Angiopoietin-2 and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Promote Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma- and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-Derived Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Spheroids Formation
2.3. The 3D Viability Assay
2.4. Migration and Invasion Assay
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
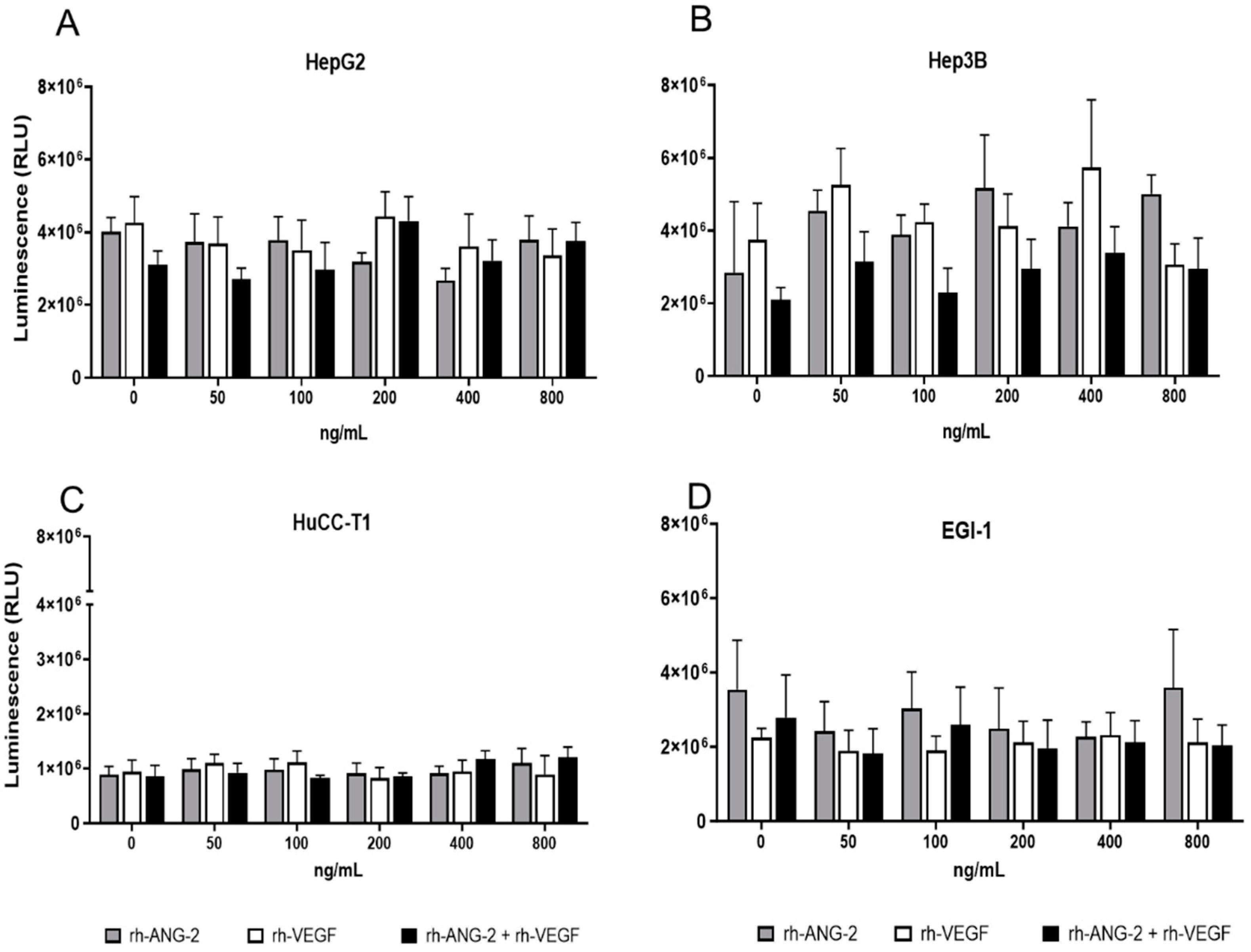
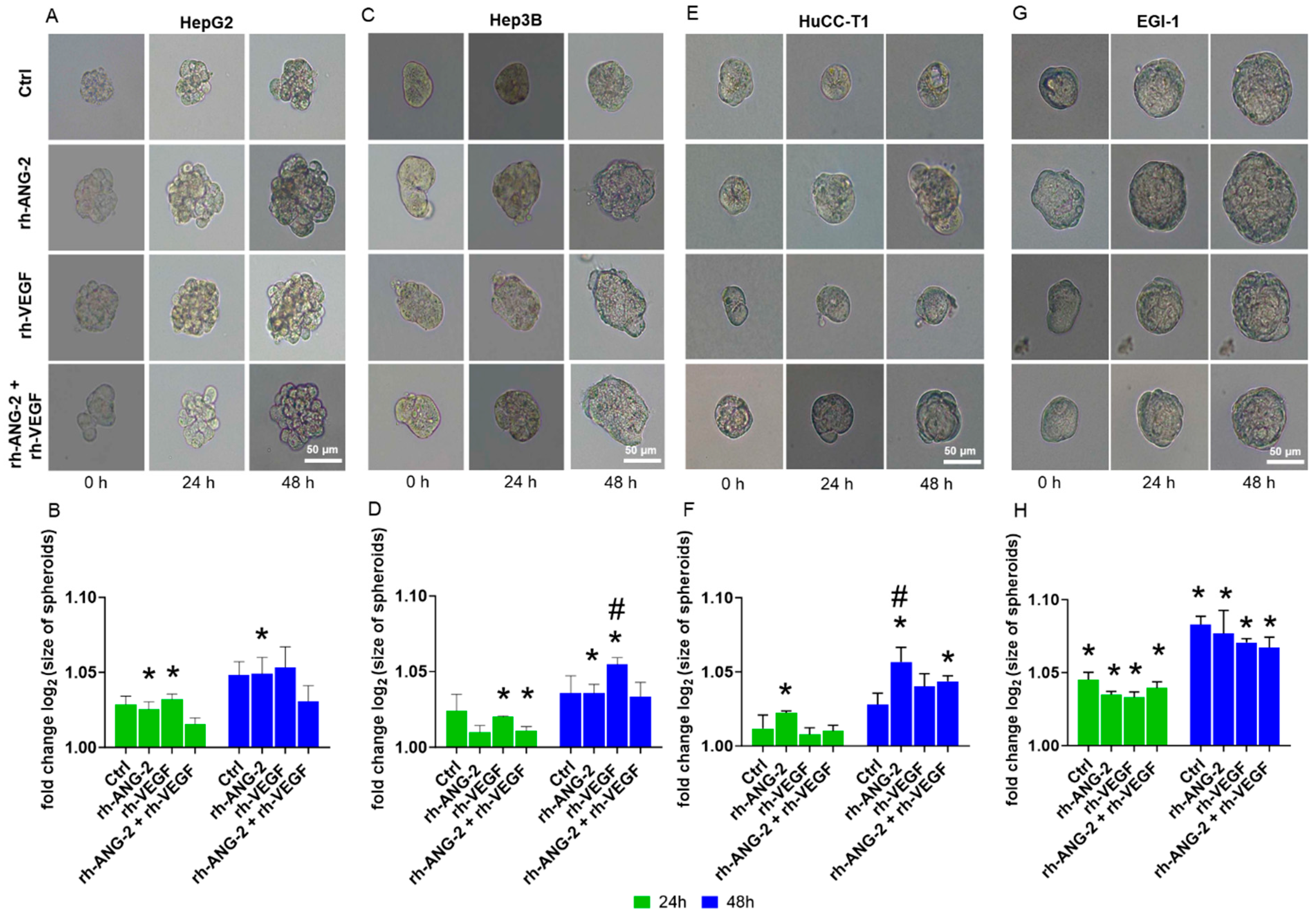
3.1. rh-ANG-2 and rh-VEGF Stimulation Did Not Affect the Viability of HCC and CCA Spheroids
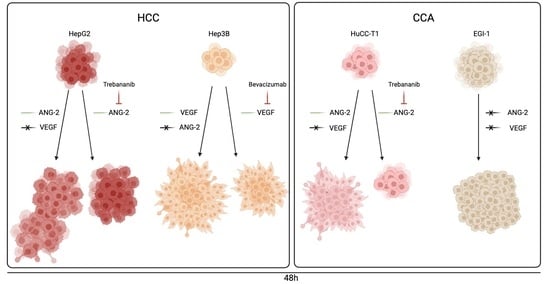
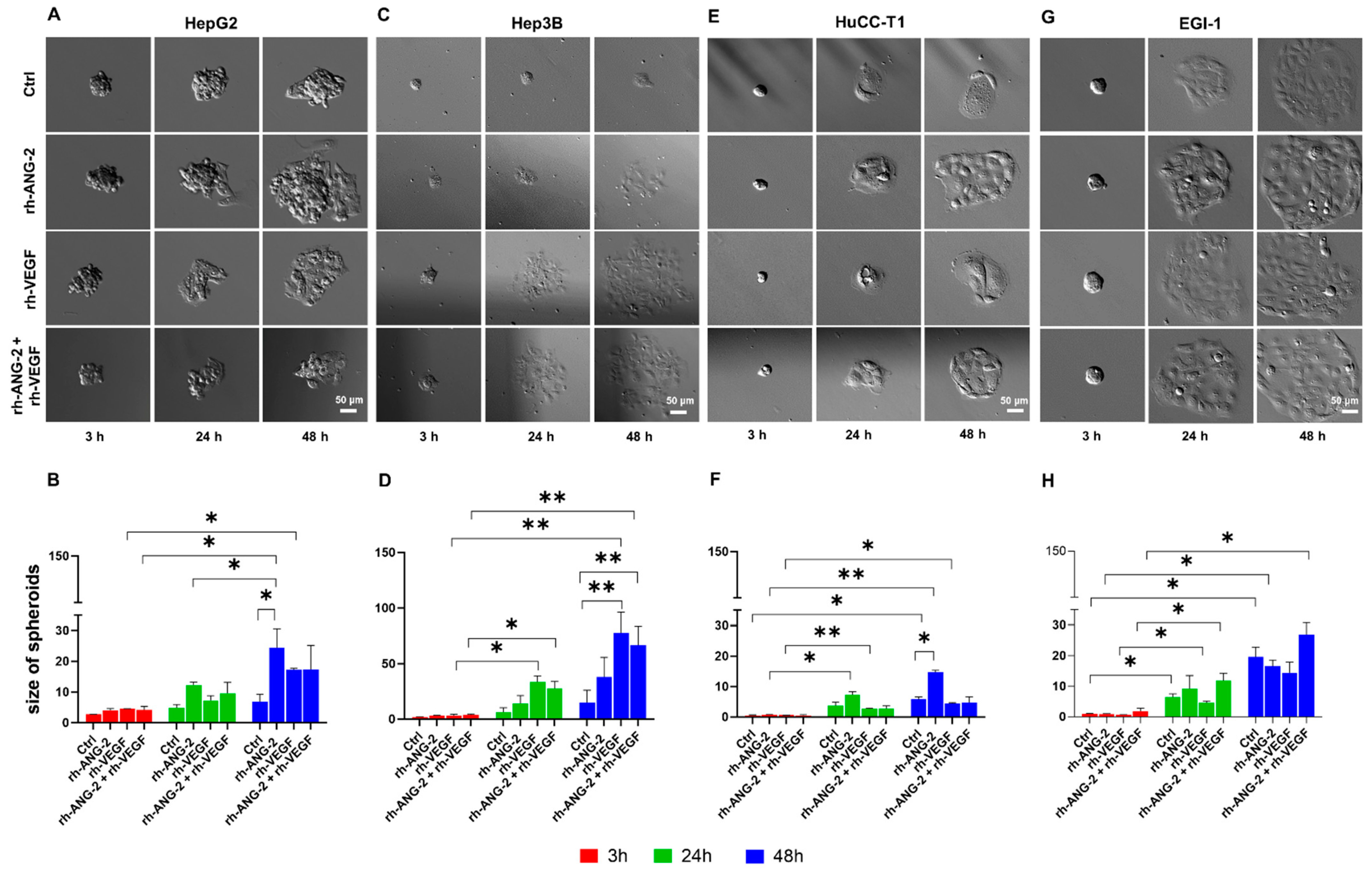
3.2. rh-ANG-2 and rh-VEGF Stimulation Increased Migration Capability in HepG2, Hep3B, and HuCC-T1 but Not EGI-1 Spheroids
3.3. Trebananib and Bevacizumab Effectively Inhibited the rh-ANG-2 and rh-VEGF-Stimulated Migration of Spheroids Derived from HepG2, HuCC-T1, and Hep3B Cell Lines
3.4. rh-ANG-2 and rh-VEGF Were Found to Enhance the Invasion Capabilities of HuCC-T1 and Hep3B Spheroids
3.5. Assessment of ANG-2 and VEGFA Receptor Expression and Activation
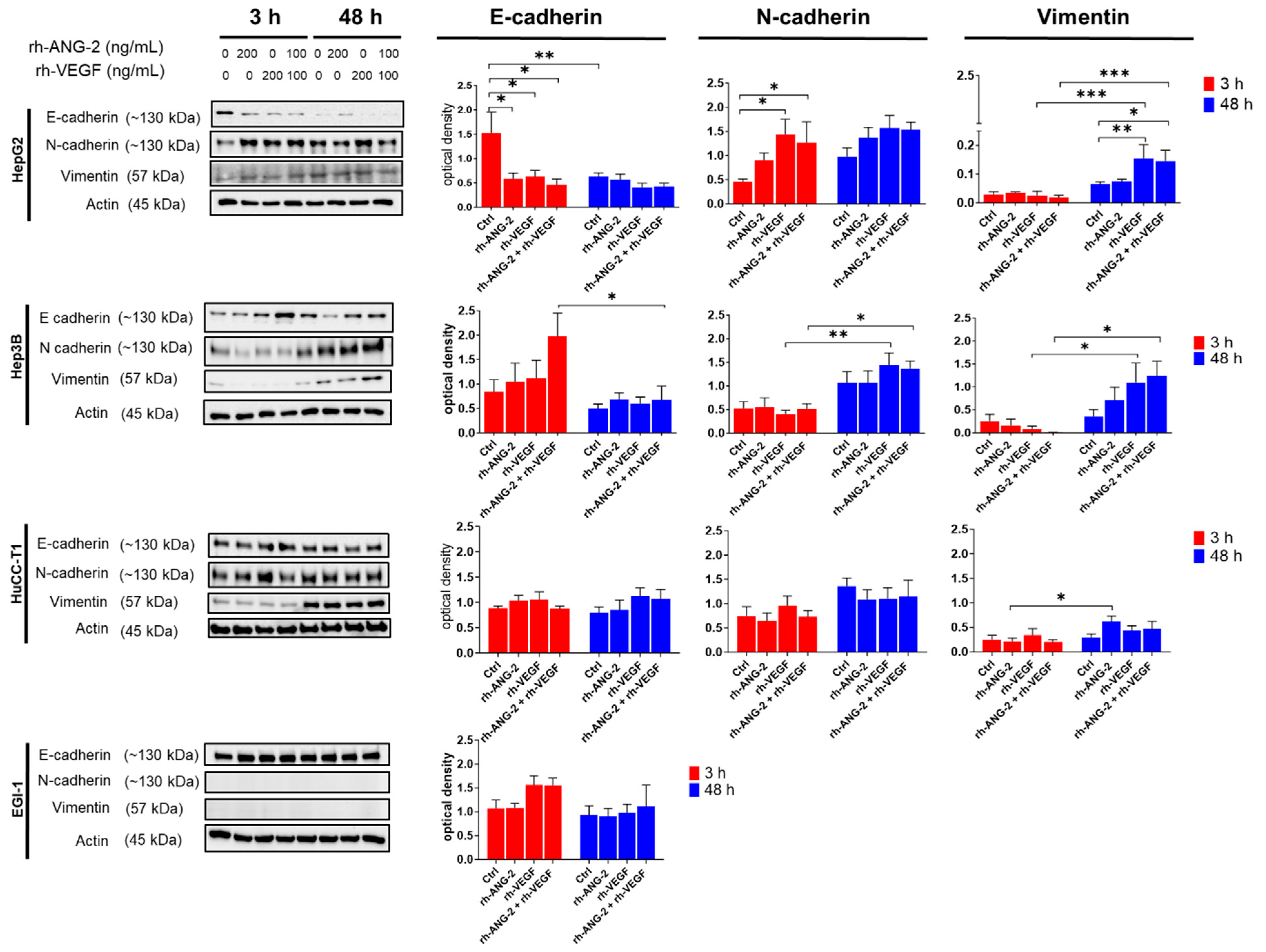
3.6. Differential Effects of rh-ANG-2 and rh-VEGF on EMT in HCC and CCA Cell Lines
3.7. The E-Cadherin to N-Cadherin Switch, Indicative of EMT Activation, Was Observed in the Outermost and Migrating Cells of the Spheroids
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, W.-S.; Lee, K.-W.; Heo, J.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-I.; Joh, J.-W. Comparison of Combined Hepatocellular and Cholangiocarcinoma with Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Surg. Today 2006, 36, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Wan, T. Survival after Surgical Resection of Distal Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prognostic Factors. Asian J. Surg. 2017, 40, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M. Updated Treatment Approach to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, D.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Roayaie, S.; Ferrer, J.; Tabak, B.; Peix, J.; Sole, M.; Tovar, V.; Alsinet, C.; et al. Integrative Molecular Analysis of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma Reveals 2 Classes That Have Different Outcomes. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.; Critelli, R.; Lei, B.; Marzocchi, G.; Cammà, C.; Giannelli, G.; Pontisso, P.; Cabibbo, G.; Enea, M.; Colopi, S.; et al. Neoangiogenesis-Related Genes Are Hallmarks of Fast-Growing Hepatocellular Carcinomas and Worst Survival. Results from a Prospective Study. Gut 2016, 65, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshida, Y.; Nijman, S.M.B.; Kobayashi, M.; Chan, J.A.; Brunet, J.-P.; Chiang, D.Y.; Villanueva, A.; Newell, P.; Ikeda, K.; Hashimoto, M.; et al. Integrative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Common Molecular Subclasses of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7385–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G. Role of Angiopoietins and Tie Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 314, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonpierre, P.C.; Suri, C.; Jones, P.F.; Bartunkova, S.; Wiegand, S.J.; Radziejewski, C.; Compton, D.; McClain, J.; Aldrich, T.H.; Papadopoulos, N.; et al. Angiopoietin-2, a Natural Antagonist for Tie2 That Disrupts In Vivo Angiogenesis. Science 1997, 277, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwii, R.G.; Sajib, M.S.; Zahra, F.T.; Mikelis, C.M. Role of Angiopoietin-2 in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cells 2019, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, E.; Christofori, G. Angiopoietins in Angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, L.; Saharinen, P. Angiopoietin Signaling in the Vasculature. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, M.A.; Sun, W.; Kim, R.; He, A.R.; Abada, P.B.; Mynderse, M.; Finn, R.S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimawaha, P.; Jusakul, A.; Junsawang, P.; Thanan, R.; Titapun, A.; Khuntikeo, N.; Techasen, A. Establishment of a Potential Serum Biomarker Panel for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cholangiocarcinoma Using Decision Tree Algorithms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, B.; Fu, L.; Hao, X.S. Correlation of Four Vascular Specific Growth Factors with Carcinogenesis and Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus Formation in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 25, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Chen, A. The VEGF Expression Associated with Prognosis in Patients with Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 20, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.B.; Han, H.J.; Kim, W.B.; Song, T.J.; Choi, S.Y. VEGF Overexpression Predicts Poor Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Open Med. 2017, 12, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-L. Expression of Angiopoietins, Tie2 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Angiogenesis and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. WJG 2006, 12, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, W.S.; Rhyu, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, D.G.; Yu, H.C.; Yeum, J.H.; Koh, G.Y.; Tarnawski, A.S. Overexpression of VEGF and Angiopoietin 2: A Key to High Vascularity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H. Angiopoietin 2 Displays a Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Dependent Synergistic Effect in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Mice. Gut 2005, 54, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabid, N.M.; Wiedemann, T.; Gulde, S.; Mohr, H.; Segaran, R.C.; Geppert, J.; Rohm, M.; Vitale, G.; Gaudenzi, G.; Dicitore, A.; et al. Angpt2/Tie2 Autostimulatory Loop Controls Tumorigenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, P.; Fang, Q.; Tao, H.-Q.; Wang, D.; Nagane, M.; Su Huang, H.-J.; Gunji, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Alitalo, K.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 Induces Human Glioma Invasion through the Activation of Matrix Metalloprotease-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8904–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenberger, B.M.; Tan, P.K.; Niederleithner, H.; Ferrara, N.; Petzelbauer, P.; Sibilia, M. Autocrine VEGF Signaling Synergizes with EGFR in Tumor Cells to Promote Epithelial Cancer Development. Cell 2010, 140, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.; Wey, J.S.; McCarty, M.F.; Belcheva, A.; Liu, W.; Bauer, T.W.; Somcio, R.J.; Wu, Y.; Hooper, A.; Hicklin, D.J.; et al. Expression and Function of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 on Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, L.; Fang, M.; Wu, M.; Yao, M.; Yao, D. Ang-2 Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Increasing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 12705–12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, G.; Koudelkova, P.; Dituri, F.; Mikulits, W. Role of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich-Rivkin, T.; Liubomirski, Y.; Bernstein, B.; Meshel, T.; Ben-Baruch, A. Inflammatory Factors of the Tumor Microenvironment Induce Plasticity in Nontransformed Breast Epithelial Cells: EMT, Invasion, and Collapse of Normally Organized Breast Textures. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1330-IN5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Jeoung, D. CAGE, a Cancer/Testis Antigen, Induces c-FLIPL and Snail to Enhance Cell Motility and Increase Resistance to an Anti-Cancer Drug. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqurashi, Y.E.; Al-Hetty, H.R.A.K.; Ramaiah, P.; Fazaa, A.H.; Jalil, A.T.; Alsaikhan, F.; Gupta, J.; Ramírez-Coronel, A.A.; Tayyib, N.A.; Peng, H. Harnessing Function of EMT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Biological View to Nanotechnological Standpoint. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Guedj, N.; Clapéron, A.; Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires, T.H.; Paradis, V.; Fouassier, L. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cholangiocarcinoma: From Clinical Evidence to Regulatory Networks. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 424–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.-N.; Tang, J.-M.; Kong, X.; Yang, J.-Y.; Zheng, F.; Guo, L.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Tian, L.; et al. VEGF Is Essential for the Growth and Migration of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5085–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.S.; Chopp, M.; Zhang, R.L.; Hozeska-Solgot, A.; Gregg, S.C.; Buller, B.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Z.G. Angiopoietin 2 Mediates the Differentiation and Migration of Neural Progenitor Cells in the Subventricular Zone after Stroke. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22680–22689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, B.; Henriques, A.C.; Silva, P.M.A.; Bousbaa, H. Three-Dimensional Spheroids as In Vitro Preclinical Models for Cancer Research. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Chen, D.; Shen, S.; Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Lencioni, R.; Kuang, M. Autocrine Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling Promotes Cell Proliferation and Modulates Sorafenib Treatment Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Huang, B.; Li, G.; Zeng, S. Apatinib Affect VEGF-Mediated Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion via Blocking VEGFR2/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Cholangiocarcinoma Cell. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Hua, Y.; Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Lai, J.; Peng, Z.; Peng, B.; et al. Apatinib Inhibits VEGF Signaling and Promotes Apoptosis in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17220–17229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, I.B.; Renard, R.A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Gale, N.W.; Thurston, G.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Wiegand, S.J. Delta-like Ligand 4 (Dll4) Is Induced by VEGF as a Negative Regulator of Angiogenic Sprouting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3219–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, N.; Katsaros, D.; Huang, W.; Park, J.-W.; Fracchioli, S.; Vezzani, C.; Rigault de la Longrais, I.A.; Yao, W.; Rubin, S.C.; et al. The Oncogene Phosphatidylinositol 3’-Kinase Catalytic Subunit Alpha Promotes Angiogenesis via Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Ovarian Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar]
- Rawal, P.; Tripathi, D.M.; Nain, V.; Kaur, S. VEGF-Mediated Tumour Growth and EMT in 2D and 3D Cell Culture Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blidisel, A.; Marcovici, I.; Coricovac, D.; Hut, F.; Dehelean, C.A.; Cretu, O.M. Experimental Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma-A Preclinical Perspective. Cancers 2021, 13, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.-H.; Xie, X.; Xu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, L. Distinctive Pharmacological Differences between Liver Cancer Cell Lines HepG2 and Hep3B. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, D.; Dávila López, M.; Goeppert, B.; Abrahamsson, S.; González Silos, R.; Nova, I.; Marcelain, K.; Roa, J.C.; Ibberson, D.; Umu, S.U.; et al. RNA Sequencing of Hepatobiliary Cancer Cell Lines: Data and Applications to Mutational and Transcriptomic Profiling. Cancers 2020, 12, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Hsieh, F.-S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Chang, S.-S.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hung, M.-H.; Kuo, C.-W.; Shih, C.-T.; Chao, T.-I.; et al. Palbociclib Enhances Radiosensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cholangiocarcinoma via Inhibiting Ataxia Telangiectasia–Mutated Kinase–Mediated DNA Damage Response. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 102, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabris, L.; Cadamuro, M.; Moserle, L.; Dziura, J.; Cong, X.; Sambado, L.; Nardo, G.; Sonzogni, A.; Colledan, M.; Furlanetto, A.; et al. Nuclear Expression of S100A4 Calcium-Binding Protein Increases Cholangiocarcinoma Invasiveness and Metastasization. Hepatology 2011, 54, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huether, A.; Höpfner, M.; Baradari, V.; Schuppan, D.; Scherübl, H. Sorafenib Alone or as Combination Therapy for Growth Control of Cholangiocarcinoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okaro, A.C. Pk11195, a Mitochondrial Benzodiazepine Receptor Antagonist, Reduces Apoptosis Threshold in Bcl-XL and Mcl-1 Expressing Human Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Gut 2002, 51, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiswald, L.-B.; Bellet, D.; Dangles-Marie, V. Spherical Cancer Models in Tumor Biology. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lee, C.; Shen, F.; Du, R.; Young, W.L.; Yang, G.-Y. Angiopoietin-2 Facilitates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Angiogenesis in the Mature Mouse Brain. Stroke 2005, 36, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, C.D.; Olsen, M.W.B.; Lund, E.L.; Kristjansen, P.E.G. Angiogenic Synergy of bFGF and VEGF Is Antagonized by Angiopoietin-2 in a Modified in Vivo Matrigel Assay. Microvasc. Res. 2004, 68, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Stamenkovic, I. Angiopoietin-2 Is Implicated in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Srinivasan, R.; Chawla, Y.; Chakraborti, A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor: Evidence for Autocrine Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines Affecting Invasion. Indian J. Cancer 2016, 53, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL-Hajjar, L.; Jalaleddine, N.; Shaito, A.; Zibara, K.; Kazan, J.M.; El-Saghir, J.; El-Sabban, M. Bevacizumab Induces Inflammation in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line and in a Mouse Model. Cell. Signal. 2019, 53, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulos, M.; Polak, K.; Prager, F.; Prunte, C.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Characteristics of Severe Intraocular Inflammation Following Intravitreal Injection of Bevacizumab (Avastin). Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolandi, S.M.; Abdolmaleki, Z.; Assarehzadegan, M.-A. Bevacizumab Regulates Inflammatory Cytokines and Inhibits VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway in an Ovalbumin-Induced Rat Model of Airway Hypersensitivity. Inflammopharmacol 2021, 29, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mérida, S.; Sancho-Tello, M.; Almansa, I.; Desco, C.; Peris, C.; Moreno, M.-L.; Villar, V.M.; Navea, A.; Bosch-Morell, F. Bevacizumab Diminishes Inflammation in an Acute Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Guerra, V.; Carr, B.I.; D’Alessandro, R. Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, B.P.; Fong, L.; Kelley, R.K. Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Complex Interface between Inflammation, Fibrosis, and the Immune Response. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; de Melo-Diogo, D.; Gaspar, V.M.; Carvalho, M.P.; Correia, I.J. 3D Tumor Spheroids: An Overview on the Tools and Techniques Used for Their Analysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.M.; Bouchier-Hayes, D.J.; Harmey, J.H. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Role in Non-Endothelial Cells: Autocrine Signalling by VEGF. In Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Meng, L.; Wang, Q.; Xi, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Y.; Ma, D. Enhanced in Vitro Invasiveness of Ovarian Cancer Cells through Up-Regulation of VEGF and Induction of MMP-2. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Price, D.J.; Miralem, T.; Jiang, S.; Steinberg, R.; Avraham, H. Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in the Stimulation of Cellular Invasion and Signaling of Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Growth Differ. 2001, 12, 129–135. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Han, H.H.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, N.H. Angiopoietin-2 Promotes ER+ Breast Cancer Cell Survival in Bone Marrow Niche. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Ning, F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wu, P.; Chen, M.; Lash, G.E. Angiopoietin 2 Stimulates Trophoblast Invasion via a Mechanism Associated with JNK Signaling. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 27, gaab014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderborght, B.; Lefere, S.; Vlierberghe, H.V.; Devisscher, L. The Angiopoietin/Tie2 Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Sugimachi, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Ohga, T.; Shirabe, K.; Shimada, M.; Wands, J.R.; Sugimachi, K. Tie2 Vascular Endothelial Receptor Expression and Function in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Tie2 Vascular Endothelial Receptor Expression and Function in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Ko, E.; Kim, K.E.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Song, P.H.; Kim, Y.-I.; et al. Gln-362 of Angiopoietin-2 Mediates Migration of Tumor and Endothelial Cells through Association with A5β1 Integrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 31330–31340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jarzynka, M.J.; Guo, P.; Imanishi, Y.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Cheng, S.-Y. Angiopoietin 2 Induces Glioma Cell Invasion by Stimulating Matrix Metalloprotease 2 Expression through the Alphavbeta1 Integrin and Focal Adhesion Kinase Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, Y.; Hu, B.; Jarzynka, M.J.; Guo, P.; Elishaev, E.; Bar-Joseph, I.; Cheng, S.-Y. Angiopoietin-2 Stimulates Breast Cancer Metastasis through the A5β1 Integrin-Mediated Pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 4254–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findley, C.M.; Cudmore, M.J.; Ahmed, A.; Kontos, C.D. VEGF Induces Tie2 Shedding via a Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt–Dependent Pathway to Modulate Tie2 Signaling. ATVB 2007, 27, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, J.S.; Fan, F.; Gray, M.J.; Bauer, T.W.; McCarty, M.F.; Somcio, R.; Liu, W.; Evans, D.B.; Wu, Y.; Hicklin, D.J.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 Promotes Migration and Invasion in Pancreatic Carcinoma Cell Lines. Cancer 2005, 104, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Its Receptors KDR and Flt-1 in Gastric Cancer Cells. WJG 2002, 8, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, C.; Yang, Z.; Fang, A.; Xu, S.; Ren, W. Expression and Prognostic Significance of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.P.; Brown, A.M.; Pitts, T.M.; Tentler, J.J.; Ciardiello, F.; Ryan, A.; Jürgensmeier, J.M.; Eckhardt, S.G. Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 and -3 with Cediranib (AZD2171): Effects on Migration and Invasion of Gastrointestinal Cancer Cell Lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2546–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V. Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Metastasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2018, 13, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüönd, F.; Sugiyama, N.; Bill, R.; Bornes, L.; Hager, C.; Tang, F.; Santacroce, N.; Beisel, C.; Ivanek, R.; Bürglin, T.; et al. Distinct Contributions of Partial and Full EMT to Breast Cancer Malignancy. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 3203–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wang, Q.; An, J.; Long, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiang, M.; Xiang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Partial EMT in Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Snapshot. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3036–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerinck, J.; Berx, G. Partial EMT Takes the Lead in Cancer Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 3174–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M. Involvement of Partial EMT in Cancer Progression. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saentaweesuk, W.; Araki, N.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Silsirivanit, A.; Seubwai, W.; Talabnin, C.; Muisuk, K.; Sripa, B.; Wongkham, S.; Okada, S.; et al. Activation of Vimentin Is Critical to Promote a Metastatic Potential of Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y.; Duan, X. Differential Expression of Fascin, E-Cadherin and Vimentin: Proteins Associated with Survival of Cholangiocarcinoma Patients. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 346, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevis, K.M.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Embedded Spheroids as Models of the Cancer Microenvironment. Adv. Biosyst. 2017, 1, 1700083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanzi, A.; Milosa, F.; Marcelli, G.; Critelli, R.M.; Lasagni, S.; Gigante, I.; Dituri, F.; Schepis, F.; Cadamuro, M.; Giannelli, G.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Promote Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma- and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-Derived Spheroids. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010087
Romanzi A, Milosa F, Marcelli G, Critelli RM, Lasagni S, Gigante I, Dituri F, Schepis F, Cadamuro M, Giannelli G, et al. Angiopoietin-2 and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Promote Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma- and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-Derived Spheroids. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanzi, Adriana, Fabiola Milosa, Gemma Marcelli, Rosina Maria Critelli, Simone Lasagni, Isabella Gigante, Francesco Dituri, Filippo Schepis, Massimiliano Cadamuro, Gianluigi Giannelli, and et al. 2024. "Angiopoietin-2 and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Promote Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma- and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-Derived Spheroids" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010087
APA StyleRomanzi, A., Milosa, F., Marcelli, G., Critelli, R. M., Lasagni, S., Gigante, I., Dituri, F., Schepis, F., Cadamuro, M., Giannelli, G., Fabris, L., & Villa, E. (2024). Angiopoietin-2 and the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Promote Migration and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma- and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma-Derived Spheroids. Biomedicines, 12(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010087