Exploring the Relationship between Gut Microbiome Composition and Blood Indole-3-acetic Acid in Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Comorbidity, Laboratory, and Clinical Variables
2.3. IAA Measurement by Tandem Mass Spectrometry Laboratory
2.4. Bacterial 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Baseline Characteristics
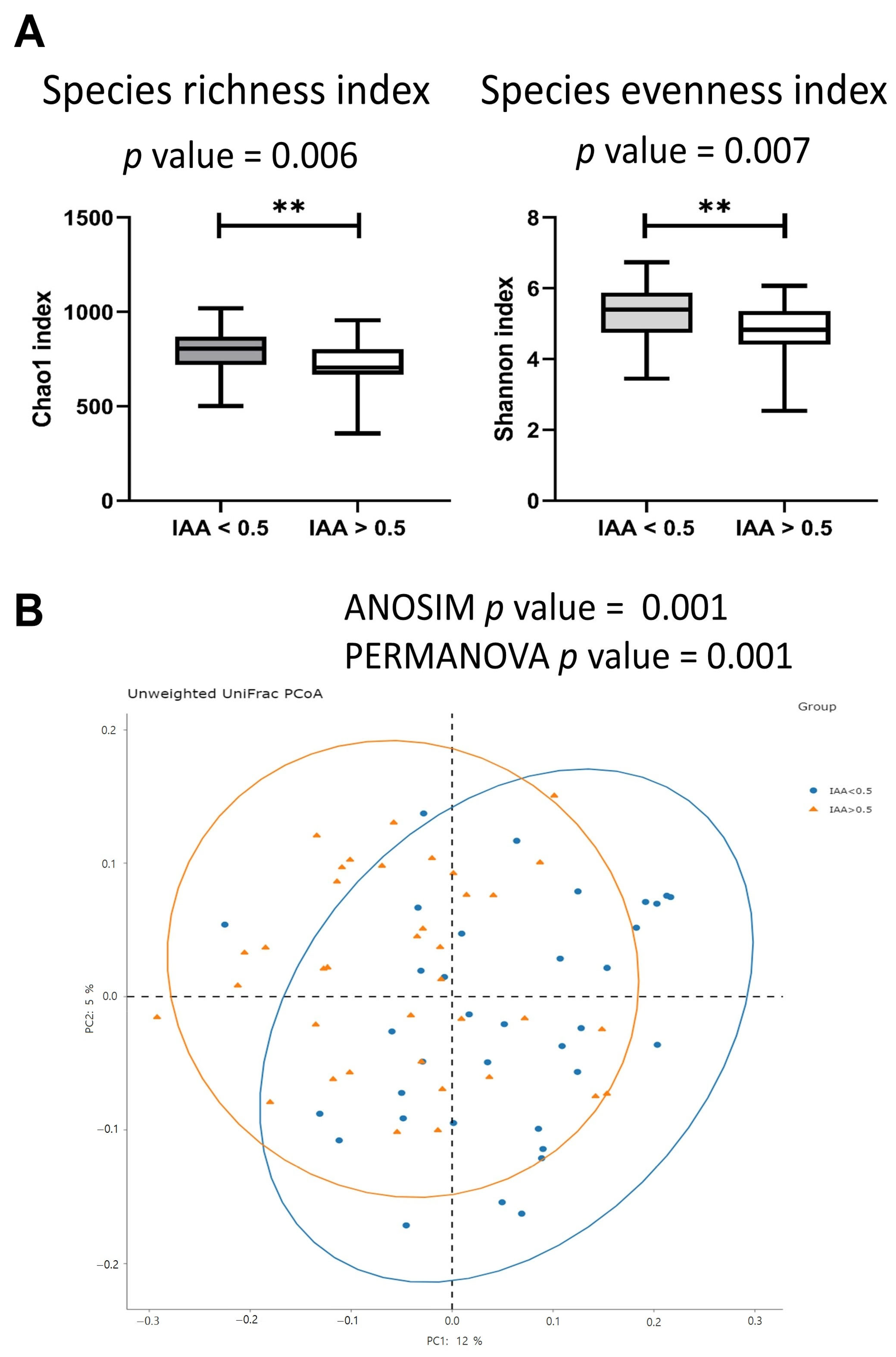
3.2. The Gut Microbiota Diversity Index Was Associated with IAA Levels
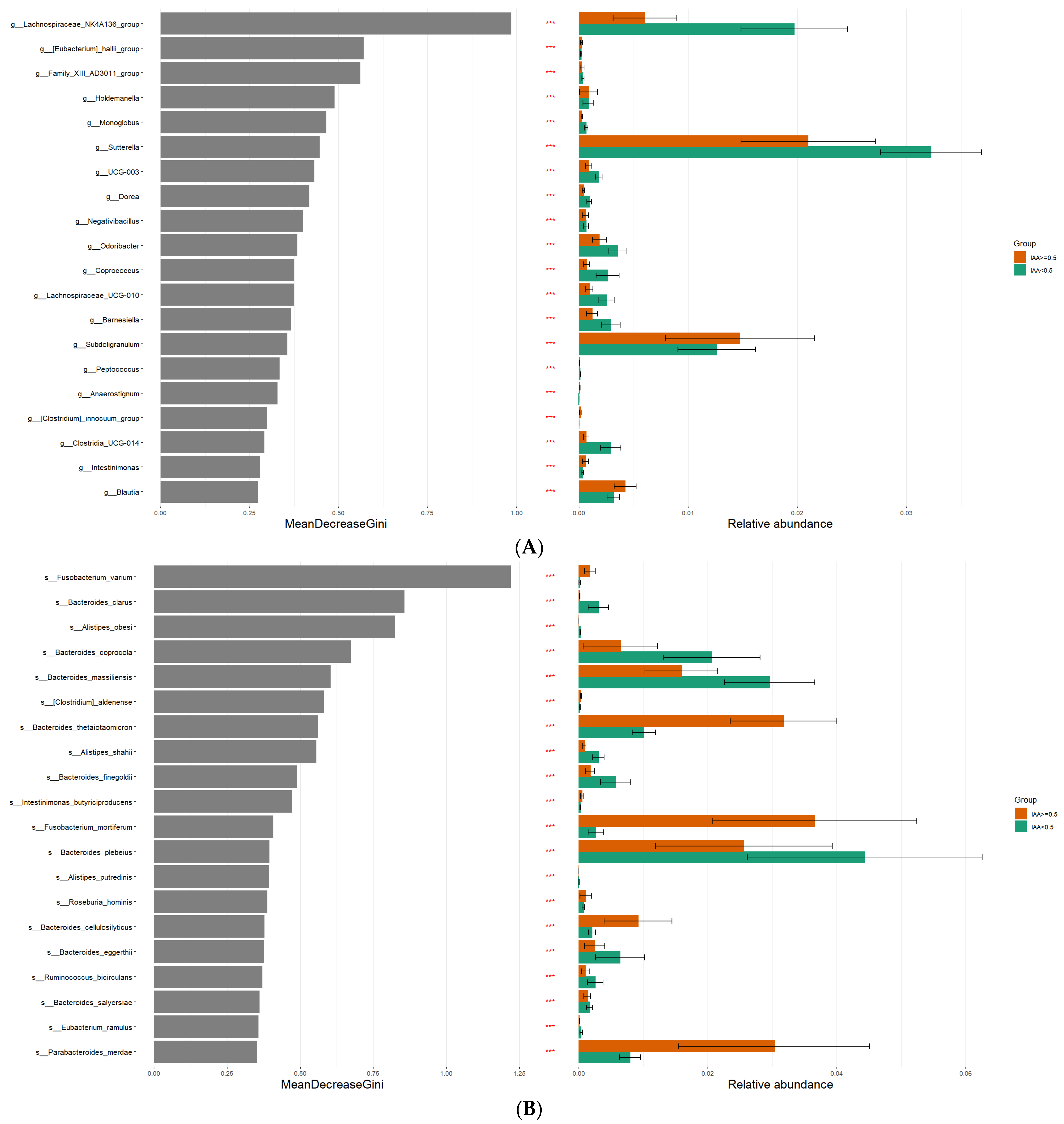
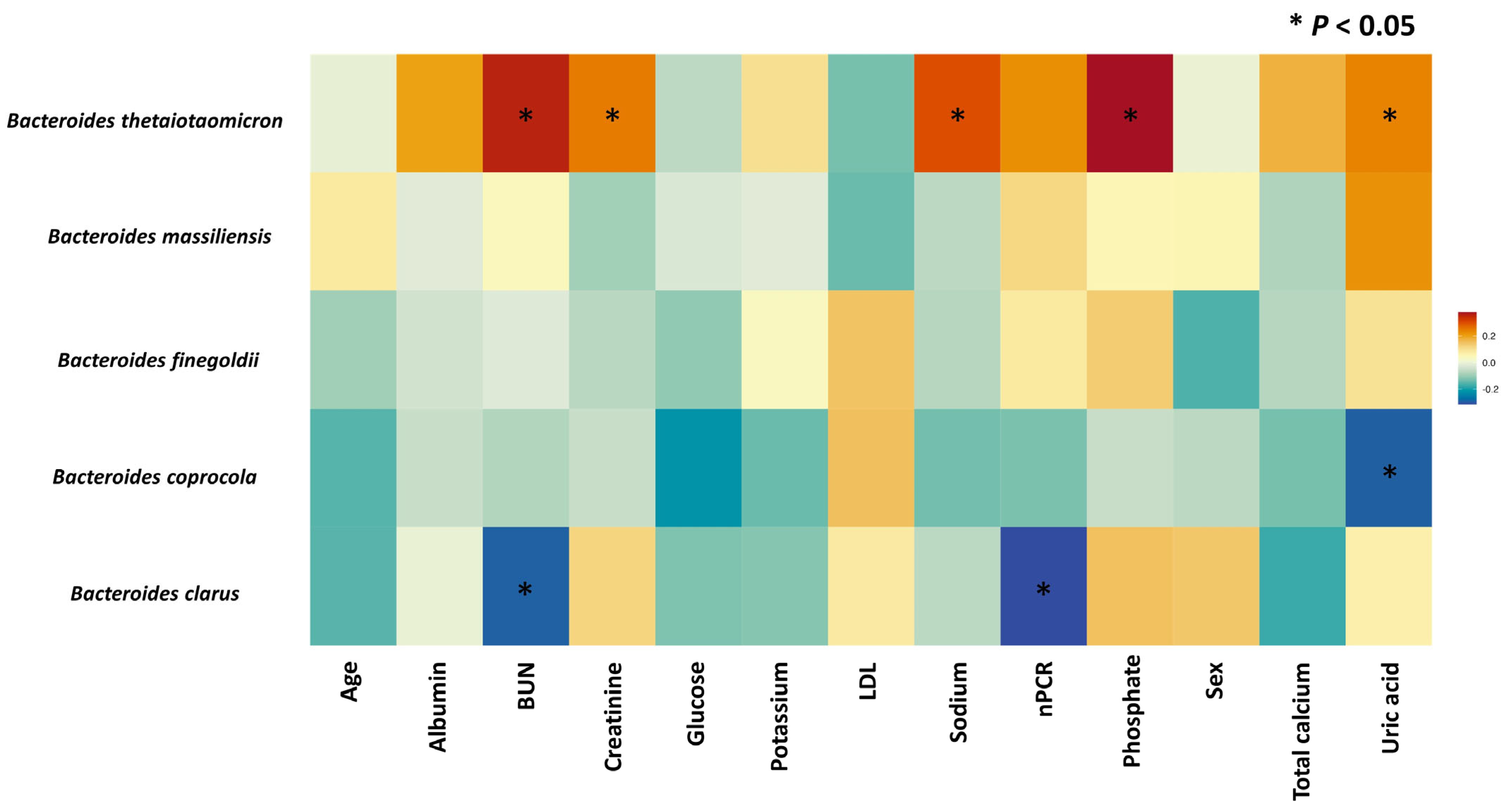
3.3. The Microbial Features Associated with IAA Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, L.; Sallee, M.; Cerini, C.; Poitevin, S.; Gondouin, B.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Fallague, K.; Brunet, P.; Calaf, R.; Dussol, B.; et al. The cardiovascular effect of the uremic solute indole-3 acetic acid. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karu, N.; McKercher, C.; Nichols, D.S.; Davies, N.; Shellie, R.A.; Hilder, E.F.; Jose, M.D. Tryptophan metabolism, its relation to inflammation and stress markers and association with psychological and cognitive functioning: Tasmanian chronic kidney disease pilot study. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, W. Indole-3-acetic acid alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis, and oxidative and inflammatory stress. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wu, P.H.; Lee, H.H.; Mubanga, M.; Chen, C.S.; Kuo, M.C.; Chiu, Y.W.; Kuo, P.L.; Hwang, S.J. Indole-3 acetic acid increased risk of impaired cognitive function in patients receiving hemodialysis. Neurotoxicology 2019, 73, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, P.-Y.; Lee, H.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Hung, S.-C.; Chen, S.-C.; Kuo, M.-C.; Chiu, Y.-W. Association between circulation indole-3-acetic acid levels and stem cell factor in maintenance hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Del-Campo, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Stenvinkel, P.; Lindholm, B.; Cueto-Manzano, A.M.; Cortes-Sanabria, L. Gut microbiota disturbances and protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease: A narrative review. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, T.; Hu, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, N. Changes in gut microbial community upon chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B.; Lawinski, J.; Olszewski, R.; Cialkowska-Rysz, A.; Gluba-Brzozka, A. The impact of ckd on uremic toxins and gut microbiota. Toxins 2021, 13, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Wu, P.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Hung, S.C. Gut dysbiosis and mortality in hemodialysis patients. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Chao, L.; Chen, K.; Shao, A.; Sun, D.; Hong, Y.; Hu, R.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, N.; et al. Alteration of the gut microbiome in chronic kidney disease patients and its association with serum free immunoglobulin light chains. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 609700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Mu, C.L.; Farzi, A.; Zhu, W.Y. Tryptophan metabolism: A link between the gut microbiota and brain. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S. Modulation of immunity by tryptophan microbial metabolites. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1209613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madella, A.M.; Van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Garssen, J.; Masereeuw, R.; Overbeek, S.A. Microbial-derived tryptophan catabolites, kidney disease and gut inflammation. Toxins 2022, 14, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.A.; Macfarlane, G.T. Enumeration of human colonic bacteria producing phenolic and indolic compounds: Effects of ph, carbohydrate availability and retention time on dissimilatory aromatic amino acid metabolism. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1996, 81, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsden, S.R.; Hilton, M.G.; Waller, J.M. The end products of the metabolism of aromatic amino acids by clostridia. Arch. Microbiol. 1976, 107, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.R.; Duncan, S.H.; Scobbie, L.; Duncan, G.; Cantlay, L.; Calder, A.G.; Anderson, S.E.; Flint, H.J. Major phenylpropanoid-derived metabolites in the human gut can arise from microbial fermentation of protein. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlemann, D.P.; Labrenz, M.; Jurgens, K.; Bertilsson, S.; Waniek, J.J.; Andersson, A.F. Transitions in bacterial communities along the 2000 km salinity gradient of the baltic sea. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The silva ribosomal rna gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and qsar modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Yang, L.; You, K.; Chen, T.; Su, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, B.; Zhou, K.; et al. Indole-3-acetic acid alters intestinal microbiota and alleviates ankylosing spondylitis in mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 762580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y. New insights into gut-bacteria-derived indole and its derivatives in intestinal and liver diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 769501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Valdes, A.M. Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases: A narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zeng, R. Gut dysbiosis and kidney diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 829349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bose, C.; Mande, S.S. Tryptophan metabolism by gut microbiome and gut-brain-axis: An in silico analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the gut microbiota on intestinal immunity mediated by tryptophan metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Covian, D.; Arboleya, S.; Hernandez-Barranco, A.M.; Alvarez-Buylla, J.R.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Gueimonde, M.; de los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G. Interactions between bifidobacterium and bacteroides species in cofermentations are affected by carbon sources, including exopolysaccharides produced by bifidobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7518–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, J.; Dongowski, G.; Hartmann, L.; Blaut, M. The human gut bacteria bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and fusobacterium varium produce putrescine and spermidine in cecum of pectin-fed gnotobiotic rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Anjum, K.; Zhong, X.; Miao, S.; Zheng, G.; Liu, W.; Li, L. Dual role of indoles derived from intestinal microbiota on human health. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 903526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, A.S.; Marcobal, A.; Dodd, D.; Nayfach, S.; Plummer, N.; Meyer, T.; Pollard, K.S.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Fischbach, M.A. Modulation of a circulating uremic solute via rational genetic manipulation of the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, K.F.; Sayols-Baixeras, S.; Baldanzi, G.; Nowak, C.; Hammar, U.; Nguyen, D.; Varotsis, G.; Brunkwall, L.; Nielsen, N.; Eklund, A.C.; et al. An online atlas of human plasma metabolite signatures of gut microbiome composition. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IAA < 0.5 μg/mL (n = 35) | IAA ≥ 0.5 μg/mL (n = 37) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Mean (SD) | 57.6 (10.8) | 60.9 (9.7) | 0.171 |
| Male, n (%) | 20.0 (57.1%) | 20.0 (54.1%) | 0.792 |
| Hemodialysis vintage, months, Mean (SD) | 83.0 (66.8) | 95.2 (83.0) | 0.497 |
| Proton pump inhibitor used, n (%) | 5.0 (14.3%) | 5.0 (13.5%) | 0.925 |
| Clinical biochemistry, Mean (SD) | |||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.0 (0.4) | 3.9 (0.3) | 0.482 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 107.7 (30.1) | 101.4 (26.3) | 0.343 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 113.4 (38.0) | 105.8 (32.5) | 0.361 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 63.9 (11.5) | 65.8 (14.2) | 0.539 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 10.9 (2.1) | 10.7 (1.8) | 0.655 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 7.1 (1.1) | 6.8 (1.7) | 0.386 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137.4 (2.3) | 137.2 (2.6) | 0.703 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.6 (0.7) | 4.4 (0.6) | 0.180 |
| Total calcium (mg/dL) | 9.2 (1.0) | 9.3 (0.9) | 0.574 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 4.8 (0.9) | 4.6 (1.1) | 0.480 |
| nPCR (g/kg/day) | 1.1 (0.2) | 1.2 (0.2) | 0.079 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.-H.; Tseng, Y.-F.; Liu, W.; Chuang, Y.-S.; Tai, C.-J.; Tung, C.-W.; Lai, K.-Y.; Kuo, M.-C.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; et al. Exploring the Relationship between Gut Microbiome Composition and Blood Indole-3-acetic Acid in Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010148
Wu P-H, Tseng Y-F, Liu W, Chuang Y-S, Tai C-J, Tung C-W, Lai K-Y, Kuo M-C, Chiu Y-W, Hwang S-J, et al. Exploring the Relationship between Gut Microbiome Composition and Blood Indole-3-acetic Acid in Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010148
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ping-Hsun, Yu-Fang Tseng, Wangta Liu, Yun-Shiuan Chuang, Chi-Jung Tai, Chun-Wei Tung, Kean-Yee Lai, Mei-Chuan Kuo, Yi-Wen Chiu, Shang-Jyh Hwang, and et al. 2024. "Exploring the Relationship between Gut Microbiome Composition and Blood Indole-3-acetic Acid in Hemodialysis Patients" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010148
APA StyleWu, P.-H., Tseng, Y.-F., Liu, W., Chuang, Y.-S., Tai, C.-J., Tung, C.-W., Lai, K.-Y., Kuo, M.-C., Chiu, Y.-W., Hwang, S.-J., Hung, W.-C., & Lin, Y.-T. (2024). Exploring the Relationship between Gut Microbiome Composition and Blood Indole-3-acetic Acid in Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines, 12(1), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010148










