The Glymphatic System and Obesity: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging ALPS Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Clinical Assessment
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements and BMI Classification
2.3. MRI Data Acquisition
2.4. DTI-ALPS Index Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Age-Adjusted Group Comparisons (ANCOVA)
- Participants with obesity vs. participants who were of normal weight;
- Participants with obesity vs. participants who were overweight;
- Participants with obesity vs. participants without obesity.
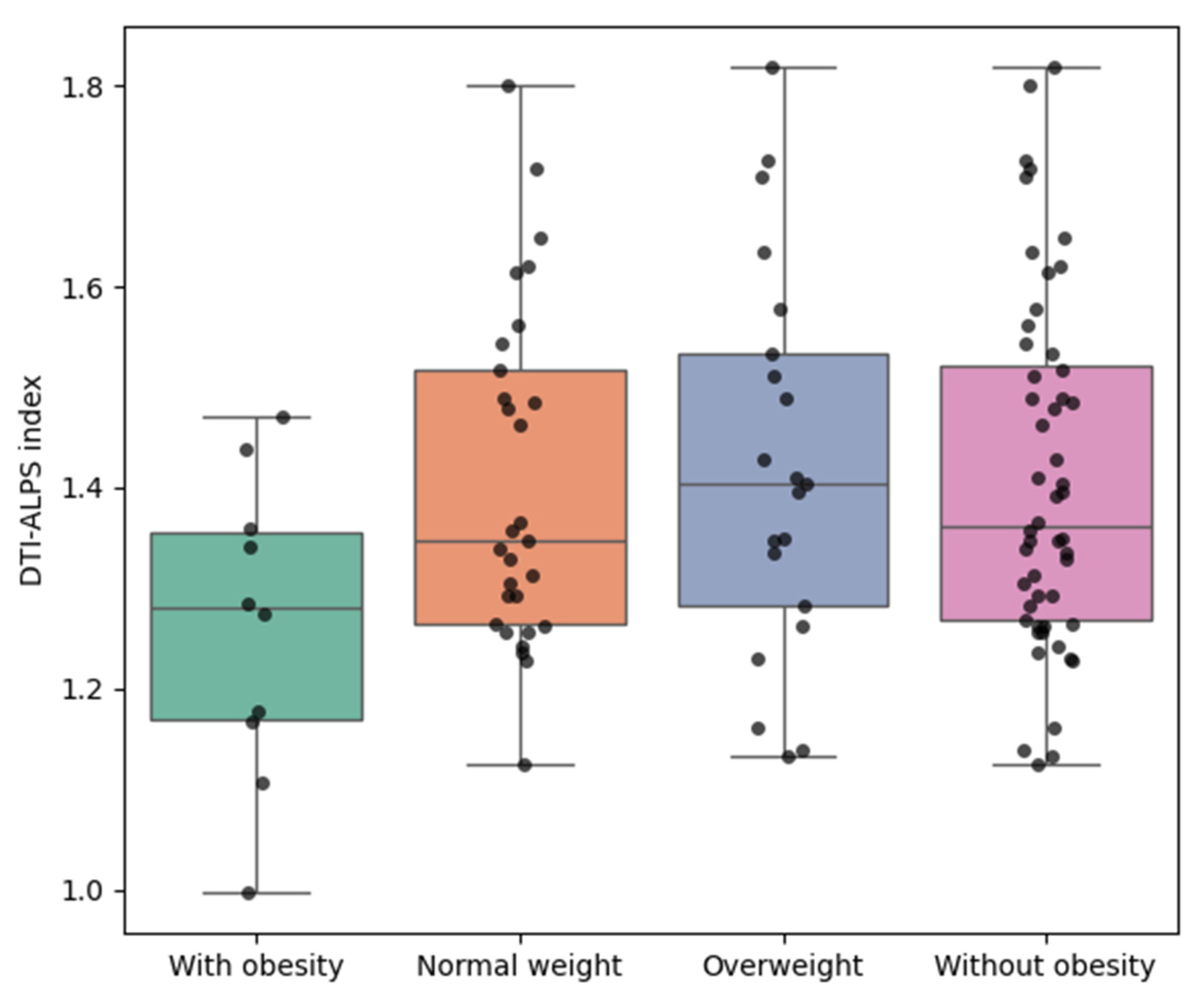
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics by BMI Category
3.2. DTI-Derived Diffusivity Measures and ALPS Index
3.3. Unadjusted Comparisons (Mann−Whitney U Tests)
- Participants with obesity (BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2);
- Participants who were normal weight (BMI ≥ 18.5 and < 23.0 kg/m2);
- Participants who were overweight (BMI ≥ 23.0 and < 25.0 kg/m2);
- Participants without obesity (BMI < 25.0 kg/m2).
3.4. Age-Adjusted Comparisons (ANCOVA)
3.5. Correlation Between DTI-ALPS Index, BMI, and Age
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazon, J.N.; de Mello, A.H.; Ferreira, G.K.; Rezin, G.T. The impact of obesity on neurodegenerative diseases. Life Sci. 2017, 182, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitman, E.S.; Aschen, S.Z.; Farias-Eisner, G.; Albano, N.; Cuzzone, D.A.; Ghanta, S.; Zampell, J.C.; Thorek, D.; Mehrara, B.J. Obesity impairs lymphatic fluid transport and dendritic cell migration to lymph nodes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heredia, F.P.; Gómez-Martínez, S.; Marcos, A. Obesity, inflammation and the immune system. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2012, 71, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yue, Y.; Ba, F.; He, T.; Tang, X.; Hu, X.; Pu, J.; Huang, C.; Lv, W.; Zhang, B.; et al. Diffusion along perivascular spaces as marker for impairment of glymphatic system in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinsztein, D.C. The roles of intracellular protein-degradation pathways in neurodegeneration. Nature 2006, 443, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliff, J.J.; Lee, H.; Yu, M.; Feng, T.; Logan, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Benveniste, H. Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaker, C.; Djemai, B.; Ciobanu, L.; Tsurugizawa, T.; Le Bihan, D. Diffusion MRI reveals in vivo and non-invasively changes in astrocyte function induced by an aquaporin-4 inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, H.; Vijayasarathi, A.; Cekic, M.; Hirata, Y.; Linetsky, M.; Ho, M.; Kim, W.; Salamon, N. Diagnostic performance of glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and mimickers. Curr. Gerontol. Geriatr. Res. 2019, 2019, 5675014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, K.I.; Park, K.M. Are there differences in brain morphology according to handedness? Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, D.G.; Nightingale, P.G. Evaluation of a shortened version of the Abbreviated Mental Test in a series of elderly patients. Clin. Rehabil. 1997, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Region, W.W.P.; IASO, I. The Asia-Pacific perspective: Redefining obesity and its treatment. Int. Obes. Task Force 2000, 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Taoka, T.; Masutani, Y.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Yasuno, F.; Kishimoto, T.; Naganawa, S. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: Diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2017, 35, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestre, H.; Mori, Y.; Nedergaard, M. The brain’s glymphatic system: Current controversies. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ran, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Lou, M. Glymphatic function plays a protective role in ageing-related cognitive decline. Age Ageing 2023, 52, afad107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Hong, H.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M. Association between body mass index and glymphatic function using diffusion tensor image-along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Atti, A.R.; Gatz, M.; Pedersen, N.L.; Johansson, B.; Fratiglioni, L. Midlife overweight and obesity increase late-life dementia risk: A population-based twin study. Neurology 2011, 76, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmer, R.A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Yaffe, K. Obesity in middle age and future risk of dementia: A 27 year longitudinal population based study. BMJ 2005, 330, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cournot, M.; Marquié, J.C.; Ansiau, D.; Martinaud, C.; Fonds, H.; Ferrières, J.; Ruidavets, J.B. Relation between body mass index and cognitive function in healthy middle-aged men and women. Neurology 2006, 67, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstad, J.; Paul, R.H.; Cohen, R.A.; Tate, D.F.; Gordon, E. Obesity is associated with memory deficits in young and middle-aged adults. Eat. Weight. Disord.-Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2006, 11, e15–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, G.; Nolan-Poupart, S.; Jones-Gotman, M.; Small, D.M. Working memory and reward association learning impairments in obesity. Neuropsychologia 2014, 65, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheke, L.G.; Bonnici, H.M.; Clayton, N.S.; Simons, J.S. Obesity and insulin resistance are associated with reduced activity in core memory regions of the brain. Neuropsychologia 2017, 96, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.M.; Tarumi, T.; Miles, S.C.; Tanaka, H.; Shah, F.; Haley, A.P. Insulin sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between BMI and working memory-related brain activation. Obesity 2010, 18, 2131–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.A.; Carlsson, C.M.; Trivedi, M.A.; Sager, M.A.; Johnson, S.C. The effect of body mass index on global brain volume in middle-aged adults: A cross sectional study. BMC Neurol. 2005, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstad, J.; Paul, R.H.; Cohen, R.A.; Tate, D.F.; Spitznagel, M.B.; Grieve, S.; Gordon, E. Relationship between body mass index and brain volume in healthy adults. Int. J. Neurosci. 2008, 118, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefer, G.; Marcus, Y.; Stern, N. Is obesity a brain disease? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2489–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstynen, T.D.; Weinstein, A.M.; Schneider, W.W.; Jakicic, J.M.; Rofey, D.L.; Erickson, K.I. Increased body mass index is associated with a global and distributed decrease in white matter microstructural integrity. Biopsychosoc. Sci. Med. 2012, 74, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeumier, K.C.; Taylor, D.V.; Amen, D.G. Elevated BMI is associated with decreased blood flow in the prefrontal cortex using SPECT imaging in healthy adults. Obesity 2011, 19, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, J.R.; Jo, M.H.; Ullah, R.; Kim, M.W.; Kim, M.O. Metabolic stress alters antioxidant systems, suppresses the adiponectin receptor 1 and induces Alzheimer’s like pathology in mice brain. Cells 2020, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.C.; Killcross, A.S.; Jenkins, T.A. Obesity and cognitive decline: Role of inflammation and vascular changes. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, S.; Tatarczyk, T.; Stadlmayr, A.; Ciardi, C.; Ress, C.; Tschoner, A.; Sandhofer, A.; Paulweber, B.; Ebenbichler, C.F.; Patsch, J.R. Effect of obesity and insulin sensitivity on adiponectin isoform distribution. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 38, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Monaco, M.L.; Palmieri, A.; Mazzarella, G.; Costagliola, C.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. New insight into adiponectin role in obesity and obesity-related diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 658913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronan, L.; Alexander-Bloch, A.F.; Wagstyl, K.; Farooqi, S.; Brayne, C.; Tyler, L.K.; Fletcher, P.C. Obesity associated with increased brain age from midlife. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 47, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzenius, J.D.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Cabeen, R.P.; Conturo, T.E.; McMichael, A.R.; Lane, E.M.; Heaps, J.M.; Salminen, L.E.; Baker, L.M.; Gunstad, J.; et al. Impact of body mass index on neuronal fiber bundle lengths among healthy older adults. Brain Imaging Behav. 2013, 7, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemot-Legris, O.; Muccioli, G.G. Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: Beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, A.M.; Batista, S. Multiple sclerosis: Implications of obesity in neuroinflammation. Obes. Brain Funct. 2017, 19, 191–210. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Dorantes, M.T.; Díaz-López, Y.E.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R. Environment and gene association with obesity and their impact on neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Bhat, H.F. Obesity and neurological disorders: Dietary perspective of a global menace. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic: Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Taoka, T.; Ito, R.; Nakamichi, R.; Nakane, T.; Kawai, H.; Naganawa, S. Diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS): Revisiting the meaning and significance of the method. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2024, 23, 268–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Yule, Z.; Song, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Microstructure changes of the brain preceded glymphatic function changes in young obesity with and without food addiction. Meta-Radiol. 2025, 3, 100137. [Google Scholar]

| Participants with Underweight | Participants with Normal Weight | Participants with Overweight | Participants with Obesity | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 34.5 (10.6) | 42.9 (12.7) | 44.3 (17.2) | 44.3 (12.6) | 0.819 |
| Male, n (%) | 0 (0.0%) | 7 (24.1%) | 12 (57.1%) | 2 (20.0%) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 46.1 (3.7) | 54.4 (7.0) | 67.1 (8.3) | 81.7 (17.2) | 0.021 |
| Height (cm) | 164.9 (0.1) | 160.3 (8.0) | 167.0 (9.9) | 170.2 (13.7) | <0.001 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 16.96 (1.39) | 21.11 (1.08) | 23.95 (0.58) | 27.87 (2.19) | 0.042 |
| Participants Without Obesity, N = 52 (83.9%) | Participants with Obesity, N = 10 (16.1%) | p-Value (t-Test) | p-Value (Mann–Whitney U Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projection fiber | ||||
| Dxx (×10−4) | 6.028 (0.538) | 5.430 (0.340) | 0.0002 | 0.0009 |
| Dyy (×10−4) | 5.118 (0.901) | 5.185 (0.780) | 0.8136 | 0.612 |
| Dzz (×10−4) | 9.708 (0.931) | 9.593 (0.601) | 0.6201 | 0.4729 |
| Association fiber | ||||
| Dxx (×10−4) | 6.556 (0.718) | 6.241 (0.691) | 0.2118 | 0.2795 |
| Dyy (×10−4) | 10.740 (0.870) | 10.241 (0.912) | 0.1358 | 0.1281 |
| Dzz (×10−4) | 3.911 (0.507) | 4.181 (0.791) | 0.3220 | 0.1653 |
| Subcortical fiber | ||||
| Dxx (×10−4) | 10.768 (1.166) | 10.711 (1.202) | 0.8916 | 0.9924 |
| Dyy (×10−4) | 7.113 (1.329) | 6.301 (1.030) | 0.0461 | 0.062 |
| Dzz (×10−4) | 5.924 (1.543) | 5.543 (0.754) | 0.2445 | 0.6529 |
| DTI-ALPS index | 1.410 (0.176) | 1.262 (0.150) | 0.0147 | 0.0361 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.M.; Wi, J.-H.; Park, B.S.; Lee, D.A.; Kim, J. The Glymphatic System and Obesity: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging ALPS Study. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112585
Park KM, Wi J-H, Park BS, Lee DA, Kim J. The Glymphatic System and Obesity: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging ALPS Study. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112585
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Kang Min, Jin-Hong Wi, Bong Soo Park, Dong Ah Lee, and Jinseung Kim. 2025. "The Glymphatic System and Obesity: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging ALPS Study" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112585
APA StylePark, K. M., Wi, J.-H., Park, B. S., Lee, D. A., & Kim, J. (2025). The Glymphatic System and Obesity: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging ALPS Study. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2585. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112585







