Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency in a Rabbit Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation
2.2.1. Scaffold
2.2.2. Cells
- 1.
- Obtaining a biopsy specimen.
- 2.
- Cell isolation and cultivation.
- 3.
- Cell characteristics.
2.3. Surgical Procedure
2.3.1. Study of the Effect of Implantation of a Collagen Membrane (Carrier) in the Limbal Defect Area of Rabbits
2.3.2. Animal Model of LSCD
2.3.3. Group Formation
2.3.4. Transplantation Procedure
2.4. Postoperative Care
2.5. Postoperative Examinations
2.6. Impression Cytology of the Ocular Surface
2.7. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
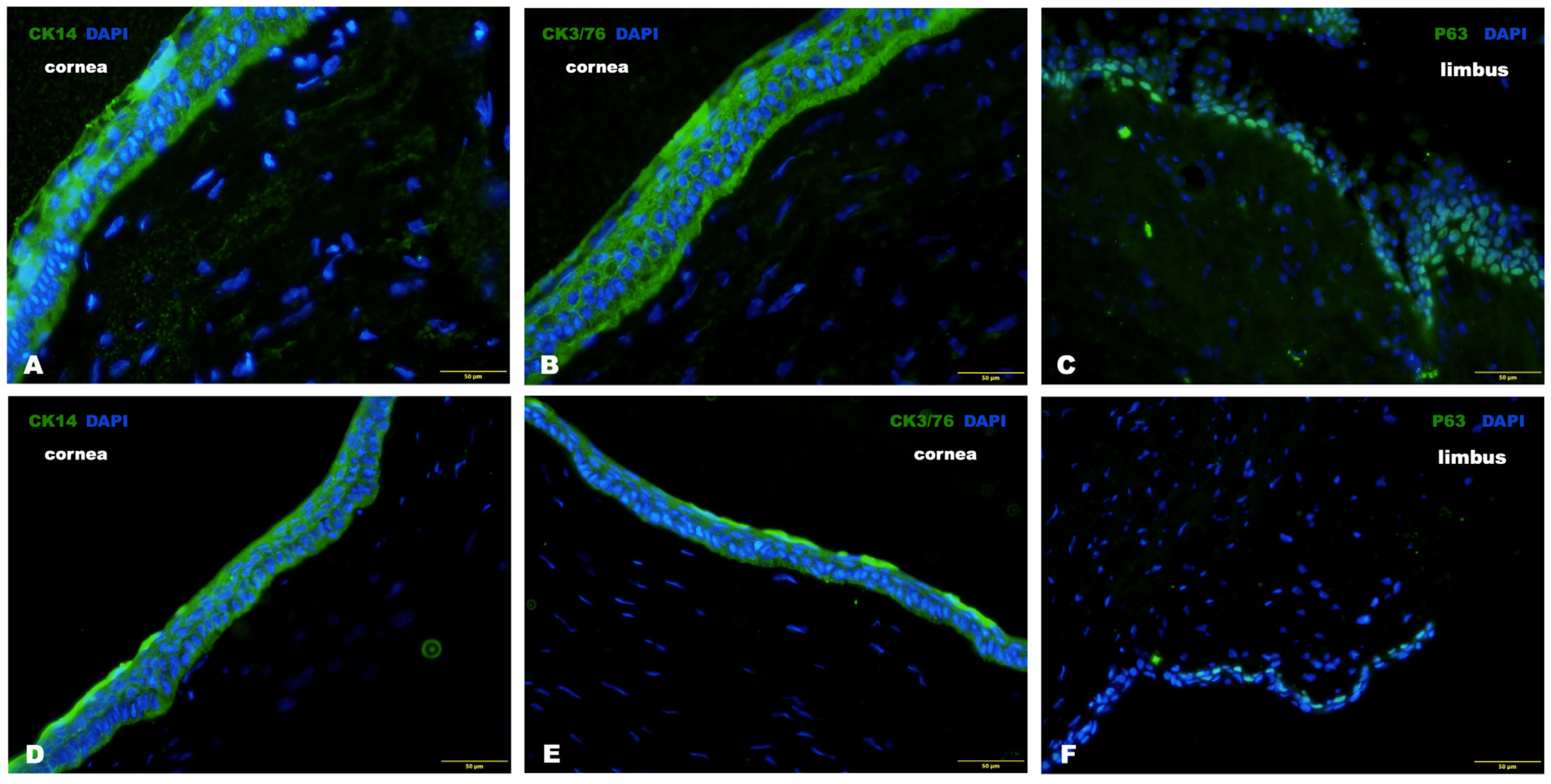
3. Results
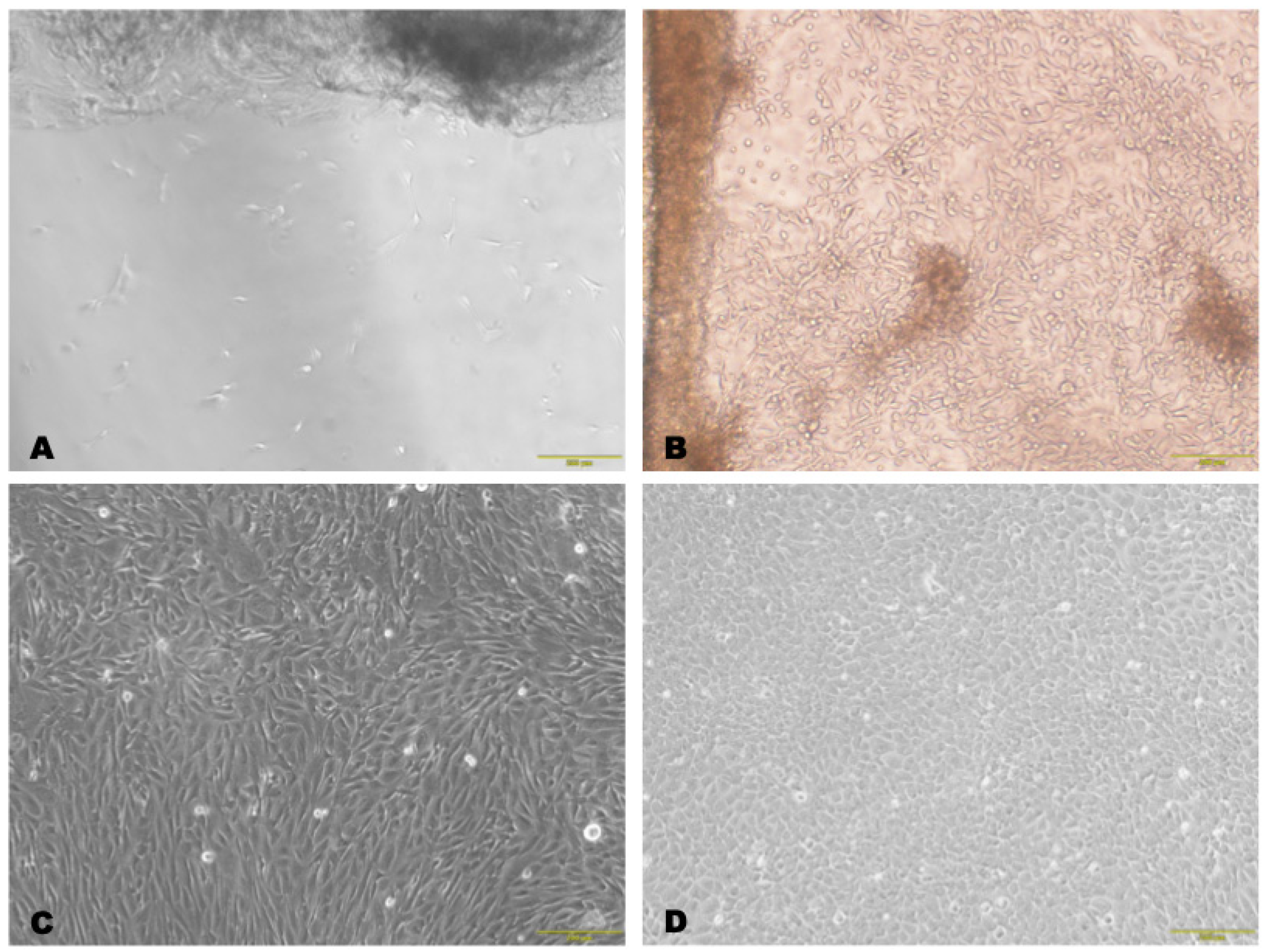
3.1. Series of Experiments In Vitro
3.1.1. Isolation of LSCs from Biopsy Specimens
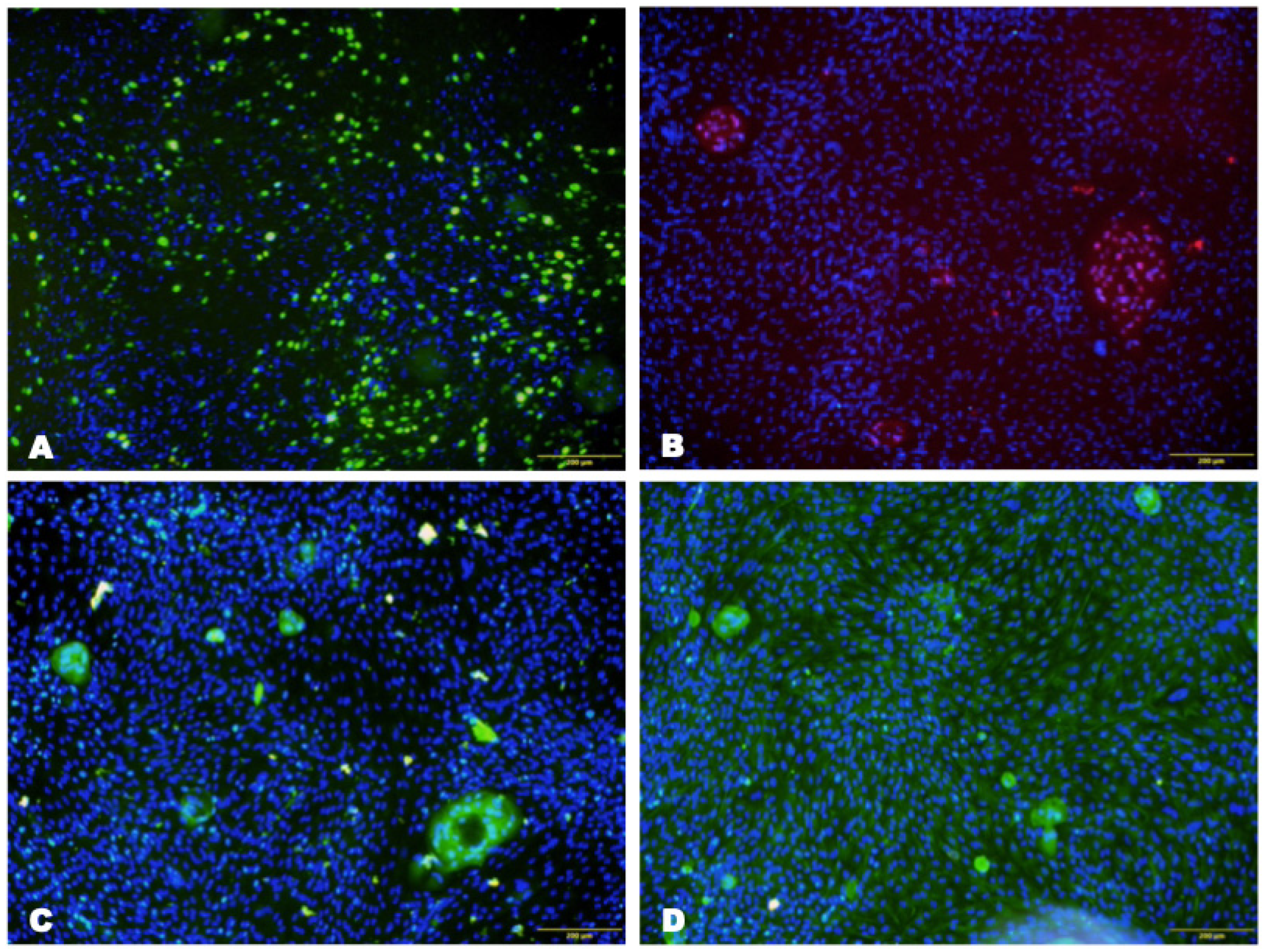
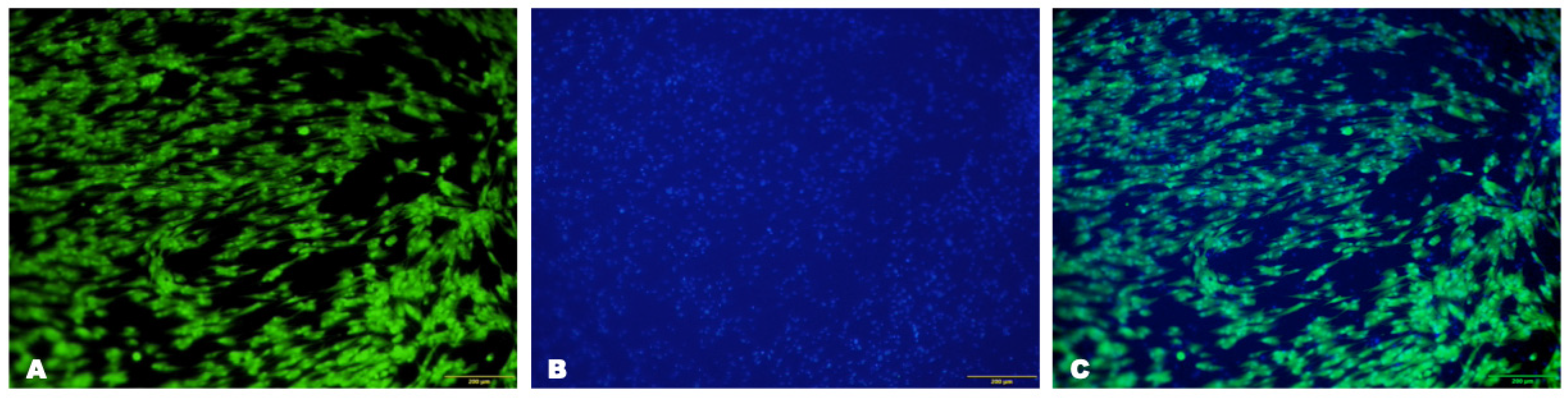
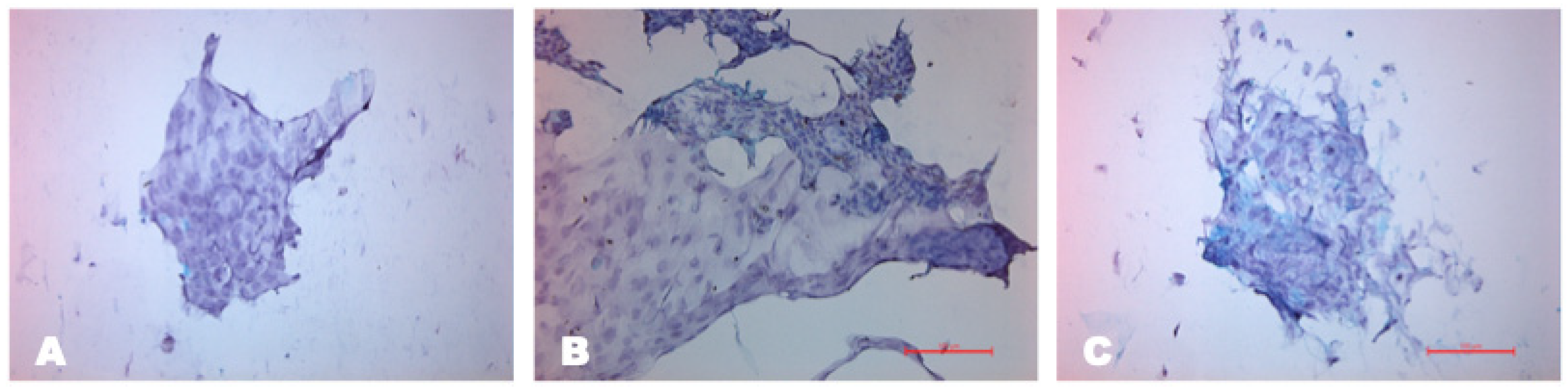
3.1.2. Characterization of Isolated Cells
3.1.3. Characterization of Cells on the Scaffold
3.2. Series of Experiments In Vivo
3.2.1. Evaluation of Local Tissue Response to Collagen Hydrogel Implantation into the Limbal Defect Area of Rabbits
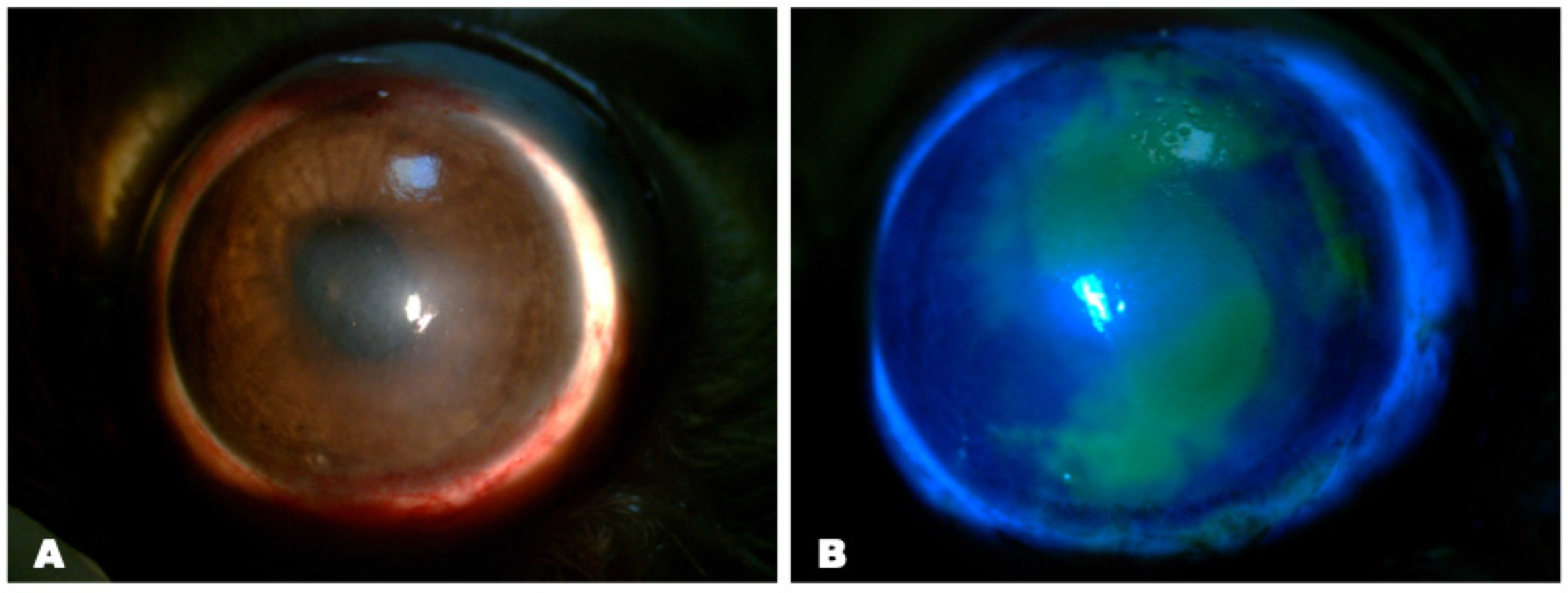
3.2.2. LSCD Modeling
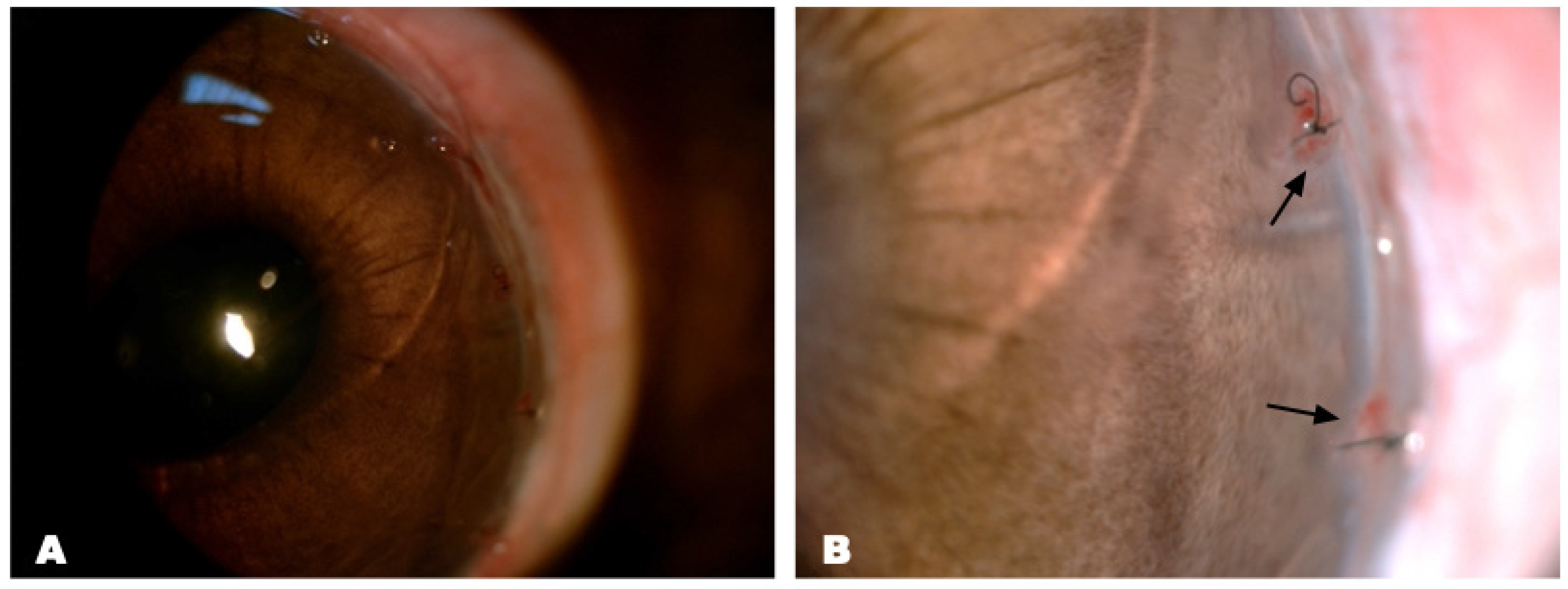
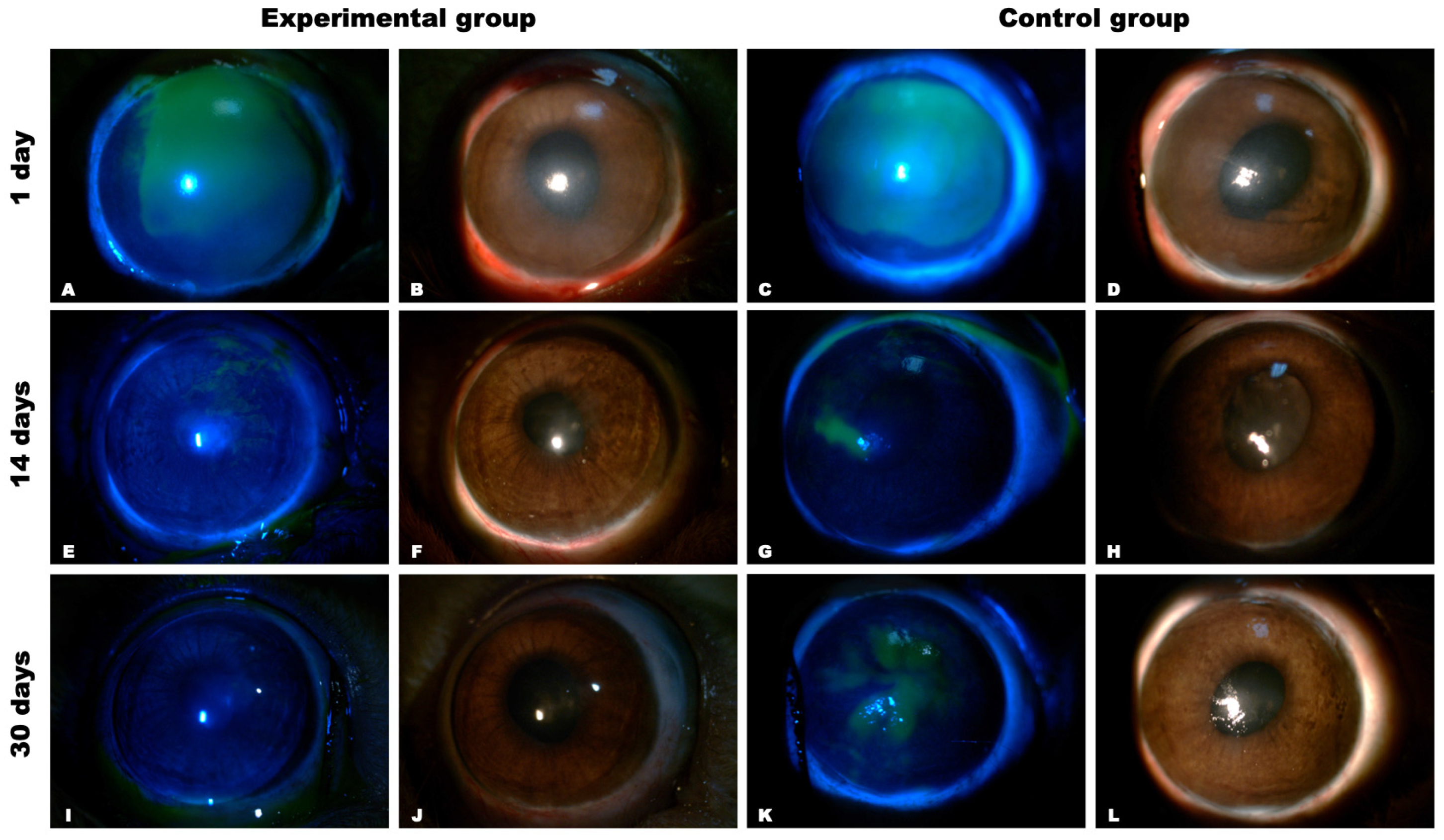
Clinical Manifestations (Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopy with Photo-Registration)
Impression Cytology
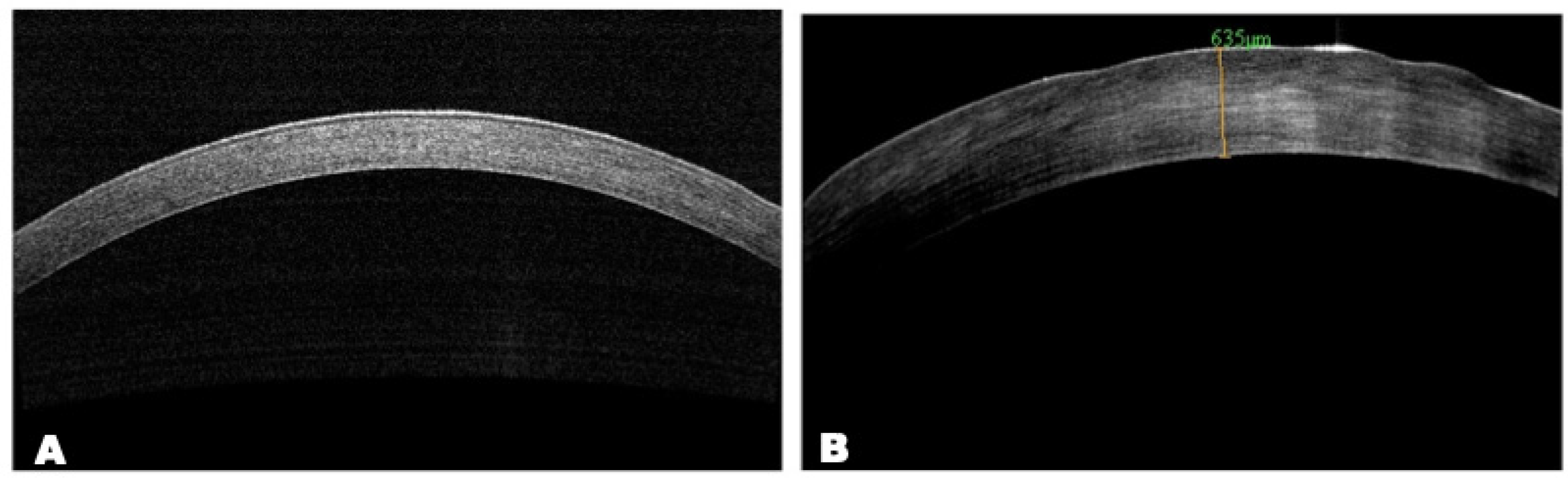
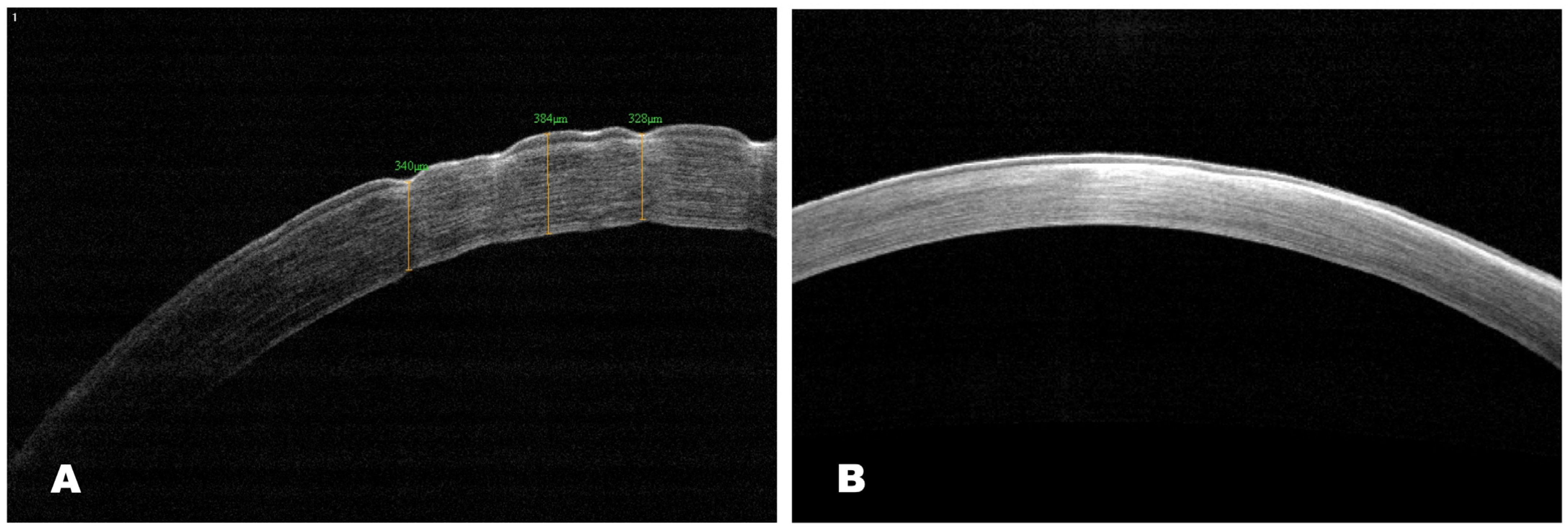
AS-OCT
3.2.3. Epithelial Regeneration after Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation
Clinical Manifestations (Biomicroscopy with Photo-Registration and Fluorescent Staining)
Impression Cytology
AS-OCT
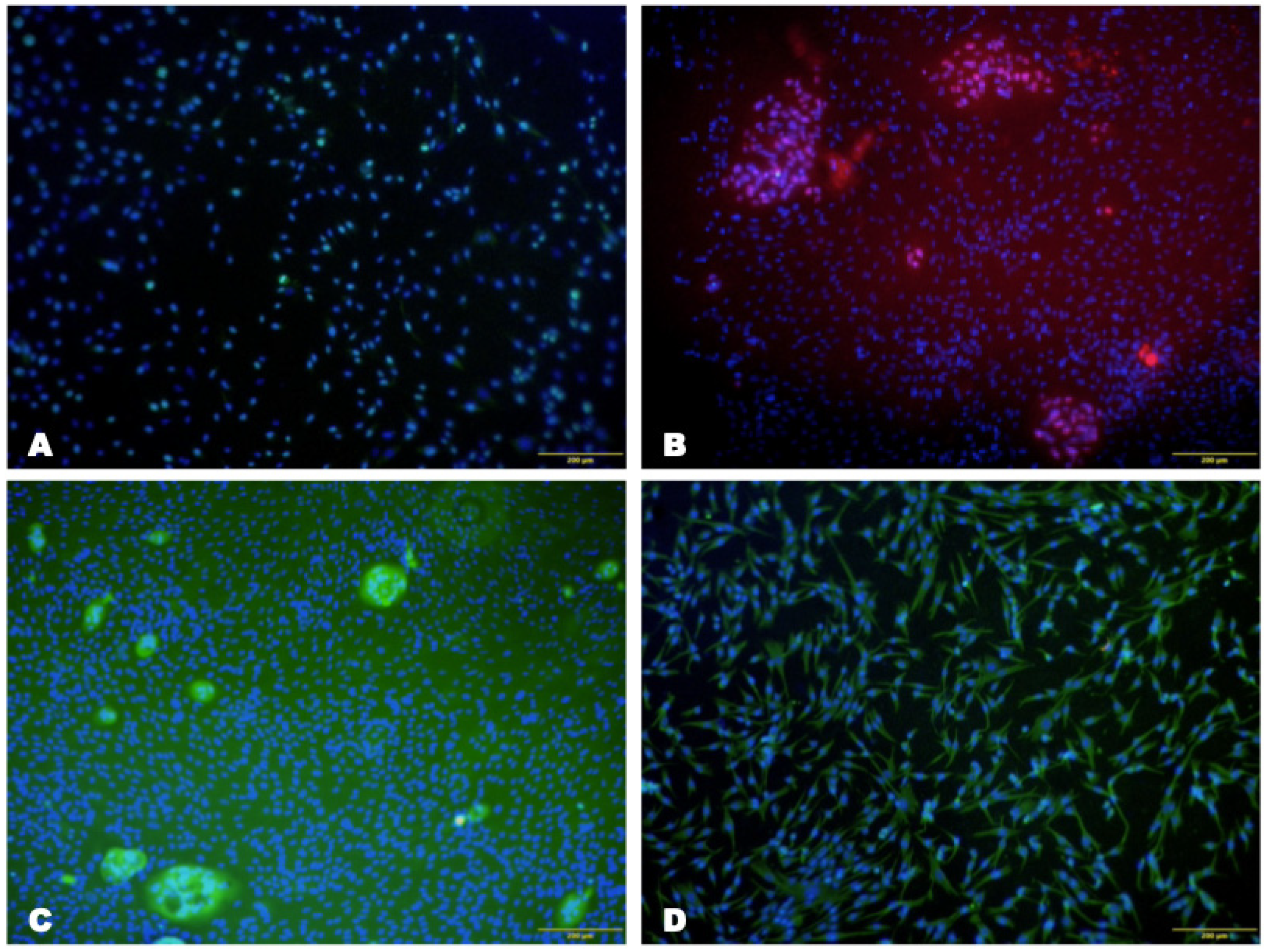
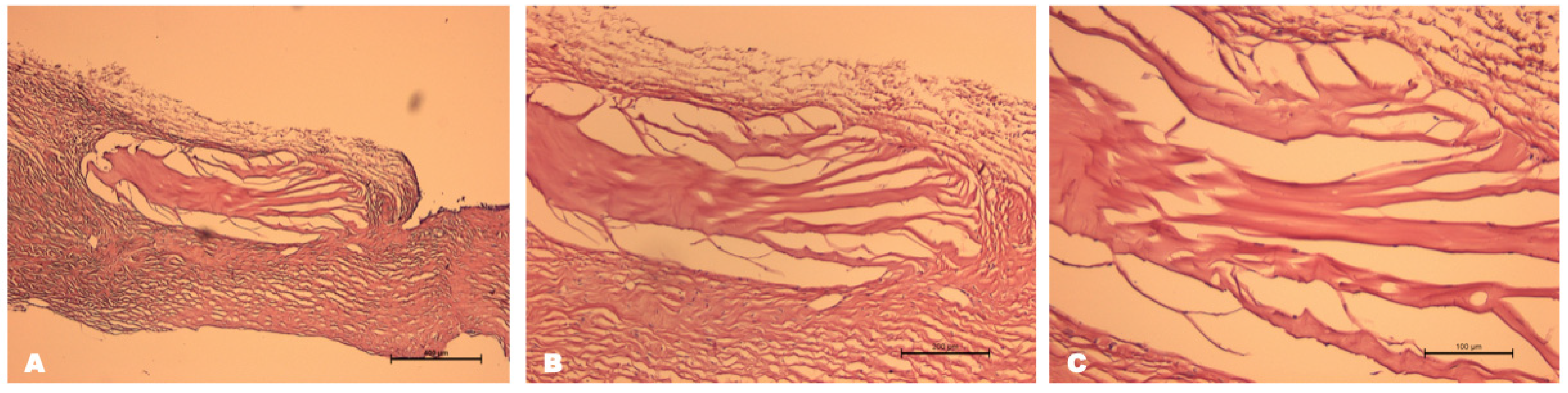
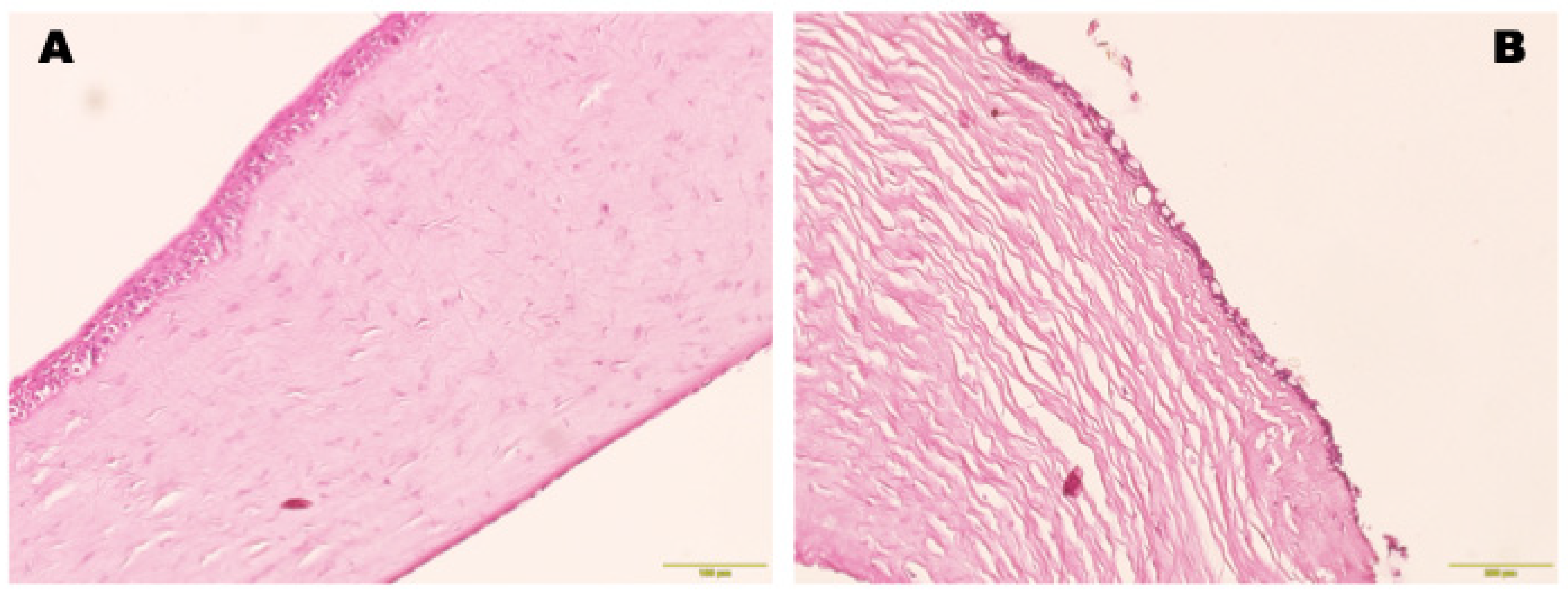
Histological Examination
Immunohistochemical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, S.X.; Borderie, V.; Chan, C.C.; Dana, R.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Gomes, J.A.P.; Pellegrini, G.; Shimmura, S.; Kruse, F.E. Global Consensus on Definition, Classification, Diagnosis, and Staging of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Cornea 2019, 38, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.C. Concept and application of limbal stem cells. Eye 1989, 3 Pt 2, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Tighe, S.; Chen, S.; Xie, H.; et al. Human limbal niche cells are a powerful regenerative source for the prevention of limbal stem cell deficiency in a rabbit model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, C.; González, S.; Roberts, J.S.; Robertson, S.Y.T.; Ruiz, M.; Zheng, J.; Deng, S.X. Human limbal epithelial stem cell regulation, bioengineering and function. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 85, 100956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkoli, F.; Eleiwa, T.K.; Elhusseiny, A.M.; Damala, M.; Rai, A.K.; Cheraqpour, K.; Ansari, M.H.; Doroudian, M.; Keshel, S.H.; Soleimani, M.; et al. Corneal stem cells niche and homeostasis impacts in regenerative medicine; concise review. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 33, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Riaz, K.M.; Bakhtiari, P.; Chan, C.C.; Welder, J.D.; Holland, E.J.; Basti, S.; Djalilian, A.R. Medically reversible limbal stem cell disease: Clinical features and management strategies. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.; Lim, E.W.L. Therapeutic Contact Lenses in the Treatment of Corneal and Ocular Surface Diseases-A Review. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 9, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niruthisard, D.; Bonnet, C.; Tanasugarn, L.; Le, B.; Deng, S.X. Autologous Serum Eye Drops in the Management of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Associated With Glaucoma Surgery. Eye Contact Lens 2023, 49, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Bakhtiari, P.; Riaz, K.; Chan, C.; Welder, J.; Basti, S.; Djalilian, A. Medical management of limbal stem cell deficiency with anti-inflammatory therapy and tear film optimization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.X.; Kruse, F.; Gomes, J.A.P.; Chan, C.C.; Daya, S.; Dana, R.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Kinoshita, S.; Rama, P.; Sangwan, V.; et al. Global Consensus on the Management of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Cornea 2020, 39, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.S.; Nikpoor, N.; Rao Donthineni, P.; Singh, V.; Chodosh, J.; Basu, S. Autologous limbal stem cell transplantation: A systematic review of clinical outcomes with different surgical techniques. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baradaran-Rafii, A.; Eslani, M.; Jamali, H.; Karimian, F.; Tailor, U.A.; Djalilian, A.R. Postoperative complications of conjunctival limbal autograft surgery. Cornea 2012, 31, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Jurkunas, U. Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation and Complications. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 33, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, H.; Abpeikar, Z.; Mahmoudian, Z.G.; Zafari, M.; Majidi, J.; Alizadeh, A.; Moradi, L.; Asadpour, S. Corneal epithelium tissue engineering: Recent advances in regeneration and replacement of corneal surface. Regen. Med. 2020, 15, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, L.P.; Larouche, D.; Morcos, M.W.; Faucher, A.; Auger, F.A.; Knoppers, B.M.; Kyrillos, R.; Bazin, R.; Germain, L. Cultured Autologous Corneal Epithelia for the Treatment of Unilateral Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency: A Case Series of 15 Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Yun, H.; Funderburgh, M.L.; Du, Y. Regenerative therapy for the Cornea. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 87, 101011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, S.; de la Mata, A.; López-Paniagua, M.; Herreras, J.M.; Pérez, I.; Calonge, M.; Nieto-Miguel, T. Subconjunctival injection of mesenchymal stem cells for corneal failure due to limbal stem cell deficiency: State of the art. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osidak, E.O.; Kalabusheva, E.P.; Alpeeva, E.V.; Belousov, S.I.; Krasheninnikov, S.V.; Grigoriev, T.E.; Domogatsky, S.P.; Vorotelyak, E.A.; Chermnykh, E.S. Concentrated collagen hydrogels: A new approach for developing artificial tissues. Materialia 2021, 20, 101217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreev, A.Y.; Osidak, E.O.; Grigoriev, T.E.; Krasheninnikov, S.V.; Zaharov, V.D.; Zaraitianc, O.V.; Borzenok, S.A.; Domogatsky, S.P. A new collagen scaffold for the improvement of corneal biomechanical properties in a rabbit model. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 207, 108580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Joseph, A.; Umapathy, T.; Tint, N.L.; Dua, H.S. Impression cytology of the ocular surface. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetti, M.; Rama, P.; Bruscolini, A.; Lambiase, A. Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation: Clinical Results, Limits, and Perspectives. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 8086269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, G.Q. The promise and perils of stem cell therapeutics. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestwich, G.D.; Healy, K.E. Why regenerative medicine needs an extracellular matrix. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, S.; Healy, K.E. Matrix-assisted cell transplantation for tissue vascularization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama, P.; Bonini, S.; Lambiase, A.; Golisano, O.; Paterna, P.; De Luca, M.; Pellegrini, G. Autologous fibrin-cultured limbal stem cells permanently restore the corneal surface of patients with total limbal stem cell deficiency. Transplantation 2001, 72, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joe, A.W.; Yeung, S.N. Concise review: Identifying limbal stem cells: Classical concepts and new challenges. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpovich, V.V.; Kulikov, A.N.; Churashov, S.V.; Chernysh, V.F.; Blinova, M.I.; Nashchekina, Y.A.; Alexandrova, O.I.; Khorolskaya, Y.I.; Machel, T.V.; Pisugina, G.A.; et al. Research of the properties of synthetic polymer matrices made for transplantation of cultured limbal stem cells to eliminate a limbal deficiency. Bull. Russ. Mil. Med. Acad. 2019, 21, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, X.W.; Hartman, L.; Tan, K.P.; Poh, R.; Myung, D.; Zheng, L.L.; Waters, D.; Noolandi, J.; Beuerman, R.W.; Frank, C.W.; et al. In vivo biocompatibility of two PEG/PAA interpenetrating polymer networks as corneal inlays following deep stromal pocket implantation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.J.; Ambrose, W.M.; Espinoza, F.A.; Mulreany, D.G.; Ng, S.; Takezawa, T.; Trexler, M.M.; Schein, O.D.; Chuck, R.S.; Elisseeff, J.H. Regeneration of corneal epithelium utilizing a collagen vitrigel membrane in rabbit models for corneal stromal wound and limbal stem cell deficiency. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e57–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortt, A.J.; Secker, G.A.; Notara, M.D.; Limb, G.A.; Khaw, P.T.; Tuft, S.J.; Daniels, J.T. Transplantation of ex vivo cultured limbal epithelial stem cells: A review of techniques and clinical results. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2007, 52, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, G.; Traverso, C.E.; Franzi, A.T.; Zingirian, M.; Cancedda, R.; De Luca, M. Long-term restoration of damaged corneal surfaces with autologous cultivated corneal epithelium. Lancet 1997, 349, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, R.J.; Li, L.M.; Chen, J.K. Reconstruction of damaged corneas by transplantation of autologous limbal epithelial cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kethiri, A.R.; Singh, V.K.; Damala, M.; Basu, S.; Rao, C.M.; Bokara, K.K.; Singh, V. Long term observation of ocular surface alkali burn in rabbit models: Quantitative analysis of corneal haze, vascularity and self-recovery. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 205, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Andreev, A.Y.; Rogovaya, O.S.; Subbot, A.M.; Domogatsky, S.P.; Avetisov, S.E.; Vorotelyak, E.A.; Osidak, E.O. Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency in a Rabbit Model. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010101
Yu Y, Andreev AY, Rogovaya OS, Subbot AM, Domogatsky SP, Avetisov SE, Vorotelyak EA, Osidak EO. Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency in a Rabbit Model. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yang, Andrey Yurevich Andreev, Olga Sergeevna Rogovaya, Anastasia Mikhailovna Subbot, Sergey Petrovich Domogatsky, Sergey Eduardovich Avetisov, Ekaterina Andreevna Vorotelyak, and Egor Olegovich Osidak. 2024. "Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency in a Rabbit Model" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010101
APA StyleYu, Y., Andreev, A. Y., Rogovaya, O. S., Subbot, A. M., Domogatsky, S. P., Avetisov, S. E., Vorotelyak, E. A., & Osidak, E. O. (2024). Matrix-Assisted Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency in a Rabbit Model. Biomedicines, 12(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010101





