A CBCT Study of Labial Alveolar Bone Thickness in the Maxillary Anterior Region in a Teaching Hospital Population in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
- a.
- Saudi patients, age ranged between 18 to 65 years.
- b.
- Non-smokers.
- c.
- Absence of any systemic disease.
- d.
- Periodontal health—absence of any signs of periodontal disease.
- e.
- Presence of normal occlusion.
- f.
- The presence of all six maxillary anterior teeth (including canine).
- a.
- Poor image quality of CBCT scan.
- b.
- Images from patients with systemic or pathological dentoalveolar conditions (e.g., cyst) that might cause abnormal bone remodeling.
- c.
- Any history or current periapical lesion.
- d.
- Presence of inflammatory processes at the apical level.
- e.
- Patient with a previous history of road traffic accidents (RTA).
- f.
- Cancer subjects.
- g.
- History of radiation or chemotherapy.
- h.
- Osteoporosis conditions.
- i.
- Tooth malalignment.
2.2. Radiographic Image Analysis: Detail of CBCT
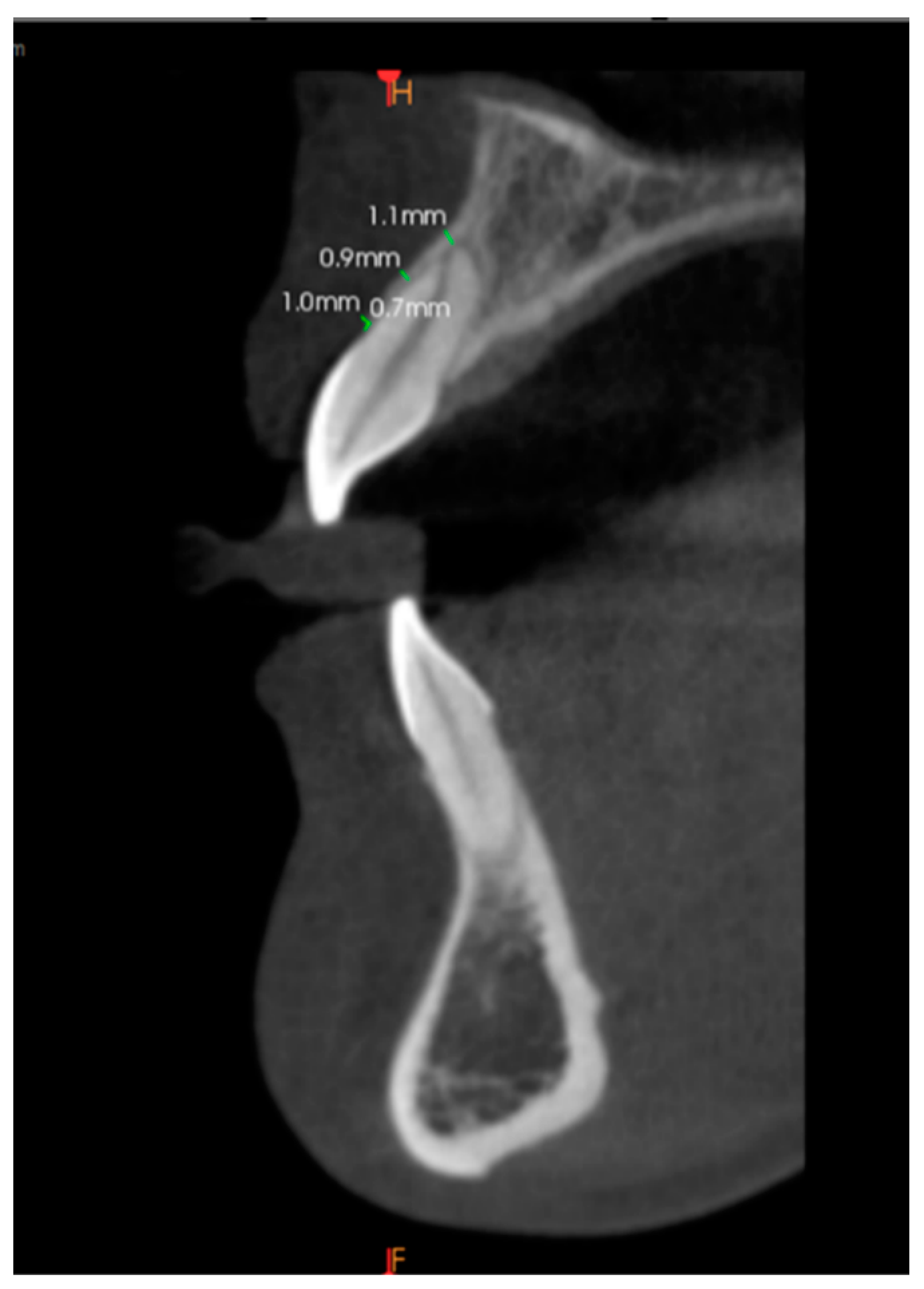
2.3. Scan Measurements
2.4. Data Collection
Alveolar Bone Thickness Measurement
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Alveolar Bone Thickness
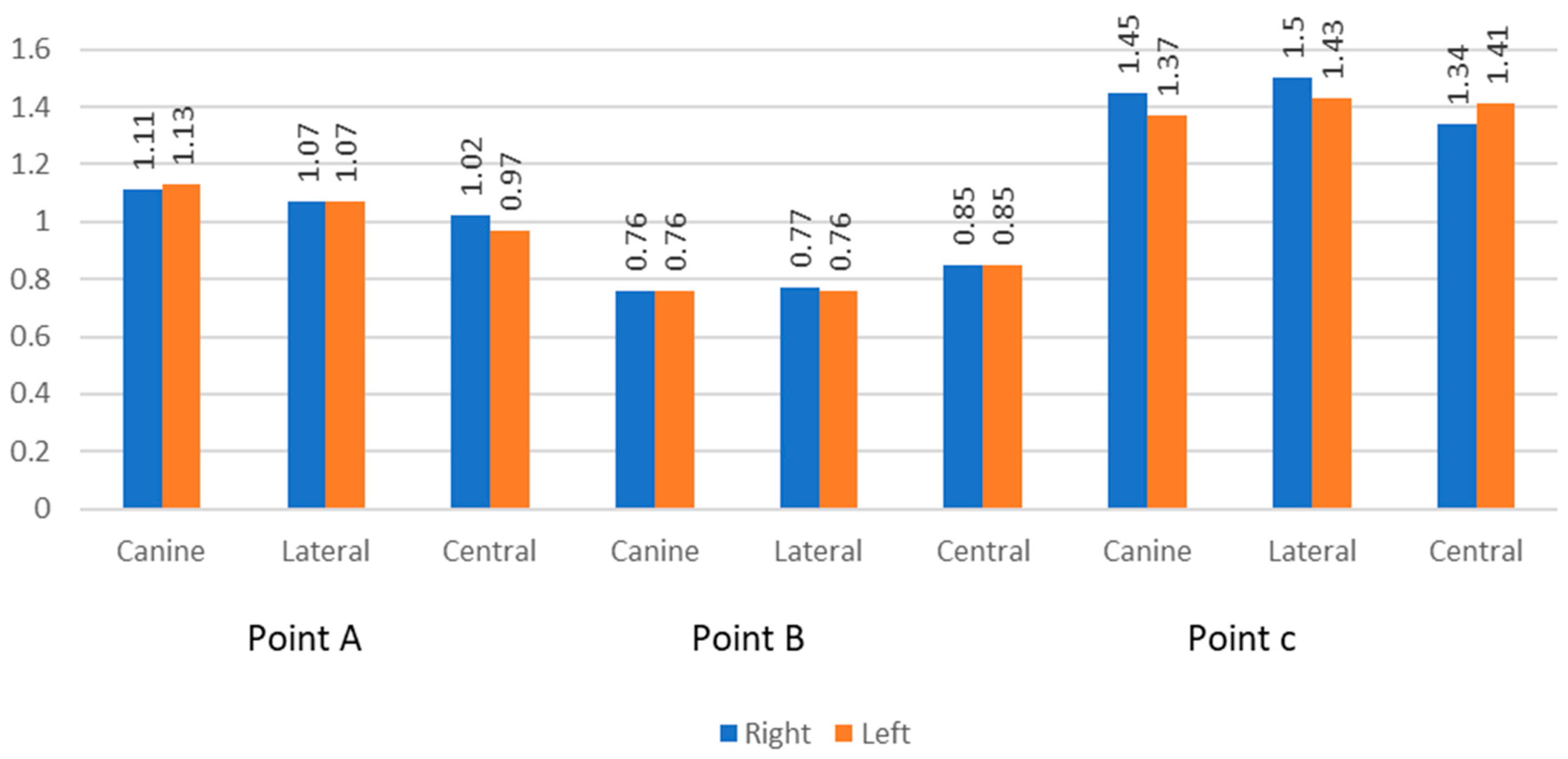
3.3. Comparison of Bone Thickness at Different Points
3.4. Comparison of Bone Thickness—Right and Left Sides
3.5. Comparison of Bone Thickness by Gender
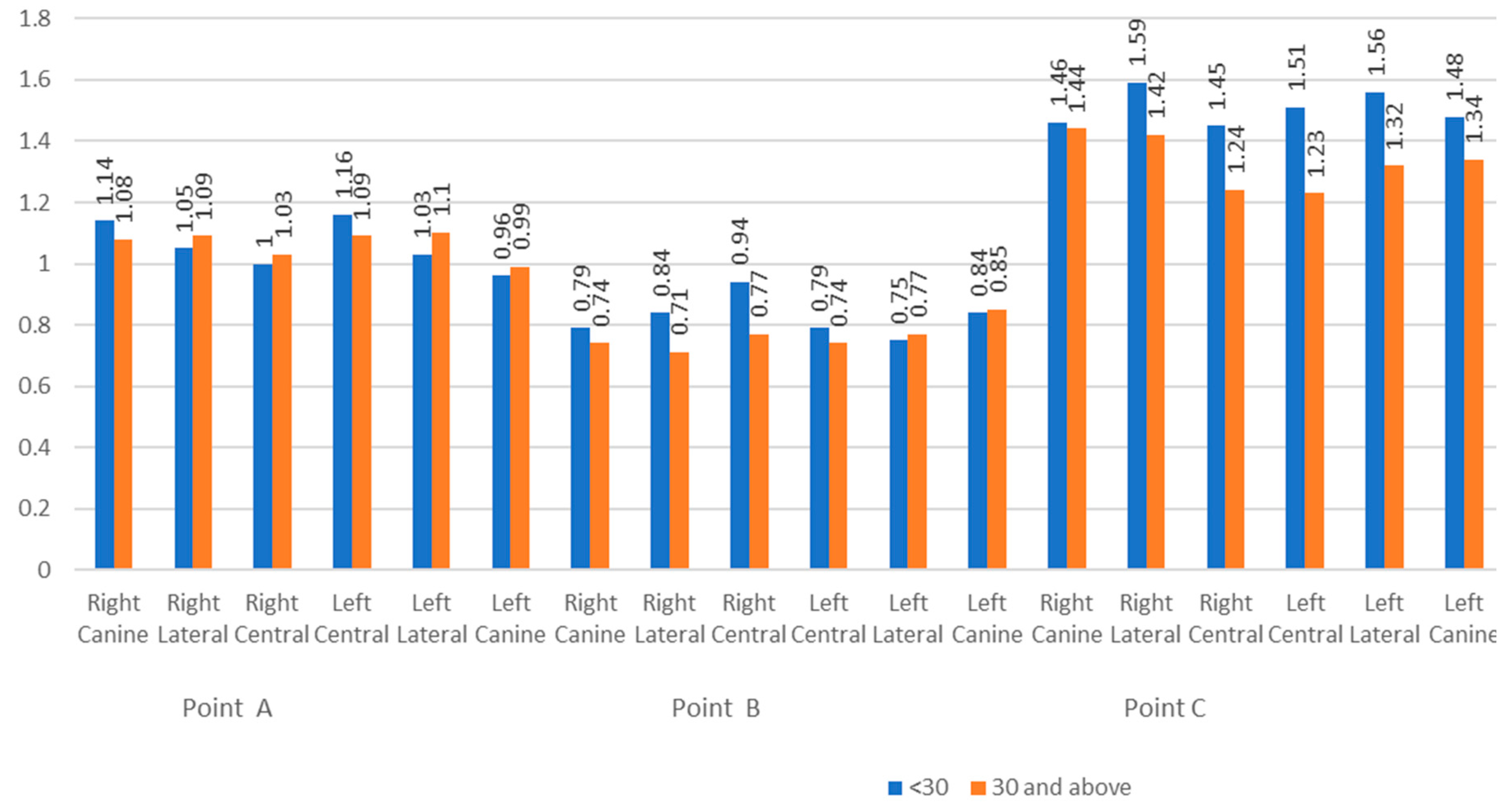
3.6. Comparison of Bone Thickness among Different Age Groups
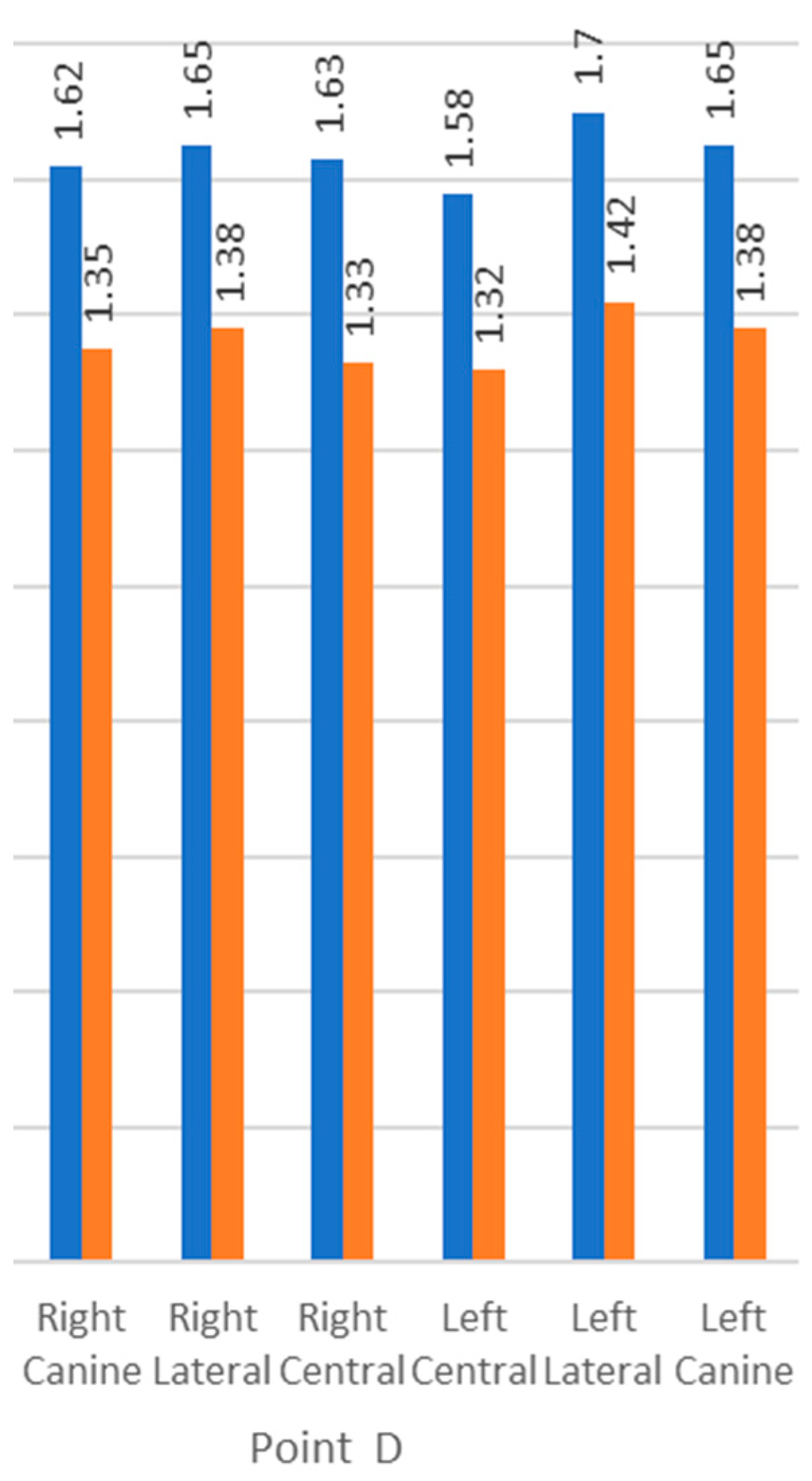
3.7. Alveolar Bone Height
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouda, A.A. The impact of the alveolar bone sites on early implant failure: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 46, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Skrypczak, A.; Weltman, R. Anterior maxilla alveolar ridge dimension and morphology measurement by cone beam computerized tomography (CBCT) for immediate implant treatment planning. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rim, K.; Ameni, C.; Garrach, B.E.; Chaouch, M.H.; Touzi, S. Anatomical dimension of the anterior maxillary alveolar process: A cone beam computed tomography study. Int. J. Sci. Res. Dent. Med. Sci. 2021, 3, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Shen, J.W.; Yu, M.F.; Chen, X.Y.; Jiang, Q.H.; He, F.M. Analysis of facial bone wall dimensions and sagittal root position in the maxillary esthetic zone: A retrospective study using cone beam computed tomography. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botermans, A.; Lidén, A.; de Carvalho Machado, V.; Chrcanovic, B.R. Immediate implant placement in the maxillary aesthetic zone: A cone beam computed tomography study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, E.A.; Cao, P.T. Smile analysis and esthetic design: “In the zone”. Inside Dent. 2009, 5, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tsigarida, A.; Toscano, J.; de Brito Bezerra, B.; Geminiani, A.; Barmak, A.B.; Caton, J.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Chochlidakis, K. Buccal bone thickness of maxillary anterior teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 1326–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Becker, K.; Kassira, H.C.; Becker, J.; Sader, R.; Schwarz, F. The dimensions of the facial alveolar bone at tooth sites with local pathologies: A retrospective cone-beam CT analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, S.V.; Perussolo, J.; Misawa, M.Y.; Zadeh, H.H.; Araújo, M.G. The Basal Bone and Alveolar Process in the Maxillary Anterior Region in Humans: A Cone Beam Computed Tomographic Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2020, 40, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Sanchis, J.; Soto-Peñaloza, D.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Peñarrocha-Diago, M.; Viña-Almunia, J. Facial alveolar bone thickness and modifying factors of anterior maxillary teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cone-beam computed tomography studies. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahdi, R.A.; Alasqah, M. Assessment of buccal bone thickness in the maxillary and mandibular canine using cone-beam computed tomography. Int. J. Med. Dent. 2021, 25, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Linjawi, A. Predictive factors affecting the maxillary alveolar bone thickness: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2020, 12, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqhtani, N.R.; Alenazi, A.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Gufran, K.; Robaian, A.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Aldossary, S.F.; Aldossry, M.F. Labial alveolar bone thickness and its correlation with buccolingual maxillary incisors angulation: A CBCT based study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Othman, B.; Khalifa, H.; Afandi, A.; Alshehri, N.A.; Sait, A.; Abdoun, S.; Zahid, T. Measuring the Facial Plate of Bone in the Upper Anterior Teeth Utilizing Cone Beam Computed Tomography at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2022, 14, e29453.1–e29453.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheerah, H.; Othman, B.; Jaafar, A.; Alsharif, A. Alveolar bone plate measurements of maxillary anterior teeth: A retrospective Cone Beam Computed Tomography study, AlMadianh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaffar, Z.J.; Shafshak, S.M.; Shokry, S. Assessment of labial and palatal alveolar bone thickness and height in maxillary anterior teeth in saudi population using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT). Int. J. Contemp. Dent. 2016, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alkazman, F.H.; Abouelkheir, H.M.; Almashat, H.; Alfahadi, H.R. Assessment of the distribution of facial root fenestration in maxillary anterior teeth in Saudi sub-population using cone-beam computed tomography: Retrospective study. Saudi Endod. J. 2021, 11, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Size Calculations—World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://cdn.who.int>sample_size_calculator_survey (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- AlTarawneh, S.; AlHadidi, A.; Hamdan, A.A.; Shaqman, M.; Habib, E. Assessment of bone dimensions in the anterior maxilla: A cone beam computed tomography study. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowzari, H.; Molayem, S.; Chiu, C.H.; Rich, S.K. Cone beam computed tomographic measurement of maxillary central incisors to determine prevalence of facial alveolar bone width ≥2 mm. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, H.-S.; Kim, J.-W.; Hwang, J.-H.; Ahn, K.-M. Frequency of bone graft in implant surgery. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 38, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Ge, Z.; Zhao, H.; Miao, L.; Pan, Y. The dimension and morphology of alveolar bone at maxillary anterior teeth in periodontitis: A retrospective analysis—Using CBCT. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlKudmani, H.; Jasser, R.A.; Andreana, S. Is bone graft or guided bone regeneration needed when placing immediate dental implants? A systematic review. Implant. Dent. 2017, 26, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircan, S.; Demircan, E. Dental cone beam computed tomography analyses of the anterior maxillary bone thickness for immediate implant placement. Implant. Dent. 2015, 24, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahás-Scocate, A.C.; de Siqueira Brandão, A.; Patel, M.P.; Lipiec Ximenez, M.E.; Chilvarquer, I.; Do Valle-Corotti, K.M. Bone tissue amount related to upper incisors inclination. Angle Orthod. 2014, 84, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braut, V.; Bornstein, M.M.; Belser, U.; Buser, D. Thickness of the anterior maxillary facial bone wall—A retrospective radiographic study using cone beam computed tomography. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2011, 31, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nahm, K.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Moon, S.C.; Choi, Y.S.; Kook, Y.A.; Kim, S.H.; Huang, J.C. Alveolar bone loss around incisors in Class I bidentoalveolar protrusion patients: A retrospective three-dimensional cone beam CT study. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2012, 41, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, L.; Kumar, G.; Keswani, T.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Chandar, S.S.; Bhaskara Rao, K.V. Protease inhibitors from marine actinobacteria as a potential source for antimalarial compound. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.L.; Liu, F.; Sun, H.J.; Lv, P.; Cao, Y.M.; Yu, M.; Yue, Y. Alveolar bone thickness around maxillary central incisors of different inclination assessed with cone-beam computed tomography. Korean J. Orthod. 2015, 45, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, R.; Flores, T.; Navarro, P.; Salamanca, C.; Beltrán, V.; Borie, E. Assessment of buccal bone thickness of aesthetic maxillary region: A cone-beam computed tomography study. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2015, 45, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahamnd, A.; Sarlati, F.; Eslami, S.; Ghassemian, M.; Youssefi, N.; Esfahani, B.J. Evaluation of impacting factors on facial bone thickness in the anterior maxillary region. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2017, 28, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, G.; Behnia, H.; Motamedian, S.R.; Shahab, S.; Gholamin, P.; Khosraviani, K.; Nowzari, H.; Khojasteh, A. Thickness of labial alveolar bone overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular anterior teeth. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2014, 25, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.A.; Khazaal Al-Jaboori, A.S. Thickness of the Buccal and Alveolar Bones Overlying Central Incisors: A Radiographic Iraqi Study. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 7226998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üner, D.D.; Izol, B.S.; Görüş, Z. Correlation between buccal and alveolar bone widths at the central incisors according to cone beam computed tomography. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.C.; Kang, D.U.; Baek, H.; Hong, J.Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Herr, Y.; Shin, S.I. Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of the alveolar ridge profile and virtual implant placement for the anterior maxilla. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2019, 49, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemian, M.; Nowzari, H.; Lajolo, C.; Verdugo, F.; Pirronti, T.; D’Addona, A. The thickness of facial alveolar bone overlying healthy maxillary anterior teeth. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohiomoba, H.; Sonis, A.; Yansane, A.; Friedland, B. Quantitative evaluation of maxillary alveolar cortical bone thickness and density using computed tomography imaging. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januário, A.L.; Duarte, W.R.; Barriviera, M.; Mesti, J.C.; Araújo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Dimension of the facial bone wall in the anterior maxilla: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph Gakonyo, B.D.; Implantology, P.; Mohamedali, A.J.; Mungure, E.K. Cone beam computed tomography assessment of the buccal bone thickness in anterior maxillary teeth: Relevance to immediate implant placement. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.G.; Takei, H.H.; Klokkevold, P.R.; Carranza, F.A. Clinical Periodontology. In Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 1776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, W.; Shen, M.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Chen, N. Cone beam computed tomographic analyses of alveolar bone anatomy at the maxillary anterior region in Chinese adults. J. Biomed. Res. 2014, 28, 498–500. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch, E. The Declaration of Helsinki Revised by the World Medical Organisation, Edinburgh 2000. Vic. Univ. Wellingt. Law Rev. 2001, 32, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Canine (n%) | Lateral Incisor (n%) | Central Incisor (n%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <1.5 | 100 | 87 | 100 |
| 1.5 TO 2 | Nil | 13 | Nil |
| >2 | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| Point | Tooth | Right | Left | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD ± mm | Mean | SD ± mm | |||
| A | Canine | 1.11 | 0.30 | 1.13 | 0.34 | 0.556 |
| Lateral | 1.07 | 0.27 | 1.07 | 0.31 | >0.99 | |
| Central | 1.02 | 0.20 | 0.97 | 0.20 | 0.035 | |
| B | Canine | 0.76 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.27 | 0.944 |
| Lateral | 0.77 | 0.41 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.823 | |
| Central | 0.85 | 0.28 | 0.85 | 0.26 | 0.896 | |
| C | Canine | 1.45 | 0.47 | 1.37 | 0.48 | 0.111 |
| Lateral | 1.50 | 0.73 | 1.43 | 0.73 | 0.194 | |
| Central | 1.34 | 0.49 | 1.41 | 0.52 | 0.254 | |
| Sex | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | ||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||
| Point | A | Right Canine | 1.10 | 0.29 | 1.12 | 0.31 | 0.853 |
| Right Lateral | 1.08 | 0.26 | 1.06 | 0.29 | 0.76 | ||
| Right Central | 1.03 | 0.20 | 1.01 | 0.21 | 0.68 | ||
| Left Central | 0.22 | 0.97 | 0.18 | 0.944 | |||
| Left Lateral | 0.28 | 1.02 | 0.35 | 0.285 | |||
| Left Canine | 0.30 | 1.11 | 0.38 | 0.713 | |||
| B | Right Canine | 0.87 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 0.20 | 0.003 | |
| Right Lateral | 0.83 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 0.285 | ||
| Right Central | 0.94 | 0.31 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.024 | ||
| Left Central | 0.89 | 0.29 | 0.80 | 0.22 | 0.217 | ||
| Left Lateral | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.73 | 0.32 | 0.559 | ||
| Left Canine | 0.85 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 0.017 | ||
| C | Right Canine | 1.57 | 0.52 | 1.33 | 0.38 | 0.071 | |
| Right Lateral | 1.71 | 0.87 | 1.30 | 0.50 | 0.048 | ||
| Right Central | 1.44 | 0.58 | 1.24 | 0.37 | 0.138 | ||
| Left Central | 1.46 | 0.53 | 1.36 | 0.51 | 0.481 | ||
| Left Lateral | 1.57 | 0.83 | 1.30 | 0.61 | 0.199 | ||
| Left Canine | 1.51 | 0.51 | 1.22 | 0.41 | 0.036 | ||
| D | Right Canine | 1.62 | 0.40 | 1.35 | 0.41 | 0.021 | |
| Right Lateral | 1.65 | 0.51 | 1.38 | 0.39 | 0.043 | ||
| Right Central | 1.63 | 0.42 | 1.33 | 0.38 | 0.013 | ||
| Left Central | 1.58 | 0.43 | 1.32 | 0.33 | 0.019. | ||
| Left Lateral | 1.70 | 0.44 | 1.42 | 0.37 | 0.017 | ||
| Left Canine | 1.65 | 0.50 | 1.38 | 0.39 | 0.04 | ||
| Point | Tooth | Right | Left | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD ± mm | Mean | SD ± mm | |||
| D | Canine | 1.48 | 0.42 | 1.51 | 0.46 | 0.453 |
| Lateral | 1.51 | 0.47 | 1.56 | 0.43 | 0.171 | |
| Central | 1.48 | 0.43 | 1.45 | 0.40 | 0.443 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljabr, A.A.; Almas, K.; Aljofi, F.E.; Aljabr, A.A.; Alzaben, B.; Alqanas, S. A CBCT Study of Labial Alveolar Bone Thickness in the Maxillary Anterior Region in a Teaching Hospital Population in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061571
Aljabr AA, Almas K, Aljofi FE, Aljabr AA, Alzaben B, Alqanas S. A CBCT Study of Labial Alveolar Bone Thickness in the Maxillary Anterior Region in a Teaching Hospital Population in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061571
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljabr, Abdulmajeed A., Khalid Almas, Faisal E. Aljofi, Abdullah A. Aljabr, Bader Alzaben, and Sarah Alqanas. 2023. "A CBCT Study of Labial Alveolar Bone Thickness in the Maxillary Anterior Region in a Teaching Hospital Population in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061571
APA StyleAljabr, A. A., Almas, K., Aljofi, F. E., Aljabr, A. A., Alzaben, B., & Alqanas, S. (2023). A CBCT Study of Labial Alveolar Bone Thickness in the Maxillary Anterior Region in a Teaching Hospital Population in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1571. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061571






