Exploring the Role of MicroRNAs in Progesterone and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Endometriosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. MiRNA Expression Profiling Using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.5. Validation of Selected miRNAs and mRNAs by Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Target Predictions Using CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq Data
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographic Data
3.2. Histopathological Examination
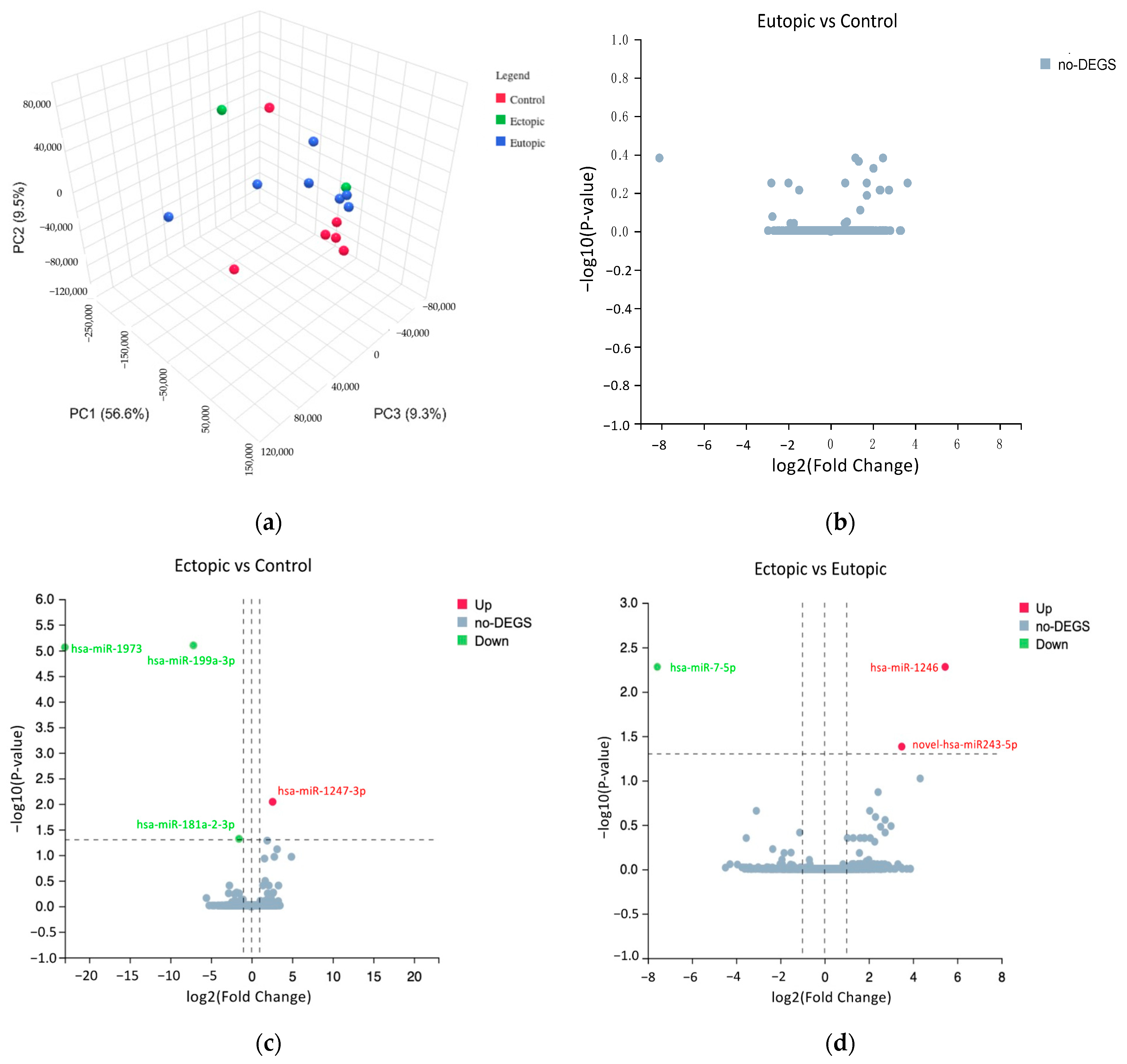
3.3. Differentially Expressed miRNAs in Ectopic versus Control and Ectopic versus Eutopic Groups
3.4. Validation of Selected miRNAs by qRT-PCR
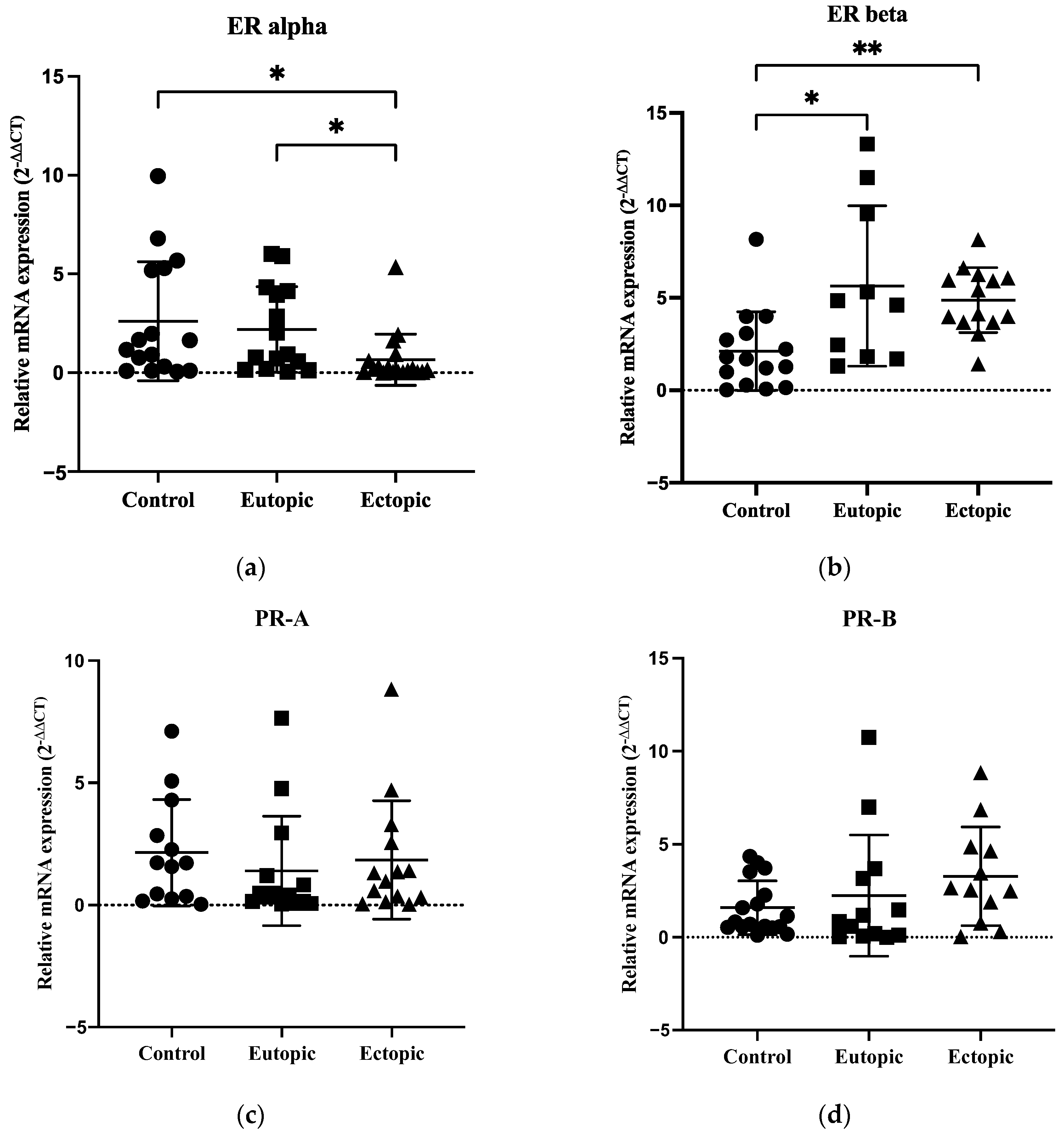
3.5. Expression of ERα Was Decreased with Overexpression of ERβ in Endometriosis, but PR-A and PR-B Showed No Significant Differences between the Groups
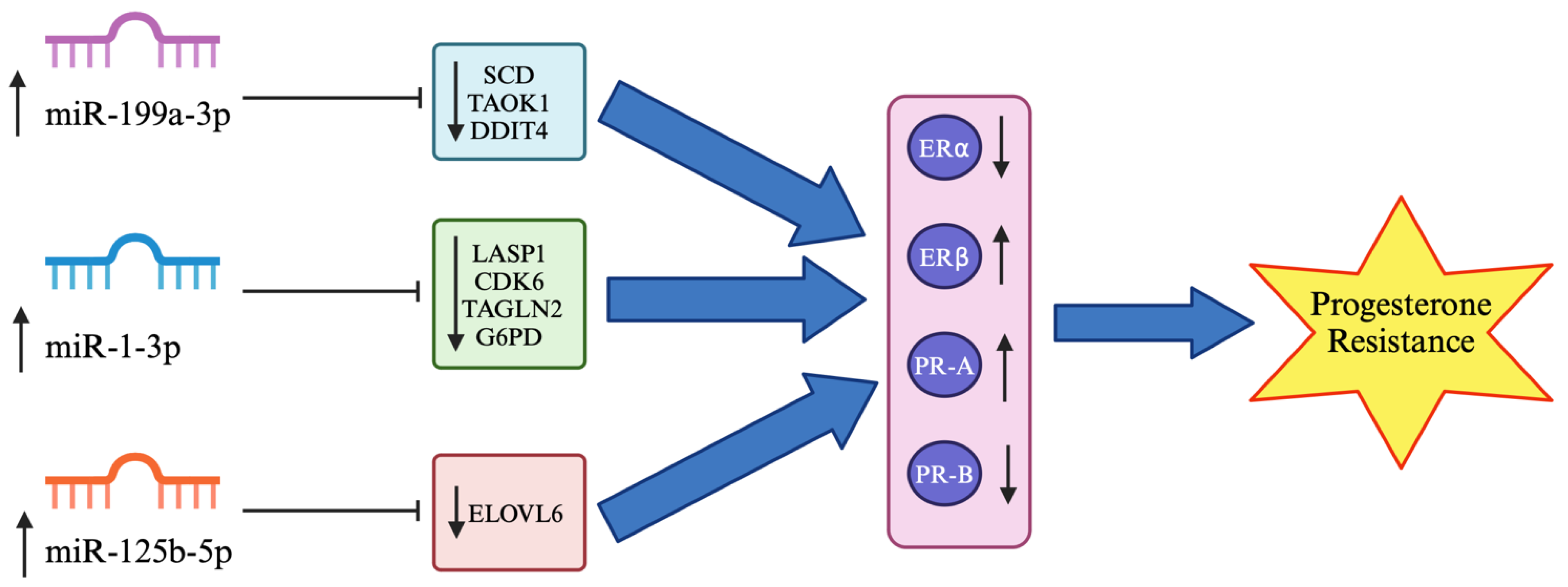
3.6. Target Prediction of Hsa-miR-199a-3p, Hsa-miR-1-3p and Hsa-miR-125b-5p
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chantalat, E.; Valera, M.C.; Vaysse, C.; Noirrit, E.; Rusidze, M.; Weyl, A.; Vergriete, K.; Buscail, E.; Lluel, P.; Fontaine, C.; et al. Estrogen Receptors and Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audebert, A.; Petousis, S.; Margioula-Siarkou, C.; Ravanos, K.; Prapas, N.; Prapas, Y. Anatomic distribution of endometriosis: A reappraisal based on series of 1101 patients. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 230, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsamantioti, E.S.; Mahdy, H. Endometriosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, J.A. Metastatic or Embolic Endometriosis, due to the Menstrual Dissemination of Endometrial Tissue into the Venous Circulation. Am. J. Pathol. 1927, 3, 93–110.43. [Google Scholar]
- Sampson, J.A. Peritoneal endometriosis due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1927, 14, 422–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavina, G.; Taylor, H.S. Endometriosis-associated infertility: From pathophysiology to tailored treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1020827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehedintu, C.; Plotogea, M.N.; Ionescu, S.; Antonovici, M. Endometriosis still a challenge. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Vercellini, P.; Cortesi, I.; Crosignani, P.G. Progestins for symptomatic endometriosis: A critical analysis of the evidence. Fertil. Steril. 1997, 68, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.G.; Rudnicki, M.; Yu, J.; Shu, Y.; Taylor, R.N. Progesterone resistance in endometriosis: Origins, consequences and interventions. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, V.A.; Vanhie, A.; Dang, T.; Taylor, H.S. Progesterone Receptor Status Predicts Response to Progestin Therapy in Endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4561–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nicholes, K.; Shih, I.M. The Origin and Pathogenesis of Endometriosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulun, S.E.; Monsavais, D.; Pavone, M.E.; Dyson, M.; Xue, Q.; Attar, E.; Tokunaga, H.; Su, E.J. Role of estrogen receptor-beta in endometriosis. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2012, 30, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulun, S.E.; Yilmaz, B.D.; Sison, C.; Miyazaki, K.; Bernardi, L.; Liu, S.; Kohlmeier, A.; Yin, P.; Milad, M.; Wei, J. Endometriosis. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1048–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, B.; Mueller, M.; Montgomery, G. Progesterone Resistance in Endometriosis: An Acquired Property? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanova, L.; Velarde, M.C.; Giudice, L.C. Altered gene expression profiling in endometrium: Evidence for progesterone resistance. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2010, 28, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.H.R.; Farooqui, N.; Zuberi, N.; Ashraf, M.; Azhar, A.; Baig, R.; Badar, B.; Rehman, R. Endometriosis, infertility and MicroRNA’s: A review. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 50, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panir, K.; Schjenken, J.E.; Robertson, S.A.; Hull, M.L. Non-coding RNAs in endometriosis: A narrative review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, F.; Shehzad, A.; Khan, T.; Kim, Y.Y. MicroRNAs: Synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical trials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Suzuki, H.I. Systems and Synthetic microRNA Biology: From Biogenesis to Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson Teague, E.M.; Van der Hoek, K.H.; Van der Hoek, M.B.; Perry, N.; Wagaarachchi, P.; Robertson, S.A.; Print, C.G.; Hull, L.M. MicroRNA-regulated pathways associated with endometriosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.R.; Miyadahira, E.H.; Afshar, Y.; Jeong, J.W.; Young, S.L.; Lessey, B.A.; Serafini, P.C.; Fazleabas, A.T. Progesterone Resistance in Endometriosis Is Modulated by the Altered Expression of MicroRNA-29c and FKBP4. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petracco, R.; Grechukhina, O.; Popkhadze, S.; Massasa, E.; Zhou, Y.; Taylor, H.S. MicroRNA 135 regulates HOXA10 expression in endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1925–E1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, T.; Xiao, L.; Luo, B.; Tan, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Duan, C.; Huang, W. miR-194-3p Represses the Progesterone Receptor and Decidualization in Eutopic Endometrium from Women with Endometriosis. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2554–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Fu, J.; Xiao, L.; Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.; Sun, H.; Xu, W.; Huang, W. miR-196a overexpression activates the MEK/ERK signal and represses the progesterone receptor and decidualization in eutopic endometrium from women with endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhu, X.X.; Li, Z.F.; Zhu, Y.P.; Lang, J.H. MicroRNA Dysregulation and Steroid Hormone Receptor Expression in Uterine Tissues of Rats with Endometriosis during the Implantation Window. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, G. Progesterone Resistance in Endometriosis: Current Evidence and Putative Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkman, S.; Taylor, H.S. MicroRNAs in endometriosis: Biological function and emerging biomarker candidatesdagger. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burney, R.O.; Hamilton, A.E.; Aghajanova, L.; Vo, K.C.; Nezhat, C.N.; Lessey, B.A.; Giudice, L.C. MicroRNA expression profiling of eutopic secretory endometrium in women with versus without endometriosis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xiao, L.; Pei, T.; Luo, B.; Tan, J.; Long, Y.; Huang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, W. miR-297 inhibits expression of progesterone receptor and decidualization in eutopic endometria of endometriosis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2023, 49, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, S. Review of Fleiss, statistical methods for rates and proportions. Res. Synth. Methods 2011, 2, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Du, J.; Shen, L.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Bai, L.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. miR-199a-3p affects adipocytes differentiation and fatty acid composition through targeting SCD. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Hao, Z.; Hu, L.; Qiao, L.; Luo, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Zhao, F.; Shen, J.; et al. MicroRNA-199a-3p regulates proliferation and milk fat synthesis of ovine mammary epithelial cells by targeting VLDLR. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 948873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrini, C.; Cubero, R.J.; Dirkx, E.; Braga, L.; Ali, H.; Prosdocimo, G.; Gutierrez, M.I.; Collesi, C.; Licastro, D.; Zentilin, L.; et al. Common Regulatory Pathways Mediate Activity of MicroRNAs Inducing Cardiomyocyte Proliferation. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2759–2771.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.M.; Teoh, J.P.; Wang, Y.; Broskova, Z.; Bayoumi, A.S.; Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Weintraub, N.L.; Kim, I.M. Carvedilol-responsive microRNAs, miR-199a-3p and -214 protect cardiomyocytes from simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H371–H383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Qin, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiong, X.; Yin, Q.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Identification of miR-1-3p, miR-143-3p and miR-145-5p association with bone metastasis of Gleason 3+4 prostate cancer and involvement of LASP1 regulation. Mol. Cell. Probes 2023, 68, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, M.F.; Fernandez, G.J.; Vanderveer, L.; Cooper, H.S.; Slifker, M.; Clapper, M.L. Dysregulation of miR-1-3p: An Early Event in Colitis-Associated Dysplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Xia, C. Quercetin Antagonizes Esophagus Cancer by Modulating miR-1-3p/TAGLN2 Pathway-Dependent Growth and Metastasis. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Li, K.; Gu, F.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Sun, M.; Hou, B. LINC00242/miR-1-3p/G6PD axis regulates Warburg effect and affects gastric cancer proliferation and apoptosis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istiqamah, N.; Matsuzaka, T.; Shimizu, M.; Motomura, K.; Ohno, H.; Hasebe, S.; Sharma, R.; Okajima, Y.; Matsuda, E.; Han, S.I.; et al. Identification of key microRNAs regulating ELOVL6 and glioblastoma tumorigenesis. BBA Adv. 2023, 3, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, S.; Ghaheri, A.; Shahhoseini, M.; Aflatoonian, R.; Afsharian, P. The Effect of Imbalanced Progesterone Receptor-A/-B Ratio on Gelatinase Expressions in Endometriosis. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, G.R.; Zeitoun, K.; Edwards, D.; Johns, A.; Carr, B.R.; Bulun, S.E. Progesterone receptor isoform A but not B is expressed in endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedaiwy, M.A.; Dahoud, W.; Skomorovska-Prokvolit, Y.; Yi, L.; Liu, J.H.; Falcone, T.; Hurd, W.W.; Mesiano, S. Abundance and Localization of Progesterone Receptor Isoforms in Endometrium in Women with and without Endometriosis and in Peritoneal and Ovarian Endometriotic Implants. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karita, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Tanabe, A.; Terai, Y.; Ohmichi, M. Does advanced-stage endometriosis affect the gene expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors in granulosa cells? Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misao, R.; Iwagaki, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Sun, W.; Tamaya, T. Dominant expression of progesterone receptor form B mRNA in ovarian endometriosis. Horm. Res. 1999, 52, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukhacheva, E.; Lin, Z.; Reierstad, S.; Cheng, Y.H.; Milad, M.; Bulun, S.E. Estrogen receptor (ER) beta regulates ERalpha expression in stromal cells derived from ovarian endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukulmez, O.; Hardy, D.B.; Carr, B.R.; Word, R.A.; Mendelson, C.R. Inflammatory status influences aromatase and steroid receptor expression in endometriosis. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.; Hirose, R.; Sakaguchi, H.; Tamaya, T. Expression of oestrogen receptor-alpha and -beta in ovarian endometriomata. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1999, 5, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, Y.H.; Huang, C.C.; Marsh, E.; Yin, P.; Milad, M.P.; Confino, E.; Reierstad, S.; Innes, J.; et al. Promoter methylation regulates estrogen receptor 2 in human endometrium and endometriosis. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, S.; Murakami, T.; Uehara, S.; Canis, M.; Sasano, H.; Okamura, K. Expression of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in peritoneal and ovarian endometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2001, 75, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Peng, J.; Shi, Y.; Sun, P. miR-92a promotes progesterone resistance in endometriosis through PTEN/AKT pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 242, 117190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Du, D.; Zhang, S. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p promotes angiogenesis in bladder cancer by targeting FOXO1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2024, 25, 2290033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. A Review on the Role of miR-1246 in the Pathoetiology of Different Cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 771835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisoulis, D.G.; Lovci, M.T.; Wilbert, M.L.; Hutt, K.R.; Liang, T.Y.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Yeo, G.W. Comprehensive discovery of endogenous Argonaute binding sites in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Halima, M.; Hammadeh, M.; Schmitt, J.; Leidinger, P.; Keller, A.; Meese, E.; Backes, C. Altered microRNA expression profiles of human spermatozoa in patients with different spermatogenic impairments. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 99, 1249–1255.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, E.; Marchionni, L.; Chitre, A.; Hayashi, M.; Martignoni, G.; Brunelli, M.; Gobbo, S.; Argani, P.; Allaf, M.; Hoque, M.O.; et al. Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma: Micro-RNA expression profiling and comparison with clear cell renal cell carcinoma and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, X.; Wan, C.; Zhu, S.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; et al. MiR-181a-2-3p as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for myelodysplastic syndrome. Hematology 2022, 27, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Xi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, H. miR-181a-2-3p Stimulates Gastric Cancer Progression via Targeting MYLK. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 687915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, L.G.L.; Meola, J.; Rosa, E.S.A.; Nogueira, A.A.; Candido Dos Reis, F.J.; Poli-Neto, O.B.; Rosa, E.S.J.C. Altered Differential Expression of Genes and microRNAs Related to Adhesion and Apoptosis Pathways in Patients with Different Phenotypes of Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Nasu, K.; Hijiya, N.; Yoshihashi, M.; Hirakawa, T.; Aoyagi, Y.; Narahara, H. hsa-miR-199a-3p Inhibits Motility, Invasiveness, and Contractility of Ovarian Endometriotic Stromal Cells. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papari, E.; Noruzinia, M.; Kashani, L.; Foster, W.G. Identification of candidate microRNA markers of endometriosis with the use of next-generation sequencing and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 113, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walasik, I.; Klicka, K.; Grzywa, T.M.; Szymusik, I.; Wlodarski, P.; Wielgos, M.; Pietrzak, B.; Ludwin, A. Circulating miR-3613-5p but not miR-125b-5p, miR-199a-3p, and miR-451a are biomarkers of endometriosis. Reprod. Biol. 2023, 23, 100796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothnick, W.B.; Swan, K.; Flyckt, R.; Falcone, T.; Graham, A. Human endometriotic lesion expression of the miR-144-3p/miR-451a cluster, its correlation with markers of cell survival and origin of lesion content. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.L.; Ali, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Alosh, B.; Hayek, K.; Daaboul, M.F.; Winer, I.; Sarkar, F.H.; Ali-Fehmi, R. Comparative Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs and their Downstream mRNAs in Ovarian Cancer and its Associated Endometriosis. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015, 7, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.Q.; Teng, H.; Xu, X.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Guo, F.J.; Liu, X.J. Microarray analysis of microRNA deregulation and angiogenesis-related proteins in endometriosis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, S.; Burn, M.; Mamillapalli, R.; Nematian, S.; Flores, V.; Taylor, H.S. Accurate diagnosis of endometriosis using serum microRNAs. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 557.e1–557.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szubert, M.; Nowak-Gluck, A.; Domanska-Senderowska, D.; Szymanska, B.; Sowa, P.; Rycerz, A.; Wilczynski, J.R. miR 31-3p Has the Highest Expression in Cesarean Scar Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wu, Z.; Ma, C.; Pan, N.; Wang, Y.; Yan, L. Endometrial miR-543 Is Downregulated during the Implantation Window in Women with Endometriosis-Related Infertility. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, C.H.; Qiao, J. Differential expression of microRNA in eutopic endometrium tissue during implantation window for patients with endometriosis related infertility. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2016, 51, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosar, E.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ersoy, G.S.; Cho, S.; Seifer, B.; Taylor, H.S. Serum microRNAs as diagnostic markers of endometriosis: A comprehensive array-based analysis. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 106, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhie, A.; O, D.; Peterse, D.; Beckers, A.; Cuellar, A.; Fassbender, A.; Meuleman, C.; Mestdagh, P.; D’Hooghe, T. Plasma miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 34, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, M.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Lin, K. Exosomes from ectopic endometrial stromal cells promote M2 macrophage polarization by delivering miR-146a-5p. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrivel, S.; Zhang, R.; Engel, M.; Altieri, B.; Braun, L.; Osswald, A.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Fassnacht, M.; Beuschlein, F.; Reincke, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA Expression in Cushing’s Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 620012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, F.; Bonilla, P.; Ravishankar, Y.G.; Contag, A.; Gopal, N.; LaCour, S.; Lee, T.; Niemz, A. Technology in MicroRNA Profiling: Circulating MicroRNAs as Noninvasive Cancer Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Qi, L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y.; Gong, X.; Aili, A.; Chen, Y.; Xue, Z.; Xue, J.; Tong, X. Analysis of differences in the transcriptomic profiles of eutopic and ectopic endometriums in women with ovarian endometriosis. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzic, M.M.; Aimagambetova, G.; Terzic, S.; Norton, M.; Bapayeva, G.; Garzon, S. Current role of Pipelle endometrial sampling in early diagnosis of endometrial cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 7716–7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saare, M.; Rekker, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Rahmioglu, N.; Zondervan, K.; Salumets, A.; Gotte, M.; Peters, M. Challenges in endometriosis miRNA studies—From tissue heterogeneity to disease specific miRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandyari, S.; Elkafas, H.; Chugh, R.M.; Park, H.S.; Navarro, A.; Al-Hendy, A. Exosomes as Biomarkers for Female Reproductive Diseases Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, W.; Ding, H.; Wu, X. Serum exosomal miRNA from endometriosis patients correlates with disease severity. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 305, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yuan, M.; Li, D.; Sun, C.; Wang, G. Serum Exosomal MicroRNAs as Potential Circulating Biomarkers for Endometriosis. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 2456340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Li, W.N.; Lin, S.C.; Hou, H.T.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lin, T.C.; Wu, M.H.; Tsai, S.J. Targeting YAP1 ameliorates progesterone resistance in endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2023, 38, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Galvankar, M.; Singh, N.; Modi, D. Spatial and temporal changes in the expression of steroid hormone receptors in mouse model of endometriosis. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brichant, G.; Nervo, P.; Albert, A.; Munaut, C.; Foidart, J.M.; Nisolle, M. Heterogeneity of estrogen receptor alpha and progesterone receptor distribution in lesions of deep infiltrating endometriosis of untreated women or during exposure to various hormonal treatments. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2018, 34, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledolter, J.; Kardon, R.H. Focus on Data: Statistical Design of Experiments and Sample Size Selection Using Power Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H. Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelch, K.E.; Schroder, A.L.; Kimball, P.A.; Sharpe-Timms, K.L.; Davis, J.W.; Nagel, S.C. Aberrant gene expression profile in a mouse model of endometriosis mirrors that observed in women. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 1615–1627.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Campos, M.A.; Espinal-Enriquez, J.; Hernandez-Lemus, E. Pathway Analysis: State of the Art. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, R.M.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, J.H.; Jeong, J.W. Progesterone and Estrogen Signaling in the Endometrium: What Goes Wrong in Endometriosis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Control Samples N (%) | Eutopic Samples N (%) | Ectopic Samples N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age ± S.D. (years) | 36.94 ± 7.04 | 35.28 ± 6.52 | 37.50 ± 7.29 |
| Race | |||
| Malay | 12 (66.67%) | 16 (88.89%) | 16 (88.89%) |
| Non-Malay | 6 (33.33%) | 2 (11.11%) | 2 (11.11%) |
| Parity | |||
| Nulliparous | 10 (55.56%) | 13 (72.22%) | 12 (66.67%) |
| Multiparous | 8 (44.44%) | 5 (27.78%) | 6 (33.33%) |
| Mean BMI ± S.D. (kg/m2) | 25.65 ± 3.38 | 24.74 ± 3.39 | 26.28 ± 5.55 |
| Clinical Features | |||
| Infertility | 7 (38.89%) | 11 (61.11%) | 9 (50%) |
| Dysmenorrhoea * | 10 (55.56%) | 14 (77.78%) | 17 (94.44%) |
| Dyspareunia | 3 (16.67%) | 6 (33.33%) | 6 (33.33%) |
| Pelvic Pain | 5 (27.78%) | 8 (44.44%) | 11 (61.11%) |
| miRNAs | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | ||
| hsa-miR-1247-3p | 0.0091 | 2.59 |
| Downregulated | ||
| hsa-miR-1973 | 8.63 × 10−6 | −22.99 |
| hsa-miR-199a-3p | 7.93 × 10−6 | −7.16 |
| hsa-miR-181a-2-3p | 0.048 | −1.55 |
| miRNAs | Adjusted p-Value | Log2 Fold Change |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | ||
| hsa-miR-1246 | 0.0052 | 5.45 |
| novel-hsa-miR-243-5p | 0.041 | 3.49 |
| Downregulated | ||
| hsa-miR-7-5p | 0.0052 | −7.57 |
| Expression Level of miRNA | Expression Level of Target Gene | Tissue or Cell Type | PCT | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated: hsa-miR-199a-3p | Reduced SCD | Adipocyte, ovine mammary epithelial cells | 0.86 | Tan et al. (2017) [32], Wang et al. (2022) [33] |
| Reduced TAOK1 | Cardiomyocyte | 0.96 | Torrini et al. (2019) [34] | |
| Reduced DDIT4 | Cardiomyocyte | 0.78 | Park et al. (2016) [35] | |
| Upregulated: hsa-miR-1-3p | Reduced LASP1 | Prostate cancer | 0.7 | Guo et al. (2023) [36] |
| Reduced CDK6 | Human colon carcinoma cells | 0.85 | Fragoso et al. (2022) [37] | |
| Reduced TAGLN2 | Esophagus carcinoma cells | 0.89 | Wang et al. (2022) [38] | |
| Reduced G6PD | Gastric cancer cell | >0.99 | Deng et al. (2021) [39] | |
| Upregulated: hsa-miR-125b-5p | Reduced ELOVL6 | HEK-293 cells | 0.92 | Istiqamah et al. (2023) [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hon, J.-X.; Wahab, N.A.; Karim, A.K.A.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Mokhtar, M.H. Exploring the Role of MicroRNAs in Progesterone and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Endometriosis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102218
Hon J-X, Wahab NA, Karim AKA, Mokhtar NM, Mokhtar MH. Exploring the Role of MicroRNAs in Progesterone and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Endometriosis. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(10):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102218
Chicago/Turabian StyleHon, Jing-Xian, Norhazlina Abdul Wahab, Abdul Kadir Abdul Karim, Norfilza Mohd Mokhtar, and Mohd Helmy Mokhtar. 2024. "Exploring the Role of MicroRNAs in Progesterone and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Endometriosis" Biomedicines 12, no. 10: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102218
APA StyleHon, J.-X., Wahab, N. A., Karim, A. K. A., Mokhtar, N. M., & Mokhtar, M. H. (2024). Exploring the Role of MicroRNAs in Progesterone and Estrogen Receptor Expression in Endometriosis. Biomedicines, 12(10), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12102218







