Rare BLK, CEL, KLF11, PDX1, and PAX4 Gene Variants in Russian Patients with Monogenic Diabetes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
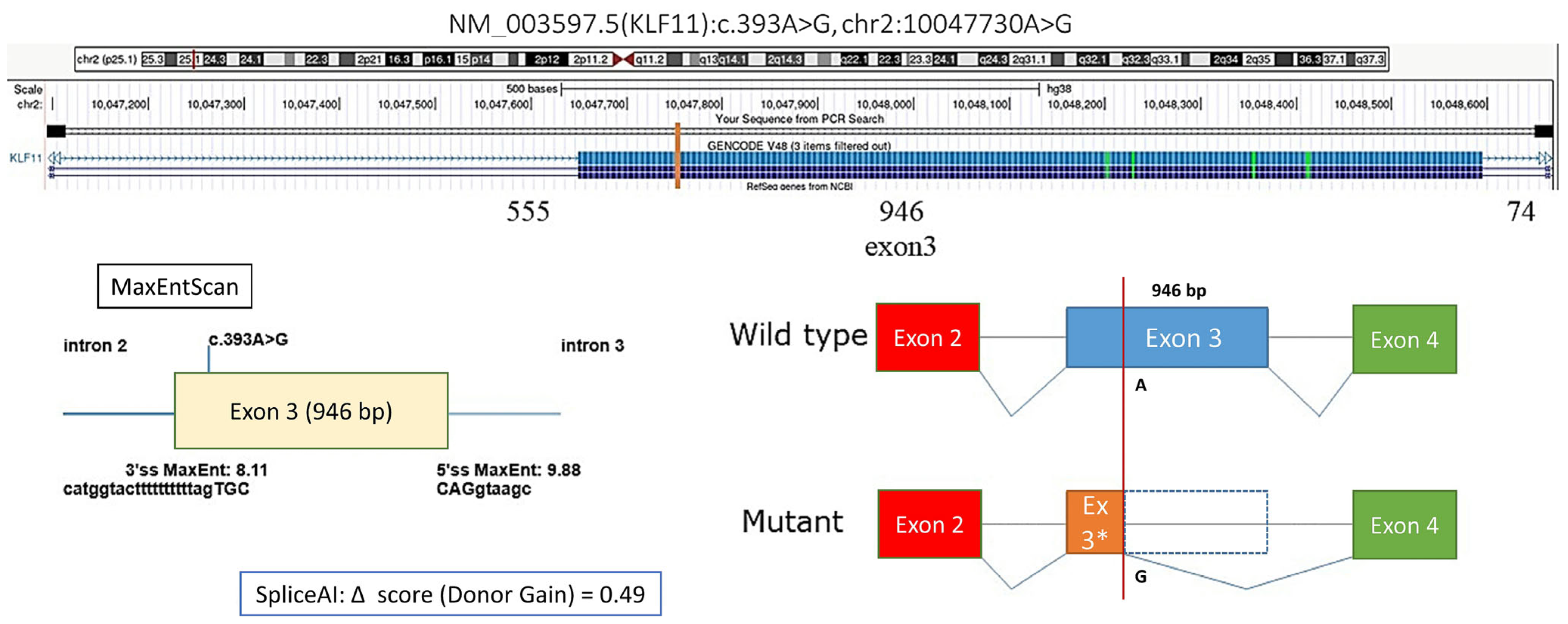
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shields, B.M.; Hicks, S.; Shepherd, M.H.; Colclough, K.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ellard, S. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY): How Many Cases Are We Missing? Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2504–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbert, C.; Lanzinger, S.; deBeaufort, C.; Iotova, V.; Pelicand, J.; Prieto, M.; Schiaffini, R.; Šumnik, Z.; Pacaud, D. Diabetes-Related Antibody-Testing Is a Valuable Screening Tool for Identifying Monogenic Diabetes—A Survey from the Worldwide SWEET Registry. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 192, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasballa, I.; Maggi, D. MODY Only Monogenic? A Narrative Review of the Novel Rare and Low-Penetrant Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, B.M.; Shepherd, M.; Hudson, M.; McDonald, T.J.; Colclough, K.; Peters, J.; Knight, B.; Hyde, C.; Ellard, S.; Pearson, E.R.; et al. Population-Based Assessment of a Biomarker-Based Screening Pathway to Aid Diagnosis of Monogenic Diabetes in Young-Onset Patients. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, I.; Martínez, R.; Rica, I.; de LaPiscina, I.M.; García-Castaño, A.; Aguayo, A.; Calvo, B.; Castaño, L. Negative Autoimmunity in a Spanish Pediatric Cohort Suspected of Type 1 Diabetes, Could It Be Monogenic Diabetes? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Ellis, J.J.; Leo, P.J.; Anderson, L.K.; Ganti, U.; Harris, J.E.; Curran, J.A.; McInerney-Leo, A.M.; Paramalingam, N.; Song, X.; et al. Comprehensive Genetic Screening: The Prevalence of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young Gene Variants in a Population-Based Childhood Diabetes Cohort. Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 20, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellard, S.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Hattersley, A.T.; Carette, C.; Castano Gonzalez, L.; De Nanclares Leal, G.; Elles, R.; Gaspar, G.; Gasperikova, D.; Hansen, T.; et al. Best Practice Guidelines for the Molecular Genetic Diagnosis of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto-Barbosa, R.; Reis, A.F.; Giuffrida, F.M.A. Update on Clinical Screening of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökşen, D.; Yeşilkaya, E.; Özen, S.; Kor, Y.; Eren, E.; Korkmaz, Ö.; Berberoğlu, M.; Karagüzel, G.; Er, E.; Abacı, A.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Monogenic Diabetes and Clinical/Laboratory Features in Turkish Children. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2021, 13, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søvik, O.; Irgens, H.U.; Molnes, J.; Sagen, J.V.; Bjørkhaug, L.; Ræder, H.; Molven, A.; Njølstad, P.R. Monogenic Diabetes Mellitus in Norway. Nor. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, E.; Rami, B.; Grabert, M.; Thon, A.; Kapellen, T.; Reinehr, T.; Holl, R.W. Phenotypical Aspects of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY Diabetes) in Comparison with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in Children and Adolescents: Experience from a Large Multicentre Database. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapla, A.; Mruthyunjaya, M.D.; Asha, H.S.; Varghese, D.; Varshney, M.; Vasan, S.K.; Venkatesan, P.; Nair, V.; Mathai, S.; Paul, T.V.; et al. Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young in India—A Distinctive Mutation Pattern Identified through Targeted next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsu, E.; Çetinkaya, S.; Bolu, S.; Hatipoğlu, N.; Savaş Erdeve, Ş.; Evliyaoğlu, O.; Baş, F.; Çayır, A.; Dündar, İ.; Akbaş, E.D.; et al. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of MODY Cases, Genetic Mutation Spectrum and Phenotype-Genotype Relationship. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2024, 16, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, D.K.; Darendeliler, F.; Poyrazoglu, S.; Al, A.D.K.; Gul, N.; Tutuncu, Y.; Gulfidan, G.; Arga, K.Y.; Cacina, C.; Ozturk, O.; et al. Monogenic Childhood Diabetes: Dissecting Clinical Heterogeneity by Next-Generation Sequencing in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2021, 25, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniakhmetov, I.R.; Khusainova, R.I.; Laptev, D.N.; Yalaev, B.I.; Karpova, Y.S.; Deev, R.V.; Salakhov, R.R.; Panteleev, D.D.; Smirnov, K.V.; Melnichenko, G.A.; et al. Genetic Structure of Hereditary Forms of Diabetes Mellitus in Russia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, T.W.; Wakeling, M.N.; Knox, O.; Colclough, K.; Wright, C.F.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T.; Weedon, M.N.; Patel, K.A. Evaluation of Evidence for Pathogenicity Demonstrates That BLK, KLF11, and PAX4 Should Not Be Included in Diagnostic Testing for MODY. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shekhda, K.M.; Ali, S.N. When to Consider a Diagnosis of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young: Precise Diagnosis Leads to Better Management and Quality of Life for the Patients. Avicenna J. Med. 2025, 15, 041–045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, M.; Liew, C.W.; Thompson, R.; Boonyasrisawat, W.; Hu, J.; Mlynarski, W.M.; El Khattabi, I.; Kim, S.H.; Marselli, L.; Rich, S.S.; et al. Mutations at the BLK Locus Linked to Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young and β-Cell Dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14460–14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amr, S.S.; Al Turki, S.H.; Lebo, M.; Sarmady, M.; Rehm, H.L.; Abou Tayoun, A.N. Using Large Sequencing Data Sets to Refine Intragenic Disease Regions and Prioritize Clinical Variant Interpretation. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zeng, N.; Wen, X.; Zhu, P.; Li, W. A Rare Combination of MODY5 and Duodenal Atresia in a Patient: A Case Report. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of CEL-MODY (MODY8): A Literature Review and Screening in Chinese Individuals Diagnosed with Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrine 2024, 83, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutney, K.; Donnola, S.B.; Flask, C.A.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.; O’Riordan, M.; Mcbennett, K.; Sferra, T.J.; Kaminski, B. Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor Therapy Is Associated with Reduced Hepatic Steatosis in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomberk, G.; Grzenda, A.; Mathison, A.; Escande, C.; Zhang, J.S.; Calvo, E.; Miller, L.J.; Iovanna, J.; Chini, E.N.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; et al. Krüppel-like Factor 11 Regulates the Expression of Metabolic Genes via an Evolutionarily Conserved Protein Interaction Domain Functionally Disrupted in Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17745–17758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanová, J.; Rypáčková, B.; Procházková, Z.; Kučera, P.; Černá, M.; Anděl, M.; Heneberg, P. Positivity for Islet Cell Autoantibodies in Patients with Monogenic Diabetes Is Associated with Later Diabetes Onset and Higher HbA1c Level. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.W.; Yuan, J.; Yang, F.Y.; Qiu, H.Y.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.K. Early-Onset Diabetes Involving Three Consecutive Generations Had Different Clinical Features from Age-Matched Type 2 Diabetes without a Family History in China. Endocrine 2022, 78, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Gong, S.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of PDX1 Variant Induced Diabetes in Chinese Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e1686–e1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.F.; Fitas, A.L.; Pires, M.O.; Matoso, P.; Ligeiro, D.; Sobral, D.; Penha-Gonçalves, C.; Demengeot, J.; Caramalho, Í.; Limbert, C. Whole Exome Sequencing in Children with Type 1 Diabetes before Age 6 Years Reveals Insights into Disease Heterogeneity. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 2024, 3076895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefond, A.; Yengo, L.; Philippe, J.; Dechaume, A.; Ezzidi, I.; Vaillant, E.; Gjesing, A.P.; Andersson, E.A.; Czernichow, S.; Hercberg, S.; et al. Reassessment of the Putative Role of BLK-p.A71T Loss-of-Function Mutation in MODY and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulus, A.D.; Yasartekin, Y.; Ortlek, H.; Ceylan, A.C. BLK-1 Mutation with Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young 11: A Case Report. Ann. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 8, 2385. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.B.; Torsvik, J.; Bjørkhaug, L.; Vesterhus, M.; Ragvin, A.; Tjora, E.; Fjeld, K.; Hoem, D.; Johansson, S.; Ræder, H.; et al. Diabetes and Pancreatic Exocrine Dysfunction Due to Mutations in the Carboxyl Ester Lipase Gene-Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (CEL-MODY): A Protein Misfolding Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34593–34605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ræder, H.; Johansson, S.; Holm, P.I.; Haldorsen, I.S.; Mas, E.; Sbarra, V.; Nermoen, I.; Eide, S.Å.; Grevle, L.; Bjørkhaug, L.; et al. Mutations in the CEL VNTR Cause a Syndrome of Diabetes and Pancreatic Exocrine Dysfunction. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondoh, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Yokoi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Kato, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kurahashi, H. Identification of a Novel Mutation in Carboxyl Ester Lipase Gene in a Patient with MODY-like Diabetes. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2022, 256, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringdal, A.; Ringdal, M.; Nordbø, A.M.; Raeder, H.; Støy, J.; Lipkind, G.M.; Steiner, D.F.; Philipson, L.H.; Bergmann, I.; Aarskog, D.; et al. Mutations in the Insulin Gene Can Cause MODY and Autoantibody-Negative Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushijima, K.; Narumi, S.; Ogata, T.; Yokota, I.; Sugihara, S.; Kaname, T.; Horikawa, Y.; Matsubara, Y.; Fukami, M.; Kawamura, T. KLF11 Variant in a Family Clinically Diagnosed with Early Childhood-Onset Type 1B Diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 20, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Akiyama, M.; Ishigaki, K.; Kanai, M.; Hosoe, J.; Shojima, N.; Hozawa, A.; Kadota, A.; Kuriki, K.; Naito, M.; et al. Identification of 28 New Susceptibility Loci for Type 2 Diabetes in the Japanese Population. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Hou, X. Clinical and Functional Characteristics of a Novel KLF11 Cys354Phe Variant Involved in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 7136869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Luo, X. A Novel KLF11 Variant in a Family with Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Sun, D.; Pang, P.; Yang, G. A Novel KLF11 c.793G>A (p.Glu265Lys) Variant Identified in a Chinese Family with Controversial Association with MODY7. Clin. Lab. 2024, 70, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancera-Rincón, P.; Luna-España, M.C.; Rincon, O.; Guzmán, I.; Alvarez, M. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young Type 7 (MODY7) and the Krüppellike Factor 11 Mutation (KLF11). A Review. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, N.; Shakirova, K.; Dashinimaev, E. PDX1 Is the Cornerstone of Pancreatic β-Cell Functions and Identity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1091757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros Abreu, G.; Tarantino, R.M.; da Fonseca, A.C.P.; de Souza, R.B.; Soares, C.A.P.D.; Cabello, P.H.; Rodacki, M.; Zajdenverg, L.; Zembrzuski, V.M.; Campos, M., Jr. PDX1-MODY: A Rare Missense Mutation as a Cause of Monogenic Diabetes. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Sharma, V.K.; Nabi, F. PDX1 Gene Mutation with Permanent Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus with Annular Pancreas, Duodenal Atresia, Hypoplastic Gall Bladder and Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency. Indian Pediatr. 2017, 54, 1052–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, A.C.P.; de Medeiros Abreu, G.; Palhinha, L.; Zembrzuski, V.M.; Junior, M.C.; Carneiro, J.R.I.; Neto, J.F.N.; Magno, F.C.C.M.; Rosado, E.L.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; et al. A Rare Potential Pathogenic Variant in the Bdnf Gene Is Found in a Brazilian Patient with Severe Childhood-Onset Obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwitzgebel, V.M.; Mamin, A.; Brun, T.; Ritz-Laser, B.; Zaiko, M.; Maret, A.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Theintz, G.E.; Michielin, O.; Melloul, D.; et al. Agenesis of Human Pancreas Due to Decreased Half-Life of Insulin Promoter Factor 1. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4398–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, S.F.; Lim, S.C.; Tan, C.S.; Fong, J.C.; Kon, W.Y.; Lian, J.X.; Subramanium, T.; Sum, C.F. A Preliminary Study to Evaluate the Strategy of Combining Clinical Criteria and next Generation Sequencing (NGS) for the Identification of Monogenic Diabetes among Multi-Ethnic Asians. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 119, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, B.; Mohammed, I.; Syed, N.; Fakhro, K.; Hussain, K. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) Due to PDX1 Mutation in a Sib-Pair Diabetes Family from Qatar. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e05141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Pineda, B.; Chowdhury, K.; Torres, M.; Oliver, G.; Gruss, P. The Pax4 Gene Is Essential for Differentiation of Insulin-Producing β Cells in the Mammalian Pancreas. Nature 1997, 386, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biason-Lauber, A.; Boehm, B.; Lang-Muritano, M.; Gauthier, B.R.; Brun, T.; Wollheim, C.B.; Schoenle, E.J. Association of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus with a Variant of PAX4: Possible Link to Beta Cell Regenerative Capacity. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimajiri, Y.; Sanke, T.; Furuta, H.; Hanabusa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Fujitani, Y.; Kajimoto, Y.; Takasu, N.; Nanjo, K. A Missense Mutation of Pax4 Gene (R121W) Is Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Japanese. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Smith, S.B.; Le May, C.; Leal, S.M.; Gautier, J.F.; Molokhia, M.; Riveline, J.P.; Rajan, A.S.; Kevorkian, J.P.; Zhang, S.; et al. PAX4 Gene Variations Predispose to Ketosis-Prone Diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 3151–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plengvidhya, N.; Kooptiwut, S.; Songtawee, N.; Doi, A.; Furuta, H.; Nishi, M.; Nanjo, K.; Tantibhedhyangkul, W.; Boonyasrisawat, W.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T.; et al. PAX4 Mutations in Thais with Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2821–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Medeiros Abreu, G.; Soares, C.d.A.P.D.; Tarantino, R.M.; da Fonseca, A.C.P.; Souza, R.B.; Pereira, M.d.F.C.; Cabello, P.H.; Rodacki, M.; Zajdenverg, L.; Zembrzuski, V.M.; et al. Identification of the First Pax4-Mody Family Reported in Brazil. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, W.; Piao, Y.; Ren, L.; Sang, Y.C. 487C>T Mutation in PAX4 Gene Causes MODY9: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine 2022, 101, e32461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, A.I.; Krasnova, T.S.; Zubkova, N.A.; Tiulpakov, A.N.; Rubtsov, P.M. Alternative Variants of Pax4 Human Transcription Factor: Comparative Transcriptional Activity. Mol. Biol. 2020, 54, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Fonseca, V.A.; Wu, H. Pax4 in Health and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | cDNA, Variant | Protein, Variant | ACMG Classification | ID | Allele Frequency (gnomAD v4.1.0) | CADD | Individual Predictions (Varsome) * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogenic | Uncertain | Benign | |||||||
| BLK | c.717G>T | p.Gln239His | VUS | rs778299790 | 1.239 × 10−6 | 22.6 | 0 | 6 | 25 |
| c.773-1G>A | - | LP | - | not described | 34.0 | 9 | 4 | 0 | |
| c.803T>C | p.Ile268Thr | VUS | - | 8.893 × 10−6 | 26.4 | 10 | 11 | 4 | |
| c.1033G>A | p.Ala345Thr | VUS | rs1300783845 | 1.24 × 10−6 | 26.3 | 6 | 14 | 2 | |
| CEL | c.391delG | p.Met131Trpfs*64 | LP | - | not described | - | - | - | - |
| c.491G>A | p.Arg164His | VUS | rs778299790 | 3.718 × 10−6 | 27.4 | 15 | 4 | 0 | |
| c.2139dup | p.Val714Argfs*6 | LP | rs768557807 | 1.49 × 10−5 | 19.4 | - | - | - | |
| KLF11 | c.40_41dupGC | p.Val15Glnfs*41 | LP | - | not described | - | - | - | - |
| c.393A>G | p.Lys131= | VUS | - | not described | 8.79 | - | - | - | |
| c.514G>A | p.Gly172Arg | VUS | rs1351414401 | 3.098 × 10−6 | 18.84 | 0 | 9 | 22 | |
| c.1447C>T | p.Pro483Ser | VUS | rs761563032 | 5.08 × 10−5 | 22.8 | 3 | 10 | 11 | |
| PAX4 | c.191C>T | p.Thr64Ile | LP | rs2535520513 | not described | 27.3 | 24 | 4 | 0 |
| c. 464G>A | p.Arg155Gln | VUS | - | 5.391 × 10−5 | 17.31 | 0 | 4 | 22 | |
| c.638C>T | p.Thr213Met | VUS | rs528075802 | 0.00003 | 27.2 | 8 | 3 | 2 | |
| c.640G>A | p.Val214Met | VUS | - | 6.815 × 10−5 | 23.8 | 9 | 5 | 6 | |
| c.771+3A>G | - | VUS | rs776955589 | 4.957 × 10−6 | 21.4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| c.1013C>T | p.Ala330Val | VUS | - | 5.349 × 10−4 | 10.1 | 0 | 6 | 25 | |
| PDX1 | c.383A>C | p.His128Pro | LP | - | 9.925 × 10−6 | 30.0 | 10 | 10 | 3 |
| c.417C>G | p.Tyr139* | LP | - | not described | 35.0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | |
| c.533A>C | p.Glu178Ala | LP | - | not described | 31.0 | 18 | 6 | 0 | |
| c.719C>G | p.Pro240Arg | VUS | rs753881947 | 7.257 × 10−6 | 9.01 | 3 | 3 | 25 | |
| Patients | Genetic Variant | Diabetes History (Years) | Age of Manifestation | * HbA1c | ** Plasma Glucose mmol/L | *** Autoantibodies U/mL | C-Peptide pmol/L | HOMA | Family History |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BLK: c.717G>T, p.Gln239His | 0.6 | 15.4 | 5.4 | 10 | IAA (18.7) | 2.39 | 18.4 | mother died, no info about T1D, maternal uncle T1DM |
| 2 | BLK: c.773-1G>A | 3.5 | 8 | 7.6 | 25 | ZnT8A (33.04) | 1.21 | 1.31 | mother T1DM, maternal grandfather T1DM |
| 3 | BLK: c.803T>C, p.Ile268Thr | 4.9 | 9.8 | 9 | 15.8 | negative | 0.01 | - | mother BLK: c.803T>C, p.Ile268Thr |
| 4 | BLK: c.1033G>A, p.Ala345Thr | 6 | 9.6 | 6.18 | 5.8 | negative | 4.01 | 10.7 | mother GDM (BLK: p.Ala345Thr), maternal grandmother T2DM |
| 5 | CEL: c.391delG, p.A131fs | 1.7 | 11 | 6.2 | 5.2 | negative | 2.92 | 2.7 | father and paternal grandmother T2DM |
| 6 | CEL: c.491G>A, p.R164H CFTR: c.220C>T, p.R74W (rs115545701)/c.2563G>A, p.V855I (rs397508397) | 9.4 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 5.3 | negative | 0.01 | - | father T1DM (CEL: c.491G>A, p.R164H) |
| 7 | CEL: c.2139dup, p.Val714ArgfsTer6 | 0.6 | 8.6 | 5.4 | 6.1 | negative | 2.04 | 3.3 | father and paternal grandmother T2DM |
| 8 | KLF11: c.40_41dupGC, p.Val15GlnfsTer41 | 7 | 10.3 | 8.9 | 14.4 | IA-2A—81.6 GADA—44.6 ZnT8A—72.9 | 0.438 | - | maternal grandfather DM |
| 9 | KLF11: 393A>G, pLys131= | 4.8 | 8 | 6.9 | 6 | negative | 0.31 | - | mother GDM KLF11: 393A>G, p.Lys131=, father T1DM |
| 10 | KLF11: c.514G>A, p.Gly172Arg | 4.7 | 13.1 | 5.8 | 6.3 | GAD—12.6 IA2 –58.1 | 1.57 | - | paternal grandmother DM |
| 11 | KLF11: c.1447C>T, p.Pro483Ser | 6 | 8.9 | 6.6 | 7.8 | negative | 2.67 | - | father T1DM and paternal grandfather T2DM |
| 12 | KLF11: c.1447C>T, p.Pro483Ser | 1.4 | 21 | 5.7 | 7.74 | GAD—298.7 | 1.28 | - | Mother DM?, brother T1DM (no high-risk antibodies or HLA were detected), maternal grandfather T2DM |
| 13 | PAX4: c.191C>T, p.Thr64Il | 5 | 12.7 | 6.4 | 13.5 | negative | 1.4 | 5.9 | mother PAX4: c.191C>T, p.T64I |
| 14 | PAX4: c.191C>T, p.Thr64Il | 0.1 | 8.7 | 7.8 | 11.4 | negative | 3.8 | - | mother and father T2DM PAX4: c.191C>T, p.Thr64Ile (mother) |
| 15 | PAX4: c. 464G>A, Arg155Gln | 1.7 | 2.3 | 13.9 | 26.5 | IA2 – 23 | 0.124 | - | father PAX4: c. 464G>A, p.R155Q |
| 16 | PAX4: c.638C>T), p.(Thr213Met) | 19 | 14 | - | 20 | negative | 0.88 | - | father T1DM, brother T2DM |
| 17 | PAX4: c.640G>A, p.Val214Met | 0.1 | 0.3 | 7.6 | 13.8 | negative | 0.65 | - | no heredity for diabetes |
| 18 | PAX4: c.771+3A>G | 0.1 | 10.6 | 7.3 | 6 | negative | 1.05 | - | no heredity for diabetes |
| 19 | PAX4: c.1013C>T, p.Ala330Val | 0.10 | 4.5 | 5.2 | 4.6 | negative | - | - | Mother and maternal grandfather T2DM |
| 20 | PDX1: c.383A>C, p.His128Pro | 3.6 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 11 | negative | 0.72 | - | no carbohydrate metabolism disorders of the mother |
| 21 | PDX1: c.417C>G, p.Tyr139Ter | 0.1 | 15.2 | 7.9 | 9.1 | negative | 0.68 | - | no heredity for diabetes |
| 22 | PDX1: c.417C>G, p.Tyr139Ter | 0.5 | 15.6 | 5.8 | 6.2 | negative | 2.08 | 4.0 | Mother–T1DM (insulin 0.3 U/kg/d (no genetic test result) and maternal grandmother T2DM (pills) |
| 23 | PDX1: c.533A>C, p.Glu178Ala | 3.1 | 11.4 | 6 | 9.9 | negative | 1.87 | 1.26 | maternal grandfather DM |
| 24 | PDX1: c.719C>G, p.Pro240Arg | 2.10 | 15.1 | 8.1 | 17 | negative | 0.34 | - | Parents died, no data on diabetes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khusainova, R.I.; Minniakhmetov, I.R.; Laptev, D.N.; Koltakova, M.P.; Deev, R.V.; Yalaev, B.I.; Dvoryanchikov, Y.V.; Sechko, E.A.; Mokrysheva, N.G. Rare BLK, CEL, KLF11, PDX1, and PAX4 Gene Variants in Russian Patients with Monogenic Diabetes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102452
Khusainova RI, Minniakhmetov IR, Laptev DN, Koltakova MP, Deev RV, Yalaev BI, Dvoryanchikov YV, Sechko EA, Mokrysheva NG. Rare BLK, CEL, KLF11, PDX1, and PAX4 Gene Variants in Russian Patients with Monogenic Diabetes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102452
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhusainova, Rita I., Ildar R. Minniakhmetov, Dmitry N. Laptev, Mariya P. Koltakova, Roman V. Deev, Bulat I. Yalaev, Yaroslav V. Dvoryanchikov, Elena A. Sechko, and Natalia G. Mokrysheva. 2025. "Rare BLK, CEL, KLF11, PDX1, and PAX4 Gene Variants in Russian Patients with Monogenic Diabetes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102452
APA StyleKhusainova, R. I., Minniakhmetov, I. R., Laptev, D. N., Koltakova, M. P., Deev, R. V., Yalaev, B. I., Dvoryanchikov, Y. V., Sechko, E. A., & Mokrysheva, N. G. (2025). Rare BLK, CEL, KLF11, PDX1, and PAX4 Gene Variants in Russian Patients with Monogenic Diabetes: Clinical and Molecular Characterization. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102452






