Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sapina, M.; Frkovic, M.; Sestan, M.; Srsen, S.; Ovuka, A.; Batnozic Varga, M.; Kramaric, K.; Brdaric, D.; Milas, K.; Gagro, A.; et al. Geospatial clustering of childhood IgA vasculitis and IgA vasculitis-associated nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelusic, M.; Sestan, M.; Giani, T.; Cimaz, R. New Insights and Challenges Associated with IgA Vasculitis and IgA Vasculitis with Nephritis—Is It Time to Change the Paradigm of the Most Common Systemic Vasculitis in Childhood? Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 853724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, S.; Pistorio, A.; Iusan, S.M.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Herlin, T.; Brik, R.; Buoncompagni, A.; Lazar, C.; Bilge, I.; Uziel, Y.; et al. EULAR/PRINTO/PRES criteria for Henoch-Schönlein purpura, childhood polyarteritisnodosa, childhood Wegener granulomatosis and childhood Takayasu arteritis: Ankara 2008. Part II: Final classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, A.; Marsili, M.; Nozzi, M.; Faricelli, R.; Chiarelli, F.; Breda, L. Serum calprotectin: Review of its usefulness and validity in paediatric rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edgeworth, J.; Freemont, P.; Hogg, N. Ionomycin-regulated phosphorylation of the myeloid calcium-binding protein p14. Nature 1989, 342, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacken, W.; Roth, J.; Sorg, C.; Kerkhoff, C. S100A9/S100A8: Myeloid representatives of the S100 protein family as prominent players in innate immunity. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 60, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, R.J.; Hamour, S.; Chavele, K.M.; Todd, S.K.; Rasmussen, N.; Flint, S.; Lyons, P.A.; Smith, K.G.; Pusey, C.D.; Cook, H.T.; et al. Leukocyte and serum S100A8/S100A9 expression reflects disease activity in ANCA-associated vasculitis and glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljaberi, N.; Tronconi, E.; Schulert, G.; Grom, A.A.; Lovell, D.J.; Huggins, J.L.; Henrickson, M.; Brunner, H.I. The use of S100 proteins testing in juvenile idiopathic arthritis and autoinflammatory diseases in a pediatric clinical setting: A retrospective analysis. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2020, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.; Van Hoovels, L.; Benucci, M.; De Luca, R.; Coccia, C.; Bernardini, P.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; Guiducci, S.; Grossi, V.; et al. Circulating Calprotectin (cCLP) in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeć-Mędrek, M.; Widuchowska, M.; Kucharz, E.J. Calprotectin in rheumatic diseases: A review. Reumatologia 2016, 54, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, R.J.; Draibe, J.B.; Caplin, B.; Fervenza, F.C.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Langford, C.A.; Monach, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; et al. Association of Serum Calprotectin (S100A8/A9) Level with Disease Relapse in Proteinase 3-Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Xu, P.C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.M.; Wu, S.J.; Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Jia, J.Y.; Jiang, J.Q.; Yan, T.K. The potential pathogenic roles of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 in patients with MPO-ANCA-positive vasculitis. BMC Immunol. 2022, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Ohara, S.; Abe, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Suyama, K.; Sato, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Hosoya, M. The role of serum myeloid-related protein 8/14 complex in Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosch, M.; Vogl, T.; Waldherr, R.; Sorg, C.; Sunderkötter, C.; Roth, J. Expression of MRP8 and MRP14 by macrophages is a marker for severe forms of glomerulonephritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosch, M.; Vogl, T.; Seeliger, S.; Wulffraat, N.; Kuis, W.; Viemann, D.; Foell, D.; Sorg, C.; Sunderkötter, C.; Roth, J. Expression of myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 in systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2622–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marionnet, C.; Bernerd, F.; Dumas, A.; Verrecchia, F.; Mollier, K.; Compan, D.; Bernard, B.; Lahfa, M.; Leclaire, J.; Medaisko, C.; et al. Modulation of gene expression induced in human epidermis by environmental stress in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestan, M.; Kifer, N.; Frkovic, M.; Sapina, M.; Srsen, S.; Batnozic Varga, M.; Ovuka, A.; Held, M.; Gudelj Gracanin, A.; Kozmar, A.; et al. Gastrointestinal involvement and its association with the risk for nephritis in IgA vasculitis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211024828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestan, M.; Srsen, S.; Kifer, N.; Sapina, M.; Batnozic Varga, M.; Ovuka, A.; Held, M.; Kozmar, A.; Frkovic, M.; Laskarin, G.; et al. Persistence and Severity of Cutaneous Manifestations in IgA Vasculitis Is Associated with Development of IgA Vasculitis Nephritis in Children. Dermatology 2022, 238, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, K.; Foell, D.; Xing, Y.; Miyagawa-Tomita, S.; Ye, F.; Ahlmann, M.; Vogl, T.; Futatani, T.; Rui, C.; Yu, X.; et al. Expression of myeloid-related protein-8 and -14 in patients with acute Kawasaki disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.; Jibiki, T.; Noma, S.; Nakajima, T.; Saito, H.; Terai, M. Gene expression profiling of the effect of high-dose intravenous Ig in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5837–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosch, M.; Strey, A.; Vogl, T.; Wulffraat, N.M.; Kuis, W.; Sunderkötter, C.; Harms, E.; Sorg, C.; Roth, J. Myeloid-related proteins 8 and 14 are specifically secreted during interaction of phagocytes and activated endothelium and are useful markers for monitoring disease activity in pauciarticular-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berntzen, H.B.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Ostensen, M.; Mowinckel, P.; Høyeraal, H.M. The L1 protein as a new indicator of inflammatory activity in patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 18, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerss, J.; Roth, J.; Holzinger, D.; Ruperto, N.; Wittkowski, H.; Frosch, M.; Wulffraat, N.; Wedderburn, L.; Stanevicha, V.; Mihaylova, D.; et al. Phagocyte-specific S100 proteins and high-sensitivity C reactive protein as biomarkers for a risk-adapted treatment to maintain remission in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A comparative study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze zurWiesch, A.; Foell, D.; Frosch, M.; Vogl, T.; Sorg, C.; Roth, J. Myeloid related proteins MRP8/MRP14 may predict disease flares in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- La, C.; Lê, P.Q.; Ferster, A.; Goffin, L.; Spruyt, D.; Lauwerys, B.; Durez, P.; Boulanger, C.; Sokolova, T.; Rasschaert, J.; et al. Serum calprotectin (S100A8/A9): A promising biomarker in diagnosis and follow-up in different subgroups of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.A.; An, J.M.; Nam, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Suh, C.H. Serum S100A8/A9, but not follistatin-like protein 1 and interleukin 18, may be a useful biomarker of disease activity in adult-onset Still’s disease. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1399–1406, Erratum in J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, M.S.; Ballanti, E.; Perricone, C.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Perricone, R. Immunomodulation in psoriatic arthritis: Focus on cellular and molecular pathways. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Schmaderer, C.; Burkhardt, K.; Haller, B.; Heemann, U.; Dugi, K.; von Eynatten, M. MRP8/14 is associated with systemic inflammation in stable coronary atherosclerosis in men. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R&D Systems. Human S100A8/S100A9 Heterodimer Quantikine ELISA Kit [Internet]. 2020. Available online: https://www.rndsystems.com/products/human-s100a8-s100a9-heterodimer-quantikine-elisa-kit_ds8900 (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- Dolezalova, P.; Price-Kuehne, F.E.; Özen, S.; Benseler, S.M.; Cabral, D.A.; Anton, J.; Brunner, J.; Cimaz, R.; O’Neil, K.M.; Wallace, C.A.; et al. Disease activity assessment in childhood vasculitis: Development and preliminary validation of the Paediatric Vasculitis Activity Score (PVAS). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
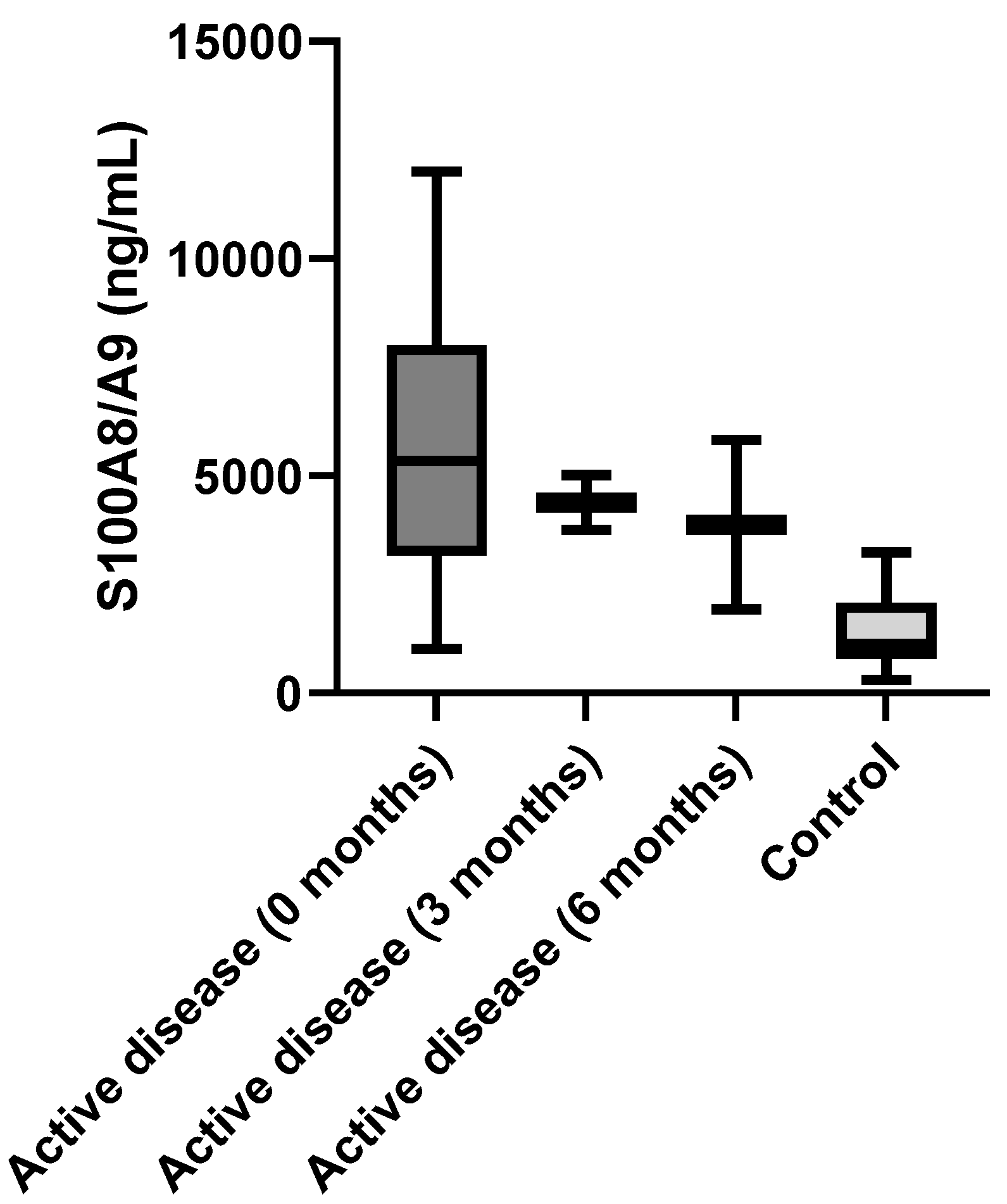

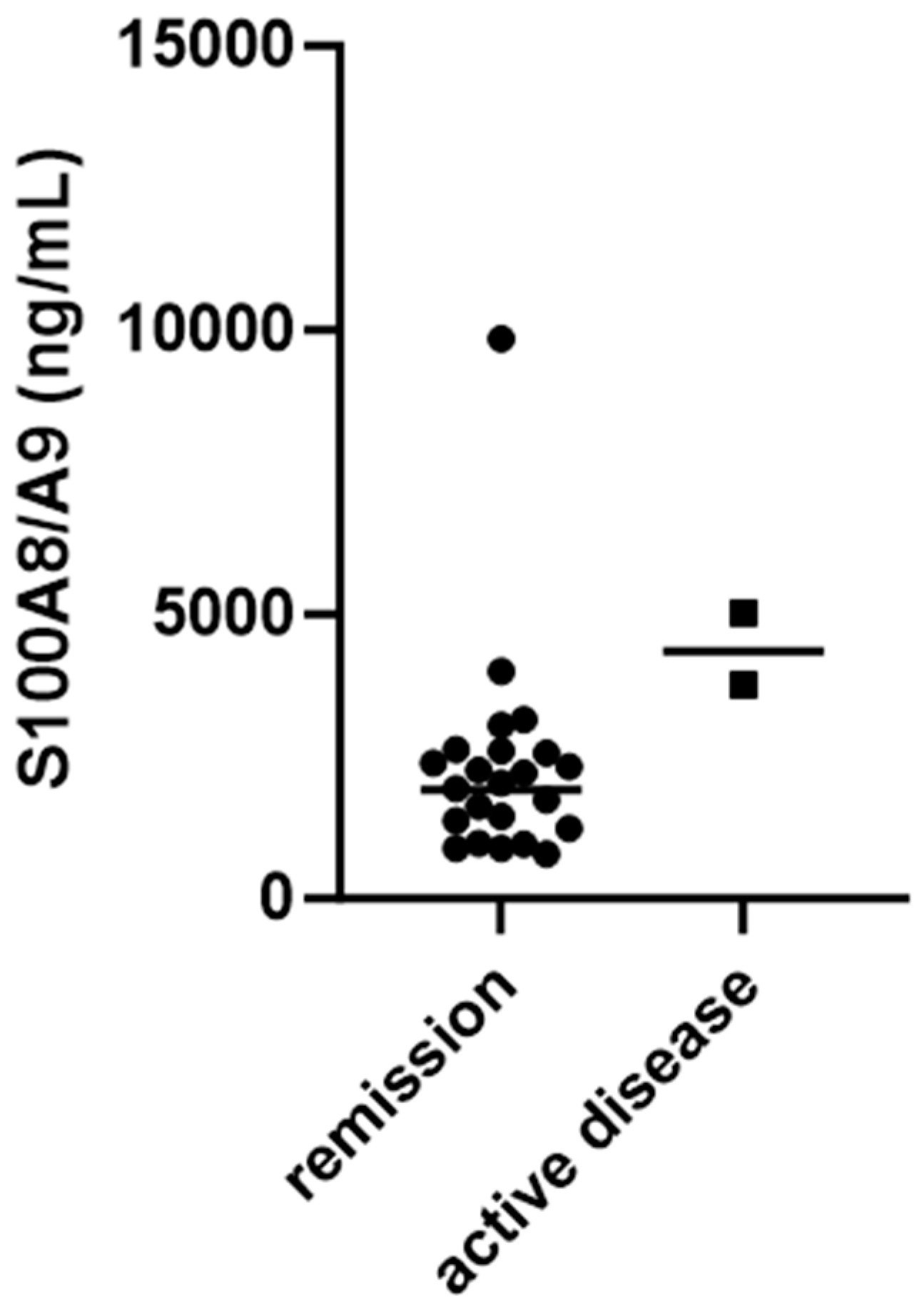
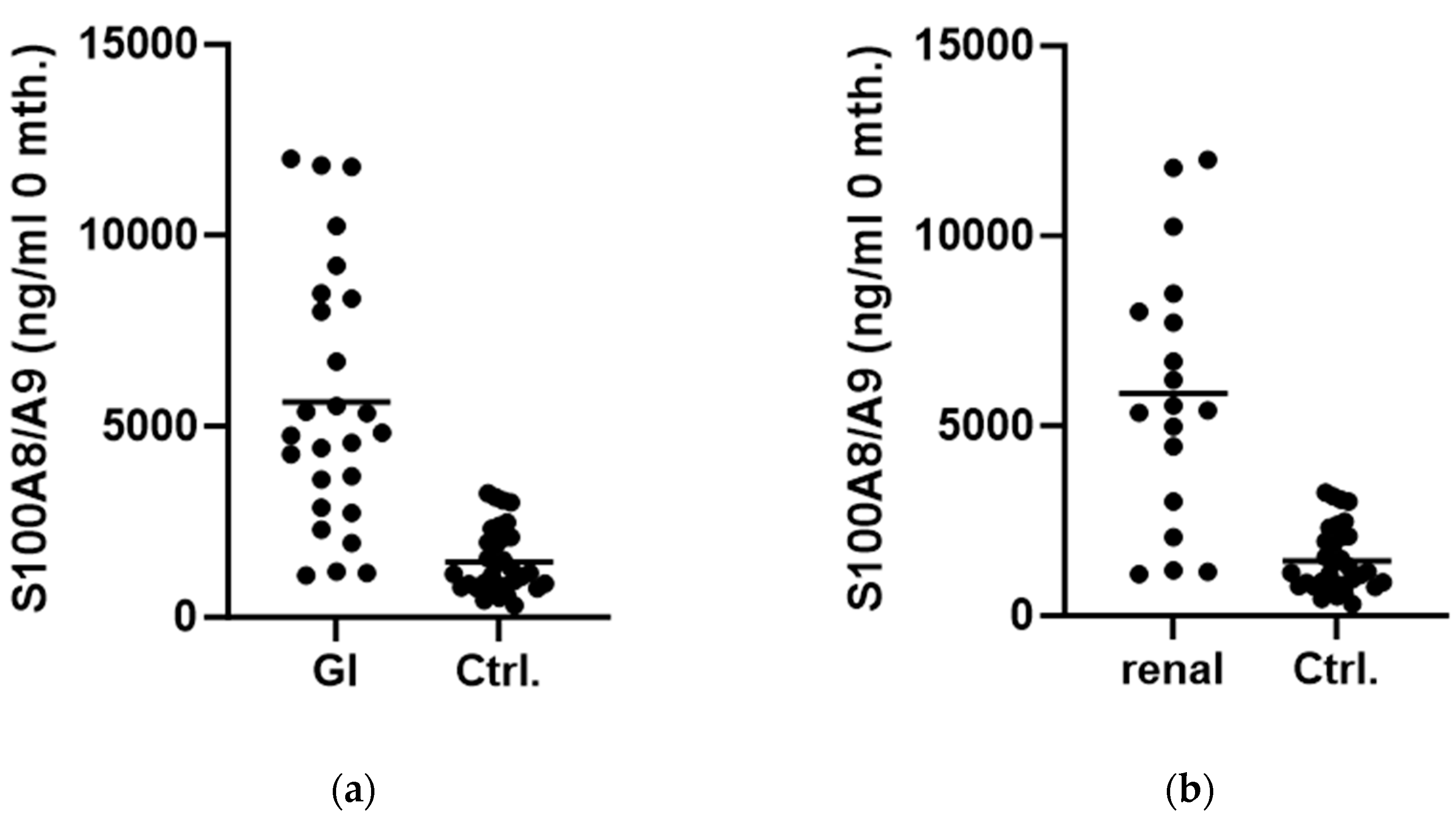


| Characteristics of the Patients | N = 69 | % of the Cohort |
| Demographics | ||
| Mean age (years) | 6.4 (3.7–9.1) | |
| Female | 33 | 47.8 |
| Male | 36 | 52.2 |
| Ratio male/female | 1.1:1 | |
| Clinics | ||
| Cutaneous manifestations 1 | 68 | 98.6 |
| Joint involvement | 56 | 81.2 |
| Gastrointestinal involvement | 26 | 37.7 |
| Nephritis | 18 | 26.1 |
| Active disease | ||
| Beginning of disease | 69 | 100 |
| After 3 months | 9 | 13.0 |
| After 6 months | 5 | 7.2 |
| Treatment | ||
| Any treatment | 61 | 88.4 |
| Glucocorticoids | 35 | 50.7 |
| NSAID 2 | 42 | 60.9 |
| Immunosuppressant | 6 | 8.7 |
| Antibiotics | 9 | 13.0 |
| Other | 48 | 69.6 |
| Control Group | N = 33 | % of the Cohort |
| Demographics | ||
| Mean age (years) | 6.6 (3.8–9.2) | |
| Female | 12 | 36.4 |
| Male | 21 | 63.6 |
| Ratio male/female | 1.75:1 |
| Parameter | Patients with IgA Vasculitis (Median, Interquartile Range) | Control Group (Median, Interquartile Range) (N = 33) | p * | p ** | p *** | p **** | p ***** | p ****** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset (N = 69) | Follow Up 3 Months (N = 63) | Follow Up 6 Months (N = 56) | ||||||||
| S100A8/A9 (ng/mL) | 5348.00 (3171.00–8000.00) | 2115.00 (1338.00–2725.00) | 2013.00 (1196.40–4126.15) | 1132.00 (797.50–2085.30) | <0.0001 | 0.0086 | 0.0011 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3364 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 15.00 (9.00–23.00) | 6.00 (4.00–9.00) | 7.00 (5.00–10.75) | 5.00 (4.00–9.25) | <0.0001 | 0.3540 | 0.0958 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3866 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 5.50 (2.52–16.28) | 0.70 (0.30–1.78) | 0.90 (0.30–1.48) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | <0.0001 | 0.1474 | 0.1010 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.5718 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 10.10 (8.28–12.10) | 7.30 (5.96–9.00) | 6.95 (5.75–8.02) | 5.50 (4.70–6.60) | <0.0001 | 0.0028 | 0.0045 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1173 |
| C3 (g/L) | 1.35 (1.20–1.52) | 1.16 (1.06–1.31) | 1.19 (1.06–1.29) | 1.05 (0.94–1.20) | 0.0062 | 0.1288 | 0.1784 | 0.0091 | 0.0058 | 0.7504 |
| C4 (g/L) | 0.26 (0.20–0.33) | 0.21 (0.16–0.25) | 0.22 (0.16–0.26) | 0.16 (0.13–0.24) | 0.0102 | 0.1491 | 0.1532 | 0.0072 | 0.0126 | 0.9835 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 3.40 (2.70–3.80) | 2.60 (2.40–3.30) | 2.70 (2.30–3.05) | 2.55 (2.23–2.85) | 0.0181 | 0.3822 | 0.7725 | 0.0010 | <0.0001 | 0.2705 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 38.70 (35.63–41.92) | 43.85 (40.65–45.48) | 44.20 (42.00–46.70) | 44.61 (40.65–47.10) | 0.0094 | 0.4796 | 0.6462 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0479 |
| Gamma globulin (g/L) | 9.60 (7.75–11.60) | 9.03 (7.32–10.72 | 9.30 (7.50–10.90) | 9.72 (8.24–12.02) | 0.8685 | 0.6838 | 0.3377 | 0.5991 | 0.2053 | 0.4876 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 64.00 (45.50–94.95) | 22.80 (13.20–40.00) | 28.00 (16.35–42.85) | 31.50 (21.00–48.00) | 0.0448 | 0.2951 | 0.0893 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.6486 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srsen, S.; Held, M.; Sestan, M.; Kifer, N.; Kozmar, A.; Supe Domic, D.; Benzon, B.; Gagro, A.; Frkovic, M.; Jelusic, M. Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040750
Srsen S, Held M, Sestan M, Kifer N, Kozmar A, Supe Domic D, Benzon B, Gagro A, Frkovic M, Jelusic M. Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040750
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrsen, Sasa, Martina Held, Mario Sestan, Nastasia Kifer, Ana Kozmar, Daniela Supe Domic, Benjamin Benzon, Alenka Gagro, Marijan Frkovic, and Marija Jelusic. 2024. "Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis" Biomedicines 12, no. 4: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040750
APA StyleSrsen, S., Held, M., Sestan, M., Kifer, N., Kozmar, A., Supe Domic, D., Benzon, B., Gagro, A., Frkovic, M., & Jelusic, M. (2024). Serum Levels of S100A8/A9 as a Biomarker of Disease Activity in Patients with IgA Vasculitis. Biomedicines, 12(4), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12040750






