Cell States and Interactions of CD8 T Cells and Disease-Enriched Microglia in Human Brains with Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Samples
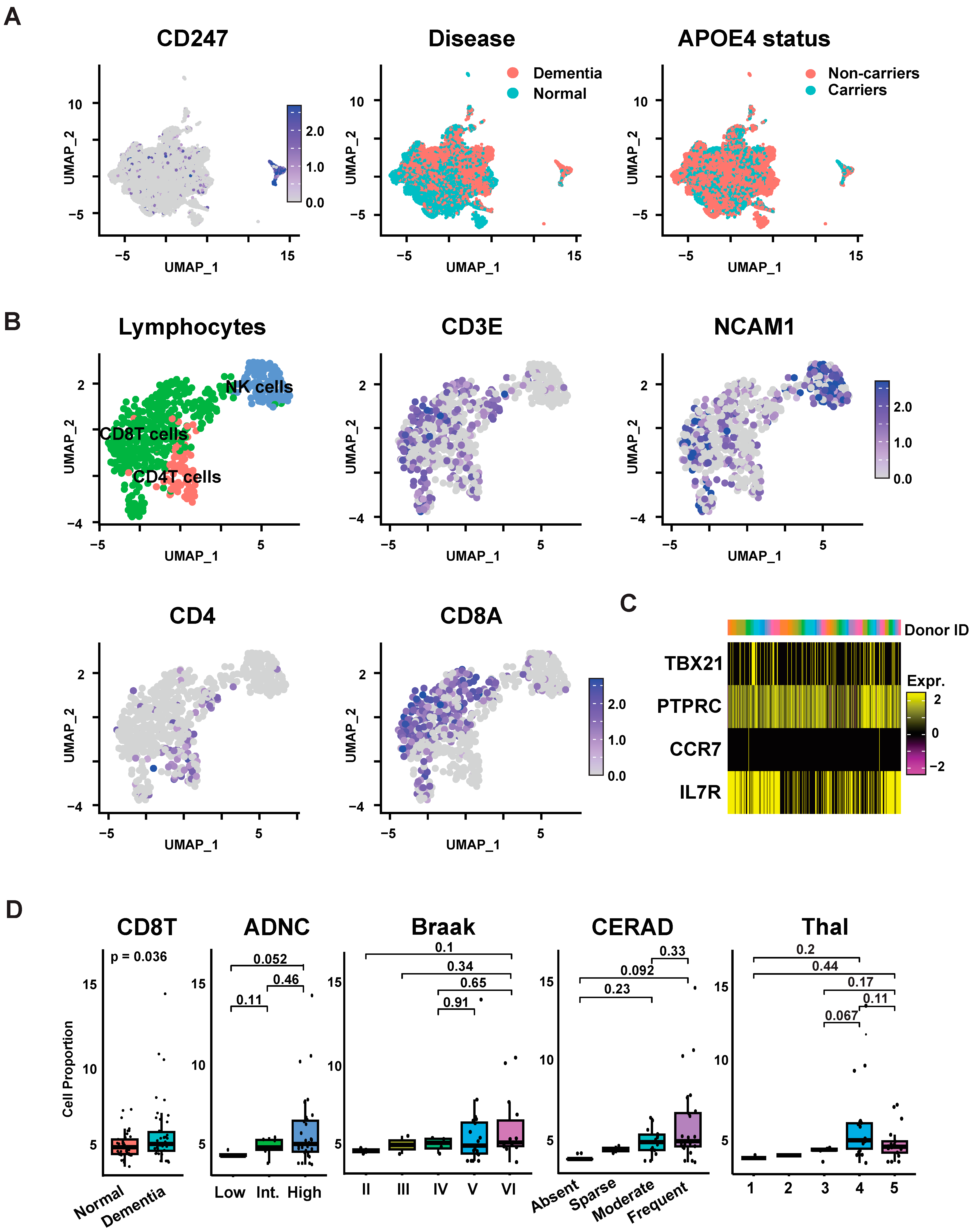
2.2. Annotation of Lymphocyte Subclasses and States
2.3. Lymphocytes Cell Proportion and Differential Gene Expression Analysis
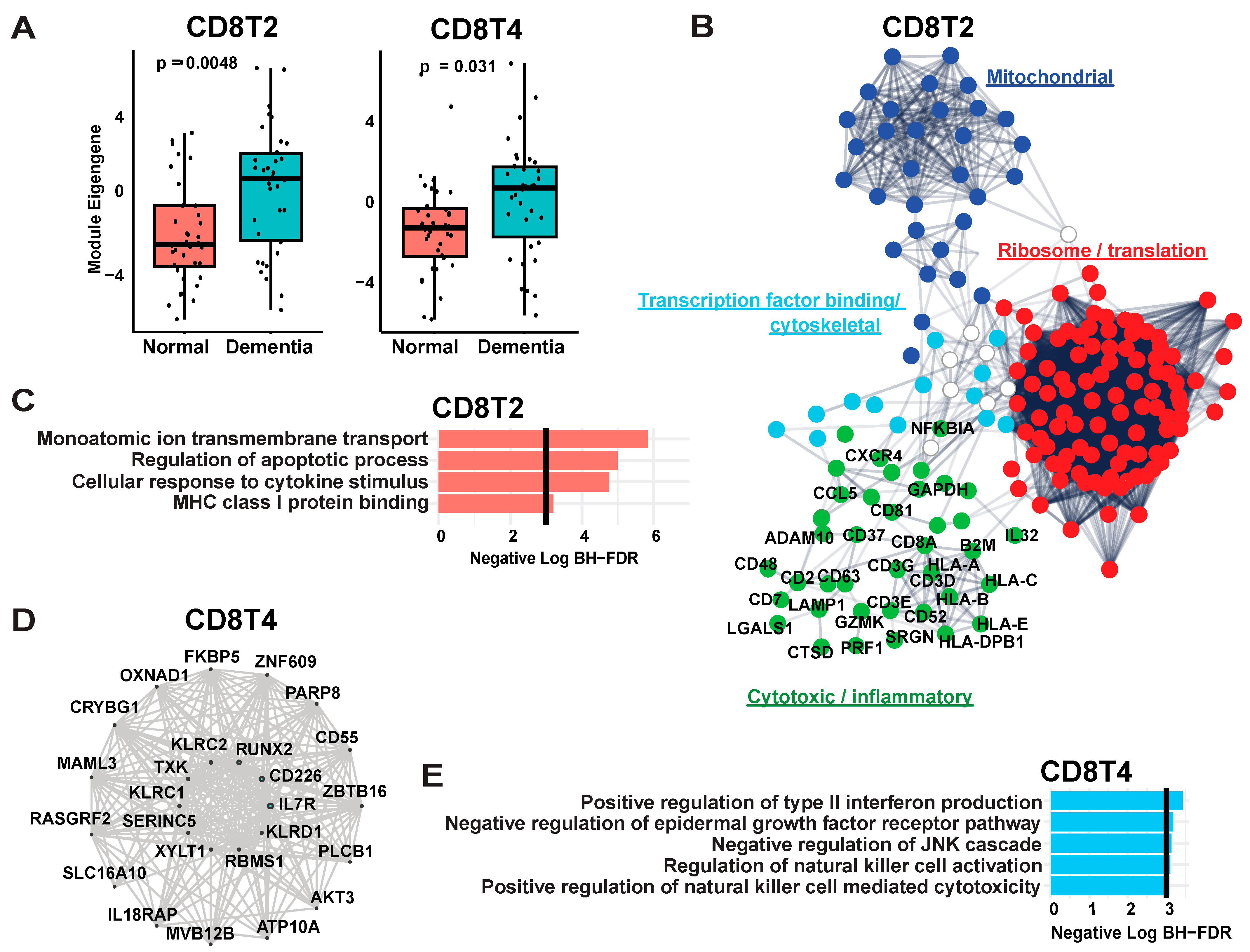
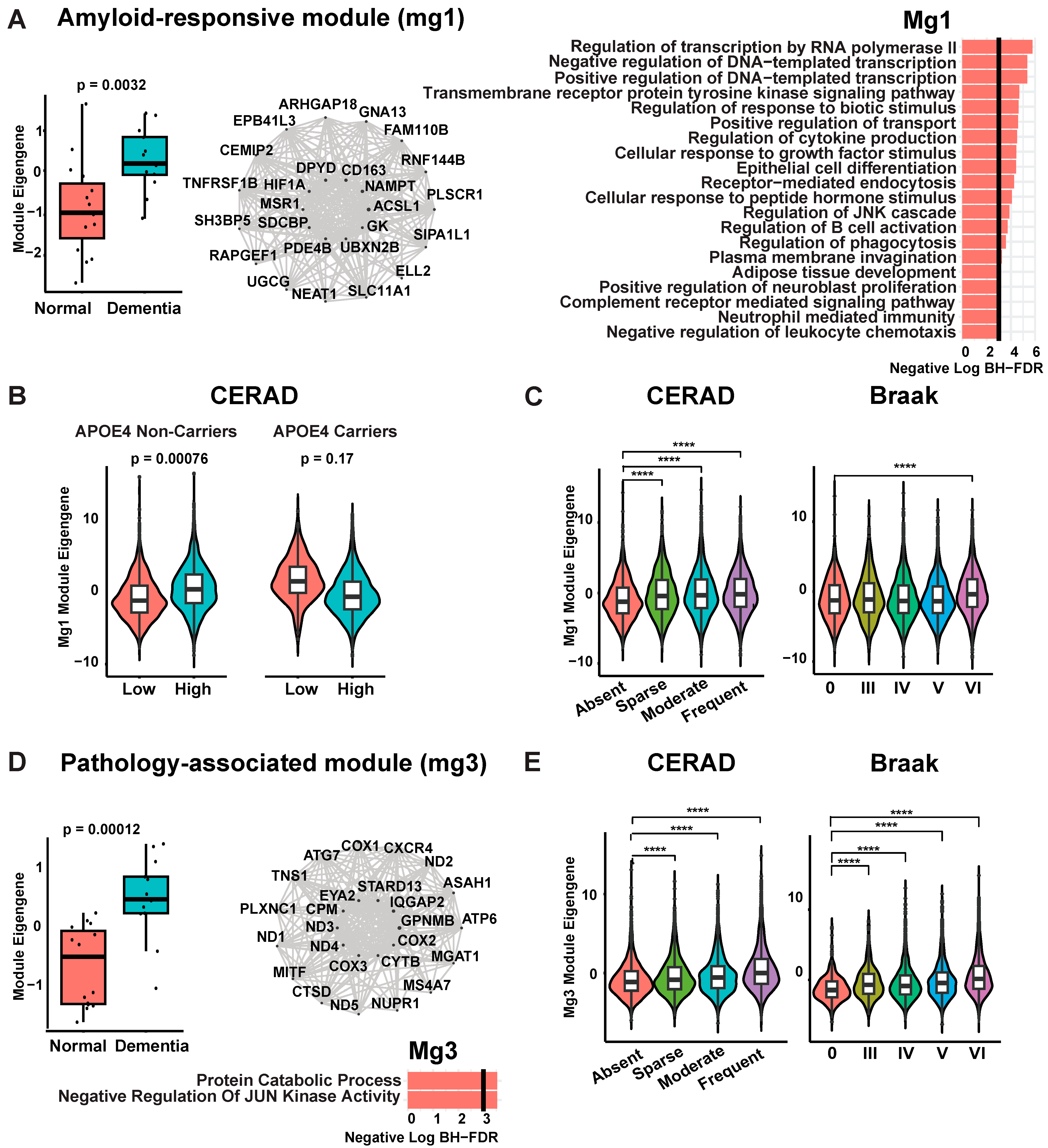
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis of Lymphocytes and Microglia
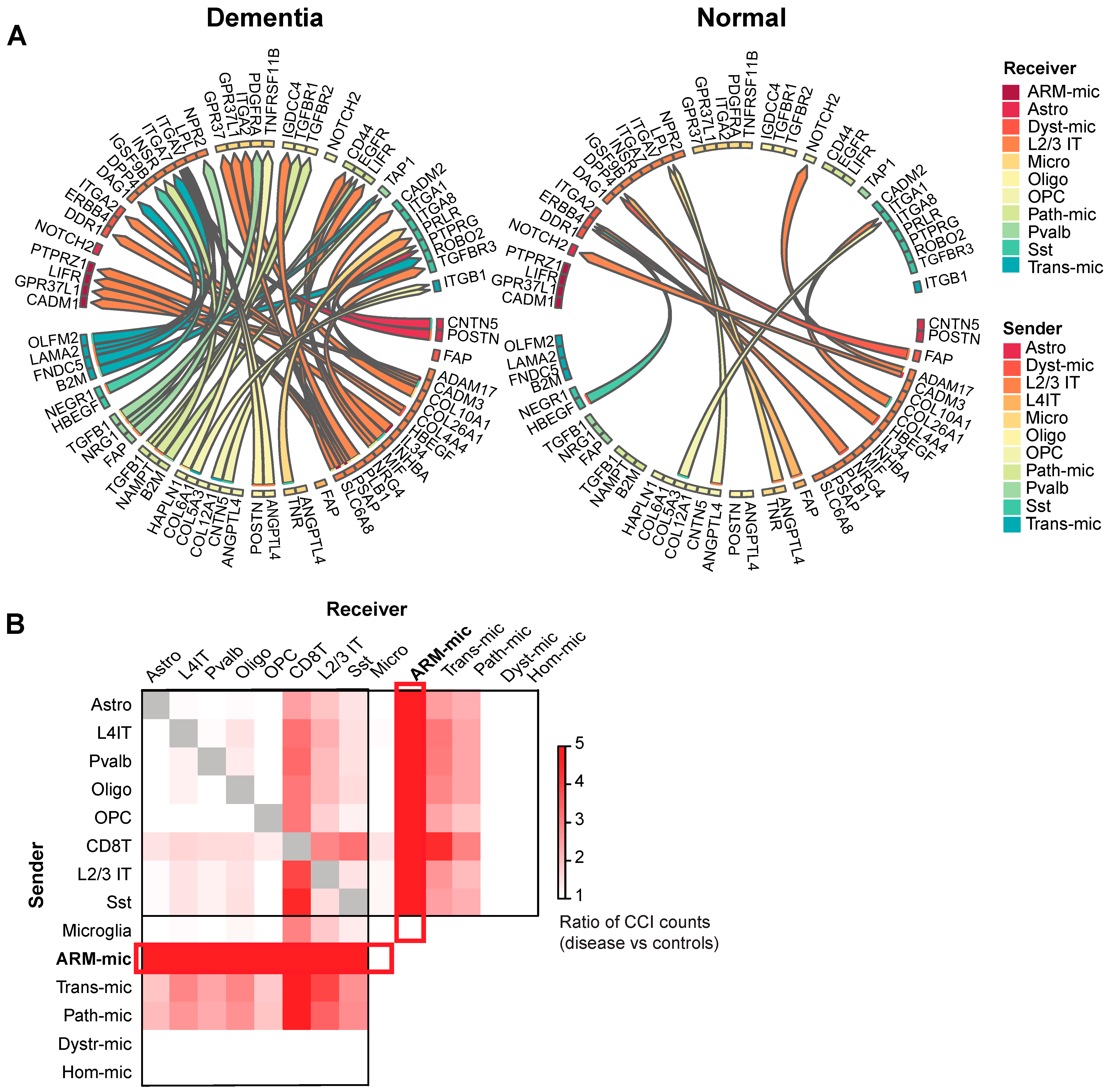
2.5. Cell–Cell Interaction Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Brain-Tissue-Associated Lymphocytes
3.1.1. Differential Composition Analysis and Marker-Based Annotation Demonstrate an Increase in Effector Memory CD8 T Cells in Samples with AD Dementia
3.1.2. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis of CD8 T Cells Reflects Terminal Differentiation and Multiple Signaling States
3.2. Characterization of Disease-Associated Microglia
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis of Microglia Defines Distinct Beta-Amyloid Responsive and Pathology-Associated Microglia That Reproduce Validated Markers and Disease Traits
3.3. Cell–Cell Interaction Analysis
3.3.1. MultiNicheNet Reveals Markedly Increased CCI Involving Depleted Neurons and Beta-Amyloid Responsive Microglia in AD Dementia Brain Samples
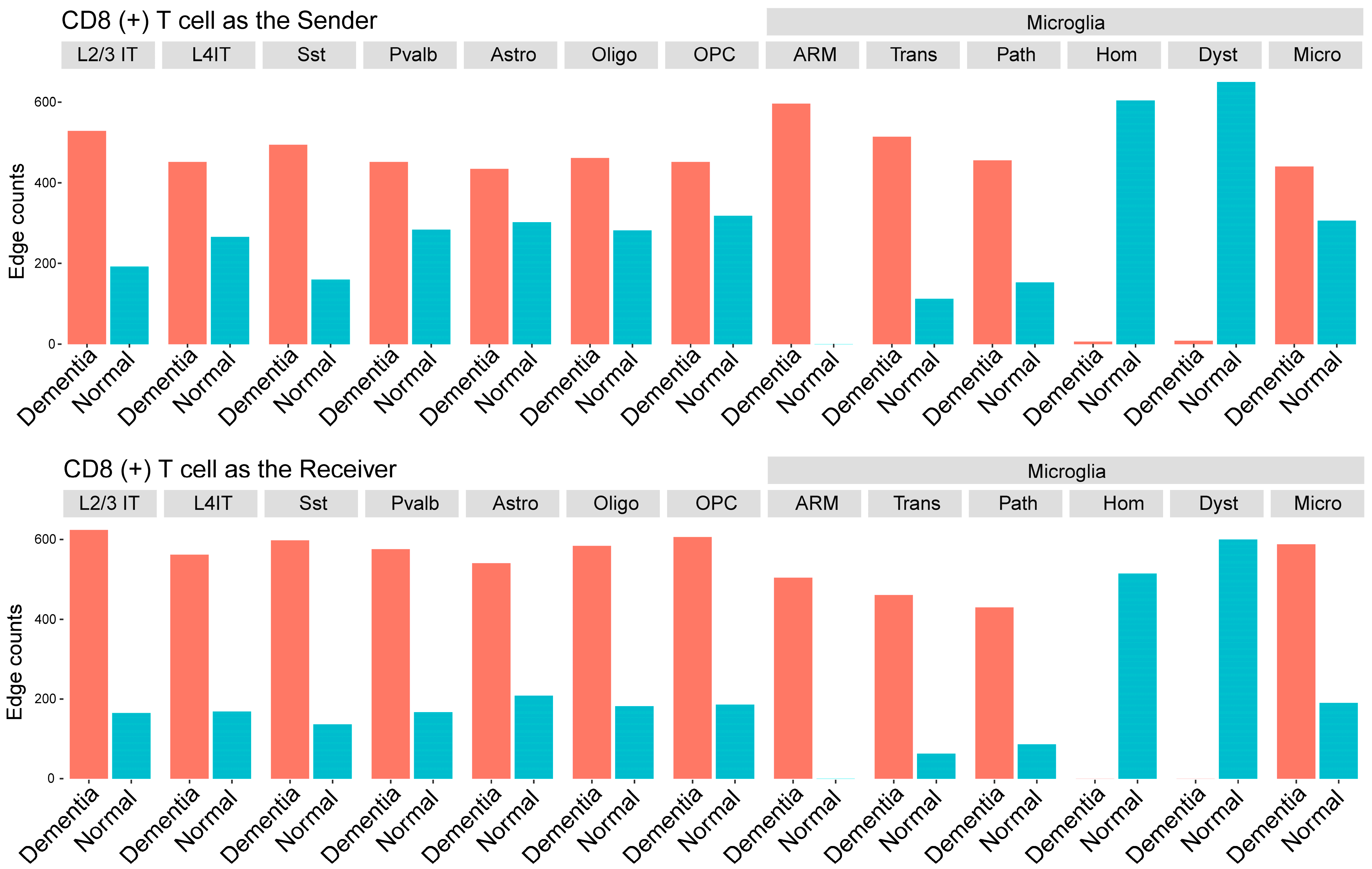
3.3.2. Disease-Associated CCIs Involving CD8 T Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Leading Edge Review Alzheimer Disease: An Update on Pathobiology and Treatment Strategies. Cell 2019, 179, 312–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.J.; Xiong, C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Fagan, A.M.; Goate, A.; Fox, N.C.; Marcus, D.S.; Cairns, N.J.; Xie, X.; Blazey, T.M.; et al. Clinical and Biomarker Changes in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, R.; Wojtas, A.; Bras, J.; Carrasquillo, M.; Rogaeva, E.; Majounie, E.; Cruchaga, C.; Sassi, C.; Kauwe, J.S.K.; Younkin, S.; et al. TREM2 Variants in Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, T.; Stefansson, H.; Steinberg, S.; Jonsdottir, I.; Jonsson, P.V.; Snaedal, J.; Bjornsson, S.; Huttenlocher, J.; Levey, A.I.; Lah, J.J.; et al. Variant of TREM2 Associated with the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingworth, P.; Harold, D.; Sims, R.; Gerrish, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Abraham, R.; Hamshere, M.L.; Pahwa, J.S.; Moskvina, V.; et al. Common Variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP Are Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haage, V.; De Jager, P.L. Neuroimmune Contributions to Alzheimer’s Disease: A Focus on Human Data. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3164–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeer, P.L.; Itagaki, S.; Tago, H.; McGeer, E.G. Reactive Microglia in Patients with Senile Dementia of the Alzheimer Type Are Positive for the Histocompatibility Glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci. Lett. 1987, 79, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, M.; Menon, V.; Habib, N.; Taga, M.F.; Ma, Y.; Yung, C.J.; Cimpean, M.; Khairallah, A.; Coronas-Samano, G.; Sankowski, R.; et al. Single Cell RNA Sequencing of Human Microglia Uncovers a Subset Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Wang, K.; Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Miao, Z.; Azevedo, J.A.; Suh, E.R.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Choi, D.; Roeder, K.; et al. APOE and TREM2 Regulate Amyloid-Responsive Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Davey, K.; Tsartsalis, S.; Khozoie, C.; Fancy, N.; Tang, S.S.; Liaptsi, E.; Weinert, M.; McGarry, A.; Muirhead, R.C.J.; et al. Diverse Human Astrocyte and Microglial Transcriptional Responses to Alzheimer’s Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 143, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, K.E.; Green, K.J.; Mamde, S.; Sun, W.; Cochoit, A.; Smith, C.L.; Chiou, K.L.; Heath, L.; Rose, S.E.; Wiley, J.; et al. Human Microglia Show Unique Transcriptional Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Song, W.M.; Andhey, P.S.; Swain, A.; Levy, T.; Miller, K.R.; Poliani, P.L.; Cominelli, M.; Grover, S.; Gilfillan, S.; et al. Human and Mouse Single-Nucleus Transcriptomics Reveal TREM2-Dependent and TREM2-Independent Cellular Responses in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren-Shaul, H.; Spinrad, A.; Weiner, A.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Dvir-Szternfeld, R.; Ulland, T.K.; David, E.; Baruch, K.; Lara-Astaiso, D.; Toth, B.; et al. A Unique Microglia Type Associated with Restricting Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2017, 169, 1276–1290.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexach, J.E.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Polioudakis, D.; Lin, L.-C.; Mitri, V.; Elkins, A.; Yin, A.; Calini, D.; Kawaguchi, R.; et al. Disease-Specific Selective Vulnerability and Neuroimmune Pathways in Dementia Revealed by Single Cell Genomics. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexach, J.E.; Polioudakis, D.; Yin, A.; Swarup, V.; Chang, T.S.; Nguyen, T.; Sarkar, A.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Lin, L.C.; et al. Tau Pathology Drives Dementia Risk-Associated Gene Networks toward Chronic Inflammatory States and Immunosuppression. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratuze, M.; Leyns, C.E.G.; Holtzman, D.M. New Insights into the Role of TREM2 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizkar, S.; Arzberger, T.; Brendel, M.; Kleinberger, G.; Deussing, M.; Focke, C.; Nuscher, B.; Xiong, M.; Ghasemigharagoz, A.; Katzmarski, N.; et al. Loss of TREM2 Function Increases Amyloid Seeding but Reduces Plaque-Associated ApoE. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemiller, S.M.; McCray, T.J.; Allan, K.; Formica, S.V.; Xu, G.; Wilson, G.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N.; Crish, S.D.; Lasagna-Reeves, C.A.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. TREM2 Deficiency Exacerbates Tau Pathology through Dysregulated Kinase Signaling in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyns, C.E.G.; Ulrich, J.D.; Finn, M.B.; Stewart, F.R.; Koscal, L.J.; Serrano, J.R.; Robinson, G.O.; Anderson, E.; Colonna, M.; Holtzman, D.M. TREM2 Deficiency Attenuates Neuroinflammation and Protects against Neurodegeneration in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11524–11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuska, K.M. The Dual Role of Microglia in the Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 1608–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Colonna, M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease at Single-Cell Level. Are There Common Patterns in Humans and Mice? J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, V.; Hinz, F.I.; Rexach, J.E.; Noguchi, K.I.; Toyoshiba, H.; Oda, A.; Hirai, K.; Sarkar, A.; Seyfried, N.T.; Cheng, C.; et al. Identification of Evolutionarily Conserved Gene Networks Mediating Neurodegenerative Dementia. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt-Johnson, S.K.; Brutkiewicz, R.R. The Complexity of Microglial Interactions with Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 592359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gate, D.; Saligrama, N.; Leventhal, O.; Yang, A.C.; Unger, M.S.; Middeldorp, J.; Chen, K.; Lehallier, B.; Channappa, D.; De Los Santos, M.B.; et al. Clonally Expanded CD8 T Cells Patrol the Cerebrospinal Fluid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2020, 577, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Firulyova, M.; Manis, M.; Herz, J.; Smirnov, I.; Aladyeva, E.; Wang, C.; Bao, X.; Finn, M.B.; Hu, H.; et al. Microglia-Mediated T Cell Infiltration Drives Neurodegeneration in Tauopathy. Nature 2023, 615, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorfi, M.; Park, J.; Hall, C.K.; Lin, C.C.J.; Chen, M.; von Maydell, D.; Kruskop, J.M.; Kang, B.; Choi, Y.; Prokopenko, D.; et al. Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells Exacerbate Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology in a 3D Human Neuroimmune Axis Model. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabitto, M.; Travaglini, K.; Ariza, J.; Kaplan, E.; Long, B.; Rachleff, V.; Ding, Y.; Mahoney, J.; Dee, N.; Goldy, J.; et al. Integrated Multimodal Cell Atlas of Alzheimer’s Disease. Res. Sq. 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, B.T.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Guidelines for the Neuropathologic Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montine, T.J.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Mirra, S.S.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Guidelines for the Neuropathologic Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Practical Approach. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayoso, A.; Lopez, R.; Xing, G.; Boyeau, P.; Valiollah Pour Amiri, V.; Hong, J.; Wu, K.; Jayasuriya, M.; Mehlman, E.; Langevin, M.; et al. A Python Library for Probabilistic Analysis of Single-Cell Omics Data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crinier, A.; Dumas, P.Y.; Escalière, B.; Piperoglou, C.; Gil, L.; Villacreces, A.; Vély, F.; Ivanovic, Z.; Milpied, P.; Narni-Mancinelli, É.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling Reveals the Trajectories of Natural Killer Cell Differentiation in Bone Marrow and a Stress Signature Induced by Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 18, 1290–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.D.; Badovinac, V.P. Defining Memory CD8 T Cell. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 416271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolders, J.; Heutinck, K.M.; Fransen, N.L.; Remmerswaal, E.B.M.; Hombrink, P.; ten Berge, I.J.M.; van Lier, R.A.W.; Huitinga, I.; Hamann, J. Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Populate the Human Brain. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Leun, A.M.; Thommen, D.S.; Schumacher, T.N. CD8+ T Cell States in Human Cancer: Insights from single-Cell Analysis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkel, J.M.; Masopust, D. Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squair, J.W.; Gautier, M.; Kathe, C.; Anderson, M.A.; James, N.D.; Hutson, T.H.; Hudelle, R.; Qaiser, T.; Matson, K.J.E.; Barraud, Q.; et al. Confronting False Discoveries in Single-Cell Differential Expression. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, S.; Reese, F.; Rahimzadeh, N.; Miyoshi, E.; Swarup, V. HdWGCNA Identifies Co-Expression Networks in High-Dimensional Transcriptomics Data. Cell Rep. Methods 2023, 3, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and Collaborative HTML5 Gene List Enrichment Analysis Tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovsky, O.; Weiner, H.L. Microglial Signatures and Their Role in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browaeys, R.; Gilis, J.; Sang-Aram, C.; De Bleser, P.; Hoste, L.; Tavernier, S.; Lambrechts, D.; Seurinck, R.; Saeys, Y. MultiNicheNet: A Flexible Framework for Differential Cell-Cell Communication Analysis from Multi-Sample Multi-Condition Single-Cell Transcriptomics Data. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongpreecha, T.; Fernandez, R.; Mrdjen, D.; Culos, A.; Gajera, C.R.; Wawro, A.M.; Stanley, N.; Gaudilliere, B.; Poston, K.L.; Aghaeepour, N.; et al. Single-Cell Peripheral Immunoprofiling of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, S.; Smolander, J.; Elo, L.L. Benchmarking Methods for Detecting Differential States between Conditions from Multi-Subject Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, A.T.L.; Riesenfeld, S.; Andrews, T.; Dao, T.P.; Gomes, T.; Marioni, J.C. EmptyDrops: Distinguishing Cells from Empty Droplets in Droplet-Based Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigala, J.L.D.; Bottero, V.; Young, D.B.; Shevchenko, A.; Mercurio, F.; Verma, I.M. Activation of Transcription Factor NF-KappaB Requires ELKS, an IkappaB Kinase Regulatory Subunit. Science 2004, 304, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R Package for Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, T.J.; Mackall, C.L. The Many Faces of IL-7: From Lymphopoiesis to Peripheral T Cell Maintenance. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6571–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huster, K.M.; Busch, V.; Schiemann, M.; Linkemann, K.; Kerksiek, K.M.; Wagner, H.; Busch, D.H. Selective Expression of IL-7 Receptor on Memory T Cells Identifies Early CD40L-Dependent Generation of Distinct CD8+ Memory T Cell Subsets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5610–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaech, S.M.; Tan, J.T.; Wherry, E.J.; Konieczny, B.T.; Surh, C.D.; Ahmed, R. Selective Expression of the Interleukin 7 Receptor Identifies Effector CD8 T Cells That Give Rise to Long-Lived Memory Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, A.; Campbell, D.; Hannum, C.; Yssel, H.; Franz-Bacon, K.; McClanashan, T.; Kitamura, T.; Nicholl, J.; Sutherland, G.R.; Lanier, L.L.; et al. DNAM-1, a Novel Adhesion Molecule Involved in the Cytolytic Function of T Lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, J.; Ko, M.; Lee, D.H.; Park, Y.; Jin, H.S. TIGIT/CD226 Axis Regulates Anti-Tumor Immunity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Hamilton, S.E.; Akue, A.D.; Hogquist, K.A.; Jameson, S.C. Virtual Memory CD8 T Cells Display Unique Functional Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13498–13503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.Y.; Kim, D.U.; Moon, B.H.; Shin, E.C. Human CD8+ T-Cell Populations That Express Natural Killer Receptors. Immune Netw. 2023, 23, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browaeys, R.; Saelens, W.; Saeys, Y. NicheNet: Modeling Intercellular Communication by Linking Ligands to Target Genes. Nat. Methods 2019, 17, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomer, E.; Buechler, J.; Salinas, P.C. Wnt Signaling Deregulation in the Aging and Alzheimer’s Brain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 437226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Büchler, J.; Dufor, T.; Palomer, E.; Teo, S.; Martin-Flores, N.; Boroviak, K.; Metzakopian, E.; Gibb, A.; Salinas, P.C. A Genetic Variant of the Wnt Receptor LRP6 Accelerates Synapse Degeneration during Aging and in Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabo7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, M.; Weiner, R.L.; Dumitrescu, L.; Hohman, T.J. Protective Genes and Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease: Moving towards Precision Interventions. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logtenberg, M.E.W.; Scheeren, F.A.; Schumacher, T.N. The CD47-SIRPα Immune Checkpoint. Immunity 2020, 52, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.C.; Giddens, M.M.; Schaefer, S.A.; Hall, R.A. GPR37 and GPR37L1 Are Receptors for the Neuroprotective and Glioprotective Factors Prosaptide and Prosaposin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9529–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglesby, T.J.; Allen, C.J.; Liszewski, M.K.; White, D.J.G.; Atkinson, J.P. Membrane Cofactor Protein (CD46) Protects Cells from Complement-Mediated Attack by an Intrinsic Mechanism. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, P.; Khetarpal, S.A.; Larach, D.B.; Hancock-Cerutti, W.F.; Millar, J.S.; Cuchel, M.; DerOhannessian, S.; Kontush, A.; Surendran, P.; Saleheen, D.; et al. Rare Variant in Scavenger Receptor BI Raises HDL Cholesterol and Increases Risk of Coronary Heart Disease. Science 2016, 351, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, X.; Li, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, L.; Zou, C.; Pei, Z.; Mao, Y.; Zou, D. PTPRG Activates M6A Methyltransferase VIRMA to Block Mitochondrial Autophagy Mediated Neuronal Death in Alzheimer’s Disease. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, J.; Ludwig, A. Novel Role of APP Cleavage by ADAM10 for Breast Cancer Metastasis. eBioMedicine 2018, 38, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, S.; Hoffmann, J.; Michler, E.; Hartig, R.; Frodl, T.; Busse, M. Dementia-Associated Changes of Immune Cell Composition within the Cerebrospinal Fluid. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 14, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala Frigerio, C.; Wolfs, L.; Fattorelli, N.; Thrupp, N.; Voytyuk, I.; Schmidt, I.; Mancuso, R.; Chen, W.T.; Woodbury, M.E.; Srivastava, G.; et al. The Major Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease: Age, Sex, and Genes Modulate the Microglia Response to Aβ Plaques. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1293–1306.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenkhuis, B.; Somarakis, A.; de Haan, L.; Dzyubachyk, O.; IJsselsteijn, M.E.; de Miranda, N.F.C.C.; Lelieveldt, B.P.F.; Dijkstra, J.; van Roon-Mom, W.M.C.; Höllt, T.; et al. Iron Loading Is a Prominent Feature of Activated Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Garcia, M.; Mahajani, S.U.; Wakhloo, D.; Tang, W.; Xue, Y.Q.; Morabito, S.; Pan, J.; Oberhauser, J.; Madira, A.E.; Shakouri, T.; et al. Molecular Signatures Underlying Neurofibrillary Tangle Susceptibility in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2022, 110, 2929–2948.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehl, N.; van Olst, L.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Teregulova, V.; Simonton, B.; Zhang, Z.; Tapp, E.; Channappa, D.; Oh, H.; Losada, P.M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Immune Dysregulation during Healthy Brain Aging and Cognitive Impairment. Cell 2022, 185, 5028–5039.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentis, A.F.A.; Dardiotis, E.; Chrousos, G.P. Apolipoprotein E4 and Meningeal Lymphatics in Alzheimer Disease: A Conceptual Framework. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1075–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, Z.; Herz, J.; Kipnis, J. Meningeal Lymphatics: From Anatomy to Central Nervous System Immune Surveillance. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israël, A. The IKK Complex, a Central Regulator of NF-KappaB Activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; James, B.T.; Boix, C.A.; Park, Y.P.; Galani, K.; Victor, M.B.; Sun, N.; Hou, L.; Ho, L.L.; Mantero, J.; et al. Epigenomic Dissection of Alzheimer’s Disease Pinpoints Causal Variants and Reveals Epigenome Erosion. Cell 2023, 186, 4422–4437.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamakawa, M.; Rexach, J.E. Cell States and Interactions of CD8 T Cells and Disease-Enriched Microglia in Human Brains with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020308
Yamakawa M, Rexach JE. Cell States and Interactions of CD8 T Cells and Disease-Enriched Microglia in Human Brains with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(2):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020308
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamakawa, Mai, and Jessica E. Rexach. 2024. "Cell States and Interactions of CD8 T Cells and Disease-Enriched Microglia in Human Brains with Alzheimer’s Disease" Biomedicines 12, no. 2: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020308
APA StyleYamakawa, M., & Rexach, J. E. (2024). Cell States and Interactions of CD8 T Cells and Disease-Enriched Microglia in Human Brains with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines, 12(2), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12020308




