Toxicological Impacts and Mechanistic Insights of Bisphenol a on Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression: A Network Toxicology, Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Preliminary Network Analysis of BPA Toxicity
2.2. Construction of BPA Targets Library
2.3. Selection of ccRCC-Related Target Network
2.4. Screening of Key Targets and Construction of Protein–Protein Interaction Network
2.5. Gene Function and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Target Proteins
2.6. Development of a BPA-ccRCC Prediction Model Using Machine Learning
2.7. Prognostic Model Comparative Analysis
2.8. Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Characterization
2.9. Molecular Docking of BPA with Key Targets
3. Result
3.1. Basic In Silico Toxicity Profiling of BPA
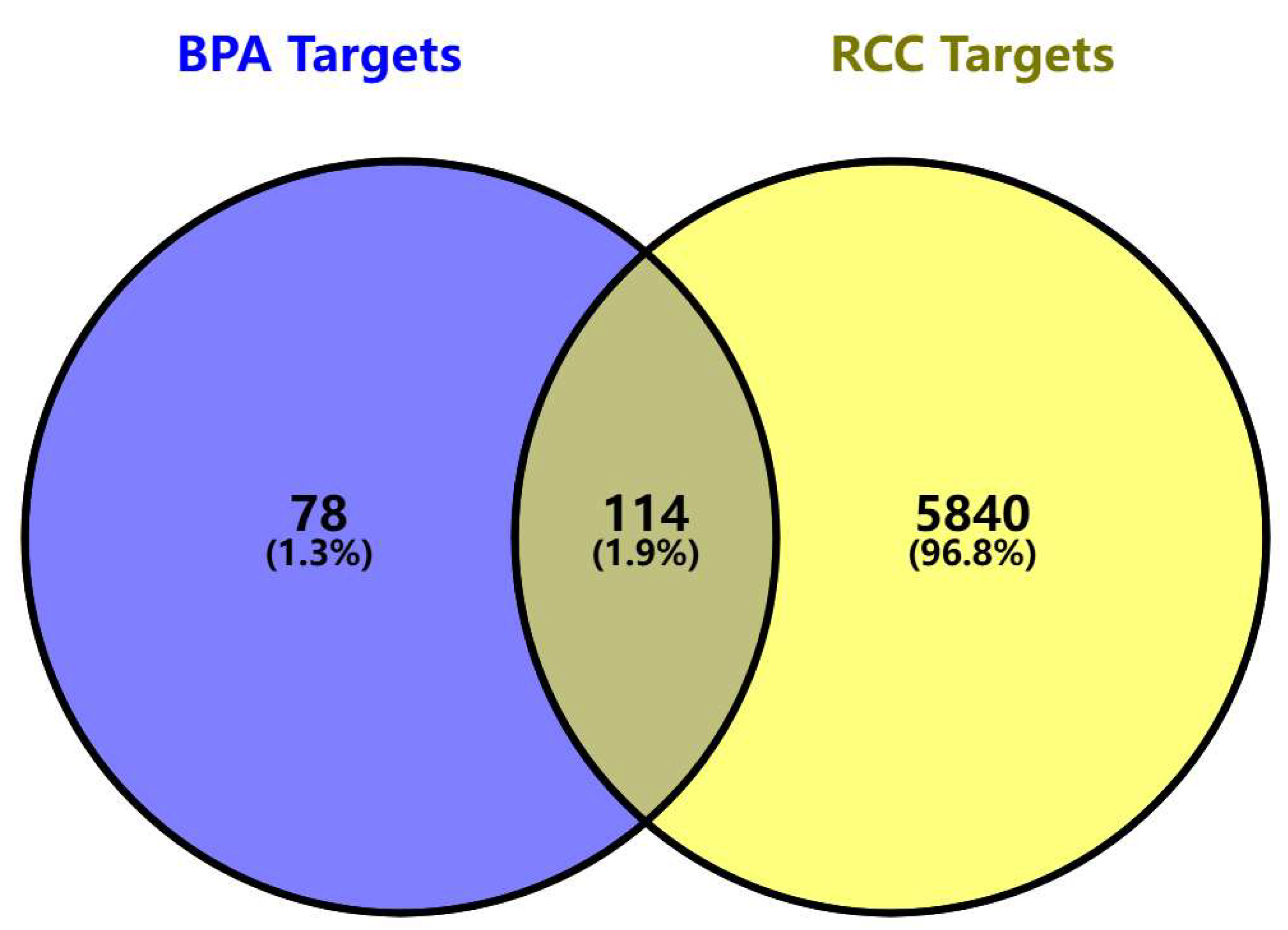
3.2. Acquisition of BPA-Elicited Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (ccRCC) Toxicity Targets
3.3. PPI Network Analysis and Key Target Screening
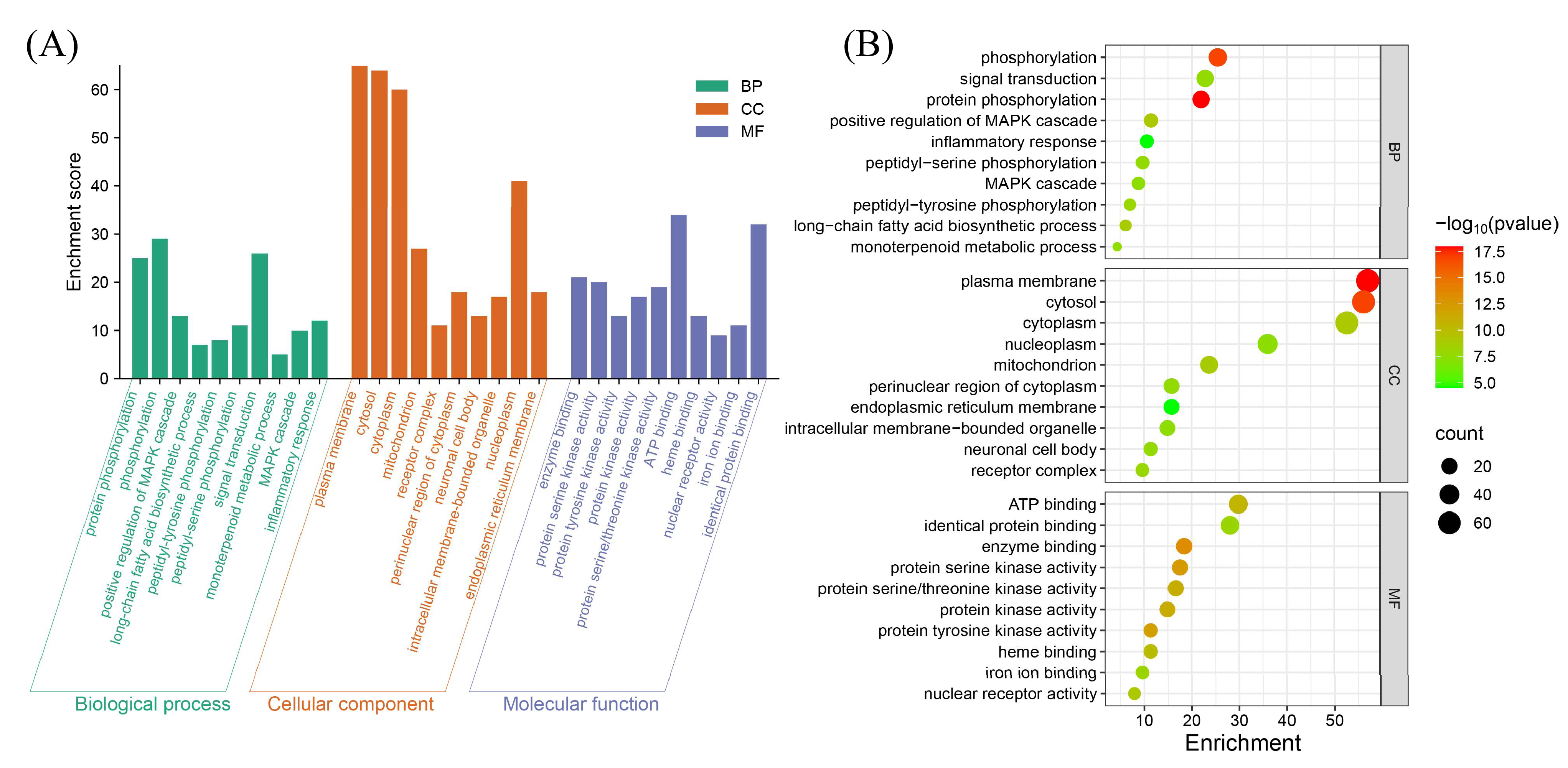
3.4. Functional Annotation and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Development and Validation of the BPA-ccRCC Prognostic Model
3.5.1. Model Construction and Optimization
3.5.2. Performance Validation
3.5.3. Elevated Immune Infiltration in the High-Risk Subgroup
3.5.4. Comparison with the Established Prognostic Models
3.6. Molecular Docking for BPA with Core Target of ccRCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barata, P.C.; Rini, B.I. Treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Current status and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Jonasch, E.; Agarwal, N.; Alva, A.; Bagshaw, H.; Baine, M.; Beckermann, K.; Carlo, M.I.; Choueiri, T.K.; Costello, B.A.; et al. NCCN Guidelines? Insights: Kidney Cancer, Version 2.2024. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2024, 22, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, A.B.; Yabroff, K.R.; Shao, Y.; Feuer, E.J.; Brown, M.L. Projections of the cost of cancer care in the United States: 2010–2020. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Z.; Prettner, K.; Kuhn, M.; Yang, J.; Jiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Geldsetzer, P.; Bärnighausen, T.; et al. Estimates and Projections of the Global Economic Cost of 29 Cancers in 204 Countries and Territories from 2020 to 2050. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, K.M.; Udesky, J.O.; Rudel, R.A.; Brody, J.G. Environmental chemicals and breast cancer: An updated review of epidemiological literature informed by biological mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 152–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Sabir, S.; Rehman, K. Bisphenol A-induced metabolic disorders: From exposure to mechanism of action. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 77, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Deng, Y.; Wan, H.; Shen, N.; Li, J.; Zeng, Q.; Chang, J.; Lu, Q.; Miao, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Urinary bisphenol A and its interaction with CYP17A1 rs743572 are associated with breast cancer risk. Chemosphere 2022, 286 Pt 3, 131880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarraj, S.; Sujitha, M.V.; Alphonse, C.R.W.; Kalaiarasan, R.; Kannan, R.R. Bisphenol-A alters hematopoiesis through EGFR/ERK signaling to induce myeloblastic condition in zebrafish model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, K.; Zheng, F.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, H.; Wang, F.; Cui, Z.; Qin, Y.; et al. Low-dose BPA and its substitute BPS promote ovarian cancer cell stemness via a non-canonical PINK1/p53 mitophagic signaling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samet, J.M.; Chiu, W.A.; Cogliano, V.; Jinot, J.; Kriebel, D.; Lunn, R.M.; Beland, F.A.; Bero, L.; Browne, P.; Fritschi, L.; et al. The IARC Monographs: Updated Procedures for Modern and Transparent Evidence Synthesis in Cancer Hazard Identification. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213—Of 12 February 2018—On the Use of Bisphenol A in Varnishes and Coatings Intended to Come into Contact with Food and Amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as Regards the Use of that Substance in Plastic Food Contact Materials (Text with EEA Relevance)—Official Journal of European Union. 2018. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2018/213/oj/eng (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Lee, J.; Choi, K.; Park, J.; Moon, H.B.; Choi, G.; Lee, J.J.; Suh, E.; Kim, H.J.; Eun, S.H.; Kim, G.H.; et al. Bisphenol A distribution in serum, urine, placenta, breast milk, and umbilical cord serum in a birth panel of mother-neonate pairs. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, L.A.; Lee, P.M.Y.; Ho, W.M.; Lam, A.T.; Lee, M.K.; Ng, S.S.M.; He, Y.; Leung, K.S.; Hartle, J.C.; Hu, H.; et al. Bisphenol A and other environmental risk factors for prostate cancer in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, è.; Chabaud, S.; Pouliot, F.; Pelletier, M.; Bolduc, S. Bisphenol A Alters the Energy Metabolism of Stromal Cells and Could Promote Bladder Cancer Progression. Cancers 2021, 13, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoram, S.; Davoodi, M.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Bahadoram, M.; Barahman, M.; Mafakher, L. Renal cell carcinoma: An overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G. Ital. Nefrol. 2022, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, K.; Su, H.; Cui, K.; Gao, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Ha, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Liu, T. Effectiveness of an intermittent fasting diet versus regular diet on fat loss in overweight and obese middle-aged and olderly people without metabolic disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, G.; Serra, A.; Pavel, A.; Torres Maia, M.; Saarimäki, L.A.; Fratello, M.; Federico, A.; Alenius, H.; Fadeel, B.; Greco, D. A Network Toxicology Approach for Mechanistic Modelling of Nanomaterial Hazard and Adverse Outcomes. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2400389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. Efficient analysis of toxicity and mechanisms of environmental pollutants with network toxicology and molecular docking strategy: Acetyl tributyl citrate as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampon, K.; Giorkallos, A.; Deldossi, M.; Baud, S.; Steffenel, L.A. Machine-learning methods for ligand-protein molecular docking. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.Y.; Zi, X.J. Network toxicology and molecular docking for the toxicity analysis of food contaminants: A case of Aflatoxin B(1). Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2024, 188, 114687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Jin, X.; Mao, C.; Kang, L.; Gong, C.; Feng, S.; Yang, J. Analysis of toxicity and mechanisms of DEHP in prostate cancer with network toxicology and molecular docking strategy. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 111, 1454–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Adegboro, A.A.; Fasoranti, D.O.; Dai, L.; Pan, Z.; Liu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Mime: A flexible machine-learning framework to construct and visualize models for clinical characteristics prediction and feature selection. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Okuno, Y.; Kamura, T.; Shimamura, T.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.J.; Wu, Z.; Ge, L.; Yang, F.; Hong, K.; Zhang, S.; Ma, L. Ferroptosis-Related Gene-Based Prognostic Model and Immune Infiltration in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 650416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lin, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, K.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Machine learning-derived natural killer cell signature predicts prognosis and therapeutic response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2025, 51, 102180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gong, Y.; Gong, K. Construction of a two-gene prognostic model related to ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2023, 12, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, Y.; Wei, X.; Chu, Y.H.; Ng, L.G.; Tan, H.S.; Koh, V.; Thike, A.A.; Poon, E.; Ng, Q.S.; Toh, C.K.; et al. A multigene assay identifying distinct prognostic subtypes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with differential response to tyrosine kinase inhibition. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Hsieh, T.H.; Lee, J.N.; Hsu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Kuo, K.K.; Wu, H.L.; Chiu, C.C.; Tsai, E.M.; Kuo, P.L. Curcumin Suppresses Phthalate-Induced Metastasis and the Proportion of Cancer Stem Cell (CSC)-like Cells via the Inhibition of AhR/ERK/SK1 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10388–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, S.; Goto, Y.; Tanigawa, K.; Tomioka, Y.; Kato, M.; Mizuno, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Seki, N. MiR-15b-5p inhibits castration-resistant growth of prostate cancer cells by targeting the muscarinic cholinergic receptor CHRM3. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bhattarai, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Park, K.H.; Dong, W.; Hung, Y.F.; Yang, Q.; et al. Brain-wide neuronal circuit connectome of human glioblastoma. Nature 2025, 641, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Luo, P.; Fei, X.; Zhang, P. A miRNAs panel promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by targeting GABBR1. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solorzano, S.R.; Imaz-Rosshandler, I.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; García-Tobilla, P.; Morales-Montor, G.; Salazar, P.; Arena-Ortiz, M.L.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M. GABA promotes gastrin-releasing peptide secretion in NE/NE-like cells: Contribution to prostate cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlato, C.; Khan, M.N.; Schioppa, T.; Thompson, R.; Maniati, E.; Montfort, A.; Jangani, M.; Canosa, M.; Kulbe, H.; Hagemann, U.B.; et al. A CCR4 antagonist reverses the tumor-promoting microenvironment of renal cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.H.; Zhu, L.L.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.K.; Yang, Q.; Yan, J.Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.Y.; Dong, F.Y.; Dai, M.; et al. GABRP regulates chemokine signalling, macrophage recruitment and tumour progression in pancreatic cancer through tuning KCNN4-mediated Ca(2+) signalling in a GABA-independent manner. Gut 2019, 68, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shen, T.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Bu, H.; Fu, D.; Fang, B.; Lv, H.; et al. KCNN4 may weaken anti-tumor immune response via raising Tregs and diminishing resting mast cells in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Bao, L.W.; Kleer, C.G.; Sabel, M.S.; Griffith, K.A.; Teknos, T.N.; Merajver, S.D. Protein kinase C epsilon is a predictive biomarker of aggressive breast cancer and a validated target for RNA interference anticancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8366–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Basu, A. Protein Kinase C-ε Promotes EMT in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Basic Clin. Res. 2014, 8, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.M.; Salama, M.F.; Hannun, Y.A. Protein Kinase C as a Therapeutic Target in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zeng, F.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Lai, X.; Wang, Q.J.; Deng, F. Crosstalk of protein kinase C ε with Smad2/3 promotes tumor cell proliferation in prostate cancer cells by enhancing aerobic glycolysis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4583–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A. Regulation of Autophagy by Protein Kinase C-ε in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Fan, M.; Zeng, F.; Deng, F. miR-21-5p/PRKCE axis implicated in immune infiltration and poor prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 978840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Cao, K.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Mao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Pan, J.; Mo, C.; Chen, J.; et al. The expression and role of protein kinase C (PKC) epsilon in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmelzle, M.; Dizdar, L.; Matthaei, H.; Baldus, S.E.; Wolters, J.; Lindenlauf, N.; Bruns, I.; Cadeddu, R.P.; Kröpil, F.; Topp, S.A.; et al. Esophageal cancer proliferation is mediated by cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9). Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 94, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, P.; Siest, G.; Meyer, U.A.; Visvikis-Siest, S. Human cytochrome P450 epoxygenases: Variability in expression and role in inflammation-related disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 144, 134–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sausville, L.N.; Gangadhariah, M.H.; Chiusa, M.; Mei, S.; Wei, S.; Zent, R.; Luther, J.M.; Shuey, M.M.; Capdevila, J.H.; Falck, J.R.; et al. The Cytochrome P450 Slow Metabolizers CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 Directly Regulate Tumorigenesis via Reduced Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Production. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4865–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, O.A.; Li, W.T.; Krishnan, A.R.; Nguyen, G.C.; Lopez, J.P.; McKay, R.R.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. The renal clear cell carcinoma immune landscape. Neoplasia 2022, 24, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamoto, K.; Yaguchi, T.; Tajima, M.; Honjo, T. Insights from a 30-year journey: Function, regulation and therapeutic modulation of PD1. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Margolis, C.A.; Gao, W.; Voss, M.H.; Li, W.; Martini, D.J.; Norton, C.; Bossé, D.; Wankowicz, S.M.; Cullen, D.; et al. Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint therapies in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Science 2018, 359, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, M.; Gao, Z.; Hu, L.; Xuan, J.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; et al. PD1/PD-L1 blockade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Mechanistic insights, clinical efficacy, and future perspectives. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierer, S.; Herrmann, E.; Köpke, T.; Neumann, J.; Eltze, E.; Hertle, L.; Wülfing, C. Lymphangiogenesis in kidney cancer: Expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossage, L.; Eisen, T.; Maher, E.R. VHL, the story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; German, P.; Bai, S.; Barnes, S.; Guo, W.; Qi, X.; Lou, H.; Liang, J.; Jonasch, E.; Mills, G.B.; et al. The PI3K/AKT Pathway and Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Genet. Genom. (Yi Chuan Xue Bao) 2015, 42, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Deng, B.; Huang, X.; Guan, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. Combination treatment with FAAH inhibitors/URB597 and ferroptosis inducers significantly decreases the growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma cells via the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fang, Z.; Gao, P.; Zheng, J. GLUD1 suppresses renal tumorigenesis and development via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 975517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, è.; Pellerin, F.A.; Chabaud, S.; Pouliot, F.; Pelletier, M.; Bolduc, S. Glucuronidated Metabolites of Bisphenols A and S Alter the Properties of Normal Urothelial and Bladder Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobroob, A.; Peerapanyasut, W.; Chattipakorn, N.; Wongmekiat, O. Damaging Effects of Bisphenol A on the Kidney and the Protection by Melatonin: Emerging Evidences from In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 3082438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Zhou, J.; Ma, K.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Cai, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z.; et al. TRIB3 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells via Activating MAPK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.J.; Yan, S.; Zhuang, Q.F.; Mao, Q.Y.; Xue, D.; He, X.Z.; Chen, J.P. miR-106b promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting Capicua through MAPK signaling in renal carcinoma cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 3595–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecka, A.M.; Niedzwiedzka, M.; Porta, C.; Szczylik, C. Hormone signaling pathways as treatment targets in renal cell cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2221–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarny-Krzymińska, K.; Krawczyk, B.; Szczukocki, D. Bisphenol A and its substitutes in the aquatic environment: Occurrence and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
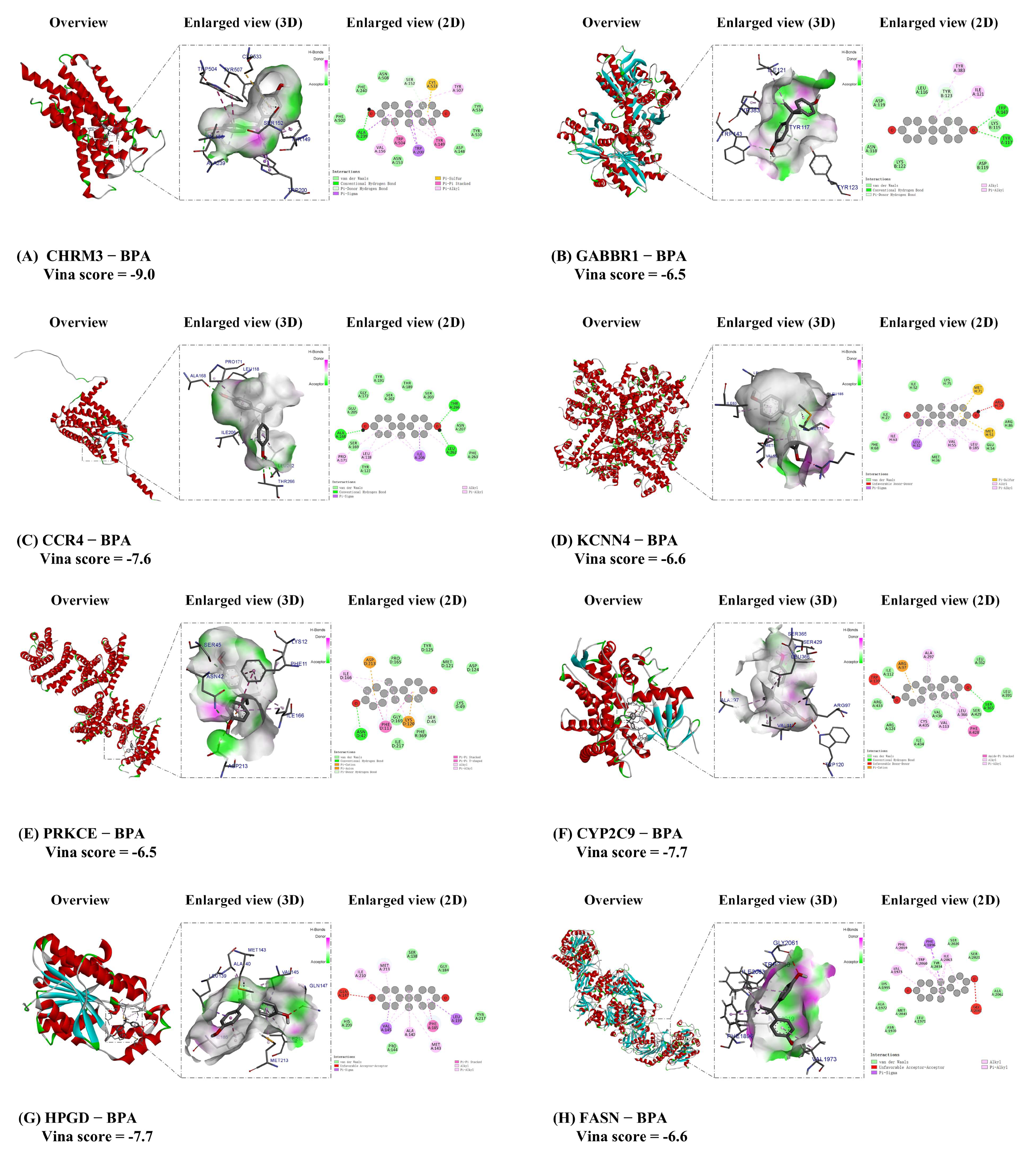





| Gene Name | Uniprot ID | PDB ID | Vina Scoremin (Kcal/mol) | Vina Score (kcal/mol) [Median (min, max)] (from 5 Molecular Docking Runs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CHRM3 | P20309 | 8EA0 | −9.0 | −7.0 (−9.0, −5.2) |
| 2 | GABBR1 | Q9UBS5 | 4MQE | −6.5 | −6.2 (−6.5, −5.6) |
| 3 | CCR4 | P51679 | Selected by AlphaFold3 | −7.6 | −5.4 (−7.6, −5.3) |
| 4 | KCNN4 | O15554 | 9OA8 | −6.6 | −6.2 (−6.6, −5.8) |
| 5 | PRKCE | Q02156 | 2WH0 | −6.5 | −5.9 (−6.5, −5.7) |
| 6 | CYP2C9 | P11712 | 5A5I | −7.7 | −7.4 (−7.7, −6.3) |
| 7 | HPGD | P15428 | 2gdz | −7.7 | −5.6 (−7.7, −5.3) |
| 8 | FASN | P49327 | 8VF7 | −6.6 | −6.6 (−7.5, −6.6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Ran, B.; Chen, B.; Bai, J.; Jian, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Q.; et al. Toxicological Impacts and Mechanistic Insights of Bisphenol a on Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression: A Network Toxicology, Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112778
Chen J, Ran B, Chen B, Bai J, Jian S, Huang Y, Yang J, Li J, Chen Z, Wei Q, et al. Toxicological Impacts and Mechanistic Insights of Bisphenol a on Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression: A Network Toxicology, Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112778
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Biao Ran, Bo Chen, Jingxing Bai, Shibo Jian, Yin Huang, Jiahao Yang, Jinze Li, Zeyu Chen, Qiang Wei, and et al. 2025. "Toxicological Impacts and Mechanistic Insights of Bisphenol a on Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression: A Network Toxicology, Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112778
APA StyleChen, J., Ran, B., Chen, B., Bai, J., Jian, S., Huang, Y., Yang, J., Li, J., Chen, Z., Wei, Q., Ai, J., Liu, L., & Cao, D. (2025). Toxicological Impacts and Mechanistic Insights of Bisphenol a on Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression: A Network Toxicology, Machine Learning and Molecular Docking Study. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112778






