Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Dose-Dependent Effects on EEG Power Spectrum and Synchronization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
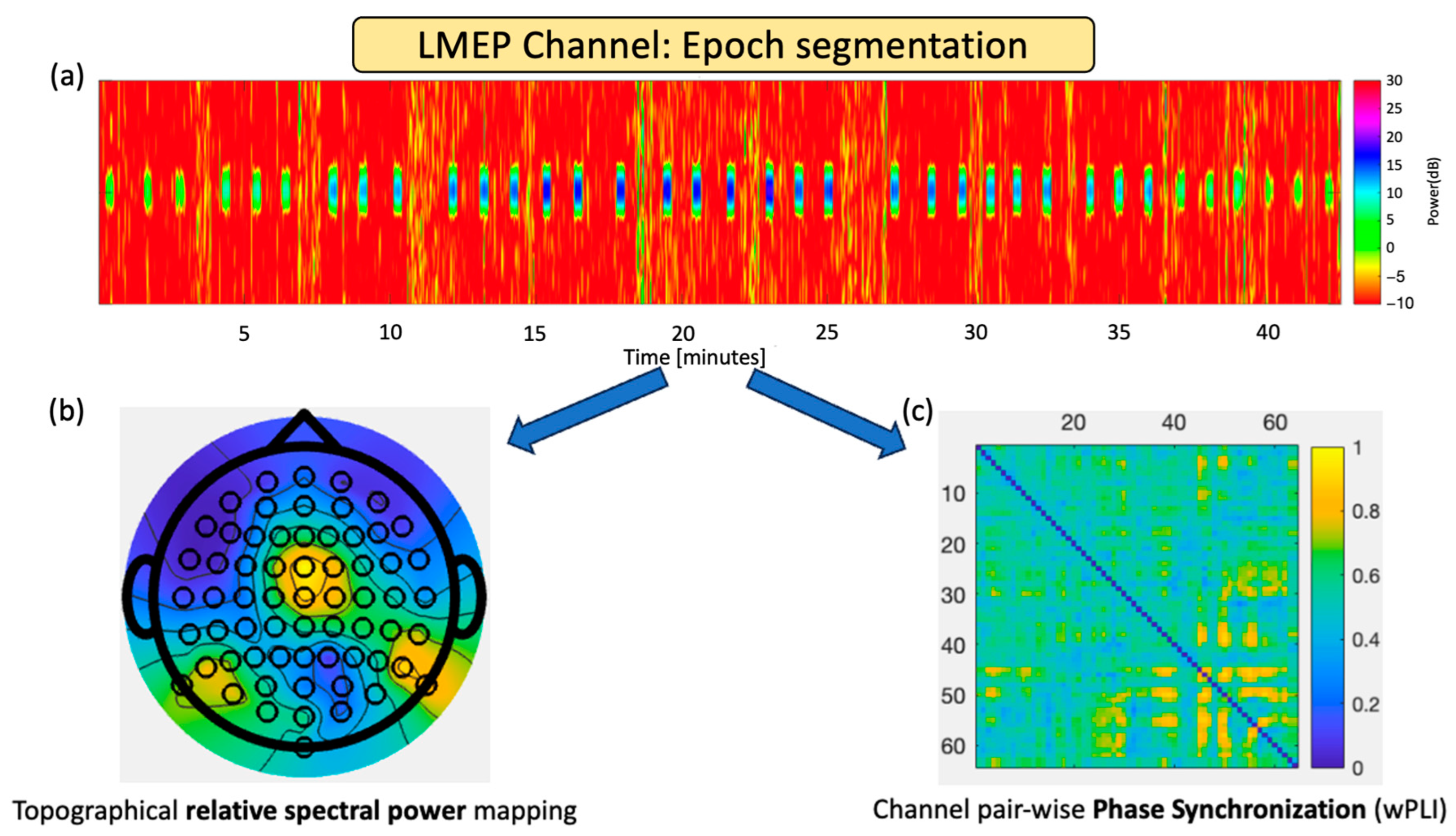
2.2. EEG Recordings and Epoch Selection
2.3. Topographical Band Power Analysis
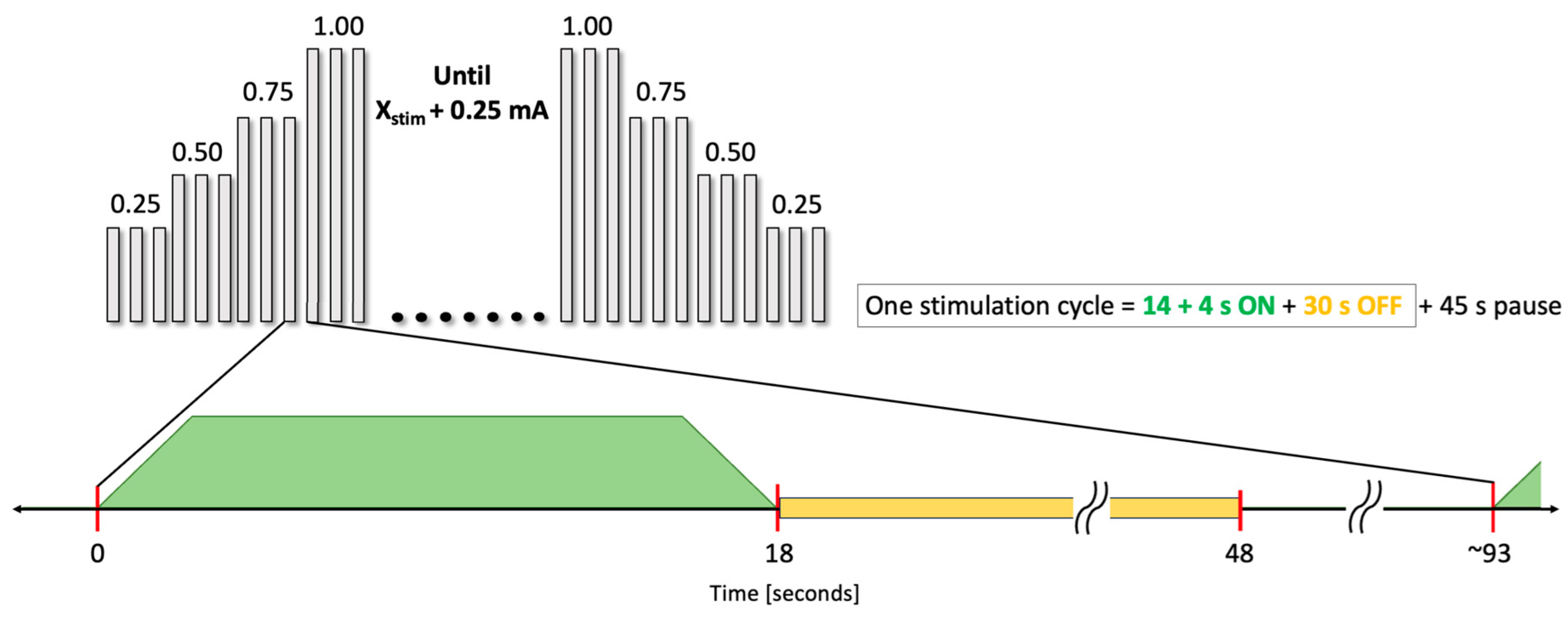
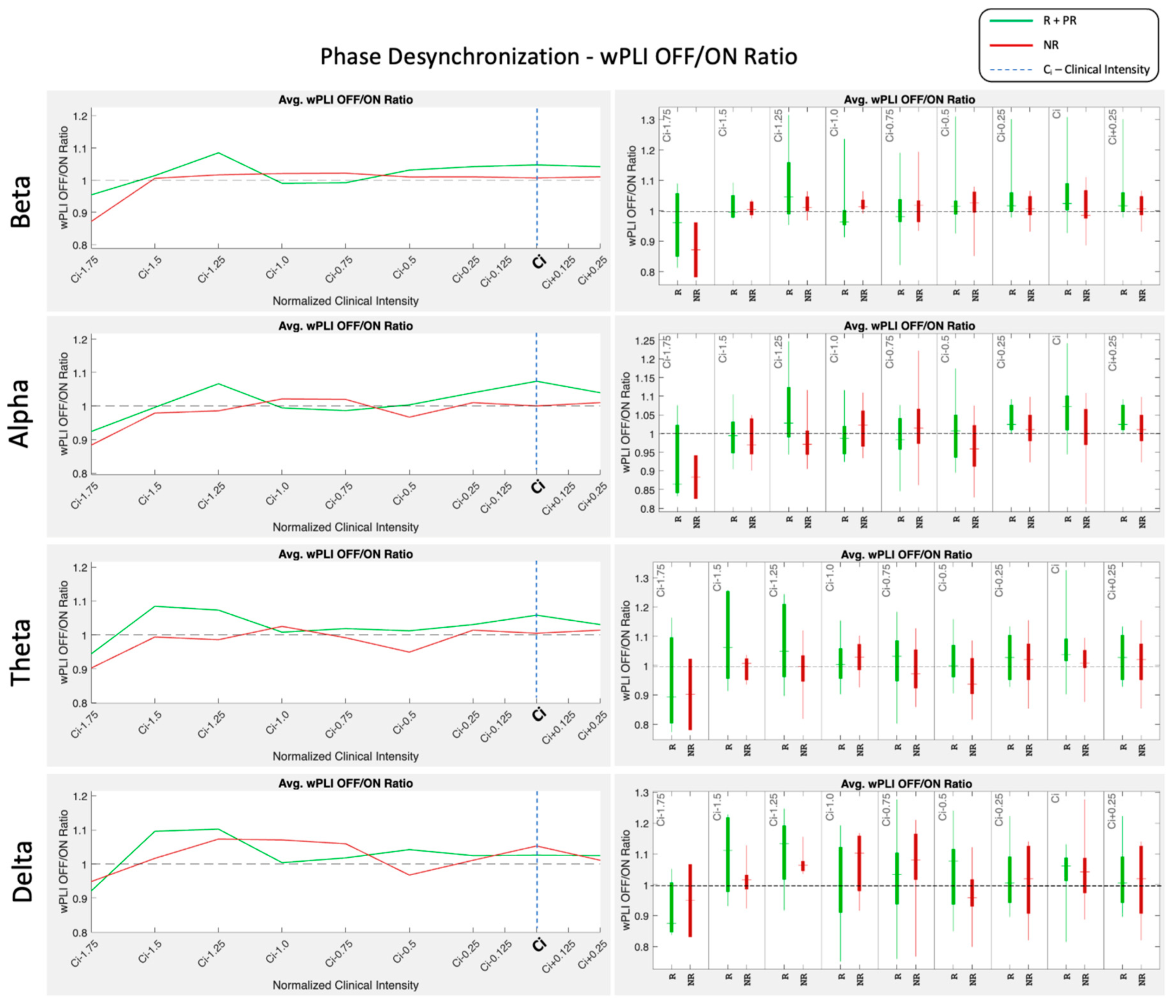
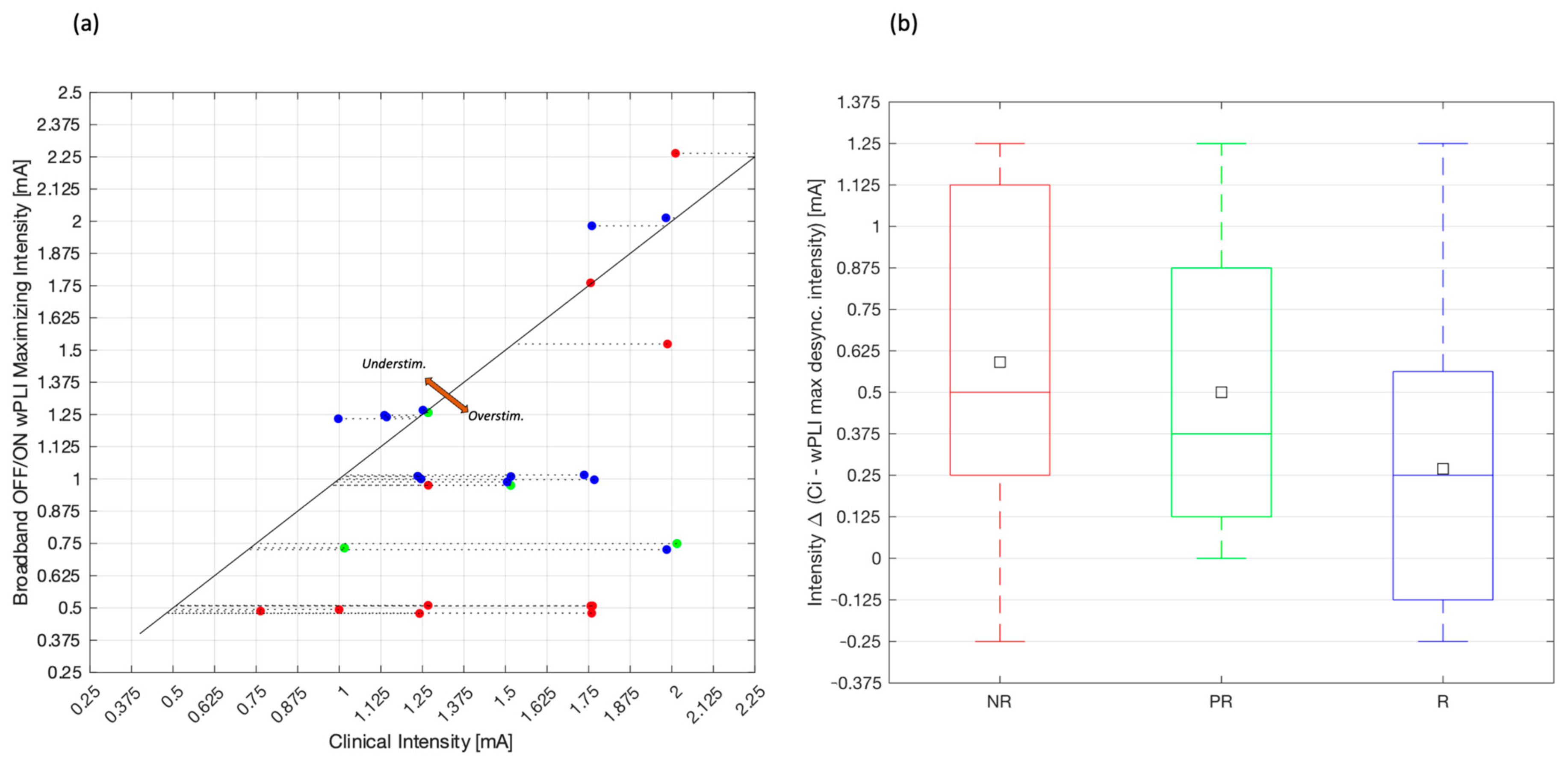
2.4. EEG Dose-Dependent Desynchronization Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Cohort Demographics and Clinical Information
- Responders (R, 13 individuals) with a seizure reduction rate greater than 50%;
- Partial-responders (PR, 4 individuals) with a seizure reduction rate between 30% and 50%;
- Non-responders (NR, 11 individuals) with a seizure reduction rate of less than 30%.
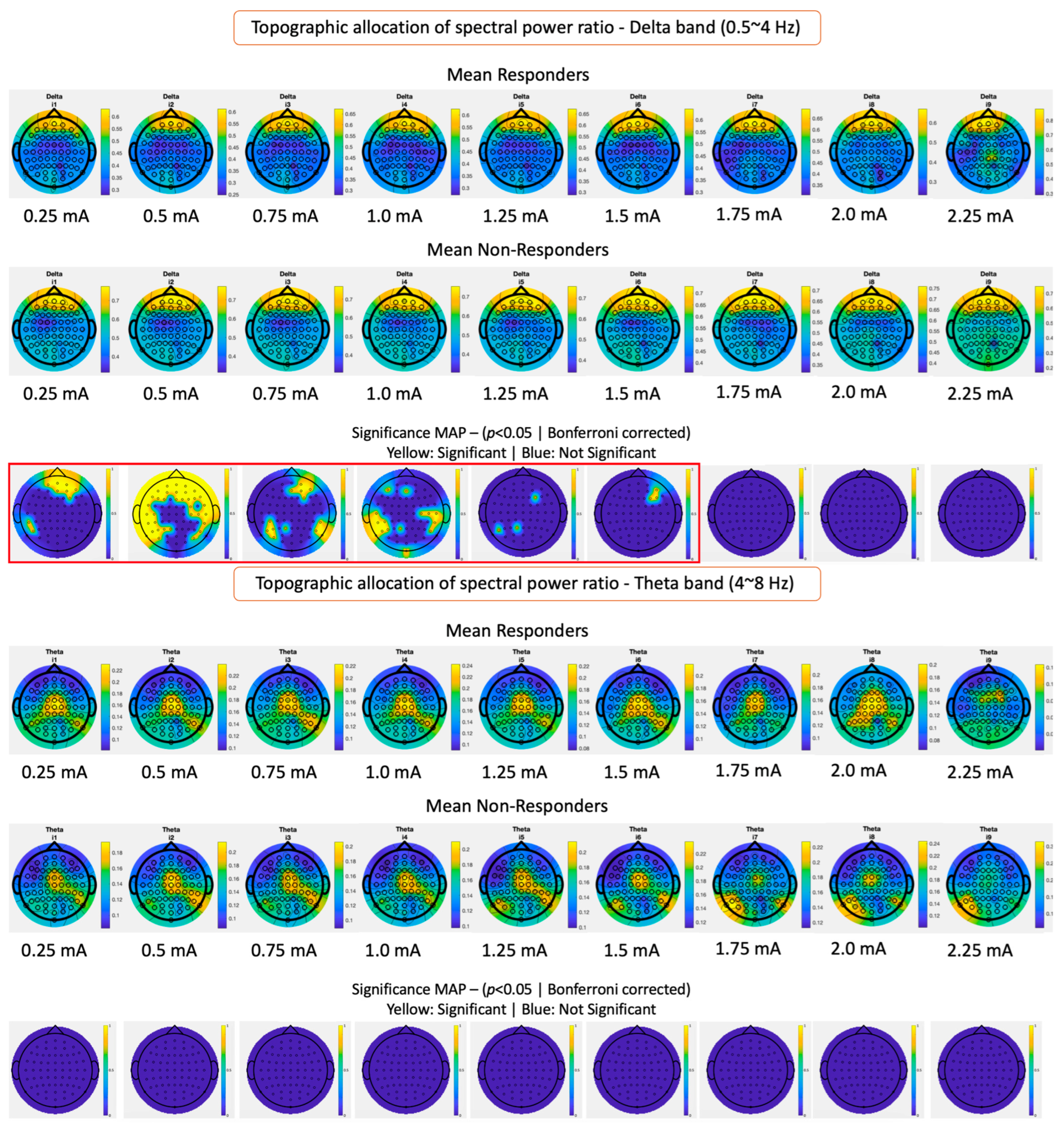
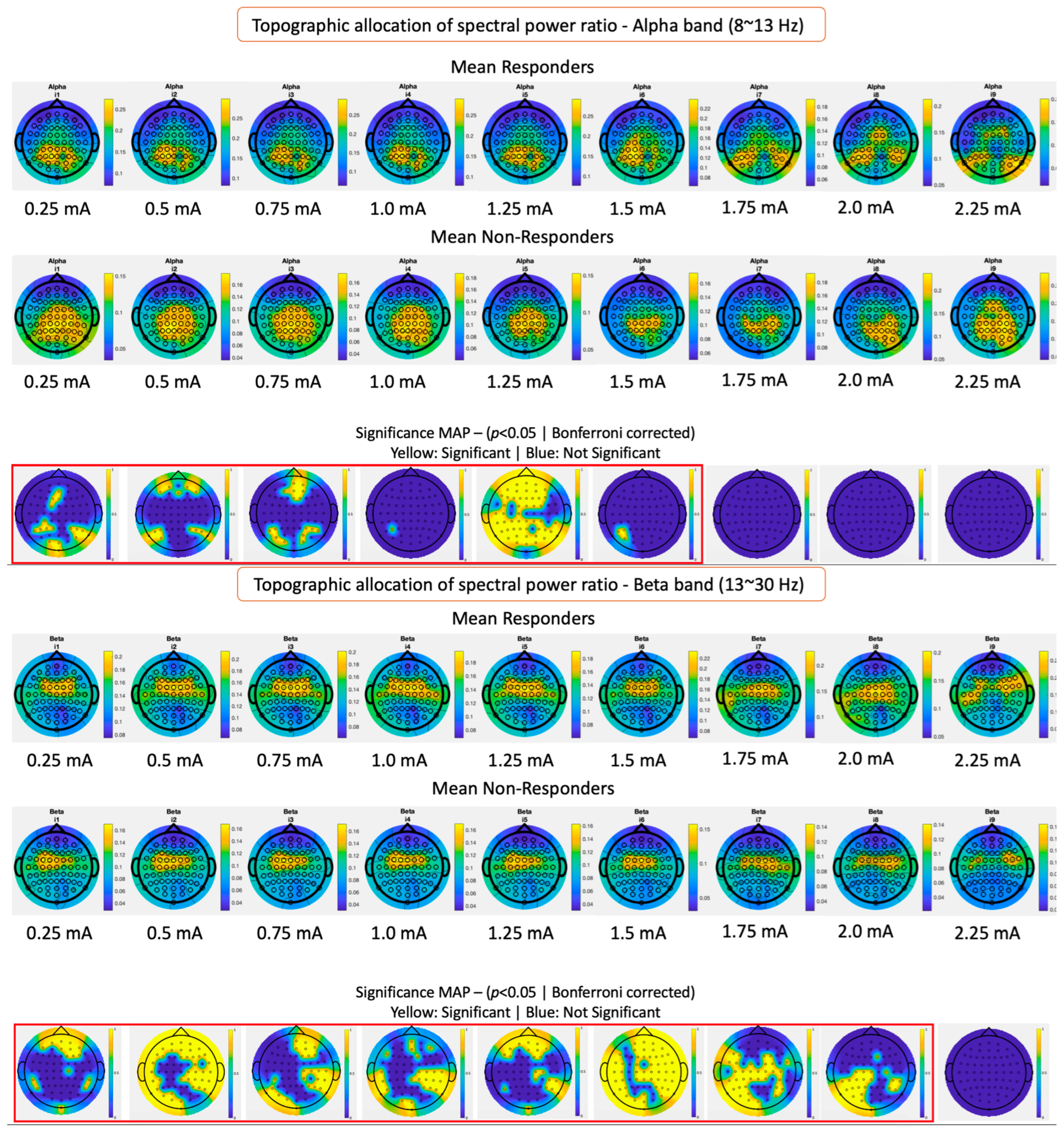
3.2. Topographical Band Power Analysis Results
3.3. EEG Dose-Dependent Desynchronization Results
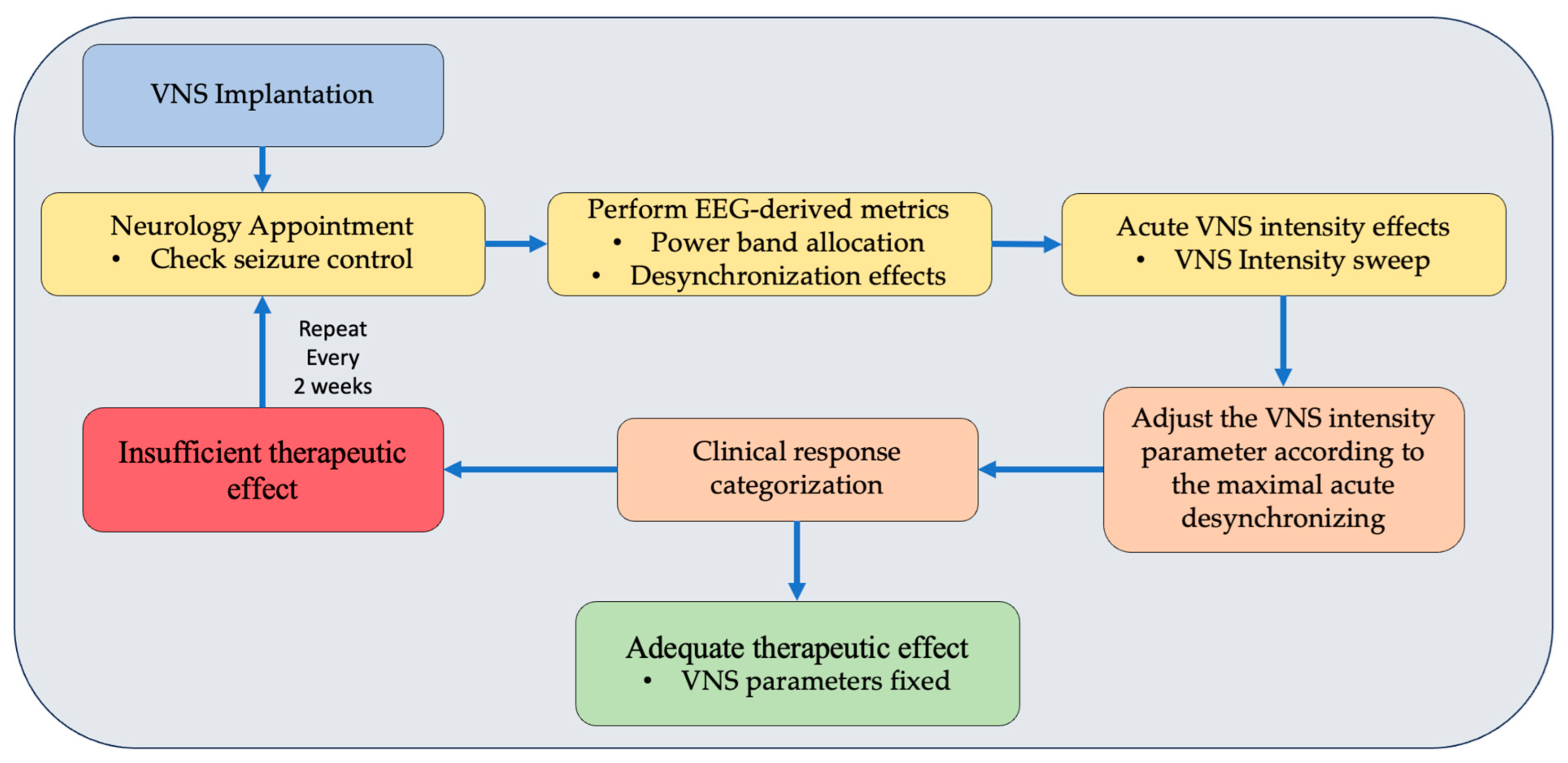
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogbonnaya, S.; Kaliaperumal, C. Vagal Nerve Stimulator: Evolving Trends. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.; DesMarteau, J.A.; Koontz, E.H.; Wilks, S.J.; Melamed, S.E. Responsive Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Drug Resistant Epilepsy: A Review of New Features and Practical Guidance for Advanced Practice Providers. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 610379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englot, D.J.; Rolston, J.D.; Wright, C.W.; Hassnain, K.H.; Chang, E.F. Rates and Predictors of Seizure Freedom with Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Intractable Epilepsy. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Moghtadaie, A.; Yazdi, S.A.M. Factors Affecting Vagus Nerve Stimulation Outcomes in Epilepsy. Neurol. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9927311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, G.; Liu, Q.Q.; Ding, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Bai, X.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Prognosis Factors of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Refractory Epilepsy. Acta Epileptol. 2022, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggio, F.; Gorini, G.; Utzeri, C.; Olla, P.; Marrosu, F.; Mocchetti, I.; Follesa, P. Chronic Vagus Nerve Stimulation Induces Neuronal Plasticity in the Rat Hippocampus. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broncel, A.; Bocian, R.; Konopacki, J. Vagal Nerve Stimulation: The Effect on the Brain Oscillatory Field Potential. Neuroscience 2022, 483, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chase, M.H.; Nakamura, Y.; Clemente, C.D.; Sterman, M.B. Afferent Vagal Stimulation: Neurographic Correlates of Induced Eeg Synchronization and Desynchronization. Brain Res. 1967, 5, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzamo, E.; Jammes, Y. Vagal Afferents and EEG Rhythms in the SI Area in Anesthetized Cats: Similarities between Responses to Electrical and Chemical (Phenyldiguanide) Stimulations. Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. 1989, 97, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalbers, M.; Vles, J.; Klinkenberg, S.; Hoogland, G.; Majoie, M.; Rijkers, K. Animal Models for Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Epilepsy. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 230, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaseja, H. EEG-Desynchronization as the Major Mechanism of Anti-Epileptic Action of Vagal Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Intractable Seizures: Clinical Neurophysiological Evidence. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschini, M.; Puligheddu, M.; Demuru, M.; Polizzi, L.; Maleci, A.; Tamburini, G.; Congia, S.; Bortolato, M.; Marrosu, F. VNS Induced Desynchronization in Gamma Bands Correlates with Positive Clinical Outcome in Temporal Lobe Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 536, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangare, A.; Marchi, A.; Pruvost-Robieux, E.; Soufflet, C.; Crepon, B.; Ramdani, C.; Chassoux, F.; Turak, B.; Landre, E.; Gavaret, M. The Effectiveness of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Correlates with Vagus Nerve Stimulation-Induced Electroencephalography Desynchronization. Brain Connect. 2020, 10, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, S.; Heyse, J.; Stumpp, L.; Liberati, G.; Santos, S.F.; Rooijakkers, H.; Nonclercq, A.; Mouraux, A.; van Mierlo, P.; Tahry, R.E. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Elicits Sleep EEG Desynchronization and Network Changes in Responder Patients in Epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 2623–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Wu, H.; Luan, G.; Wang, Q. The Distribution and Heterogeneity of Excitability in Focal Epileptic Network Potentially Contribute to the Seizure Propagation. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1137704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bod, R.; Tóth, K.; Essam, N.; Tóth, E.Z.; Erõss, L.; Entz, L.; Bagó, A.G.; Fabó, D.; Ulbert, I.; Wittner, L. Synaptic Alterations and Neuronal Firing in Human Epileptic Neocortical Excitatory Networks. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1233569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzone, J.; Boscarino, M.; Tufo, T.; Lorenzo, G.D.; Ricci, L.; Colicchio, G.; Lazzaro, V.D.; Tombini, M.; Assenza, G. Vagal Nerve Stimulation Cycles Alter EEG Connectivity in Drug-Resistant Epileptic Patients: A Study with Graph Theory Metrics. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 142, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Hu, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, G.; Liu, Q.; Ji, T.; Xie, H.; et al. A Prediction Model Integrating Synchronization Biomarkers and Clinical Features to Identify Responders to Vagus Nerve Stimulation among Pediatric Patients with Drug-resistant Epilepsy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1838–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, F.; Ma, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, K.; Bu, J.; Zhang, R. Immediate Effects of Vagal Nerve Stimulation in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Revealed by Magnetoencephalographic Recordings. Brain Connect. 2023, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.A.; Danaphongse, T.T.; Abe, S.T.; Stevens, M.E.; Ezhil, V.; Seyedahmadi, A.; Adcock, K.S.; Rennaker, R.L.; Kilgard, M.P.; Hays, S.A. High Intensity VNS Disrupts VNS-Mediated Plasticity in Motor Cortex. Brain Res. 2021, 1756, 147332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, S.; Stumpp, L.; Liberati, G.; Delbeke, J.; Nonclercq, A.; Mouraux, A.; Tahry, R.E. Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation-Induced Pupillary Responses in Epileptic Patients. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, S.; Stumpp, L.; Bouckaert, C.; Delbeke, J.; Smets, H.; Cury, J.; Santos, S.F.; Rooijakkers, H.; Nonclercq, A.; Raedt, R.; et al. Vagus Nerve Stimulation-Induced Laryngeal Motor Evoked Potentials: A Possible Biomarker of Effective Nerve Activation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diessen, E.; Numan, T.; van Dellen, E.; van der Kooi, A.W.; Boersma, M.; Hofman, D.; van Lutterveld, R.; van Dijk, B.W.; van Straaten, E.C.W.; Hillebrand, A.; et al. Opportunities and Methodological Challenges in EEG and MEG Resting State Functional Brain Network Research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraschini, M.; Demuru, M.; Crobe, A.; Marrosu, F.; Stam, C.J.; Hillebrand, A. The Effect of Epoch Length on Estimated EEG Functional Connectivity and Brain Network Organisation. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 036015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinck, M.; Oostenveld, R.; van Wingerden, M.; Battaglia, F.; Pennartz, C.M.A. An Improved Index of Phase-Synchronization for Electrophysiological Data in the Presence of Volume-Conduction, Noise and Sample-Size Bias. NeuroImage 2011, 55, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Brain Functional Connectivity and Network Characteristics Changes after Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Patients with Refractory Epilepsy. Transl. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 20220308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.X.; Qin, Y.-L. A Two-Sample Test for High-Dimensional Data with Applications to Gene-Set Testing. Ann. Stat. 2010, 38, 808–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahoum, F.; Boffini, M.; Kann, L.; Faini, S.; Gordon, C.; Tzadok, M.; Tahry, R.E. VNS Parameters for Clinical Response in Epilepsy. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorfer, J.B.; Begnaud, J.; Keith, A.; Szaflarski, J.P. 3T FMRI Thalamic Activation with Vagus Nerve Stimulation. In Proceedings of the AES 2019 Annual Meeting. American Epilepsy Society. Presentation Date: 12/9/2019. 2019. Available online: https://aesnet.org/abstractslisting/3t-fmri-thalamic-activation-with-vagus-nerve-stimulation (accessed on 23 January 2024).
- Verner, R.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Allendorfer, J.B.; Vonck, K.; Giannicola, G.; Group, M.S.; McDermott, D.; Brown, M.G.; Kaye, L.; Macken, M.; et al. Modulation of the Thalamus by Microburst Vagus Nerve Stimulation: A Feasibility Study Protocol. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1169161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhansali, A.; Eissa, T.; van Drongelen, W. Spectral Changes in the Electroencephalogram (EEG) Following Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS). In Proceedings of the AES 2016 Annual Meeting Abstract Database. 2016. Available online: https://aesnet.org/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Yokoyama, R.; Akiyama, Y.; Enatsu, R.; Suzuki, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kanno, A.; Ochi, S.; Mikuni, N. The Immediate Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Intractable Epilepsy: An Intra-Operative Electrocorticographic Analysis. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, C.; Aubert, S.; Daquin, G.; Carron, R.; Scavarda, D.; McGonigal, A.; Bartolomei, F. Responders to Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) in Refractory Epilepsy Have Reduced Interictal Cortical Synchronicity on Scalp EEG. Epilepsy Res. 2015, 113, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, S.A.; Rennaker, R.L.; Kilgard, M.P. Chapter 11 Targeting Plasticity with Vagus Nerve Stimulation to Treat Neurological Disease. Prog. Brain Res. 2013, 207, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, L.K.; Moore, R.J.; Bechmann, N.A.; Ethridge, V.T.; Gargas, N.M.; Cunningham, S.D.; Kuang, Z.; Whicker, J.K.; Rohan, J.G.; Hatcher-Solis, C.N. Vagus Nerve Stimulation-Induced Cognitive Enhancement: Hippocampal Neuroplasticity in Healthy Male Rats. Brain Stimul. 2022, 15, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-T.; Gaulding, S.J.; Dancel, C.L.E.; Thorn, C.A. Local Activation of A2 Adrenergic Receptors Is Required for Vagus Nerve Stimulation Induced Motor Cortical Plasticity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.A.; Hulsey, D.R.; Adcock, K.S.; Rennaker, R.L.; Kilgard, M.P.; Hays, S.A. Vagus Nerve Stimulation Intensity Influences Motor Cortex Plasticity. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.A.; Danaphongse, T.T.; Pruitt, D.T.; Adcock, K.S.; Mathew, J.K.; Abe, S.T.; Abdulla, D.M.; Rennaker, R.L.; Kilgard, M.P.; Hays, S.A. A Limited Range of Vagus Nerve Stimulation Intensities Produce Motor Cortex Reorganization When Delivered during Training. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 391, 112705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridha, Z.; de Gee, J.W.; Shi, Y.; Alkashgari, R.; Williams, J.; Suminski, A.; Ward, M.P.; Zhang, W.; McGinley, M.J. Graded Recruitment of Pupil-Linked Neuromodulation by Parametric Stimulation of the Vagus Nerve. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamy, R.; Kaur, M.; Pizarro, D.; Toth, E.; Pati, S. Practice Trends and the Outcome of Neuromodulation Therapies in Epilepsy: A Single-center Study. Epilepsia Open 2019, 4, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzadok, M.; Verner, R.; Kann, L.; Tungala, D.; Gordon, C.; Tahry, R.E.; Fahoum, F. Rapid Titration of VNS Therapy Reduces Time-to-Response in Epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 134, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subject ID | Sex | Age Epilepsy Onset | Epilepsy Type | Clinical VNS Output Current [mA] | Clinical VNS Frequency [Hz] | Clinical VNS Pulse Width [us] | Response to Therapy Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 7 | Idiopathic generalized | 1.75 | 25 | 250 | NR |
| 2 | M | 25 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1 | 30 | 250 | PR |
| 3 | M | 15 | Unknown | 1.25 | 30 | 250 | R |
| 4 | M | 18 | Focal | 1.5 | 25 | 250 | PR |
| 5 | M | 36 | Focal, structural | 1.5 | 25 | 250 | R |
| 6 | F | 1 | Idiopathic generalized | 2 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 7 | M | 30 | Focal, structural | 1.25 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 8 | F | 8 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1.25 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 9 | F | 16 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1.25 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 10 | F | 14 | Idiopathic generalized | 1.125 | 30 | 250 | R |
| 11 | M | 18 | Focal, structural | 2 | 25 | 250 | NR |
| 12 | F | 12 | Focal, genetic | 1.25 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 13 | F | 13 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1.75 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 14 | F | 28 | Focal, structural | 1 | 30 | 500 | NR |
| 15 | F | 36 | Focal, unknown etiology | 2 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 16 | F | 5 | Plurifocal, unknown etiology + structural | 1.75 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 17 | M | 8 | Bi-focal, structural | 1 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 18 | M | 6 | Plurifocal, unknown etiology | 2 | 30 | 250 | PR |
| 19 | M | 9 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1.125 | 20 | 250 | R |
| 20 | F | 20 | Focal, unknown etiology | 1.25 | 20 | 250 | PR |
| 21 | F | 20 | Focal, structural | 1.75 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 22 | F | Idiopathic generalized | 2 | 25 | 250 | R | |
| 23 | M | 25 | Focal, unknown etiology | 0.75 | 25 | 250 | NR |
| 24 | F | 23 | Focal, auto-immune | 1.5 | 30 | 250 | R |
| 25 | M | 45 | Focal, structural | 1.75 | 30 | 250 | NR |
| 26 | M | 8 | Focal, structural | 1.75 | 30 | 250 | R |
| 27 | F | 15 | Idiopathic generalized | 1.75 | 20 | 250 | NR |
| 28 | M | 13 | Idiopathic generalized | 1.25 | 30 | 500 | R |
| VNS Intensity | Delta | Theta | Alpha | Beta | Gamma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 mA | 0.1110 | 0.7138 | 0.3424 | 0.0003 * | 0.7696 |
| 0.5 mA | 0.0005 * | 0.7892 | 0.0520 | <0.0001 * | 0.7466 |
| 0.75 mA | 0.1165 | 0.7944 | 0.1312 | 0.0027 * | 0.7988 |
| 1.0 mA | 0.0083 * | 0.7575 | 0.2035 | <0.0001 * | 0.7415 |
| 1.25 mA | 0.0136 * | 0.8008 | 0.0029 * | 0.0003 * | 0.7929 |
| 1.5 mA | 0.0998 | 0.7789 | 0.3677 | <0.0001 * | 0.5589 |
| 1.75 mA | 0.6534 | 0.7554 | 0.7299 | <0.0001 * | 0.7329 |
| 2.0 mA | 0.4272 | 0.7727 | 0.7580 | 0.0013 * | 0.2258 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Germany Morrison, E.; Danthine, V.; Santalucia, R.; Torres, A.; Cakiroglu, I.; Nonclercq, A.; El Tahry, R. Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Dose-Dependent Effects on EEG Power Spectrum and Synchronization. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030557
Germany Morrison E, Danthine V, Santalucia R, Torres A, Cakiroglu I, Nonclercq A, El Tahry R. Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Dose-Dependent Effects on EEG Power Spectrum and Synchronization. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(3):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030557
Chicago/Turabian StyleGermany Morrison, Enrique, Venethia Danthine, Roberto Santalucia, Andrés Torres, Inci Cakiroglu, Antoine Nonclercq, and Riëm El Tahry. 2024. "Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Dose-Dependent Effects on EEG Power Spectrum and Synchronization" Biomedicines 12, no. 3: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030557
APA StyleGermany Morrison, E., Danthine, V., Santalucia, R., Torres, A., Cakiroglu, I., Nonclercq, A., & El Tahry, R. (2024). Characterization of Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) Dose-Dependent Effects on EEG Power Spectrum and Synchronization. Biomedicines, 12(3), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030557






