RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitors Significantly Modulate the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-β2 in the 2-D and 3-D Cultures of Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- 【Two-dimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) cultures of human corneal stroma fibroblasts (HCSFs)】
- 【Trans-endothelial electron resistance (TEER) measurement of the 2-D-cultured HCSF monolayers】
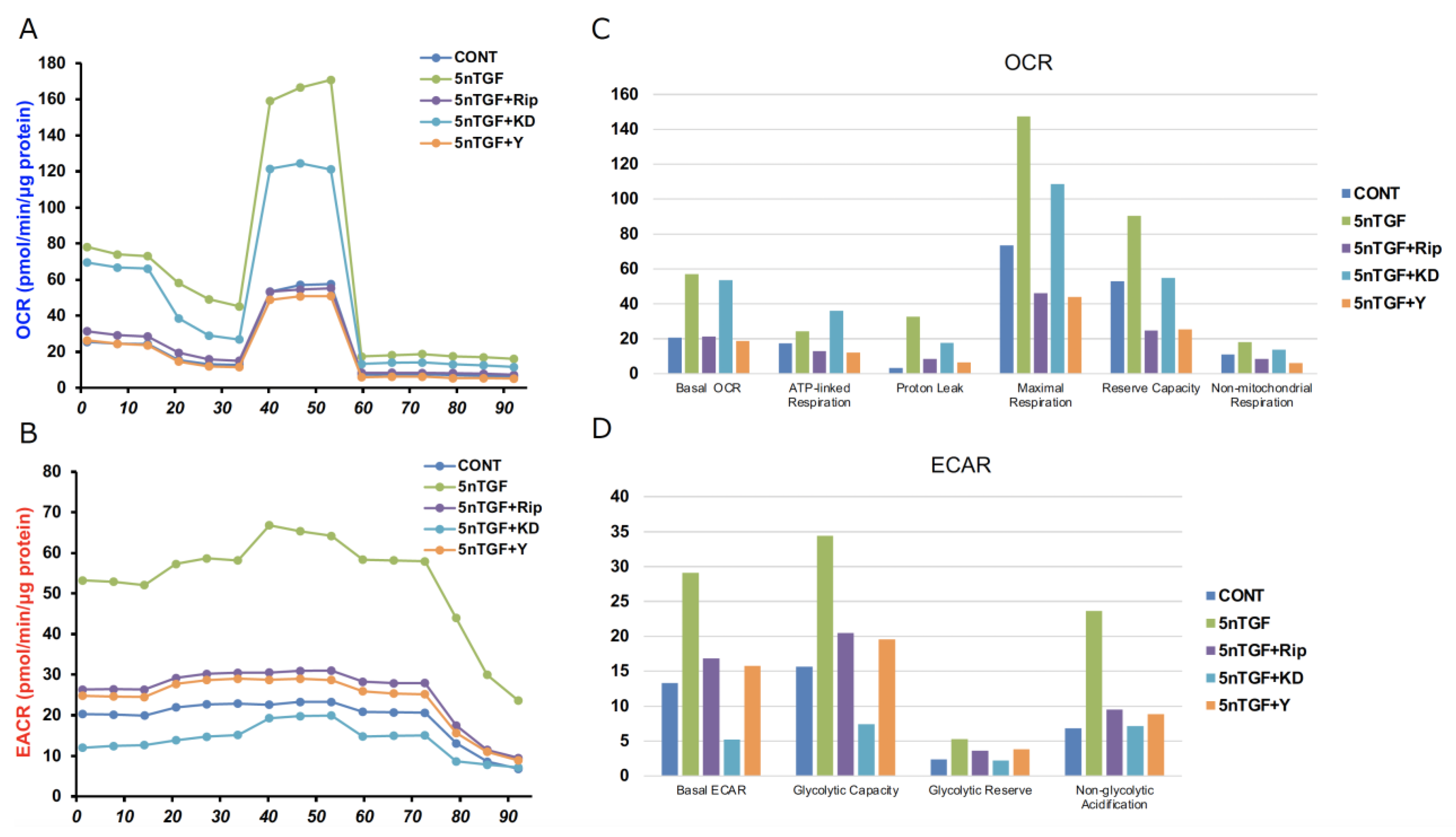
- 【Measurement of real-time cellular metabolic functions】
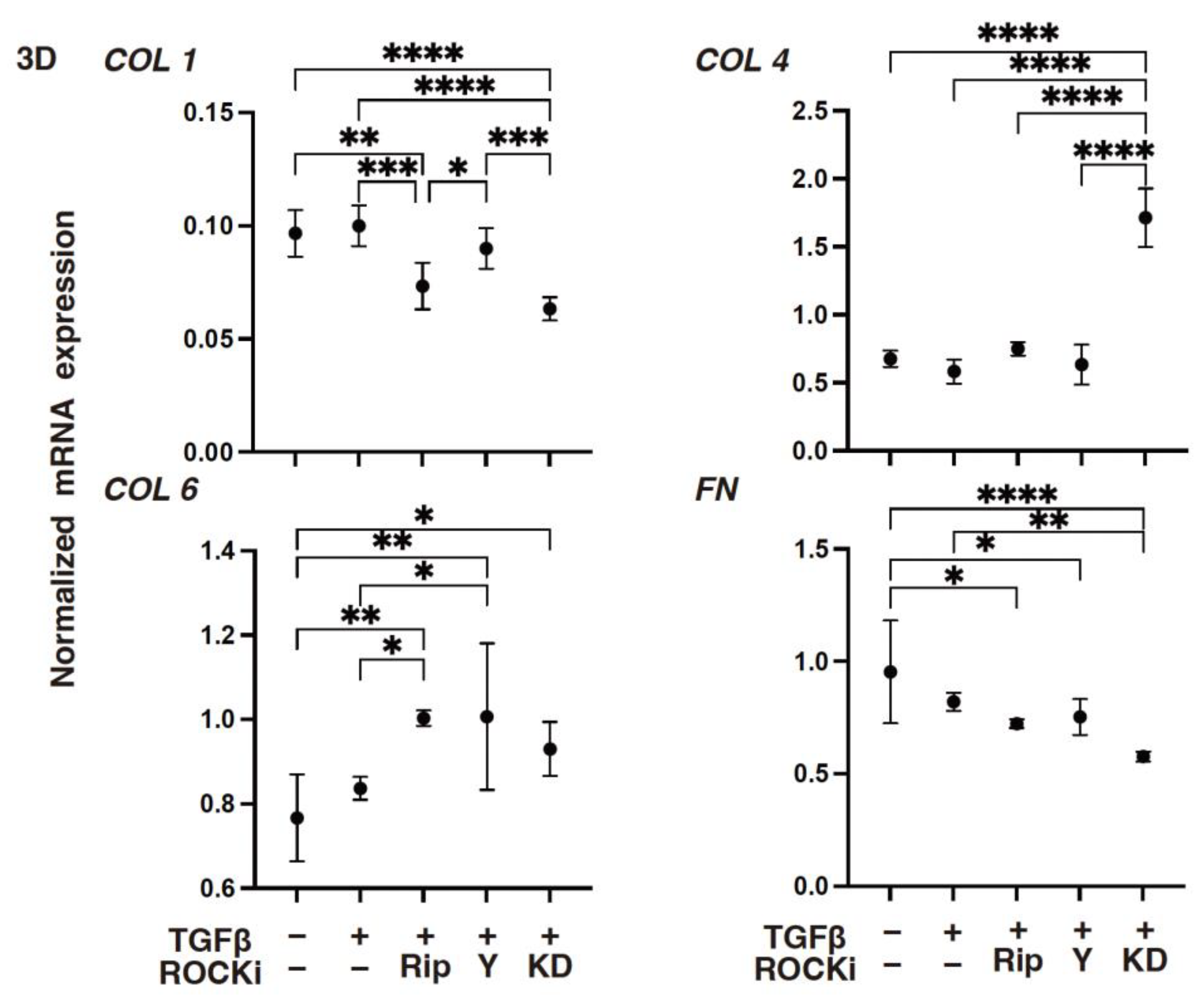
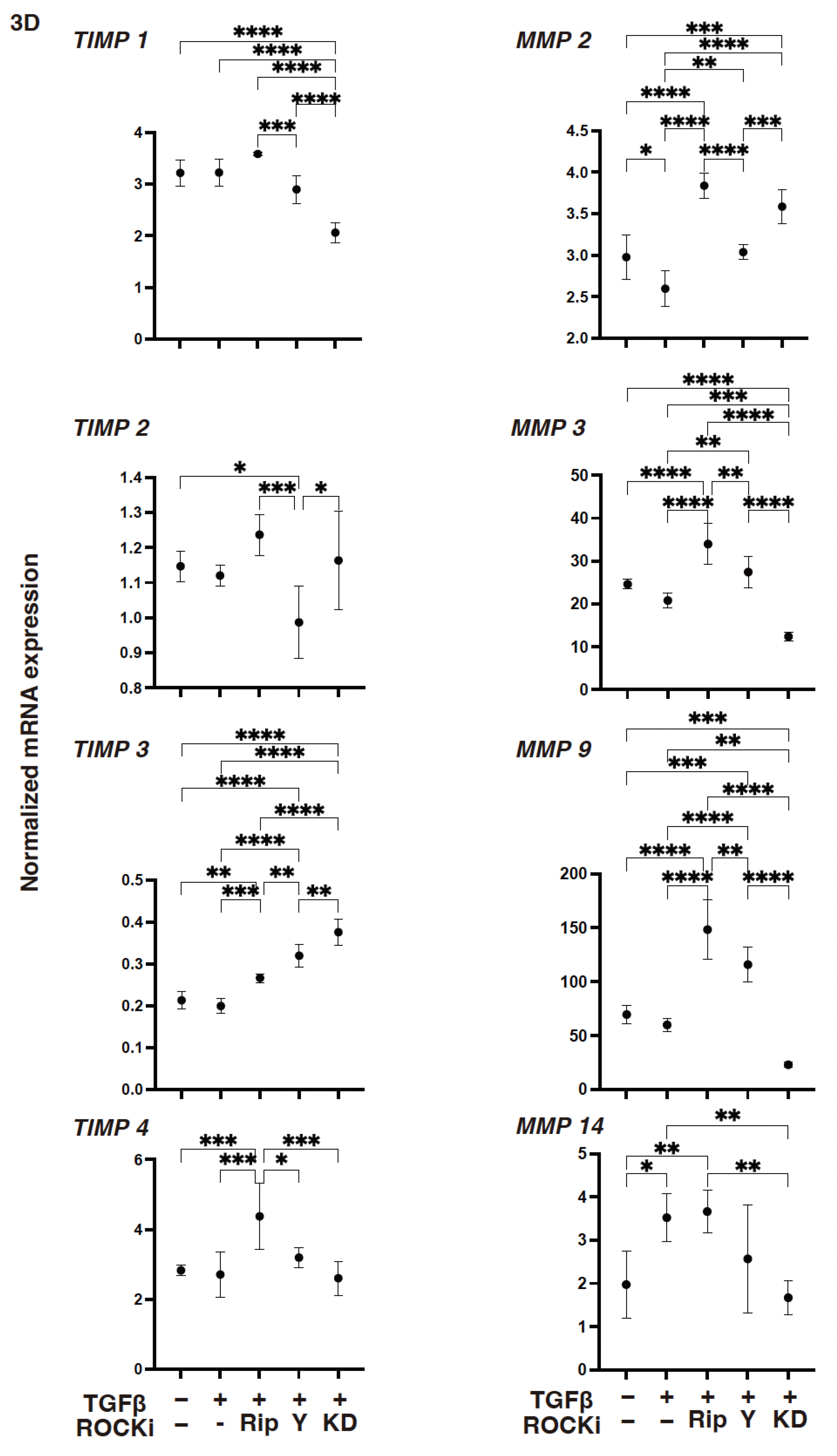
- 【Quantitative PCR】
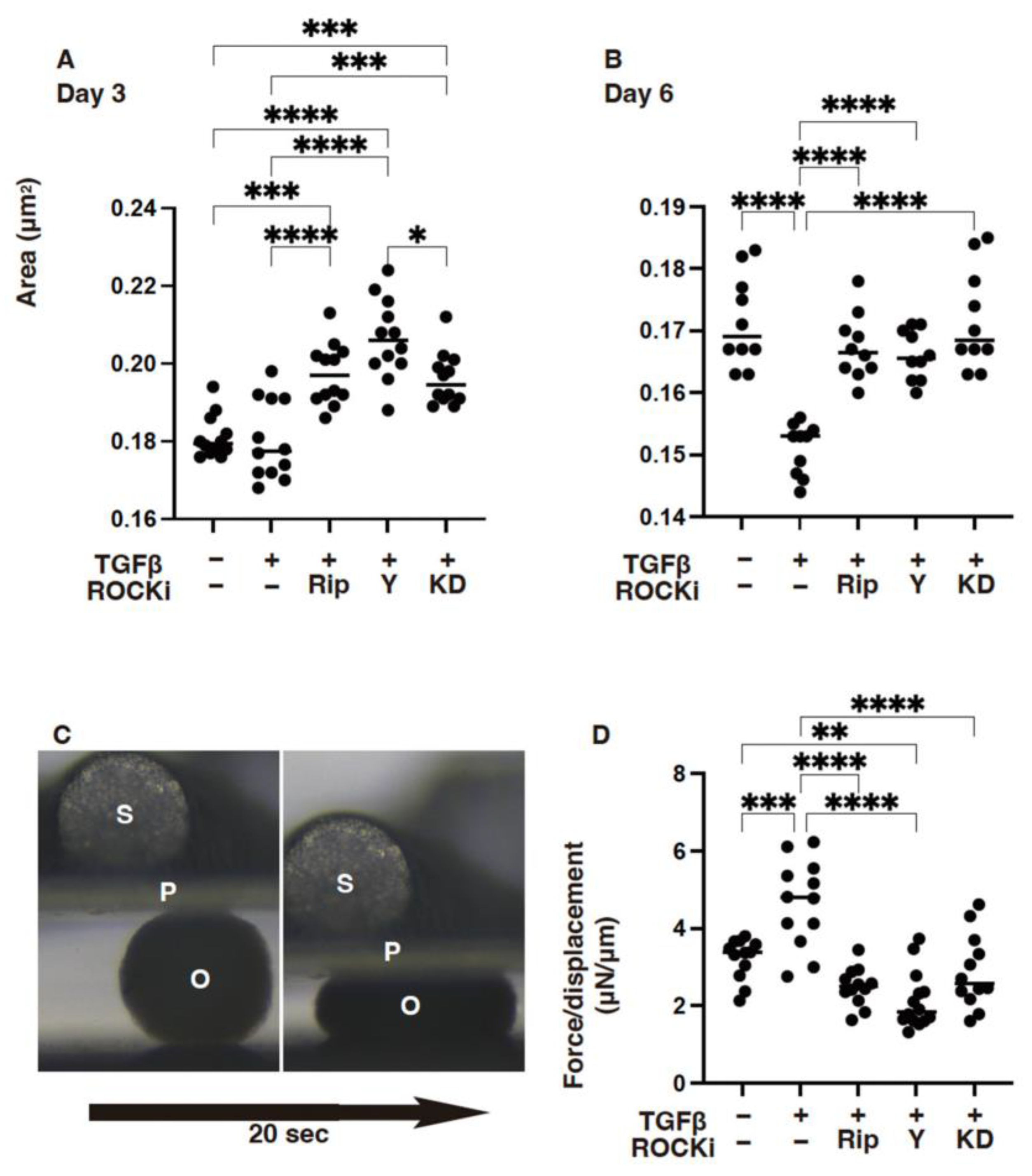
- 【Measurement of the physical properties, size, and stiffness of 3-D HCSF spheroids】
- 【Statistical analysis】
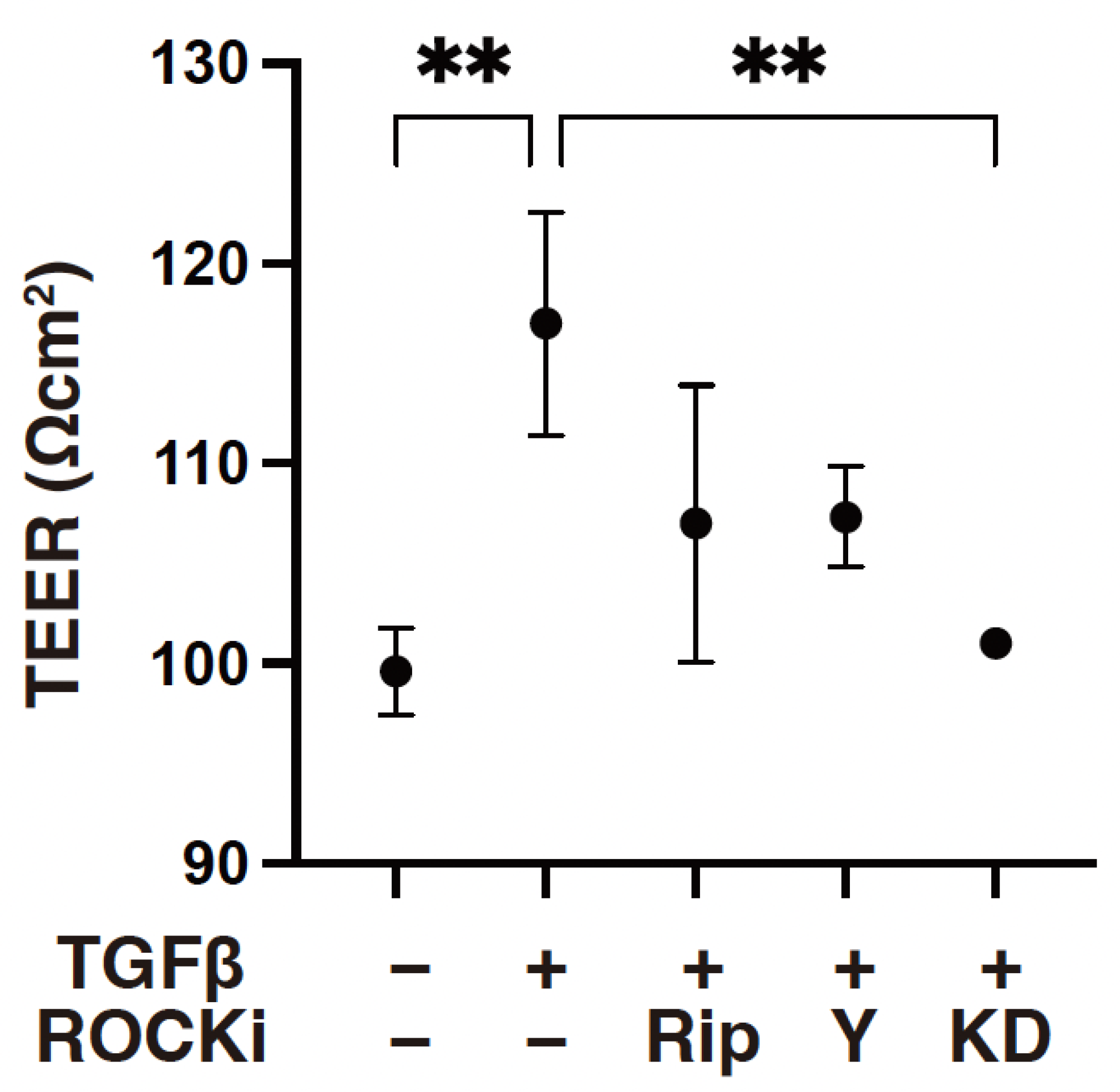
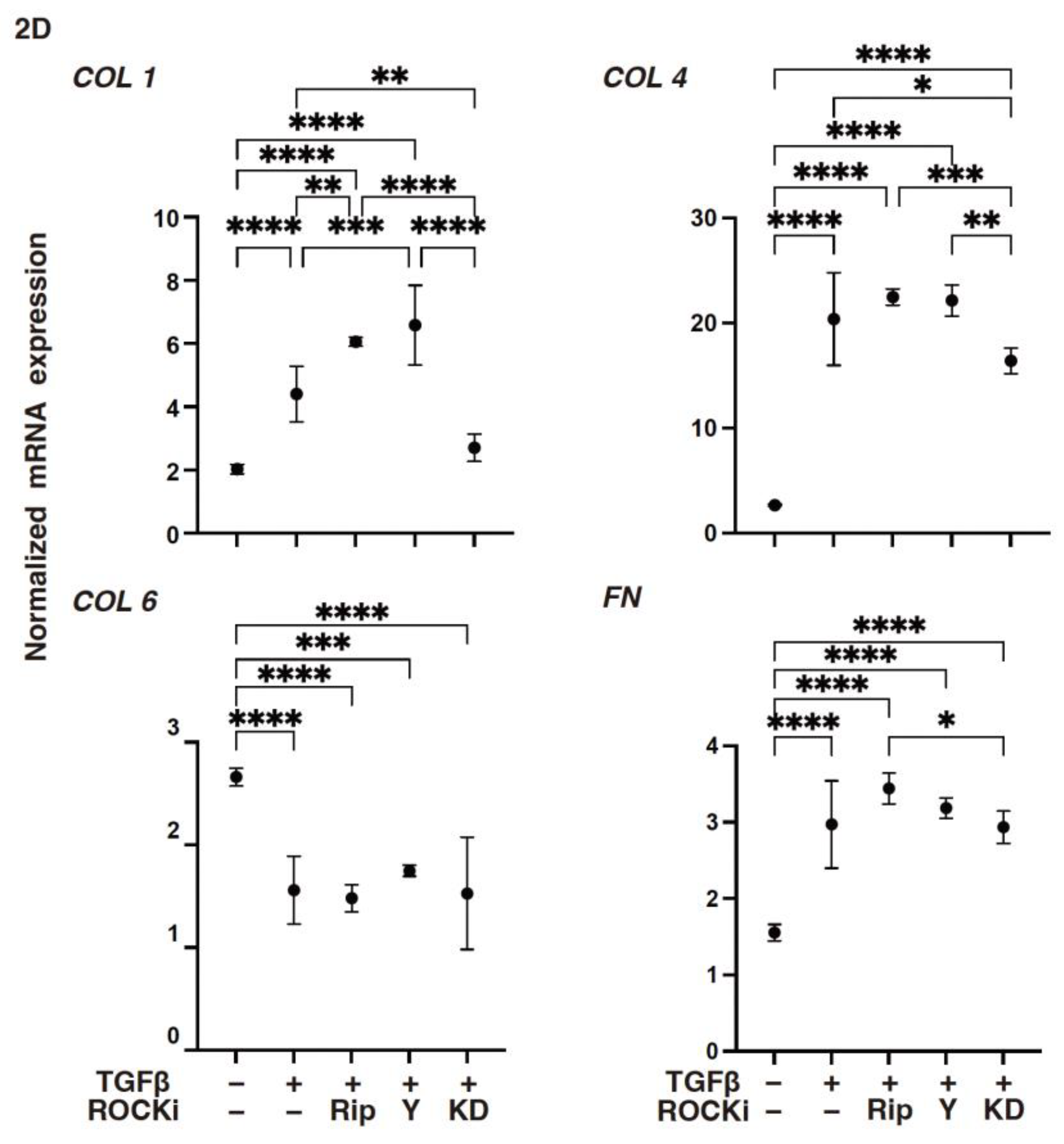
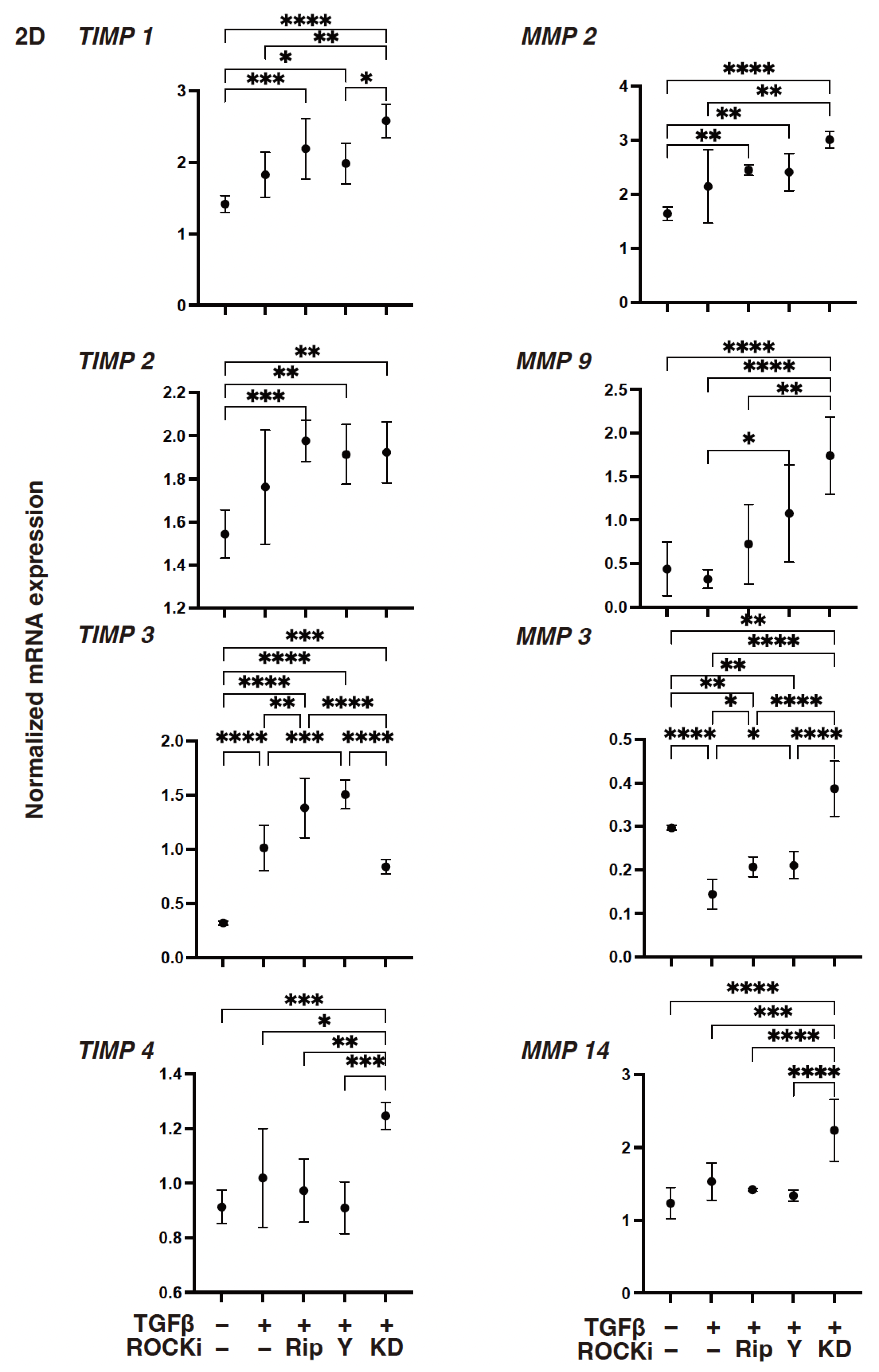
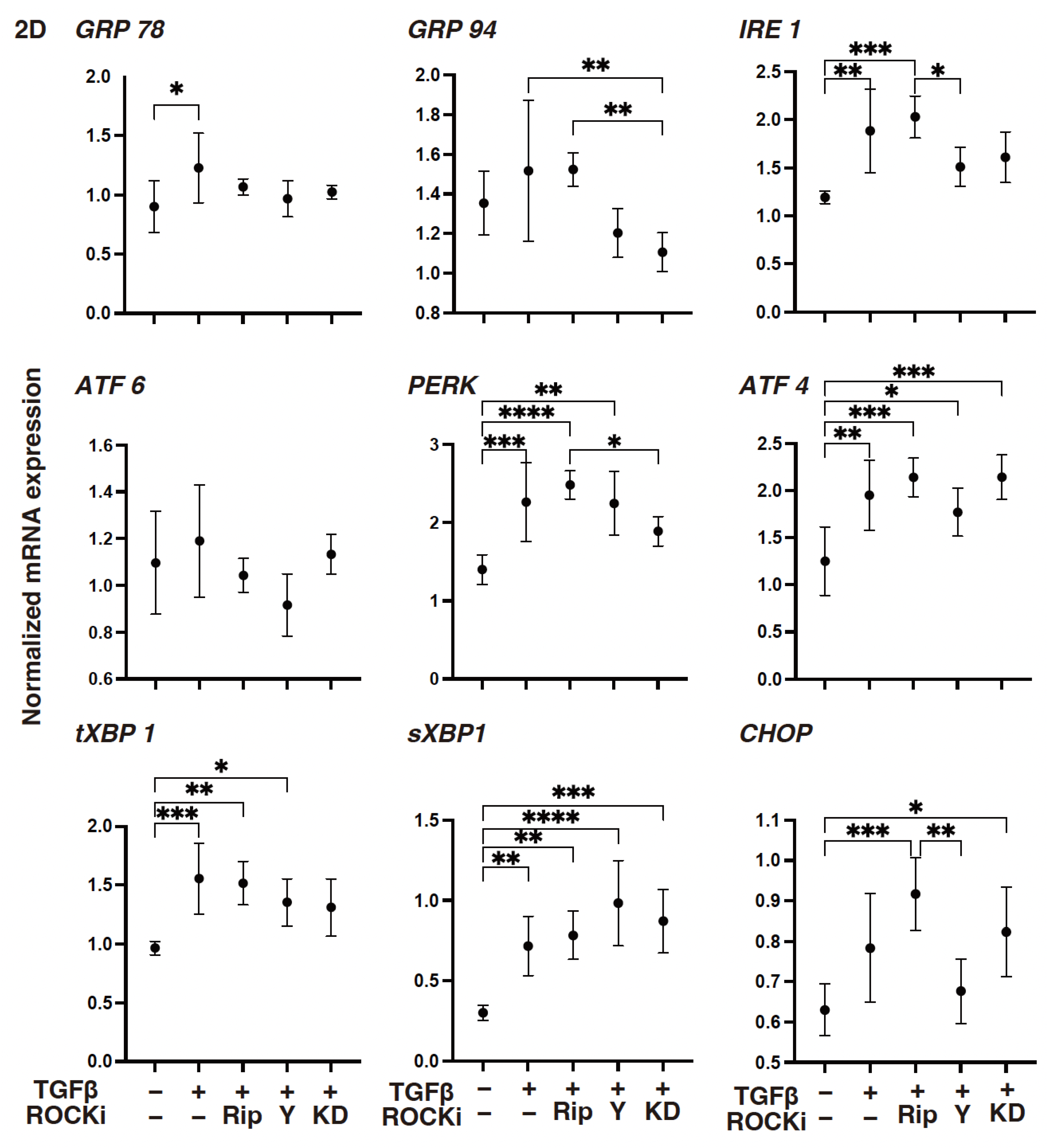
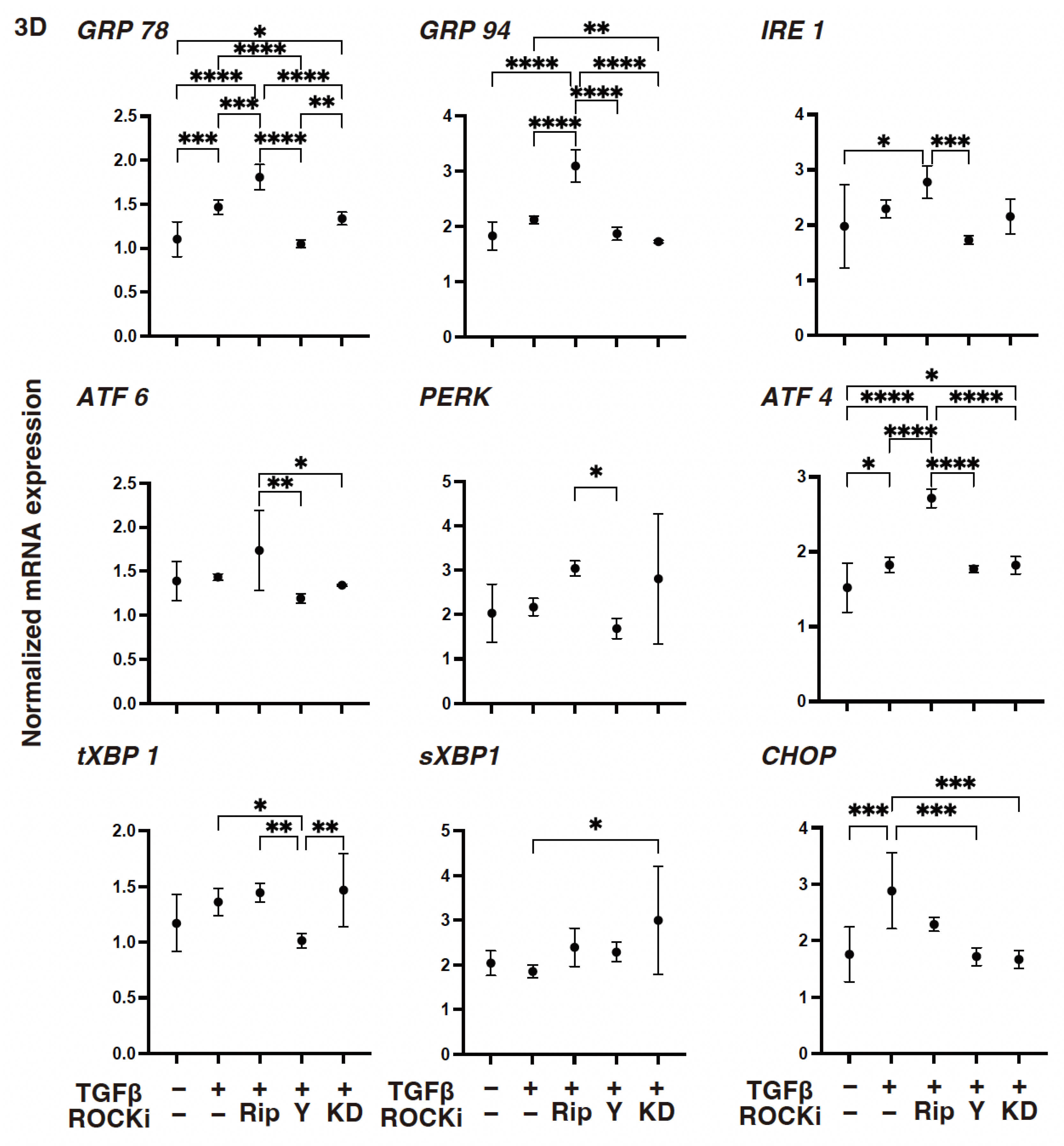
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DelMonte, D.W.; Kim, T. Anatomy and physiology of the cornea. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.S. Anatomy of cornea and ocular surface. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, J.R.; Birk, D.E. The molecular basis of corneal transparency. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.E. Corneal wound healing. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 197, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, J.V.; Huang, J.; Barry-Lane, P.A.; Kao, W.W.; Petroll, W.M.; Cavanagh, H.D. Transforming growth factor(beta)-mediated corneal myofibroblast differentiation requires actin and fibronectin assembly. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Carrington, L.M.; Albon, J.; Anderson, I.; Kamma, C.; Boulton, M. Differential regulation of key stages in early corneal wound healing by TGF-beta isoforms and their inhibitors. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Barbosa, F.L.; Torricelli, A.A.; Santhiago, M.R.; Wilson, S.E. Transforming growth factor β and platelet-derived growth factor modulation of myofibroblast development from corneal fibroblasts in vitro. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 120, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, A.; Ida, Y.; Sato, T.; Furuhashi, M.; Ohguro, H.; Watanabe, M. TGF-β2 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in 2D Planer and 3D Spheroids of the Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts in Different Manners. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, J.V.; Petroll, W.M.; Barry, P.A.; Cavanagh, H.D. Expression of alpha-smooth muscle (alpha-SM) actin during corneal stromal wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1995, 36, 809–819. [Google Scholar]
- Desmoulière, A.; Geinoz, A.; Gabbiani, F.; Gabbiani, G. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, S.A.; Anderson, S.C.; SundarRaj, N. Downstream effects of ROCK signaling in cultured human corneal stromal cells: Microarray analysis of gene expression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 2168–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubimov, A.V.; Saghizadeh, M. Progress in corneal wound healing. Progress. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-B.; Zhong, Y.-S.; Cheng, Y.; Shen, X. Rho/ROCK pathway and neural regeneration: A potential therapeutic target for central nervous system and optic nerve damage. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 4, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, H.; Abe, S.; Yoshitomi, T. Effects of Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitors Y-27632 and Y-39983 on isolated rabbit ciliary arteries. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 55, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, J.M.; Kurisetty, V.; Mitchell, D.C.; Bryan, B.A. Rho Kinase Proteins Regulate Global miRNA Expression in Endothelial Cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2013, 10, 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Narumiya, S.; Ishizaki, T.; Watanabe, N. Rho effectors and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett. 1997, 410, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 1998, 279, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.; Nobes, C.D. Rho GTPases: Molecular switches that control the organization and dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, O.; Fujisawa, K.; Ishizaki, T.; Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Narumiya, S. ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waki, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Oka, T.; Azuma, M. Reduction of intraocular pressure by topical administration of an inhibitor of the Rho-associated protein kinase. Curr. Eye Res. 2001, 22, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Utsunomiya, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Gojo, A.; Kurata, H.; Tajima, N. Involvement of the Rho/Rho Kinase Signaling Pathway in Platelet-Derived Growth Factor BB-induced Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Diabetic Rat Retina. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 51, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Yoo, J. Rho activation is required for transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lens epithelial cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2007, 31, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Koizumi, N.; Ueno, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Hamuro, J.; Kinoshita, S. The New Therapeutic Concept of Using a Rho Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Corneal Endothelial Dysfunction. Cornea 2011, 30, S54–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P. Ripasudil: First global approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 2211–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Inoue, R.; Kakutani, K.; Nakano, S.; Kinoshita, S.; Koizumi, N. Effect of the Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) on Corneal Endothelial Wound Healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guerriero, E.; Sado, Y.; SundarRaj, N. Rho-mediated regulation of TGF-beta1- and FGF-2-induced activation of corneal stromal keratocytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, Y.; Umetsu, A.; Furuhashi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Hikage, F.; Ohguro, H. The EP2 agonist, omidenepag, alters the physical stiffness of 3D spheroids prepared from human corneal stroma fibroblasts differently depending on the osmotic pressure. Faseb J. 2022, 36, e22067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, H.; Jalilian, I.; Murphy, C.J.; Thomasy, S.M. Modulation of human corneal stromal cell differentiation by hepatocyte growth factor and substratum compliance. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 176, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikage, F.; Atkins, S.; Kahana, A.; Smith, T.J.; Chun, T.H. HIF2A-LOX Pathway Promotes Fibrotic Tissue Remodeling in Thyroid-Associated Orbitopathy. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Ohta, M.; Inoue, T.; Mizuno, K.; Isobe, T.; Tanabe, S.; Tanihara, H. Effects of K-115 (Ripasudil), a novel ROCK inhibitor, on trabecular meshwork and Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Chang, H.C.; Bayeva, M.; Shapiro, J.S.; Ramos-Alonso, L.; Kouzu, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, T.; Yar, S.; Sawicki, K.T.; et al. mRNA-binding protein tristetraprolin is essential for cardiac response to iron deficiency by regulating mitochondrial function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, e6291–e6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay. Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, B.M.; Chen, C.S. Deconstructing the third dimension: How 3D culture microenvironments alter cellular cues. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnier, F.; Keating, M.E.; Wróbel, T.P.; Majzner, K.; Baranska, M.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Blanco, A.; Byrne, H.J. Cell viability assessment using the Alamar blue assay: A comparison of 2D and 3D cell culture models. Toxicol. Vitr. An. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2015, 29, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiju, T.M.; Carlos de Oliveira, R.; Wilson, S.E. 3D in vitro corneal models: A review of current technologies. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 200, 108213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, Y.; Umetsu, A.; Furuhashi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Tsugeno, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Hikage, F.; Ohguro, H. ROCK 1 and 2 affect the spatial architecture of 3D spheroids derived from human corneal stromal fibroblasts in different manners. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, T.; Manser, E.; Tan, L.; Lim, L. A novel serine/threonine kinase binding the Ras-related RhoA GTPase which translocates the kinase to peripheral membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29051–29054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, T.; Maekawa, M.; Fujisawa, K.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Fujita, A.; Watanabe, N.; Saito, Y.; Kakizuka, A.; Morii, N.; et al. The small GTP-binding protein Rho binds to and activates a 160 kDa Ser/Thr protein kinase homologous to myotonic dystrophy kinase. Embo J. 1996, 15, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SundarRaj, N.; Kinchington, P.R.; Wessel, H.; Goldblatt, B.; Hassell, J.; Vergnes, J.P.; Anderson, S.C. A Rho-associated protein kinase: Differentially distributed in limbal and corneal epithelia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Lu, J.; Yu, F.S. Role of small GTPase Rho in regulating corneal epithelial wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.C.; Stone, C.; Tkach, L.; SundarRaj, N. Rho and Rho-kinase (ROCK) signaling in adherens and gap junction assembly in corneal epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 978–986. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.; Matthew Petroll, W. Microtubule regulation of corneal fibroblast morphology and mechanical activity in 3-D culture. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 85, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lakshman, N.; Petroll, W.M. Quantitative assessment of local collagen matrix remodeling in 3-D culture: The role of Rho kinase. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 3683–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yu, F.S. Rho kinases regulate corneal epithelial wound healing. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C378–C387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohguro, H.; Ida, Y.; Hikage, F.; Umetsu, A.; Ichioka, H.; Watanabe, M.; Furuhashi, M. STAT3 Is the Master Regulator for the Forming of 3D Spheroids of 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Cells 2022, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Yano, T.; Sato, T.; Umetsu, A.; Higashide, M.; Furuhashi, M.; Ohguro, H. mTOR Inhibitors Modulate the Physical Properties of 3D Spheroids Derived from H9c2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Hosoda, K.; Fujikura, J.; Fujimoto, M.; Iwakura, H.; Tomita, T.; Ishii, T.; Arai, N.; Hirata, M.; Ebihara, K.; et al. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of Rho-associated kinase II enhances adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29574–29583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, D.T.V.; Hong, K.; Khun, T.; Zheng, M.; Ul-Haq, A.; Jun, H.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Chun, K.H. Anti-adipogenic effects of KD025 (SLx-2119), a ROCK2-specific inhibitor, in 3T3-L1 cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hikage, F.; Ichioka, H.; Watanabe, M.; Umetsu, A.; Ohguro, H.; Ida, Y. ROCK inhibitors modulate the physical properties and adipogenesis of 3D spheroids of human orbital fibroblasts in different manners. FASEB Bioadv. 2021, 3, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassumeh, S.; von Studnitz, A.; Priglinger, S.G.; Fuchshofer, R.; Luft, N.; Moloney, G.; Dirisamer, M.; Ohlmann, A. Ex vivo excimer laser ablation of cornea guttata and ROCK inhibitor-aided endothelial recolonization of ablated central cornea. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e773–e780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, M.; Miall, A.; Chou, A.; Buhl, L.; Deshpande, N.; Price, M.O.; Price, F.W.; Jurkunas, U.V. Enhanced Migration of Fuchs Corneal Endothelial Cells by Rho Kinase Inhibition: A Novel Ex Vivo Descemet’s Stripping Only Model. Cells 2024, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umetsu, A.; Ida, Y.; Sato, T.; Higashide, M.; Nishikiori, N.; Furuhashi, M.; Ohguro, H.; Watanabe, M. RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitors Significantly Modulate the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-β2 in the 2-D and 3-D Cultures of Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122784
Umetsu A, Ida Y, Sato T, Higashide M, Nishikiori N, Furuhashi M, Ohguro H, Watanabe M. RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitors Significantly Modulate the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-β2 in the 2-D and 3-D Cultures of Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122784
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmetsu, Araya, Yosuke Ida, Tatsuya Sato, Megumi Higashide, Nami Nishikiori, Masato Furuhashi, Hiroshi Ohguro, and Megumi Watanabe. 2024. "RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitors Significantly Modulate the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-β2 in the 2-D and 3-D Cultures of Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122784
APA StyleUmetsu, A., Ida, Y., Sato, T., Higashide, M., Nishikiori, N., Furuhashi, M., Ohguro, H., & Watanabe, M. (2024). RHO-Associated Coiled-Coil-Containing Protein Kinase Inhibitors Significantly Modulate the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TGF-β2 in the 2-D and 3-D Cultures of Human Corneal Stroma Fibroblasts. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122784







