Exhaled Breath Analysis Detects the Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus from the Airways of Children with Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
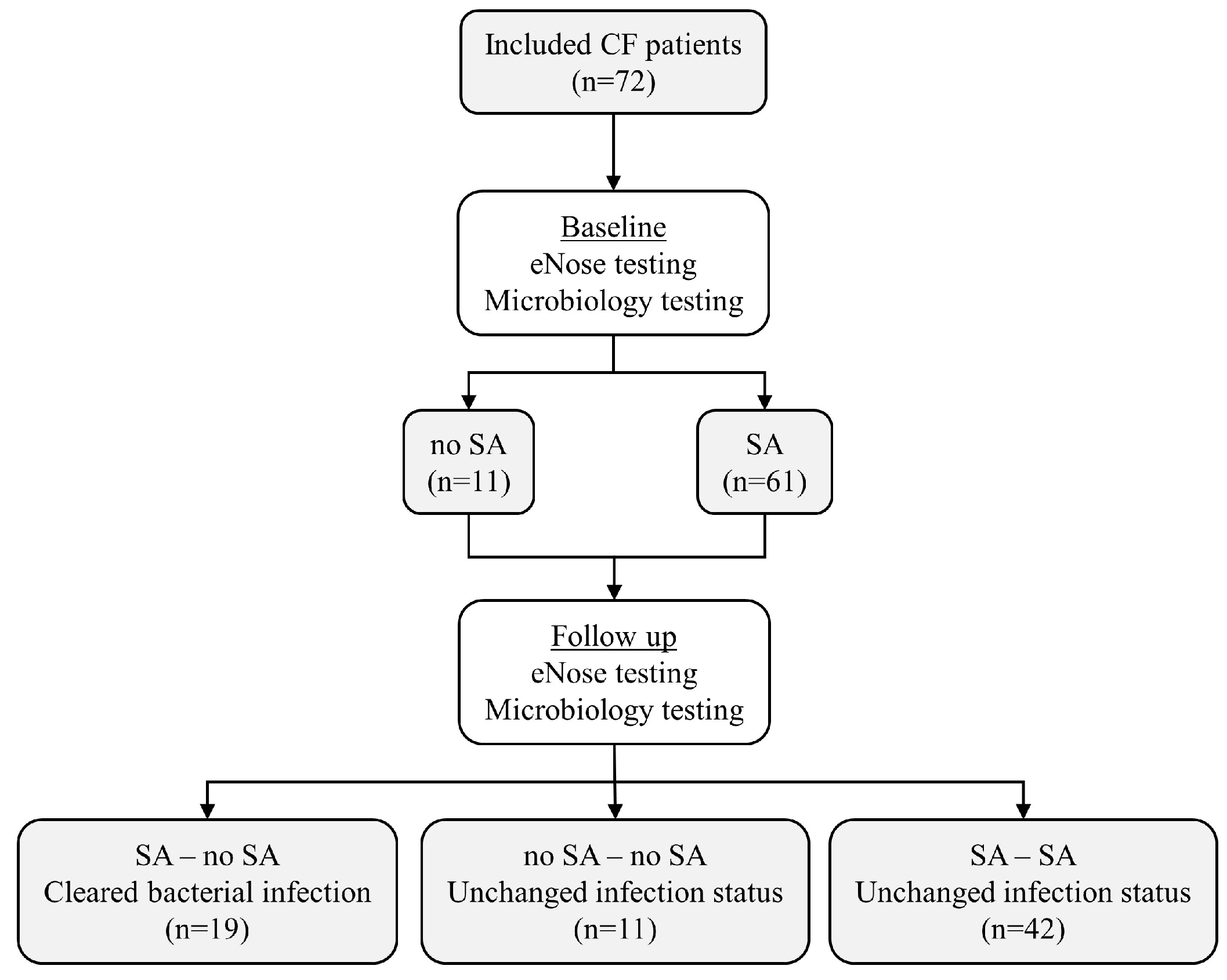
2.1. Design and Study Population
2.2. Exhaled Breath Analysis
2.3. eNose Respiratory Maneuvers
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
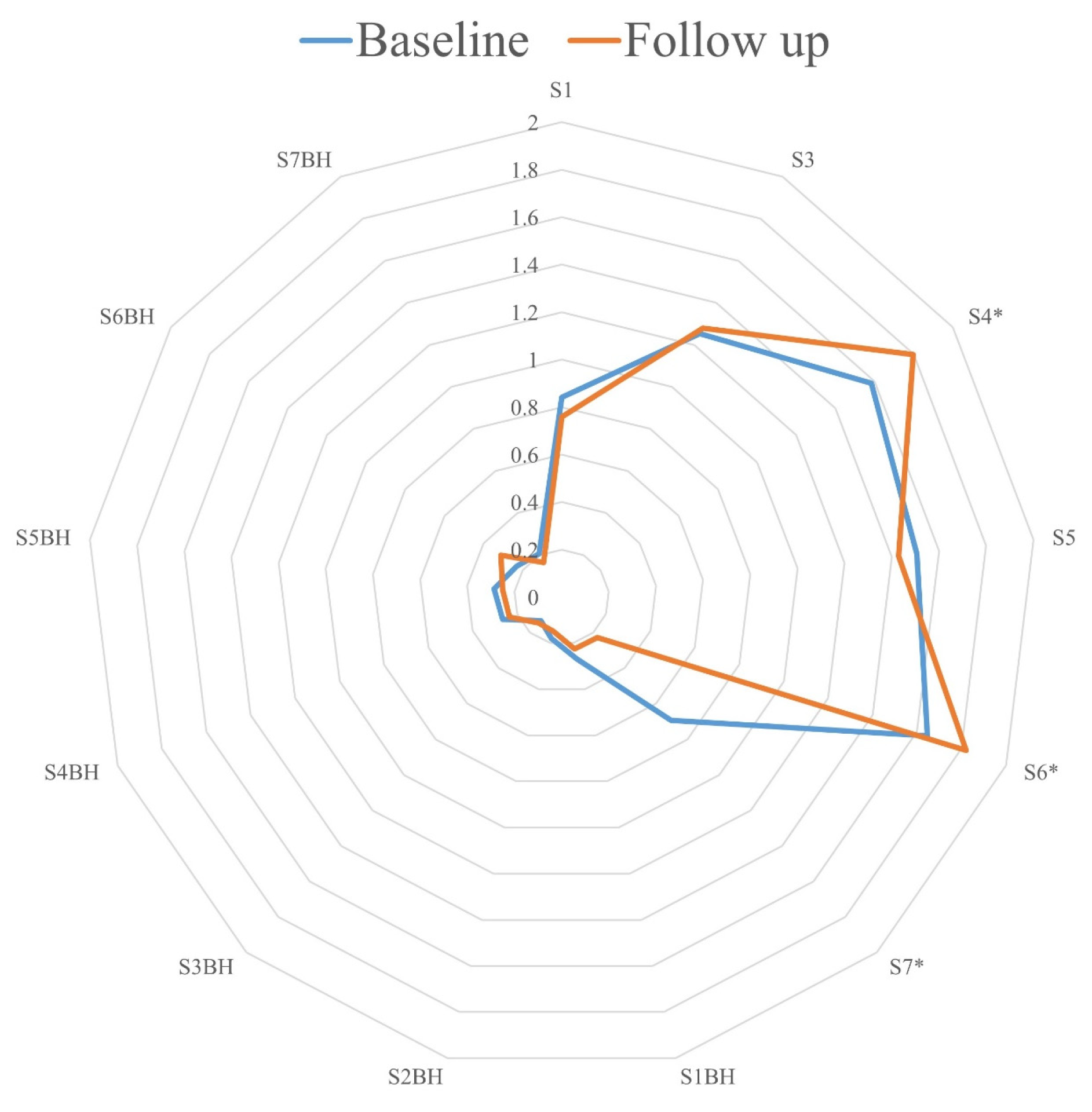
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grasemann, H.; Ratjen, F. Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naehrlich, L. The Changing Face of Cystic Fibrosis and Its Implications for Screening. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Bicker, J.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A.; Fortuna, A. Cystic fibrosis: Physiopathology and the latest pharmacological treatments. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, D.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Welsh, M.J. Origins of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssens, L.S.; Duchateau, J.; Casimir, G.J. CFTR protein: Not just a chloride channel? Cells 2021, 10, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Criq, V.; Gray, M.A. Role of CFTR in epithelial physiology. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.C.; Mall, M.A.; Gutierrez, H.; Macek, M.; Madge, S.; Davies, J.C.; Burgel, P.R.; Tullis, E.; Castaños, C.; Castellani, C.; et al. The future of cystic fibrosis care: A global perspective. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 65–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou-Suckow, Z.; Duerr, J.; Hagner, M.; Agrawal, R.; Mall, M.A. Airway mucus, inflammation and remodeling: Emerging links in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, S.T.; Dittrich, A.S.; Garratt, L.W.; Turkovic, L.; Frey, D.L.; Stick, S.M.; Mall, M.A.; Kicic, A. Interleukin-1 is associated with inflammation and structural lung disease in young children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.; Ranganathan, S.C.; Hart, E. Australian Respiratory Early Surveillance Team for Cystic Fibrosis (AREST CF). Staphylococcus aureus in early cystic fibrosis lung disease. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2013, 48, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B. Lung Infections Associated with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 194–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Pennoni, G.; Mencarini, V.; Palladino, N.; Peccini, L.; Principi, N. Antimicrobial treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with cystic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.N.; Fogarty, A.; McKeever, T.M.; Goss, C.H.; Rosenfeld, M.; Smyth, A.R. Early respiratory bacterial detection and antistaphylococcal antibiotic prophylaxis in young children with cystic fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2018, 15, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColley, S.A.; Schechter, M.S.; Morgan, W.J.; Pasta, D.J.; Craib, M.L.; Konstan, M.W. Risk factors for mortality before age 18 years in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2017, 52, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, J.; Rosenfeld, M.; McNamara, S.; Ramsey, B.; Gibson, R.L. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2002, 34, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, L.D.; Sterk, P.J.; Schultz, M.J. Volatile metabolites of pathogens: A systematic review. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robroeks, C.M.H.H.T.; van Berkel, J.J.B.N.; Dallinga, J.W.; Jöbsis, Q.; Zimmermann, L.J.; Hendriks, H.J.; Wouters, M.F.M.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; van de Kant, K.D.G.; van Schooten, F.-J.; et al. Metabolomics of volatile organic compounds in cystic fibrosis patients and controls. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangell, C.; Gard, S.; Douglas, T.; Park, J.; de Klerk, N.; Keil, T.; Brennan, S.; Ranganathan, S.; Robins-Browne, R.; Sly, P.D.; et al. Inflammatory responses to individual microorganisms in the lungs of children with cystic fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, A.; Kos, R.; de Vries, R.; Brinkman, P.; Dagelet, J.; Rutjes, N.; Majoor, C.; Terheggen-Lagro, S.; Weersink, E.; Bos, L.; et al. eNose Technology for Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. In Cystic Fibrosis and Bronchiectasis: Clinical and Mechanistic Studies; American Thoracic Society: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; p. A6181. [Google Scholar]
- Joensen, O.; Paff, T.; Haarman, E.G.; Skovgaard, I.M.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Nielsen, K.G. Exhaled breath analysis using electronic nose in cystic fibrosis and primary ciliary dyskinesia patients with chronic pulmonary infections. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, G.S.; McKone, E.F.; Pasta, D.J.; Millar, S.J.; Wagener, J.S.; Johnson, C.A.; Konstan, M.W. Sustained benefit from ivacaftor demonstrated by combining clinical trial and cystic fibrosis patient registry data. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisert, K.B.; Heltshe, S.L.; Pope, C.; Jorth, P.; Wu, X.; Edwards, R.M.; Radey, M.; Accurso, F.J.; Wolter, D.J.; Cooke, G.; et al. Restoring cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function reduces airway bacteria and inflammation in people with cystic fibrosis and chronic lung infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Herrera, J.; Krishnan, S.; Zain, M.; Greenberg, J.; Cataneo, R.N. Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 729, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, A.W.; Bos, L.D.; van der Schee, M.P.; van Schooten, F.-J.; Sterk, P.J. Exhaled molecular fingerprinting in diagnosis and monitoring: Validating volatile promises. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paff, T.; van der Schee, M.; Daniels, J.; Pals, G.; Postmus, P.; Sterk, P.; Haarman, E. Exhaled molecular profiles in the assessment of cystic fibrosis and primary ciliary dyskinesia. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2013, 12, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannier, M.A.G.E.; Van De Kant, K.D.G.; Jöbsis, Q.; Dompeling, E. Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of an electronic nose in children with asthma and cystic fibrosis. J. Breath. Res. 2019, 13, 036009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, E.; Licht, J.-C.; Wee, W.B.; Post, M.; Ratjen, F.; Grasemann, H. Exhaled Volatile Organic Compound Profiles Differ between Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, J.-C.; Seidl, E.; Slingers, G.; Waters, V.; de Vries, R.; Post, M.; Ratjen, F.; Grasemann, H. Exhaled breath profiles to detect lung infection with Staphylococcus aureus in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Davis, S.D.; Polineni, D.; Manion, M.; Rosenfeld, M.; Dell, S.D.; Chilvers, M.A.; Ferkol, T.W.; Zariwala, M.A.; Sagel, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis of primary ciliary dyskinesia. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, e24–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.M.; White, T.B.; Ren, C.L.; Hempstead, S.E.; Accurso, F.; Derichs, N.; Howenstine, M.; McColley, S.A.; Rock, M.; Rosenfeld, M.; et al. Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: Consensus guidelines from the cystic fibrosis foundation. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, S4–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Miller, M.R.; Thompson, B.; Aliverti, A.; Barjaktarevic, I.; Cooper, B.G.; Culver, B.; Derom, E.; Hall, G.L.; et al. ERS/ATS technical standard on interpretive strategies for routine lung function tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojevic, S.; Kaminsky, D.A.; Miller, M.R.; Thompson, B.; Aliverti, A.; Barjaktarevic, I.; Cooper, B.G.; Culver, B.; Derom, E.; Hall, G.L.; et al. Implications of adopting the Global Lungs Initiative 2012 all-age reference equations for spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Saiman, L.; Siegel, J. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Consensus Conference on Infection Control Participants. Infection control recommendations for patients with cystic fibrosis: Microbiology, important pathogens, and infection control practices to prevent patient-to-patient transmission. Am. J. Infect. Control 2003, 31, S1–S62. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, R.; Dagelet, Y.W.; Spoor, P.; Snoey, E.; Jak, P.M.; Brinkman, P.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.K.; Elskamp, F.; de Jongh, F.H.; et al. Clinical and inflammatory phenotyping by breathomics in chronic airway diseases irrespective of the diagnostic label. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.; Weldon, S.; Elborn, S.; Downey, D.G.; Taggart, C. The effect of CFTR modulators on airway infection in cystic fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotes, K.A.; Donaldson, S.H. Current state of CFTR modulators for treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 65, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensinck, M.M.; Carlon, M.S. One size does not fit all: The past, present and future of cystic fibrosis causal therapies. Cells 2022, 11, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerincx, A.H.; Geurts, B.P.; van Loon, J.; Tiemes, V.; Jansen, J.J.; Harren, F.J.M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Merkus, P.J.F.M.; Cristescu, S.M.; Buydens, L.M.C.; et al. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in cystic fibrosis patients using breath VOC profiles. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 046014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Heer, K.; van der Schee, M.P.; Zwinderman, K.; Berk, I.A.H.v.D.; Visser, C.E.; van Oers, R.; Sterk, P.J. Electronic nose technology for detection of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in prolonged chemotherapy-induced neutropenia: A proof-of-principle study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, D.; Griffin, M.; Nymon, A.; Koeppen, K.; Ashare, A. Throat Swabs and Sputum Culture as Predictors of P. aeruginosa or S. aureus Lung Colonization in Adult Cystic Fibrosis Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, J.-C.; Grasemann, H. Potential of the Electronic Nose for the Detection of Respiratory Diseases with and without Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Advances in electronic-nose technologies for the detection of volatile biomarker metabolites in the human breath. Metabolites 2015, 5, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Muller, M.; van der Noort, V.; Theelen, W.; Schouten, R.; Hummelink, K.; Muller, S.; Wolf-Lansdorf, M.; Dagelet, J.; Monkhorst, K.; et al. Prediction of response to anti-PD-1 therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer by electronic nose analysis of exhaled breath. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcaro, G.; Nasir, M.; Franchina, F.A.; Rees, C.A.; Aliyeva, M.; Daphtary, N.; Wargo, M.J.; Lundblad, L.K.A.; Hill, J.E. Breath metabolome of mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.; Brinkman, P.; Fens, N.; Dijkers, E.; Bootsma, S.; De Jongh, F.H.; Sterk, P.J. Integration of electronic nose technology with spirometry: Validation of a new approach for exhaled breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 046001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Schot, R.; Mertens, B.J.; Le Cessie, S.; Gauw, S.A.; Spanevello, A.; Resta, O.; Willard, N.P.; Vink, T.J.; Rabe, K.F.; et al. An electronic nose in the discrimination of patients with asthma and controls. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroletti, C.; Zetterquist, W.; Nordvall, L.; Alving, K. Evaluation of exhaled nitric oxide in schoolchildren at different exhalation flow rates. Pediatr. Res. 2002, 52, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stafler, P.; Davies, J.C.; Balfour-Lynn, I.M.; Rosenthal, M.; Bush, A. Bronchoscopy in cystic fibrosis infants diagnosed by newborn screening. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2011, 46, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Pennazza, G.; Carratu, P.; Resta, O. Electronic nose technology in respiratory diseases. Lung 2017, 195, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.; Sterk, P.J. eNose breathprints as composite biomarker for real-time phenotyping of complex respiratory diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 995–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographics | Total Cohort | Group 1 (No SA–No SA) | Group 2 (SA–SA) | Group 3 (SA–No SA) | p Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Included subjects | 72 | 11 | 42 | 19 | - |
| Male sex | 35 (48.6%) | 5 (45.5%) | 20 (47.6%) | 10 (52.6%) | 0.912 |
| Age in years | 13.8 (9.8–16.4) | 14.8 (10.5–16.2) | 15.0 (9.9–16.6) | 12.4 (9.4–15.6) | 0.254 |
| Preschool (< 5 years) | 4 (5.6%) | 1 (9.1%) | 2 (4.8%) | 1 (5.3%) | - |
| School age (6–12 years) | 28 (38.9%) | 3 (27.3%) | 15 (35.7%) | 10 (52.6%) | - |
| Adolescent (≥13 years) | 40 (55.6%) | 7 (63.6%) | 25 (59.5%) | 8 (42.1%) | - |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 18.6 (16.8–20.3) | 19.2 (17.0–21.9) | 18.5 (16.8–19.8) | 18.5 (15.8–20.7) | 0.707 |
| ppFEV1 | 93.0 (78.5–102.0) | 82.0 (59.0–10.6.0) | 92.5 (81.8–102.3) | 97.0 (90–102.0) | 0.296 |
| Pancreatic insufficiency | 64 (88.9%) | 9 (81.8%) | 36 (85.7%) | 19 (100%) | 0.186 |
| Time from baseline to follow-up in months | 8.0 (4.6–11.5) | 11.2 (6.8–19.2) | 8.1 (5.4–11.4) | 6.0 (2.0–10.2) | 0.077 |
| Treatment | |||||
| Saline, hypertonic | 38 (52.8%) | 7 (63.6%) | 19 (45.2%) | 12 (63.2%) | 0.317 |
| Salbutamol | 59 (81.9%) | 10 (90.9%) | 31 (73.8%) | 18 (94.7%) | 0.101 |
| Dornase alfa | 44 (61.1%) | 6 (54.5%) | 26 (61.9%) | 12 (63.2%) | 0.885 |
| Inhaled antibiotics | 10 (13.9%) | 1 (9.1%) | 6 (14.3%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.872 |
| Azithromycin | 8 (11.1%) | 3 (27.2%) | 4 (9.5%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0.159 |
| CFTR modulators | 27 (37.5%) | 5 (45.5%) | 15 (28.6%) | 7 (36.8%) | 0.836 |
| Ivacaftor | 4 (5.6%) | - (0%) | 3 (7.1%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0.653 |
| Ivacaftor/tezacaftor/elexacaftor | 11 (15.3%) | 2 (18.2%) | 6 (14.3%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.948 |
| Ivacaftor/lumacaftor | 8 (11.1%) | 1 (9.1%) | 5 (11.9%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0.961 |
| Ivacaftor/tezacaftor | 4 (5.6%) | 2 (18.2%) | 1 (2.4%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0.125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seidl, E.; Licht, J.-C.; de Vries, R.; Ratjen, F.; Grasemann, H. Exhaled Breath Analysis Detects the Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus from the Airways of Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020431
Seidl E, Licht J-C, de Vries R, Ratjen F, Grasemann H. Exhaled Breath Analysis Detects the Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus from the Airways of Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020431
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeidl, Elias, Johann-Christoph Licht, Rianne de Vries, Felix Ratjen, and Hartmut Grasemann. 2024. "Exhaled Breath Analysis Detects the Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus from the Airways of Children with Cystic Fibrosis" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020431
APA StyleSeidl, E., Licht, J.-C., de Vries, R., Ratjen, F., & Grasemann, H. (2024). Exhaled Breath Analysis Detects the Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus from the Airways of Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Biomedicines, 12(2), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020431






