Role of HNFA1 Gene Variants in Pancreatic Beta Cells Function and Glycaemic Control in Young Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measurements and Protocol
2.3. DNA Extraction, Genotyping, and SNPs Selection
2.4. Data Analysis
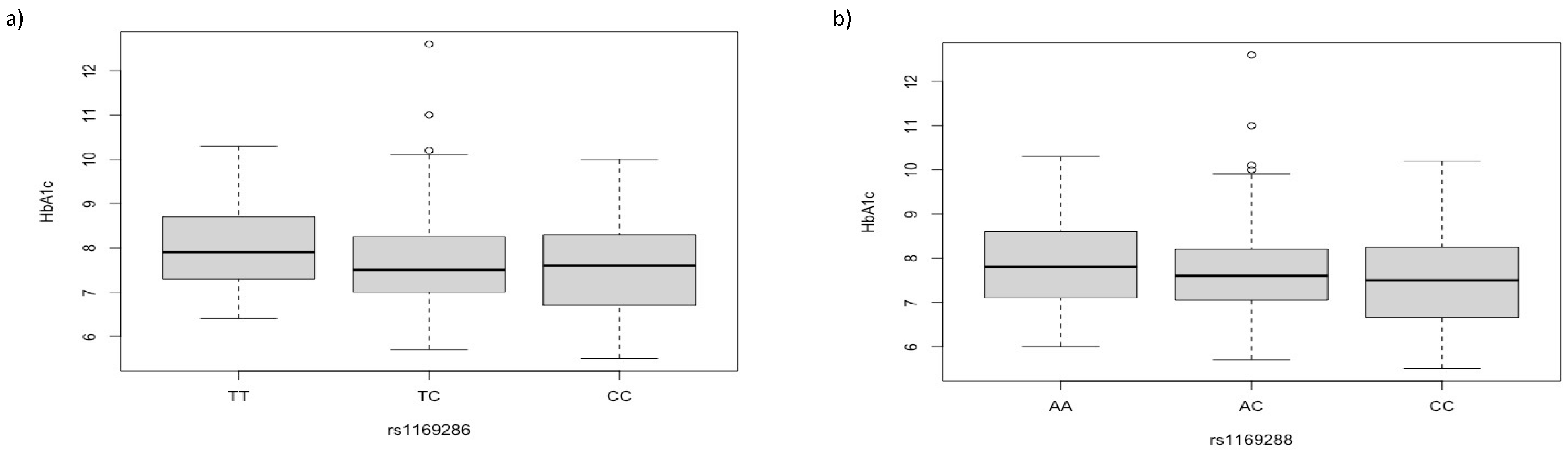
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, R.V.; Bernardo, T.; Martins, S.; Sequeira, A. Monogenic diabetes: A new pathogenic variant of HNF1A gene. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e231837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staník, J.; Dusatkova, P.; Cinek, O.; Valentínová, L.; Hučková, M.; Škopková, M.; Dusatkova, L.; Stanikova, D.; Pura, M.; Klimeš, I.; et al. De novo mutations of GCK, HNF1A and HNF4A may be more frequent in MODY than previously assumed. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, S.; Frayling, T.M.; Groves, C.J.; Levy, J.C.; Hitman, G.A.; Sampson, M.; Walker, M.; Menzel, S.; Hattersley, A.T.; Cardon, L.R.; et al. Evidence from a large, U.K. family collection that genes influencing age of onset of type 2 diabetes map to chromosome 12p and to the MODY3/NIDDM2 locus on 12q24. Diabetes 2004, 53, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weedon, M.N.; Owen, K.R.; Shields, B.; Hitman, G.; Walker, M.; McCarthy, M.I.; Hattersley, A.T.; Frayling, T.M. A large-scale sssociation analysis of common variation of the HNF1alpha gene with type 2 diabetes in the U.K. Caucasian population. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beysel, S.; Pinarli, F.A.; Eyerci, N.; Kizilgul, M.; Hepsen, S.; Alhan, A.; Kan, S.; Caliskan, M.; Bozkurt, E.; Cakal, E. HNF1A gene p.I27L is associated with co-existing preeclampsia in gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosik, J.; Szostak, B.; Machaj, F.; Pawlik, A. The role of genetics and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2020, 84, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjesing, A.P.; Rui, G.; Lauenborg, J.; Have, C.T.; Hollensted, M.; Andersson, E.; Grarup, N.; Sun, J.; Quan, S.; Brandslund, I.; et al. High prevalence of diabetes-predisposing variants in MODY genes among Danish women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T. Clinical implications of a molecular genetic classification of monogenic beta-cell diabetes. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 4, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.I.; Frantz, J.D.; Oh, B.C.; Hansen, L.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Shoelson, S.E. Diabetes mutations delineate an atypical POU domain in HNF-1alpha. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Jiang, B.G.; Sun, L.L. HNF1A: From monogenic diabetes to type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 829565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.; Brown, J.; Ntoumanis, N.; Leslie, G. Barriers and facilitators to physical activity participation in adults living with type 1 diabetes: A scoping review protocol. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakay, M.; Pandey, R.; Hakonarson, H. Genes involved in type 1 diabetes: An update. Genes 2013, 4, 499–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani Asl, S.; Azimnasab-Sorkhabi, P.; Abolfathi, A.A.; Aghdam, Y.H. Identification of nucleotide polymorphism within the NeuroD1 candidate gene and its association with type 1 diabetes susceptibility in Iranian people by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Maddhuri, S.; Nallari, P.; Ananthapur, V.; Kalyani, S.; Krishna, M.; Cherkuri, N.; Patibandala, S. Association of ABCC8 and KCNJ11 gene variants with type 1 diabetes in south Indians. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2021, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasetti, A.; Castorani, V.; Comegna, L.; Franchini, S.; Prezioso, G.; Provenzano, M.; Di Giulio, C.; Iannucci, D.; Matonti, L.; Tumini, S.; et al. Role of the KCNJ gene variants in the clinical outcome of type 1 diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.L.C.M.; Hougaard, P.; Pörksen, S.; Nielsen, L.B.; Fredheim, S.; Svensson, J.; Thomsen, J.; Vikre-Jørgensen, J.; Hertel, T.; Petersen, J.S.; et al. Partial remission definition: Validation based on the insulin dose-adjusted HbA1c (IDAA1c) in 129 Danish children with new-onset type 1 diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 15, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, B.; Cheng, P.; Beck, R.W.; Kollman, C.; Ruedy, K.J.; Weinzimer, S.A.; Slover, R.; Bremer, A.A.; Fuqua, J.; Tamborlane, W.; et al. CGM-measured glucose values have a strong correlation with C-peptide, HbA1c and IDAAC, but do poorly in predicting C-peptide levels in the two years following onset of diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagl, K.; Hermann, J.M.; Plamper, M.; Schröder, C.; Dost, A.; Kordonouri, O.; Rami-Merhar, B.; Holl, R.W. Factors contributing to partial remission in type 1 diabetes: Analysis based on the insulin dose-adjusted HbA1c in 3657 children and adolescents from Germany and Austria. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.M.; Whitehouse, R.H. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stage of puberty. Arch. Dis. Child. 1976, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight- for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; p. 312.
- de Bock, M.; Codner, E.; Craig, M.E.; Huynh, T.; Maahs, D.M.; Mahmud, F.H.; Marcovecchio, L.; DiMeglio, L.A. ISPAD clinical practice consensus guidelines 2022: Glycemic targets and glucose monitoring for children, adolescents and young people with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, H.B.; Hougaard, P.; Swift, P.; Hansen, L.; Holl, R.W.; Hoey, H.; Bjoerndalen, H.; de Beaufort, C.; Chiarelli, F.; Danne, T.; et al. New definition for the partial remission period in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Jing, W.; Samuels, D.C.; Sheng, Q.; Shyr, Y.; Guo, Y. Strategies for processing and quality control of Illumina genotyping arrays. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, K.C.; Chuang, L.-M.; Wang, M. Transcription factor 1 and beta-cell function in glucose-tolerant subjects. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattersley, A.; Bruining, J.; Shield, J.; Njolstad, P.; Donaghue, K.C. The diagnosis and management of monogenic diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Diabetes 2009, 10, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, A.M.; Shields, B.M.; Shepherd, M.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T.; Pearson, E.R. Increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in monogenic diabetes as a result of mutations in the HNF1A Gene. Diabetes Med. 2010, 27, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malecki, M.; Skupien, J.; Gorczynska-Kosiorz, S.; Klupa, T.; Nazim, J.; Moczulski, D.K.; Sieradzki, J. Renal malformations may be linked to mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha (MODY3) gene. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2774–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, L.W.; Brown, J.E.; Gloyn, A.L. Species-Specific Differences in the Expression of the HNF1A, HNF1B and HNF4A Genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, D.Q.; Bussen, M.; Sehayek, E.; Ananthanarayanan, M.; Shneider, B.L.; Suchy, F.J.; Shefer, S.; Bollileni, J.S.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Breslow, J.L.; et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha is an essential regulator of bile acid and plasma cholesterol metabolism. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufibach, L.E.; Duncan, S.A.; Battle, M.; Deeb, S.S. Transcriptional regulation of the human hepatic lipase (LIPC) gene promoter. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Parrizas, M.; Maestro, M.A.; Ferrer, J. A transcription factor regulatory circuit in differentiated pancreatic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14481–14486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakauskas, S.M.; Kourany, W.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, D.; Stevens, R.D.; Koves, T.R.; Hohmeier, H.E.; Muoio, D.M.; Newgard, C.B.; Le, T.H. Increased Insulin Sensitivity in Mice Lacking Collectrin, a Downstream Target of HNF-1alpha. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Antinozzi, P.A.; Hagenfeldt, K.A.; Maechler, P.; Wollheim, C.B. Molecular targets of a human HNF1 alpha mutation responsible for pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4257–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magaña-Cerino, J.M.; Luna-Arias, J.P.; Labra-Barrios, M.L.; Avendaño-Borromeo, B.; Boldo-León, X.M.; Martínez-López, M.C. Identification and functional analysis of c.422_423InsT, a novel mutation of the HNF1A gene in a patient with diabetes. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2016, 5, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penaforte-Saboia, J.G.; Barra Couri, C.E.; Oliveira Fernandes, V.; Dias Rangel Montenegro, A.P.; De Araújo Batista, L.A.; Zajdenverg, L. Lower Insulin-Dose Adjusted A1c (IDAA1c) is associated with less complications in individuals with type 1 diabetes treated with hematopoetic stem-cell transplantation and conventional therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, L.A.; Aukrust, I.; Flannick, J.; Molnes, J.; Burtt, N.; Molven, A.; Groop, L.; Altshuler, D.; Johansson, S.; Bjørkhaug, L.; et al. Functional investigations of HNF1A identify rare variants as risk factors for type 2 diabetes in the general population. Diabetes 2017, 66, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HNF1A SNPs | Type | Nucleotide Change (Aminoacid Change) | Chr:Position | Reference Allele | Alternative Allele | MAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1169288 | Missense Variant | c.79A > C (p.Ile27Leu) | 12:121416650 | A | C | 36.0% |
| rs1169286 | Intron | c.326 + 2159T > C | 12:121419056 | T | C | 45.0% |
| rs7979478 | Intron | c.326 + 3366A > C | 12:121420263 | A | G | 56.5% |
| rs2259816 | Synonymous Variant | c.1620G > A (p.Val540=) | 12:121435587 | G | T | 41.0% |
| HC (n = 140) | T1D (n = 277) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, (%, females) | 57% | 46% | 0.044 |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 12.5 ± 3.5 | 13.2 ± 3.2 | 0.055 |
| Standardized BMI (mean ± SD) | −0.39 ± 1.1 | 0.16 ± 1.1 | <0.0001 |
| Disease duration (years, mean ± SD) | - | 5.4 ± 3.6 | |
| HbA1c (%, mean ± SD) | - | 7.8 ± 1.0 | |
| IDAA1c (U/kg/die, mean ± SD) | - | 10.8 ± 1.6 |
| Clinical Parameters | rs1169286 | p-Value | rs1169288 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDAA1c | TT | TC | CC | 0.0097 | AA | AC | CC | 0.044 |
| ≤9 (n = 39) | 15.0% | 54.0% | 31.0% | 31.0% | 49.0% | 20.0% | ||
| >9 (n = 238) | 33.0% | 4.0% | 1.0% | 43.0% | 44.0% | 13.0% | ||
| HbA1c | 0.0052 | 0.07 | ||||||
| <7 (n = 64) | 19.0% | 51.0% | 30.0% | 37.5% | 40.5% | 22.0% | ||
| ≥7 (n = 213) | 34.0% | 48.0% | 18.0% | 43.0% | 45.0% | 12.0% | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robino, A.; Tornese, G.; Tinti, D.; Dovc, K.; Castorani, V.; Conti, A.; Franceschi, R.; Rabbone, I.; Bonfanti, R.; Battelino, T.; et al. Role of HNFA1 Gene Variants in Pancreatic Beta Cells Function and Glycaemic Control in Young Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071951
Robino A, Tornese G, Tinti D, Dovc K, Castorani V, Conti A, Franceschi R, Rabbone I, Bonfanti R, Battelino T, et al. Role of HNFA1 Gene Variants in Pancreatic Beta Cells Function and Glycaemic Control in Young Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071951
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobino, Antonietta, Gianluca Tornese, Davide Tinti, Klemen Dovc, Valeria Castorani, Andrea Conti, Roberto Franceschi, Ivana Rabbone, Riccardo Bonfanti, Tadej Battelino, and et al. 2023. "Role of HNFA1 Gene Variants in Pancreatic Beta Cells Function and Glycaemic Control in Young Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071951
APA StyleRobino, A., Tornese, G., Tinti, D., Dovc, K., Castorani, V., Conti, A., Franceschi, R., Rabbone, I., Bonfanti, R., Battelino, T., & Catamo, E. (2023). Role of HNFA1 Gene Variants in Pancreatic Beta Cells Function and Glycaemic Control in Young Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1951. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071951








