Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Isocnicin and Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma: A Natural Compound’s Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of 8α-O-(3′,4′-dihydroxy-2′-methylenebutanoyloxy)-dehydromelitensine (Isocnicin)
2.2. Cell Lines and Conditions for Treatment
2.3. The Viability Test
2.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of DNA Cell Cycle
2.5. Radiation and Isocnicin Combined Therapy
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Calculation of Viability and IC50 of GBM Cells After Isocnicin Treatment
3.2. Combined Effects of Isocnicin and Radiation on Glioblastoma Cells
3.3. Isocnicin Enhanced Radiation-Induced G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in Glioblastoma Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Shete, S.; Etzel, C.J.; Scheurer, M.; Alexiou, G.; Armstrong, G.; Tsavachidis, S.; Liang, F.W.; Gilbert, M.; Aldape, K.; et al. Polymorphisms of LIG4, BTBD2, HMGA2, and RTEL1 genes involved in the double-strand break repair pathway predict glioblastoma survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyritsis, A.P.; Levin, V.A. An algorithm for chemotherapy treatment of recurrent glioma patients after temozolomide failure in the general oncology setting. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, V.A.; Ellingson, B.M. Understanding brain penetrance of anticancer drugs. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier. BMC Neurol. 2009, 9 (Suppl. S1), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyritsis, A.P.; Bondy, M.L.; Levin, V.A. Modulation of glioma risk and progression by dietary nutrients and antiinflammatory agents. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhai, K.; Siddiqui, M.; Abdellatif, B.; Liskova, A.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Natural Compounds in Glioblastoma Therapy: Preclinical Insights, Mechanistic Pathways, and Outlook. Cancers 2021, 13, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukoulitsa, E.; Skaltsa, H.; Karioti, A.; Demetzos, C.; Dimas, K. Bioactive sesquiterpene lactones from Centaurea species and their cytotoxic/cytostatic activity against human cell lines in vitro. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M. Drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1959–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E. Thin-Layer Chromatography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, R. Chelate von Diarylborsauren mit aliphatischen Oxyalkylaminen als Reagenzien fur den Nachweis von Oxyphenyl-benzo-γ-pyronen. Naturwissenchaften 1957, 44, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzun, B.S.; Hajdu, Z.; Orban-Gyapai, O.; Zomborszki, Z.P.; Jedlinszki, N.; Forgo, P.; Kıvcak, B.; Hohmann, J. Isolation of Chemical Constituents of Centaurea virgata Lam. and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of the Plant Extract and Compounds. Med. Chem. 2017, 13, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastamoulas, M.; Chondrogiannis, G.; Kanavaros, P.; Vartholomatos, G.; Bai, M.; Briasoulis, E.; Arvanitis, D.; Galani, V. Cytokine effects on cell survival and death of A549 lung carcinoma cells. Cytokine 2013, 61, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Tsamis, K.I.; Vartholomatos, E.; Peponi, E.; Tzima, E.; Tasiou, I.; Lykoudis, E.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyritsis, A.P. Combination treatment of TRAIL, DFMOand radiation for malignant glioma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 123, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chondrogiannis, G.; Kastamoulas, M.; Kanavaros, P.; Vartholomatos, G.; Bai, M.; Baltogiannis, D.; Sofikitis, N.; Arvanitis, D.; Galani, V. Cytokine effects on cell viability and death of prostate carcinoma cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 536049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Vartholomatos, E.; Tsamis, K.I.; Peponi, E.; Markopoulos, G.; A Papathanasopoulou, V.; Tasiou, I.; Ragos, V.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyritsis, A.P.; et al. Combination treatment for glioblastoma with temozolomide, DFMO and radiation. J. BUON 2019, 24, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Plaha, P. Advances in the management of glioblastoma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Meng, L.; Dong, L.; Jiang, X. Progress and prospect in tumor treating fields treatment of glioblastoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, A.; Tiek, D.; Song, X.; Huang, T.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.Y. The Many Facets of Therapy Resistance and Tumor Recurrence in Glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, A.D.; Lianos, G.D.; Schizas, D.; Machairas, N.; Mitsis, M.; Alexiou, G.A. Natural Compounds and Cancer: Current Evidences. Maedica 2024, 19, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Kabir, M.T.; Mamun, A.A.; Sarwar, M.S.; Nasrin, F.; Emran, T.B.; Alanazi, I.S.; Rauf, A.; Albadrani, G.M.; Sayed, A.A.; et al. Natural Small Molecules Targeting NF-κB Signaling in Glioblastoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 703761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukhtanloo, M.; Mohtashami, E.; Maghrouni, A.; Mollazadeh, H.; Mousavi, S.H.; Roshan, M.K.; Tabatabaeizadeh, S.A.; Hosseini, A.; Vahedi, M.M.; Jalili-Nik, M.; et al. Natural products as promising targets in glioblastoma multiforme: A focus on NF-κB signaling pathway. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 72, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, L.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Bungau, S.; Toma, M.M.; Gitea, D.; et al. Current Perspective on the Natural Compounds and Drug Delivery Techniques in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Cancers 2021, 13, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcella, A.; Sanchez, M. Natural substances to potentiate canonical glioblastoma chemotherapy. J. Chemother. 2021, 33, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoi, V.; Galani, V.; Vartholomatos, E.; Zacharopoulou, N.; Tsoumeleka, E.; Gkizas, G.; Bozios, G.; Tsekeris, P.; Chousidis, I.; Leonardos, I.; et al. Curcumin and Radiotherapy Exert Synergistic Anti-Glioma Effect In Vitro. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, K.M.; Mahesh, V.B.; Brann, D.W. Curcumin suppresses growth and chemoresistance of human glioblastoma cells via AP-1 and NFkappaB transcription factors. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, C.; Cao, B.; Qian, Y.; Cheng, C.; Dai, M.; Guo, X.; Shao, J. In vivo Radiosensitization of human glioma U87 cells induced by upregulated expression of DUSP-2 after treatment with curcumin. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2015, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoi, V.; Galani, V.; Lianos, G.D.; Voulgaris, S.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Alexiou, G.A. The Role of Curcumin in Cancer Treatment. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Curcumin, a dietary component, has anticancer, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization effects by down-regulating the MDM2 oncogene through the PI3K/mTOR/ETS2 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotto-Filho, A.; Braganhol, E.; Edelweiss, M.I.; Behr, G.A.; Zanin, R.; Schröder, R.; Simões-Pires, A.; Battastini, A.M.; Moreira, J.C. The curry spice curcumin selectively inhibits cancer cells growth in vitro and in preclinical model of glioblastoma. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gersey, Z.C.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Barbarite, E.; Sanchez, A.; Walters, W.M.; Ohaeto, K.C.; Komotar, R.J.; Graham, R.M. Curcumin decreases malignant characteristics of glioblastoma stem cells via induction of reactive oxygen species. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoi, V.; Galani, V.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Alexiou, G.A. Radiosensitization and Radioprotection by Curcumin in Glioblastoma and Other Cancers. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoi, V.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Galani, V.; Lazari, D.; Sioka, C.; Voulgaris, S.; Alexiou, G.A. The Role of Curcumin in Cancer: A Focus on the PI3K/Akt Pathway. Cancers 2024, 16, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoi, V.; Papagrigoriou, T.; Tsiftsoglou, O.S.; Alexiou, G.A.; Giannakopoulou, M.; Tzima, E.; Tsekeris, P.; Zikou, A.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Lazari, D.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Linearol in Combination with Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapetrou, P.; Dimitriadis, K.; Galani, V.; Zoi, V.; Giannakopoulou, M.; Papathanasopoulou, V.A.; Sioka, C.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Lazari, D.; et al. Antitumor activity of 5-hydroxy-3′,4′,6,7-tetramethoxyflavone in glioblastoma cell lines and its antagonism with radiotherapy. Biomol. Concepts 2024, 15, 20220039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Weber-Johnson, K.; Sun, L.Q.; Paschoud, N.; Mirimanoff, R.O.; Coucke, P.A. Effect of pentoxifylline on radiation-induced G2-phase delay and radiosensitivity of human colon and cervical cancer cells. Radiat. Res. 1998, 149, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Keyomarsi, K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baytop, T. Türkiye’de Bitkilerle Tedavi (Treatment with Plants in Turkey); Nobel Tıp Kitapevi: İstanbul, Turkey, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzlacı, E.; İsbilen, D.F.A.; Bulut, G. Turkish folk medicinal plants, VIII: Lalapaşa (Edirne). Marmara Pharm. J. 2010, 14, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csupor-Löffler, B.; Hajdú, Z.; Réthy, B.; Zupkó, I.; Máthé, I.; Rédei, T.; Falkay, G.; Hohmann, J. Antiproliferative activity of Hungarian Asteraceae species against human cancer cell lines. Part II. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostad, S.N.; Rajabi, A.; Khademi, R.; Farjadmand, F.; Eftekhari, M.; Hadjiakhoondi, A.; Khanavi, M. Cytotoxic Potential of Centaurea bruguieriana ssp. belangeriana: The MTT Assay. Acta Medica Iran. 2016, 54, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csapi, B.; Hajdú, Z.; Zupkó, I.; Berényi, A.; Forgo, P.; Szabó, P.; Hohmann, J. Bioactivity-guided isolation of antiproliferative compounds from Centaurea arenaria. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1664–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, S.B.; Demir, S.; Aydın-Kose, F.; Ballar, P.; Karaalp, C. Cytotoxic properties of five Centaurea L. species from Anatolia. Planta Med. 2011, 77, PM149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Dayi, O.; Pekmez, M.; Bona, M.; Aras-Perk, A.; Arda, N. Total phenolic contents, antioxidant activities, cytotoxicity of three Centaurea species: C. calcitrapa subsp. calcitropa, C. ptosimopqppa, C. spicata. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2011, 1, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgo, P.; Zupkó, I.; Molnár, J.; Vasas, A.; Dombi, G.; Hohmann, J. Bioactivity-guided isolation of antiproliferative compounds from Centaurea jacea L. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.Q.; Bu, X.M.; Jiang, W.; Wan, Y.Z.; Song, W. Compound Taxus exerts marked anti-tumor activity and radiosensitization effect on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D. Paradol Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Glioblastoma Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiftsoglou, O.S.; Krigas, N.; Gounaris, C.; Papitsa, C.; Nanouli, M.; Vartholomatos, E.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Isyhou, R.; Alexiou, G.; Lazari, D. Isolation of Secondary Metabolites from Achillea grandifolia Friv. (Asteraceae) and Main Compounds’ Effects on a Glioblastoma Cellular Model. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartholomatos, E.; Alexiou, G.A.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Lazari, D.; Tsiftsoglou, O.; Chousidis, I.; Leonardos, I.; Kyritsis, A.P. Deglucohellebrin: A Potent Agent for Glioblastoma Treatment. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazari, D.; Alexiou, G.A.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Vartholomatos, E.; Hodaj, E.; Chousidis, I.; Leonardos, I.; Galani, V.; Kyritsis, A.P. N-(p-coumaroyl) serotonin inhibits glioblastoma cells growth through triggering S-phase arrest and apoptosis. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 132, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Lazari, D.; Markopoulos, G.; Vartholomatos, E.; Hodaj, E.; Galani, V.; Kyritsis, A.P. Moschamine inhibits proliferation of glioblastoma cells via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705744. [Google Scholar]





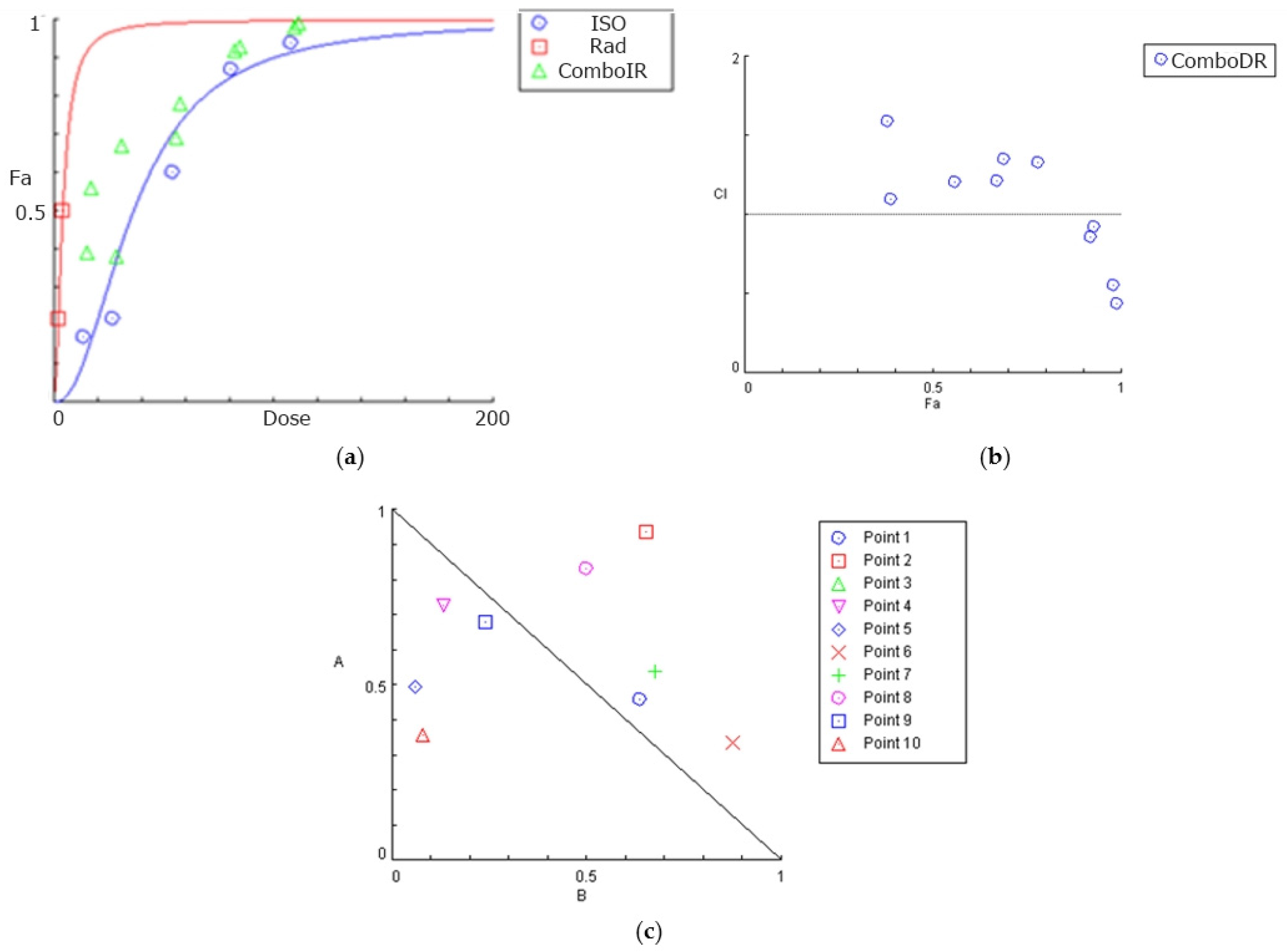







| Isocnicin (μΜ) | Radiation (Gy) | Effect | CI | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.5 | 2 | 0.52 | 0.82968 | Synergism |
| 7 | 2 | 0.63 | 0.82580 | Synergism |
| 14 | 2 | 0.72 | 0.95187 | Synergism |
| 21 | 2 | 0.8 | 0.91873 | Synergism |
| 28 | 2 | 0.86 | 0.82875 | Synergism |
| 3.5 | 4 | 0.56 | 1.13838 | Antagonism |
| 7 | 4 | 0.67 | 0.99624 | Synergism |
| 14 | 4 | 0.78 | 0.91184 | Synergism |
| 21 | 4 | 0.85 | 0.81458 | Synergism |
| 28 | 4 | 0.88 | 0.81639 | Synergism |
| Isocnicin (μΜ) | Radiation (Gy) | Effect | CI | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.5 | 2 | 0.39 | 1.09717 | Antagonism |
| 27 | 2 | 0.38 | 1.58854 | Antagonism |
| 54 | 2 | 0.69 | 1.35368 | Antagonism |
| 81 | 2 | 0.92 | 0.85612 | Synergism |
| 108 | 2 | 0.98 | 0.55446 | Synergism |
| 13.5 | 4 | 0.56 | 1.20989 | Antagonism |
| 27 | 4 | 0.67 | 1.21640 | Antagonism |
| 54 | 4 | 0.78 | 1.33175 | Antagonism |
| 81 | 4 | 0.93 | 0.92070 | Synergism |
| 108 | 4 | 0.99 | 0.43865 | Synergism |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsafa, E.; Dimitriadis, K.; Kalampoki, L.; Papapetrou, P.; Georgalis, P.A.; Bozios, G.; Sioka, C.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Alexiou, G.A.; et al. Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Isocnicin and Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma: A Natural Compound’s Potential. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122793
Tsafa E, Dimitriadis K, Kalampoki L, Papapetrou P, Georgalis PA, Bozios G, Sioka C, Tsekeris P, Kyritsis AP, Alexiou GA, et al. Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Isocnicin and Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma: A Natural Compound’s Potential. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122793
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsafa, Effrosyni, Kyriakos Dimitriadis, Lamprini Kalampoki, Panagiota Papapetrou, Pavlos A. Georgalis, Georgios Bozios, Chrissa Sioka, Pericles Tsekeris, Athanassios P. Kyritsis, George A. Alexiou, and et al. 2024. "Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Isocnicin and Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma: A Natural Compound’s Potential" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122793
APA StyleTsafa, E., Dimitriadis, K., Kalampoki, L., Papapetrou, P., Georgalis, P. A., Bozios, G., Sioka, C., Tsekeris, P., Kyritsis, A. P., Alexiou, G. A., & Lazari, D. (2024). Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Isocnicin and Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma: A Natural Compound’s Potential. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2793. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122793









