Prognostic Significance of the Bone Marrow-to-Aorta Uptake Ratio on 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Measurement of FDG PET/CT Parameters
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Enrolled Patients
3.2. Correlation between PET/CT Parameters and Clinical Factors
3.3. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergquist, A.; von Seth, E. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 29, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, A.; Rosmorduc, O.; Duclos-Vallée, J.C. New epidemiologic trends in cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Central Cancer Registry; National Cancer Center. Annual Report of Cancer Statistics in Korea in 2016; Ministry of Health and Welfare: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Banales, J.M.; Cardinale, V.; Carpino, G.; Marzioni, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Invernizzi, P.; Lind, G.E.; Folseraas, T.; Forbes, S.J.; Fouassier, L.; et al. Expert consensus document: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current knowledge and future perspectives consensus statement from the European Network for the Study of Cholangiocarcinoma (ENS-CCA). Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, M.C.; Venere, R.; Ribichini, E.; Covotta, F.; Cardinale, V.; Alvaro, D. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Evolving strategies in management and treatment. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.W.; Oh, C.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Park, J.W.; Cho, H.; Ki, M. Incidence and overall survival of biliary tract cancers in South Korea from 2006 to 2015: Using the national health information database. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. An overview of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: From here to where? Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1171098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.P.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, M.H.; Lim, C.H.; Park, S.B.; Yoon, J.K.; Park, J.M. Prognostic value of metabolic parameters measured by pretreatment dual-time-point 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with intrahepatic or perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A STROBE study. Medicine 2021, 100, e26015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Heij, L.R.; Czigany, Z.; Dahl, E.; Dulk, M.D.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Neumann, U.P.; Bednarsch, J. The prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Czigany, Z.; Heij, L.R.; Bouwense, S.A.W.; van Dam, R.; Lang, S.A.; Ulmer, T.F.; Neumann, U.P.; Bednarsch, J. The Value of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in cholangiocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albazaz, R.; Patel, C.N.; Chowdhury, F.U.; Scarsbrook, A.F. Clinical impact of FDG PET-CT on management decisions for patients with primary biliary tumours. Insights Imaging 2013, 4, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and 18-fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the diagnostic accuracy of staging in patients with cholangiocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seban, R.D.; Assié, J.B.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Massiani, M.A.; Bonardel, G.; Chouaid, C.; Deleval, N.; Richard, C.; Mezquita, L.; Girard, N.; et al. Prognostic value of inflammatory response biomarkers using peripheral blood and [18F]-FDG PET/CT in advanced NSCLC patients treated with first-line chemo- or immunotherapy. Lung Cancer 2021, 159, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Song, G.J.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, S.H.; Oh, M.H.; Yun, J.H.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.W. Relationship of FDG uptake of the reticuloendothelial system with tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Life 2023, 13, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, K.; Mabuchi, S.; Komura, N.; Yokoi, E.; Kozasa, K.; Sasano, T.; Kawano, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Watabe, T.; Kodama, M.; et al. Prognostic significance of bone marrow FDG uptake in patients with gynecological cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, I.Y.; Jang, S.J. Prognostic value of dual-time-point [(18)F]FDG PET/CT for predicting distant metastasis after treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, D.U.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.J. Splenic FDG uptake predicts poor prognosis in patients with unresectable cholangiocarcinoma. Nuklearmedizin 2014, 53, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bural, G.G.; Torigian, D.A.; Chen, W.; Houseni, M.; Basu, S.; Alavi, A. Increased 18F-FDG uptake within the reticuloendothelial system in patients with active lung cancer on PET imaging may indicate activation of the systemic immune response. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 13, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, H.J.; Heo, N.H.; Lee, S.M. [18F]FDG uptake of bone marrow on PET/CT for predicting distant recurrence in breast cancer patients after surgical resection. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, H.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, S.J. Predicting survival in patients with pancreatic cancer by integrating bone marrow FDG uptake and radiomic features of primary tumor in PET/CT. Cancers 2021, 13, 3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaeghere, E.A.; Laloo, F.; Lippens, L.; Van Bockstal, M.; De Man, K.; Naert, E.; Van Dorpe, J.; Van de Vijver, K.; Tummers, P.; Makar, A.; et al. Splenic 18F-FDG uptake on baseline PET/CT is associated with oncological outcomes and tumor immune state in uterine cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Na, J.O.; Kang, D.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.M. Prognostic significance of FDG uptake of bone marrow on PET/CT in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after curative surgical resection. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wiele, C.; VandeVyver, F.; Debruyne, C.; Philippé, J.; van Meerbeeck, J.P. FDG uptake by the bone marrow in NSCLC patients is related to TGF-beta but not to VEGF or G-CSF serum levels. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, D.U.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Ahn, S.H. Factors associated with diffusely increased splenic F-18 FDG uptake in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 48, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pak, K.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, D.U.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Impact of cytokines on diffuse splenic 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake during positron emission tomography/computed tomography. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2013, 34, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Li, K.; Niu, N.; Shao, Y.; Ding, D.; Thomas, D.L.; Jing, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Hu, H.; Osipov, A.; et al. Immune cell atlas of cholangiocarcinomas reveals distinct tumor microenvironments and associated prognoses. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Chen, J. Immune microenvironment of cholangiocarcinoma: Biological concepts and treatment strategies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1037945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, G.; Hau, H.M.; Dietel, C.; Benzing, C.; Krenzien, F.; Brandl, A.; Wiltberger, G.; Matia, I.; Prager, I.; Schierle, K.; et al. Prognostic significance of macrophage invasion in hilar cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Shen, W.; Yue, J.Q.; Yao, W.Y.; Liu, S.L.; Jin, Y.P.; Dong, P.; Ma, F.; Wu, X.S.; Gong, W. Combining immunoscore with clinicopathologic features in cholangiocarcinoma: An influential prognostic nomogram. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 11359–11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Azony, A.; Basha, M.A.A.; Almalki, Y.E.; Abdelmaksoud, B.; Hefzi, N.; Alnagar, A.A.; Mahdey, S.; Ali, I.S.; Nasr, I.; Abdalla, A.A.E.-H.M. The prognostic value of bone marrow retention index and bone marrow-to-liver ratio of basline 18F-FDG PET/CT in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, C.N.; Sandstrom, K.; Regula, N.; Ehrsson, Y.T.; Johansson, H.; Sorensen, J.; Laurell, G. Prognostic value of bone marrow and tumor 18F-FDG uptake on PET/CT in patients with oropharyngeal cancer and the interplay between inflammation and FDG uptake. Head. Neck 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, S.; Akers, A.; Stephenson, K.; Smith, S.; Kennedy, L.; Alpini, G.; Francis, H. Comprehensive review of molecular mechanisms during cholestatic liver injury and cholangiocarcinoma. J. Liver 2018, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroudinia, A.; Karam, M.B.; Ghadimi, N.; Yousefi, F. Steatotic hepatitis presenting as a huge hypermetabolic liver mass. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e399–e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattonen, S.A.; Davidzon, G.A.; Benson, J.; Leung, A.N.C.; Vasanawala, M.; Horng, G.; Shrager, J.B.; Napel, S.; Nair, V.S. Bone marrow and tumor radiomics at (18)F-FDG PET/CT: Impact on outcome prediction in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiology 2019, 293, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
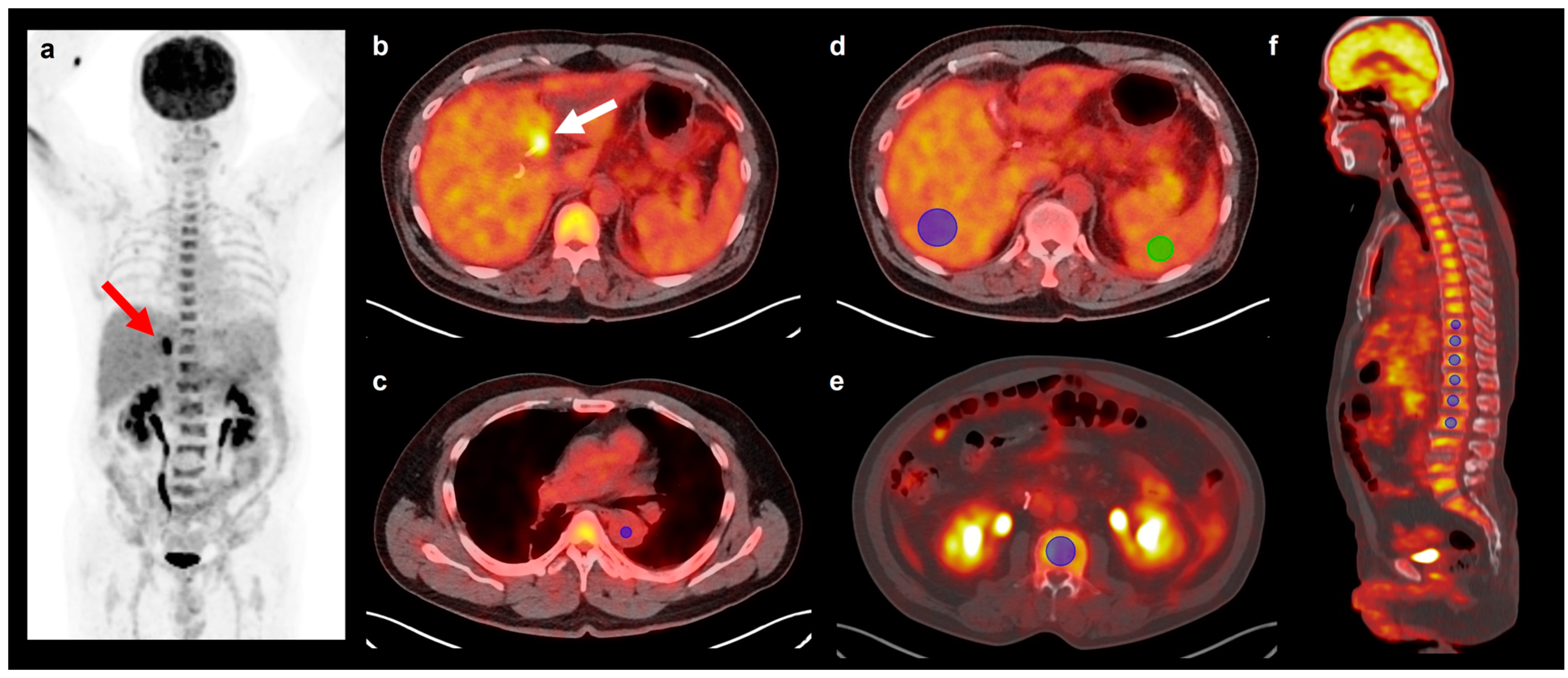
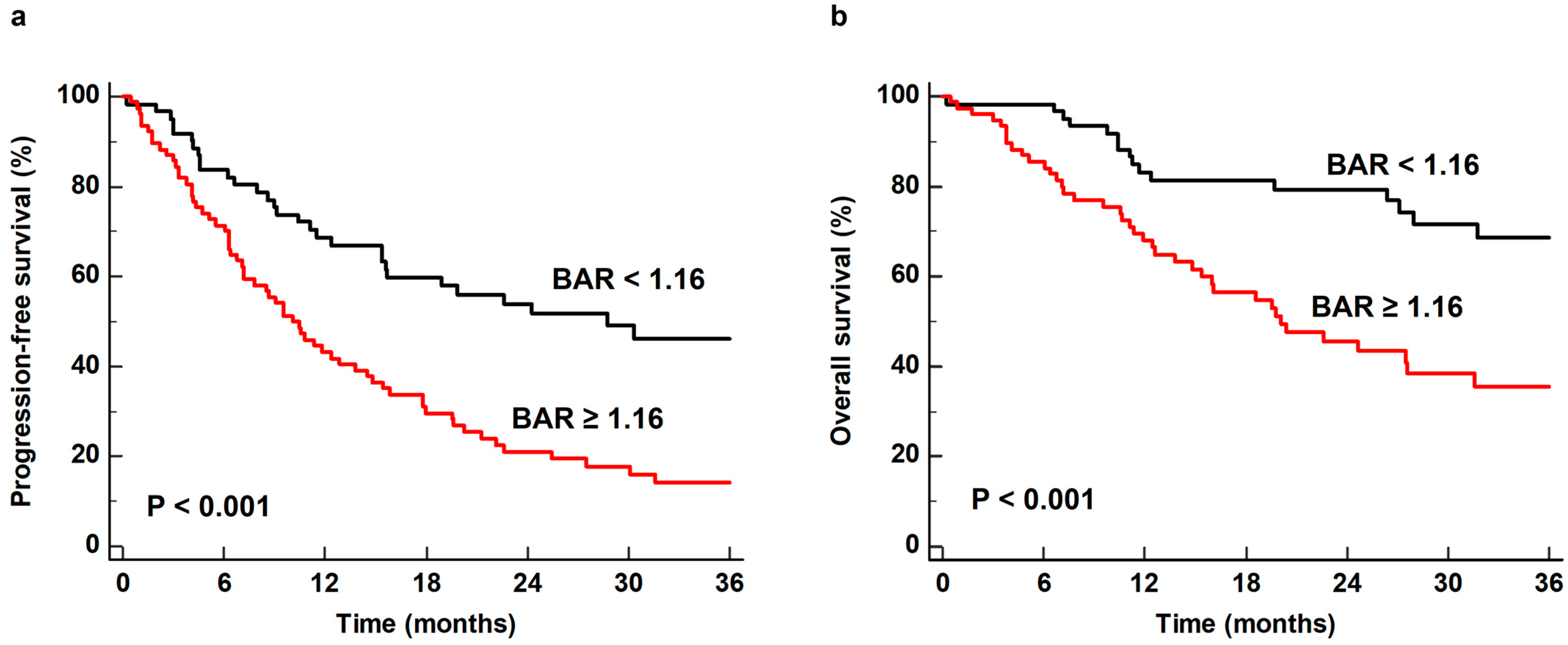
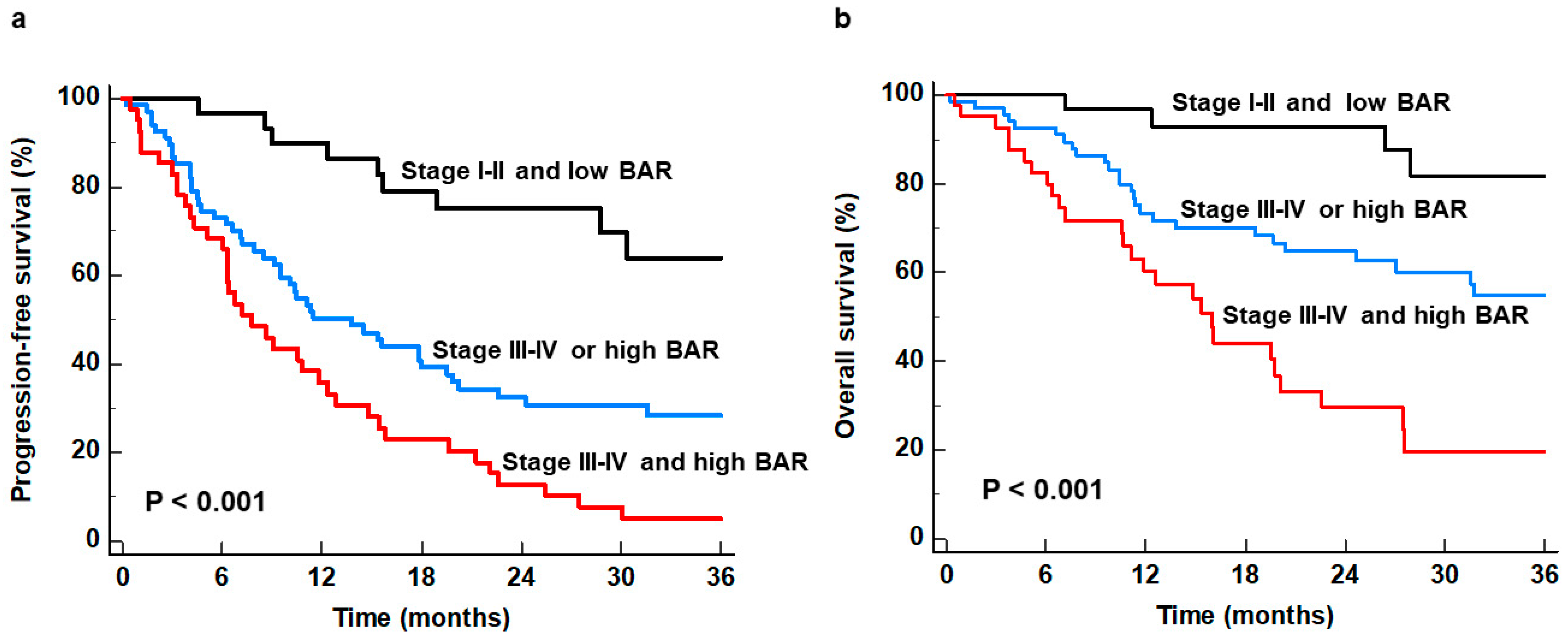
| Variables | Number of Patients (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66 (35–89) * | |
| Sex | Men | 97 (70.3%) |
| Women | 41 (29.7%) | |
| Tumor classification | Intrahepatic | 23 (16.7%) |
| Perihilar | 60 (43.5%) | |
| Distal bile duct | 55 (39.9%) | |
| T stage | T1 | 22 (15.9%) |
| T2 | 43 (31.2%) | |
| T3 | 38 (27.5%) | |
| T4 | 35 (25.4%) | |
| Lymph node metastasis | Negative | 81 (58.7%) |
| Positive | 57 (41.3%) | |
| Distant metastasis | Negative | 120 (87.0%) |
| Positive | 18 (13.0%) | |
| TNM stage | Stage I | 14 (10.1%) |
| Stage II | 52 (37.7%) | |
| Stage III | 57 (41.3%) | |
| Stage IV | 15 (10.9%) | |
| Blood tests | CA19-9 (U/mL) | 151.2 (0.8–14,456.0) * |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.15 (0.03–1030.0) * | |
| WBC (×1012 cells/L) | 6.97 (3.38–24.68) * | |
| NLR | 3.14 (0.99–3.98) * | |
| PLR | 176.31 (38.54–670.47) * | |
| FDG PET/CT parameters | Tumor SUV | 5.97 (2.72–17.93) * |
| BM SUV | 2.14 (1.10–3.99) * | |
| Liver SUV | 2.49 (1.51–3.69) * | |
| Spleen SUV | 2.07 (1.17–5.29) * | |
| BAR | 1.20 (0.68–2.33) * | |
| LAR | 1.39 (1.04–2.34) * | |
| SAR | 1.18 (0.82–2.09) * | |
| BLR | 0.85 (0.48–1.91) * | |
| SLR | 0.85 (0.58–1.66) * | |
| Variables | PFS | OS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | ||
| Age (1-year increase) | 0.166 | 0.986 (0.966–1.006) | 0.204 | 0.983 (0.958–1.009) | |
| Sex (women vs. men) | 0.847 | 0.960 (0.638–1.446) | 0.839 | 1.055 (0.627–1.775) | |
| Tumor classification (intrahepatic vs.) | Perihilar | 0.657 | 0.881 (0.502–1.545) | 0.939 | 1.028 (0.501–2.106) |
| Distal bile duct | 0.092 | 0.647 (0.362–1.157) | 0.176 | 0.586 (0.270–2.106) | |
| T stage (T1 vs.) | T2 | 0.038 | 2.204 (1.043–4.658) | 0.257 | 1.708 (0.677–4.304) |
| T3 | 0.125 | 1.818 (0.848–3.895) | 0.515 | 1.375 (0.528–3.581) | |
| T4 | <0.001 | 3.639 (1.725–7.677) | 0.019 | 2.980 (1.195–7.433) | |
| Lymph node metastasis (negative vs. positive) | <0.001 | 2.144 (1.424–3.226) | <0.001 | 2.500 (1.481–4.219) | |
| Distant metastasis (negative vs. positive) | <0.001 | 2.632 (1.563–4.430) | <0.001 | 3.351 (1.784–6.295) | |
| TNM stage (stage I–II vs.) | Stage III | 0.003 | 1.996 (1.262–3.063) | 0.019 | 2.011 (1.122–3.604) |
| Stage IV | <0.001 | 3.624 (1.967–6.678) | <0.001 | 4.616 (2.172–9.810) | |
| CA19-9 (1.0 U/mL increase) | 0.139 | 1.000 (1.000–1.001) | 0.373 | 1.000 (1.000–1.001) | |
| CRP (1.0 mg/dL increase) | 0.773 | 1.000 (0.999–1.002) | 0.645 | 0.999 (0.996–1.002) | |
| WBC (1.0 × 1012 cells/L increase) | 0.377 | 1.027 (0.968–1.091) | 0.071 | 1.067 (0.995–1.144) | |
| NLR (1.0 increase) | 0.658 | 1.002 (0.942–1.065) | 0.905 | 1.005 (0.926–1.091) | |
| PLR (1.0 increase) | 0.936 | 0.999 (0.998–1.002) | 0.659 | 0.999 (0.997–1.002) | |
| Tumor SUV (1.0 increase) | 0.074 | 1.048 (0.995–1.104) | 0.046 | 1.067 (1.001–1.136) | |
| BM SUV (1.0 increase) | 0.065 | 1.395 (0.979–1.988) | 0.305 | 1.286 (0.795–2.080) | |
| Liver SUV (1.0 increase) | 0.834 | 0.955 (0.619–1.473) | 0.296 | 0.745 (0.429–1.295) | |
| Spleen SUV (1.0 increase) | 0.649 | 1.011 (0.726–1.407) | 0.360 | 0.790 (0.477–1.309) | |
| BAR (1.0 increase) | <0.001 | 2.850 (1.539–5.276) | 0.003 | 3.370 (1.520–7.470) | |
| LAR (1.0 increase) | 0.066 | 3.132 (0.926–10.596) | 0.112 | 3.106 (0.769–12.538) | |
| SAR (1.0 increase) | 0.044 | 2.135 (1.018–4.478) | 0.048 | 2.635 (1.001–6.947) | |
| BLR (1.0 increase) | 0.013 | 2.806 (1.242–6.342) | 0.033 | 3.214 (1.098–9.408) | |
| SLR (1.0 increase) | 0.664 | 1.277 (0.424–3.847) | 0.947 | 0.950 (0.206–4.378) | |
| Variables | PFS | OS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||||
| p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | ||
| Age (1-year increase) | 0.669 | 0.882 | 0.609 | 0.753 | |||||
| Sex (women vs. men) | 0.540 | 0.561 | 0.340 | 0.356 | |||||
| Tumor classification (intrahepatic vs.) | Perihilar | 0.470 | 0.449 | 0.308 | 0.271 | ||||
| Distal bile duct | 0.224 | 0.194 | 0.466 | 0.410 | |||||
| TNM stage (stage I–II vs.) | Stage III | 0.004 | 1.938 (1.243–3.019) | 0.004 | 2.451 (1.325–4.535) | 0.019 | 2.019 (1.125–3.622) | 0.026 | 1.969 (1.085–3.576) |
| Stage IV | 0.002 | 2.828 (1.490–5.367) | 0.001 | 4.436 (1.781–11.049) | 0.001 | 3.592 (1.639–7.875) | <0.001 | 3.926 (1.805–8.542) | |
| Tumor SUV (1.0 increase) | 0.324 | 0.293 | 0.173 | 0.148 | |||||
| BAR (1.0 increase) | 0.016 | 2.308 (1.169–4.557) | - | - | 0.030 | 2.645 (1.101–6.354) | - | - | |
| SAR (1.0 increase) | 0.337 | 0.167 | 0.270 | 0.137 | |||||
| BLR (1.0 increase) | - | - | 0.221 | - | - | 0.165 | |||
| Subgroups | PFS | OS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | |
| Stage I–II and low BAR | - | 1.00 | - | 1.00 |
| Stage III–IV or high BAR | 0.004 | 3.662 (1.794–7.475) | 0.012 | 3.814 (1.337–10.877) |
| Stage III–IV and high BAR | <0.001 | 6.559 (3.148–13.667) | <0.001 | 9.062 (3.138–26.171) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.W.; Yoo, I.D.; Hong, S.-p.; Kang, B.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Bae, S.H.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, S.M. Prognostic Significance of the Bone Marrow-to-Aorta Uptake Ratio on 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050944
Lee JW, Yoo ID, Hong S-p, Kang B, Kim JS, Kim YK, Bae SH, Jang SJ, Lee SM. Prognostic Significance of the Bone Marrow-to-Aorta Uptake Ratio on 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050944
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jeong Won, Ik Dong Yoo, Sun-pyo Hong, Beodeul Kang, Jung Sun Kim, Yung Kil Kim, Sang Ho Bae, Su Jin Jang, and Sang Mi Lee. 2024. "Prognostic Significance of the Bone Marrow-to-Aorta Uptake Ratio on 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050944
APA StyleLee, J. W., Yoo, I. D., Hong, S.-p., Kang, B., Kim, J. S., Kim, Y. K., Bae, S. H., Jang, S. J., & Lee, S. M. (2024). Prognostic Significance of the Bone Marrow-to-Aorta Uptake Ratio on 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Biomedicines, 12(5), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050944






