Navigating the Intersection: Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diagnostic Methods to Identify Sarcopenia in IBD Patients
2.1. Muscle Mass Assessment
2.2. Muscle Strength Assessment
2.3. Physical Performance Assessment
2.4. Malnutrition Risk Screening
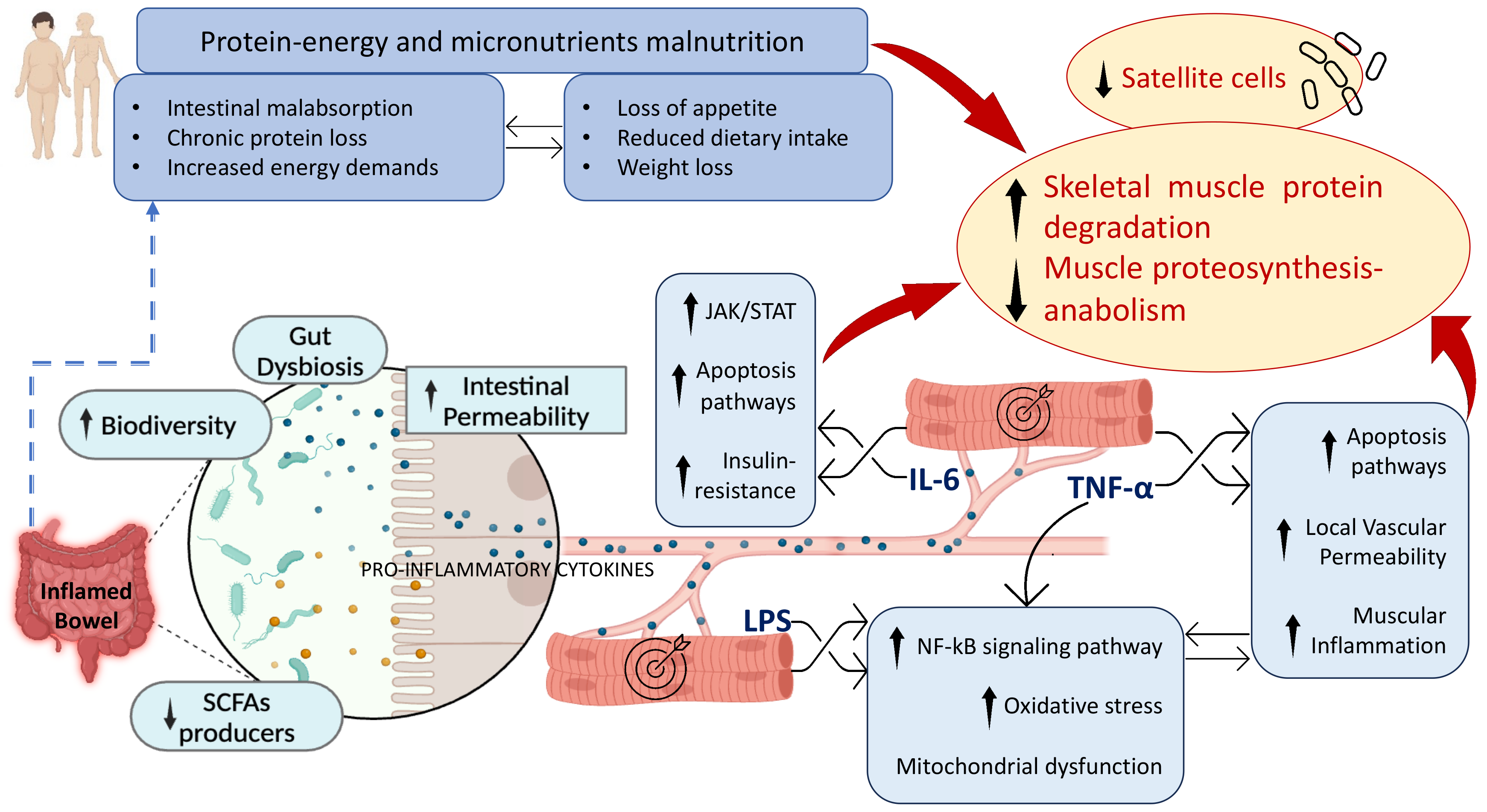
3. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Sarcopenia in IBD
3.1. Primary Sarcopenia
3.2. Inflammation in IBD
3.3. Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Permeability
3.4. Malnutrition
4. Impact of Sarcopenia on IBD Clinical Settings
4.1. Outcomes in IBD
4.2. Role of IBD Medications
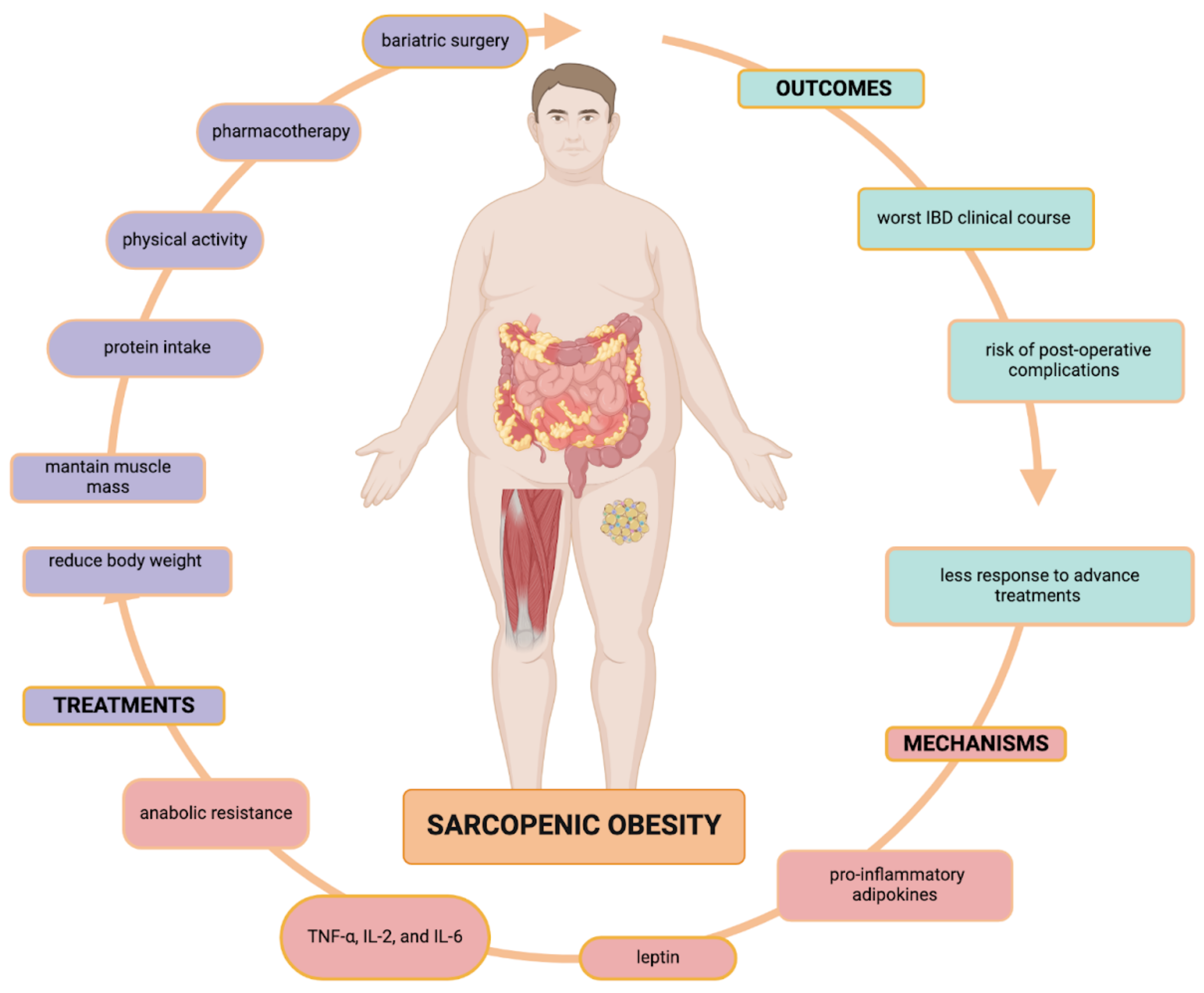
4.3. Sarcopenic Obesity
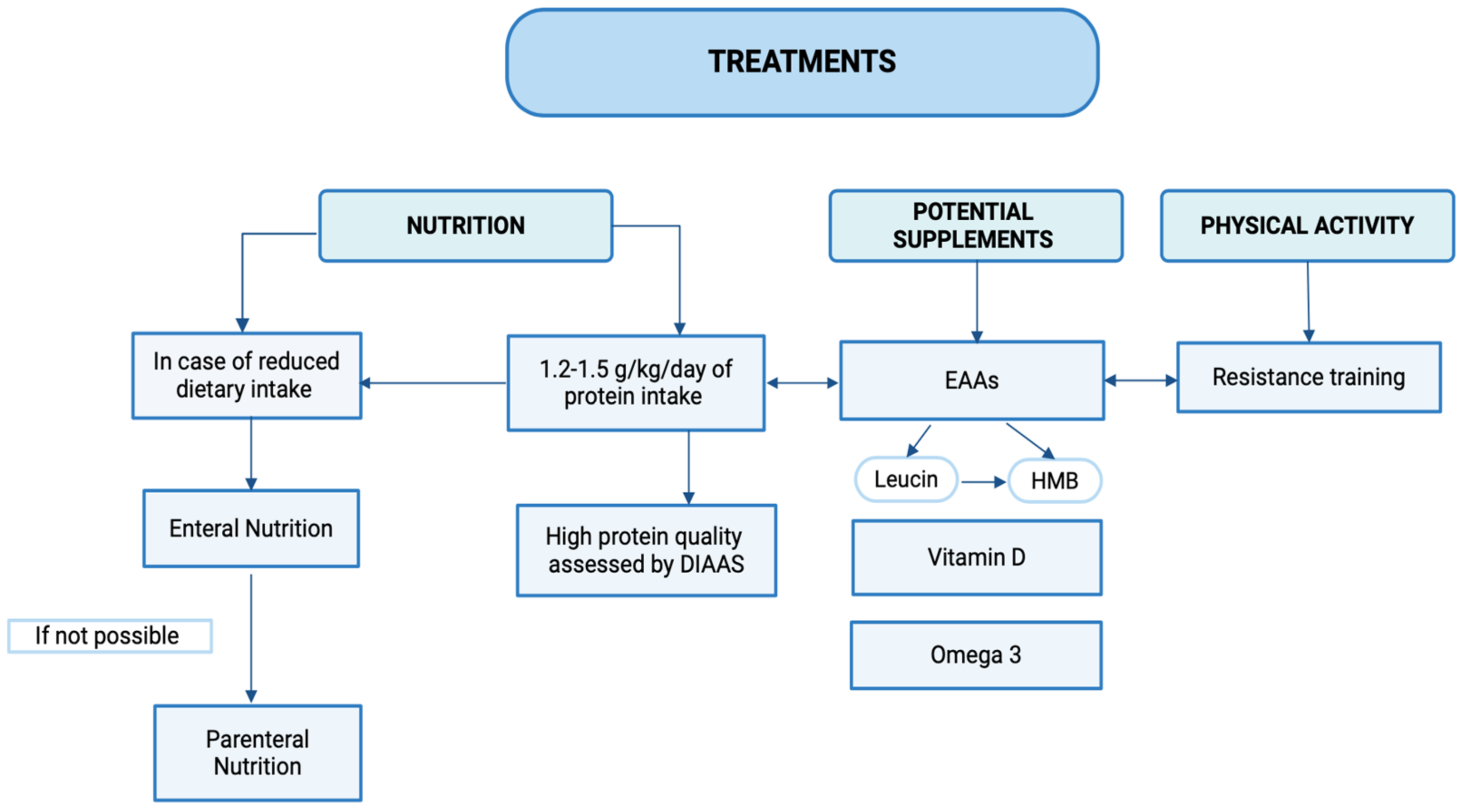
5. Treatments
5.1. Supplements
5.2. Resistance Training
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and Clinical Relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990S–991S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Balntzi, V.; Gray, S.R.; Lara, J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Global Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Severe Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; McNicholas, D.; Creavin, B.; Kelly, M.E.; Walsh, T.; Beddy, D. Sarcopenia and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, A.; Quinlan, J.I.; Overthrow, K.; Greig, C.; Lord, J.M.; Armstrong, M.J.; Cooper, S.C. Sarcopenia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Overview. Nutrients 2021, 13, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; McGinley, E.L. Infection-Related Hospitalizations Are Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, R.; Sousa, U.H.; Reis, T.L.M.; Santana, G.O. Nutritional Status as a Predictor of Hospitalization in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 10, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M.; Lui, L.-Y.; Taylor, B.C.; McCulloch, C.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Lapidus, J.; Orwoll, E.; Ensrud, K.E. Clinical Definitions of Sarcopenia and Risk of Hospitalization in Community-Dwelling Older Men: The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, D.Q.; Varma, P.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Rajadurai, A.S.; Moore, G.T. Low Muscle Mass at Initiation of Anti-TNF Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Is Associated with Early Treatment Failure: A Retrospective Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Xie, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X. Sarcopenia Assessed by Computed Tomography or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Is Associated with the Loss of Response to Biologic Therapies in Adult Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ryu, D.; Gariani, K. Sarcopenic Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Cardiovascular Disease, Mortality, and Management. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1185221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.G. The Global Burden of IBD: From 2015 to 2025. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminerio, J.L.; Koutroubakis, I.E.; Ramos-Rivers, C.; Hashash, J.G.; Dudekula, A.; Regueiro, M.; Baidoo, L.; Barrie, A.; Swoger, J.; Schwartz, M.; et al. Impact of Obesity on the Management and Clinical Course of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, P.L.; Stewart, K.O.; Peloquin, J.M.; Sturgeon, H.C.; Nguyen, D.; Sauk, J.; Garber, J.J.; Yajnik, V.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Chan, A.T.; et al. Body Mass Index, Genetic Susceptibility, and Risk of Complications Among Individuals with Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nic Suibhne, T.; Raftery, T.C.; McMahon, O.; Walsh, C.; O’Morain, C.; O’Sullivan, M. High Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Adults with Crohn’s Disease: Associations with Disease and Lifestyle Factors. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, E241–E248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.W.; Gurwara, S.; Silver, H.J.; Horst, S.N.; Beaulieu, D.B.; Schwartz, D.A.; Seidner, D.L. Sarcopenia Is Common in Overweight Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and May Predict Need for Surgery. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermans, L.L.G.C.; Rabou, J.; Basrai, M.; Schweinlin, A.; Bischoff, S.C.; Cussenot, O.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Renken, R.J.; Gómez, E.; Sánchez-González, P.; et al. Screening, Diagnosis and Monitoring of Sarcopenia. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 48, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; McCloskey, E.; Bruyère, O.; Cesari, M.; Rolland, Y.; Rizzoli, R.; Araujo de Carvalho, I.; Amuthavalli Thiyagarajan, J.; Bautmans, I.; Bertière, M.-C.; et al. Sarcopenia in Daily Practice: Assessment and Management. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Wall, C.; Levine, A.; Midha, V.; Mahajan, R.; Sood, A. Nutritional Screening and Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Indian. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 41, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonen, H.P.F.X.; Van Zanten, A.R.H. Bioelectric Impedance Analysis for Body Composition Measurement and Other Potential Clinical Applications in Critical Illness. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2021, 27, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagae, M.; Umegaki, H.; Yoshiko, A.; Fujita, K. Muscle Ultrasound and Its Application to Point-of-Care Ultrasonography: A Narrative Review. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Midha, V.; Mahajan, R.; Verma, S.; Kakkar, C.; Grover, J.; Singh, D.; Kaur, R.; Masih, A.; Bansal, N.; et al. Evaluation of Nutritional Characteristics Reveals Similar Prevalence of Malnutrition in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 580–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.Q.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Lau, K.K.; Moore, G.T. Body Composition Analysis Using Abdominal Scans from Routine Clinical Care in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.P.; Kedia, S.; Madhusudhan, K.S.; Bopanna, S.; Goyal, S.; Jain, S.; Vikram, N.K.; Sharma, R.; Makharia, G.K.; Ahuja, V. Body Composition in Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: Correlation with Disease Severity and Duration. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2017, 1215035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boparai, G.; Kedia, S.; Kandasamy, D.; Sharma, R.; Madhusudhan, K.S.; Dash, N.R.; Sahu, P.; Pal, S.; Sahni, P.; Panwar, R.; et al. Combination of Sarcopenia and High Visceral Fat Predict Poor Outcomes in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamba, S.; Inatomi, O.; Takahashi, K.; Morita, Y.; Imai, T.; Ohno, M.; Kurihara, M.; Takebayashi, K.; Kojima, M.; Iida, H.; et al. Assessment of Body Composition From CT Images at the Level of the Third Lumbar Vertebra in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.A.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Espinosa, N.; Raptis, D.A.; Buck, F.M. Dixon-Based MRI for Assessment of Muscle-Fat Content in Phantoms, Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Achillodynia: Comparison to Visual Assessment of Calf Muscle Quality. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianca, V.; Albano, D.; Messina, C.; Gitto, S.; Ruffo, G.; Guarino, S.; Del Grande, F.; Sconfienza, L.M. Sarcopenia: Imaging Assessment and Clinical Application. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Bignotti, B.; Torri, L.; Rossi, F. Sarcopenia: How to Measure, When and Why. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooren, C.E.G.M.; Lodewick, T.M.; Beelen, E.M.J.; van Dijk, D.P.J.; Bours, M.J.L.; Haans, J.J.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Pierik, M.J.; Bakers, F.C.H.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E. The Reproducibility of Skeletal Muscle Signal Intensity on Routine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Crohn’s Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.Q.; Moore, G.T.; Strauss, B.J.G.; Hamilton, A.L.; De Cruz, P.; Kamm, M.A. Visceral Adiposity Predicts Post-Operative Crohn’s Disease Recurrence. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covello, C.; Becherucci, G.; Scaldaferri, F.; Laterza, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mentella, M.C. Popular Diets and Nutritional Assessment in the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Overview of Current Evidence. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.C.; Alves Junior, C.A.S.; Silva, A.M.; Silva, D.A.S. Phase Angle and Body Composition: A Scoping Review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 56, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerenziani, S.; Biancone, L.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Balestrieri, P.; Stasi, E.; Ribolsi, M.; Rescio, M.P.; Altomare, A.; Cocca, S.; Pallone, F.; et al. Nutritional Status and Bioelectrical Phase Angle Assessment in Adult Crohn Disease Patients Receiving Anti-TNFα Therapy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzoferrato, M.; de Sire, R.; Ingravalle, F.; Mentella, M.C.; Petito, V.; Martone, A.M.; Landi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Mele, M.C.; Lopetuso, L.R.; et al. Characterization of Sarcopenia in an IBD Population Attending an Italian Gastroenterology Tertiary Center. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.M.; Yoon, W.E.; Kim, S.H.; Myung, H.J.; Moon, J.S. Evaluation of Nutritional Status Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Intest. Res. 2022, 20, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzocchi, A.; Ponti, F.; Albisinni, U.; Battista, G.; Guglielmi, G. DXA: Technical Aspects and Application. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriyan, R. Body Composition Techniques. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, P.T.; Rosen, P. Prehospital care: Procedures or transport? J. Emerg. Med. 1986, 4, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, C.V.; Diessel, E.; Genant, H.K. Clinical Applications of Body Composition Measurements Using DXA. J. Clin. Densitom. 2003, 6, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsley, P.R.; Kitsell, F.; Samuel, D.; Stokes, M. Validity of Measuring Distal Vastus Medialis Muscle Using Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging versus Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Man. Ther. 2014, 19, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, W.R.; Reid, K.F.; Phillips, E.M.; Krivickas, L.S.; Hughes, V.A.; Roubenoff, R.; Fielding, R.A. Muscle Fiber Size and Function in Elderly Humans: A Longitudinal Study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, S.; Brau, F.; Forino, R.; Berti, A.; D’Ignazio, F.; Loreti, C.; Bellieni, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Di Caro, F.; Biscotti, L.; et al. Sarcopenia: Diagnosis and Management, State of the Art and Contribution of Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Patterson, K.M.; Stover, C.D.; Geddam, D.A.R.; Tribby, A.C.; Lajza, D.G.; Young, K.C. Site-Specific Thigh Muscle Loss as an Independent Phenomenon for Age-Related Muscle Loss in Middle-Aged and Older Men and Women. Age 2014, 36, 9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caresio, C.; Molinari, F.; Emanuel, G.; Minetto, M.A. Muscle Echo Intensity: Reliability and Conditioning Factors. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2015, 35, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulinacci, G.; Pirola, L.; Gandola, D.; Ippolito, D.; Viganò, C.; Laffusa, A.; Gallo, C.; Invernizzi, P.; Danese, S.; Massironi, S. P466 Ultrasound Muscle Assessment for Sarcopenia Screening in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Prospective Study (SarcUS-IBD). J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, I937–I938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.L.; Herath, M.; Burns, M.; Holt, D.; Ebeling, P.R.; Milat, F.; Gibson, P.R.; Moore, G.T. The Value of Whole-Body Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Assessing Body Composition in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Prospective Study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, K.; Kearns, C.F.; Midorikawa, T.; Abe, T. Prediction and Validation of Total and Regional Skeletal Muscle Mass by Ultrasound in Japanese Adults. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 96, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, N.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Narici, M.V. Ultrasonographic Assessment of Human Skeletal Muscle Size. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaes, T.; Thomis, M.; Onkelinx, S.; Coudyzer, W.; Cornelissen, V.; Vanhees, L. Reliability and Validity of the Ultrasound Technique to Measure the Rectus Femoris Muscle Diameter in Older CAD-Patients. BMC Med. Imaging 2012, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Fujita, E.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Loenneke, J.P.; Akamine, T. Ultrasound-Derived Forearm Muscle Thickness Is a Powerful Predictor for Estimating DXA-Derived Appendicular Lean Mass in Japanese Older Adults. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 2341–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Smoliner, C.; Zocher, D.; Scheufele, R.; Valentini, L.; Lochs, H.; Pirlich, M. Determinants of Hand Grip Strength, Knee Extension Strength and Functional Status in Cancer Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsionis, G.; Pakos, E.E.; Stafilas, K.S.; Paschos, N.; Papakostas, T.; Beris, A.E. Normative Data on Hand Grip Strength in a Greek Adult Population. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.C.; Denison, H.J.; Martin, H.J.; Patel, H.P.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. A Review of the Measurement of Grip Strength in Clinical and Epidemiological Studies: Towards a Standardised Approach. Age Ageing 2011, 40, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulens, M.; Vansant, G.; Lysens, R.; Claessens, A.L.; Muls, E.; Brumagne, S. Study of Differences in Peripheral Muscle Strength of Lean versus Obese Women: An Allometric Approach. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, C.J.; Barakat, H.A.; Dohm, G.L.; Pories, W.J.; MacDonald, K.G.; Cunningham, P.R.G.; Swanson, M.S.; Houmard, J.A. Muscle Fiber Type Is Associated with Obesity and Weight Loss. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E1191–E1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Fan, Y.; Yang, F. Exploring the Causal Relationship between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Sarcopenia-Related Traits: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Aging 2023, 16, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenmakers, A.J. Muscle Function in Critically Ill Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Kaymak, B.; Frontera, W.; Ata, A.M.; Ricci, V.; Ekiz, T.; Chang, K.-V.; Han, D.-S.; Michail, X.; Quittan, M.; et al. Diagnosing Sarcopenia: Functional Perspectives and a New Algorithm from the ISarcoPRM. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, Jrm00209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskey, N.; Peña-Sánchez, J.N.; Jones, J.L.; Fowler, S.A. Development of a Screening Tool to Detect Nutrition Risk in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 27, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, I.; Prager, M.; Valentini, L.; Büning, C. Inflammation-Driven Malnutrition: A New Screening Tool Predicts Outcome in Crohn’s Disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, L.; Bannert, K.; Rohde, S.; Berlin, P.; Reiner, J.; Wiese, M.; Doller, J.; Lerch, M.M.; Aghdassi, A.A.; Meyer, F.; et al. Preclinical Insights into the Gut-Skeletal Muscle Axis in Chronic Gastrointestinal Diseases. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8304–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticinesi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Milani, C.; Nouvenne, A.; Tana, C.; Del Rio, D.; Maggio, M.; Ventura, M.; Meschi, T. Aging Gut Microbiota at the Cross-Road between Nutrition, Physical Frailty, and Sarcopenia: Is There a Gut-Muscle Axis? Nutrients 2017, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayer, A.A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A. Sarcopenia Definition, Diagnosis and Treatment: Consensus Is Growing. Age Ageing 2022, 51, Afac220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Yao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Zuo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, F.; et al. Irisin Ameliorates Age-Associated Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pár, A.; Hegyi, J.P.; Váncsa, S.; Pár, G. Sarcopenia-2021: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapy. Orv. Hetil. 2021, 162, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banack, H.R.; LaMonte, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Zhu, K.; Evans, W.J.; Shankaran, M.; Wactawski-Wende, J. Association of Muscle Mass Measured by D3-Creatine (D3Cr), Sarcopenic Obesity, and Insulin-Glucose Homeostasis in Postmenopausal Women. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, E0278723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priego, T.; Martín, A.I.; González-Hedström, D.; Granado, M.; López-Calderón, A. Role of Hormones in Sarcopenia. Vitam. Horm. 2021, 115, 535–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remelli, F.; Vitali, A.; Zurlo, A.; Volpato, S. Vitamin D Deficiency and Sarcopenia in Older Persons. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Ding, F.; Hou, L.; Deng, Y.; Cui, T.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Determination of Skeletal Muscle Mass by Aspartate Aminotransferase/Alanine Aminotransferase Ratio, Insulin and FSH in Chinese Women with Sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.-R.; Lee, S.; Song, S.-K. A Review of Sarcopenia Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Future Direction. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2022, 37, E146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdijk, L.B.; Snijders, T.; Drost, M.; Delhaas, T.; Kadi, F.; van Loon, L.J.C. Satellite Cells in Human Skeletal Muscle; from Birth to Old Age. Age 2014, 36, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belenguer-Varea, Á.; Tarazona-Santabalbina, F.J.; Avellana-Zaragoza, J.A.; Martínez-Reig, M.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Inglés, M. Oxidative Stress and Exceptional Human Longevity: Systematic Review. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 149, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Lian, Z.; Yu, K. Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Aging: Focus on Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 964130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Pender, C.L.; Bar-Ziv, R.; Zhang, H.; Wickham, K.; Willey, E.; Durieux, J.; Ahmad, Q.; Dillin, A. Mitochondria as Cellular and Organismal Signaling Hubs. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 38, 179–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Nezu, Y.; Tagawa, R.; Higami, Y. Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Responses in White Adipose Tissue: Lipoatrophy, Whole-Body Metabolism and Lifespan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellen, R.H.; Girotto, O.S.; Marques, E.B.; Laurindo, L.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Mendes, C.G.; Garcia, L.N.H.; Bechara, M.D.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sinatora, R.V.; et al. Insights into Pathogenesis, Nutritional and Drug Approach in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Fernández, J.; Fernández-Montero, A.; Córdova-Martínez, A.; Pastor, D.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Roche, E. Sarcopenia: Molecular Pathways and Potential Targets for Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Püschel, G.P.; Klauder, J.; Henkel, J. Macrophages, Low-Grade Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia: A Mutual Ambiguous Relationship in the Development of Metabolic Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, J.K.; de Souto Barreto, P.; Fougère, B.; Rolland, Y.; Vellas, B.; Cesari, M. Chronic Inflammation and Sarcopenia: A Regenerative Cell Therapy Perspective. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 103, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, S.; Rossmeislova, L.; Koppo, K. The Role of Inflammation in Age-Related Sarcopenia. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, O.M.; de Sire, R.; Petito, V.; Testa, A.; Villani, G.; Scaldaferri, F.; Castiglione, F. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Sarcopenia: The Role of Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in the Development of Muscle Failure. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 694217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, A.-L.; Hu, H.-Y.; Rong, Y.-D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Zhou, X.-Z. A Study on Relationship between Elderly Sarcopenia and Inflammatory Factors IL-6 and TNF-α. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2017, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, M.; Pluijm, S.M.F.; Stel, V.S.; Bosscher, R.J.; Deeg, D.J.H. Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam Physical Activity as a Determinant of Change in Mobility Performance: The Longitudinal Aging Study Amsterdam. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taaffe, D.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Rowe, J.; Seeman, T.E. Cross-Sectional and Prospective Relationships of Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein with Physical Performance in Elderly Persons: MacArthur Studies of Successful Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2000, 55, M709–M715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesti, J.K.; Guttridge, D.C. Inflammation Based Regulation of Cancer Cachexia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 168407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaji, U.N.; Nardone, O.M.; Cannatelli, R.; Smith, S.C.; Ghosh, S.; Iacucci, M. Small Molecule Oral Targeted Therapies in Ulcerative Colitis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, R.; Mudter, J.; Finotto, S.; Müllberg, J.; Jostock, T.; Wirtz, S.; Schütz, M.; Bartsch, B.; Holtmann, M.; Becker, C.; et al. Blockade of Interleukin 6 Trans Signaling Suppresses T-Cell Resistance against Apoptosis in Chronic Intestinal Inflammation: Evidence in Crohn Disease and Experimental Colitis in Vivo. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbacher, P.; Eckl, P. Impact of Oxidative Stress on Exercising Skeletal Muscle. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 356–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, R.; Mignini, I.; Varca, S.; Calvez, V.; Termite, F.; Esposto, G.; Laterza, L.; Scaldaferri, F.; Ainora, M.E.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Piecing a Complex Puzzle Together. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Akash, M.S.H.; Liaqat, A.; Kamal, S.; Qadir, M.I.; Rasul, A. Role of Interleukin-6 in Development of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2017, 27, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serri, O.; St-Jacques, P.; Sartippour, M.; Renier, G. Alterations of Monocyte Function in Patients with Growth Hormone (GH) Deficiency: Effect of Substitutive GH Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.M.; Della Gatta, P.; Suzuki, K.; Nieman, D.C. Cytokine Expression and Secretion by Skeletal Muscle Cells: Regulatory Mechanisms and Exercise Effects. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alula, K.M.; Jackson, D.N.; Smith, A.D.; Kim, D.S.; Turner, K.; Odstrcil, E.; Kaipparettu, B.A.; Dassopoulos, T.; Venuprasad, K.; Feagins, L.A.; et al. Targeting Mitochondrial Damage as a Therapeutic for Ileal Crohn’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderVeen, B.N.; Fix, D.K.; Carson, J.A. Disrupted Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Dynamics, Mitophagy, and Biogenesis during Cancer Cachexia: A Role for Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 3292087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, D.N.; Panopoulos, M.; Neumann, W.L.; Turner, K.; Cantarel, B.L.; Thompson-Snipes, L.; Dassopoulos, T.; Feagins, L.A.; Souza, R.F.; Mills, J.C.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction during Loss of Prohibitin 1 Triggers Paneth Cell Defects and Ileitis. Gut 2020, 69, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for Intestinal Bacteria, Viruses, and Fungi in Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339.E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Lan, P.; Mou, X. The Microbiome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strober, W.; Fuss, I.; Mannon, P. The Fundamental Basis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krimpen, S.J.; Jansen, F.A.C.; Ottenheim, V.L.; Belzer, C.; van Der Ende, M.; van Norren, K. The Effects of Pro-, Pre-, and Synbiotics on Muscle Wasting, a Systematic Review-Gut Permeability as Potential Treatment Target. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelli, M.; Franza, L.; Pignataro, G.; Ojetti, V.; Covino, M.; Piccioni, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F. Interaction between Lipopolysaccharide and Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldars-García, L.; Marin, A.C.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J.P. The Interplay between Immune System and Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Muscle Wasting: The Gut Microbiota as a New Therapeutic Target? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2186–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Goel, R.; Kim, S.; Richards, E.M.; Carter, C.S.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K.; Buford, T.W. Intestinal Permeability Biomarker Zonulin Is Elevated in Healthy Aging. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, E1–E810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuoco, L.; Vescovo, G.; Castaman, R.; Ravara, B.; Cammarota, G.; Angelini, A.; Salvagnini, M.; Dalla Libera, L. Skeletal Muscle Wastage in Crohn’s Disease: A Pathway Shared with Heart Failure? Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 127, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Jiang, J.; Yang, T.; Ma, L.; Fu, Z. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Improves Physiological Function and Cognitive Ability in Aged Mice by the Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, E1900603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermüller, B.; Singer, G.; Kienesberger, B.; Klymiuk, I.; Sperl, D.; Stadlbauer, V.; Horvath, A.; Miekisch, W.; Gierschner, P.; Grabherr, R.; et al. The Effects of Prebiotic Supplementation with OMNi-LOGiC® FIBRE on Fecal Microbiome, Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds, and Gut Permeability in Murine Neuroblastoma-Induced Tumor-Associated Cachexia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Claus, S.P.; Le Roy, C.I.; Grangette, C.; Pot, B.; Martinez, I.; Walter, J.; Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Synbiotic Approach Restores Intestinal Homeostasis and Prolongs Survival in Leukaemic Mice with Cachexia. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1456–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Loumaye, A.; Catry, E.; Walgrave, H.; Cherbuy, C.; Leclercq, S.; Van Hul, M.; Plovier, H.; Pachikian, B.; et al. Increased Gut Permeability in Cancer Cachexia: Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18224–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, K.; Wakino, S.; Irie, J.; Miyamoto, J.; Matsui, A.; Tajima, T.; Itoh, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yoshifuji, A.; Kimura, I.; et al. Contribution of Uremic Dysbiosis to Insulin Resistance and Sarcopenia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosicki, G.J.; Fielding, R.A.; Lustgarten, M.S. Gut Microbiota Contribute to Age-Related Changes in Skeletal Muscle Size, Composition, and Function: Biological Basis for a Gut-Muscle Axis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Ge, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Ding, B.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Z. Intestinal Permeability Associated with the Loss of Skeletal Muscle Strength in Middle-Aged and Older Adults in Rural Area of Beijing, China. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stehle, J.R.; Leng, X.; Kitzman, D.W.; Nicklas, B.J.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; High, K.P. Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein, a Surrogate Marker of Microbial Translocation, Is Associated with Physical Function in Healthy Older Adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, S.; Kim, H.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Reza, M.M.; Martin, K.A.; Kundu, P.; Cox, L.M.; Selkrig, J.; Posma, J.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Influences Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function in Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, Eaan5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustgarten, M.S. The Role of the Gut Microbiome on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Physical Function: 2019 Update. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, R.A.; Reeves, A.R.; Jasuja, R.; Liu, C.; Barrett, B.B.; Lustgarten, M.S. Muscle Strength Is Increased in Mice That Are Colonized with Microbiota from High-Functioning Older Adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 127, 110722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; Fielding, R.; Visser, M.V.; Van Loon, L.J.; Rolland, Y.; Orwoll, E.; Reid, K.; Boonen, S.; Dere, W.; Epstein, S.; et al. Tools in the Assessment of Sarcopenia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.E.; Bhattacharya, A.; Sataranatarajan, K.; Qaisar, R.; Sloane, L.; Rahman, M.M.; Kinter, M.; Van Remmen, H. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Butyrate Improves Metabolism and Reduces Muscle Atrophy during Aging. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hara, N.; Sugimoto, R.; Mifuji-Moroka, R.; Tanaka, H.; Eguchi, A.; Iwasa, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Iwata, K.; Takei, Y.; et al. The Associations between Circulating Bile Acids and the Muscle Volume in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De La Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Liu, W.; Piao, M.; Zhu, H. A Review of the Relationship between the Gut Microbiota and Amino Acid Metabolism. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddharth, J.; Chakrabarti, A.; Pannérec, A.; Karaz, S.; Morin-Rivron, D.; Masoodi, M.; Feige, J.N.; Parkinson, S.J. Aging and Sarcopenia Associate with Specific Interactions between Gut Microbes, Serum Biomarkers and Host Physiology in Rats. Aging 2017, 9, 1698–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Fu, B.C. Diet, the Gut Microbiome, and Epigenetics. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Surette, M.; Bercik, P. The Interplay between the Intestinal Microbiota and the Brain. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Austin, P.; Ballmer, P.; Biolo, G.; Bischoff, S.C.; Compher, C.; Correia, I.; Higashiguchi, T.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Definitions and Terminology of Clinical Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. Nutritional Status and Its Detection in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massironi, S.; Rossi, R.E.; Cavalcoli, F.A.; Della Valle, S.; Fraquelli, M.; Conte, D. Nutritional Deficiencies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Therapeutic Approaches. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, P.; Ribolsi, M.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Emerenziani, S.; Altomare, A.; Cicala, M. Nutritional Aspects in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Borralho Nunes, P.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial Diagnosis, Monitoring of Known IBD, Detection of Complications. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, N.; Figgins, B.; Altshuler, E.; Pham, A.; Kamel, A.Y. Concurrent Zinc and Vitamin B6 Deficiencies in Acutely Exacerbated Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Case Reports. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2022, 37, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownson, E.; Saunders, J.; Jatkowska, A.; White, B.; Gerasimidis, K.; Seenan, J.P.; Macdonald, J. Micronutrient Status and Prediction of Disease Outcome in Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Receiving Biologic Therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, Izad174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Zhang, B. The Impact of Zinc and Zinc Homeostasis on the Intestinal Mucosal Barrier and Intestinal Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeywickrama, H.M.; Uchiyama, M.; Sumiyoshi, T.; Okuda, A.; Koyama, Y. The Role of Zinc on Nutritional Status, Sarcopenia, and Frailty in Older Adults: A Scoping Review. Nutr. Rev. 2023, Nuad094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, T.; Li, W.; He, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Causal Relationship of Genetically Predicted Serum Micronutrients Levels with Sarcopenia: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 913155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz-Góngora, V.; Palazuelos-González, R.; Domínguez-Flores, O. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Older Adults in Latin-America: A Narrative Review. Food Nutr. Bull. 2023, 3795721231214587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dronkelaar, C.; Fultinga, M.; Hummel, M.; Kruizenga, H.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Tieland, M. Minerals and Sarcopenia in Older Adults: An Updated Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2023, 24, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasanmade, A.A.; Adedokun, O.J.; Olson, A.; Strauss, R.; Davis, H.M. Serum Albumin Concentration: A Predictive Factor of Infliximab Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Response in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 48, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroki, L.M.; Mangano, M.; Allsworth, J.E.; Menias, C.O.; Massad, L.S.; Powell, M.A.; Mutch, D.G.; Thaker, P.H. Pre-Operative Assessment of Muscle Mass to Predict Surgical Complications and Prognosis in Patients with Endometrial Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieffers, J.R.; Bathe, O.F.; Fassbender, K.; Winget, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Postoperative Infection and Delayed Recovery from Colorectal Cancer Resection Surgery. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.-A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A New Proposal with Evaluation in a Cohort of 6336 Patients and Results of a Survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, K.W.; van Vugt, J.L.A.; Tegels, J.J.W.; Snijders, C.; Hulsewé, K.W.E.; Hoofwijk, A.G.M.; Stoot, J.H.; Von Meyenfeldt, M.F.; Beets, G.L.; Derikx, J.P.M.; et al. Functional Compromise Reflected by Sarcopenia, Frailty, and Nutritional Depletion Predicts Adverse Postoperative Outcome after Colorectal Cancer Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ding, X.; Maggiore, G.; Pietrobattista, A.; Satapathy, S.K.; Tian, Z.; Jing, X. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Poor Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, L.; Cao, T.; Yang, J.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, N.; Li, J. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Impact on Postoperative Outcome in Patients with Crohn’s Disease Undergoing Bowel Resection. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertani, L.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Bellini, M.; Mumolo, M.G.; Costa, F. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Is There a Role for Nutritional Suggestions? Nutrients 2021, 13, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, H.; Araki, T.; Okita, Y.; Kondo, S.; Kawamura, M.; Hiro, J.; Toiyama, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Impact of Sarcopenia on Surgical Site Infection after Restorative Proctocolectomy for Ulcerative Colitis. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Yamada, A.; Komaki, Y.; Komaki, F.; Cohen, R.D.; Dalal, S.; Hurst, R.D.; Hyman, N.; Pekow, J.; Shogan, B.D.; et al. Low Skeletal Muscle Index Adjusted for Body Mass Index Is an Independent Risk Factor for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Surgical Complications. Crohns Colitis 2020, 2, Otaa064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erős, A.; Soós, A.; Hegyi, P.; Szakács, Z.; Benke, M.; Szűcs, Á.; Hartmann, P.; Erőss, B.; Sarlós, P. Sarcopenia as an Independent Predictor of the Surgical Outcomes of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Surg. Today 2020, 50, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoedler, S.; Schliermann, R.; Knoedler, L.; Wu, M.; Hansen, F.J.; Matar, D.Y.; Obed, D.; Vervoort, D.; Haug, V.; Hundeshagen, G.; et al. Impact of Sarcopenia on Outcomes in Surgical Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 4238–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Jiang, L.; Yu, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Qi, W.; Cao, Q.; Bai, R.; Zhou, W. The Importance of Sarcopenia as a Prognostic Predictor of the Clinical Course in Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushing, K.C.; Kordbacheh, H.; Gee, M.S.; Kambadakone, A.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Sarcopenia Is a Novel Predictor of the Need for Rescue Therapy in Hospitalized Ulcerative Colitis Patients. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, M.C.; Seah, D.; Faleck, D.M.; Shah, S.C.; Chao, C.-Y.; An, Y.-K.; Radford-Smith, G.; Bessissow, T.; Dubinsky, M.C.; Ford, A.C.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Optimal Salvage Therapy in Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whaley, K.G.; Rosen, M.J. Contemporary Medical Management of Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeds, I.L.; Sundel, M.H.; Gabre-Kidan, A.; Safar, B.; Truta, B.; Efron, J.E.; Fang, S.H. Outcomes for Ulcerative Colitis with Delayed Emergency Colectomy Are Worse When Controlling for Preoperative Risk Factors. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2019, 62, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grova, M.; Crispino, F.; Maida, M.; Vitello, A.; Renna, S.; Casà, A.; Tesè, L.; Macaluso, F.S.; Orlando, A. Sarcopenia Is a Negative Predictive Factor for Endoscopic Remission in Patients with Crohn’s Disease Treated with Biologics. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.P.; Jadaun, J.S.; Narnoliya, L.K.; Pandey, A. Prebiotic Oligosaccharides: Special Focus on Fructooligosaccharides, Its Biosynthesis and Bioactivity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.S.; Malietzis, G.; Lung, P.F.C.; Penez, L.; Yip, W.M.; Gabe, S.; Jenkins, J.T.; Hart, A. The Body Composition Profile Is Associated with Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease and May Offer an Alternative Dosing Paradigm. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsalos, O.; Dalton, B.; Leppanen, J.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Himmerich, H. Impact of TNF-α Inhibitors on Body Weight and BMI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, K.; Fallon, K.; Ruut, T.; Lane, D.; McKay, R.; Shadbolt, B.; Ang, S.; Cook, M.; Platten, J.; Pavli, P.; et al. Infliximab Reverses Inflammatory Muscle Wasting (Sarcopenia) in Crohn’s Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 41, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.C.D.; Malaguti, C.; de Azevedo Lucca, F.; Cabalzar, A.L.; da Rocha Ribeiro, T.C.; Gaburri, P.D.; Chebli, L.A.; Chebli, J.M.F. Impact of Biological Therapy on Body Composition of Patients with Chron’s Disease. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2017, 63, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stidham, R.W.; Lee, T.C.H.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Deshpande, A.R.; Sussman, D.A.; Singal, A.G.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Saini, S.D.; Vijan, S.; Waljee, A.K. Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis: The Efficacy of Anti-TNF Agents for the Treatment of Crohn’s Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchimont, N.; Putzeys, V.; Collette, J.; Vermeire, S.; Rutgeerts, P.; De Vos, M.; Van Gossum, A.; Franchimont, D.; Fiasse, R.; Pelckmans, P.; et al. Rapid Improvement of Bone Metabolism after Infliximab Treatment in Crohn’s Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, M.T.; Geller, J.L.; Vasiliauskas, E.A.; Kam, L.Y.; Vora, P.; Martyak, L.A.; Yang, H.; Hu, B.; Lin, Y.-C.; Keenan, G.; et al. Treatment with Infliximab Is Associated with Increased Markers of Bone Formation in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massironi, S.; Viganò, C.; Palermo, A.; Pirola, L.; Mulinacci, G.; Allocca, M.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Inflammation and Malnutrition in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puleo, F.; Meirelles, K.; Navaratnarajah, M.; Fitzpatrick, L.; Shumate, M.L.; Cooney, R.N.; Lang, C.H. Skeletal Muscle Catabolism in Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Induced Murine Colitis. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barazzoni, R.; Busetto, L.; Campmans-Kuijpers, M.; Cardinale, V.; Chermesh, I.; Eshraghian, A.; Kani, H.T.; Khannoussi, W.; Lacaze, L.; et al. European Guideline on Obesity Care in Patients with Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases-Joint European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism/United European Gastroenterology Guideline. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 663–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dulai, P.S.; Zarrinpar, A.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Sandborn, W.J. Obesity in IBD: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Disease Course and Treatment Outcomes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, C.B.; Jan, A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut off Points. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Michalak, A.; Kasztelan-Szczerbińska, B.; Cichoż-Lach, H. Impact of Obesity on the Course of Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease–A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.V.; Schultz, C.G.; Ooi, S.; Goess, C.; Costello, S.P.; Vincent, A.D.; Schoeman, S.N.; Lim, A.; Bartholomeusz, F.D.; Travis, S.P.L.; et al. Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Gains in Adiposity despite High Prevalence of Myopenia and Osteopenia. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, R.V.; Trott, M.J.; Bartholomeusz, F.D.; Andrews, J.M. Systematic Review: Body Composition in Adults with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connelly, T.M.; Juza, R.M.; Sangster, W.; Sehgal, R.; Tappouni, R.F.; Messaris, E. Volumetric Fat Ratio and Not Body Mass Index Is Predictive of Ileocolectomy Outcomes in Crohn’s Disease Patients. Dig. Surg. 2014, 31, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Telang, R.; Kociszewska, D.; Thorne, P.R.; Vlajkovic, S.M. A High-Fat Diet Induces Low-Grade Cochlear Inflammation in CD-1 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, V.; Procaccini, C.; Calì, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Fontana, S.; Zappacosta, S.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. A Key Role of Leptin in the Control of Regulatory T Cell Proliferation. Immunity 2007, 26, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, D.; Shantaram, D.; Smith, A.; Hsueh, W.A. Adipose Tissue T Regulatory Cells: Implications for Health and Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1278, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Pérez-Torres, I.; Soto, M.E. Mechanisms Underlying Metabolic Syndrome-Related Sarcopenia and Possible Therapeutic Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.P.; Singh, N.P.; Guan, H.; Busbee, B.; Price, R.L.; Taub, D.D.; Mishra, M.K.; Fayad, R.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Leptin Antagonist Ameliorates Chronic Colitis in IL-10−/− Mice. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.I.; Dobson, J.P.; Greene, N.P.; Wiggs, M.P.; Shimkus, K.L.; Wudeck, E.V.; Davis, A.R.; Laureano, M.L.; Fluckey, J.D. Abnormal Protein Turnover and Anabolic Resistance to Exercise in Sarcopenic Obesity. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardif, N.; Salles, J.; Guillet, C.; Tordjman, J.; Reggio, S.; Landrier, J.-F.; Giraudet, C.; Patrac, V.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Migne, C.; et al. Muscle Ectopic Fat Deposition Contributes to Anabolic Resistance in Obese Sarcopenic Old Rats through EIF2α Activation. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.B.; Lee, D.; Long, M.D.; Kappelman, M.D.; Martin, C.F.; Sandler, R.S.; Lewis, J.D. Dietary Patterns and Self-Reported Associations of Diet with Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M. Alterations in Human Muscle Protein Metabolism with Aging: Protein and Exercise as Countermeasures to Offset Sarcopenia. Biofactors 2014, 40, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, C.; Xie, T.; Yang, J.; Dai, X.; Lv, T.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Wei, Y.; Gong, J.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Depletion Correlates with Disease Activity in Ulcerative Colitis and Is Reversed after Colectomy. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Ekhator, C.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Naveed, H.; Karski, A.; Cook, D.E.; Reddy, S.M.; Affaf, M.; Khan, S.J.; Bellegarde, S.B.; et al. Revolutionizing Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management: A Comprehensive Narrative Review of Innovative Dietary Strategies and Future Directions. Cureus 2023, 15, E44304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bager, P.; Escher, J.; Forbes, A.; Hébuterne, X.; Hvas, C.L.; Joly, F.; Klek, S.; Krznaric, Z.; Ockenga, J.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 352–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.H.; Oikawa, S.Y.; Phillips, S.M. Dietary Protein to Maintain Muscle Mass in Aging: A Case for Per-Meal Protein Recommendations. J. Frailty Aging 2016, 5, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ispoglou, T.; Witard, O.C.; Duckworth, L.C.; Lees, M.J. The Efficacy of Essential Amino Acid Supplementation for Augmenting Dietary Protein Intake in Older Adults: Implications for Skeletal Muscle Mass, Strength and Function. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhou, C.; Yan, Q.; Tan, Z.; Kang, J.; Tang, S. Elucidating the Underlying Mechanism of Amino Acids to Regulate Muscle Protein Synthesis: Effect on Human Health. Nutrition 2022, 103–104, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondanelli, M.; Opizzi, A.; Antoniello, N.; Boschi, F.; Iadarola, P.; Pasini, E.; Aquilani, R.; Dioguardi, F.S. Effect of Essential Amino Acid Supplementation on Quality of Life, Amino Acid Profile and Strength in Institutionalized Elderly Patients. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solerte, S.B.; Gazzaruso, C.; Bonacasa, R.; Rondanelli, M.; Zamboni, M.; Basso, C.; Locatelli, E.; Schifino, N.; Giustina, A.; Fioravanti, M. Nutritional Supplements with Oral Amino Acid Mixtures Increases Whole-Body Lean Mass and Insulin Sensitivity in Elderly Subjects with Sarcopenia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 69E–77E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, R.; Piccolotto, R.; Negut, C.; Tiengo, A.; Avogaro, A. Oral Amino Acids in Elderly Subjects: Effect on Myocardial Function and Walking Capacity. Gerontology 2005, 51, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakopoulos, C.; Jones, J.; Bannerman, E.; Greig, C.A. Effectiveness of Nutritional and Exercise Interventions to Improve Body Composition and Muscle Strength or Function in Sarcopenic Obese Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Res. 2017, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.-H.; Liu, J.Y.W.; Välimäki, M. Effectiveness of Non-Pharmacological Interventions on the Management of Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 135, 110937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, X.; Hu, Q.; Chen, L.; Zuo, H. The Effect of Leucine Supplementation on Sarcopenia-Related Measures in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 17 Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 929891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gui, Q.; Yang, Y. The Effectiveness of Leucine on Muscle Protein Synthesis, Lean Body Mass and Leg Lean Mass Accretion in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Arnau, F.M.; Fonfría-Vivas, R.; Cauli, O. Beneficial Effects of Leucine Supplementation on Criteria for Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, J.-Y. Effects of Leucine-Rich Protein Supplements in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2022, 102, 104758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhao, A.; He, J. Effect of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (HMB) on the Muscle Strength in the Elderly Population: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 914866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.J.; Hossain, T.; Hill, D.S.; Phillips, B.E.; Crossland, H.; Williams, J.; Loughna, P.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M.; et al. Effects of Leucine and Its Metabolite β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Human Skeletal Muscle Protein Metabolism. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukovich, M.D.; Stubbs, N.B.; Bohlken, R.M. Body Composition in 70-Year-Old Adults Responds to Dietary Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Similarly to That of Young Adults. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, J.; Du, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Huang, G.; Niu, K. Effect of Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate Supplementation on Muscle Loss in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 61, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, D.E.; Langan, A.; Dimidi, E.; Wandrag, L.; Harridge, S.D.R.; Hart, N.; Connolly, B.; Whelan, K. β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate and Its Impact on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Physical Function in Clinical Practice: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farquhar, I.; Fairclough, J.A. Sciatic Block in Lower Limb Surgery. Injury 1990, 21, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, P.B.; Joseph, C.; Angioi, M. Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Upper and Lower Body Muscle Strength Levels in Healthy Individuals. A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2015, 18, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, C.; Chu, W.-C.; Kang, Y.-N. The Optimal Strategy of Vitamin D for Sarcopenia: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgis, C.M.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Mokbel, N.; Cheng, K.; Gunton, J.E. Vitamin D Signaling Regulates Proliferation, Differentiation, and Myotube Size in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceglia, L.; Harris, S.S. Vitamin D and Its Role in Skeletal Muscle. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 92, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Deng, F. The Role of Vitamin D in Immune System and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3167–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, A.S.; Smith, H.J.; Drake, J.L.; Tisdale, M.J. Mechanism of Attenuation of Skeletal Muscle Protein Catabolism in Cancer Cachexia by Eicosapentaenoic Acid. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3604–3609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allaire, J.; Couture, P.; Leclerc, M.; Charest, A.; Marin, J.; Lépine, M.-C.; Talbot, D.; Tchernof, A.; Lamarche, B. A Randomized, Crossover, Head-to-Head Comparison of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid Supplementation to Reduce Inflammation Markers in Men and Women: The Comparing EPA to DHA (ComparED) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therdyothin, A.; Phiphopthatsanee, N.; Isanejad, M. The Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Sarcopenia: Mechanism of Action and Potential Efficacy. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, P.-T.; Zeng, B.-Y.; Zeng, B.-S.; Liao, Y.-C.; Stubbs, B.; Kuo, J.S.; Sun, C.-K.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Chen, T.-Y.; et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Sarcopenia Management: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 90, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chiu, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Lo, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-H. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Muscle Performance among the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supinski, G.S.; Vanags, J.; Callahan, L.A. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Preserves Diaphragm Force Generation Following Endotoxin Administration. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Liang, J.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y. Relationship Between Dietary Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Level and Sarcopenia. A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 738083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, C.; Robinson, S.M.; Witham, M.D.; Dodds, R.M.; Granic, A.; Buckland, C.; De Biase, S.; Finnegan, S.; Rochester, L.; Skelton, D.A.; et al. Resistance Exercise as a Treatment for Sarcopenia: Prescription and Delivery. Age Ageing 2022, 51, Afac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Nakamura, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Kakimoto, K.; Fukunishi, S.; Asai, A.; Nishiguchi, S.; Higuchi, K. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Sarcopenia: Its Mechanism and Clinical Importance. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Gettigan, N.; Allen, K.; Saeidi, R.; O’ Toole, A.; Boland, K. A Systematic Review of the Effect of Structured Exercise on Inflammation and Body Composition in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2023, 38, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Sports Medicine; Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Proctor, D.N.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A.; Minson, C.T.; Nigg, C.R.; Salem, G.J.; Skinner, J.S. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and Physical Activity for Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1510–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruas, J.L.; White, J.P.; Rao, R.R.; Kleiner, S.; Brannan, K.T.; Harrison, B.C.; Greene, N.P.; Wu, J.; Estall, J.L.; Irving, B.A.; et al. A PGC-1α Isoform Induced by Resistance Training Regulates Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Cell 2012, 151, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, K.G.; Abbasi-Neureither, I.; Köppel, M.; Huber, G. Structured Physical Activity Interventions as a Complementary Therapy for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease—A Scoping Review and Practical Implications. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinna, E.M.; Yarasheski, K.E. Exercise Treatment to Counteract Protein Wasting of Chronic Diseases. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, K.; Guan, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, C. Mechanism and Physical Activities in Bone-Skeletal Muscle Crosstalk. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1287972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas Vega, S.; Knicker, A.; Hollmann, W.; Bloch, W.; Strüder, H.K. Effect of Resistance Exercise on Serum Levels of Growth Factors in Humans. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamrick, M.W. The Skeletal Muscle Secretome: An Emerging Player in Muscle-Bone Crosstalk. Bonekey Rep. 2012, 1, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.; Baker, K.; Speight, R.A.; Thompson, N.P.; Tew, G.A. Randomised Clinical Trial: Combined Impact and Resistance Training in Adults with Stable Crohn’s Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelam, P.B.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, V. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Emerging Concepts and Evidence. JGH Open 2024, 8, E13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; O’Connor, L.E.; Sands, L.P.; Slebodnik, M.B.; Campbell, W.W. Effects of Dietary Protein Intake on Body Composition Changes after Weight Loss in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backx, E.M.P.; Tieland, M.; Borgonjen-van Den Berg, K.J.; Claessen, P.R.; van Loon, L.J.C.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M. Protein Intake and Lean Body Mass Preservation during Energy Intake Restriction in Overweight Older Adults. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villareal, D.T.; Aguirre, L.; Gurney, A.B.; Waters, D.L.; Sinacore, D.R.; Colombo, E.; Armamento-Villareal, R.; Qualls, C. Aerobic or Resistance Exercise, or Both, in Dieting Obese Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouwborst, I.; Verreijen, A.; Memelink, R.; Massanet, P.; Boirie, Y.; Weijs, P.; Tieland, M. Exercise and Nutrition Strategies to Counteract Sarcopenic Obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadelha, A.B.; Paiva, F.M.L.; Gauche, R.; de Oliveira, R.J.; Lima, R.M. Effects of Resistance Training on Sarcopenic Obesity Index in Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 65, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-T.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ho, S.-Y.; Wu, H.-J. Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and IGF-1 in the Elderly with Sarcopenic Obesity. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kojima, N.; Fujino, K.; Hosoi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Somekawa, S.; Niki, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Yoshida, H. Exercise and Nutritional Supplementation on Community-Dwelling Elderly Japanese Women with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| DIAGNOSTIC METHODS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Advantages | Limits | IBD | |
| CT [22,23,24,25] | CSA Myosteatosis Myofibrosis | High precision Reliable outcomes | Ionizing radiation High costs | Commonly used in IBD clinical practice |
| MRI [29,30,31,32,34] | CSA Muscle quality Myofibrosis Myosteatosis | Non-exposure to radiation Accurate for body composition | High costs Long image capture time Limited availability | Commonly used in IBD clinical practice |
| US [21,43,44,45,46,47,48,49] | CSA Muscle thickness Myofibrosis Myosteatosis | Accurate Easily repeatable Safe Low-cost | Lack of standardized cut-offs Operator- dependent | Commonly used in IBD clinical practice Influenced by inflammation |
| DXA [38,39,40,41,42] | Visceral tissue Subcutaneous adipose tissue Total lean mass | Non-invasive Low radiation exposure Low-cost | Indirect assessment Influenced by hydration status | Valid tool for analyzing body composition |
| BIA [20,35,36,37,38] | Fat mass Muscle mass Membrane integrity Cellularity | Rapid Portable Non-invasive Low-cost | Indirect assessment Influenced by hydration status | Reliability in assessing body composition Influenced by inflammation |
| SARCOPENIA AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Author, (Year), Study Type | Outcomes | Patients (n) | Results |
| Erös et al. (2020), systematic review [147] | Sarcopenia on surgical outcomes | 885 | Need for surgery (OR: 2.665; 95% CI 1.121–6.336; p = 0.027); postoperative complications OR = 6.097; 95% CI 1.756–21.175; p = 0.004 |
| Liu et al. (2022), prospective cohort study [142] | Sarcopenia on clinical outcomes | 110 | Rates of surgery (OR = 6.651; 95% CI: 2.333–18.959; p < 0.001); re-hospitalization (OR = 6.344; 95% CI: 2.874–14.003; p < 0.001); death, p = 0.003 |
| Knoedler et al. (2023), systematic review [148] | Sarcopenia on surgical outcomes | 97,643 | Surgical complications (OR 1.92; 95% CI:1.20–3.07; p = 0.007) |
| Ge et al. (2021), retrospective cohort study [149] | Sarcopenia on clinical course of ASUC | 233 | Colectomy (OR = 3.411; 95% CI, 1.147–10.141; p = 0.027); postoperative complications (OR = 4.157; 95% CI: 1.364–12.667; p = 0.012) |
| Grova et al. (2023), retrospective observational study [154] | Sarcopenia on endoscopic remission | 358 | Endoscopic remission (OR = 5.2; 95% CI 1.60–16.8; p = 0.006) |
| SARCOPENIA AND IBD MEDICATIONS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author, (Year), Study Type | Outcomes | Patients (n) | Medication | Results |
| Santos et al. (2017), prospective cohort study [159] | Anti-TNF-α therapy on BC | 23 | Anti-TNF-α | ↑ LM p < 0.0001 ↑ FM p < 0.0001 |
| Liu et al. (2023), retrospective cohort study [10] | Sarcopenia and LOR to biologic agents | 94 | Anti-TNF-α | Primary LOR (OR = 2.87, 95% CI: 1.07–7.69) |
| Subramaniam et al. (2015), prospective cohort study [158] | Anti-TNF-α on muscle volume and strength | 19 | Anti-TNF-α | ↑ muscle volume (p = 0.010) ↑ muscle strength (p = 0.002) |
| Ding et al. (2017), systematic review [156] | BC on anti-TNF-α therapy response | 106 | Anti-TNF-α | Primary non-response (OR = 2.93; CI: 1.28–6.71, p = 0.01) |
| Patsalos et al. (2020), systematic review [157] | Anti-TNF-a on body weight and BMI | 1245 | Anti-TNF α | ↑ body weight (SMCC = 0.23, 95% CI 0.10–0.37; p = 0.0006) ↑ BMI (SMCC = 0.26, 95% CI 0.13–0.39; p < 0.0001) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calvez, V.; Becherucci, G.; Covello, C.; Piccirilli, G.; Mignini, I.; Esposto, G.; Laterza, L.; Ainora, M.E.; Scaldaferri, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Navigating the Intersection: Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061218
Calvez V, Becherucci G, Covello C, Piccirilli G, Mignini I, Esposto G, Laterza L, Ainora ME, Scaldaferri F, Gasbarrini A, et al. Navigating the Intersection: Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(6):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061218
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalvez, Valentin, Guia Becherucci, Carlo Covello, Giulia Piccirilli, Irene Mignini, Giorgio Esposto, Lucrezia Laterza, Maria Elena Ainora, Franco Scaldaferri, Antonio Gasbarrini, and et al. 2024. "Navigating the Intersection: Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease" Biomedicines 12, no. 6: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061218
APA StyleCalvez, V., Becherucci, G., Covello, C., Piccirilli, G., Mignini, I., Esposto, G., Laterza, L., Ainora, M. E., Scaldaferri, F., Gasbarrini, A., & Zocco, M. A. (2024). Navigating the Intersection: Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines, 12(6), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061218









