Increased Immunohistochemical Expression of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) in Renal Cancer with Venous Tumor Thrombus Is Associated with Worse Prognosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Cohort
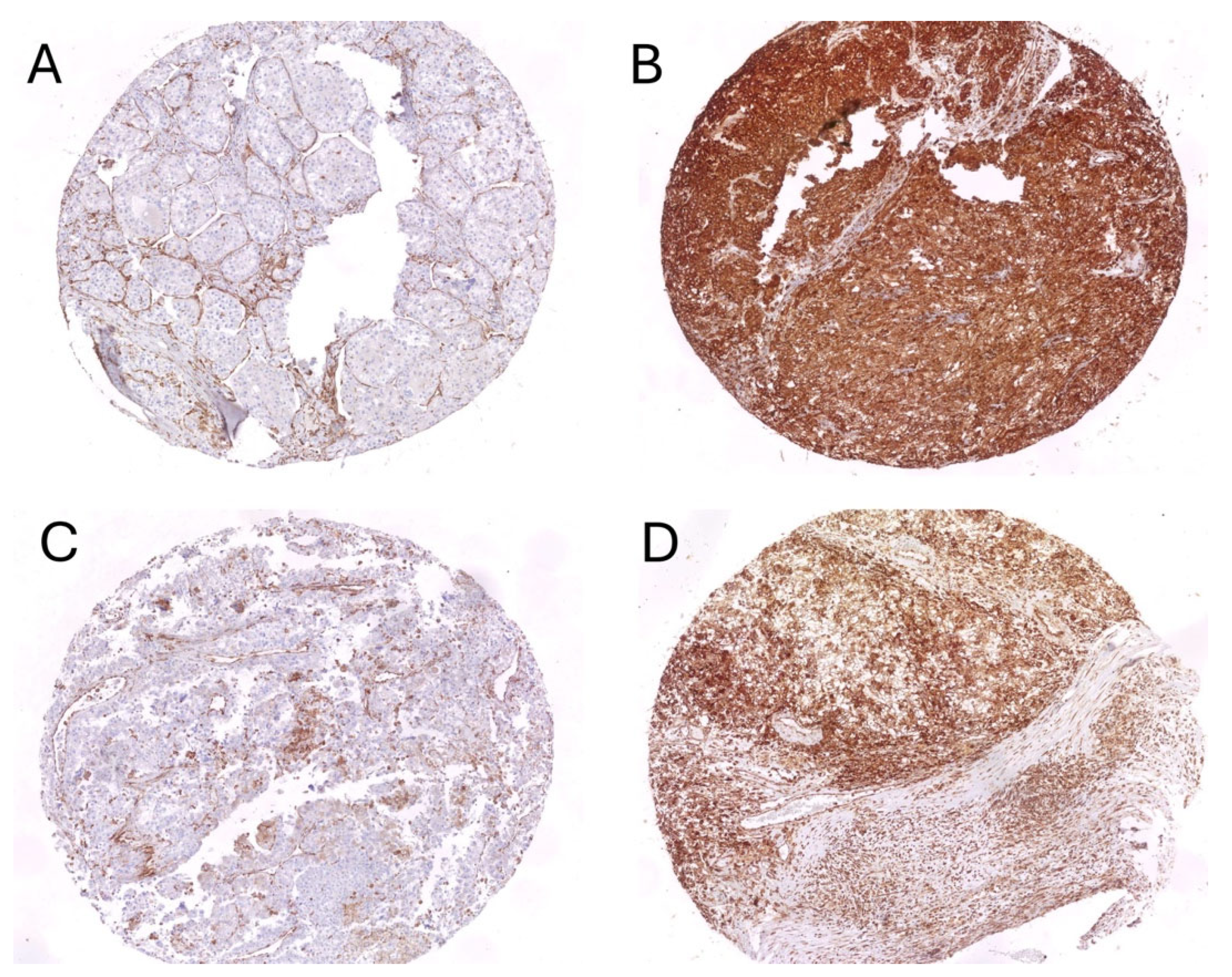
2.2. Tissue Microarrays
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
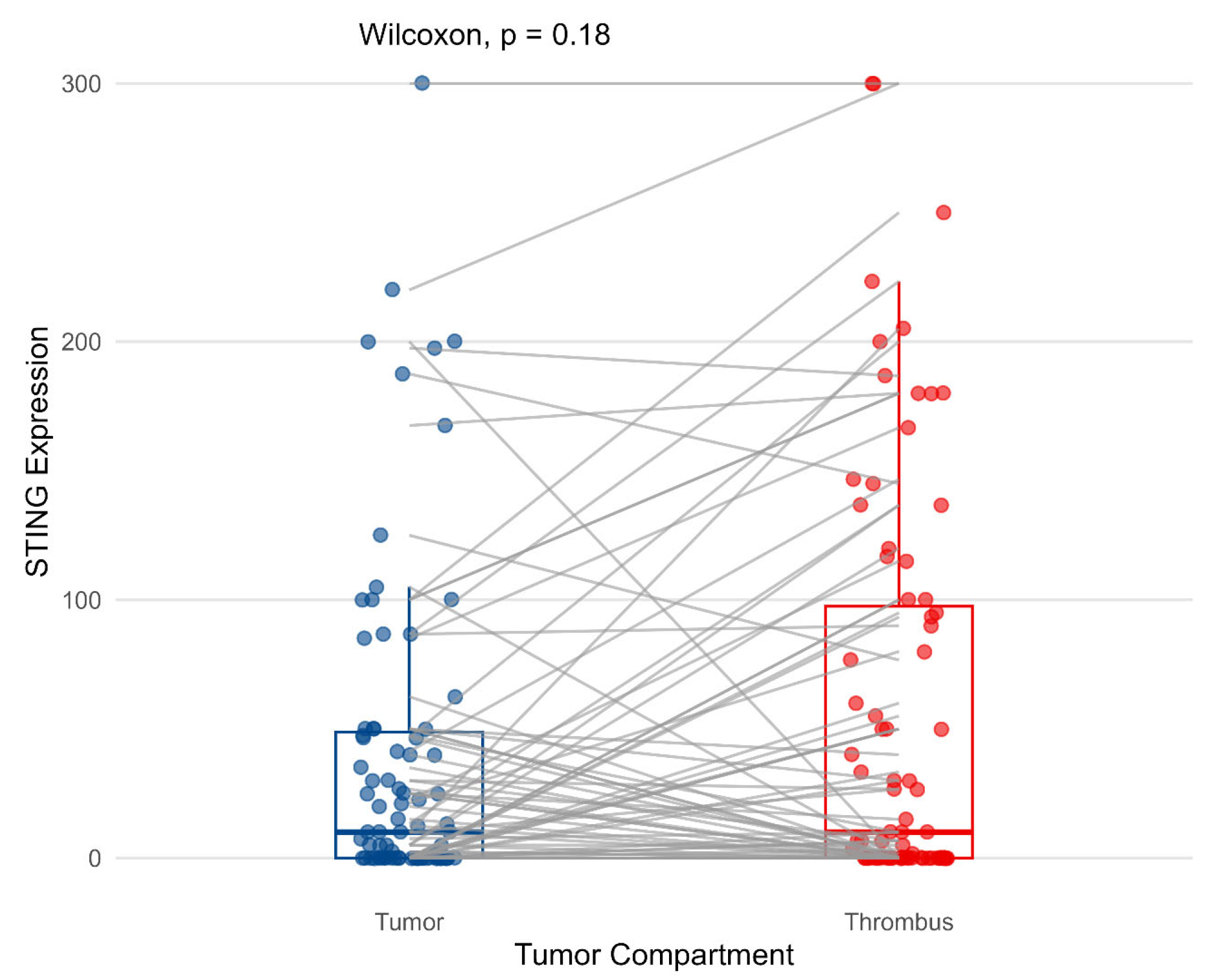
3.2. Cytoplasmic Expression of STING on Tumor Cells and Its Correlations with Pathological Features
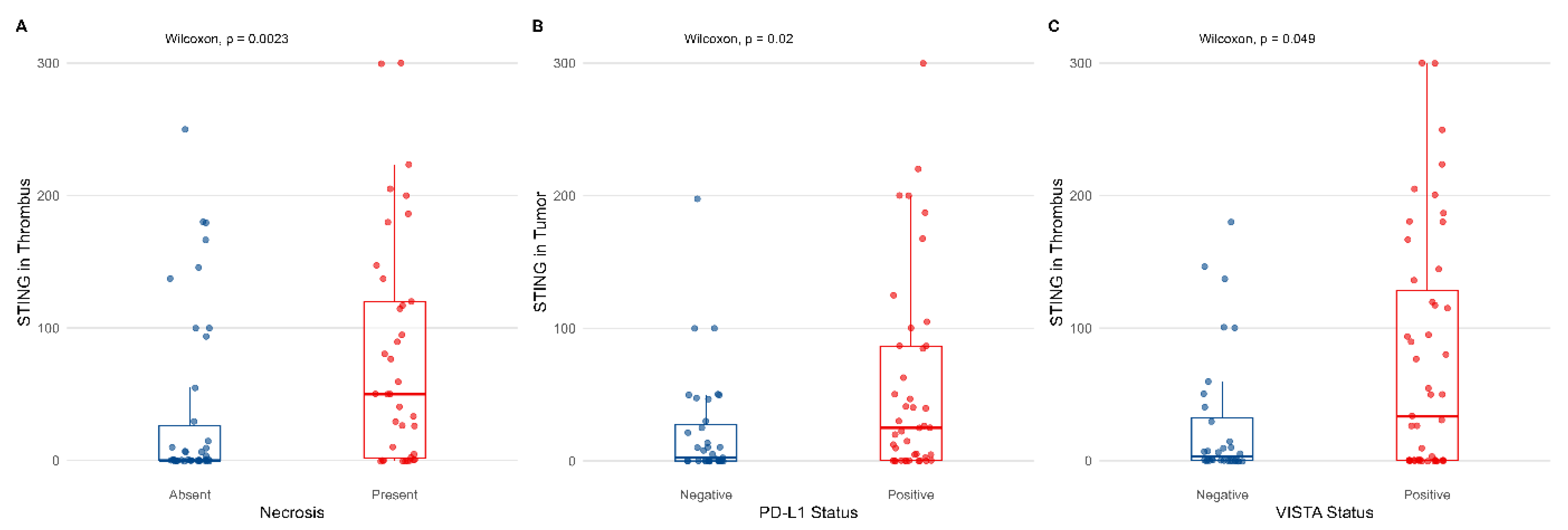
3.3. Association Between STING Expression and Markers of Inflammatory Response
3.4. Association Between TILs and Clinicopathological Variables in Different Compartments
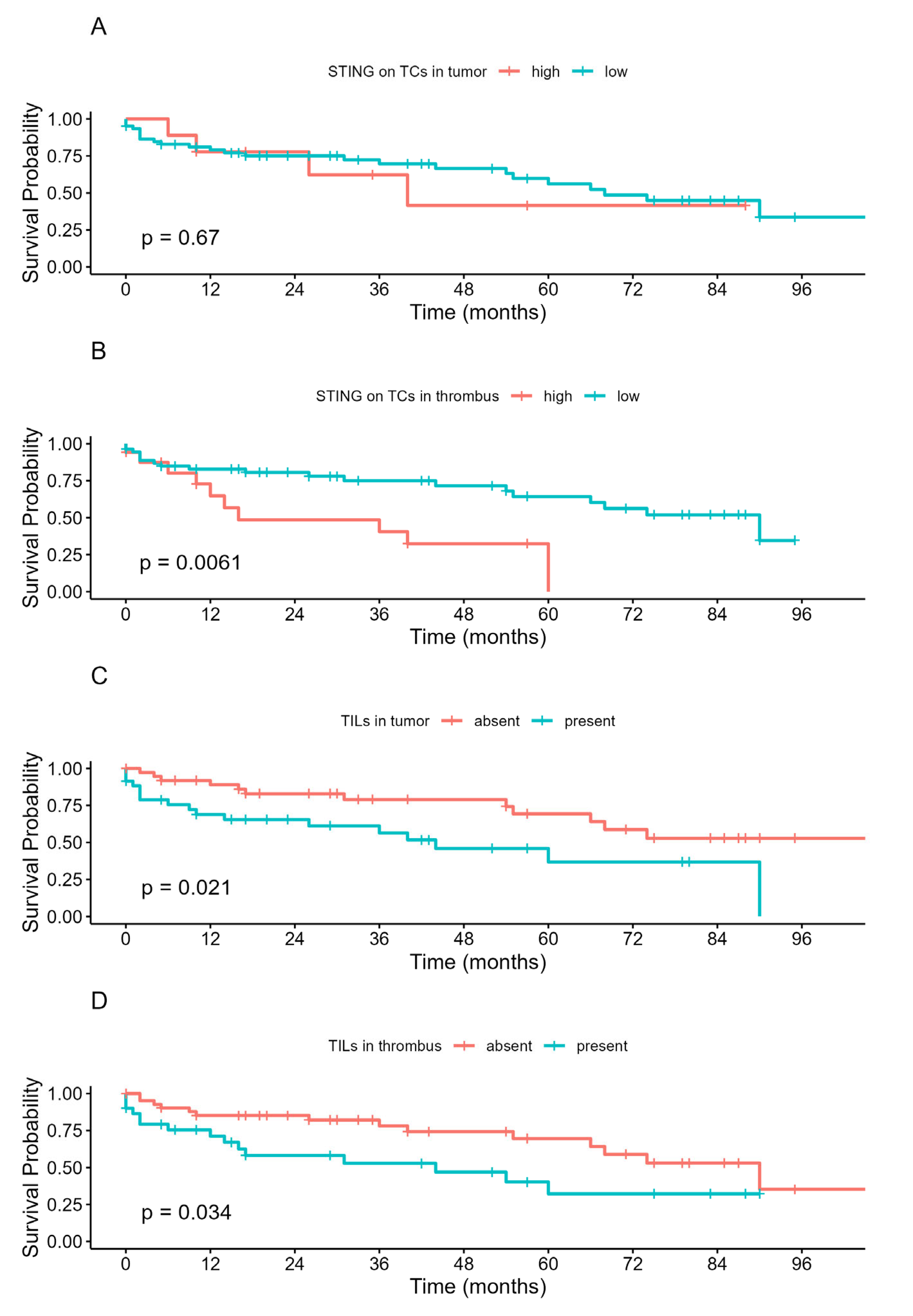
3.5. The Prognostic Value of STING and TILs in the Studied Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khagi, Y.; Kurzrock, R.; Patel, S.P. Next generation predictive biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibition. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Chi, K.N. Targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Current treatment and future directions. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2010, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motwani, M.; Pesiridis, S.; Fitzgerald, K.A. DNA sensing by the cGAS-STING pathway in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheradame, L.; Guerrera, I.C.; Gaston, J.; Schmitt, A.; Jung, V.; Goudin, N.; Pouillard, M.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Modesti, M.; Judde, J.G.; et al. STING protects breast cancer cells from intrinsic and genotoxic-induced DNA instability via a non-canonical, cell-autonomous pathway. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6627–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, L.; Glickman, L.H.; McWhirter, S.M.; Kanne, D.B.; Sivick, K.E.; Katibah, G.E.; Woo, S.R.; Lemmens, E.; Banda, T.; Leong, J.J.; et al. Direct Activation of STING in the Tumor Microenvironment Leads to Potent and Systemic Tumor Regression and Immunity. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuri, T.; Kosaka, A.; Ishibashi, K.; Kumai, T.; Hirata, Y.; Ohara, K.; Nagato, T.; Oikawa, K.; Aoki, N.; Harabuchi, Y.; et al. Intratumoral administration of cGAMP transiently accumulates potent macrophages for anti-tumor immunity at a mouse tumor site. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Sierra, R.A.; Trillo-Tinoco, J.; Cao, Y.; Innamarato, P.; Payne, K.K.; de Mingo Pulido, A.; Mandula, J.; Zhang, S.; Thevenot, P.; et al. The Unfolded Protein Response Mediator PERK Governs Myeloid Cell-Driven Immunosuppression in Tumors through Inhibition of STING Signaling. Immunity 2020, 52, 668–682.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ager, C.R.; Boda, A.; Rajapakshe, K.; Lea, S.T.; Di Francesco, M.E.; Jayaprakash, P.; Slay, R.B.; Morrow, B.; Prasad, R.; Dean, M.A.; et al. High potency STING agonists engage unique myeloid pathways to reverse pancreatic cancer immune privilege. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Qi, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Q.N.; Wei, D.L.; Wei, X.L.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.L.; Ju, H.Q.; et al. Targeting the STING pathway in tumor-associated macrophages regulates innate immune sensing of gastric cancer cells. Theranostics 2020, 10, 498–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Xu, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Cai, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Xu, Q.; et al. SHP2-Mediated Inhibition of DNA Repair Contributes to cGAS-STING Activation and Chemotherapeutic Sensitivity in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3215–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, E.; McCabe, N.; Kennedy, R.D.; Parkes, E.E. DNA Repair Deficiency in Breast Cancer: Opportunities for Immunotherapy. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 4325105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calio, A.; Brunelli, M.; Gobbo, S.; Pedron, S.; Segala, D.; Argani, P.; Martignoni, G. Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) immunohistochemical expression in the spectrum of perivascular epithelioid cell (PEC) lesions of the kidney. Pathology 2021, 53, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marletta, S.; Marcolini, L.; Calio, A.; Pedron, S.; Antonini, P.; Martelli, F.M.; Stefanizzi, L.; Martignoni, G. Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) immunohistochemical expression in fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cell carcinoma: Biological and potential predictive implications. Virchows Arch. 2025, 487, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msaouel, P.; Malouf, G.G.; Su, X.; Yao, H.; Tripathi, D.N.; Soeung, M.; Gao, J.; Rao, P.; Coarfa, C.; Creighton, C.J.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization Identifies Distinct Genomic and Immune Hallmarks of Renal Medullary Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 720–734.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, C.; Taurelli Salimbeni, B.; Santoro, C.; Trapani, D.; Antonarelli, G.; Curigliano, G. Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes across Breast Cancer Subtypes: Current Issues for Biomarker Assessment. Cancers 2023, 15, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, X.; Guan, C.; Gu, M. The prognostic and predictive value of tumor infiltrating Macrophage and Neutrophil in patient with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in renal cell carcinoma. Medicine 2020, 99, e23181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapala, L.; Kunc, M.; Sharma, S.; Peksa, R.; Popeda, M.; Biernat, W.; Radziszewski, P. Immune checkpoint receptor VISTA on immune cells is associated with expression of T-cell exhaustion marker TOX and worse prognosis in renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 4131–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UICC International Union Against Cancer. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors; Sobin, L., Wittekind, C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Zapala, L.; Kunc, M.; Sharma, S.; Peksa, R.; Popeda, M.; Biernat, W.; Radziszewski, P. Evaluation of PD-L1 (E1L3N, 22C3) expression in venous tumor thrombus is superior to its assessment in renal tumor in predicting overall survival in renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 200.e1–200.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peksa, R.; Sharma, S.; Kunc, M.; Popeda, M.; Qu, L.; Frankiewicz, M.; Folwarski, M.; Radziszewski, P.; Zapala, L. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 is diversely expressed in the primary tumour and venous thrombus of clear cell renal cancer and correlates with poor overall survival. Contemp. Oncol. 2024, 28, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marletta, S.; Calio, A.; Bogina, G.; Rizzo, M.; Brunelli, M.; Pedron, S.; Marcolini, L.; Stefanizzi, L.; Gobbo, S.; Princiotta, A.; et al. STING is a prognostic factor related to tumor necrosis, sarcomatoid dedifferentiation, and distant metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2023, 483, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.K.; Biecek, M.; Survminer, P. Drawing Survival Curves Using “ggplot2”. R Package Version 0.4.8. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survminer (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Zhao, K.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Yin, K. Targeting STING in cancer: Challenges and emerging opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Wang, Z.; Johnson, G.N.; Ho, Y.J.; Ganesh, K.; Umeda, S.; Gan, S.; Mujal, A.M.; Delconte, R.B.; et al. STING inhibits the reactivation of dormant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2023, 616, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Boire, A.; Jin, X.; Valiente, M.; Er, E.E.; Lopez-Soto, A.; Jacob, L.; Patwa, R.; Shah, H.; Xu, K.; et al. Carcinoma-astrocyte gap junctions promote brain metastasis by cGAMP transfer. Nature 2016, 533, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.S.; Baixauli, F.; Kyle, R.L.; Puleston, D.J.; Cameron, A.M.; Sanin, D.E.; Hippen, K.L.; Loschi, M.; Thangavelu, G.; Corrado, M.; et al. Mitochondrial Integrity Regulated by Lipid Metabolism Is a Cell-Intrinsic Checkpoint for Treg Suppressive Function. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 422–437.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Ji, H.; Li, S.; Yang, S.; Xu, D.; et al. An Analysis of the Expression and Association with Immune Cell Infiltration of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Pan-Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, H.; Cloer, E.W.; Zhang, J.; Mei, L.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Hepperla, A.J.; Simon, J.M.; et al. STING Suppresses Mitochondrial VDAC2 to Govern RCC Growth Independent of Innate Immunity. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2203718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Guo, M.; Shen, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, M. The use of an oxidative stress scoring system in prognostic prediction for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Sasaki, S.; Sato, Y.; Harashima, H. Cancer Immunotherapy with Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with a Stimulator of Interferon Genes Agonist against Renal Tumor Lung Metastasis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, L.; Pan, X.; Shen, Y.; Ye, M.; Wang, G.; Cui, C.; Zhou, Q.; Tseng, Y.; Gong, Z.; et al. Targeting tumor monocyte-intrinsic PD-L1 by rewiring STING signaling and enhancing STING agonist therapy. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 503–518.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; An, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zheng, T.; Li, X. STING: A master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Kanne, D.B.; Leong, M.; Glickman, L.H.; McWhirter, S.M.; Lemmens, E.; Mechette, K.; Leong, J.J.; Lauer, P.; Liu, W.; et al. STING agonist formulated cancer vaccines can cure established tumors resistant to PD-1 blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 283ra52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yan, L.; Liu, N.; Xu, M.; Cai, H. IFI16 promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating PD-L1 in immunomicroenvironment through STING-TBK1-NF-kB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garza, R.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, A.; Salinas-Carmona, M.C.; Mejia-Torres, M. Biomarkers for evaluating the clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2024, 52, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahoud, J.; Potez, M.; Guske, C.; Miller, J.; Ali, J.; Carter, M.; Khambati, F.; Johnson, J.; Fazili, A.; Gullapalli, K.; et al. Optimizing clear cell renal cell carcinoma tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes under controlled hypoxic conditions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Feature | n (Percentage,%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Grade | G2-G3 | 55 (67) |
| G4 | 27 (33) | |
| Tumor | 3a | 79 (96.5) |
| 3b | 1 (1.5) | |
| 3c | - | |
| 4 | 1 (1.5) | |
| Nodes | 0 | 67 (73) |
| 1 | 15 (27) | |
| Metastases | 0 | 59 (72) |
| 1 | 23 (28) | |
| Sarcomatoid features | absent | 76 (93) |
| present | 6 (7) | |
| Rhabdoid features | present | 73 (89) |
| absent | 9 (11) | |
| Tumor necrosis | present | 38 (46) |
| absent | 44 (54) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.; Kunc, M.; Pęksa, R.; Ciarka, A.; Łyzińska, W.; Qu, L.; Radziszewski, P.; Zapała, Ł. Increased Immunohistochemical Expression of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) in Renal Cancer with Venous Tumor Thrombus Is Associated with Worse Prognosis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112674
Sharma S, Kunc M, Pęksa R, Ciarka A, Łyzińska W, Qu L, Radziszewski P, Zapała Ł. Increased Immunohistochemical Expression of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) in Renal Cancer with Venous Tumor Thrombus Is Associated with Worse Prognosis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112674
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Sumit, Michał Kunc, Rafał Pęksa, Aleksandra Ciarka, Weronika Łyzińska, Le Qu, Piotr Radziszewski, and Łukasz Zapała. 2025. "Increased Immunohistochemical Expression of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) in Renal Cancer with Venous Tumor Thrombus Is Associated with Worse Prognosis" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112674
APA StyleSharma, S., Kunc, M., Pęksa, R., Ciarka, A., Łyzińska, W., Qu, L., Radziszewski, P., & Zapała, Ł. (2025). Increased Immunohistochemical Expression of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) in Renal Cancer with Venous Tumor Thrombus Is Associated with Worse Prognosis. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112674





