Abstract
In the etiology of discogenic pain, attention is paid to the role of neurotrophic factors, which include classic neurotrophins (NTs). This study aimed to assess changes in the concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in the intervertebral discs (IVDs) of the lumbosacral (L/S) spine depending on the advancement of degenerative changes, pain severity, habits, and comorbidities. The study group included 113 patients who underwent microdiscectomy due to degenerative IVD disease of the L/S spine. The severity of degenerative IVD changes was assessed using the five-point Pfirrmann scale, and the pain intensity was assessed according to the visual analog scale (VAS). In turn, the control group included 81 participants from whom IVDs of the L/S section of the spine were collected post-mortem during forensic autopsy or organ donation. At the mRNA level, we noted NT-3 overexpression in the test samples compared with the controls (fold change (FC) = 9.12 ± 0.56; p < 0.05), while NT-4 transcriptional activity was decreased in the test samples compared with the controls (FC = 0.33 ± 0.07; p < 0.05). However, at the protein level, the concentrations of NT-3 (134 ± 5.78 pg/mL vs. 6.78 ± 1.17 pg/mL; p < 0.05) and NT-4 (316.77 ± 8.19 pg/mL vs. 76.92 ± 4.82 pg/mL; p < 0.05) were significantly higher in the test samples compared with the control samples. Nevertheless, the concentration of both proteins did not statistically significantly change depending on the advancement of degenerative changes and the pain intensity (p > 0.05). In addition, higher levels of NT-3 and NT-4 were noted in IVD samples from patients who consumed alcohol, smoked tobacco, were overweight/obese, or had comorbid diabetes compared with patients without these risk factors (p < 0.05). Our analysis confirmed that differences in the degenerative process of IVD, energy metabolism, and lifestyle are related to changes in the concentration profiles of NT-3 and NT-4.
1. Introduction
The intervertebral discs (IVDs) are intervertebral cartilage with flat and shallow fibrocartilage located between the facing surfaces of the vertebral bodies [1]. An analysis of the available literature indicates that degenerative IVD disease affects 90% of the general population [2]. Most patients experience this disease asymptomatically [2]. Approximately 85% of cases of IVD degeneration of the L/S spine occur in the L5–S1 space [3]. IVD degeneration can also be associated with age, gender, ethnic origin, the nature of work performed, genetic factors, the type of physical activity, and quality of life [3]. In the etiology of discogenic pain, attention is paid to the role of neurotrophic factors, which include classic neurotrophins (NTs), transforming growth factors, fibroblast growth factors, insulin-like growth factors, platelet-derived growth factors, neuropoietins, and a group of non-neuronal growth factors [4].
NTs are low-molecular-weight growth factors that regulate cellular processes that determine the proper functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system [5,6]. They are characterized by neurotrophic effects, i.e., stimulating and regulating neurogenesis [5,6]. It should be borne in mind that the amount of NTs synthesized and released is only sufficient for a certain number of neurons [5,6].
There are three families of factors with neurotrophic properties, namely, (1) classic NTs, (2) glial-cell-line-derived neurotrophic factor family ligands (GFLs), and (3) neurokines (neuropoietic neurokines). The first identified factor in the neurotrophin family was the nerve growth factor (NGF). This group also includes brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), NT-3, NT-4, NT-6, and NT-7, the latter two of which have not been identified in mammals [7,8,9].
All NTs are synthesized in the form of biologically inactive precursor proteins. The synthesized NTs contain a signal peptide (pre-protein) and a precursor protein (pro-protein). The formation of the precursor form of neurotrophin (proNT) is conditioned by cutting off the hydrophobic region of the pre-protein molecule at the N-terminus of the amino acid. It is currently believed that NGF and NT-3 arise from the duplication of one common gene, while BDNF and NT-4 come from a different “ancestor gene” [4,6].
The biological effects of NTs result from their interactions with receptors from the tropomyosin-related kinase (Trk) and p75NTR family, which are members of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) family [10,11,12]. However, all NTs can interact with the p75NTR receptor, which acts as a co-receptor for Trk receptors, or induce other signaling pathways independently of Trk receptors [10,11,12]. The binding of neurotrophin to the Trk receptor, for which it has the greatest affinity, causes the dimerization of the receptor, trans-autophosphorylation, and, consequently, the activation of signaling pathways, including extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (Ras/ERK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (Akt/PI3K), phospholipase C, gamma 1 pathway (PLC-γ1), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [10,11,12]. In turn, the interaction of neurotrophin with the p75NTR receptor results in the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NFkB) [10,11,12].
This results in a wide spectrum of complex effects of NTs. However, their role and significance in the etiopathogenesis of discogenic pain in the course of degenerative IVD disease is still not sufficiently understood [6].
Moreover, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, no studies have assessed the influences of gender, energy metabolism (i.e., overweight/obesity), lifestyle (i.e., smoking tobacco and alcohol consumption), and glycemic levels on the concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in patients with degenerative IVD disease of the L/S spine. Another reason for undertaking research in this area was our previous observations regarding the relationship between the concentrations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial-cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) in IVD samples from patients with degenerative IVD disease compared with control samples [13]. The research conducted so far indicates that smoking tobacco products significantly increases the risk of IVD degeneration [14,15,16,17]. Alcohol consumption has also been shown to adversely affect the development of IVD degeneration [18]. Moreover, alcohol significantly affects the perception of pain [19,20]. Overweight/obesity is another undoubted factor accelerating IVD degeneration [21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Moreover, overweight/obesity increases the risk of glycemic disorders, including the development of insulin resistance [28,29].
Therefore, this study aimed to assess changes in the concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in the IVDs of the L/S section of the spine depending on the advancement of degenerative changes, pain intensity, habits, lifestyle, and comorbidities.
2. Materials and Methods
This section builds upon our previous works in [13,30,31].
2.1. Ethical Considerations
This research was conducted per the guidelines of the 2013 Declaration of Helsinki on human experimentation. Data confidentiality and patient anonymity were consistently maintained. Patient-identifying information was removed before the database analysis. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. Consent to conduct this study was obtained from the Bioethics Committee operating at the District Medical Chamber in Krakow (no. 162/KBL/OIL/2021).
The collection of postmortem materials for research is regulated by the Act of 1 July 2005, on the collection, storage, and transplantation of cells, tissues, and organs (Journal of Laws of 2020, item 2134) [32].
2.2. Study Group
The study group consisted of 113 patients, including 55 women and 58 men, who underwent microdiscectomy due to degenerative IVD disease of the L/S spine. Qualification for the neurosurgical procedure included assessing each patient’s clinical condition, the period of severe IVD pain in the L/S spine (6–12 weeks), assessing the results of magnetic resonance imaging of the L/S spine, and a neurological examination. The degree of advancement of degenerative changes in the km was determined using the 5-point Pfirrmann scale [33]. Each patient was asked to mark the point corresponding to the pain intensity in the L/S spine on the 10-point visual analog scale (VAS). The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study group are presented in Table 1. They are the same as those shown in the previous works [30,31]. In total, 7 people had a primary education, 59 vocational, 39 secondary, and 8 higher. The details are provided in our previous work [34].

Table 1.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study group.
2.3. Control Group
The control group included 81 participants, including 53 women and 38 men, from whom IVDs of the L/S section of the spine were collected post-mortem during forensic autopsy or organ donation. The inclusion and exclusion criteria for the study group are presented in Table 2. They are the same as those shown in previous works [30,31].

Table 2.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for the control group.
To verify the absence of degenerative changes in the IVD samples, staining was performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) dyes according to the manufacturer’s recommendations (H&E staining kit; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA). Two independent investigators evaluated each slide.
2.4. Securing the Collected Material for Molecular Testing
The IVD samples collected from the study and control groups were thoroughly washed to remove blood and then placed in Eppendorf tubes with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to protect the material for ribonucleic acid extraction and protein isolation. The prepared materials were stored in low-temperature conditions (−80 °C) until the beginning of the molecular analyses.
2.5. NT-3 and NT-4 mRNA Expression Profiles in the IVDs of the L/S Spine Obtained from the Study and Control Groups Using the Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Technique Preceded by Reverse Transcription (RT-qPCR)
After qualitative and quantitative analysis of the extracted RNA, RT-qPCR was performed using complementary primer pairs (Genomed, Warsaw, Poland; Table 3). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphoaldehyde dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an endogenous control for the RT-qPCR reaction. Three technical replicates were performed in 50 µL of the reaction mixture for each biological replicate. The specificity of the RT-qPCR reaction was confirmed by determining the melting temperature (Tm) for each amplimer. Changes in gene expression were normalized relative to mRNA expression (using the 2−∆∆Ct method).

Table 3.
Nucleotide sequences of primers used in the RT-qPCR reaction for NT-3, NT-4, and GAPDH mRNA.
2.6. Assessment of the NT-3 and NT-4 Protein Concentration Profiles in the IVDs of the L/S Spine Obtained from the Study and Control Groups
The concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in the IVDs of degenerated and healthy patients were determined using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the anti-NT-3 antibody (Neurotrophin-3 Polyclonal Antibody, BS-0160R, STI, Poznań, Poland) and the anti-NT-4 antibody (Neurotrophin-4 Polyclonal Antibody, BS-0158R, STI, Poznań, Poland), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. GAPDH was used as the endogenous control in both assays (Santa Cruz Biotech, Dallas, TX, USA).
A detailed protocol for performing ELISA and Western blot tests has been provided in previous works [30,31].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the results was performed assuming a threshold of statistical significance of p < 0.05 in the Statistica 13 PL program (Statsoft, Kraków, Poland).
The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the compliance of the data distribution with the normal distribution, which was confirmed. Therefore, parametric methods, i.e., Student’s t-test for independent groups or one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test, were used in the next stage of the statistical analysis. The homogeneity of variances was checked using Levene’s test.
3. Results
3.1. Expression Changes in the mRNA and Protein Levels of NT-3 and NT-4 in Control and Test Samples
First, the expression patterns of the NT-3 and NT-4 mRNA and the proteins they encode were compared between the examined and control samples. The overexpression of NT-3 was noted in the tested samples compared with the control samples, both at the mRNA and protein levels (Figure 1; p < 0.05). In turn, a decrease in NT-4 expression at the mRNA level was demonstrated in the tested samples, along with a significantly higher concentration of NT-4 protein, compared with the control samples (Figure 1; p < 0.05).
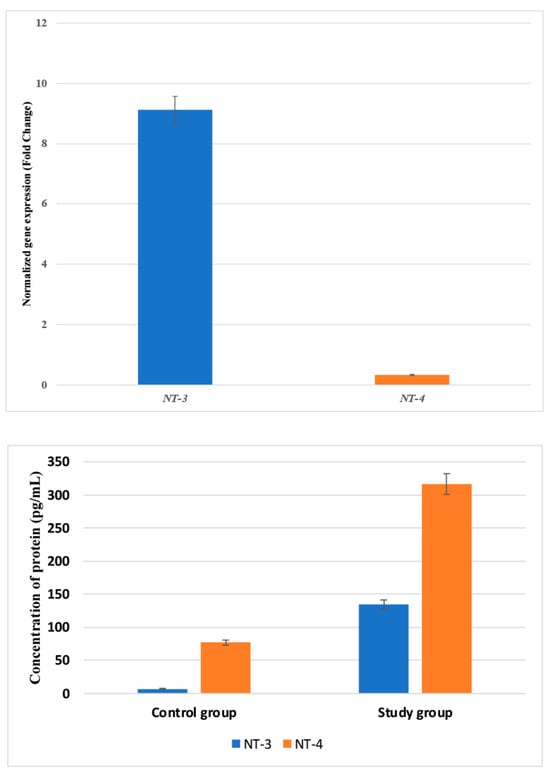
Figure 1.
Variances in the expression patterns of NT-3 and NT-4 at the mRNA and protein levels in the study and control groups. NT-3, neurotrophin-3; NT-4, neurotrophin-4. Data are presented as means with standard deviation.
3.2. Concentrations of mRNA and Protein of NT-3 and NT-4 in Control and Examined Samples, Considering the Stage of Radiological Degenerative Changes in IVDs according to the Pfirrmann Scale
The IVD samples were assessed depending on the radiological advancement of the degenerative changes (Table 3). Based on the statistical analysis, statistically significant differences were noted in the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 mRNA and proteins depending on the stage of degenerative changes (Table 4; p < 0.05), with the highest NT-3 expression observed in IVD samples representing stage 3 lesions according to the Pfirrmann scale (Table 4; p < 0.05).

Table 4.
Concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in intervertebral discs of the L/S section taken from the study and control groups determined using an ELISA test.
The silencing of the transcriptional activity of NT-4 was demonstrated at the mRNA level, with the lowest expression for this transcript recorded in samples representing grades 2 and 4 of radiological advancement of lesions according to the Pfirrmann scale (Table 4). At the protein level, the highest concentration of NT-4 was found in IVD samples representing stage 4 degenerative changes according to the Pfirrmann scale (Table 4; p < 0.05).
The expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 at both the mRNA and protein levels did not differ significantly between IVD samples with degeneration grades of 3 and 4 according to the Pfirrmann scale (Table 4; p > 0.05).
3.3. The Concentrations of mRNA and Protein of NT-3 and NT-4 in the Tested Samples Depending on the Pain Degree Measured with the VAS
Then, we assessed whether the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 at the mRNA and protein levels significantly changed depending on the pain severity (Table 5). The analysis of variance (ANOVA) did not show significant changes in the NT-3 and NT-4 mRNA expression profiles depending on the pain intensity measured with the VAS (Table 5; p > 0.05). Overexpression of NT-3 mRNA was noted, regardless of the pain intensity, while expression silencing was found for NT-4 mRNA.

Table 5.
Concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 in the intervertebral discs of the L/S section affected by the degenerative process depending on the degree of pain felt.
The ANOVA did not show significant changes in the concentration of both proteins depending on the degree of pain experienced by the patient (Table 3; p > 0.05). However, the highest concentration of NT-3 was recorded in the group of patients declaring a pain intensity at level 5, and in the case of NT-4, at levels 5 and 6 (Table 3). Moreover, the concentration of NT-3 could not be determined for pain intensities of grades 2 and 3, and the concentration of NT-4 was below the detection threshold for grades 2–4 according to the VAS (Table 5; p > 0.05).
3.4. Variances in the Expression Profiles of NT-3 and NT-4 at the mRNA and Protein Levels in IVD Samples Obtained from the Study and Control Groups
In the next step, we analyzed whether the expression profiles of NT-3 and NT-4 at the mRNA and protein levels were dependent on gender, BMI, co-occurrence of diabetes, alcohol consumption, and smoking (Table 6; p < 0.05). We noted significantly higher expressions of both analyzed NTs in obese compared with overweight (Table 6; p < 0.05) and normal-body-weight (Table 6; p < 0.05) patients; patients with concomitant diabetes (Table 6; p < 0.05); patients consuming alcohol compared with those who did not consume it (Table 6; p < 0.05); and patients smoking tobacco products compared with those who did not declare smoking tobacco (Table 6; p < 0.05). We did not confirm whether the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 in patients with IVD degeneration were gender-dependent (Table 6; p > 0.05).

Table 6.
The expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 at the mRNA and protein levels in IVD samples obtained from the study group.
3.5. Regression Analysis of Variables Potentially Associated with BDNF, GDNF, and GAP-43 Levels in IVDs and Serum Samples from the Study Groups
In the final step, linear and multiple regression analyses of the clinical variables were performed to determine the associations with NT-3 and NT-4 expression, as shown in Table 7. A linear regression analysis considering one factor (predictor—age) showed no effect on the expressions of the NT-3 and NT-4 studied. In contrast, both regression analyses considering one or several predictors found the concentrations of NT-3 and NT-4 to be correlated with BMI, smoking, and alcohol consumption (Table 7).

Table 7.
Univariate and multivariate regression analyses of the variables that may be associated with NT-3 and NT-4 levels determined in the degenerative IVDs.
4. Discussion
Increased NT expression in severely degenerated IVDs has been associated with chronic low back pain associated with the progression of disc degeneration [35].
It has been suggested that the involvement of NT-3 and NT-4 in the etiopathogenesis of degenerative IVD disease and the development and progression of the accompanying pain [36] is related to the signal transduction initiated by the interaction of NT-3 or NT-4 with TrkA, the TrkB receptor, TrkC, or p75NTR [37]. Given these observations, it can be assumed that NT-3 and NT-4 do not directly affect the occurrence of discogenic pain and the development of IVD degenerative disease of the L/S spine; rather, they exert an indirect effect, acting as activators of several signaling pathways and thereby changing the expression profiles of other neurotrophic factors that are more important in the neo-inversion process.
So far, research focusing on NT-3 and NT-4 has focused on improving the understanding of these NTs and the possibility of their therapeutic use in demyelinating and neurodegenerative diseases, depression, and mood disorders [38]. This observation is important in the context of degenerative IVD because patients with depression and anxiety disorders tend to somatize their symptoms, feeling them more than their clinical condition would indicate.
Therefore, depression and anxiety are associated with an increased perception of pain intensity, while a prolonged duration of acute pain leads to worsened mood [39,40]. This may be a reason for the lack of statistically significant changes in the NT-3 concentration depending on the degree of pain.
Nevertheless, the involvement of NT-3 in the etiology of discogenic pain is probable considering the high expression of the TrkC receptor demonstrated in neurons of the corticospinal tract, to which only NT-3 has affinity among NTs. However, this requires additional research [41,42].
Sahenk et al. [43] assessed the possibility of using NT-3 applied to muscle cells using an adenovirus vector in the treatment of Charcot–Marie–Tooth neuropathy [43]. The researchers obtained promising results in the field of peripheral nerve regeneration, although further analyses and research are necessary [43].
Research conducted by Omura et al. [44] indicates that the expression levels of BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4 vary depending on the type of damage that led to nerve damage [44].
NT-3 expression did not undergo any statistically significant changes, regardless of the cause of sciatic nerve damage, while the NT-4 level decreased after sciatic nerve transection [44]. Wang et al. [45] indicated that NT-4 may be a new effective drug with anti-inflammatory effects in the central nervous system by modulating the TrkB/PI3K/Akt/forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) pathway [45]. In addition, Omar et al. showed that they are crucial factors in the pathogenesis of neurological diseases and can also constitute new therapeutic targets in diseases of the central nervous system resulting from trauma, nerve degeneration, and the disruption of blood flow through blood vessels [46].
Moreover, we observed silencing of NT-4 expression at the mRNA level with simultaneous overexpression in IVDs obtained from patients in the study group compared with control samples. This may be due to several reasons, including the simultaneous influences of various factors on the transcript as well as their synergistic effects. Transcription and translation processes take place in different cell compartments, and both processes are not strictly synchronized [47,48]. Moreover, these processes are interconnected because the resulting mRNA molecule is a template for protein synthesis [49,50,51]. After transcription, mRNA can be translated many times [52,53], which may partially explain our results. It is also possible that the resulting NT-3 and NT-4 transcripts are degraded by, for example, microRNA (miRNA) molecules showing incomplete complementarity to the target mRNA, which reduces the mRNA pool constituting the template for protein synthesis [54,55]. Another potential reason for the observed changes may be the potentially extended half-lives of NT-3 and NT-4 proteins, which allow them to accumulate in the cells even when expression at the mRNA level is silenced, although this has not yet been assessed.
A novel aspect of our research Is the assessment of the expression profiles of NT-3 and NT-4 in patients with IVD degeneration, including metabolic disorders and habits. Some observations indicate that glycemic disorders and alcohol consumption influence the expression of these NTs. Ihara et al. reported a decrease in NT-3 mRNA expression in the muscle tissue of rats with pharmacologically induced diabetes compared with rats without induced diabetes. The researchers suggested that the reduction in NT-3’s transcriptional activity may be a marker of early damage to sensory neurons [56]. The research conducted by Li et al. produced compelling results regarding the influences of alcohol and tobacco consumption on the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 [57]. Li et al. showed an increase in the expressions of NT-4 and BDNF in a group of rats treated with naloxone, an opioid receptor antagonist that reverses the action of opioids and abolishes the reactions caused by them, with a simultaneous decrease in the expressions of NT-4 and BDNF in rats administered heroin compared with the control. The observed changes in the expression profiles of BDNF and NT-4 in this group of rats indicate that the mentioned neurotrophic factors have a neuroprotective effect on the nucleus accumbens (nAc) in the event of sudden cessation of chronic heroin use. Furthermore, an increase in the expression of NT-3 was noted in the group of rats addicted to heroin, alongside a decrease in expression in rats administered naloxone, which indicates the activation of adaptive mechanisms and the nAc striving for homeostasis [58]. Moreover, a significant increase in NT-3 expression was found in the hippocampus after chronic exposure to ethanol [59], which is consistent with our observations and may suggest that patients declaring alcohol consumption who have been drinking for a long time may have developed an addiction syndrome [59]. This hypothesis is confirmed by the observations of Requena-Ocaña et al., who found that BDNF and NT-3 act as factors compensating for cognitive impairment in the early stages of alcohol addiction, although these properties are lost at later stages. The NT-3 expression profile also depended on education in alcohol-dependent patients, i.e., NT-3 expression was decreased in patients with higher education, while NT-3 was overexpressed in people without higher education. This is likely due to impaired neurogenesis [60] and is consistent with our observations, where the majority of patients did not have higher education [34]. This is also confirmed by the research of Silva-Peña et al., who linked low education and alcohol abuse with reduced NT-3 and BDNF concentrations [61]. In addition, the research by Yang et al. indicates that smoking tobacco products is associated with reduced NT-3 expression in the rat hippocampus [62]. In contrast with the pattern reported by Yang et al. [62], we noted an overexpressed NT-3 expression profile in degenerated IVD samples obtained from smokers in our study. Kimata et al. noted an increase in the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 in the tears of atopic keratoconjunctivitis (AKC) patients who were passive smokers compared with a group of passive smokers without AKC and healthy volunteers, suggesting that passive smoking increases the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4 in tears, which, in turn, may exacerbate AKC. Moreover, significant changes in the expressions of these NTs occurred only in AKC patients who were passive smokers, indicating that AKC was the factor determining the changes in the expression patterns of NT-3 and NT-4 and the associated inflammation [63]. This suggests that although we found overexpression of NT-3 and NT-4 among patients with degenerative IVD disease who used tobacco products in our study, the main factor causing the changes in NT-3 and NT-4 expression is the degenerative IVD process, not just smoking.
Based on the study of the NT-3 and NT-4 concentration profiles, their involvement in the etiology of degenerative IVD disease of the L/S spine section seems probable, although further analyses are necessary. In addition, after a comparative analysis between our results and studies by other authors, it can be concluded that habits and lifestyles are associated with degenerative changes in IVDs. Our multiple regression analysis confirmed this.
In light of our thorough analysis of the existing literature, it becomes evident that our investigation into the expression profile of NT-3 and NT-4 within the degenerative disease IVD of the L/S spine marks a pioneering endeavor in this field. This study stands out for its innovative approach and significant contribution to understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying such conditions. Our findings not only add valuable insights but also set a new standard for future research in this area.
Our research has limitations. Firstly, comparing the obtained results with the observations of other researchers, particularly regarding the influences of lifestyle and habits on the expression profiles of NT-3 and NT-4, it is necessary to consider performing brain imaging and combining the obtained expression results with sociodemographic data. Moreover, the groups compared should be equal in number, especially concerning habits. Thirdly, other methods could be used to assess the expressions of NT-3 and NT-4, as well as to investigate and determine the mechanisms that modulate NT-3 and NT-4 expression.
5. Conclusions
Given the results of our research and the observations of other researchers, it seems that NT-3 and NT-4 do not directly affect the occurrence of discogenic pain and the development of degenerative IVD disease of the L/S spine; rather, they have an indirect effect, functioning as activators of several signaling pathways, which results in changes in the expression profiles of other more important neurotrophic factors in the neo-inversion process. Moreover, the results obtained in our study indicate that the degenerative process within the IVDs is the main factor determining the changes in NT-3 and NT-4 expression, not the use of tobacco products or alcohol consumption, although these factors accelerate the development of degenerative spine disease. However, further research is necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S. and D.G.; methodology, R.S. and D.G.; software, B.O.G.; validation, E.G. and F.B.; formal analysis, W.D.; investigation, R.S., D.S. and D.G.; data curation, R.S., D.S., D.G. and B.O.G.; writing—original draft preparation, D.G.; writing—review and editing, R.S. and B.O.G.; supervision, R.S. and B.O.G.; project administration, R.S. and B.O.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was conducted following the guidelines of the 2013 Declaration of Helsinki on human experimentation. Consent to conduct this study was obtained from the Bioethics Committee operating at the District Medical Chamber in Krakow (no. 162/KBL/OIL/2021 (11 June 2021)).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support this study’s findings are included in this article. The data will not be shared due to third-party rights and commercial confidentiality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gilbert, H.T.J.; Hodson, N.; Baird, P.; Richardson, S.M.; Hoyland, J.A. Acidic pH Promotes Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Acid-Sensing Ion Channel-3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnaz, S.; Capadona, C.; Wong, T.; Goldberg, J.L.; Medary, B.; Sommer, F.; McGrath, L.B., Jr.; Härtl, R. Fundamentals of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. World Neurosurg. 2022, 157, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oichi, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Saito, T. Pathomechanism of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. JOR Spine 2020, 3, e1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, L.; Domingues, O.; Zimmer, J.; Michel, T. Revisiting the Role of Neurotrophic Factors in Inflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D. Neurotrophic Factors: An Overview. In Neurotrophic Factors: Methods and Protocols; Skaper, S.D., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-1-4939-7571-6. [Google Scholar]
- Skup, M. Neurotrophins: Evolution of Concepts on Rational Therapeutic Approaches. Postep. Biochem 2018, 64, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.F.; Xapelli, S. Intervention of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Other Neurotrophins in Adult Neurogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1331, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragona, M.; Porcino, C.; Guerrera, M.C.; Montalbano, G.; Laurà, R.; Cometa, M.; Levanti, M.; Abbate, F.; Cobo, T.; Capitelli, G.; et al. The BDNF/TrkB Neurotrophin System in the Sensory Organs of Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Matsui, K.; Mizui, T. BDNF Pro-Peptide: Physiological Mechanisms and Implications for Depression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 377, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, C. Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Death in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, R.B.; Williams, K.S. The P75 Neurotrophin Receptor: At the Crossroad of Neural Repair and Death. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitre, M.; Mariga, A.; Chao, M.V. Neurotrophin Signalling: Novel Insights into Mechanisms and Pathophysiology. Clin. Sci. 2016, 131, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Sobański, D.; Bryś, K.; Och, W.; Garczarek, M.; Ulasavets, U.; Stasiowski, M.; Dammermann, W.; Strojny, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Effect of Glycemic Disorders and Habits on the Concentration of Selected Neurotrophic Factors in Patients with Lumbosacral Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.R.; Dhawale, A.A.; Brown, M.D. Association between Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Cigarette Smoking: Clinical and Experimental Findings. JBJS Rev. 2015, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, S.; Asfour, S.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Travascio, F. Effects of Tobacco Smoking on the Degeneration of the Intervertebral Disc: A Finite Element Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, F.; Wu, D.; Li, H. A Retrospective Study: Does Cigarette Smoking Induce Cervical Disc Degeneration? Int. J. Surg. 2018, 53, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraz, M.; Demir, E. Relationship of Lumbar Disc Degeneration with Hemoglobin Value and Smoking. Neurochirurgie 2020, 66, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampara, P.; Banala, R.R.; Vemuri, S.K.; Av, G.R.; Gpv, S. Understanding the Molecular Biology of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Potential Gene Therapy Strategies for Regeneration: A Review. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissoneault, J.; Lewis, B.; Nixon, S.J. Characterizing Chronic Pain and Alcohol Use Trajectory among Treatment-Seeking Alcoholics. Alcohol 2019, 75, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, R.; Mallah, N.; Nedjat, S.; Beasley, M.J.; Takkouche, B. Association between Alcohol Consumption and Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 129, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapetanakis, S.; Gkantsinikoudis, N.; Chaniotakis, C.; Charitoudis, G.; Givissis, P. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy for the Treatment of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Obese Patients: Health-Related Quality of Life Assessment in a 2-Year Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2018, 113, e638–e649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingg, R.W.; Kendall, R. Obesity, Vascular Disease, and Lumbar Disk Degeneration: Associations of Comorbidities in Low Back Pain. PMR 2017, 9, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan-Ekşi, E.E.; Kara, M.; Berikol, G.; Orhun, Ö.; Turgut, V.U.; Ekşi, M.Ş. A New Radiological Index for the Assessment of Higher Body Fat Status and Lumbar Spine Degeneration. Skelet. Radiol. 2022, 51, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, S.-U.; Choi, K.H. Relationship between Obesity and Lumbar Spine Degeneration: A Cross-Sectional Study from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2010–2012. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoi, A.M.; Pannu, G.; D’oro, A.; Buser, Z.; Pham, M.H.; Patel, N.N.; Hsieh, P.C.; Liu, J.C.; Acosta, F.L.; Hah, R. The Clinical Correlations between Diabetes, Cigarette Smoking and Obesity on Intervertebral Degenerative Disc Disease of the Lumbar Spine. Asian Spine J. 2017, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Ambrosio, L.; Ngo, K.; Vadalà, G.; Denaro, V.; Fan, Y.; Sowa, G.; Kang, J.D.; Vo, N. The Role of Type I Diabetes in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine 2019, 44, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Kokozidou, M.; Auffarth, A.; Schulze-Tanzil, G. The Relationship between Diabetes Mellitus Type II and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration in Diabetic Rodent Models: A Systematic and Comprehensive Review. Cells 2020, 9, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Type 2 Diabetes: Associations and Therapeutic Implications. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Gralewski, M.; Gładysz, D.; Bryś, K.; Garczarek, M.; Gadzieliński, M.; Marcol, W.; Sobański, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Evaluation of the Concentration of Growth Associated Protein-43 and Glial Cell-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Degenerated Intervertebral Discs of the Lumbosacral Region of the Spine. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Gładysz, D.; Gralewski, M.; Bryś, K.; Garczarek, M.; Gadzieliński, M.; Marcol, W.; Sobański, D.; Grabarek, B.O. Usefulness of Detecting Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration of the Lumbosacral Spine. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2023, 29, e938663-1–e938663-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustawa z Dnia 1 Lipca 2005 r. o Pobieraniu, Przechowywaniu i Przeszczepianiu Komórek, Tkanek i Narządów. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=wdu20051691411 (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Pfirrmann, C.W.; Metzdorf, A.; Zanetti, M.; Hodler, J.; Boos, N. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine 2001, 26, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszkiewicz, R.; Ulasavets, U.; Dobosz, P.; Drewniak, S.; Niewiadomska, E.; Grabarek, B.O. Assessment of Quality of Life, Pain Level and Disability Outcomes after Lumbar Discectomy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, L.; Wuertz-Kozak, K.; Le Maitre, C.L.; Wignall, F.; Richardson, S.M.; Hoyland, J.; Ruiz Wills, C.; González Ballester, M.A.; Neidlin, M.; Alexopoulos, L.G.; et al. Multiscale Regulation of the Intervertebral Disc: Achievements in Experimental, In Silico, and Regenerative Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, Z. Involvement of the G-Protein-Coupled Receptor 4 in the Increased Expression of RANK/RANKL/OPG System and Neurotrophins by Nucleus Pulposus Cells under the Degenerated Intervertebral Disc-Like Acidic Microenvironment. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e1328436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghanlou, A.E.; Yazdanian, M.; Roshani, S.; Demirli, A.; Seydyousefi, M.; Metz, G.A.S.; Faghfoori, Z. Neuroprotective Effects of Pre-Ischemic Exercise Are Linked to Expression of NT-3/NT-4 and TrkB/TrkC in Rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 194, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, A.S.; de Barros, J.L.V.M.; Teixeira, A.L. Is Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3): A Potential Therapeutic Target for Depression and Anxiety? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvez-Sánchez, C.M.; Montoro, C.I.; Duschek, S.; Reyes del Paso, G.A. Depression and Trait-Anxiety Mediate the Influence of Clinical Pain on Health-Related Quality of Life in Fibromyalgia. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelides, A.; Zis, P. Depression, Anxiety and Acute Pain: Links and Management Challenges. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Evolution of Nerve Growth Factor Inhibition in Clinical Medicine. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41584-020-00528-4 (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Carvalho, C.R.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Modern Trends for Peripheral Nerve Repair and Regeneration: Beyond the Hollow Nerve Guidance Conduit. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahenk, Z.; Galloway, G.; Clark, K.R.; Malik, V.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Kaspar, B.K.; Chen, L.; Braganza, C.; Montgomery, C.; Mendell, J.R. AAV1.NT-3 Gene Therapy for Charcot–Marie–Tooth Neuropathy. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, T.; Sano, M.; Omura, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Doi, M.; Sawada, T.; Nagano, A. Different Expressions of BDNF, NT3, and NT4 in Muscle and Nerve after Various Types of Peripheral Nerve Injuries. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.H. NT-4 Attenuates Neuroinflammation via TrkB/PI3K/FoxO1 Pathway after Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage in Neonatal Rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.A.; Kumar, J.; Teoh, S.L. Neurotrophin-3 and Neurotrophin-4: The Unsung Heroes That Lies behind the Meninges. Neuropeptides 2022, 92, 102226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 172, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P. Organization and Regulation of Gene Transcription. Nature 2019, 573, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Yang, F.; Jin, H.; Wang, X. The Regulation of Protein Translation and Its Implications for Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riba, A.; Di Nanni, N.; Mittal, N.; Arhné, E.; Schmidt, A.; Zavolan, M. Protein Synthesis Rates and Ribosome Occupancies Reveal Determinants of Translation Elongation Rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15023–15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michlewski, G.; Cáceres, J.F. Post-Transcriptional Control of miRNA Biogenesis. RNA 2019, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jens, M.; Rajewsky, N. Competition between Target Sites of Regulators Shapes Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, B.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, X. Real-Time Imaging of Translation on Single mRNA Transcripts in Live Cells. Cell 2016, 165, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Xu, M.; Tian, X.; Cai, S.; Zeng, S. Research Advances in the Detection of miRNA. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F. Integrative Analysis of miRNA-mRNA and miRNA-miRNA Interactions. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, e907420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, C.; Shimatsu, A.; Mizuta, H.; Murabe, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakao, K. Decreased Neurotrophin-3 Expression in Skeletal Muscles of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Neuropeptides 1996, 30, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, B.; Li, R.; Yin, D.; Wang, Y.; Liang, W. Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factors, Neurotrophin-3, and Neurotrophin-4 in the Nucleus Accumbens during Heroin Dependency and Withdrawal. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimbar, L.; Moleta, Y. Naloxone Effectiveness: A Systematic Review. J. Addict. Nurs. 2018, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.W.; Mooney, S.M. Chronic Exposure to Ethanol Alters Neurotrophin Content in the Basal Forebrain-Cortex System in the Mature Rat: Effects on Autocrine-Paracrine Mechanisms. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 60, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena-Ocaña, N.; Araos, P.; Flores, M.; García-Marchena, N.; Silva-Peña, D.; Aranda, J.; Rivera, P.; Ruiz, J.J.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.J.; et al. Evaluation of Neurotrophic Factors and Education Level as Predictors of Cognitive Decline in Alcohol Use Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Peña, D.; García-Marchena, N.; Alén, F.; Araos, P.; Rivera, P.; Vargas, A.; García-Fernández, M.I.; Martín-Velasco, A.I.; Villanúa, M.Á.; Castilla-Ortega, E.; et al. Alcohol-Induced Cognitive Deficits Are Associated with Decreased Circulating Levels of the Neurotrophin BDNF in Humans and Rats. Addict. Biol. 2019, 24, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-T.; Chang, C.-N.; Wu, J.H.; Chung, C.-Y.; Weng, H.-H.; Cheng, W.-C.; Lee, T.-H. Cigarette Smoking Decreases Neurotrophin-3 Expression in Rat Hippocampus after Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 60, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata, H. Passive Smoking Elevates Neurotrophin Levels in Tears. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).