The Influence of Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Infection and Associated Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Major Factors Involved in H. pylori Infection and Pathogenesis
3. Major Microbiota Patterns Observed in the Gastric Area
4. Gastric Microbiota Dynamics in H. pylori Colonization and Associated Conditions
5. The Effect of Resident Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics on H. pylori-Mediated Inflammation
6. Gastric Microbiota Functions in the H. pylori-Associated GC Pathogenesis
7. H. pylori-Associated PUD Pathogenesis and Microbiota
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Rocha, M.; Pereira-Marques, J.; Ferreira, R.M.; Figueiredo, C. Gastric Cancer: The Microbiome Beyond Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 444, 157–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsberger, V.; Gerhard, M.; Mejías-Luque, R. Effects of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Intestinal Microbiota, Immunity and Colorectal Cancer Risk. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1339750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrand, L.; Lindberg, M. Helicobacter pylori and the Gastric Microbiota. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda-Robles, A.; Rubio-Tomás, T.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Álvarez-Mercado, A.I. Impact of Dietary Patterns on H. pylori Infection and the Modulation of Microbiota to Counteract Its Effect. A Narrative Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Ferino, L.; Sharafutdinov, I.; Backert, S. Gastric Epithelial Barrier Disruption, Inflammation and Oncogenic Signal Transduction by Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 444, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Impact of the Helicobacter pylori Oncoprotein CagA in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 444, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, N.; Yuasa, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sawa, H.; Miura, M.; Matsui, A.; Higashi, H.; Musashi, M.; Iwabuchi, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Transgenic Expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA Induces Gastrointestinal and Hematopoietic Neoplasms in Mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botham, C.M.; Wandler, A.M.; Guillemin, K. A Transgenic Drosophila Model Demonstrates That the Helicobacter pylori CagA Protein Functions as a Eukaryotic Gab Adaptor. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Peterson, T.S.; Kent, M.L.; Guillemin, K. H. pylori Virulence Factor CagA Increases Intestinal Cell Proliferation by Wnt Pathway Activation in a Transgenic Zebrafish Model. Dis. Model. Mech. 2013, 6, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Marshall, B.J.; Jain, U. Helicobacter pylori VacA, a Distinct Toxin Exerts Diverse Functionalities in Numerous Cells: An Overview. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, N.; Backert, S.; Pachathundikandi, S.K. Immune Cell Signaling by Helicobacter pylori: Impact on Gastric Pathology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1149, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Signal Transduction of Helicobacter pylori during Interaction with Host Cell Protein Receptors of Epithelial and Immune Cells. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Neddermann, M.; Asche, C.I.; Backert, S. Subversion of Host Kinases: A Key Network in Cellular Signaling Hijacked by Helicobacter pylori CagA. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 105, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafutdinov, I.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Linz, B.; Rohde, M.; Vieth, M.; Tay, A.C.-Y.; Lamichhane, B.; Tuan, V.P.; Fauzia, K.A.; Sticht, H.; et al. A Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism in Helicobacter pylori Promotes Gastric Cancer Development. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1345–1358.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter Pylori Virulence Factors Exploiting Gastric Colonization and Its Pathogenicity. Toxins 2019, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, S.; Engstrand, L.; Jonsson, H. Lactobacillus gastricus Sp. Nov., Lactobacillus antri Sp. Nov., Lactobacillus kalixensis Sp. Nov. and Lactobacillus ultunensis Sp. Nov., Isolated from Human Stomach Mucosa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruggiero, P. Use of Probiotics in the Fight against Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2014, 5, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Farid, A.; Abid, R.; Rehman, M.; Alsanie, W.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.; Asdaq, S.; Hefft, D.; Saqib, S.; et al. Identification, Biochemical Characterization, and Safety Attributes of Locally Isolated Lactobacillus fermentum from Bubalus bubalis (Buffalo) Milk as a Probiotic. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Probiotic Therapy in Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Potential Strategy against a Serious Pathogen? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1573–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, J.M.; Peek, R.M. The Gastric Microbiome, Its Interaction with Helicobacter pylori, and Its Potential Role in the Progression to Stomach Cancer. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, B. Immunological Perspective: Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 2944156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Camargo, M.C.; El-Omar, E.; Liou, J.-M.; Peek, R.; Schulz, C.; Smith, S.I.; Suerbaum, S. Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.L.; Lacy, D.B.; Ohi, M.D. The Helicobacter pylori Cag Type IV Secretion System. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Arnold, I.C.; Lind, J.; Neddermann, M.; Falkeis-Veits, C.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Brönstrup, M.; Tegge, W.; Hong, M.; et al. T4SS-Dependent TLR5 Activation by Helicobacter pylori Infection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Neddermann, M.; Lind, J.; Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Sharafutdinov, I.; Gutiérrez-Escobar, A.J.; Brönstrup, M.; Tegge, W.; Hong, M.; Rohde, M.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 5 Activation by the CagY Repeat Domains of Helicobacter pylori. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, M.; Yahiro, K.; Yamasaki, E.; Kurazono, H.; Akada, J.; Yamaoka, Y.; Niidome, T.; Hatakeyama, M.; Suzuki, H.; Yamamoto, T.; et al. Helicobacter pylori VacA, Acting through Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase α, Is Crucial for CagA Phosphorylation in Human Duodenum Carcinoma Cell Line AZ-521. Dis. Models Mech. 2016, 9, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewald, X.; Gebert-Vogl, B.; Prassl, S.; Barwig, I.; Weiss, E.; Fabbri, M.; Osicka, R.; Schiemann, M.; Busch, D.H.; Semmrich, M.; et al. Integrin Subunit CD18 Is the T-Lymphocyte Receptor for the Helicobacter pylori Vacuolating Cytotoxin. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Blaser, N.; Backert, S. Mechanisms of Inflammasome Signaling, microRNA Induction and Resolution of Inflammation by Helicobacter Pylori. In Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Induction, Resolution and Escape by Helicobacter pylori; Backert, S., Ed.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 421, pp. 267–302. ISBN 978-3-030-15137-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pachathundikandi, K.; Backert, S. Heptose 1,7-Bisphosphate Directed TIFA Oligomerization: A Novel PAMP-Recognizing Signaling Platform in the Control of Bacterial Infections. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachathundikandi, S.K.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Backert, S. Masking of Typical TLR4 and TLR5 Ligands Modulates Inflammation and Resolution by Helicobacter pylori. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, O.; Maubach, G.; Naumann, M. Helicobacter pylori Regulates TIFA Turnover in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 102, 151307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.M.; Retnakumar, R.J.; Chouhan, D.; Devi, T.N.B.; Dharmaseelan, S.; Devadas, K.; Thapa, N.; Tamang, J.P.; Lamtha, S.C.; Chattopadhyay, S. Helicobacter pylori in Human Stomach: The Inconsistencies in Clinical Outcomes and the Probable Causes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 713955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodley, Y.; Linz, B.; Bond, R.P.; Nieuwoudt, M.; Soodyall, H.; Schlebusch, C.M.; Bernhöft, S.; Hale, J.; Suerbaum, S.; Mugisha, L.; et al. Age of the Association between Helicobacter pylori and Man. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, B.; Balloux, F.; Moodley, Y.; Manica, A.; Liu, H.; Roumagnac, P.; Falush, D.; Stamer, C.; Prugnolle, F.; Van Der Merwe, S.W.; et al. An African Origin for the Intimate Association between Humans and Helicobacter pylori. Nature 2007, 445, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, Y.; Brunelli, A.; Ghirotto, S.; Klyubin, A.; Maady, A.S.; Tyne, W.; Muñoz-Ramirez, Z.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Manica, A.; Linz, B.; et al. Helicobacter pylori’s Historical Journey through Siberia and the Americas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2015523118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, A.N.; Retnakumar, R.J.; Francis, A.; Chhetri, P.; Thapa, N.; Chattopadhyay, S. Peptic Ulcer and Gastric Cancer: Is It All in the Complex Host–Microbiome Interplay That Is Encoded in the Genomes of “Us” and “Them”? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 835313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Selbach, M. The Versatility of Helicobacter pylori CagA Effector Protein Functions: The Master Key Hypothesis. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-L.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Sheu, B.-S. The Impacts of H. pylori Virulence Factors on the Development of Gastroduodenal Diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer: Global Trends, Risk Factors and Prevention. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2019, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Haas, R.; Gerhard, M.; Naumann, M. The Helicobacter pylori Type IV Secretion System Encoded by the Cag Pathogenicity Island: Architecture, Function, and Signaling. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 413, 187–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and Gastric Cancer: A Paradigm for Hit-and-Run Carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argent, R.H.; Thomas, R.J.; Letley, D.P.; Rittig, M.G.; Hardie, K.R.; Atherton, J.C. Functional Association between the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factors VacA and CagA. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tegtmeyer, N.; Zabler, D.; Schmidt, D.; Hartig, R.; Brandt, S.; Backert, S. Importance of EGF Receptor, HER2/Neu and Erk1/2 Kinase Signalling for Host Cell Elongation and Scattering Induced by the Helicobacter pylori CagA Protein: Antagonistic Effects of the Vacuolating Cytotoxin VacA. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, E.M.; Demir, T.D.; Seymen, N.; Said, S.S.; Oktem-Okullu, S.; Tiftikci, A.; Cicek, B.; Tokat, F.; Tozun, N.; Ince, U.; et al. The Crosstalk between H. pylori Virulence Factors and the PD1:PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Progression to Gastric Cancer. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 239, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzecka, U.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Sticht, H.; Backert, S. Trimer Stability of Helicobacter pylori HtrA Is Regulated by a Natural Mutation in the Protease Domain. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 212, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the Human Gut Microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugon, P.; Dufour, J.-C.; Colson, P.; Fournier, P.-E.; Sallah, K.; Raoult, D. A Comprehensive Repertoire of Prokaryotic Species Identified in Human Beings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Mitchell, A.L.; Boland, M.; Forster, S.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Tarkowska, A.; Lawley, T.D.; Finn, R.D. A New Genomic Blueprint of the Human Gut Microbiota. Nature 2019, 568, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syromyatnikov, M.; Nesterova, E.; Gladkikh, M.; Smirnova, Y.; Gryaznova, M.; Popov, V. Characteristics of the Gut Bacterial Composition in People of Different Nationalities and Religions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional Interactions between the Gut Microbiota and Host Metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.M.; Yang, Y.S.; Peng, L.H. Microbiota in the Stomach: New Insights. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Seo, H.; Kang, C.-S.; Shin, T.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.-M.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, Y.-K. Dysbiotic Change in Gastric Microbiome and Its Functional Implication in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, E.M.; Eckburg, P.B.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Purdom, E.A.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Molecular Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiota in the Human Stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-Y.; Tung, S.-Y.; Pan, H.-Y.; Yen, C.-W.; Xu, H.-W.; Lin, Y.-J.; Deng, Y.-F.; Hsu, W.-T.; Wu, C.-S.; Li, C. Increased Abundance of Clostridium and Fusobacterium in Gastric Microbiota of Patients with Gastric Cancer in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.F.; Lindberg, M.; Jakobsson, H.; Bäckhed, F.; Nyrén, P.; Engstrand, L. Comparative Analysis of Human Gut Microbiota by Barcoded Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, B.; Backert, S. Helicobacter pylori and the Gut Microbiota. Microbiota Health Dis. 2021, 3, e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchtung, T.A.; Fofanova, T.Y.; Stewart, C.J.; Nash, A.K.; Wong, M.C.; Gesell, J.R.; Auchtung, J.M.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F. Investigating Colonization of the Healthy Adult Gastrointestinal Tract by Fungi. mSphere 2018, 3, e00092-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.M. Gut Microbiota and Cardiometabolic Outcomes: Influence of Dietary Patterns and Their Associated Components. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 369S–377S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, N.; Yang, H. Factors Affecting the Composition of the Gut Microbiota, and Its Modulation. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serban, D.E. The Gut Microbiota in the Metagenomics Era: Sometimes a Friend, Sometimes a Foe. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 70, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lehr, K.; Nikitina, D.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Steponaitiene, R.; Thon, C.; Skieceviciene, J.; Schanze, D.; Zenker, M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Kupcinskas, J.; et al. Microbial Composition of Tumorous and Adjacent Gastric Tissue Is Associated with Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolig, A.S.; Cech, C.; Ahler, E.; Carter, J.E.; Ottemann, K.M. The Degree of Helicobacter pylori-Triggered Inflammation Is Manipulated by Preinfection Host Microbiota. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Malekzadeh, R.; Ploner, A.; Shakeri, R.; Sotoudeh, M.; Fahimi, S.; Nasseri-Moghaddam, S.; Kamangar, F.; Abnet, C.C.; Winckler, B.; et al. Variations of Gastric Corpus Microbiota Are Associated with Early Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Dysplasia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.H.; Qin, Y.; Sham, P.C.; Lau, K.S.; Chu, K.-M.; Leung, W.K. Alterations in Gastric Microbiota After H. pylori Eradication and in Different Histological Stages of Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, T.B.; Devadas, K.; George, M.; Gandhimathi, A.; Chouhan, D.; Retnakumar, R.J.; Alexander, S.M.; Varghese, J.; Dharmaseelan, S.; Chandrika, S.K.; et al. Low Bifidobacterium Abundance in the Lower Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Helicobacter pylori-Related Gastric Ulcer and Gastric Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, C.; Ciucci, S.; Palladini, A.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Zippo, A.G.; Sterbini, F.P.; Masucci, L.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Spuul, P.; et al. Nonlinear Machine Learning Pattern Recognition and Bacteria-Metabolite Multilayer Network Analysis of Perturbed Gastric Microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianiro, G.; Molina-Infante, J.; Gasbarrini, A. Gastric Microbiota. Helicobacter 2015, 20, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gerhard, M.; Gao, J.-J.; Mejias-Luque, R.; Zhang, L.; Vieth, M.; Ma, J.-L.; Bajbouj, M.; Suchanek, S.; et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori on Gastrointestinal Microbiota: A Population-Based Study in Linqu, a High-Risk Area of Gastric Cancer. Gut 2020, 69, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miftahussurur, M.; Waskito, L.A.; El-Serag, H.B.; Ajami, N.J.; Nusi, I.A.; Syam, A.F.; Matsumoto, T.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Doohan, D.; Fauzia, K.A.; et al. Gastric Microbiota and Helicobacter pylori in Indonesian Population. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndegwa, N.; Ploner, A.; Andersson, A.F.; Zagai, U.; Andreasson, A.; Vieth, M.; Talley, N.J.; Agreus, L.; Ye, W. Gastric Microbiota in a Low-Helicobacter pylori Prevalence General Population and Their Associations with Gastric Lesions. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadeerhan, G.; Gerhard, M.; Gao, J.-J.; Mejías-Luque, R.; Zhang, L.; Vieth, M.; Ma, J.-L.; Bajbouj, M.; Suchanek, S.; Liu, W.-D.; et al. Microbiota Alteration at Different Stages in Gastric Lesion Progression: A Population-Based Study in Linqu, China. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 561–575. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, H.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, N.; Park, J.H.; Nam, R.H.; Seok, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-R.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.M.; et al. Analysis of Gastric Microbiota by Pyrosequencing: Minor Role of Bacteria Other than Helicobacter pylori in the Gastric Carcinogenesis. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Smet, A.; Hansen, R.; Kupcinskas, J.; Rokkas, T.; Andersen, L.; Machado, J.C.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Systematic Review: Gastric Microbiota in Health and Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 582–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, W.F.; Sarquis, D.P.; Khayat, A.S.; Khayat, B.C.M.; Demachki, S.; Anaissi, A.K.M.; Ishak, G.; Santos, N.P.C.; Dos Santos, S.E.B.; Burbano, R.R.; et al. Gastric Cancer Microbiome. Pathobiology 2021, 88, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Marques, J.; Ferreira, R.M.; Machado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C. The Influence of the Gastric Microbiota in Gastric Cancer Development. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 50–51, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Feng, Y.; Muthupalani, S.; Mannion, A.J.; Sheh, A.; Whary, M.T.; Holcombe, H.R.; Piazuelo, B.M.; Bravo, L.E.; et al. Gastric Non-Helicobacter pylori Urease-Positive Staphylococcus Epidermidis and Streptococcus Salivarius Isolated from Humans Have Contrasting Effects on H. pylori-Associated Gastric Pathology and Host Immune Responses in a Murine Model of Gastric Cancer. mSphere 2022, 7, e00772-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberstein, B.; Quintanilha, A.G.; Santos, M.A.A.; Pajecki, D.; Moura, E.G.; Alves, P.R.A.; Filho, F.M.; Souza, J.A.U.D.; Gama-Rodrigues, J. Digestive Tract Microbiota In Healthy Volunteers. Clinics 2007, 62, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicksved, J.; Lindberg, M.; Rosenquist, M.; Enroth, H.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Molecular Characterization of the Stomach Microbiota in Patients with Gastric Cancer and in Controls. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mărginean, C.O.; Meliț, L.E.; Săsăran, M.O. Gastric Microenvironment—A Partnership between Innate Immunity and Gastric Microbiota Tricks Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, C.; Osaki, T.; Hanawa, T.; Yonezawa, H.; Kurata, S.; Kamiya, S. Analysis of the Microbial Ecology between Helicobacter pylori and the Gastric Microbiota of Mongolian Gerbils. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Delgado, S.; Leite, A.M.O.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Mayo, B. Probiotic and Technological Properties of Lactobacillus Spp. Strains from the Human Stomach in the Search for Potential Candidates against Gastric Microbial Dysbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Gonçalves, N.; Boal-Carvalho, I.; Afonso, L.; Lopes, P.; Roncon-Albuquerque, R.; Henrique, R.; Moreira-Dias, L.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M. Helicobacter pylori Induces Increased Expression of Toll-Like Receptors and Decreased Toll-Interacting Protein in Gastric Mucosa That Persists Throughout Gastric Carcinogenesis. Helicobacter 2013, 18, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles-Jimenez, F.; Vazquez-Jimenez, F.; Medrano-Guzman, R.; Mantilla, A.; Torres, J. Stomach Microbiota Composition Varies between Patients with Non-Atrophic Gastritis and Patients with Intestinal Type of Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachuei, V.; Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Rahimi, F.; Forootan, M. Colonization by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Staphylococcus Aureus of Antral Biopsy Specimens from Gastritis Patients Uninfected with Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Villamil, J.I.; Tapia, D.; Borlee, G.I.; Borlee, B.R.; Walker, D.H.; Torres, A.G. Burkholderia pseudomallei as an Enteric Pathogen: Identification of Virulence Factors Mediating Gastrointestinal Infection. Infect. Immun. 2020, 89, e00654-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, Y.; Dieye, Y.; Loke, M.F.; Goh, K.L.; Vadivelu, J. Streptococcus mitis Induces Conversion of Helicobacter pylori to Coccoid Cells during Co-Culture In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Fischer, A.; Plickert, R.; Wiedemann, T.; Loddenkemper, C.; Göbel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Rieder, G. Helicobacter pylori Induced Gastric Immunopathology Is Associated with Distinct Microbiota Changes in the Large Intestines of Long-Term Infected Mongolian Gerbils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Pereira, V.; Saxena, S.; Ghosh, T.S.; Anbumani, D.; Bag, S.; Das, B.; Nair, G.B.; Abraham, P.; Mande, S.S. Gastric Microbiome of Indian Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection, and Their Interaction Networks. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Miao, J.; Luo, L.; Long, G.; Chen, B.; Shu, X.; Gu, W.; Peng, K.; Li, F.; Zhao, H.; et al. The Effects of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Microbiota Associated with Gastric Mucosa and Immune Factors in Children. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawner, K.M.; Morrow, C.D.; Smith, P.D. Gastric Microbiome and Gastric Cancer. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban-Arques, A.; Wurm, P.; Trajanoski, S.; Schauer, S.; Kienesberger, S.; Halwachs, B.; Högenauer, C.; Langner, C.; Gorkiewicz, G. Propionibacterium acnes Overabundance and Natural Killer Group 2 Member D System Activation in Corpus-dominant Lymphocytic Gastritis. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velickovic, M.; Arsenijevic, A.; Acovic, A.; Arsenijevic, D.; Milovanovic, J.; Dimitrijevic, J.; Todorovic, Z.; Milovanovic, M.; Kanjevac, T.; Arsenijevic, N. Galectin-3, Possible Role in Pathogenesis of Periodontal Diseases and Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 638258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.-M.; Hagiwara, S.; Hsu, D.K.; Liu, F.-T.; Yoshie, O. Galectin-3 Plays an Important Role in Innate Immunity to Gastric Infection by Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymiuk, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Stadlmann, A.; Thannesberger, J.; Kastner, M.-T.; Högenauer, C.; Püspök, A.; Biowski-Frotz, S.; Schrutka-Kölbl, C.; Thallinger, G.G.; et al. The Human Gastric Microbiome Is Predicated upon Infection with Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Song, J.; Yang, X.; Ye, L.; Wu, Z.; Xie, P.; Zhong, Q.; et al. dupA+ H. pylori Reduces Diversity of Gastric Microbiome and Increases Risk of Erosive Gastritis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Sheh, A.; Feng, Y.; Muthupalani, S.; Ge, L.; Wang, C.; Kurnick, S.; Mannion, A.; Whary, M.T.; Fox, J.G. Helicobacter Pylori-Infected C57BL/6 Mice with Different Gastrointestinal Microbiota Have Contrasting Gastric Pathology, Microbial and Host Immune Responses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasawa, Y.; Shibahara-Sone, H.; Iino, T.; Ishikawa, F. Bifidobacterium Bifidum BF-1 Suppresses Helicobacter pylori-Induced Genes in Human Epithelial Cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 4526–4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, I.M.; Pavoni, M.; Saccomanno, L.; Fiorini, G.; Pesci, V.; Foschi, C.; Piccirilli, G.; Bernardini, G.; Holton, J.; Figura, N.; et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Five Probiotic Strains Against Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Falsafi, T.; Kermanshahi, R.K.; Ramezani, R. Antagonistic and Immunomodulant Effects of Two Probiotic Strains of Lactobacillus on Clinical Strains of Helicobacter pylori. Galen. Med. J. 2020, 9, e1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Huang, W.-C.; Su, C.-H.; Lin, W.-D.; Wu, W.-T.; Yu, B.; Hsu, Y.-M. Effects of Multi-Strain Probiotics on Immune Responses and Metabolic Balance in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki-Kakelar, H.; Dehghani, J.; Barzegari, A.; Barar, J.; Shirmohamadi, M.; Sadeghi, J.; Omidi, Y. Lactobacillus Plantarum Induces Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cells via Modulation of Signaling Pathways in Helicobacter pylori. Bioimpacts 2020, 10, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmohammadi, M.; Yadegar, A.; Ebrahimi, M.T.; Zali, M.R. Effects of a Potential Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus Gasseri ATCC 33323 on Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammatory Response and Gene Expression in Coinfected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Probiotics Antimicro. Prot. 2021, 13, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Peng, C.; Xu, X.; Li, N.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N. Probiotics Mitigate Helicobacter pylori-Induced Gastric Inflammation and Premalignant Lesions in INS-GAS Mice with the Modulation of Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-H.; Lin, T.-L.; Huang, M.-Z.; Li, S.-W.; Wu, H.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-H.; Lai, H.-C. Gut Commensal Parabacteroides Goldsteinii MTS01 Alters Gut Microbiota Composition and Reduces Cholesterol to Mitigate Helicobacter pylori-Induced Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 916848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakarya, S.; Gunay, N. Saccharomyces Boulardii Expresses Neuraminidase Activity Selective for A2,3-linked Sialic Acid That Decreases Helicobacter pylori Adhesion to Host Cells. APMIS 2014, 122, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S.A.; Mohiuddin, M.M.; Shlimon, S.; Chahal, J.; MacPherson, C.W.; Jass, J.; Tompkins, T.A.; Creuzenet, C. In Vitro Framework to Assess the Anti-Helicobacter pylori Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria Secretions as Alternatives to Antibiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Gergova, G.; Markovska, R.; Yordanov, D.; Mitov, I. Bacteriocin-like Inhibitory Activities of Seven Lactobacillus delbrueckii Subsp. Bulgaricus Strains against Antibiotic Susceptible and Resistant Helicobacter pylori Strains. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Ge, L.; Li, Y. Probiotic Effect on Helicobacter pylori Attachment and Inhibition of Inflammation in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiraworawong, T.; Spinler, J.K.; Werawatganon, D.; Klaikeaw, N.; Venable, S.F.; Versalovic, J.; Tumwasorn, S. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Gastric-Derived Lactobacillus Plantarum XB7 in the Context of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsahi, A.; Mahmoudi, H.; Ebrahimi, A.; Aeini, Z.; Esmaeili, D. Evaluation of the Effect of Lactobacillus Planetarium Probiotics Produced from Broad Bean Seed in Prevention of Helicobacter pylori in Stomach Tissue of C57BL/6 Mice. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2018, 10, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Z.; He, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, H. The Effects of Probiotics Supplementation on Helicobacter pylori Standard Treatment: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews with Meta-Analyses. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, M.T.; Peek, R.M. Gastrointestinal Malignancy and the Microbiome. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1534–1546.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niikura, R.; Hayakawa, Y.; Nagata, N.; Miyoshi-Akiayama, T.; Miyabayashi, K.; Tsuboi, M.; Suzuki, N.; Hata, M.; Arai, J.; Kurokawa, K.; et al. Non-Helicobacter pylori Gastric Microbiome Modulates Prooncogenic Responses and Is Associated with Gastric Cancer Risk. Gastro Hep Adv. 2023, 2, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, Z.Z. Meta-Analysis Reveals Helicobacter pylori Mutual Exclusivity and Reproducible Gastric Microbiome Alterations during Gastric Carcinoma Progression. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2197835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waskito, L.A.; Rezkitha, Y.A.A.; Vilaichone, R.; Sugihartono, T.; Mustika, S.; Dewa Nyoman Wibawa, I.; Yamaoka, Y.; Miftahussurur, M. The Role of Non-Helicobacter pylori Bacteria in the Pathogenesis of Gastroduodenal Diseases. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, C.S.; Kim, B.K.; Han, D.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, B.Y.; Song, K.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.F. Differences in Gastric Mucosal Microbiota Profiling in Patients with Chronic Gastritis, Intestinal Metaplasia, and Gastric Cancer Using Pyrosequencing Methods. Helicobacter 2014, 19, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, E.; Doss, S.; Polsley, K. Peptic Ulcer Disease. Prim. Care 2023, 50, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, R.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, W.; Yang, A. Impact of Helicobacter pylori on the Gastric Microbiome in Patients with Chronic Gastritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e050476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, S.; Ye, F.; Zhang, G. The Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on the Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Patients with Duodenal Ulcer. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2016, 25, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbey, G.; Hanafiah, A.; Sproston, E. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Microbiota. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2020, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, P.B.; Jin, Y.; Reyes, V.E.; Crowe, S.E. The Role of the Local Immune Response in the Pathogenesis of Peptic Ulcer Formation. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 29, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandra, M.G. Risk Factors for Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. Stud. 2023, 3, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Umaru, I. Peptic Ulcer Disease and Its Implications. Res. Gastric Manag. Hepatol. 2023, 1, 01–04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yu, K.; Xin, Y.; Gao, X.; Bu, F.; Zhao, D.; Ren, D.; Lu, J.; Wang, D. Association between Gut Microbiota and Peptic Ulcer Disease, Particularly Gastric Ulcer and Duodenal Ulcer: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1277300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xia, C.; Li, Q.; Jin, L.; Zheng, L.; Wu, Z. Comparisons Between Bacterial Communities in Mucosa in Patients with Gastric Antrum Ulcer and a Duodenal Ulcer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltin, D. Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori-Induced Peptic Ulcer Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
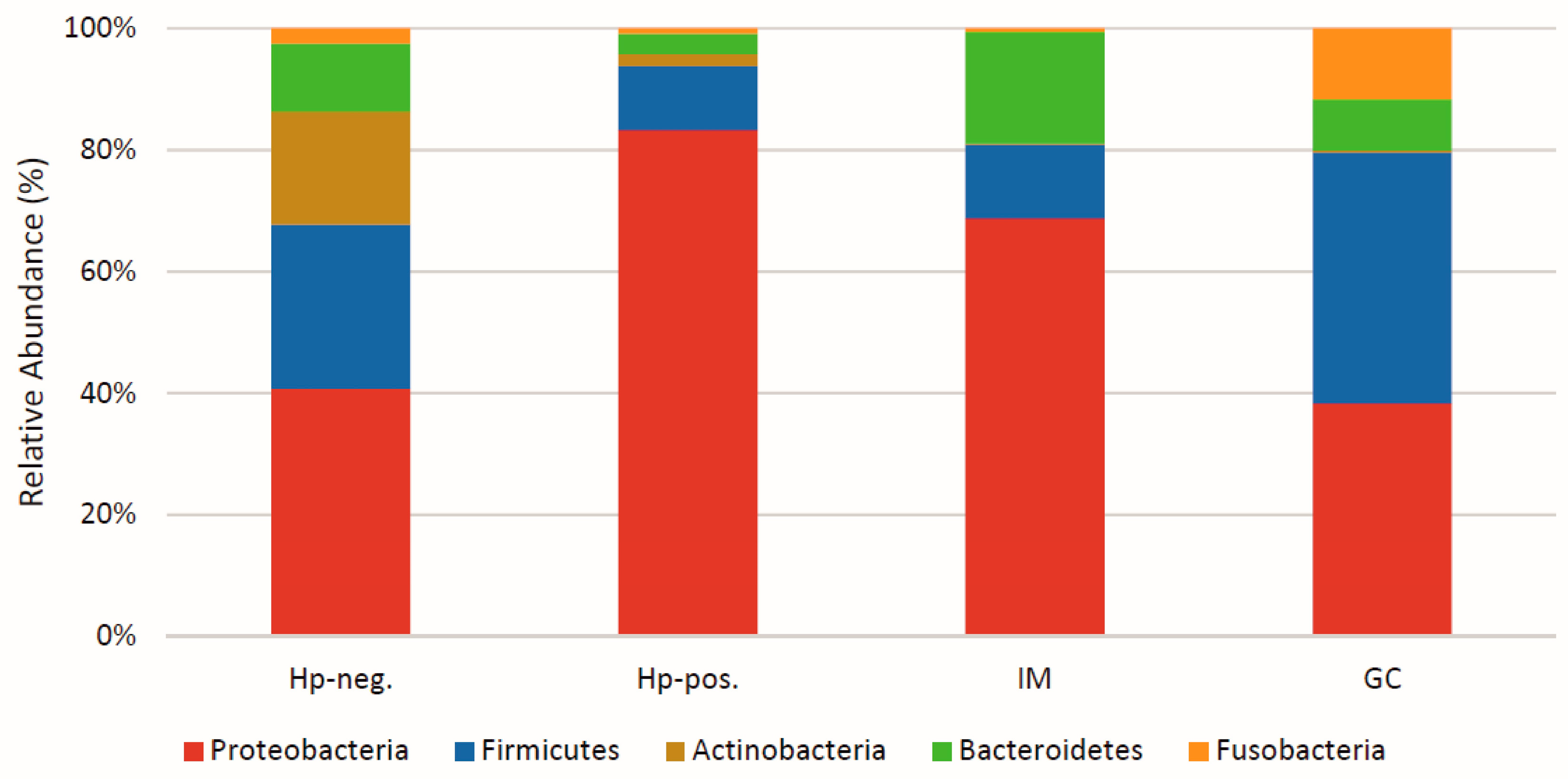
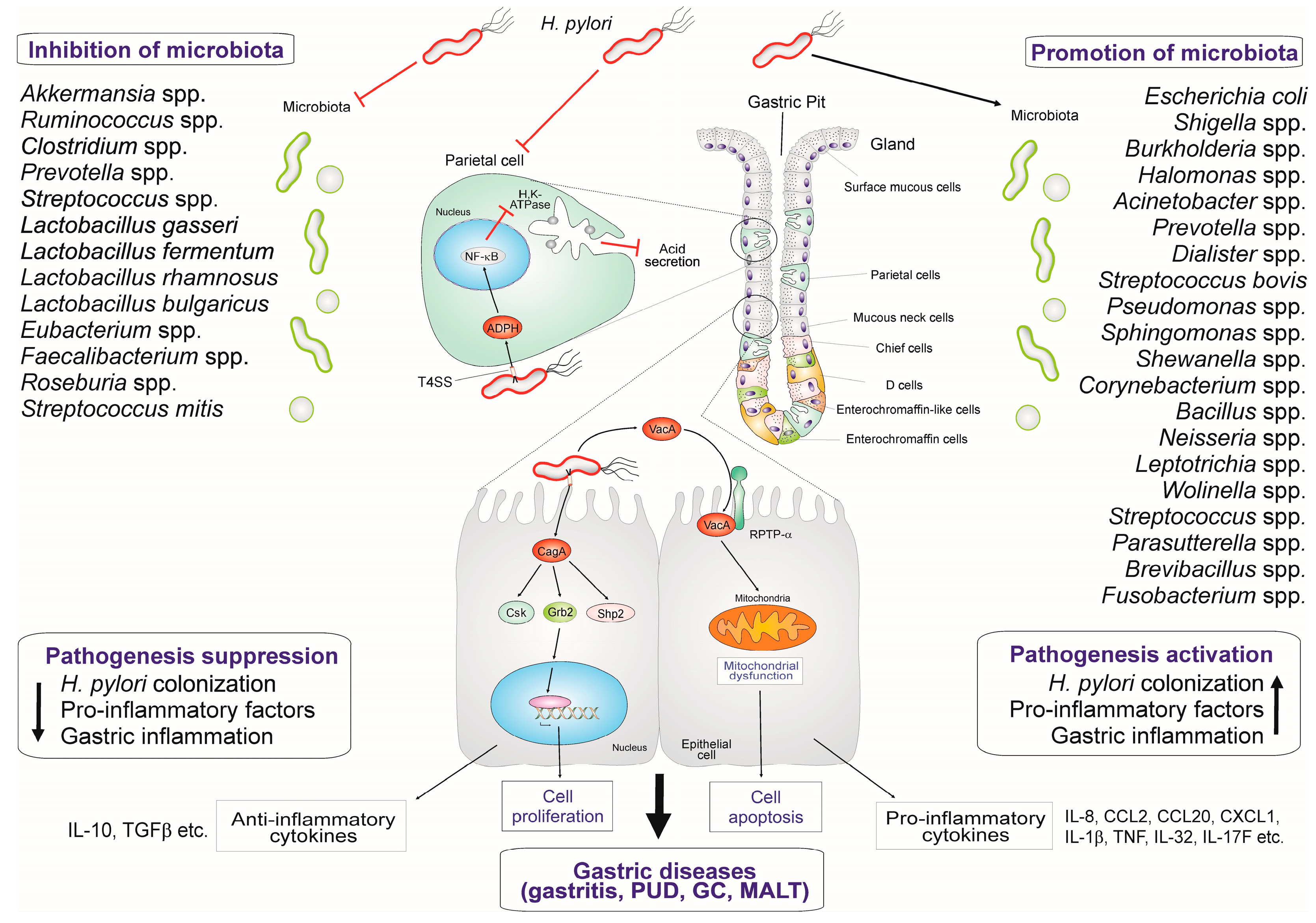
| S. No. | Phylum | Genus | Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Firmicute | Lactobacillus Peptostreptococcus Protococcus Streptococcus Clostridium Eubacterium Faecalibacterium Roseburia Dorea Ruminococcus | Probiotic strain Butyrate producer Green algae Commensal strain Probiotic strain Butyrate producer Butyrate producer Butyrate producer Butyrate producer Keystone sp. | [4,51,52,60,62] |
| 2. | Bacteroidetes | Bacteroides Prevotella Xylanibacter | Probiotic strain Probiotic strain Probiotic strain | [4,52,60,62] |
| 3. | Actinobacteria | Bifidobacterium | Probiotic strain | [51,52,62,67] |
| 4. | Proteobacteria | Escherichia coli Actinobacter Haemophillus Serratia Neisseria Stenotrophomonas Burkholderia | Commensal strain Probiotic strain Keystone sp. Keystone sp. Commensal strain Keystone sp. Keystone sp. | [21,62,68] |
| 5. | Verrucomicrobia | Akkermansia muciniphila | Keystone sp. | [53,69] |
| S. No. | Bacterial Genera Present in H. pylori Colonization | Location | Disease Connection | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Porphyromonas sp. Neisseria sp. S. coleohominis | Gastric mucosa | Gastritis | [69] |
| 2. | Akkermansia sp. | Gastrointestinal tract | Chronic Gastritis | [53,69] |
| 3. | Escherichia Shigella Burkholderia Halomonas | Gastrointestinal region | Gastritis and GC | [21,88] |
| 4. | Clostridium | Gastrointestinal tract | Gastritis and GC | [56,65] |
| 5. | Lactobacillus Streptococcus Veillonella | Gastric mucosa | Gastritis and GC | [21,68,80] |
| 6. | Pseudomonas Sphingomonas Shewanella Corynebacterium Bacillus Neisseria Leptotrichia | Gastrointestinal tract | GC | [76] |
| 7. | Prevotella | Gastrointestinal tract, mouth and vagina | GC | [68,76,80] |
| 8. | Pseudomonas sp. | Gastric mucosa | GC | [85] |
| 9. | Wolinella sp. | Gastric mucosa | GC | [90] |
| 10. | S. parasanguinis | Gastric mucosa | GC | [69] |
| 11. | Acinetobacter | Gastrointestinal tract | GC | [76] |
| 12. | Parasutterella Brevibacillus Fusobacterium | Gastric mucosa | GC | [37] |
| 13. | Oscillospira Oscillibacter Lachnoclostridium | Gastrointestinal tract | GC | [37] |
| 14. | S. bovis | Gastrointestinal tract | Colon cancer | [80] |
| 15. | Dialister | Gastrointestinal tract | GC | [67] |
| 16. | B. pseudomallei | Gastric mucosa | Influence the gastric microbiota or opportunistic pathogen | [87,88] |
| 17. | Oscillospira | Gastrointestinal tract | H. pylori-associated diseases. | [37,67] |
| S. No. | Name of Probiotic Bacteria/Strains | Effect in Gastric Region in H. pylori Infection Condition | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | L. johnsoni L. murinus L. reuteri | H. pylori growth inhibition | [62,69] |
| 2. | L. casei L. paracasei L. acidophilus B. lactis S. thermophilus | Bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects against H. pylori | [100] |
| 3 | Bifidobacterium | Probiotic alone altered the diversity and composition of gastric microbiota without inhibiting effect against H. pylori. | [100] |
| 4. | L. acidophilus ATCC4356, L. rhamnosus PTCC1607 | H. pylori growth inhibition Prevent H. pylori from attaching to the gastric MKN-45 cells Stimulates the production of IFNγ by macrophages (U937 cells) | [101] |
| 5. | L. fermentum P2 L. casei L21 L. rhamnosus JB3 | All probiotics reduce H. pylori levels, vacA gene expression, and specific immunoglobulin levels in stomach. Increased serum level of IFNγ and IL-1β leading to immune response Multi-LAB restores the antioxidant activities suppressed by H. pylori, adjust metabolite composition, and increase in essential amino acids important for immune function. | [102] |
| 6. | L. plantarum | Inhibits H. pylori and GC cell line (AGS). Increase in gene expression of PTEN, Bax and TLR-4. Decrease in AKT gene expression. Increases cell apoptosis. | [103] |
| 7. | L. gasseri ATCC 33323 | Reduces inflammation caused by H. pylori. Reduces the expression of Bcl-2, B- catenin, integrin-α5, integrin B-1, and IL-8 in stomach cells infected with H. pylori. | [104] |
| 8. | L. salivarius L. rhamnosus | Restores the anti- inflammatory bacteria reduced by H. pylori. Down regulates the pro-inflammatory signaling including NF-KB, TNF, IL17 in H. pylori infected cells. | [105] |
| 9. | P. goldsteinii MTS01 | Reduces the harmful effect of VacA and cagA of H. pylori. Changes the microbiota and lowers the cholesterol level easing the H. pylori induced inflammatory reaction to take place. | [106] |
| 10. | S. boulardii | Shows neuraminidase activity and removes surface α (2–3)-linked sialic acid (it acts as a ligand for H. pylori) on the cell surface of duodenal region. | [107] |
| 11. | LAB | Restricts the growth of H. pylori Reduces the urease activity of H. pylori. Hinders the H. pylori flagella-mediated motility. Reduces the ability of H. pylori to induce the pro-inflammatory IL-8 in the human gastric cells. | [108] |
| 12. | L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus | Bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance is produced Suppresses the secretion of pro- inflammatory cytokine IL-8 by gastric epithelial cells. Shows strong anti H. pylori activity. | [109,110] |
| 13. | L. salivarius B101 L. rhamnosus B103 L. plantarum XB7 | Suppresses IL-8 secretion and mRNA expression Inhibits NF-KB activation Suppresses c-Jun activation | [111] |
| 14. | L. plantarum ATCC8014 | Reduces gastric inflammation and shows anti H. pylori effect. | [112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verma, J.; Anwar, M.T.; Linz, B.; Backert, S.; Pachathundikandi, S.K. The Influence of Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Infection and Associated Diseases. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010061
Verma J, Anwar MT, Linz B, Backert S, Pachathundikandi SK. The Influence of Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Infection and Associated Diseases. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerma, Jagriti, Md Tanveer Anwar, Bodo Linz, Steffen Backert, and Suneesh Kumar Pachathundikandi. 2025. "The Influence of Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Infection and Associated Diseases" Biomedicines 13, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010061
APA StyleVerma, J., Anwar, M. T., Linz, B., Backert, S., & Pachathundikandi, S. K. (2025). The Influence of Gastric Microbiota and Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Infection and Associated Diseases. Biomedicines, 13(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13010061







