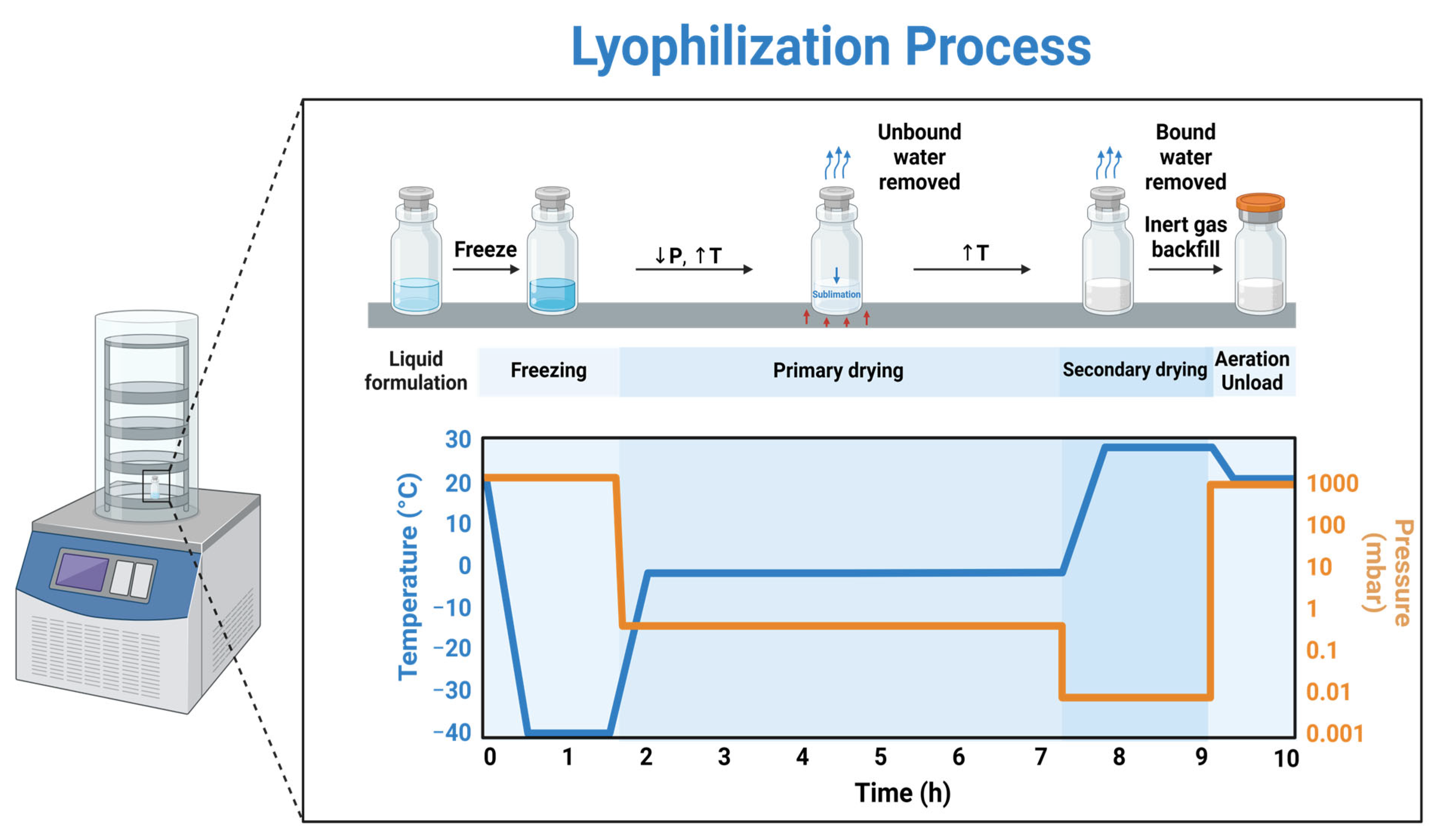
2.4. Lyophilization
2.5. Protein Concentrations
2.6. Scratch Assay
2.7. DiD-Labeled sEV Uptake
2.8. In Vitro Inflammation Model
2.9. In Vitro Oxidative Stress Model
2.10. Immunochemistry
2.11. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results
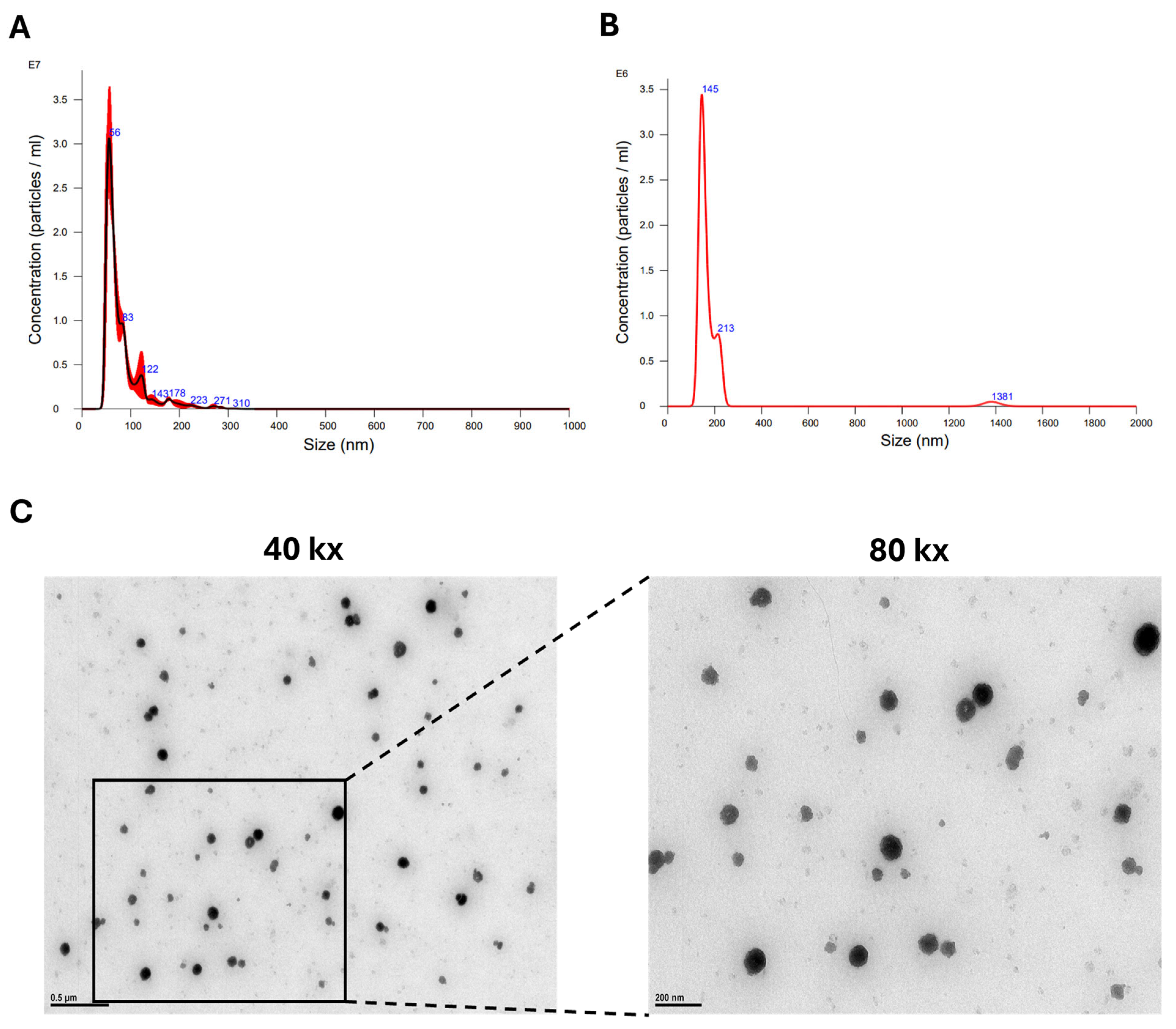
3.1. Optimal Method of hASC sEV Preparation
3.2. Lyophilization Has No Effect on Concentration or Morphology of hASC sEVs
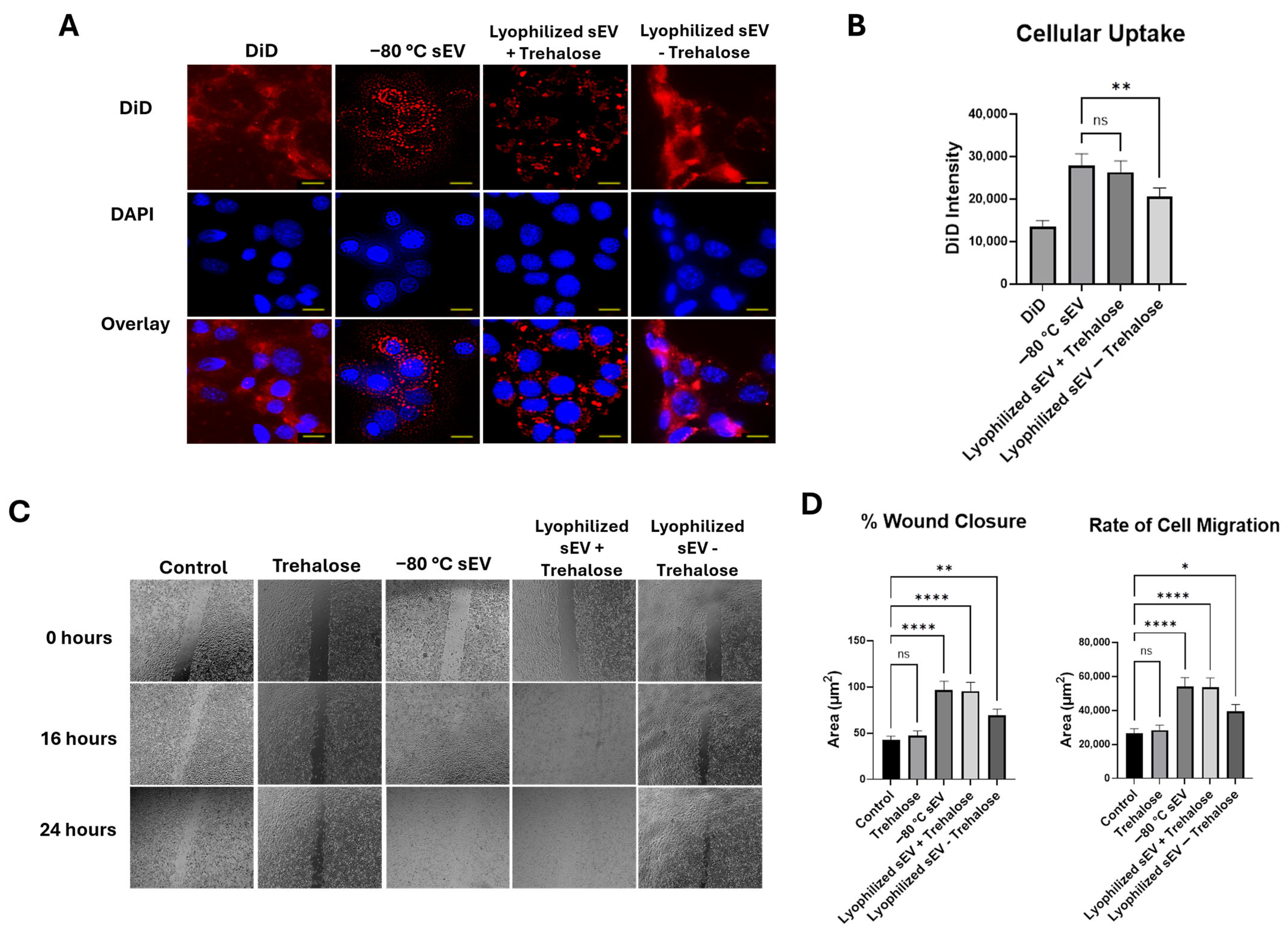
3.3. Lyophilized sEVs Stored at Room Temperature Promote Wound Healing in Neuronal Cells
3.4. Lyophilized sEVs Promote Wound Healing Efficiently After 1 Month at Room Temperature
3.5. Lyophilized sEVs Promote Wound Healing Efficiently After 2 Months at Room Temperature
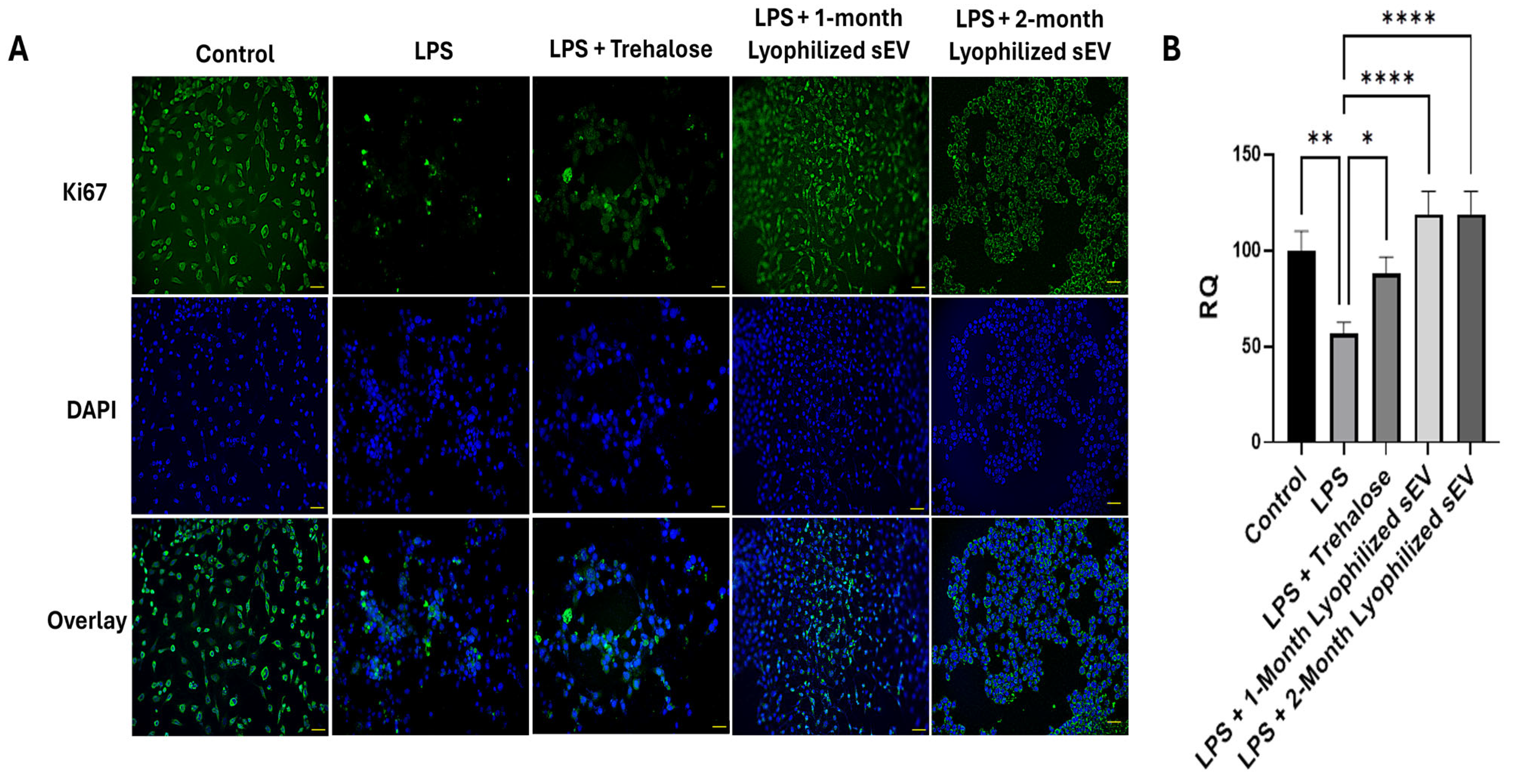
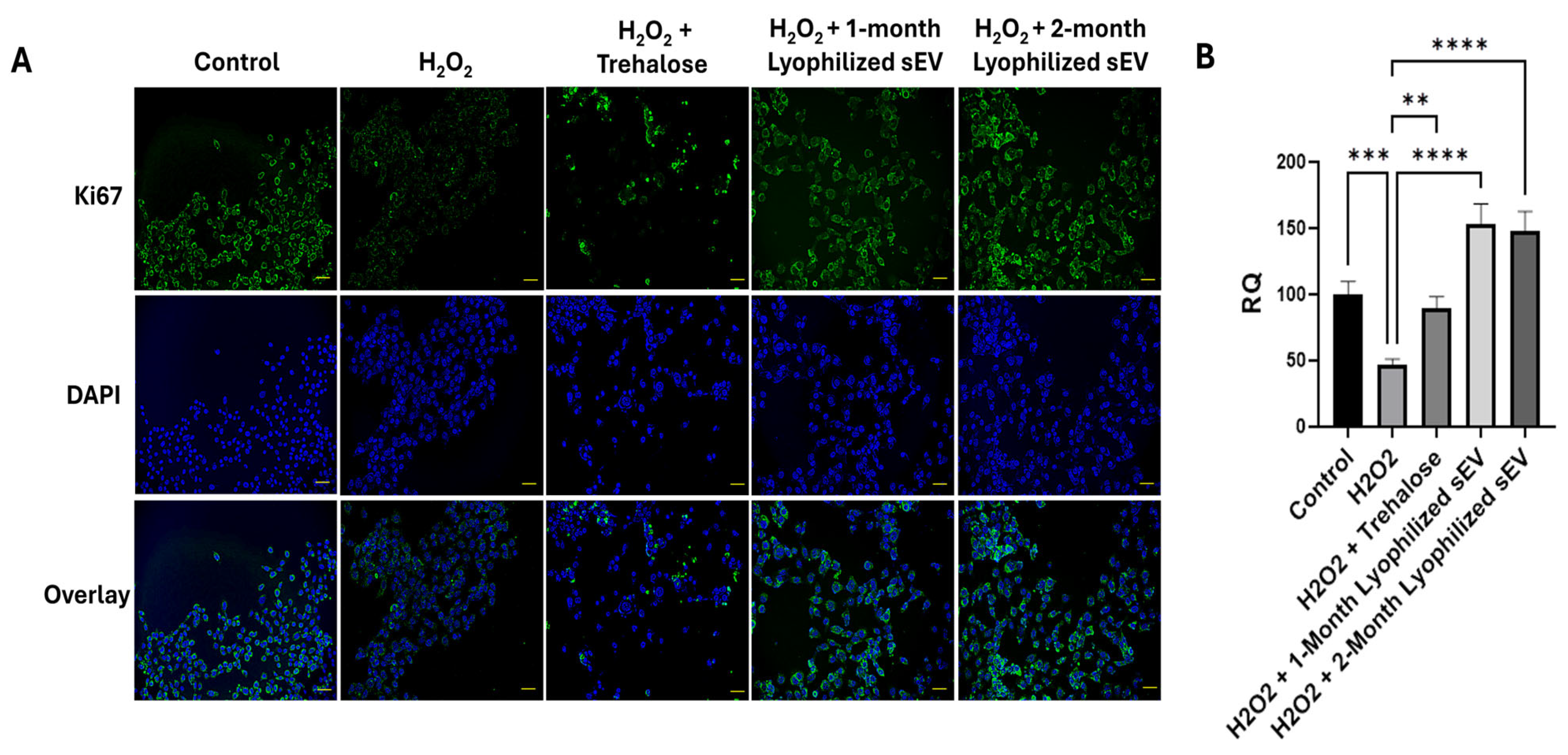
3.6. Lyophilized sEVs Rescue Cell Proliferation in Neuronal Cells with Underlying Inflammation In Vitro
3.7. Lyophilized sEVs Decrease Oxidative Stress in Neuronal Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mollayeva, T.; Mollayeva, S.; Colantonio, A. Traumatic brain injury: Sex, gender and intersecting vulnerabilities. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Daneshvar, D.H. The neuropathology of traumatic brain injury. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 127, pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, S.A.; Tajiri, N.; Shinozuka, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Grimmig, B.; Diamond, D.M.; Sanberg, P.R.; Bickford, P.C.; Kaneko, Y.; Borlongan, C.V. Long-term upregulation of inflammation and suppression of cell proliferation in the brain of adult rats exposed to traumatic brain injury using the controlled cortical impact model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.A.; Moss, L.D.; Lee, J.Y.; Tajiri, N.; Acosta, S.; Hudson, C.; Parag, S.; Cooper, D.R.; Borlongan, C.V.; Bickford, P.C. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in exosomes drives regenerative function and modulates inflammation-linked networks following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, B.L.; Gardner, R.C.; Godbout, J.; Dams-O’Connor, K.; Keene, C.D. Traumatic Brain Injury and Risk of Neurodegenerative Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dams-O’Connor, K.; Juengst, S.B.; Bogner, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Corrigan, J.D.; Giacino, J.T.; Harrison-Felix, C.L.; Hoffman, J.M.; Ketchum, J.M.; Lequerica, A.H.; et al. Traumatic brain injury as a chronic disease: Insights from the United States Traumatic Brain Injury Model Systems Research Program. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Y.; Gao, G.Y.; Feng, J.F.; Mao, Q.; Chen, L.G.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Qiu, B.H.; Huang, X.J. Traumatic brain injury in China. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, G.A. Update on TBI and Cognitive Impairment in Military Veterans. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.; Helmick, K.; Malik, S.; Gregory, E.; Agimi, Y.; Marion, D. Continuum of the United States military’s traumatic brain injury care: Adjusting to the changing battlefield. Neurosurg. Focus. 2018, 45, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; DeWitt, D.S.; Prough, D.S. Impact & Blast Traumatic Brain Injury: Implications for Therapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrugger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syzdykbayev, M.; Kazymov, M.; Aubakirov, M.; Kurmangazina, A.; Kairkhanov, E.; Kazangapov, R.; Bryzhakhina, Z.; Imangazinova, S.; Sheinin, A. A Modern Approach to the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury. Medicines 2024, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Mansuri, M.S.; Williams, K.R.; Nairn, A.C. Exosomes as Emerging Biomarker Tools in Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Disorders-A Proteomics Perspective. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, M.; Cui, Y.; Xing, J.; Teng, L.; Xi, Z.; Yang, Z. Exosomes as smart drug delivery vehicles for cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1093607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Li, A.; Hu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z. Recent developments in isolating methods for exosomes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, S.M.; Kuhnell, D.; Orr-Asman, M.A.; Biesiada, J.; Zhang, X.; Medvedovic, M.; Thomas, H.E. Balancing yield, purity and practicality: A modified differential ultracentrifugation protocol for efficient isolation of small extracellular vesicles from human serum. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez-Valero, A.; Monguio-Tortajada, M.; Carreras-Planella, L.; Franquesa, M.; Beyer, K.; Borras, F.E. Size-Exclusion Chromatography-based isolation minimally alters Extracellular Vesicles’ characteristics compared to precipitating agents. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaram, A.; Jay, S.M. Preservation and Storage Stability of Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Applications. AAPS J. 2017, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, G.D.; Barabadi, M.; Tan, J.L.; Morton, D.A.V.; Frith, J.E.; Lim, R. To Protect and to Preserve: Novel Preservation Strategies for Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenviriyakul, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Preservation of exosomes at room temperature using lyophilization. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, M.M.; Amer, M.S.; Abo-El-Sooud, K.; Abdallah, A.N.; El-Tookhy, O.S. Preservation techniques of stem cells extracellular vesicles: A gate for manufacturing of clinical grade therapeutic extracellular vesicles and long-term clinical trials. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2020, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Miao, Y.; Xu, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Tang, X.; Cai, C.; Xu, H. Injectable nimodipine-loaded nanoliposomes: Preparation, lyophilization and characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 410, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, A.K.; Chandra, P.K.; Hazari, S.; Ledet, G.; Pramar, Y.V.; Dash, S.; Mandal, T.K. Stability of lyophilized siRNA nanosome formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 423, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascucci, L.; Scattini, G. Imaging extracelluar vesicles by transmission electron microscopy: Coping with technical hurdles and morphological interpretation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bassit, G.; Patel, R.S.; Carter, G.; Shibu, V.; Patel, A.A.; Song, S.; Murr, M.; Cooper, D.R.; Bickford, P.C.; Patel, N.A. MALAT1 in Human Adipose Stem Cells Modulates Survival and Alternative Splicing of PKCdeltaII in HT22 Cells. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, L.D.; Sode, D.; Patel, R.; Lui, A.; Hudson, C.; Patel, N.A.; Bickford, P.C. Intranasal delivery of exosomes from human adipose derived stem cells at forty-eight hours post injury reduces motor and cognitive impairments following traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 150, 105173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, B.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Xue, C.; Han, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhao, R.C. MSC-derived exosomes promote recovery from traumatic brain injury via microglia/macrophages in rat. Aging 2020, 12, 18274–18296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Pan, J. Adipose-derived stem cell exosomes ameliorate traumatic brain injury through the NLRP3 signaling pathway. Neuroreport 2023, 34, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, C.; Ghirardello, A.; Bertazza, L.; Gasparotto, M.; Zanatta, E.; Iaccarino, L.; Valadi, H.; Doria, A.; Gatto, M. Size-Exclusion Chromatography Combined with Ultrafiltration Efficiently Isolates Extracellular Vesicles from Human Blood Samples in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, R.E.; Teeuwen, L.; Czarnewski, P.; Gucluler Akpinar, G.; Sandberg, A.; Cao, X.; Pernemalm, M.; Orre, L.M.; Gabrielsson, S.; Eldh, M. Molecular evaluation of five different isolation methods for extracellular vesicles reveals different clinical applicability and subcellular origin. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanantham, A.; Jin, Y. Impact of Storage Conditions on EV Integrity/Surface Markers and Cargos. Life 2022, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Qin, G.; He, S.H.; Zimmerman, A.; et al. Exosomes/microvesicles from induced pluripotent stem cells deliver cardioprotective miRNAs and prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis in the ischemic myocardium. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 192, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponnetto, F.; Manini, I.; Skrap, M.; Palmai-Pallag, T.; Di Loreto, C.; Beltrami, A.P.; Cesselli, D.; Ferrari, E. Size-dependent cellular uptake of exosomes. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.S.; Impreso, S.; Lui, A.; Vidyarthi, G.; Albear, P.; Patel, N.A. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Contained in Exosomes Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Promotes Repair and Modulates Inflammation in a Chronic Dermal Wound Healing Model. Biology 2022, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Storage Time | Sample | Protein Concentration (μg/mL) | p-Value | Size (nm) | p-Value | Concentration (particles/mL) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Weeks | −80 °C sEV | 2.047 ± 0.036 | 0.0014 | 157 ± 32 | 0.1840 | 2.59 × 107 | |
| Lyophilized sEV + trehalose | 2.039 ± 0.037 | 157 ± 17 | 2.42 × 107 | 0.2535 | |||
| Lyophilized sEV—trehalose | 1.163 ± 0.027 | 182 ± 159 | 1.74 × 106 | ||||
| 1 Month | −80 °C sEV | 2.122 ± 0.015 | 0.8468 | 159 ± 39 | 0.0782 | 5.03 × 107 | 0.1454 |
| Lyophilized sEV | 2.158 ± 0.025 | 131 ± 23 | 1.44 × 107 | ||||
| 2 Months | −80 °C sEV | 2.003 ± 0.024 | 0.9135 | 155 ± 56 | 0.7649 | 2.12 × 107 | 0.3788 |
| Lyophilized sEV | 2.022 ± 0.017 | 151 ± 64 | 1.03 × 107 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, B.; Patel, R.; Wang, B.; Evans-Nguyen, T.; Patel, N.A. Lyophilized Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEVs) Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Maintain Efficacy to Promote Healing in Neuronal Injuries. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020275
Jones B, Patel R, Wang B, Evans-Nguyen T, Patel NA. Lyophilized Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEVs) Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Maintain Efficacy to Promote Healing in Neuronal Injuries. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020275
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Brianna, Rekha Patel, Bangmei Wang, Theresa Evans-Nguyen, and Niketa A. Patel. 2025. "Lyophilized Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEVs) Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Maintain Efficacy to Promote Healing in Neuronal Injuries" Biomedicines 13, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020275
APA StyleJones, B., Patel, R., Wang, B., Evans-Nguyen, T., & Patel, N. A. (2025). Lyophilized Small Extracellular Vesicles (sEVs) Derived from Human Adipose Stem Cells Maintain Efficacy to Promote Healing in Neuronal Injuries. Biomedicines, 13(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020275





