Design and Synthesis of Immunoadjuvant QS-21 Analogs and Their Biological Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
2.1.1. General Considerations
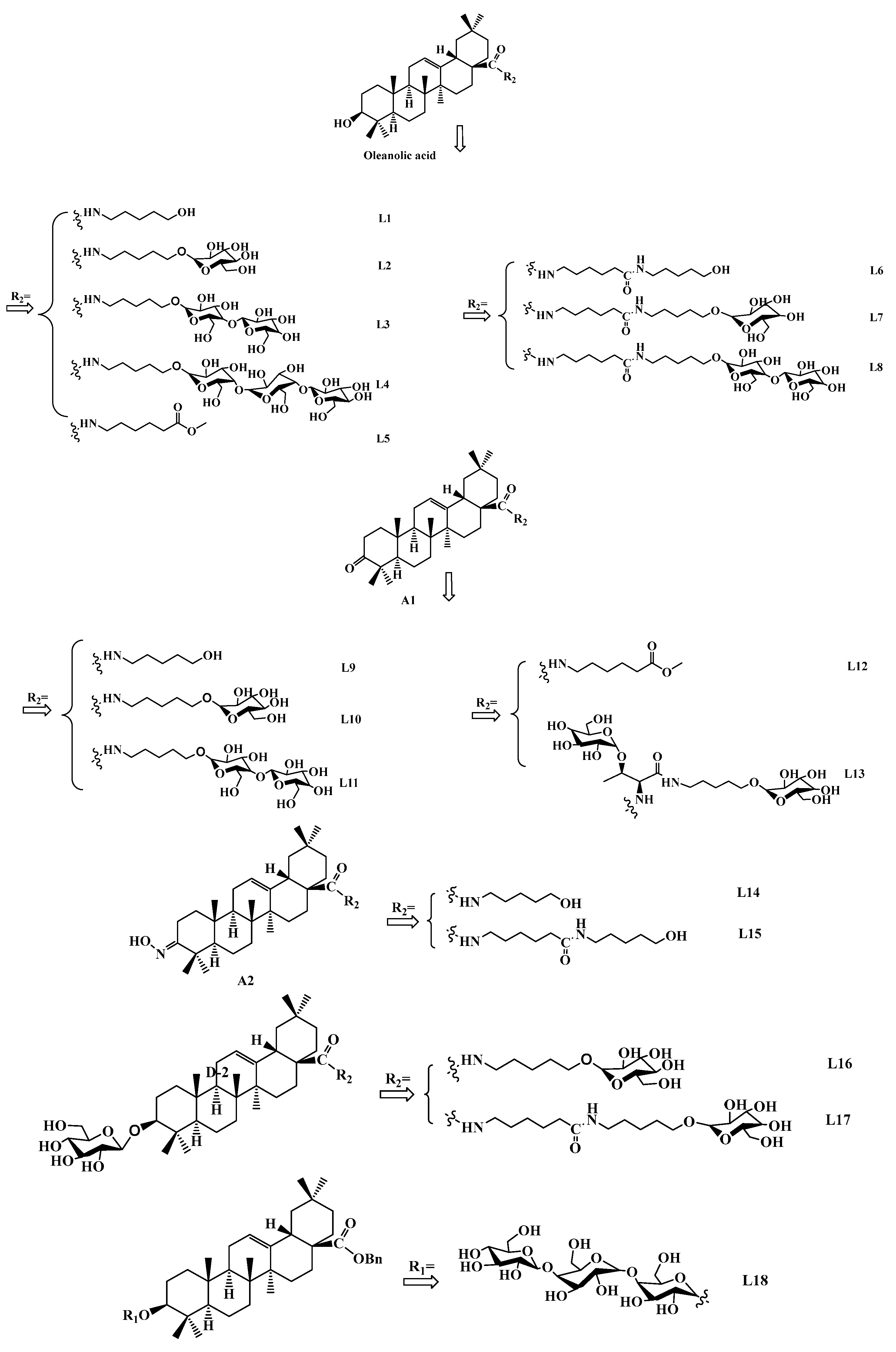
2.1.2. General Procedure to Prepare QS-21 Analogues L1–L15
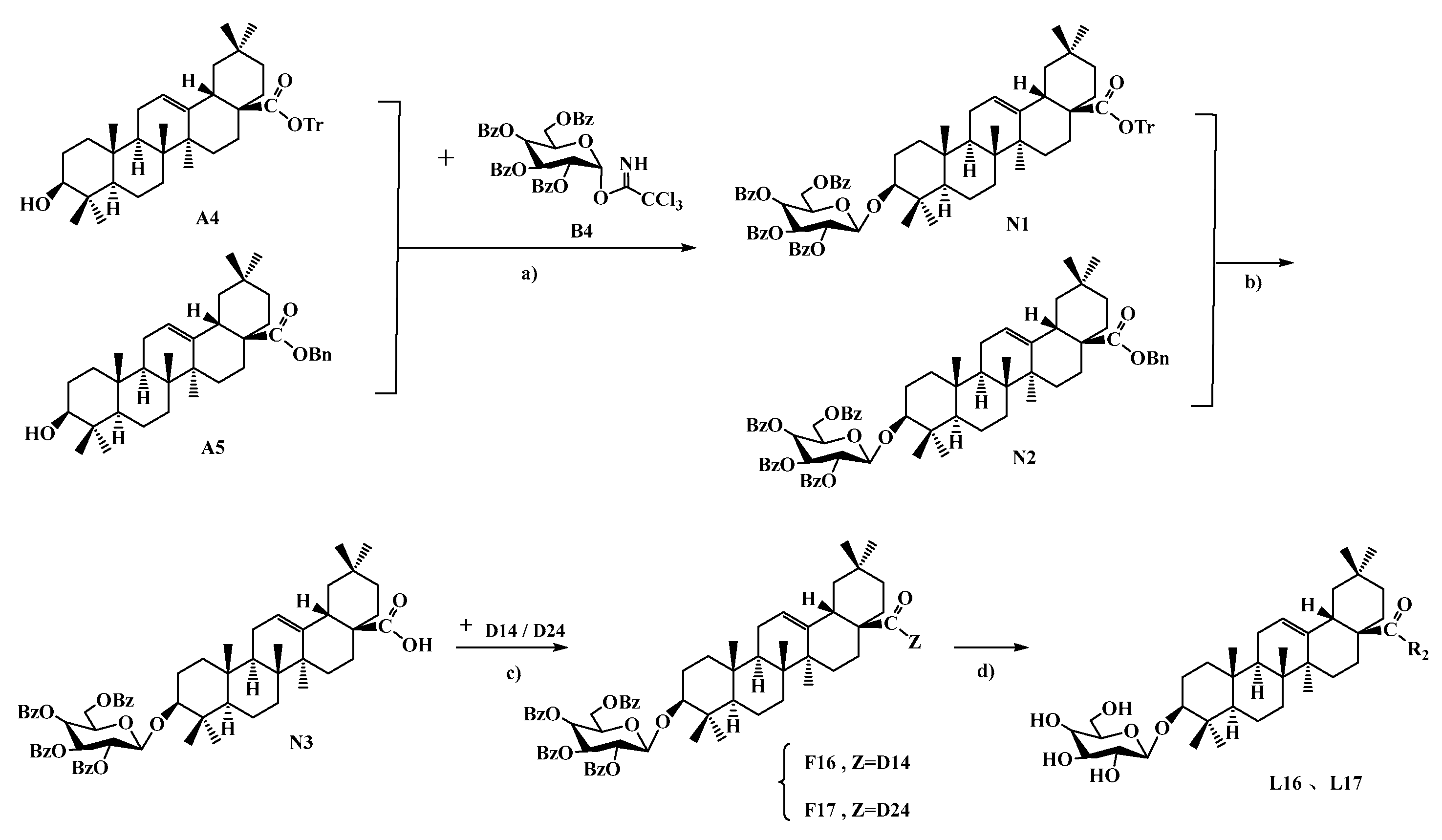
2.1.3. General Procedure to Prepare QS-21 Analogues L16–L17
2.1.4. General Procedure to Prepare QS-21 Analogues L18
2.2. Biological Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Synthesis
3.2. Biological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacaille-Dubois, M.A. Updated insights into the mechanism of action and clinical profile of the immunoadjuvant QS-21: A review. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 152905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowicz, W.E.; Fernández-Tejada, A. Quillaja saponin variants with central glycosidic linkage modifications exhibit distinct conformations and adjuvant activities. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Tejada, A.; Chea, E.K. Development of a minimal saponin vaccine adjuvant based on QS-21. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Kim, Y.J. Synthesis of the potent immunostimulatory adjuvant QS-21A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3256–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Manabe, S. Synthesis of the immunostimulatory adjuvant QS-21 and an approach to elucidating its mechanism of action. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2012, 24, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pink, J.R.; Kieny, M.P. 4th meeting on novel adjuvants currently in/close to human clinical testing: World Health Organization-Organisation Mondiale de la Santé Fondation Mérieux, Annecy, France, 23–25 June 2003. Vaccine 2004, 22, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensil, C.R. Saponins as vaccine adjuvants. Crit Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1996, 13, 1–55. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8853958/ (accessed on 29 December 2023).
- Newman, M.J.; Wu, J.Y. Induction of cross-reactive cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses specific for HIV-1 gp120 using saponin adjuvant (QS-21) supplemented subunit vaccine formulations. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashala, O.; Amador, R. Safety, tolerability and immunogenicity of new formulations of the Plasmodium falciparum malaria peptide vaccine SPf66 combined with the immunological adjuvant QS-21. Vaccine 2002, 20, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathi, G.; Damani, P. Preclinical evaluation of the synthetic adjuvant QS-21 and its constituent isomeric saponins. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4260–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnandji, S.T. First results of phase 3 trial of RTS, S/AS01 malaria vaccine in African children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellas, B.; Black, R. Long-term follow-up of patients immunized with AN1792: Reduced functional decline in antibody responders. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2009, 6, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.; Adams, M.M. Synthesis of QS-21-xylose: Establishment of the immunopotentiating activity of synthetic QS-21 adjuvant with a melanoma vaccine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 47, 6395–6398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Eschen, K.; Morrison, R. The candidate tuberculosis vaccine Mtb72F/AS02A: Tolerability and immunogenicity in humans. Hum. Vaccines 2009, 5, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandepapelière, P.; Horsmans, Y. Vaccine adjuvant systems containing monophosphoryl lipid A and QS-21 induce strong and persistent humoral and T cell responses against hepatitis B surface antigen in healthy adult volunteers. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensil, C.R.; Patel, U. Separation and characterization of saponins with adjuvant activity from Quillaja saponaria Molina cortex. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.L.; Kensil, C.R. Isomerization and formulation stability of the vaccine adjuvant QS-21. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragupathi, G.; Gardner, J.R. Natural and synthetic saponin adjuvant QS-21 for vaccines against cancer. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2011, 10, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Tejada, A. Design, synthesis and evaluation of optimized saponin variants derived from the vaccine adjuvant QS-21. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 1359–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Xie, Y. Advances in saponin-based adjuvants. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1787–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Liao, J.X. Synthetic Investigation toward QS-21 analogues. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 8613–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, R.; Ruiz-de-Angulo, A. Replacing the Rhamnose-Xylose Moiety of QS-21 with Simpler Terminal Disaccharide Units Attenuates Adjuvant Activity in Truncated Saponin Variants. Chemistry 2021, 27, 4731–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirardello, M.; Ruiz-de-Angulo, A. Exploiting structure-activity relationships of QS-21 in the design and synthesis of streamlined saponin vaccine adjuvants. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound | Hemolysis Rate (%) | Compound | Hemolysis Rate (%) | Compound | Hemolysis Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QS-21 | 84.075 | L7 | 0.786 | L14 | 8.643 |
| L1 | 0.262 | L8 | 1.100 | L15 | 68.413 |
| L2 | 0.209 | L9 | 2.462 | L16 | 2.436 |
| L3 | 0.576 | L10 | 50.498 | L17 | 1.572 |
| L4 | 0.786 | L11 | 32.740 | L18 | 4.164 |
| L5 | 2.252 | L12 | 59.455 | ||
| L6 | 1.467 | L13 | 4.924 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, W.; Wang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, G. Design and Synthesis of Immunoadjuvant QS-21 Analogs and Their Biological Evaluation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020469
Yuan W, Wang Z, Zou Y, Zheng G. Design and Synthesis of Immunoadjuvant QS-21 Analogs and Their Biological Evaluation. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020469
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Wei, Ziming Wang, Yening Zou, and Guojun Zheng. 2024. "Design and Synthesis of Immunoadjuvant QS-21 Analogs and Their Biological Evaluation" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020469
APA StyleYuan, W., Wang, Z., Zou, Y., & Zheng, G. (2024). Design and Synthesis of Immunoadjuvant QS-21 Analogs and Their Biological Evaluation. Biomedicines, 12(2), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020469





