Ethnic Variations in the Levels of Bone Biomarkers (Osteoprostegerin, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand and Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B) in People with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Anthropometry and Vital Sign Measurements
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Detection of OPG, RANKL, and GPNMB Plasma Levels Using R&D Custom Multiplexing Assay
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Population under Study
3.2. Expression of Bone Markers in Circulation
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkandari, A.; Alarouj, M.; Elkum, N.; Sharma, P.; Devarajan, S.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Tuomilehto, J.; Bennakhi, A. Adult Diabetes and Prediabetes Prevalence in Kuwait: Data from the Cross-Sectional Kuwait Diabetes Epidemiology Program. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, P.; Abu-Farha, M.; Abubaker, J.; Channanath, A.M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Thanaraj, T.A. Generalizability of GWA-Identified Genetic Risk Variants for Metabolic Traits to Populations from the Arabian Peninsula. Genes. 2021, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaaswarkhanth, M.; Dos Santos, A.L.C.; Gokcumen, O.; Al-Mulla, F.; Thanaraj, T.A. Genome-Wide Selection Scan in an Arabian Peninsula Population Identifies a TNKS Haplotype Linked to Metabolic Traits and Hypertension. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, P.; Elkum, N.; Alkayal, F.; John, S.E.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Alsmadi, O. Genetic risk variants for metabolic traits in Arab populations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.E.; Coleman, C.M. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Bone Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Busse, B.; Eastell, R.; Ferrari, S.; Frost, M.; Muller, R.; Burden, A.M.; Rivadeneira, F.; Napoli, N.; Rauner, M. Bone fragility in diabetes: Novel concepts and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C.; Eastell, R.; Pierroz, D.D.; Lane, N.E.; Al-Daghri, N.; Suzuki, A.; Napoli, N.; Mithal, A.; Chakhtoura, M.; El-Hajj Fuleihan, G.; et al. Biochemical Markers of Bone Fragility in Patients with Diabetes. A Narrative Review by the IOF and the ECTS. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e923–e936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picke, A.K.; Campbell, G.; Napoli, N.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Rauner, M. Update on the impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on bone metabolism and material properties. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, R55–R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botella Martinez, S.; Varo Cenarruzabeitia, N.; Escalada San Martin, J.; Calleja Canelas, A. The diabetic paradox: Bone mineral density and fracture in type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.W.; Huh, J.W.; Noh, Y.M.; Seo, H.E.; Lee, D.H. Exploring the Paradox of Bone Mineral Density in Type 2 Diabetes: A Comparative Study Using Opportunistic Chest CT Texture Analysis and DXA. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenkre, J.S.; Bassett, J. The bone remodelling cycle. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 55, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Schwartz, A.V.; Sigurdsson, S.; Hue, T.F.; Lang, T.F.; Harris, T.B.; Rosen, C.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Hauksdottir, A.M.; et al. Circulating sclerostin associated with vertebral bone marrow fat in older men but not women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2584–E2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, P.; Al-Khairi, I.; Jamal, M.; Al-Sabah, S.; Ali, H.; Dsouza, C.; Alshawaf, E.; Al-Ali, W.; Al-Khaledi, G.; Al-Mulla, F.; et al. Association between Factors Involved in Bone Remodeling (Osteoactivin and OPG) with Plasma Levels of Irisin and Meteorin-like Protein in People with T2D and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 752892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2021, 39, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, S.S.; Kohli, V.S. Role of RANKL-RANK/osteoprotegerin molecular complex in bone remodeling and its immunopathologic implications. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopouli, A.E.; Klonaris, C.N.; Theocharis, S.E. Role of OPG/RANKL/RANK axis on the vasculature. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. RANKL inhibition: A new target of treating diabetes mellitus? Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 14, 20420188231170754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondegowda, N.G.; Fenutria, R.; Pollack, I.R.; Orthofer, M.; Garcia-Ocana, A.; Penninger, J.M.; Vasavada, R.C. Osteoprotegerin and Denosumab Stimulate Human Beta Cell Proliferation through Inhibition of the Receptor Activator of NF-kappaB Ligand Pathway. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, J.; Rennekamp, W.; Niebergall, U.; Schoppet, M.; Jahr, H.; Brendel, M.D.; Horsch, D.; Hofbauer, L.C. Cytokine-induced osteoprotegerin expression protects pancreatic beta cells through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling against cell death. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1243–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, N.; Bourgoin, L.; Biver, E.; Douni, E.; Ferrari, S. RANKL inhibition improves muscle strength and insulin sensitivity and restores bone mass. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiechl, S.; Wittmann, J.; Giaccari, A.; Knoflach, M.; Willeit, P.; Bozec, A.; Moschen, A.R.; Muscogiuri, G.; Sorice, G.P.; Kireva, T.; et al. Blockade of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (RANKL) signaling improves hepatic insulin resistance and prevents development of diabetes mellitus. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Hayashi, M.; Sasaki, F.; Nakashima, T. RANKL biology: Bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm. Regen. 2020, 40, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachliotis, I.D.; Polyzos, S.A. Osteoprotegerin/Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Ligand/Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Axis in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Yang, M.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Tu, P. Serum Osteoprotegerin Is a Potential Biomarker of Insulin Resistance in Chinese Postmenopausal Women with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 8724869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taya, M.; Hammes, S.R. Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B (GPNMB) and Cancer: A Novel Potential Therapeutic Target. Steroids 2018, 133, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, K.; Tabu, K.; Sasaki, F.; Takami, Y.; Morinaga, Y.; Mawatari, S.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanoue, S.; Kanmura, S.; Tamai, T.; et al. Glycoprotein Nonmetastatic Melanoma B (Gpnmb)-Positive Macrophages Contribute to the Balance between Fibrosis and Fibrolysis during the Repair of Acute Liver Injury in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xie, X. GPNMB enhances bone regeneration by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis: Potential role for tissue engineering bone. J. Cell Biochem. 2013, 114, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmagid, S.M.; Barbe, M.F.; Rico, M.C.; Salihoglu, S.; Arango-Hisijara, I.; Selim, A.H.; Anderson, M.G.; Owen, T.A.; Popoff, S.N.; Safadi, F.F. Osteoactivin, an anabolic factor that regulates osteoblast differentiation and function. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2334–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, L.T.; Fan, G.Q.; Zhang, L.Q.; Pang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, T.; Li, X.F.; et al. Serum glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB) level as a potential biomarker for diabetes mellitus-related cataract: A cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1110337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.M.; Li, Y.F.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.Q.; Wei, J.; Wang, J.Q.; Xiao, T.; Xie, C.; Hong, J.; Ning, G.; et al. Gpnmb secreted from liver promotes lipogenesis in white adipose tissue and aggravates obesity and insulin resistance. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, V.; Kratky, D. Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Protein B (GPNMB): The Missing Link Between Lysosomes and Obesity. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2023, 131, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickl, B.; Qadri, F.; Bader, M. Anti-inflammatory role of Gpnmb in adipose tissue of mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frara, N.; Abdelmagid, S.M.; Sondag, G.R.; Moussa, F.M.; Yingling, V.R.; Owen, T.A.; Popoff, S.N.; Barbe, M.F.; Safadi, F.F. Transgenic Expression of Osteoactivin/gpnmb Enhances Bone Formation in vivo and Osteoprogenitor Differentiation ex vivo. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, F.; Cordova, L.A.; Pajarinen, J.; Lin, T.H.; Yao, Z.; Goodman, S.B. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone 2016, 86, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguoma, V.M.; Coffee, N.T.; Alsharrah, S.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Refaei, F.H.; Al-Mulla, F.; Daniel, M. Prevalence of overweight and obesity, and associations with socio-demographic factors in Kuwait. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguoma, V.M.; Abu-Farha, M.; Coffee, N.T.; Alsharrah, S.; Al-Refaei, F.H.; Abubaker, J.; Daniel, M.; Al-Mulla, F. Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Phenotypes among Arabs and South Asians: Prevalence and Relationship with Cardiometabolic Indicators. Nutrients 2022, 14, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedblad, B.; Nilsson, P.; Janzon, L.; Berglund, G. Relation between insulin resistance and carotid intima-media thickness and stenosis in non-diabetic subjects. Results from a cross-sectional study in Malmo, Sweden. Diabet. Med. 2000, 17, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez de Ciriza, C.; Lawrie, A.; Varo, N. Osteoprotegerin in Cardiometabolic Disorders. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 564934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerre, M. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) as a biomarker for diabetic cardiovascular complications. Springerplus 2013, 2, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, B.F.; Xing, L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 473, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcadet, L.; Bouredji, Z.; Argaw, A.; Frenette, J. The Roles of RANK/RANKL/OPG in Cardiac, Skeletal, and Smooth Muscles in Health and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 903657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueland, T.; Yndestad, A.; Oie, E.; Florholmen, G.; Halvorsen, B.; Froland, S.S.; Simonsen, S.; Christensen, G.; Gullestad, L.; Aukrust, P. Dysregulated osteoprotegerin/RANK ligand/RANK axis in clinical and experimental heart failure. Circulation 2005, 111, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, T.W.; Wong, S.S.; Hong, Y.; Kanaya, A.M.; Khan, S.S.; Hayman, L.L.; Shah, S.H.; Welty, F.K.; Deedwania, P.C.; Khaliq, A.; et al. Epidemiology of Diabetes and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease among Asian American Adults: Implications, Management, and Future Directions: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateeq, H.; Zia, A.; Husain, Q.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, M. Effect of inflammation on bones in diabetic patients with periodontitis via RANKL/OPG system-A review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguwaihes, A.M.; Alhozali, A.; Yahia, M.M.; Abdel-Nabi, T.; Hassan Hatahet, M.; Albalkhi, N.I.; Al Sifri, S. The prevalence of cardiovascular disease in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Saudi Arabia—CAPTURE study. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziomalos, K.; Athyros, V.G.; Karagiannis, A. Cardiovascular Risk in Middle East Populations: A Call to Action. Angiology 2015, 66, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Voltan, R.; Rimondi, E.; Melloni, E.; Milani, D.; Cervellati, C.; Gemmati, D.; Celeghini, C.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G.; et al. TRAIL, OPG, and TWEAK in kidney disease: Biomarkers or therapeutic targets? Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1145–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, J.; Stopinski, M.; Mucha, K.; Pac, M.; Golebiowski, M.; Niewczas, M.A.; Paczek, L.; Foroncewicz, B. Circulating Osteoprotegerin in Chronic Kidney Disease and All-Cause Mortality. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2413–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, G.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y. The association of osteoprotegerin and RANKL with osteoporosis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, A.; Nakatsuka, A.; Eguchi, J.; Murakami, K.; Teshigawara, S.; Kanzaki, M.; Nunoue, T.; Hida, K.; Wada, N.; Yasunaka, T.; et al. Beneficial impact of Gpnmb and its significance as a biomarker in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, H.D.; Huang, G.L.; Man, L.B. GPNMB overexpression is associated with extensive bone metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 23, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Characteristic | Arab 46.6% | Asian 53.4% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes Status Non-Diabetic (69.24%) T2D (30.76%) | 521 (40.9) 365 (57.8) | 753 (59.1) 267 (42.2) | <0.001 a |
| Age, median (IQR) | 48 (15) | 41 (15) | <0.001 b |
| Gender, n (%) Male (55.7%) Female (44.3%) | 438 (42.0) 461 (52.1) | 606 (52.0) 424 (47.9) | <0.001 a |
| BMI, median (IQR) | 31.0 (7.9) | 26.4 (4.9) | <0.001 b |
| Waist-hip ratio, median (IQR) | 0.9 (0.08) | 0.09 (0.07) | <0.001 b |
| TC (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 5.0 (1.4) | 5.2 (1.3) | <0.001 b |
| HDL (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 1.12 (0.4) | 1.12 (0.4) | 0.317 b |
| LDL (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 3.2 (1.3) | 3.4 (1.2) | <0.001 b |
| TG (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 1.3 (0.9) | 1.3 (1.0) | 0.277 b |
| FPG (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 5.5 (2.2) | 5.2 (1.1) | <0.001 b |
| HbA1c (%), median (IQR) | 6.3 (2.4) | 6.3 (1.9) | 0.023 b |
| HOMA-IR, median (IQR) | 2.0 (2.3) | 1.9 (2.0) | 0.383 b |
| Insulin (mU/L), median (IQR) | 8.1 (6.9) | 7.7 (6.5) | 0.005 b |
| Variable a | Arabs | Asians | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Diabetic | Diabetic | p-Value b | Non-Diabetic | Diabetic | p-Value b | |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.058 | <0.001 | ||||
| Male | 239 (55.6) | 191 (44.4) | 309 (64.9) | 167 (35.1) | ||
| Female | 282 (61.8) | 174 (38.2) | 144 (78.7) | 39 (21.3) | ||
| Age, (years) | 43.0 (13.0) | 55.0 (13.0) | <0.001 | 39.0 (13) | 50.0 (11.5) | <0.001 |
| BMI (Kg) | 29.9 (6.9) | 32.4 (8.2) | <0.001 | 26.1 (4.65) | 27.4 (5.55) | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 5.1 (1.4) | 4.8 (1.39) | <0.001 | 5.2 (1.25) | 5.2 (1.31) | 0.734 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.14 (0.46) | 1.09 (0.40) | 0.003 | 1.08 (0.40) | 1.01 (0.30) | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.32 (1.10) | 2.90 (1.26) | <0.001 | 3.4 (1.30) | 3.30 (1.36) | 0.210 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.20 (0.82) | 1.48 (0.98) | <0.001 | 1.22 (0.87) | 1.59 (1.08) | <0.001 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.0 (0.70) | 7.6 (3.38) | <0.001 | 4.9 (0.60) | 7.60 (3.72) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.5 (0.64) | 7.5 (2.35) | <0.001 | 5.60 (0.70) | 7.5 (2.63) | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.60 (1.31) | 3.86 (4.82) | <0.001 | 1.64 (1.49) | 3.93 (3.61) | <0.001 |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 7.1 (5.4) | 10.7 (10.8) | <0.001 | 7.49 (6.4) | 10.9 (9.32) | <0.001 |
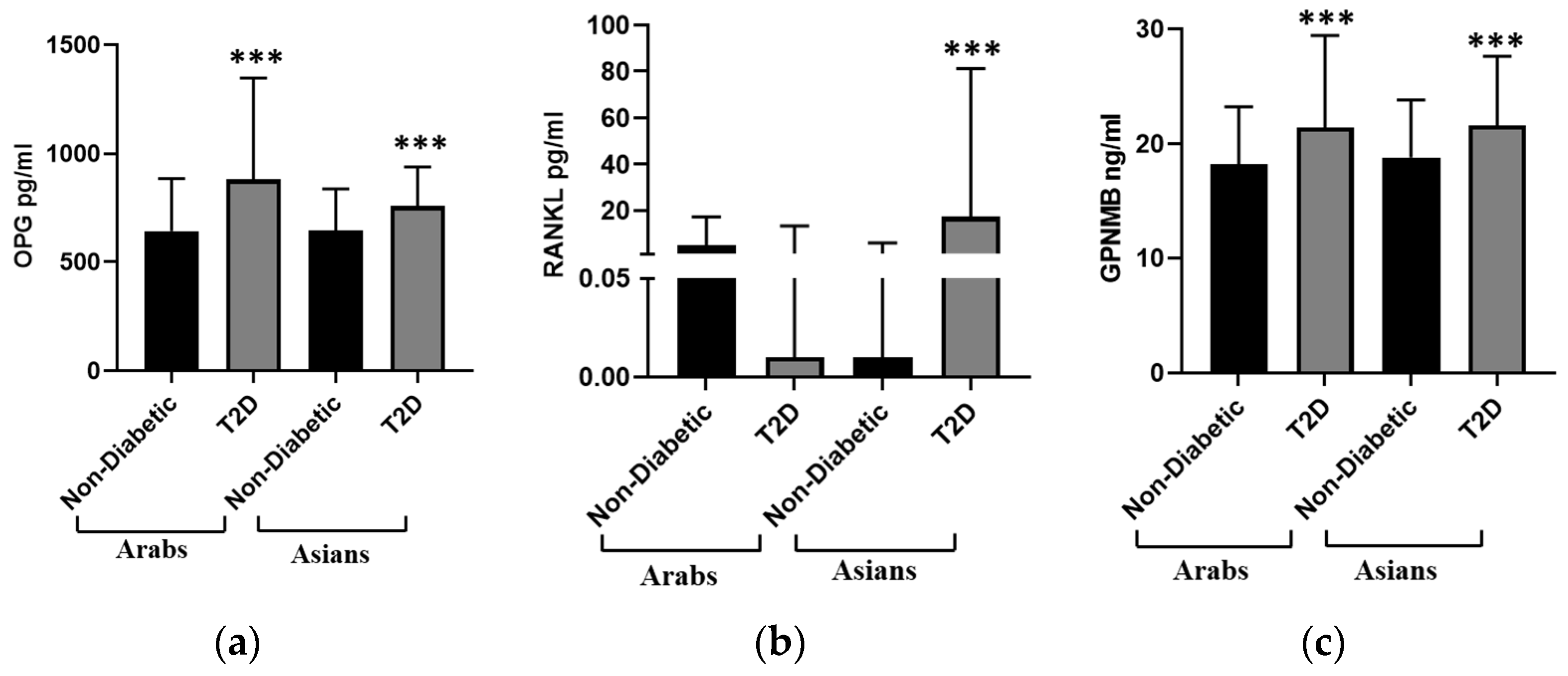
| GPNMB (ng/mL) | 18.21 (5) | 21.42 (8) | <0.001 | 18.81 (5) | 21.61 (6) | <0.001 |
| OPG (pg/mL) | 643.0 (243.3) | 881.8 (465.7) | <0.001 | 644.8 (192.1) | 758.4 (181.1) | <0.001 |
| RANKL (pg/mL) | 5.13 (12.18) | 0.01 (13.43) | 0.306 | 0.01 (6.0) | 17.3 (63.9) | <0.001 |
| RANKL/OPG | 0.0066 (0.02) | 0.0001 (0.01) | <0.001 | 0.00001 (0.01) | 0.0245 (0.04) | <0.001 |
| Correlation * | Arab | Asians | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2D | Non-Diabetic | T2D | Non-Diabetic | |
| (OPG, GPNMB) | 0.473 (<0.001) | 0.273 (<0.001) | 0.314 (0.010) | 0.282 (<0.001) |
| (OPG, RANKL) | 0.020 (0.782) | −0.115 (0.010) | −0.077 (0.543) | 0.020 (0.589) |
| (GPNMB, RANKL) | 0.047 (0.516) | 0.121 (0.006) | 0.401 (0.001) | 0.055 (0.133) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cherian, P.; Al-Khairi, I.; Abu-Farha, M.; Alramah, T.; Albatineh, A.N.; Alhomaidah, D.; Safadi, F.; Ali, H.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Tuomilehto, J.; et al. Ethnic Variations in the Levels of Bone Biomarkers (Osteoprostegerin, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand and Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B) in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051019
Cherian P, Al-Khairi I, Abu-Farha M, Alramah T, Albatineh AN, Alhomaidah D, Safadi F, Ali H, Abdul-Ghani M, Tuomilehto J, et al. Ethnic Variations in the Levels of Bone Biomarkers (Osteoprostegerin, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand and Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B) in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051019
Chicago/Turabian StyleCherian, Preethi, Irina Al-Khairi, Mohamed Abu-Farha, Tahani Alramah, Ahmed N. Albatineh, Doha Alhomaidah, Fayez Safadi, Hamad Ali, Muhammad Abdul-Ghani, Jaakko Tuomilehto, and et al. 2024. "Ethnic Variations in the Levels of Bone Biomarkers (Osteoprostegerin, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand and Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B) in People with Type 2 Diabetes" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051019
APA StyleCherian, P., Al-Khairi, I., Abu-Farha, M., Alramah, T., Albatineh, A. N., Alhomaidah, D., Safadi, F., Ali, H., Abdul-Ghani, M., Tuomilehto, J., Koistinen, H. A., Al-Mulla, F., & Abubaker, J. (2024). Ethnic Variations in the Levels of Bone Biomarkers (Osteoprostegerin, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa-Β Ligand and Glycoprotein Non-Metastatic Melanoma Protein B) in People with Type 2 Diabetes. Biomedicines, 12(5), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12051019









