Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Collation
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Coagulation Co-Expression Network Construction and Differential Analysis
2.4. Construction of a Prognostic Model and Survival Analysis
2.5. Nomogram Model Construction
2.6. GSVA and GSEA
2.7. Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis
2.8. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
2.9. Cell Culture
2.10. Transfection
2.11. Real Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.12. Western Blotting
2.13. Colony Formation Assay
2.14. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.15. Apoptosis and Necrosis Assay
2.16. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.17. Transwell Assay
2.18. Wound-Healing Assay
2.19. Platelet Activation Analysis
2.20. Animal Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Identification of mRNA Modules Associated with Coagulation
3.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis and Identification of Coagulation-Associated Gene Sets
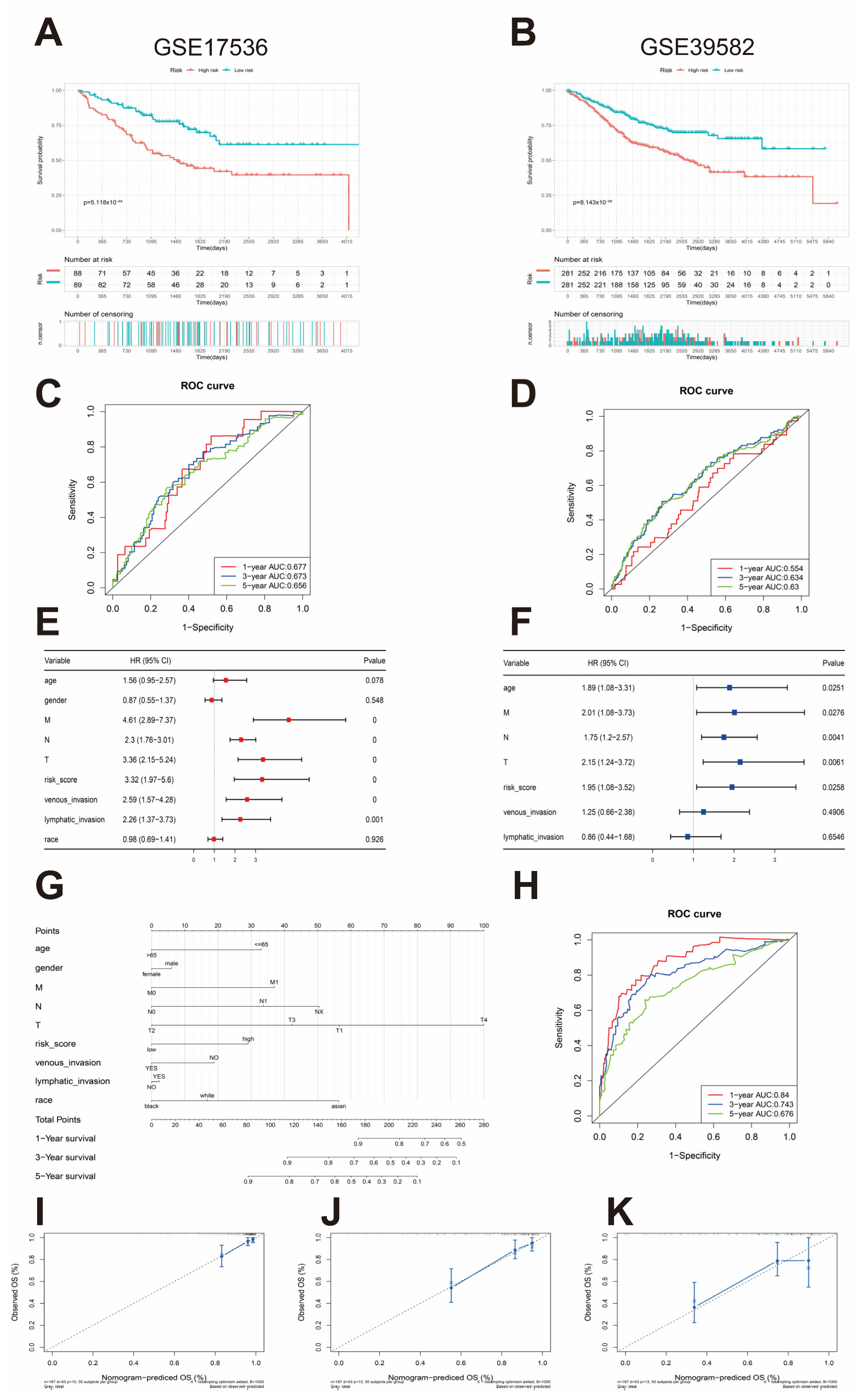
3.3. Development of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Risk Signature
3.4. External Validation of the Risk Assessment Model
3.5. Nomogram Construction and Validation and Independent Prognostic Factor Analysis
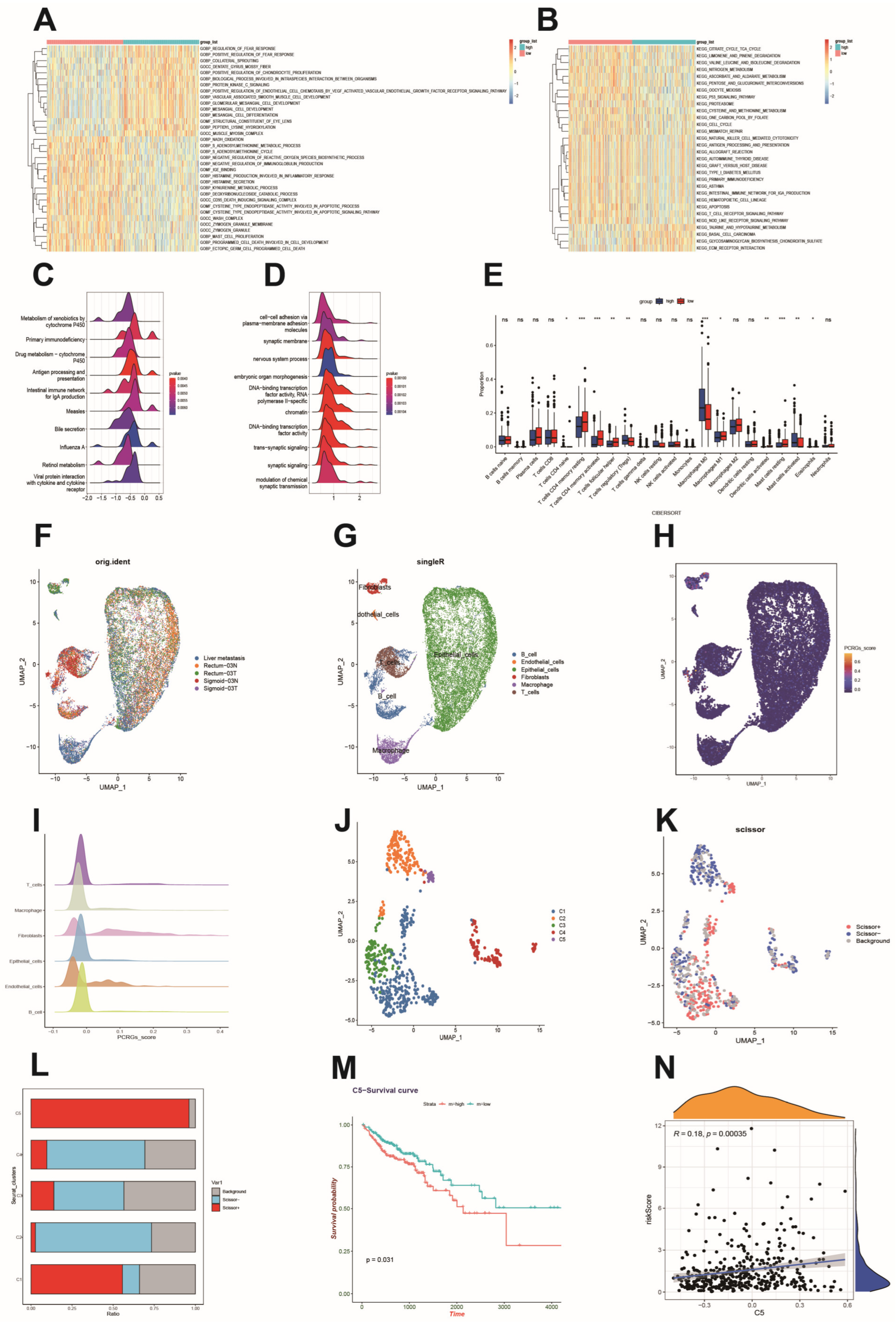
3.6. Functional Analysis Based on the Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Risk Signature
3.7. Immune Cell Infiltration and Its Correlation with Hub Genes
3.8. Single-Cell Sequencing Reveals a Relationship between Risk Scores and the Tumor Microenvironment
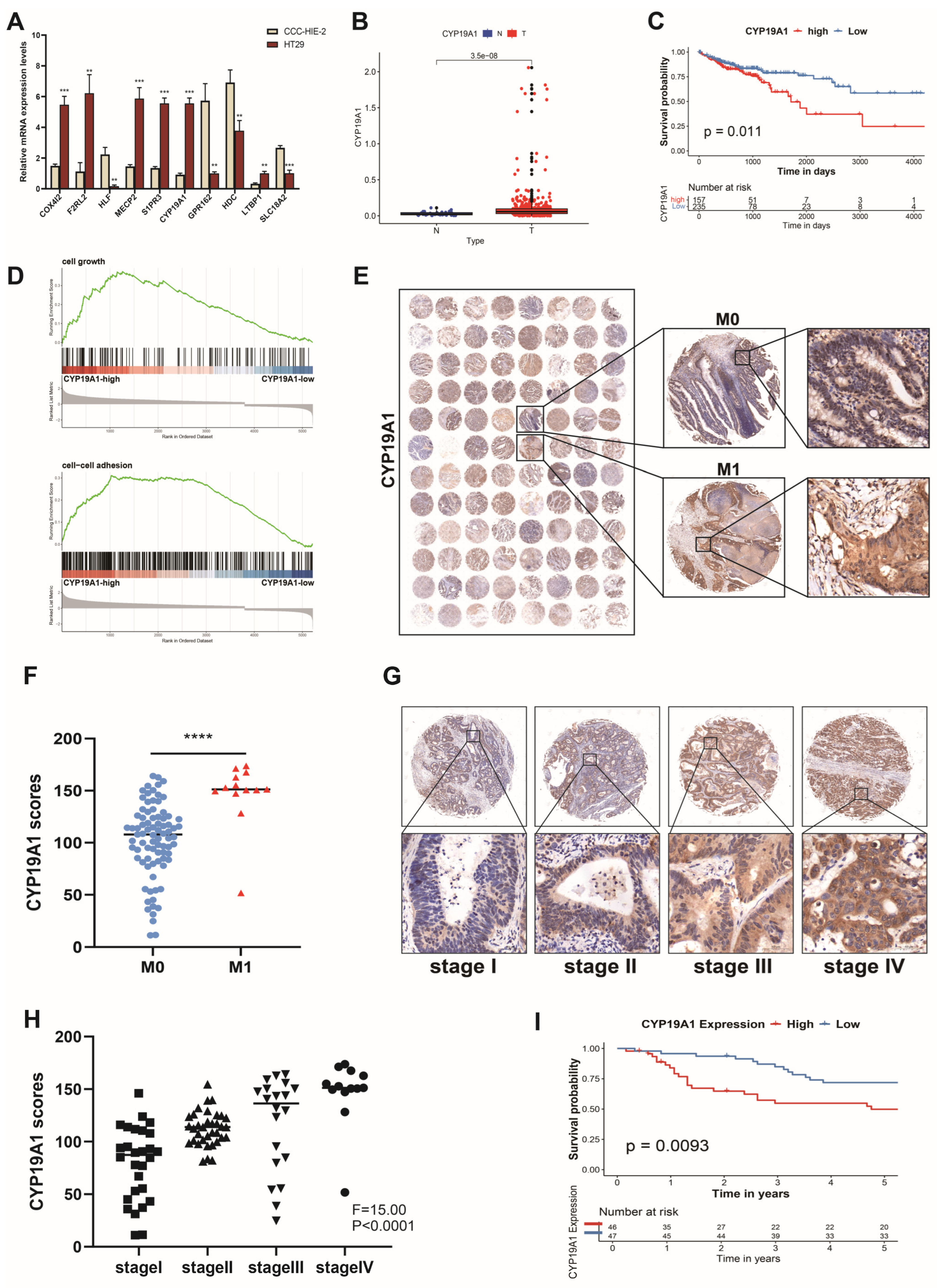
3.9. High CYP19A1 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in CRC
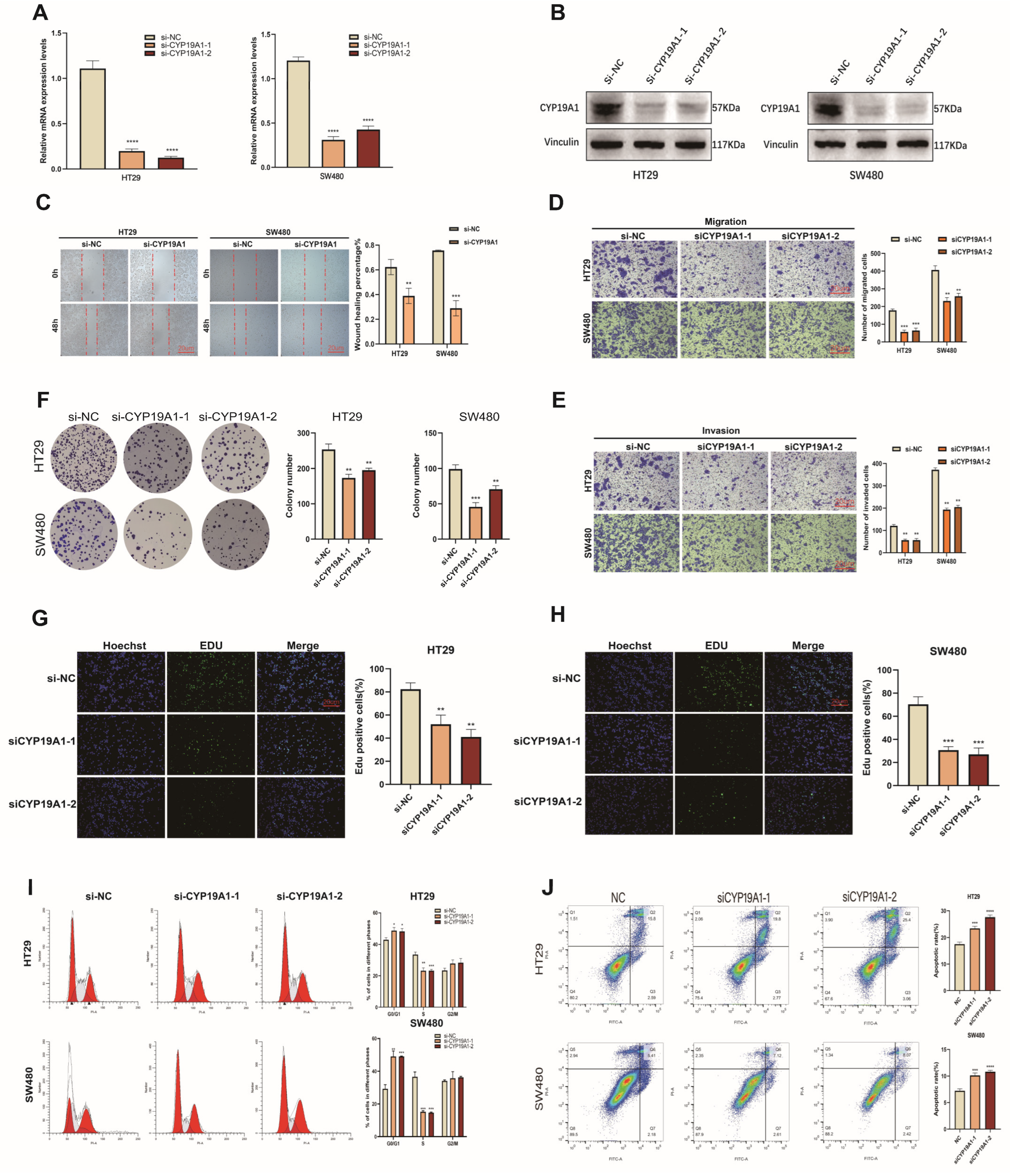
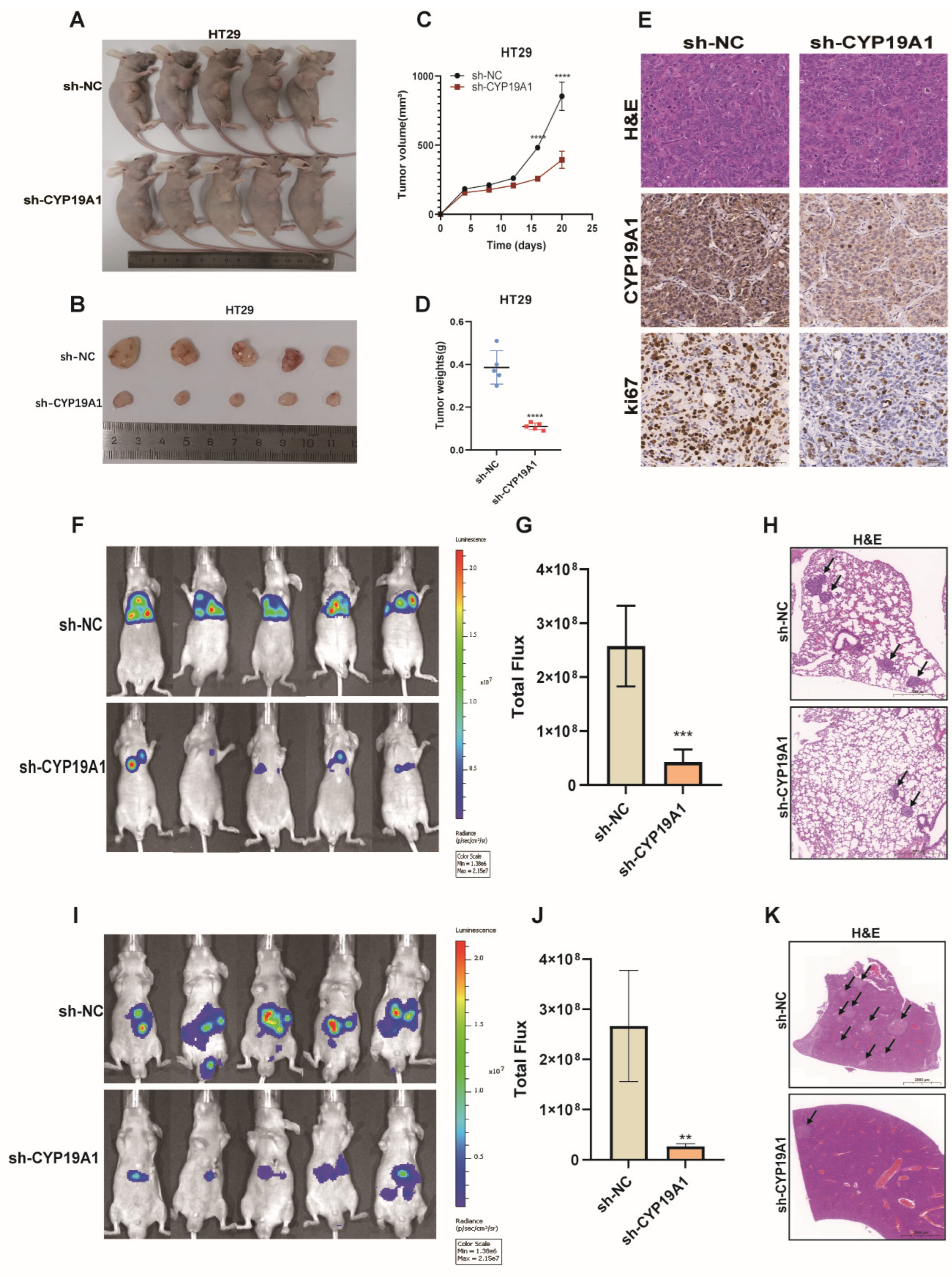
3.10. CYP19A1 Promotes CRC Growth and Metastasis
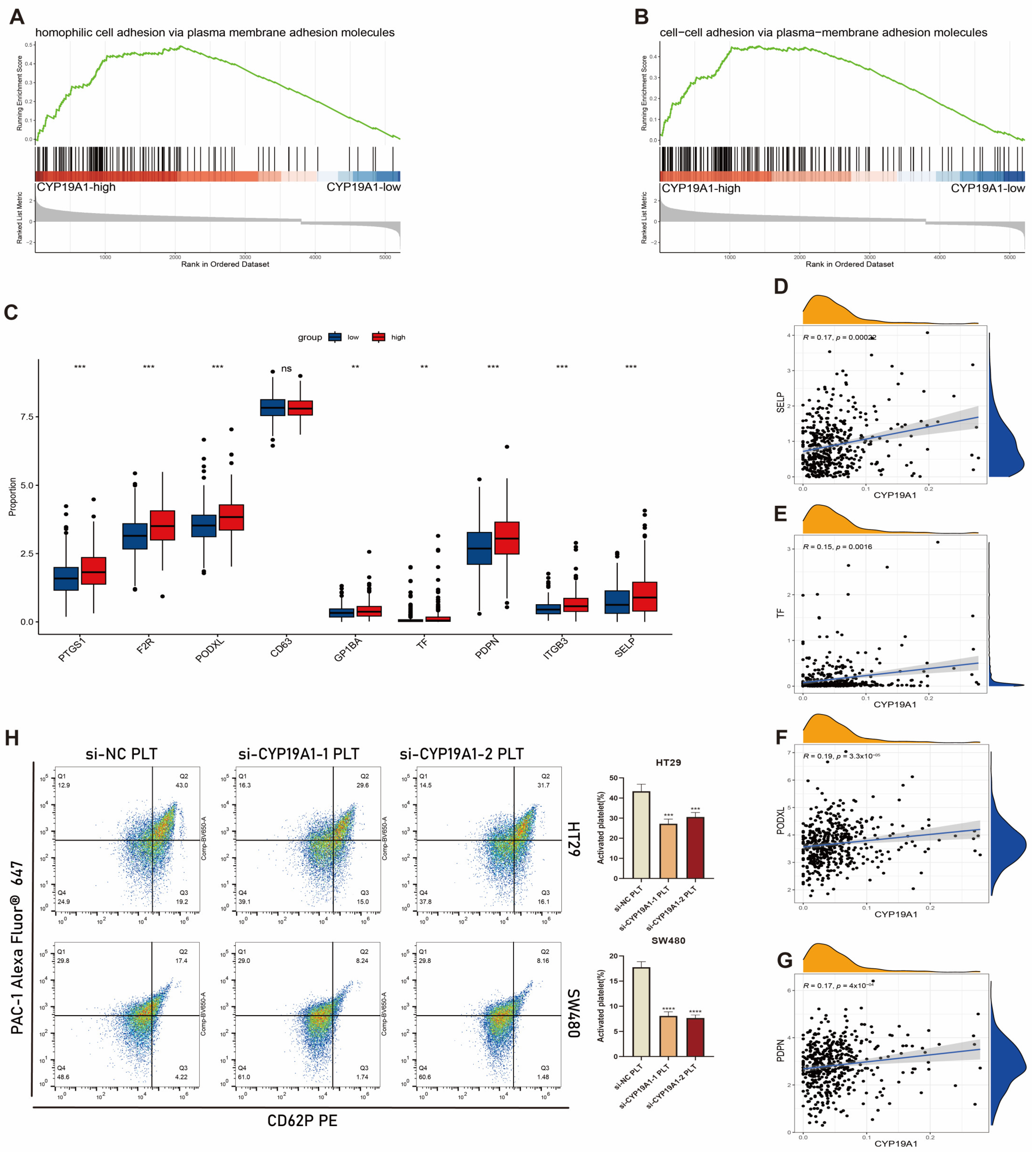
3.11. CYP19A1 Expression in CRC Cells Activates on Platelet Activation In Vitro
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaedcke, J.; Grade, M.; Camps, J.; Søkilde, R.; Kaczkowski, B.; Schetter, A.J.; Difilippantonio, M.J.; Harris, C.C.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Møller, S.; et al. The rectal cancer microRNAome—microRNA expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4919–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cui, J.; Chen, C.; Song, S.; Huang, M.; Peng, J.; Lan, P.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J. Clinical outcomes after surgical resection of colorectal cancer in 1294 patients. Hepatogastroenterology 2012, 59, 1398–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Delaunoit, T.; Limburg, P.J.; Goldberg, R.M.; Lymp, J.F.; Loftus, E.V., Jr. Colorectal cancer prognosis among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, L.; Karaman, N.; Yilmaz, K.B.; Ozaslan, C.; Atalay, C.; Altinok, M. Characteristics and risk factors for colorectal cancer recurrence. J. BUON 2010, 15, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Donati, M.B. Cancer and thrombosis: From Phlegmasia alba dolens to transgenic mice. Thromb. Haemost. 1995, 74, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylman, J.L.; Mitrugno, A.; Atallah, M.; Tormoen, G.W.; Shatzel, J.J.; Yunga, S.T.; Wagner, T.H.; Leppert, J.T.; Mallick, P.; McCarty, O.J.T. The Predictive Value of Inflammation-Related Peripheral Blood Measurements in Cancer Staging and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, S.A.; Pantel, K. Tumor-Educated Platelets as Liquid Biopsy in Cancer Patients. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.G.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets as a Noninvasive Biomarker Source for Cancer Detection and Progression Monitoring. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, M.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinger, M.H.; Jelkmann, W. Role of blood platelets in infection and inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002, 22, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haemmerle, M.; Stone, R.L.; Menter, D.G.; Afshar-Kharghan, V.; Sood, A.K. The Platelet Lifeline to Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In’t Veld, S.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-educated platelets. Blood 2019, 133, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylman, J.L.; Mitrugno, A.; Tormoen, G.W.; Wagner, T.H.; Mallick, P.; McCarty, O.J.T. Platelet count as a predictor of metastasis and venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. Converg. Sci. Phys. Oncol. 2017, 3, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Harrison, P.; Belting, M.; Böing, A.; Campello, E.; Carter, B.S.; Collier, M.E.; Coumans, F.; Ettelaie, C.; van Es, N.; et al. Extracellular vesicles, tissue factor, cancer and thrombosis—Discussion themes of the ISEV 2014 Educational Day. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastida, E.; Ordinas, A.; Escolar, G.; Jamieson, G.A. Tissue factor in microvesicles shed from U87MG human glioblastoma cells induces coagulation, platelet aggregation, and thrombogenesis. Blood 1984, 64, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallah, S.; Wan, J.Y.; Nguyen, N.P. Venous thrombosis in patients with solid tumors: Determination of frequency and characteristics. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Lyman, G.H. Risk factors for chemotherapy-associated venous thromboembolism in a prospective observational study. Cancer 2005, 104, 2822–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Troup, D.B.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Rudnev, D.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Soboleva, A.; Tomashevsky, M.; Edgar, R. NCBI GEO: Mining tens of millions of expression profiles—Database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D760–D765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zuo, S.; Liu, Y. The aging-related risk signature in colorectal cancer. Aging 2021, 13, 7330–7349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Stein, T.I.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H.; et al. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M., III; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosches, M.A.; Yamawaki, T.M.; Naumann, R.K.; Jacobi, A.A.; Tushev, G.; Laurent, G. Evolution of pallium, hippocampus, and cortical cell types revealed by single-cell transcriptomics in reptiles. Science 2018, 360, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fei, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Ge, W.; et al. Construction of a human cell landscape at single-cell level. Nature 2020, 581, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, M.; Liu, J.; Mei, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Xue, N.; Hong, H.; Xie, J.; et al. TEAD4 functions as a prognostic biomarker and triggers EMT via PI3K/AKT pathway in bladder cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunicki, T.J. Platelet membrane glycoproteins and their function: An overview. Blut 1989, 59, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.E.; Harrison, P.; Mackie, I.J.; Machin, S.J. Platelet activation markers and the primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS). Lupus 1998, 7 (Suppl. S2), S48–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergei, I.; Kälsch, T.; März, W.; Krämer, B.K.; Kälsch, A.I. Platelet and Monocyte Activity Markers and Mortality in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pericacho, M.; Alonso-Martín, S.; Larrucea, S.; González-Manchón, C.; Fernández, D.; Sánchez, I.; Ayuso, M.S.; Parrilla, R. Diminished thrombogenic responses by deletion of the Podocalyxin Gene in mouse megakaryocytes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Gu, H.; Ruan, C.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y. Blocking podoplanin inhibits platelet activation and decreases cancer-associated venous thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2021, 200, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zheng, K.; Ma, C.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, T.; Jiang, Y. PTPS Facilitates Compartmentalized LTBP1 S-Nitrosylation and Promotes Tumor Growth under Hypoxia. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 95–107.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mo, M.; Chen, X.; Chao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; He, N.; Yuan, X.; et al. Targeting inhibition of prognosis-related lipid metabolism genes including CYP19A1 enhances immunotherapeutic response in colon cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhou, D.; Tang, S.; Yin, X.; Xu, F.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, T.; et al. Deletions at SLC18A1 increased the risk of CRC and lower SLC18A1 expression associated with poor CRC outcome. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Ai, W.; Asfaha, S.; Bhagat, G.; Friedman, R.A.; Jin, G.; Park, H.; Shykind, B.; Diacovo, T.G.; Falus, A.; et al. Histamine deficiency promotes inflammation-associated carcinogenesis through reduced myeloid maturation and accumulation of CD11b+Ly6G+ immature myeloid cells. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Liao, W.; Shu, P.; Ma, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y. Targeting sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 inhibits T-cell exhaustion and regulates recruitment of proinflammatory macrophages to improve antitumor efficacy of CAR-T cells against solid tumor. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Liu, Y.J.; Zeng, S.H.; Gao, H.J.; Chen, Y.G.; Zou, X. Identification of COX4I2 as a hypoxia-associated gene acting through FGF1 to promote EMT and angiogenesis in CRC. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gan, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhang, H.; Lai, M. Methyl CpG binding protein 2 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by regulating N6-methyladenosine methylation through methyltransferase-like 14. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, L.R.; Bulun, S.E. Estrogen production and action. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45 (Suppl. S3), S116–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharb, R.; Haider, K.; Neha, K.; Yar, M.S. Aromatase inhibitors: Role in postmenopausal breast cancer. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, e2000081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, G.; Wang, M.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102225
Su G, Wang M, Qian J, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Wang N, Wang K, Wang Q, Wang Y, Li D, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(10):2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102225
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Guoqing, Meiqin Wang, Jinghang Qian, Yang Wang, Yu Zhu, Nannan Wang, Ke Wang, Qifan Wang, Yi Wang, Dongzheng Li, and et al. 2024. "Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer" Biomedicines 12, no. 10: 2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102225
APA StyleSu, G., Wang, M., Qian, J., Wang, Y., Zhu, Y., Wang, N., Wang, K., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Li, D., & Yang, L. (2024). Comprehensive Analysis of a Platelet- and Coagulation-Related Prognostic Gene Signature Identifies CYP19A1 as a Key Tumorigenic Driver of Colorectal Cancer. Biomedicines, 12(10), 2225. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102225






