Interferons in Autoimmunity: From Loss of Tolerance to Chronic Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lymphocytes Regulating Immune Function: Loss of Tolerance
Differentiation of CD4+ T Lymphocyte Subsets
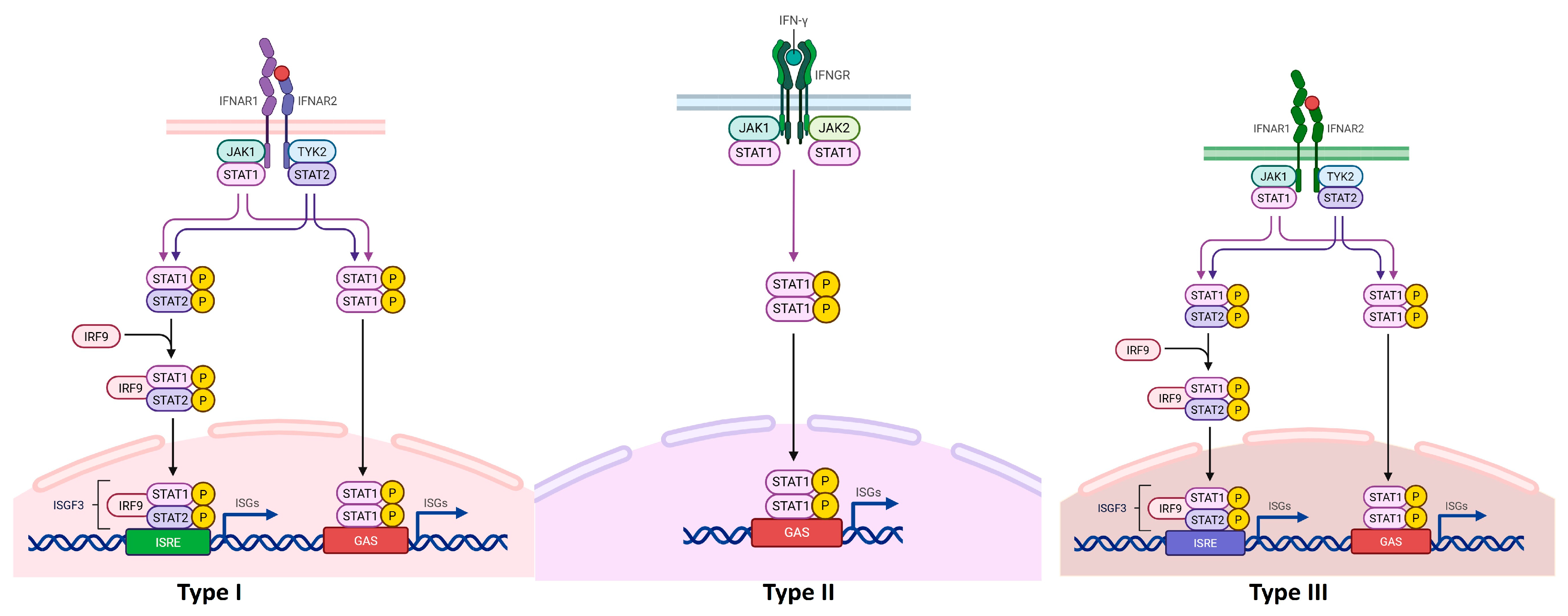
3. Interferons
| Disease | Predominant IFN Axis | Key Source Cells | Confirmed Modalities (H-Gen/H-Obs/H-Int/M/O) | Hallmark Biomarkers | Therapeutic Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE/CLE [84,85] | Type I (α/β); keratinocyte IFN-κ in skin | pDCs, monocytes; keratinocytes (skin) | H-Obs, H-Int (IFNAR blockade), M, O | ISG score, SIGLEC1, CXCL10; cutaneous IFN-κ | Anifrolumab approved; pDC-targeting in late phase; TLR7/9 and IRAK4 inhibitors in development |
| Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) [86] | Type I » Type II (context) | pDCs, salivary epithelial cells | H-Obs, M, O | ISG signature in glands/blood; SIGLEC1; CXCL13/CXCL10 | Investigational IFN pathway blockade; nucleic acid sensing targets under study |
| Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [85] | Type II (γ) with Type I in subsets | T/NK cells (IFN-γ), synovial myeloid cells | H-Obs, M, O | GAS-driven transcripts; IFN-high synovial endotype | JAK inhibitors mitigate IFN-γ signaling; mixed data for direct IFN-I blockade |
| Systemic sclerosis (SSc) [87] | Type I dominant | pDCs, fibroblasts | H-Obs, M, O | Blood/skin ISG high; CXCL10; SIGLEC1 | pDC and TLR inhibition being explored; antifibrotic combinations of interest |
| Dermatomyositis (DM) [88] | Type I dominant | pDCs, muscle/skin stromal cells | H-Obs, M, O | MHC-I upregulation; ISG in muscle/skin; myositis-specific Abs | JAK inhibitors used off-label; pDC/IFN-targeted trials ongoing |
| Multiple sclerosis (MS) [89] | Therapeutic Type I (β); Type II in relapse | CNS-resident cells, myeloid cells; T/NK (IFN-γ) | H-Int (IFN-β), H-Obs, M | Response to IFN-β; CSF chemokines | IFN-β approved; JAK/TYK2 under evaluation for subsets |
| Type 1 diabetes (T1D) [90] | Type I/II (islet antiviral tone vs. inflammation) | β-cells (IFN-β), myeloid and T/NK cells | H-Obs, M, O | Islet ISG; CXCL10; HLA class I hyperexpression | Early trials of JAK/TYK2; careful balance to preserve antiviral defense |
| Psoriasis [91] | Type I (lesional) with IL-23/Th17 axis | Keratinocytes, myeloid cells | H-Obs, M, O | Cutaneous ISG; IFN-κ; pDC-derived IFN early in lesions | TYK2 (deucravacitinib) approved; anti-IFN not standard |
| IBD (Crohn’s/UC) [92] | Type III (λ) at epithelium; Type I in subsets | Epithelial cells, myeloid cells | H-Obs, M, O | Epithelial ISG; mixed IFN-λ effects on repair | Caution with IFN agonism; pathway inhibitors investigational |
| Interferonopathies (e.g., SAVI, AGS) [93] | Constitutive Type I | Intrinsic (genetic activation in immune/stromal cells) | H-Gen, H-Int (JAK), H-Obs, M | Very high ISG; genetic diagnosis | JAK inhibitors clinically beneficial; cGAS–STING inhibitors emerging |
3.1. IFNs in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
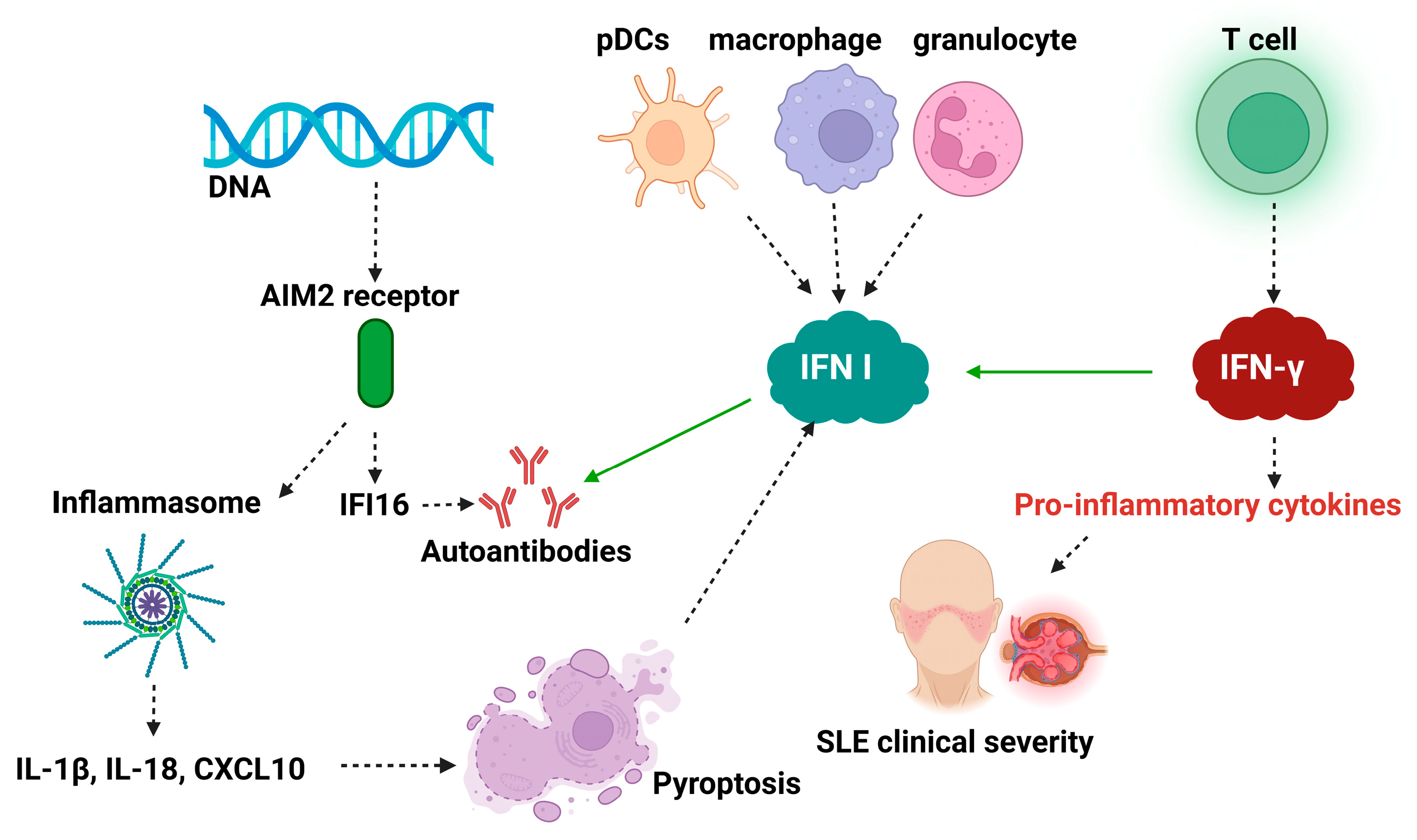
3.2. IFN-I in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3.3. IFN-I in RA
3.4. IFN in Sjögren’s Syndrome
3.5. IFN in Systemic Sclerosis
3.6. IFN-λ in ADs
3.7. IFNs in Other ADs
4. Clinical Translation and Therapeutic Landscape
4.1. From Association to Causation in IFN Biology
4.2. IFN Pathway Therapies Under Clinical Development or Approved
| Agent/Class | Target/Mechanism | Indication(s) Tested | Trial Phase/Status | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anifrolumab | Anti-IFNAR1 mAb (blocks type I IFN receptor) | SLE | Phase 3 → Approved | Reduced disease activity, skin/joint benefit, steroid sparing. |
| Sifalimumab/Rontalizumab | Anti-IFN-α mAbs (neutralize IFN-α subtypes) | SLE | Phase 2 (terminated) | ISG suppression, modest efficacy signals. |
| Litifilimab (BIIB059) | Anti-BDCA2 mAb (inhibits pDC IFN-I production) | CLE, SLE | Phase 2 → Phase 3 | Reduced cutaneous disease activity, lowered IFN-I outputs. |
| JAK inhibitors (ruxolitinib, baricitinib, tofacitinib) | Block JAK1/2/3 signaling downstream of IFNAR | SAVI, interferonopathies, SLE (investigational) | Approved in other indications; proof-of-concept in IFN-driven disease | Improved systemic and pulmonary disease in interferonopathies. |
| Deucravacitinib | Selective TYK2 inhibitor (IL-12/23 and IFN signaling) | Psoriasis; investigational in other autoimmune diseases | Approved in psoriasis | Effective in TYK2-driven inflammation; potential relevance to IFN-driven autoimmunity. |
| IFN-β | IFN agonist | Multiple sclerosis | Approved | Longstanding disease-modifying therapy; anti-inflammatory effects. |
| IFN-λ agonists | Type III IFN agonists | Hepatitis, COVID-19 | Phase 2–3 (not autoimmune) | Antiviral protection; uncertain role in autoimmunity. |
4.3. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Autoimmune Disease |
| AIM2 | Absent in Melanoma 2 |
| ALR | AIM2-Like Receptor |
| ATRA | All-Trans Retinoic Acid |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CD | Dendritic Cells |
| cDC/pDC | Conventional/Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (CDm(p) |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| DAMP | Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| EAE | Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte–Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor |
| GI Tract | Gastrointestinal Tract |
| IFNGS/ISG | IFN Gene Signature/Interferon-Stimulated Genes |
| IL | Interleukins |
| CMI/RIMC | Cell-Mediated Immunity |
| IRF | Interferon Regulatory Factor |
| ISRE | Interferon-Stimulated Response Element |
| JAK1 | Janus Kinase 1 |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA |
| miRNA | Micro RNA |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NETs | Neutrophil Extracellular Traps |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLR | NOD-Like Receptors |
| NOD | Nucleotide-binding Oligomerization Domain |
| PAMP | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| PBMC | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells |
| PCD | Programmed Cell Death |
| PRR | Pattern Recognition Receptors |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| IR/RI | Immune Response |
| RIP | Primary Immune Response |
| RLR | RIG-I-Like Receptors (Retinoic acid Inducible Gene-I-like Receptors) |
| ROI | Reactive Oxygen Intermediates |
| SI | Immune System |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| SLO | Secondary Lymphoid Organs |
| SS | Sjögren’s Syndrome |
| SSc | Systemic Sclerosis |
| STAT | Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription |
| STING | Stimulator of Interferon Genes |
| T1D | Type 1 Diabetes |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptors |
| Treg | Regulatory T Cells |
| TYK2 | Tyrosine Kinase 2 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Shirafkan, F.; Hensel, L.; Rattay, K. Immune Tolerance and the Prevention of Autoimmune Diseases Essentially Depend on Thymic Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1339714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabas, A.Z.; Cole, C.D.; Graeff, R.M.; Lafreniere, R.; Weir, D.M. Tolerance, Loss of Tolerance and Regaining Tolerance to Self by Immune-Mediated Events. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, W.; Harigai, M.; Amano, K.; Hidaka, T.; Itoh, K.; Aoki, K.; Nakashima, M.; Nagasawa, H.; Komano, Y.; Nanki, T.; et al. Impact of the HLA-DRB1 Shared Epitope on Responses to Treatment with Tofacitinib or Abatacept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, A.M.; Buckner, J.H. Genetic Basis of Defects in Immune Tolerance Underlying the Development of Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 972121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harroud, A.; Hafler, D.A. Common Genetic Factors among Autoimmune Diseases. Science 2023, 380, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Pu, T.-Y.; Chuang, T.-H.; Hsu, L.-C. Involvement of Nucleic Acid-Sensing Toll-Like Receptors in Human Diseases and Their Controlling Mechanisms. J. Biomed. Sci. 2025, 32, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Bañuelos, E.; Goldman, D.W.; Andrade, V.; Darrah, E.; Petri, M.; Andrade, F. Uncoupling Interferons and the Interferon Signature Explains Clinical and Transcriptional Subsets in SLE. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, M.; Lu, Q. Translating Epigenetics into Clinic: Focus on Lupus. Clin. Epigenet. 2017, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pender, M.P.; Burrows, S.R. Epstein–Barr Virus and Autoimmune Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 623944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, V.R. Sex Hormones in Acquired Immunity and Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Kurien, B.T.; Zimmerman, S.L.; Kaufman, K.M.; Taft, D.H.; Kottyan, L.C.; Lazaro, S.; Weaver, C.A.; Ice, J.A.; Adler, A.J.; et al. X Chromosome Dose and Sex Bias in Autoimmune Diseases: Increased 47,XXX in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darrah, E.; Andrade, F. NETs: The Missing Link between Cell Death and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases? Front. Immunol. 2013, 3, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Rich, S.S.; Raychaudhuri, S. Autoimmune Diseases—Connecting Risk Alleles with Molecular Traits of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayter, S.M.; Cook, M.C. Updated Assessment of the Prevalence, Spectrum and Case Definition of Autoimmune Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, A.; Liston, A. The Immunogenetic Architecture of Autoimmune Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a007260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Huszthy, P.C.; Fossum, E.; Konttinen, Y.; Nakken, B.; Szodoray, P. Selected Aspects in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 351732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, D.; Rose, N.R.; Moudgil, K.D. Common Innate Pathways to Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 212, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C. Cytokine Regulation and Function in T Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, N.; Lee, Y.; Farber, D.L. A Guide to Adaptive Immune Memory. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 810–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, S.; Marchingo, J.M.; Horton, M.B.; Hodgkin, P.D. The Regulation of Lymphocyte Activation and Proliferation. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 51, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. T Helper 2 (Th2) Cell Differentiation, Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (ILC2) Development and Regulation of Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 Production. Cytokine 2015, 75, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, I.F.; Berges, J.; Luther, R.J.; Mailhé, M.P.; Garcia, S.; Bandeira, A.; Weaver, C.; Liston, A.; Freitas, A.A. IL-2 Coordinates IL-2-Producing and Regulatory T Cell Interplay. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2707–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez Ayala, A.; Hsu, C.Y.; Oles, R.E.; Matsuo, K.; Loomis, L.R.; Buzun, E.; Carrillo Terrazas, M.; Gerner, R.R.; Lu, H.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Commensal Bacteria Promote Type I Interferon Signaling to Maintain Immune Tolerance in Mice. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221, e20230063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plitas, G.; Rudensky, A.Y. Regulatory T Cells: Differentiation and Function. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciurkiewicz, M.; Herder, V.; Beineke, A. Beneficial and Detrimental Effects of Regulatory T Cells in Neurotropic Virus Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y. T Cell Dysfunction and Exhaustion in Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Jeon, B.; Ochs, H.D.; Lee, J.S.; Gee, H.Y.; Seo, S.; Geum, D.; Piccirillo, C.A.; Eisenhut, M.; et al. Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked (IPEX) syndrome: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya, S.K.; Lam, B.; Lau, K.; Larkin, J., III. Th17 cells in immunity and autoimmunity. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 986789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hirota, K. The pathogenicity of Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 283–297, Corrected in 2019, 41, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belpaire, A.; Naves, R.; Goebeler, M.; Schmidt, A.; Kerstan, A. From IL-17 to IFN-γ in Inflammatory Skin Disorders: Is Transdifferentiation a Potential Treatment Target? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 932265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, L.; Kallies, A. Molecular Mechanisms Governing CD8 T Cell Differentiation and Function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2025, 43, 515–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.R.; Nelson, M.H.; Himes, R.A.; Li, Z.; Mehrotra, S.; Paulos, C.M. Th17 cells in cancer: The ultimate identity crisis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gruijter, N.M.; Jebson, B.; Rosser, E.C. Cytokine Production by Human B Cells: Role in Health and Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 210, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddy, M.E.; Alter, A.; Bar-Or, A. Distinct Profiles of Human B Cell Effector Cytokines: A Role in Immune Regulation? J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duddy, M.; Niino, M.; Adatia, F.; Hebert, S.; Freedman, M.; Atkins, H.; Kim, H.J.; Bar-Or, A. Distinct Effector Cytokine Profiles of Memory and Naïve Human B Cell Subsets and Implication in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fousert, E.; Toes, R.; Desai, J. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Take the Central Stage in Driving Autoimmune Responses. Cells 2020, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelman, S.; Lavine, K.J.; Randolph, G.J. Origin and Functions of Tissue Macrophages. Immunity 2014, 40, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, Y. The contribution of Macrophages to SLE pathogenesis. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 207, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-T.; Gao, F.; Gu, K.; Chen, D.-K. The Role of Monocytes and Macrophages in AI Disease: A comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldano, S.; Trombetta, A.C.; Contini, P.; Tomatis, V.; Ruaro, B.; Brizzolara, R.; Montagna, P.; Sulli, A.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; et al. Increase in circulating cells coexpressing M1 and M2 macrophage surface markers in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1842–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, V.; Curina, A.; Genua, M.; Ghisletti, S.; Simonatto, M.; Sabò, A.; Amati, B.; Ostuni, R.; Natoli, G. Opposing macrophage polarization programs show extensive epigenomic and transcriptional cross-talk. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funes, S.C.; Rios, M.; Escobar-Vera, J.; Kalergis, A.M. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology 2018, 154, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakowska, J.; Arcimowicz, Ł.; Jankowiak, M.; Papak, I.; Markiewicz, A.; Dziubek, K.; Kurkowiak, M.; Kote, S.; Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K.; Połom, K.t. Autoimmunity and Cancer. Two sides of the same coin. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 793234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOh, S.; OLi, M. TGF-β: Guardian of T Cell Function. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, M.Y.; Belyanina, T.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Kiselev, I.S.; Mamedov, A.E. Contribution of CMH II genes to an association with AI diseases. Acta Naturae 2019, 11, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollid, L.M.; Pos, W.; Wucherpfennig, K.W. Molecular Mechanisms for contribution of MHC molecules to AI diseases. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkoshi, Z. Cancer and Autoimmune disease. A tale of Two Immunological Opposites. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 821598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkoshi, Z. High Treg inflammations promote (most) non-Hematologic Cancers, while low Treg inflamation promote Lymphoid Cancer. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkoshi, Z. The binary Classification of Chronic Diseases. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, W.; Saunders, M.E. Immunity to Pathogens. In The Immune Response: Basic and Clinical Principles; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schoggins, W.J. Interferon-stimulated genes: What do they all do? Ann. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, P.L.; Byrne, A.B.; Hijano, D.R.; Talarico, L.B. Human type I IFN Antiviral Effects in Respiratory and reemerging viral infections. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1372494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.N.; Gan, Z.; Hou, J.; Yang, Y.C.; Huang, L.; Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Nie, P. Identification and Establishment of Type IV Interferon and the Characterization of Interferon-υ including Its Class II Cytokine Receptors IFN-υR1 and IL-10R2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-N.; Jiang, D.-S.; Li, H. Interferon Regulatory Factors: At the Crossroads of Immunity, Metabolism, and Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.Y.; Mangan, N.E.; Cumming, H.; Horvat, J.C.; Mayall, J.R.; Stifter, S.A.; De Weerd, N.; Roisman, L.C.; Rossjohn, J.; Robertson, S.A.; et al. Interferon-ε Protects the Female Reproductive Tract from Viral and Bacterial Infection. Science 2013, 339, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chen, R.; Yin, W.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Hao, C. Effects of AIM2 and IFI16 on Infectious Diseases and Inflammation. Viral Immunol. 2023, 36, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kanzler, H.; Duramad, O.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.-J. Specialization kinetics and repertoire of IFN I responses by human plasmacitoid predendritic cells. Blood. 2006, 107, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantlo, E.; Bukreyeva, N.; Maruyama, J.; Paessler, S.; Huang, C. Antiviral Activities of Type I Interferons to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Antivir. Res. 2020, 179, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachogianis, N.I. Association between DNA Damage Response, Fibrosis and Type I IFN signature in SSc. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 582401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and Distinct Functions of type I and type III IFNs. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galani, I.E.; Triantafyllia, V.; Eleminiadou, E.E.; Koltsida, O.; Stavropoulos, A.; Manioudaki, M.; Thanos, D.; Doyle, S.E.; Kotenko, S.V.; Thanopoulou, K.; et al. Interferon-λ Mediates Non-Redundant Frontline Antiviral Protection against Influenza Virus Infection without Compromising Host Fitness. Immunity 2017, 46, 875–890.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, J.; Mahlakõiv, T.; Mordstein, M.; Duerr, C.U.; Michiels, T.; Stockinger, S.; Staeheli, P.; Hornef, M.W. IFN-λ determines the intestinal epithelial antiviral host defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7944–7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordstein, M.; Neugebauer, E.; Ditt, V.; Jessen, B.; Rieger, T.; Falcone, V.; Sorgeloos, F.; Ehl, S.; Mayer, D.; Kochs, G.; et al. Lambda Interferon Renders Epithelial Cells of the Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Tracts Resistant to Viral Infections. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5670–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, D.M.; Minty, G.E.; Golec, D.P.; Lu, J.; May, J.; Namdar, A.; Shah, R.R.; Puchta, A.; Pelletier, A.R.; Oliveira, A.C.; et al. Differential Expression of IFN-λ Receptor Regulates the Antiviral Activity of Type III Interferons against Enteric Viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic-Rakovic, V.; Whitfield, J.R. Between immunomodulation and immunotolerance: The role of IFNγ in SARS-CoV-2 disease. Cytokine 2021, 146, 155637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, J.R. IFN-γ in Autoimmunity: A Complicated Player on a Complex Stage. Cytokine 2015, 74, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matatall, K.A.; Shen, C.-C.; Challen, G.A.; King, K.Y. Type II IFN promotes differential of myeloid-biased hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 3023–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.-J. Interplay between Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription Signaling Activated by Type I Interferons and Viral Antagonism. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. IFN receptor signaling in malignancy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, F.Z.; Farrari, J.D. STAT: A shape shifting anti-viral super STAT. Jak-Stat 2013, 2, e23633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.H.; Goh, C.Q.; Chua, J.J.E. Emerging Roles of Type I Interferons in Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoros, A.; Platanitis, E.; Kernbauer-Hölzl, E.; Rosebrock, F.; Müller, M.; Decker, T. Canonical and Noncanonical Aspects of JAK–STAT Signaling: Lessons from Interferons for Cytokine Responses. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerd, N.A.; Nguyen, T. The IFNs and their receptors. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, Z.Y. SARS-CoV-2, NS proteins and their roles in host immune evasion. Viruses 2022, 14, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, F.; Dzakah, E.E.; Wang, H.; Tang, S. Roles and Functions of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins in Host Immune Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 940756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 175, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, M.C.; Pettersson, T.; Henriksson, E.; Nadali, M.; Savolainen, O.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Bokarewa, M.I. Survivin Promotes a Glycolytic Switch in CD4+ T Cells. iScience 2022, 25, 105526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I IFN responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrycharz, E.; Hukowska-Szematowicz, B. Host miRNA signature in viral Infections in humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.C.; Tate, M.D.; Hertzog, P.J. MicroRNA as type I IFN-regulated transcripts and modulators of innate immune response. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postal, M.; Vivaldo, J.F.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Paredes, J.L.; Appenzeller, S.; Niewold, T.B. Type I Interferon in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 67, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, C.; Garrec, C.; Tomasello, E.; Dalod, M. The Role of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (pDCs) in Immunity during Viral Infections and Beyond. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 1008–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yum, S.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Deng, Y.; Sun, L.; Zuo, X.; Chen, Z.J. cGAS Activation in Classical Dendritic Cells Causes Autoimmunity in TREX1-Deficient Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2411747121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehmer, D.; Zanoni, I. Interferons in Health and Disease. Cell 2025, 188, 4480–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnier, J.L.; Kahlenberg, J.M. The Role of Cutaneous Type I Interferons in Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Diseases. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Pringle, S.; Bootsma, H.; Kroese, F.G.M. Epithelial–Immune Cell Interplay in Primary Sjögren Syndrome Salivary Gland Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, V.; Assassi, S.; Allanore, Y.; Kuwana, M.; Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D.; Del Galdo, F. Type 1 Interferon Activation in Systemic Sclerosis: A Biomarker, a Target or the Culprit. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2022, 34, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Casal-Dominguez, M.; Derfoul, A.; Pak, K.; Plotz, P.; Miller, F.W.; Milisenda, J.C.; Grau-Junyent, J.M.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Paik, J.; et al. Identification of Distinctive Interferon Gene Signatures in Different Types of Myositis. Neurology 2019, 93, e1193–e1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Bao, R.; Li, L.; Deisenhammer, F.; Arnason, B.G.W.; Reder, A.T. Interferon-β Corrects Massive Gene Dysregulation in Multiple Sclerosis: Short-Term and Long-Term Effects on Immune Regulation and Neuroprotection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 49, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newby, B.N.; Mathews, C.E. Type I Interferon Is a Catastrophic Feature of the Diabetic Islet Microenvironment. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G. Novel Therapies in Plaque Psoriasis: A Review of Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitors. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, K.K.; Mambu, J.; Boehmer, D.; Sposito, B.; Millet, V.; de Sousa Casal, J.; Muendlein, H.I.; Spreafico, R.; Fenouil, R.; Spinelli, L.; et al. Type III Interferons Induce Pyroptosis in Gut Epithelial Cells and Impair Mucosal Repair. Cell 2024, 187, 7533–7550.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, Y.J.; Stetson, D.B. The Type I Interferonopathies: 10 Years on. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskardin, T.L.W.; Niewold, T.B. Type I IFN in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechler, E.C.; Batliwalla, F.M.; Karypis, G.; Gaffney, P.M.; Ortmann, W.A.; Espe, K.J.; Shark, K.B.; Grande, W.J.; Hughes, K.M.; Kapur, V.; et al. Interferon-Inducible Gene Expression Signature in Peripheral Blood Cells of Patients with Severe Lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.C.; Rosen, A.; Kolfenbach, J.R.; Costenbader, K.H.; Bernatsky, S.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Magder, L.S.; Petri, M.; Niewold, T.B. Precise Probes of Type II Interferon Activity Define the Origin of Interferon-Stimulated Genes Induced in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17609–17614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.H.; Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Fournier, D.R.; Piech, T.; Campbell, T.G.; Meyer, R.E.; Fishburn, M.W.; Cabrera, C.; Patel, P.P.; et al. The Simoa HD-1 Analyzer: A Novel Fully Automated Digital Immunoassay Analyzer with Single-Molecule Sensitivity and Multiplexing. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Papa, N.; Minniti, A.; Lorini, M.; Carbonelli, V.; Maglione, W.; Pignataro, F.; Montano, N.; Caporali, R.; Vitali, C. The Role of Interferons in the Pathogenesis of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Type I Interferons in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 633821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Carrio, J.; Alperi-López, M.; López-Mejías, R.; Fernández-Rozas, S.; Ballina-García, F.J.; González-Gay, M.A. Association between Type I Interferon Pathway Activation and Clinical Features in Rheumatoid Arthritis. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J. Type I IFNs in Pathogenesis and Treatment of AI diseases. Clinic Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2020, 59, 248–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raftopoulou, S.; Triantafyllopoulou, A.; Mavragani, C.P. The Role of Type I Interferons in Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Diseases with CNS Involvement. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1026449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aicardi, J.; Goutieres, F.A. A progressive familial encephalopathy with calcification of basal ganglia and chronic cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytosis. Ann. Neurol. 1984, 15, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.F.; Yalavarthi, S.; Zhao, W.; Thacker, S.G.; Anderson, M.; Sandy, A.R.; McCune, W.J.; Kaplan, M.J. A Distinct Subset of Proinflammatory Neutrophils Isolated from Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induces Type I Interferons. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3284–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shao, M.; Zeng, X.; Qian, P.; Huang, H. Signaling Pathways in the Regulation of Cytokine Release Syndrome in Human Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barturen, G.; Babaei, S.; Català-Moll, F.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Makowska, Z.; Martorell-Marugán, J.; Toro-Domínguez, D.; Pantano, L.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Teruel, M.; et al. Integrative Analysis Reveals a Molecular Stratification of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Ruiz, K.; Niewold, T.B. Type I IFNs in autoimmunity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarras, A.; Alase, A.; Antanaviciute, A.; Carr, I.M.; Yusof, Y.M.; Wittmann, M.; Emery, P.; Tsokos, G.C.; Vital, E.M.; Isaacs, J.D.; et al. Functionally Impaired Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Non-Haematopoietic Sources of Type I Interferon Characterize Human Autoimmunity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, L.; Vosslamber, S.; Tjarnlund, A.; de Jong, T.D.; Betteridge, Z.; McHugh, N.; Plestilova, L.; Padyukov, L.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Bultink, I.E.M.; et al. Autoantibody Specificities and Type I Interferon Pathway Activation in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 84, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musella, M. The Yin and Yang of type I IFNs in Cancer promotion and Immune activatin. Biology 2021, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanias, E.; Decker, T. Regulation networks involving STATs, IFNs and NF-kB in inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.K. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: Risks, mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R. IFN λ in inflamation and AI Rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kaplan, M.J. Bite of the wolf: Innate immune response propagate autoimmunity in lupus. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e144918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.K.; Ronnblom, L. Type I IFNs in host defense and inflammatory diseases. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, F.J.; Crow, M.K.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Interferon Target-Gene Expression and Epigenomic Signatures in Health and Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smale, S.T.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Natoli, G. Chromatin Contributions to the Regulation of Innate Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londe, A.C.; Santiago, R.P.; Crispim, J.C.O. Type I Interferons in Autoimmunity. J. Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, E.; Osman, N.; Yassin, E.; Abdelrahman, H.; Abdelrahman, A. Lymphocyte Apoptosis and Its Association with Disease Severity in Juvenile Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2024, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Lei, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Lymphocyte Apoptosis and Macrophage Function: Correlation with Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 24, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhil, A.; Sasidharan, S.; Jayakrishnan, M.P.; Chandan, R.; Sreedharanunni, S. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Latest Insight into Etiopathogenesis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewold, T.B.; Hua, J.; Lehman, T.J.; Harley, J.B.; Crow, M.K. Age- and Sex-Related Patterns of Serum Interferon-α Activity in Lupus Families. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyachi, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Kojima, S.; Ida, T.; Suzuki, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Mimura, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Tanaka, S.; Furuta, S.; et al. Relationship of systemic type I interferon activity with clinical phenotypes, disease activity, and damage accrual in systemic lupus erythematosus in treatment-naive patients: A retrospective longitudinal analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochos, B.; Rosen, L.C. Interferon and Autoantigens: Intersection in Autoimmunity. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1165225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandokumar, K.S.; Nundel, K. Editorial: SLE predisposition factors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1118180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, O. IFNs and Autoimmune disorders. Jt. Bone Spine 2009, 17, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneparo, V.; Landolfo, S.; Gariglio, M.; De Andrea, M. The Absent in Melanoma 2-Like Receptor IFN-Inducible Protein 16: A Key Player in Innate Immunity, Viral Infection, and Tumorigenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.; Franco, R.; Chinenov, Y.; Carlucci, P.M.; Botsios, C.; Pernis, A.B. The Role of NETosis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Cell. Immunol. 2019, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, D.; Moudgil, K.D. Interferons in Autoimmune and Inflammatory diseases. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, V.; Gunnarsson, I.; Dorschner, J.; Eketjäll, S.; Zickert, A.; Niewold, T.B.; Svenungsson, E.; Rönnblom, L. High Levels of Circulating Interferons Type I, II and III Associate with Distinct Clinical Features of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munroe, M.E.; Lu, R.; Zhao, Y.D.; Fife, D.A.; Robertson, J.M.; Guthridge, J.M.; Niewold, T.B.; James, J.A. Altered Type II Interferon Precedes Autoantibody Accrual and Elevated Type I Interferon Activity Prior to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Classification. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, T.M.; Ong, S.G.; Ling, G.S. Type I Interferons in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karle, C.; Burkhardt, H. Characteristics of the (Auto)Reactive T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis According to the Immune Epitope Database. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Endres, J.; Fox, D.A. The Roles of Interferon-γ versus Interleukin-17 in the Pathogenic Effects of Human Th17 Cells. Mod. Rheumatol. 2013, 23, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, C.-Q. Contribution of Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Biomed. Res. 2019, 34, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelchtermans, H.; Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. How IFNγ keeps Autoimmune diseases in check. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, K.; Heremans, H.; Vandeputte, M.; Huang, S.; Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. Accelerated Collagen-Induced Arthritis in IFN-γ Receptor-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 5507–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottenberg, J.-E.; Cagnard, N.; Lucchesi, C.; Letourneur, F.; Mistou, S.; Lazure, T.; Jacques, S.; Ba, N.; Ittah, M.; Lepajolec, C.; et al. Activation of IFN Pathways and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Recruitment in Target Organs of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.I. Sjögren’s Syndrome. Lancet 2005, 366, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezos, A.; Gravani, F.; Tassidou, A.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Voulgarelis, M.; Koutsilieris, M.; Crow, M.K.; Mavragani, C.P. Type I and Type II Interferon Signatures in Sjögren’s Syndrome. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 63, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, E.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Manoussakis, M.N. Expression of Type III Interferons (IFN-λ) and Their Receptor in Sjögren’s Syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, G.; Rudnik, M.; Distler, O. Involvement of the Myeloid Cell Compartment in Fibrogenesis and Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Assassi, S. Dysregulation of Type I IFN signaling in SSc. Curr. Treat. Opt. Rheumatol. 2021, 7, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Assassi, S. The Role of type I IFN in Systemic sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Q.; Pers, J.-O.; Cornec, D. A Cytokine Network Profile Delineates a Common Th1/Type 1 B Effector Cell Signature in Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.R.; Kozyrev, S.V.; Baechler, E.C.; Reddy, M.V.P.; Plenge, R.M.; Bauer, J.W.; Ortmann, W.A.; Koeuth, T.; González Escribano, M.F.; Pons-Estel, B.; et al. A Common Haplotype of Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 (IRF5) Is Associated with Increased Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaug, B.; Assassi, S. Type I IFN dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Cytokine. 2020, 132, 154635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzi, E.; Bulik, M.; Tabib, T.; Morse, C.; Sembrat, J.; Trejo Bittar, H.E.; Rojas, M.; Lafyatis, R. Disparate Interferon Signaling and Shared Aberrant Basaloid Cells in Lung Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, O.; Kochs, G. MX genes. Host determinants controlling influenza virus infection. Hum. Genet. 2019, 139, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Arias, T.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M. Type III Interferons (Lambda Interferons) in Rheumatic Autoimmune Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2020, 68, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagam, S.; Klein, R.S. Type III Interferons: Emerging Roles in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 764062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basyal, B.; Sharma, M.; Goosenberg, E. Autoimmune Pancreatitis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560769/ (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Wang, W.M.; Jin, H.Z. Role of Interferon Regulatory Factor-Mediating Signaling in Psoriasis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3794–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-J. Type I Interferons: Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds with Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonas, A.; Conrad, C. Psoriazis: Classical and paradoxical. The Yin and Yang of TNF and type I IFN. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, K.; Witte, K.; Witte, E.; Proesch, S.; Schulze-Tanzil, G.; Nasilowska, K.; Thilo, J.; Asadullah, K.; Sterry, W.; Volk, H.-D.; et al. IL-29 Is Produced by TH17 Cells and Mediates the Cutaneous Antimicrobial Defense in Psoriasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 204ra129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzammil, M.A.; Fariha, F.; Patel, T.; Sohail, R.; Kumar, M.; Khan, E.; Khanam, B.; Kumar, S.; Khatri, M.; Varrassi, G.; et al. Advancements in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review of Diagnostics, Management, Epidemiology, Prevalence, Patient Outcomes, Quality of Life, and Clinical Presentation. Cureus 2023, 15, e41120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.V.; Constant, D.A.; Meiss, G.; Pekow, J. Interferon-λ in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, H.; Negishi, H.; Taniguchi, T. The IRF Family Transcription Factors at the Interface of Innate and Adaptive Immune Response. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2013, 78, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottum, P.A.; Arellano, G.; Reyes, L.I.; Iruretagoyena, M.; Naves, R. Opposing Roles of Interferon-γ on Cells of the Central Nervous System in Autoimmune Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano, G.; Ottum, P.A.; Reyes, L.I.; Burgos, P.I.; Naves, R. Stage-Specific Role of Interferon-γ in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, L.M.E.; Martino, G.; Salmaggi, A.; Filippi, M.; Milanese, C.; Antonelli, A.; Nespolo, A.; Capra, R.; Comi, G. Effect of Interferon-γ on T Lymphocytes from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 1995, 1 (Suppl. S1), S38–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroqui, L.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Op de Beeck, A.; Coomans de Brachène, A.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Eizirik, D.L. Type I Interferons as Key Players in Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction in Type 1 Diabetes. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021, 359, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlich, H.; Valdes, A.M.; Noble, J.; Carlson, J.A.; Varney, M.; Concannon, P.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Todd, J.A.; Bonella, P.; Fear, A.L.; et al. HLA DR-DQ Haplotypes and Genotypes and Type 1 Diabetes Risk: Analysis of the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium Families. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal-Ben-Ari, S.; Barrera, I.; Ehrlich, M.; Rosenblum, K. PKR: A Kinase to Remember. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 11, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, S.; Roberts, P.C.; Brown, L.E.; Truong, H.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Archer, D.R.; Barber, G.N. Essential Role for the dsRNA-Dependent Protein Kinase PKR in Innate Immunity to Viral Infection. Immunity 2000, 13, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.; Tsomos, E.; Hammerstad, S.S.; Tomer, Y. Interferon-α: The Key Trigger of Type 1 Diabetes. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 94, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaolaza, P.S.; Balcacean, D.; Zapardiel-Gonzalo, J.; Nelson, G.; Lenchik, N.I.; Becker, M.; Leete, P.; Richardson, S.J.; Rodriguez-Calvo, T.; Kent, S.C.; et al. Islet Expression of Type I Interferon Response Sensors Is Associated with Immune Infiltration and Viral Infection in Type 1 Diabetes. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yon, J.-W. Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus, Human. In Encyclopedia of Immunology, 2nd ed.; Delves, P.J., Roitt, I.M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 1401–1406. [Google Scholar]
- De George, D.J. Inflammation versus regulation: How IFNγ contributes to type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1205590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R. Synergism of TNF-α and IFNγ Triggers Inflammatory cells death, tissue damage and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell 2021, 184, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L. Systemic lupus erythematosus therapies: A decade of progress and prospects in clinical trials. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, L.O.; Frémond, M.-L. Interferonopathies: From concept to clinical practice. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 38, 101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.; Badonyi, M.; Kechiche, R.; Insalaco, A.; Zecca, M.; De Benedetti, F.; Orcesi, S.; Chiapparini, L.; Comoli, P.; Federici, S.; et al. Interface Gain-of-Function Mutations in TLR7 Cause Systemic and Neuro-Inflammatory Disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 44, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliani, J.; Yang, W.L.; McGinn, J.T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P. Anti-interferon-α receptor 1 antibodies attenuate inflammation and organ injury following hemorrhagic shock. J. Trauma. Acute Care Surg. 2019, 86, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Suh, C.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, H.-A.; Lee, S.-K. Elevated Circulating Levels of the Interferon-γ–Induced Chemokines Are Associated with Disease Activity and Cutaneous Manifestations in Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensous, N.; Lazaro, E.; Blanco, P.; Richez, C. Anifrolumab: First Biologic Approved in the EU Not Restricted to Patients with a High Degree of Disease Activity for the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, J.L.; Niewold, T.B. Type I Interferon Antagonists in Clinical Development for Lupus. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 1025–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Kalunian, K.; Navarra, S.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Werth, V.P.; Huang, X.; Roth, D.A.; Ji, B.; Basak, S.; et al. Trial of Anti-BDCA2 Antibody Litifilimab for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, S. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, C.; Mason, A.; Edwards, C.J. Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitors in Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2024, 23, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipi, M.; Jack, S. Interferons in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2020, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Iwasaki, A. Type I and Type III Interferons—Induction, Signaling, Evasion, and Application to Combat COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarras, A.; Wittmann, M.; Vital, E.M. Emerging Concepts of Type I Interferons in SLE Pathogenesis and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Targeting Interferons and Their Pathways in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tummala, R. Anifrolumab, a Monoclonal Antibody to the Type I Interferon Receptor Subunit 1, for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: An Overview from Clinical Trials. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greth, W.; Robbie, G.J.; Brohawn, P.; Hultquist, M.; Yao, B. Targeting the Interferon Pathway with Sifalimumab for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunotherapy 2017, 9, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalunian, K.C.; Merrill, J.T.; Maciuca, R.; Diehl, L.F.; Wallace, D.J.; Petri, M.; Gordon, C.; Zhang, D.; Kinaszczuk, M.; Ishii, T.; et al. A Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Rontalizumab (rhuMAb Interferon-α) in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (ROSE). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.M.; Furie, R. The Development of Litifilimab (BIIB 059) for Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunotherapy 2024, 16, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R. Challenges, Opportunities, and Therapeutic Potential of JAK Inhibitors and Their Derived PROTACs (2022–2023). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2025, 35, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, C.H.; Park, C.J.; Kim, Y.S. The Expanding Therapeutic Potential of Deucravacitinib beyond Psoriasis: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihaescu, G.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Roznovan, C.N.; Ditu, L.-M.; Comanici, M.M.; Savu, O. Interferons in Autoimmunity: From Loss of Tolerance to Chronic Inflammation. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102472
Mihaescu G, Gradisteanu Pircalabioru G, Roznovan CN, Ditu L-M, Comanici MM, Savu O. Interferons in Autoimmunity: From Loss of Tolerance to Chronic Inflammation. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102472
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihaescu, Grigore, Gratiela Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, Claudiu Natanael Roznovan, Lia-Mara Ditu, Mihaela Maria Comanici, and Octavian Savu. 2025. "Interferons in Autoimmunity: From Loss of Tolerance to Chronic Inflammation" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102472
APA StyleMihaescu, G., Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G., Roznovan, C. N., Ditu, L.-M., Comanici, M. M., & Savu, O. (2025). Interferons in Autoimmunity: From Loss of Tolerance to Chronic Inflammation. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2472. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102472









