Microvascular Metrics on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: Analysis of Diabetic Eye Images from Real-World Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
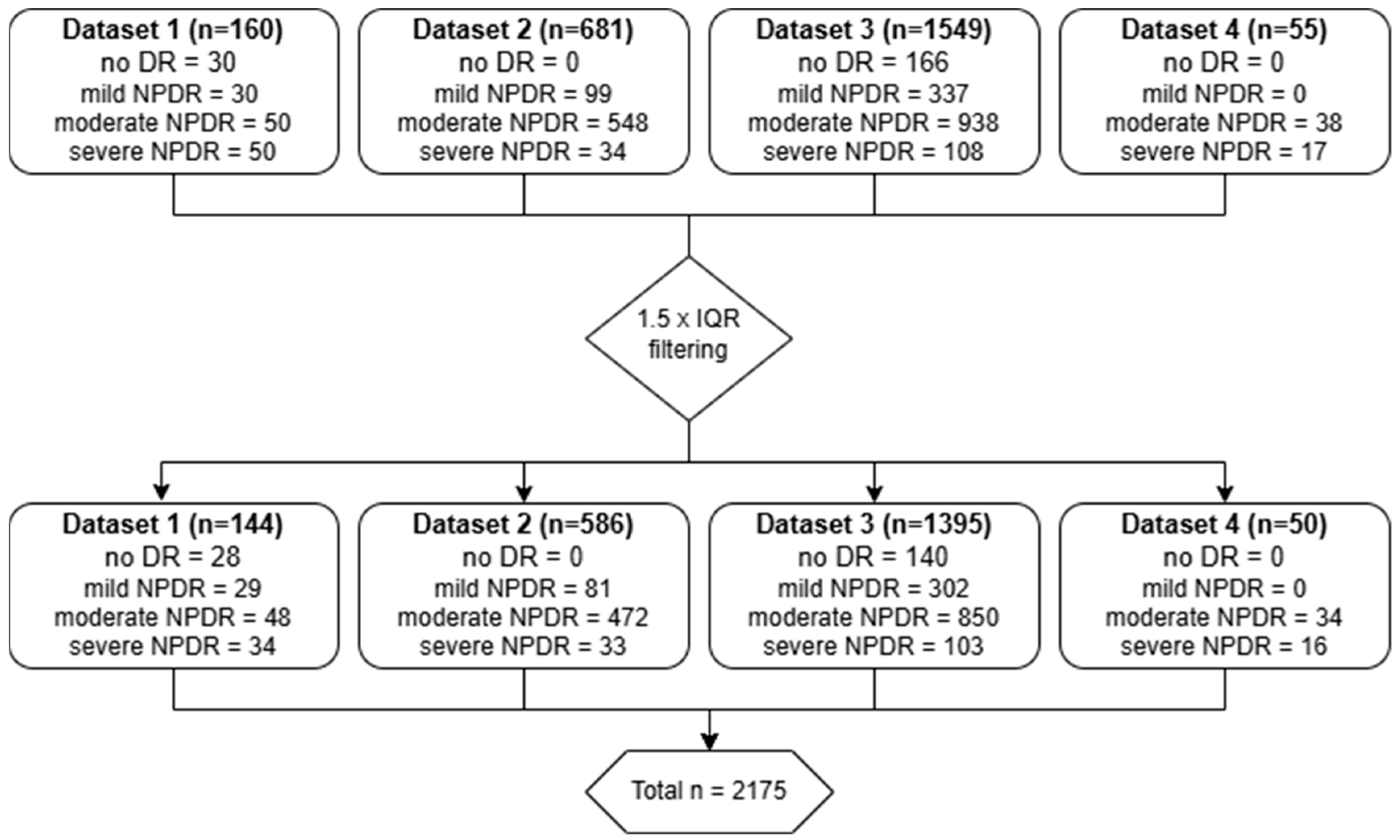
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Image Segmentation and Counting
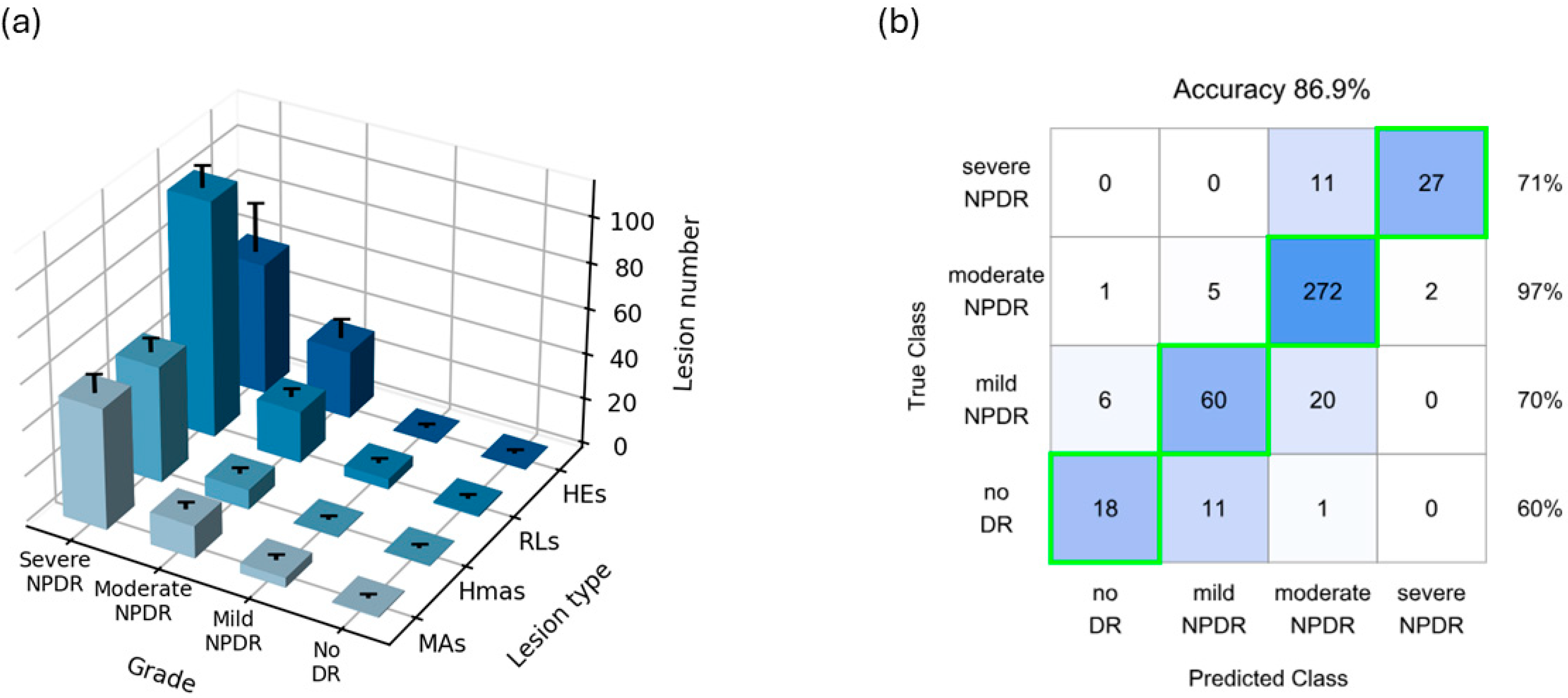
2.3. Prediction Model
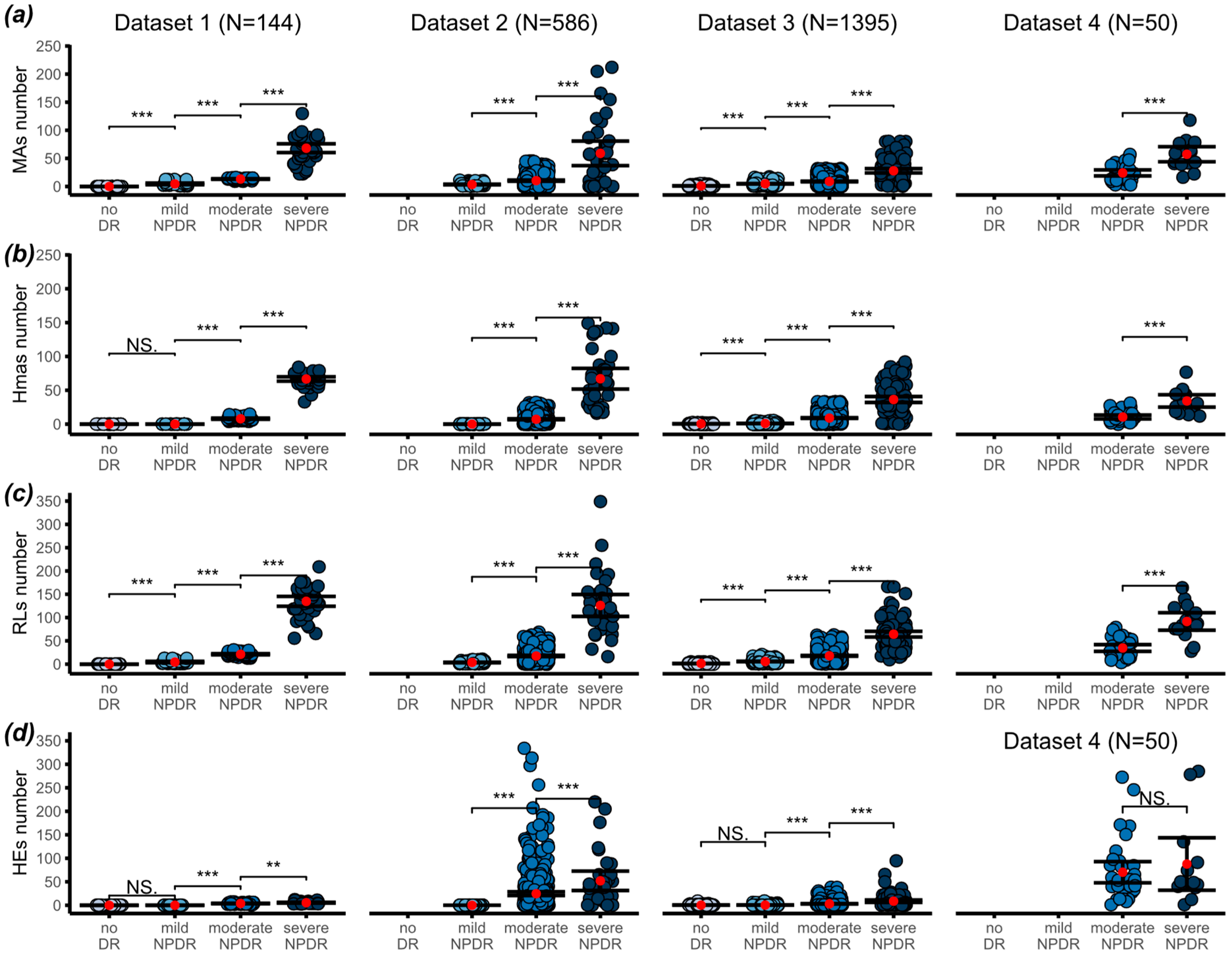
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition [Internet]. Available online: www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Vujosevic, S.; Toma, C. Diabetic retinopathy: An inflammatory disease. In Annals of Eye Science; AME Publishing Company: Hong Kong, China, 2018; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Muqit, M. ICO Guidelines for Diabetic Eye Care 2017; ICO: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tarr, J.M.; Kaul, K.; Chopra, M.; Kohner, E.M.; Chibber, R. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy. ISRN Ophthalmol. 2013, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A.C.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiology and treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohner, E.M.; Stratton, I.M.; Aldington, S.J.; Turner, R.C.; Matthews, D.R. Microaneurysms in the development of diabetic retinopathy (UKPDS 42). Diabetologia 1999, 42, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrulli, S.; Corvi, F.; Cozzi, M.; Monteduro, D.; Zicarelli, F.; Staurenghi, G. Microaneurysms visualisation using five different optical coherence tomography angiography devices compared to fluorescein angiography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romila, A.; Potop, V.; Ciuluvica, R.; Monica, B.; Mehedinti Hincu, M.; Jurja, S. Correlation between metabolic status and diabetic retinopathy evolution in type 1 diabetes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.; Pires, I.; Rosa, A.; Duarte, L.; Bernardes, R.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Microaneurysm turnover is a biomarker for diabetic retinopathy progression to clinically significant macular edema: Findings for type 2 diabetics with nonproliferative retinopathy. Ophthalmologica 2009, 223, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.L.; Nunes, S.G.; Cunha-Vaz, J.G. Microaneurysm turnover at the macula predicts risk of development of clinically significant macular edema in persons withmild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Nunes, S.; Lobo, C. Biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Manag. 2014, 4, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappuru, R.K.R.; Ribeiro, L.; Lobo, C.; Alves, D.; Cunha-Vaz, J. Microaneurysm turnover is a predictor of diabetic retinopathy progression. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha-Vaz, J.; Ribeiro, L.; Costa, M.; Simó, R. Diabetic Retinopathy Phenotypes of Progression to Macular Edema: Pooled Analysis From Independent Longitudinal Studies of up to 2 Years’ Duration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, BIO206–BIO210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.A.; Scott, I.U.; Haller, J.A.; Maguire, A.M.; Marcus, D.; McDonald, H.R. Single-field fundus photography for diabetic retinopathy screening: A report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology 2004, 111, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attiku, Y.; He, Y.; Nittala, M.G.; Sadda, S.V.R. Current status and future possibilities of retinal imaging in diabetic retinopathy care applicable to low- and medium-income countries. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 2968–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanegrungsunk, O.; Patikulsila, D.; Sadda, S.R. Ophthalmic imaging in diabetic retinopathy: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2022, 50, 1082–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilkhanian, H.; Liu, H.; Fasih-Ahmed, S.; Gnanaraj, R.; Verma, A.; Oncel, D.; He, Y.; Nittala, M.G.; Attiku, Y.; Kadomoto, S.; et al. The relationship of diabetic retinopathy severity scales with frequency and surface area of diabetic retinopathy lesions. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.C.; Menolotto, M.; Bolster, N.M.; Livingstone, I.A.T.; Giardini, M.E. A review of feature-based retinal image analysis. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 2017, 12, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carneado, J.; Almazán-Moga, A.; Ramírez-Lamelas, D.T.; Cuscó, C.; Alonso de la Fuente, J.I.; Pastor, J.C.; López Gálvez, M.I.; Ponsati, B. Quantification of Microvascular Lesions in the Central Retinal Field: Could It Predict the Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs--an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Ophthalmology 1991, 98 (Suppl. S5), 786–806. [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.D.; Goldberg, M.F. ETDRS Grading of Diabetic Retinopathy: Still the Gold Standard? Ophthalmic Res. 2019, 62, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attiku, Y.; Nittala, M.G.; Velaga, S.B.; Ramachandra, C.; Bhat, S.; Solanki, K.; Jayadev, C.; Choudhry, N.; Orr, S.M.A.; Jiang, S.; et al. Comparison of diabetic retinopathy severity grading on ETDRS 7-field versus ultrawide-field assessment. Eye 2023, 37, 2946–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domalpally, A.; Barrett, N.; Reimers, J.; Blodi, B. Comparison of Ultra-Widefield Imaging and Standard Imaging in Assessment of Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scale. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2021, 1, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadda, S.R.; Nittala, M.G.; Taweebanjongsin, W.; Verma, A.; Velaga, S.B.; Alagorie, A.R.; Sears, C.M.; Silva, P.S.; Aiello, L.P. Quantitative Assessment of the Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 218, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.P.; Ferris, F.L.; Klein, R.E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T.; et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Kang, H. Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for diabetic retinopathy screening. Inf. Sci. 2019, 501, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B.; Mo, B.; Gong, D.; Chen, N.; Ding, D.; et al. Learn to segment retinal lesions and beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 7403–7410. [Google Scholar]
- Porwal, P.; Pachade, S.; Kamble, R.; Kokare, M.; Deshmukh, G.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.; Meriaudeau, F. Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset (IDRiD): A Database for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening Research. Data 2018, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevska, A.O.; Pohosian, O.A.; Goncharuk, K.O.; Sofyna, D.F.; Chernenko, O.O.; Tronko, K.M.; Kozhan, N.I.E.; Korol, A.R. Detecting diabetic retinopathy using an artificial intelligence-based software platform: A pilot study. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 108, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Nakao, S.; Kaizu, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakama, T.; Arima, M.; Yoshida, S.; Oshima, Y.; Takeda, A.; Ikeda, Y.; et al. High-Resolution Imaging by Adaptive Optics Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy Reveals Two Morphologically Distinct Types of Retinal Hard Exudates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockett, C.W.; Praveen, P.A.; Ong, T.C.; Amutha, A.; Isom, S.P.; Jensen, E.T.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Hamman, R.F., Jr.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Lawrence, J.M.; et al. Clinical profile at diagnosis with youth-onset type 1 and type 2 diabetes in two pediatric diabetes registries: SEARCH (United States) and YDR (India). Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 22, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokholm, L.; Pedersen, F.N.; Andersen, N.; Andresen, J.; Bek, T.; Dinesen, S.; Hajari, J.; Heegaard, S.; Højlund, K.; Laugesen, C.S. Presence and development of diabetic retinopathy in 16,999 patients with type 1 diabetes in the Danish Registry of Diabetic Retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, P.A.; Madhu, S.V.; Mohan, V.; Das, S.; Kakati, S.; Shah, N.; Chaddha, M.; Bhadada, S.K.; Das, A.K.; Shukla, D.K.; et al. Registry of Youth Onset Diabetes in India (YDR): Rationale, Recruitment, and Current Status. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.A.; Madhu, S.V.; Viswanathan, M.; Das, S.; Kakati, S.; Shah, N.; Chadha, M.; Bhadada, S.K.; Kaur, T.; Dhaliwal, R.S.; et al. Demographic and clinical profile of youth onset diabetes patients in India-Results from the baseline data of a clinic based registry of people with diabetes in India with young age at onset-[YDR-02]. Pediatr. Diabetes 2021, 22, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, K. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Is Associated with Lower Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy. Am. J. Nurs. 2024, 124, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milluzzo, A.; Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Sciacca, L.; Agodi, A. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Type 2 Diabetes Retinopathy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswarappa, D.C.; Rajalakshmi, R.; Mohamed, A.; Kavya, S.; Munirathnam, H.; Manayath, G.; Kumar, M.A.; Raman, R.; Vignesh, T.; Ramasamy, K.; et al. Severity of diabetic retinopathy and its relationship with age at onset of diabetes mellitus in India: A multicentric study. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 3255–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjølie, A.K.; Klein, R.; Porta, M.; Orchard, T.; Fuller, J.; Parving, H.H.; Bilous, R.; Aldington, S.; Chaturvedi, N. Retinal microaneurysm count predicts progression and regression of diabetic retinopathy. Post-hoc results from the DIRECT Programme. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, D.M.S.; Moura, J.C.C.; Freire, C.R.; Taleb, A.C.; Valentim, R.A.M.; Morais, P.S.G. Machine learning applied to retinal image processing for glaucoma detection: Review and perspective. BioMed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, M.K.; Yan, J.; Xu, H.; Rehman, Z.U.; Jabbar, A. Transfer Learning-Based Model for Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Using Retinal Images. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, R.S.; Cope, D.; Ip, J.; Lotosh, M.; Shah, A.; Weng, J.; Tang, R. “Garbage in, garbage out” revisited: What do machine learning application papers report about human-labeled training data? Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 795–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia, A.O.; Zhu, C.Z.; Althubiti, S.A.; Al-Alimi, D.; Xiao, Y.L.; Ouyang, P.B.; Al-Qaness, M.A.A. Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Images Using CNN Classification Models. Electronics 2022, 11, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.E.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Looking forward to 2030. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1077669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowski, A.; Brona, P.; Lim, G.; Ruamviboonsuk, P.; Tan, G.S.W.; Abramoff, M.; Ting, D.S. Artificial intelligence for diabetic retinopathy screening: A review. Eye 2020, 34, 451–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, A.E.; Davidson, O.Q.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, A.Y. Artificial Intelligence and Diabetic Retinopathy: AI Framework, Prospective Studies, Head-to-head Validation, and Cost-effectiveness. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wang, H.; She, C.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Tao, Y. Artificial intelligence promotes the diagnosis and screening of diabetic retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 946915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuscó, C.; Esteve-Bricullé, P.; Almazán-Moga, A.; Fernández-Carneado, J.; Ponsati, B. Microvascular Metrics on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: Analysis of Diabetic Eye Images from Real-World Data. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122753
Cuscó C, Esteve-Bricullé P, Almazán-Moga A, Fernández-Carneado J, Ponsati B. Microvascular Metrics on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: Analysis of Diabetic Eye Images from Real-World Data. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122753
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuscó, Cristina, Pau Esteve-Bricullé, Ana Almazán-Moga, Jimena Fernández-Carneado, and Berta Ponsati. 2024. "Microvascular Metrics on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: Analysis of Diabetic Eye Images from Real-World Data" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122753
APA StyleCuscó, C., Esteve-Bricullé, P., Almazán-Moga, A., Fernández-Carneado, J., & Ponsati, B. (2024). Microvascular Metrics on Diabetic Retinopathy Severity: Analysis of Diabetic Eye Images from Real-World Data. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122753







