Altered Expression of Intestinal Tight Junctions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pathogenetic Mechanism of Intestinal Hyperpermeability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Endotoxin and Cytokines Measurements
2.3. Histopathological Evaluation and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
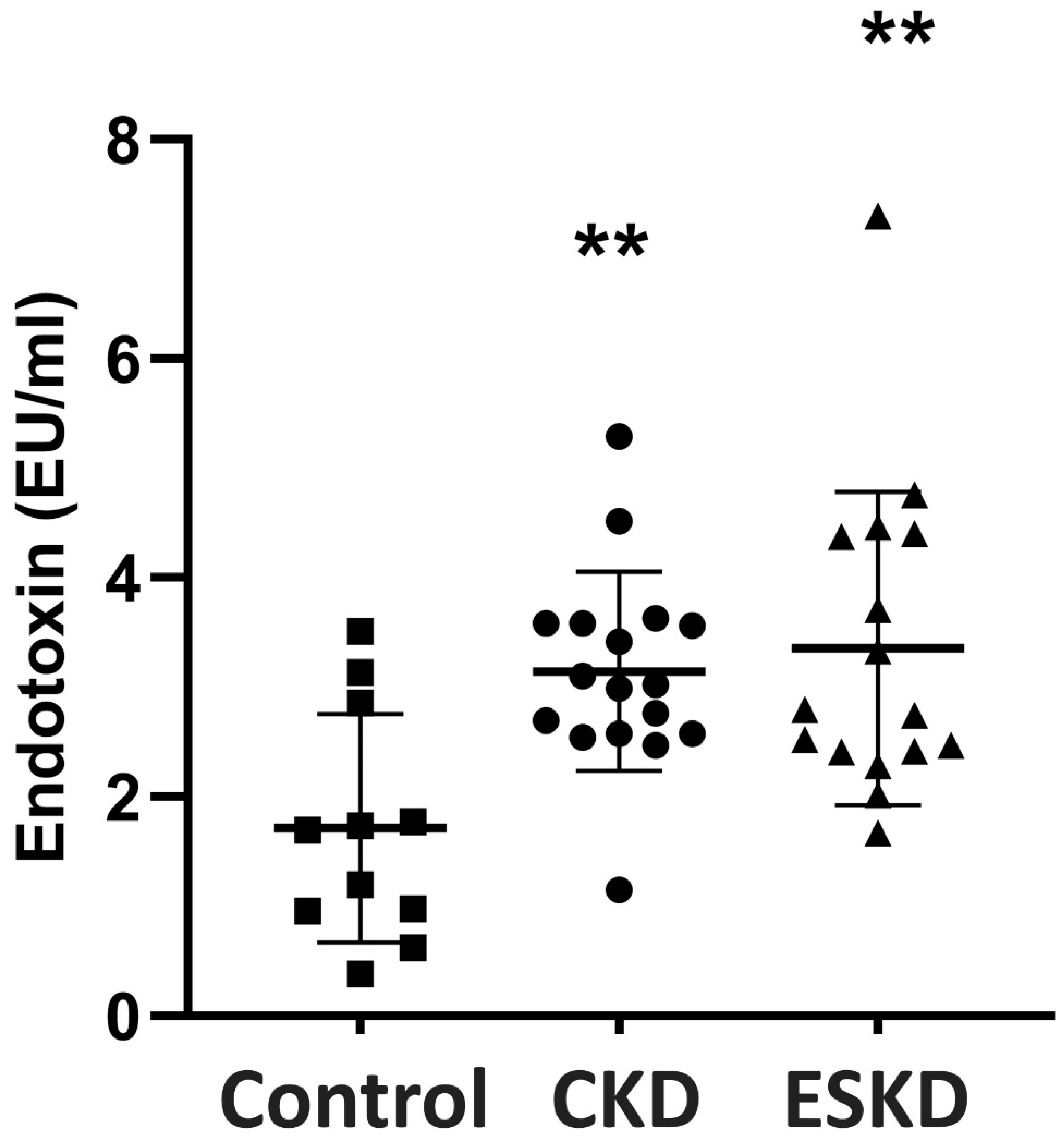
3.2. Endotoxin Concentrations
3.3. Cytokine Levels
3.4. Intestinal Histopathology
3.5. Immunohistochemistry for TJ Proteins and Intraepithelial CD3(+) T-Lymphocytes
3.6. Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anders, H.J.; Andersen, K.; Stecher, B. The intestinal microbiota, a leaky gut, and abnormal immunity in kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Interactions between inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in end-stage renal disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2003, 13, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.J.; Shapiro, L.; King, A.J.; Falagas, M.E.; Strom, J.A.; Dinarello, C.A. Plasma levels of IL-1 beta, TNF alpha and their specific inhibitors in undialyzed chronic renal failure, CAPD and hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1994, 45, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Stenvinkel, P. Persistent inflammation as a catalyst for other risk factors in chronic kidney disease: A hypothesis proposal. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4 (Suppl. S1), S49–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akchurin, O.M.; Kaskel, F. Update on inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberg, B.P.; McMenamin, E.; Lucas, F.L.; McMonagle, E.; Morrow, J.; Ikizler, T.A.; Himmelfarb, J. Increased prevalence of oxidant stress and inflammation in patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D. Gut microbial translocation in the pathogenesis of systemic inflammation in patients with end-stage renal disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2020–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, F.; Jiang, H.; Liu, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, Z.; Xie, L. Gut bacterial translocation may aggravate microinflammation in hemodialysis patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Duarte, J.B.; de Aguilar-Nascimento, J.E.; Nascimento, M.; Nochi, R.J. Bacterial translocation in experimental uremia. Urol. Res. 2004, 32, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Dure-Smith, B.; Miller, R.; Mirahmadi, M.K. Pathology of gastrointestinal tract in chronic hemodialysis patients: An autopsy study of 78 cases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1985, 80, 608–611. [Google Scholar]
- Denneberg, T.; Lindberg, T.; Berg, N.O.; Dahlqvist, A. Morphology, dipeptidases and disaccharidases of small intestinal mucosa in chronic renal failure. Acta Med. Scand. 1974, 195, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.; Magnusson, K.E.; Sundqvist, T.; Denneberg, T. Impaired intestinal barrier function measured by differently sized polyethylene glycols in patients with chronic renal failure. Gut 1991, 32, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balda, M.S.; Matter, K. Transmembrane proteins of tight junctions. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 11, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, E.E.; Lynch, R.D. The tight junction: A multifunctional complex. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2004, 286, C1213–C1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Osanai, M.; Murata, M.; Kojima, T.; Sawada, N. Transmembrane proteins of tight junctions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Van Itallie, C.M. Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Papageorgiou, I.; Charonis, A. Enterocytes’ tight junctions: From molecules to diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2011, 2, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madara, J.L. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis Award lecture. Pathobiology of the intestinal epithelial barrier. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 137, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Van Itallie, C.M. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269 Pt 1, G467–G475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Yuan, J.; Nazertehrani, S.; Ni, Z.; Liu, S. Chronic kidney disease causes disruption of gastric and small intestinal epithelial tight junction. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Goshtasbi, N.; Yuan, J.; Jellbauer, S.; Moradi, H.; Raffatellu, M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Uremic plasma impairs barrier function and depletes the tight junction protein constituents of intestinal epithelium. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Yuan, J.; Norris, K. Role of urea in intestinal barrier dysfunction and disruption of epithelial tight junction in chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ning, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, R.; Bai, M.; Sun, S. Specific alterations in gut microbiota in patients with chronic kidney disease: An updated systematic review. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Wong, J.; Pahl, M.; Piceno, Y.M.; Yuan, J.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Ni, Z.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Andersen, G.L. Chronic kidney disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Triantos, C.; Maroulis, I.; Gogos, C. The Role of the Gut Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. 2018, 11, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-K.; Lim, P.-S.; Jin, J.-S.; Wu, M.-Y.; Chen, C.-H. Impaired Gut Epithelial Tight Junction Expression in Hemodialysis Patients Complicated with Intradialytic Hypotension. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2670312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Worrell, R.T.; Pritts, T.A.; Montrose, M.H.; Watson, A.J.M.; Marchiando, A.M.; Bradford, E.; Shen, L.; Turner, J.R.; Kannan, K.B.; et al. Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: Reversible and irreversible damage imaged in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G187–G196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Piceno, Y.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Pahl, M.; Andersen, G.L.; Vaziri, N.D. Expansion of urease- and uricase-containing, indole- and p-cresol-forming and contraction of short-chain fatty acid-producing intestinal microbiota in ESRD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.L.; Savoj, J.; Nakata, M.B.; Vaziri, N.D. Altered microbiome in chronic kidney disease: Systemic effects of gut-derived uremic toxins. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P.; Meijers, B.K.; Bammens, B.R.; Verbeke, K. Uremic toxins originating from colonic microbial metabolism. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, S12–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bain, M.A.; Faull, R.; Fornasini, G.; Milne, R.W.; Evans, A.M. Accumulation of trimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide in end-stage renal disease patients undergoing haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadat, Y.R.; Niknafs, B.; Khatibi SM, H.; Ardalan, M.; Majdi, H.; Bahmanpoor, Z.; Abediazar, S.; Vahed, S.Z. Gut microbiota; an overlooked effect of phosphate binders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 868, 172892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalrymple, L.S.; Go, A.S. Epidemiology of acute infections among patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraya, N.; Wesson, D.E. Acid-base status and progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, C.-C.; Kwan, B.C.-H.; Chow, K.-M.; Lai, K.-B.; Chung, K.-Y.; Leung, C.-B.; Li, P.K.-T. Endotoxemia is related to systemic inflammation and atherosclerosis in peritoneal dialysis patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, C.W.; Harrison, L.E.; Eldehni, M.T.; Jefferies, H.J.; Szeto, C.C.; John, S.G.; Sigrist, M.K.; Burton, J.O.; Hothi, D.; Korsheed, S.; et al. Circulating endotoxemia: A novel factor in systemic inflammation and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Increased Intestinal Permeability and Decreased Barrier Function: Does It Really Influence the Risk of Inflammation? Inflamm. Intest. Dis. 2016, 1, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-B.; Mark, M.R.; Gray, A.; Huang, A.; Xie, M.H.; Zhang, M.; Goddard, A.; Wood, W.I.; Gurney, A.L.; Godowski, P.J. Toll-like receptor-2 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular signalling. Nature 1998, 395, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Stenvinkel, P.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hakim, R.M. The elephant in uremia: Oxidant stress as a unifying concept of cardiovascular disease in uremia. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1524–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, S.; Pergola, P.E.; Zager, R.A.; Vaziri, N.D. Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Chertow, G.M.; Devarajan, P.; Levin, A.; Andreoli, S.P.; Bangalore, S.; Warady, B.A. Chronic Inflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Role of Nrf2. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.-T.; Shen, L.; Zuo, L.; Shashikanth, N.; Ong, M.D.M.; Wu, L.; Zha, J.; Edelblum, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Inflammation-induced Occludin Downregulation Limits Epithelial Apoptosis by Suppressing Caspase-3 Expression. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, E.; Solomatina, L.; Zhuravleva, Y.; Sarapultsev, A. The Pathogenesis of End-Stage Renal Disease from the Standpoint of the Theory of General Pathological Processes of Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Ma, Y.; Yan, B.; Pei, W.; Wu, Q.; Ding, C.; Huang, C. The promotion mechanism of prebiotics for probiotics: A review. Front Nutr. 2022, 9, 1000517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andary, C.M.; Al, K.F.; Chmiel, J.A.; Gibbons, S.; Daisley, B.A.; Parvathy, S.N.; Vareki, S.M.; Bowdish, D.M.; Silverman, M.S.; Burton, J.P. Dissecting mechanisms of fecal microbiota transplantation efficacy in disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, S1471-4914(23)00284-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leceta, J.; Galindo-Villegas, J. Editorial: Overcoming challenges in mucosal immunity: 2022. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1327091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Control (n = 11) | Stage I–IV CKD (n = 17) | ESKD (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 49.7 ± 18.5 | 58.5 ± 12.5 | 57.7 ± 13.4 |
| Sex (males/females) | 5/7 | 10/7 | 11/5 |
| Urea (mL/dL) | 30 ± 3.9 | 63.8 ± 39 * | 123.5 ± 39 ** |
| Creatinine (mL/dL) | 0.75 ± 0.09 | 0.75 ± 0.4 * | 5.9 ± 2.3 ** |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 106.6 ± 19 | 56.5 ± 23.7 ** | <15 |
| Causes of CKD | |||
| Diabetic Nephropathy | N/A | 2 | 5 |
| Hypertensive Nephropathy | N/A | 0 | 4 |
| Glomerulonephritis | N/A | 13 | 2 |
| Interstitial Nephritis | N/A | 0 | 2 |
| Other | N/A | 2 | 1 |
| Unknown | N/A | 0 | 2 |
| CKD Classification | |||
| Stage I (eGFR ≥ 90) | N/A | 3 | 0 |
| Stage II (eGFR = 60–89) | N/A | 2 | 0 |
| Stage IIIA (eGFR = 45–59) | N/A | 7 | 0 |
| Stage IIIB (eGFR = 30–44) | N/A | 4 | 0 |
| Stage IV (eGFR = 15–29) | N/A | 1 | 0 |
| Stage V (eGFR < 15) | N/A | 0 | 16 |
| Renal replacement method | |||
| Hemodialysis | 10 | ||
| Peritoneal dialysis | 6 |
| Cytokine | Controls (n = 11) | Stage I–IV CKD (n = 17) | ESKD (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β (pg/mL) | 0 (0–0.53) | 0 (0–0) | 0 (0–0) |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 0.83 (0.57–1.85) | 10.36 (8.35–19.36) ** | 19.33 (0.58–59.43) ** |
| IL-8 (pg/mL) | 3.42 (2.5–6.94) | 41 (14.87–102) * | 126.3 (33.9–475) *** |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 0.28 (0.18–0.37) | 2.8 (0.96–4.23) *** | 1.85 (0.64–3.1) ** |
| TNF-a (pg/mL) | 0.41 (0–1.3) | 0 (0–4.7) | 0 (0–4) |
| Histopathological Features | Controls (n = 11) | Stage I–IV CKD (n = 17) | ESKD (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apoptotic body count | 10 (5–10) | 5 (5–10) | 7.5 (5–10) |
| Villous length (mm) | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.40 ± 0.13 | 0.34 ± 0.1 |
| Intraepithelial CD3+ lymphocytes/100 intestinal epithelial cells | 15 (15–20) | 5 (5–7.5) | 10 (5–17.5) |
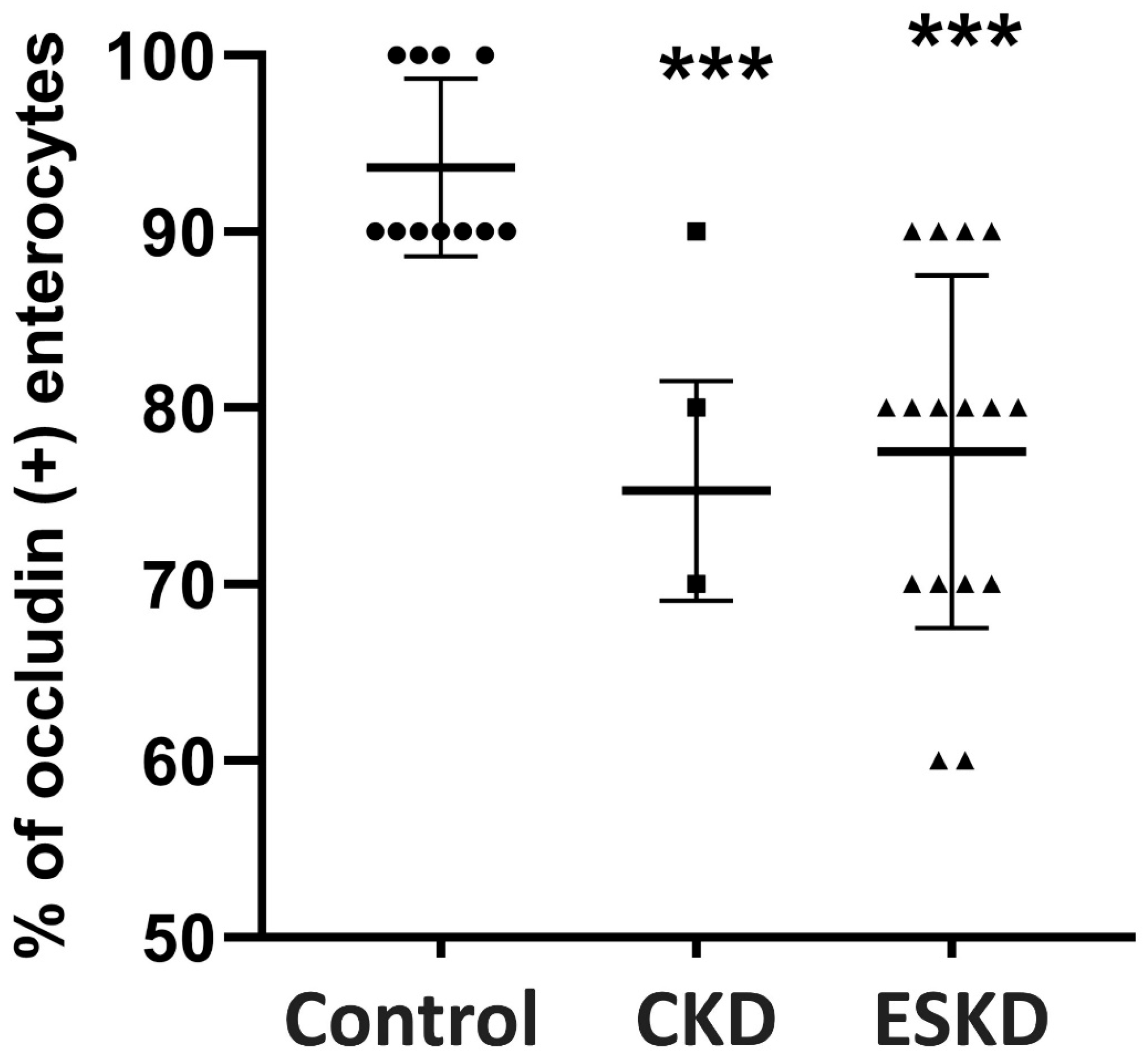
| Occludin Expression | Controls (n = 11) | CKD Stage I–IV (n = 17) | ESKD (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the villi | |||
| Τip | 91.8 ± 7.5 | 44.7 ± 25 ** | 53.7 ± 29 ** |
| Μiddle | 97.3 ± 4.7 | 84.7 ± 6.2 ** | 86.3 ± 7.2 * |
| Crypt | 99 ± 3 | 97 ± 5.9 | 93.1 ± 11.3 |
| Total expression | 93.6 ± 5 | 75.3 ± 6.2 ** | 77.5 ± 10 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgopoulou, G.-A.; Papasotiriou, M.; Bosgana, P.; de Lastic, A.-L.; Koufou, E.-E.; Papachristou, E.; Goumenos, D.S.; Davlouros, P.; Kourea, E.; Zolota, V.; et al. Altered Expression of Intestinal Tight Junctions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pathogenetic Mechanism of Intestinal Hyperpermeability. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020368
Georgopoulou G-A, Papasotiriou M, Bosgana P, de Lastic A-L, Koufou E-E, Papachristou E, Goumenos DS, Davlouros P, Kourea E, Zolota V, et al. Altered Expression of Intestinal Tight Junctions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pathogenetic Mechanism of Intestinal Hyperpermeability. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020368
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgopoulou, Georgia-Andriana, Marios Papasotiriou, Pinelopi Bosgana, Anne-Lise de Lastic, Eleni-Evangelia Koufou, Evangelos Papachristou, Dimitrios S. Goumenos, Periklis Davlouros, Eleni Kourea, Vasiliki Zolota, and et al. 2024. "Altered Expression of Intestinal Tight Junctions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pathogenetic Mechanism of Intestinal Hyperpermeability" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020368
APA StyleGeorgopoulou, G.-A., Papasotiriou, M., Bosgana, P., de Lastic, A.-L., Koufou, E.-E., Papachristou, E., Goumenos, D. S., Davlouros, P., Kourea, E., Zolota, V., Thomopoulos, K., Mouzaki, A., & Assimakopoulos, S. F. (2024). Altered Expression of Intestinal Tight Junctions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pathogenetic Mechanism of Intestinal Hyperpermeability. Biomedicines, 12(2), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020368











