Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases
Abstract
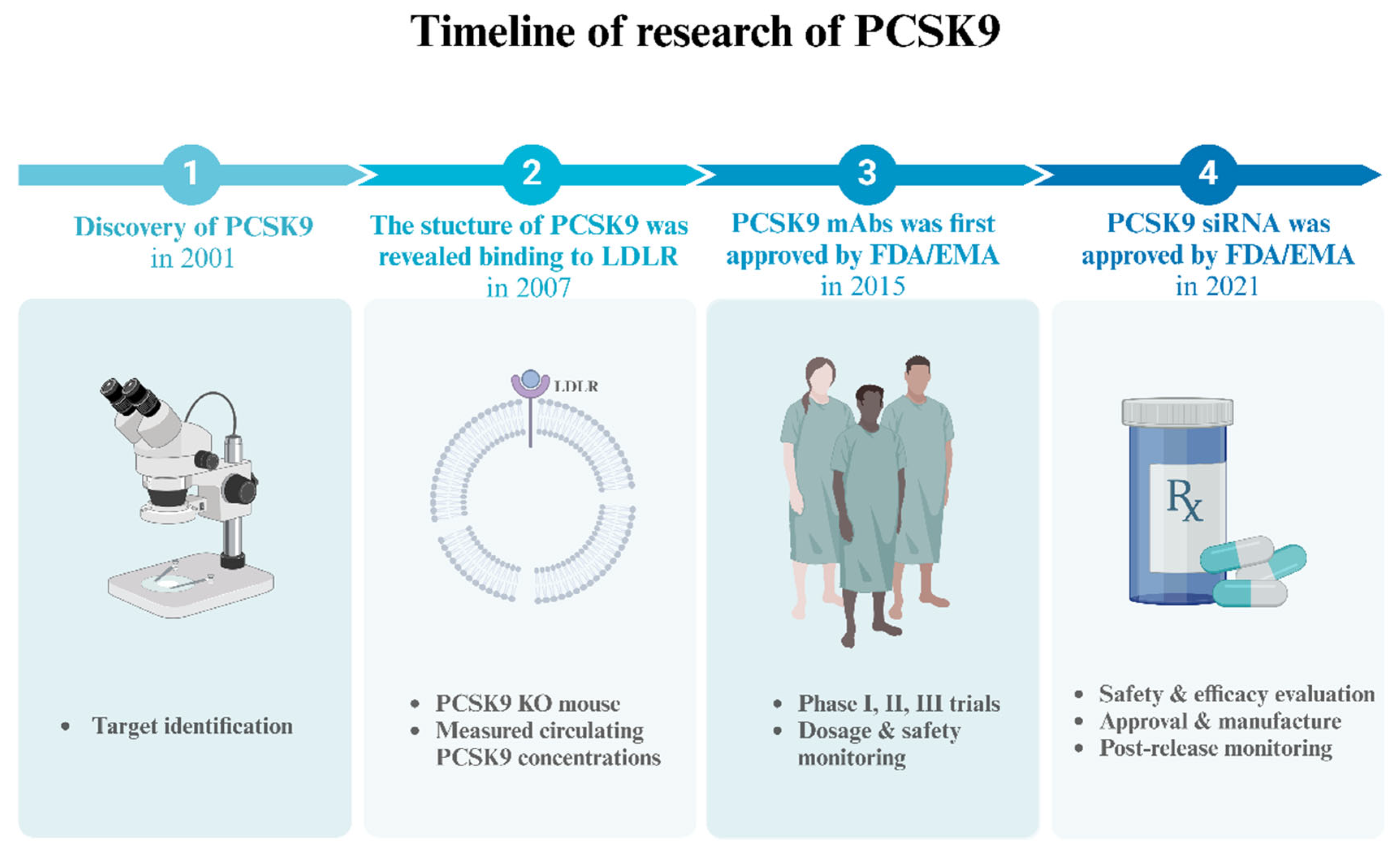
1. Introduction
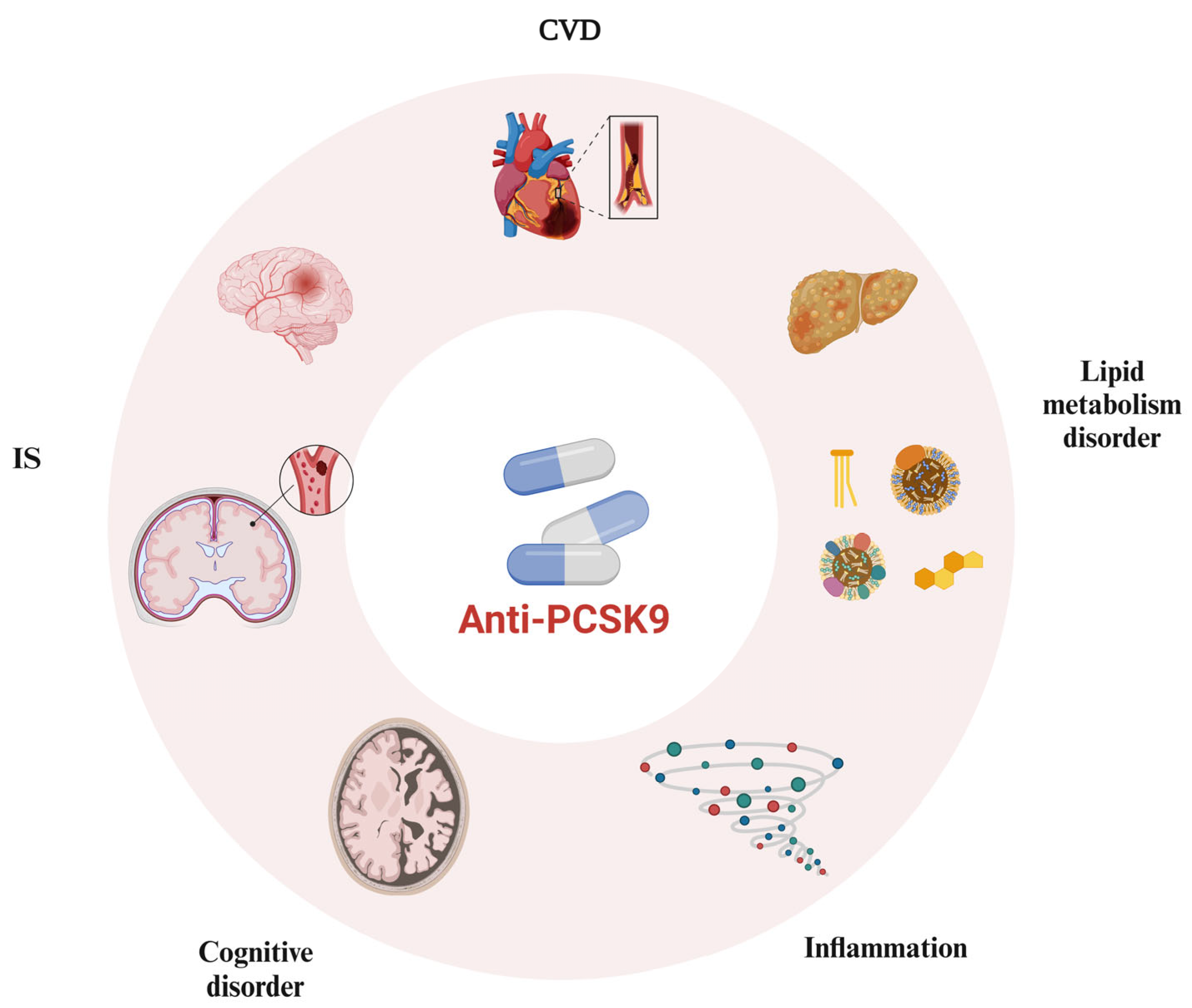
2. Enhanced Application of PCSK9 Inhibitors in the Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Systems
2.1. Involvement of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Lipid Metabolism
2.2. Involvement of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Anti-Atherosclerotic and Plaque-Stabilizing Effects
2.3. Involvement of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Anti-Inflammatory Effects
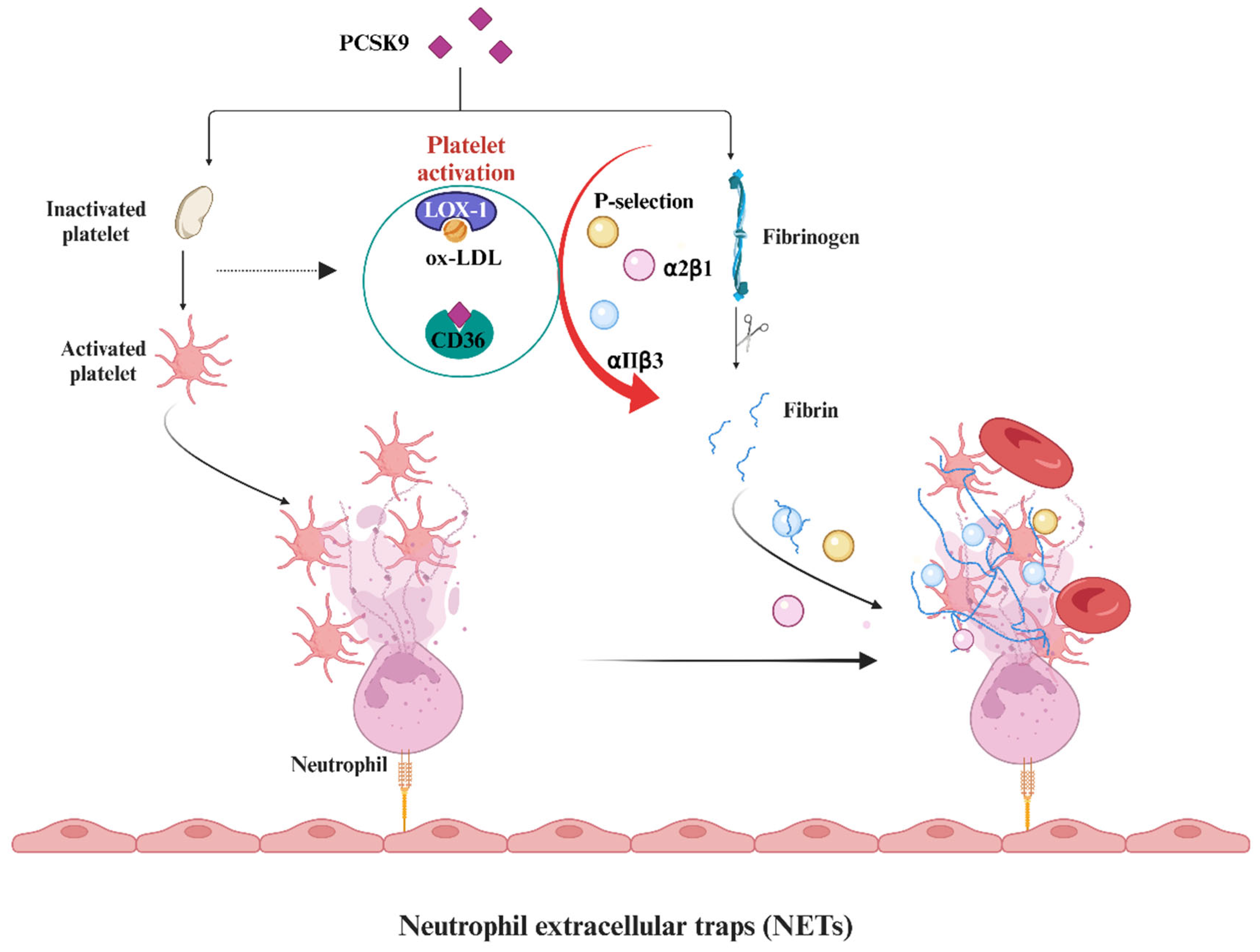
2.4. Involvement of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Antiplatelet Aggregation and Antithrombosis
3. PCSK9 Inhibitors and the Central Nervous System
4. PCSK9 Inhibitors and Other Systems
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: Current features and implications. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Hacke, W.; Fisher, M.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Lau, F.; Giugliano, R.P. Lipoprotein(a) and its Significance in Cardiovascular Disease. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannesen, C.D.L.; Mortensen, M.B.; Langsted, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G. ApoB and Non-HDL Cholesterol Versus LDL Cholesterol for Ischemic Stroke Risk. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 92, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polychronopoulos, G.; Tziomalos, K. Novel treatment options for the management of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Chan, D.C.; Watts, G.F. The Knowns and Unknowns of Contemporary Statin Therapy for Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabès, J.-P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; Cruaud, C.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Erlich, D.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Jasmin, S.B.; Stifani, S.; Basak, A.; Prat, A.; Chrétien, M. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joy, T.R. Novel therapeutic agents for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 135, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Steg, P.G.; Szarek, M.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Edelberg, J.M.; Goodman, S.G.; Hanotin, C.; Harrington, R.A.; et al. Alirocumab and Cardiovascular Outcomes after Acute Coronary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Revkin, J.; Amarenco, P.; Brunell, R.; Curto, M.; Civeira, F.; Flather, M.; Glynn, R.J.; Gregoire, J.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Cardiovascular Efficacy and Safety of Bococizumab in High-Risk Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Landmesser, U.; Leiter, L.A.; Kallend, D.; Dufour, R.; Karakas, M.; Hall, T.; Troquay, R.P.; Turner, T.; Visseren, F.L.; et al. Inclisiran in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk with Elevated LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, M.J.; Hofherr, A.; Schumi, J.; Rekic, D.; Knochel, J.; Nilsson, C.A.M.; Rudvik, A.; Wernevik, L.; Ryden-Bergsten, T.; Carlsson, B.C.L. Etesian: A Phase 2b Study of the Efficacy, Safety and Tolerability of Azd8233, a Pcsk9-Targeted Antisense Oligonucleotide, in Patients with Dyslipidemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitlinger, M.; Bauer, M.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Stoekenbroek, R.M.; Lambert, G.; Berger-Sieczkowski, E.; Lagler, H.; Oesterreicher, Z.; Wulkersdorfer, B.; Luhrs, P.; et al. A phase I study assessing the safety, tolerability, immunogenicity, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering activity of immunotherapeutics targeting PCSK9. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vroom, M.M.; Lu, H.; Lewis, M.; Thibodeaux, B.A.; Brooks, J.K.; Longo, M.S.; Ramos, M.M.; Sahni, J.; Wiggins, J.; Boyd, J.D.; et al. VXX-401, a novel anti-PCSK9 vaccine, reduces LDL-C in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.G.; Mazzola, A.M.; Braun, M.C.; Platt, C.; Vafai, S.B.; Kathiresan, S.; Rohde, E.; Bellinger, A.M.; Khera, A.V. Efficacy and Safety of an Investigational Single-Course CRISPR Base-Editing Therapy Targeting PCSK9 in Nonhuman Primate and Mouse Models. Circ. J. 2023, 147, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, S.; Mayer, G.; Benjannet, S.; Bergeron, E.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Nassoury, N.; Mayer, H.; Nimpf, J.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G. The Proprotein Convertase PCSK9 Induces the Degradation of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR) and Its Closest Family Members VLDLR and ApoER2. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Lagace, T.A.; Garuti, R.; Zhao, Z.; McDonald, M.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Binding of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Epidermal Growth Factor-like Repeat A of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Decreases Receptor Recycling and Increases Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18602–18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Pedersen, T.R.; Park, J.G.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Gaciong, Z.A.; Ceska, R.; Toth, K.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Schiele, F.; et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of achieving very low LDL-cholesterol concentrations with the PCSK9 inhibitor evolocumab: A prespecified secondary analysis of the FOURIER trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1962–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.G.; Steg, P.G.; Poulouin, Y.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Garon, G.; Harrington, R.A.; Jukema, J.W.; Manvelian, G.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Alirocumab in 8242 Patients Eligible for 3 to 5 Years of Placebo-Controlled Observation in the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaba, P.; O’Donoghue, M.L.; Park, J.-G.; Wiviott, S.D.; Atar, D.; Kuder, J.F.; Im, K.; Murphy, S.A.; De Ferrari, G.M.; Gaciong, Z.A.; et al. Association Between Achieved Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels and Long-Term Cardiovascular and Safety Outcomes: An Analysis of FOURIER-OLE. Circulation 2023, 147, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.K.; Troquay, R.P.T.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Leiter, L.A.; Scott Wright, R.; Vikarunnessa, S.; Talloczy, Z.; Zang, X.; Maheux, P.; Lesogor, A.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of inclisiran in patients with high cardiovascular risk and elevated LDL cholesterol (ORION-3): Results from the 4-year open-label extension of the ORION-1 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, N.S.; Patel, N.; Kalra, R.; Ahmad, A.; Venkatraman, A.; Arora, G.; Arora, P. Neurological effects of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors: Direct comparisons. Eur. Heart J.—Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2018, 4, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatasakis, A.; Danek, B.A.; Karacsonyi, J.; Rangan, B.V.; Roesle, M.K.; Knickelbine, T.; Miedema, M.D.; Khalili, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Abdullah, S.; et al. Effect of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia: A Meta-Analysis of 35 Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, K.; Chen, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J.; Dai, Z.; Huang, H.; et al. PSCK9 inhibitors reduced early recurrent stroke in patients with symptomatic intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Fazio, S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Kanevsky, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Im, K.; Lira Pineda, A.; Wasserman, S.M.; Češka, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a), PCSK9 Inhibition, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circulation 2019, 139, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Noureen, A.; Kronenberg, F.; Utermann, G. Structure, function, and genetics of lipoprotein (a). J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1339–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, P.A.; Zhu, W.Q.; Zhao, W.X.; Huang, P.P.; Ran, J.L.; Tang, Y.X.; Huang, X.S.; Li, R. Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin-type 9 inhibitors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 565, 119982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, F.J.; Giugliano, R.P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Koren, M.J.; Langslet, G.; Bays, H.; Blom, D.; Eriksson, M.; Dent, R.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Reduction in Lipoprotein(a) With PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody Evolocumab (AMG 145). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, G.F.; Chan, D.C.; Somaratne, R.; Wasserman, S.M.; Scott, R.; Marcovina, S.M.; Barrett, P.H.R. Controlled study of the effect of proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 inhibition with evolocumab on lipoprotein(a) particle kinetics. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, G.F.; Chan, D.C.; Pang, J.; Ma, L.; Ying, Q.; Aggarwal, S.; Marcovina, S.M.; Barrett, P.H.R. PCSK9 Inhibition with alirocumab increases the catabolism of lipoprotein(a) particles in statin-treated patients with elevated lipoprotein(a). Metabolism 2020, 107, 154221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubtsova, A.; Chamberland, A.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Essalmani, R.; Fazel, A.; Bergeron, J.J.; Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. PCSK9 deficiency unmasks a sex- and tissue-specific subcellular distribution of the LDL and VLDL receptors in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2133–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Pang, L.; Zhang, R.; Murgolo, N.J.; Lan, H.; Hedrick, J.A. PCSK9 binds to multiple receptors and can be functionally inhibited by an EGF-A peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kysenius, K.; Muggalla, P.; Mätlik, K.; Arumäe, U.; Huttunen, H.J. PCSK9 regulates neuronal apoptosis by adjusting ApoER2 levels and signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollstein, T.; Vogt, A.; Grenkowitz, T.; Stojakovic, T.; Marz, W.; Laufs, U.; Bolukbasi, B.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Scharnagl, H.; Kassner, U. Treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors reduces atherogenic VLDL remnants in a real-world study. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 116, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Groen, A.K. Metabolic effects of PCSK9 inhibition with Evolocumab in subjects with elevated Lp(a). Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, M.; Canuel, M.; Sun, X.; Asselin, M.-C.; Paramithiotis, E.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Can Mediate Degradation of the Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP-1). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Tang, Z.-H.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.-F.; Jiang, Z.-S.; Liu, L.-S. PCSK9 siRNA inhibits HUVEC apoptosis induced by ox-LDL via Bcl/Bax–caspase9–caspase3 pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 359, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, G. Investigation of highly expressed PCSK9 in atherosclerotic plaques and ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkapli, R.; Muid, S.A.; Wang, S.M.; Nawawi, H. PCSK9 Inhibitors Reduce PCSK9 and Early Atherogenic Biomarkers in Stimulated Human Coronary Artery Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Su, G. Effect of evolocumab on the progression and stability of atherosclerotic plaques as evaluated by grayscale and iMAP-IVUS. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Puri, R.; Anderson, T.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Cho, L.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Koenig, W.; Somaratne, R.; Kassahun, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Effect of Evolocumab on Progression of Coronary Disease in Statin-Treated Patients. JAMA 2016, 316, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, H.; Horinaka, S.; Ishimitsu, T. Effect of evolocumab therapy on coronary fibrous cap thickness assessed by optical coherence tomography in patients with acute coronary syndrome. J. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Kong, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, S.; Qu, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, Z.; Luo, X. Effect of PCSK9 inhibition in combination with statin therapy on intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: A high-resolution MRI study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1127534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lepor, N.E.; Cantón, G.; Contreras, L.; Hippe, D.S.; Isquith, D.A.; Balu, N.; Kedan, I.; Simonini, A.A.; Yuan, C.; et al. Serial magnetic resonance imaging detects a rapid reduction in plaque lipid content under PCSK9 inhibition with alirocumab. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 37, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.-H.; Peng, J.; Ren, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, T.-T.; Li, T.-H.; Wang, Z.; Wei, D.-H.; Liu, L.-S.; Zheng, X.-L.; et al. New role of PCSK9 in atherosclerotic inflammation promotion involving the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Atherosclerosis 2017, 262, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Shahanawaz, J.; Shmookler Reis, R.J.; Varughese, K.I.; Sawamura, T.; Mehta, J.L. Cross-talk between LOX-1 and PCSK9 in vascular tissues. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.L.; Zhou, S.; Fan, Y.; Deng, X.; Theus, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z. PCSK9 regulates expression of scavenger receptors and ox-LDL uptake in macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunzioni, I.; Tavori, H.; Covarrubias, R.; Major, A.S.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; DeVay, R.M.; Hong, L.; Fan, D.; Predazzi, I.M.; et al. Local effects of human PCSK9 on the atherosclerotic lesion. J. Pathol. 2015, 238, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landlinger, C.; Pouwer, M.G.; Juno, C.; van der Hoorn, J.W.A.; Pieterman, E.J.; Jukema, J.W.; Staffler, G.; Princen, H.M.G.; Galabova, G. The AT04A vaccine against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 reduces total cholesterol, vascular inflammation, and atherosclerosis in APOE*3Leiden.CETP mice. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühnast, S.; van der Hoorn, J.W.A.; Pieterman, E.J.; van den Hoek, A.M.; Sasiela, W.J.; Gusarova, V.; Peyman, A.; Schäfer, H.-L.; Schwahn, U.; Jukema, J.W.; et al. Alirocumab inhibits atherosclerosis, improves the plaque morphology, and enhances the effects of a statin. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernelot Moens, S.J.; Neele, A.E.; Kroon, J.; van der Valk, F.M.; Van den Bossche, J.; Hoeksema, M.A.; Hoogeveen, R.M.; Schnitzler, J.G.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Manvelian, G.; et al. PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies reverse the pro-inflammatory profile of monocytes in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Sabouri-Rad, S.; Gotto, A.M.; Pirro, M.; Banach, M.; Awan, Z.; Barreto, G.E.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 and inflammation: A review of experimental and clinical evidence. Eur. Heart J.—Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 5, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohula, E.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Verma, S.; Park, J.G.; Sever, P.S.; Lira Pineda, A.; Honarpour, N.; Wang, H.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Inflammatory and Cholesterol Risk in the FOURIER Trial. Circulation 2018, 138, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogeveen, R.M.; Opstal, T.S.J.; Kaiser, Y.; Stiekema, L.C.A.; Kroon, J.; Knol, R.J.J.; Bax, W.A.; Verberne, H.J.; Cornel, J.H.; Stroes, E.S.G. PCSK9 Antibody Alirocumab Attenuates Arterial Wall Inflammation Without Changes in Circulating Inflammatory Markers. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Paolisso, P.; D’Onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; La Grotta, R.; Frigé, C.; Ferraraccio, F.; Panarese, I.; et al. Evidence of an anti-inflammatory effect of PCSK9 inhibitors within the human atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis 2023, 378, 117180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Jia, D.; Yao, Z.; Chang, L.; Pan, G.; Zhong, H.; et al. PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) Enhances Platelet Activation, Thrombosis, and Myocardial Infarct Expansion by Binding to Platelet CD36. Circulation 2021, 143, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Nocella, C.; Farcomeni, A.; Bartimoccia, S.; Santulli, M.; Vasaturo, F.; Carnevale, R.; Menichelli, D.; Violi, F.; Pignatelli, P.; et al. Relationship of PCSK9 and Urinary Thromboxane Excretion to Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, C.-G.; Guo, Y.-L.; Xu, R.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, J.-J. The Relationship between the Plasma PCSK9 Levels and Platelet Indices in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.; Brunssen, C.; Morawietz, H. Contribution of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 and LOX-1 modulating compounds to vascular diseases. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pęczek, P.; Leśniewski, M.; Mazurek, T.; Szarpak, L.; Filipiak, K.J.; Gąsecka, A. Antiplatelet Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Primary Hypercholesterolemia. Life 2021, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Kleiman, K.; Meng, H.; Knight, J.S.; Eitzman, D.T. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) Deficiency is Protective Against Venous Thrombosis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marston, N.A.; Gurmu, Y.; Melloni, G.E.M.; Bonaca, M.; Gencer, B.; Sever, P.S.; Pedersen, T.R.; Keech, A.C.; Roselli, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; et al. The Effect of PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9) Inhibition on the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism. Circulation 2020, 141, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barale, C.; Bonomo, K.; Frascaroli, C.; Morotti, A.; Guerrasio, A.; Cavalot, F.; Russo, I. Platelet function and activation markers in primary hypercholesterolemia treated with anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody: A 12-month follow-up. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, S.; Prat, A.; Marcinkiewicz, E.; Paquin, J.; Chitramuthu, B.P.; Baranowski, D.; Cadieux, B.; Bennett, H.P.J.; Seidah, N.G. Implication of the proprotein convertase NARC-1/PCSK9 in the development of the nervous system. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kriz, J.; Zhou, A.; Hatten, M.E.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G. PCSK9 reduces the protein levels of the LDL receptor in mouse brain during development and after ischemic stroke. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelezz, S.A.; Hendawy, N. HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4 axis and glutamate as novel targets for PCSK9 inhibitor in high fat cholesterol diet induced cognitive impairment and amyloidosis. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmastroni, E.; Molari, G.; De Beni, N.; Colpani, O.; Galimberti, F.; Gazzotti, M.; Zambon, A.; Catapano, A.L.; Casula, M. Statin use and risk of dementia or Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 29, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Bavishi, C.; Riaz, H.; Farid, T.A.; Khan, S.; Atlas, M.; Hirsch, G.; Ikram, S.; Bolli, R. Increased Risk of Adverse Neurocognitive Outcomes With Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin-Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2017, 10, e003153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, M.J.; Urbach, D.V.; van Nieuwenhuizen, E.; Zhao, J.; Yellin, O.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; Pordy, R.; Manvelian, G. Alirocumab treatment and neurocognitive function according to the CANTAB scale in patients at increased cardiovascular risk: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis 2021, 331, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seijas-Amigo, J.; Mauriz-Montero, M.J.; Suarez-Artime, P.; Gayoso-Rey, M.; Estany-Gestal, A.; Casas-Martínez, A.; González-Freire, L.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, A.; Pérez-Rodriguez, N.; Villaverde-Piñeiro, L.; et al. Cognitive Function with PCSK9 Inhibitors: A 24-Month Follow-Up Observational Prospective Study in the Real World—MEMOGAL Study. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2023, 23, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscica, M.; Korthauer, L.E.; Giugliano, R.P.; Guo, J.; Sabatine, M.S.; Sever, P.; Keech, A.; Atar, D.; Kurtz, C.; Ruff, C.T.; et al. No association between APOE genotype and lipid lowering with cognitive function in a randomized controlled trial of evolocumab. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authors/Task Force, M.; Catapano, A.L.; Graham, I.; De Backer, G.; Wiklund, O.; Chapman, M.J.; Drexel, H.; Hoes, A.W.; Jennings, C.S.; Landmesser, U.; et al. 2016 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: The Task Force for the Management of Dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Developed with the special contribution of the European Assocciation for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Atherosclerosis 2016, 253, 281–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Pradhan, A.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J. Cardiovascular benefits and diabetes risks of statin therapy in primary prevention: An analysis from the JUPITER trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.J.; Looker, H.C.; Akbar, T.; Betteridge, D.J.; Durrington, P.N.; Hitman, G.A.; Neil, H.A.; Fuller, J.H.; Colhoun, H.M. Effect of atorvastatin on glycaemia progression in patients with diabetes: An analysis from the Collaborative Atorvastatin in Diabetes Trial (CARDS). Diabetologia 2016, 59, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhi, C.; Le May, C.; Gmyr, V.; Vandewalle, B.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Krempf, M.; Pattou, F.; Costet, P.; Cariou, B. PCSK9 is expressed in pancreatic delta-cells and does not alter insulin secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyot, M.L.; Roubtsova, A.; Lussier, R.; Chamberland, A.; Essalmani, R.; Murthy Madiraju, S.R.; Seidah, N.G.; Prentki, M.; Prat, A. Substantial PCSK9 inactivation in beta-cells does not modify glucose homeostasis or insulin secretion in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.F.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Patel, R.S.; Fairhurst-Hunter, Z.; Lyall, D.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Horta, B.L.; Hypponen, E.; Power, C.; et al. PCSK9 genetic variants and risk of type 2 diabetes: A mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Pratico, D.; Mazidi, M.; Davies, I.G.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Seidah, N.; Libby, P.; Kroemer, G.; Ren, J. PCSK9 in metabolism and diseases. Metabolism 2024, 156064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, E.S.; Tan, H.C.; Le, D.H.T.; Huynh, T.T.; Wills, B.; Seidah, N.G.; Ooi, E.E.; Yacoub, S. Dengue virus induces PCSK9 expression to alter antiviral responses and disease outcomes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Hammel, P.; Hebbar, M.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Raoul, J.L.; Chone, L.; Francois, E.; Artru, P.; Biagi, J.J.; et al. FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Types | Drug Name | Description | Trials | Clinical Trial Name | Clinical Trial Phase | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCSK9 mAbs | Alirocumab [11] | Monoclonal antibodies | ODYSSEY OUTCOMES | NCT01663402 | 3 | Targeting to bind with PCSK9 |
| Evolocumab [12] | FOURIER | NCT01764633 | 3 | |||
| Bococizumab [13] | SPIRE | NCT01975376 NCT01975389 | 3 * | |||
| siRNA | Inclisiran [14] | Small interfering RNA | ORION | NCT02597127 | 3 | Binding to PCSK9 mRNA and silencing the expression of the target PCSK9 gene |
| ASO | AZD8233 [15] | Antisense oligonucleotide | ETESIAN | NCT04641299 | 2b | Inhibiting the gene transcript of a target protein PCSK9 in the nucleus |
| Vaccines | AT04A [16] AT06A [16] | Vaccine | - | NCT02508896 | 1 | Leveraging the immune system to counteract PCSK9 |
| - | NCT02508896 | 1 | ||||
| VXX-401 [17] | - | NCT05762276 | 1 | |||
| Oral PCSK9 inhibitors | AZD0780 | Antisense oligonucleotide | PURSUIT | NCT06173570 ** | 2b | Suppressing the expression of the PCSK9 gene |
| MK-0616 | Macrocyclic peptide | - | NCT05952856 ** NCT05952869 ** NCT06008756 ** | 3 | Binding to PCSK9 and inhibiting the combination between PCSK9 and LDLR | |
| Gene therapy | VERVE-101 [18] | Gene editing technique | VT-1001 | NCT05398029 ** | 1 | Disrupting target PCSK9 gene via CRISPR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Zhou, J.; et al. Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122729
Li Z, Zhu L, Xu Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Sun H, Li S, Wang M, Jiang T, Zhou J, et al. Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122729
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhenzhen, Lin Zhu, Yeqiong Xu, Yiting Zhang, Yukai Liu, Huiling Sun, Shuo Li, Meng Wang, Teng Jiang, Junshan Zhou, and et al. 2024. "Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122729
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhu, L., Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Sun, H., Li, S., Wang, M., Jiang, T., Zhou, J., & Deng, Q. (2024). Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122729








