Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox Family: Non-Coding RNA and Epigenetic Regulation in Gliomas
Abstract
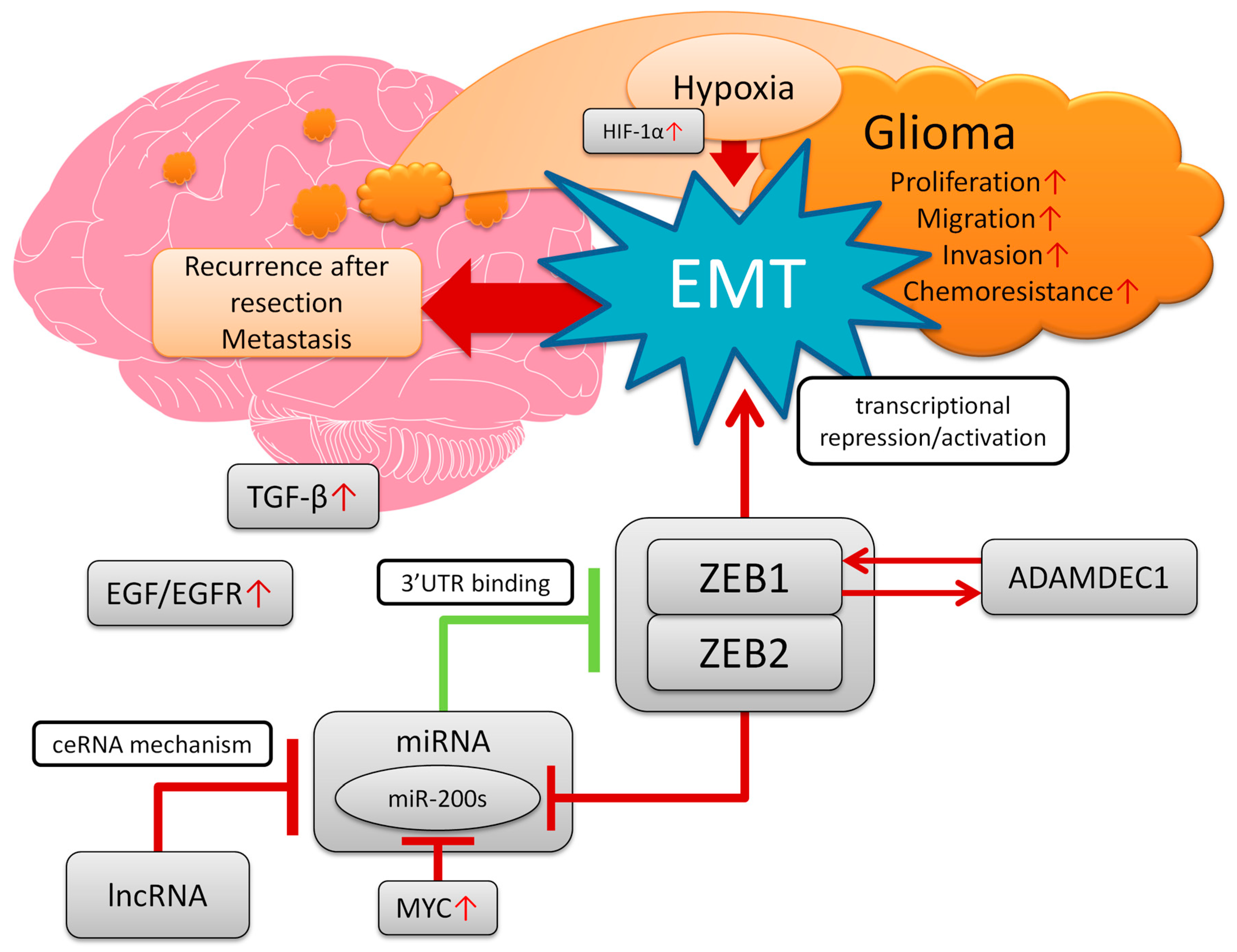
1. Introduction
2. MiRNA Targeting ZEBs
2.1. MiR-200 Family
2.2. Cancer Stem Cell
2.3. Predicting Prognosis
2.4. MiRNAs as Therapeutic Targets
3. LncRNA Affecting ZEBs
3.1. Hypoxia-Induced EMT
3.2. ZEB1-AS1
3.3. TGF-β
3.4. LncRNA Contributes to EMT-Dependetnt Chemoresistance
3.5. LncRNA Controlled by ZEB
4. Epigenetic Regulation of ZEBs
5. Discussion and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Stetson, L.; Virk, S.M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Epidemiology of gliomas. In Current Understanding and Treatment of Gliomas; Raizer, J., Parsa, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 163, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cahill, D.; Turcan, S. Origin of Gliomas. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witthayanuwat, S.; Pesee, M.; Supaadirek, C.; Supakalin, N.; Thamronganantasakul, K.; Krusun, S. Survival analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batash, R.; Asna, N.; Schaffer, P.; Francis, N.; Schaffer, M. Glioblastoma Multiforme, Diagnosis and Treatment; Recent Literature Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deorah, S.; Lynch, C.F.; Sibenaller, Z.A.; Ryken, T.C. Trends in brain cancer incidence and survival in the United States: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, 1973 to 2001. Neurosurg. Focus 2006, 20, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardak, Z.; Choe, K.S. Molecular pathways and potential therapeutic targets in glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2013, 13, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldape, K.; Zadeh, G.; Mansouri, S.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A. Glioblastoma: Pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Their, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumor progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, U.D.; Joseph, J.V.; Kruyt, F.A.E. EMT- and MET-related processes in nonepithelial tumors: Importance for disease progression, prognosis, and therapeutic opportunities. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, U.D.; Nikkhah, G.; Maciaczyk, J. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2013, 331, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, S.; Vandamme, N.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; Berx, G. EMT transcription factors in cancer development re-evaluated: Beyond EMT and MET. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, L.A.; Woolard, K.; Son, M.J.; Li, A.; Lee, J.; Ene, C.; Mantey, S.A.; Maric, D.; Song, H.; Belova, G.; et al. Effect of brain- and tumor-derived connective tissue growth factor on glioma invasion. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1162–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Song, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, H.; Long, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Fang, L.; Wu, A.; Luo, W.; et al. ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis in glioma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depner, C.; Zum Buttel, H.; BögÜrcü, N.; Cuesta, A.M.; Aburto, M.R.; Seidel, S.; Finkelmeier, F.; Foss, F.; Hofmann, J.; Kaulich, K.; et al. EphrinB2 repression through ZEB2 mediates tumour invasion and anti-angiogenic resistance. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Lei, Y.; Wang, H.; Dang, Y.; Fang, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. Repression of the expression of TET2 by ZEB1 contributes to invasion and growth in glioma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, B.; Fu, C.; Dang, Y.; Fang, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, L. Repression of the expression of PPP3CC by ZEB1 confers activation of NF-κB and contributes to invasion and growth in glioma cells. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 48, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaishi, M.; Fujii, Y.; Sugiura, Y.; Takano, I.; Takigawa, T.; Yokoo, H.; Suzuki, K. Increased Twist and ZEB2 expression in a cutaneous metastasis of high-grade glioma. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, S.; Schuhwerk, H.; Brabletz, T.; Stemmler, M.P. Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Moncada, F.; Castellón, E.A.; Contreras, H.R. The Transcription Factors Zeb1 and Snail Induce Cell Malignancy and Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype in Prostate Cells, Increasing Androgen Synthesis Capacity and Therapy Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1393, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wang, M.; Guo, W.; Huang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Du, H.; Song, L.; Peng, X. Double-negative feedback loop between ZEB2 and miR-145 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties in prostate cancer cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Shen, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, T. ZEB1 stimulates breast cancer growth by up-regulating hTERT expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, X.; Qin, X.; Zhao, Y. TCF4 promotes colorectal cancer drug resistance and stemness via regulating ZEB1/ZEB2 expression. Protoplasma 2020, 257, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H. Post-Translational Modification of ZEB Family Members in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, K.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, H. MicroRNA-629 promotes the tumorigenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting FOXO1 and activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancer Biomarkers 2020, 29, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tong, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, G.; Shen, E.; Huang, Y. MiR-25-3p targets PTEN to regulate the migration, invasion, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wu, L.; Luo, S.; Qin, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y. MicroRNA-1284 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Shi, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, M. MiR-125 inhibited cervical cancer progression by regulating VEGF and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. MicroRNA-139-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting ELTD1 and regulating cell cycle in glioblastoma multiforme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 467, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, Y. MiR-595 targeting regulation of SOX7 expression promoted cell proliferation of human glioblastoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Shin, C.H.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, H.H. MicroRNA-296-5p promotes invasiveness through downregulation of nerve growth factor receptor and caspase-8. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Liao, Y.; Shen, C. miRNA-429 Inhibits Astrocytoma Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting BMI1. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xiu, X.; Wang, J. MiR-590-3p suppresses cancer cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma multiforme by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 468, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Xu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, N. MicroRNA-940 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells via targeting ZEB2. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 7351–7363. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Kong, K.K.; Xu, X.K.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, F.Y.; Peng, X.F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Li, J.L.; et al. Downregulation of miR-205 is associated with glioblastoma cell migration, invasion, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, by targeting ZEB1 via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.X.; Ding, B.J.; Li, H.Z.; Wang, L.; Xia, F.; Du, F.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, X.D.; Jia, J.F.; et al. Identification of microRNA-205 as a potential prognostic indicator for human glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, P.; Su, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells promotes tissue factor expression via the miR200a/ZEB1 axis. Brain Res. 2022, 1778, 147782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galardi, S.; Savino, M.; Scagnoli, F.; Pellegatta, S.; Pisati, F.; Zambelli, F.; Illi, B.; Annibali, D.; Beji, S.; Orecchini, E.; et al. Resetting cancer stem cell regulatory nodes upon MYC inhibition. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1872–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zuo, C.; Zhang, K.; Lei, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, K.; Wang, S.; et al. Long Non−Coding RNA H19 Regulates Glioma Cell Growth and Metastasis via miR-200a-Mediated CDK6 and ZEB1 Expression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 757650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. MiR-200c and miR-141 inhibit ZEB1 synergistically and suppress glioma cell growth and migration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 3385–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Hidalgo, L.; San-Miguel, T.; Megías, J.; Serna, E.; Calabuig-Fariñas, S.; Monleón, D.; Gil-Benso, R.; Cerdá-Nicolás, M.; López-Ginés, C. The status of egfr modulates the effect of mirna-200c on zeb1 expression and cell migration in glioblastoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, E.; Lopez-Gines, C.; Monleon, D.; Muñoz-Hidalgo, L.; Callaghan, R.C.; Gil-Benso, R.; Martinetto, H.; Gregori-Romero, A.; Gonzalez-Darder, J.; Cerda-Nicolas, M. Correlation between EGFR amplification and the expression of MicroRNA-200c in primary glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, E.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Ji, X.; Cheng, M.; Wang, H.; Fang, Z.; Zhao, B. A central role for MeCP2 in the epigenetic repression of miR-200c during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Ma, P.; Cai, R.; Guan, Q.; Wang, M.; Jin, B.Z. Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of glioma cancer cells by modulating the miR-200c/141-ZEB1 axis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3395–3412. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Yu, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Alvarez, A.A.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.; Feng, H. TGF-β-activated lncRNA LINC00115 is a critical regulator of glioma stem-like cell tumorigenicity. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e48170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Pascual, A.; Hale, J.S.; Kordowski, A.; Pugh, J.; Silver, D.J.; Bayik, D.; Roversi, G.; Alban, T.J.; Rao, S.; Chen, R.; et al. ADAMDEC1 maintains a growth factor signaling loop in cancer stem cells. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1574–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Pang, H.; Qi, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, R. Low microRNA-622 expression predicts poor prognosis and is associated with ZEB2 in glioma. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7387–7397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sui, Q. MicroRNA-769-3p inhibits tumor progression in glioma by suppressing ZEB2 and inhibiting the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghipour, N.; Kumar, S.U.; Massoud, T.F.; Paulmurugan, R. A rationally identified panel of microRNAs targets multiple oncogenic pathways to enhance chemotherapeutic effects in glioblastoma models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Browne, G.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 132, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fillmore, R.; Xi, Y. MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 344, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurashige, J.; Kamohara, H.; Watanabe, M.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Iwatsuki, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kinoshita, K.; Saito, S.; Baba, Y.; Baba, H. MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, S656–S664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, N.; Seike, M.; Soeno, C.; Chiba, M.; Miyanaga, A.; Noro, R.; Sugano, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Kubota, K.; Gemma, A. miR-200/ZEB axis regulates sensitivity to nintedanib in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, G.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Manikandan, M.; Rao, H.P.S.; Subbiah, S.; Ilangovan, R.; Murugan, A.K.; Munirajan, A.K. Dysregulation of miR-200 family microRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, F.S.; Mahfouz, R.; Assi, H.I. Egfr as a clinical marker in glioblastomas and other gliomas. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, V.; Moutinho, C.; Villanueva, A.; Boque, R.; Silva, P.; Carneiro, F.; Esteller, M. Dynamic epigenetic regulation of the microRNA-200 family mediates epithelial and mesenchymal transitions in human tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.Y.; Wright, J.A.; Attema, J.L.; Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Smith, E.; Thomas, D.; Lopez, A.F.; Drew, P.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; et al. Epigenetic modulation of the miR-200 family is associated with transition to a breast cancer stem-celllike state. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2256–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Shi, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, A.; Han, L.; Jiang, K.; Kang, C.; Zhang, Q. DNMT1 and EZH2 mediated methylation silences the microRNA-200b/a/429 gene and promotes tumor progression. Cancer Lett. 2015, 359, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, D.; Gil, J.; Dumont, P.; Rizzo, S.; Monté, D.; Quatannens, B.; Hudson, D.; Visakorpi, T.; Fuks, F.; De Launoit, Y. The methyl-CpG-binding protein MECP2 is required for prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, L. Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of MeCP2 inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Liang, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, S.T.; Li, B.R.; Yu, Y.X.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, R. MeCP2 inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer via suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7959–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillotson, R.; Bird, A. The Molecular Basis of MeCP2 Function in the Brain. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 1602–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Hassiotou, F.; Nowak, A. Glioblastoma stem-like cells: At the root of tumor recurrence and a therapeutic target. Carcinogenesis 2014, 36, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, J.; Westhoff, M.A.; Wagner, J.E.; Halatsch, M.E.; Trentmann, S.; Knippschild, U.; Wirtz, C.R.; Burster, T. Cancer stem cells: The potential role of autophagy, proteolysis, and cathepsins in glioblastoma stem cells. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317692227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lathia, J.D.; Mack, S.C.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Valentim, C.L.L.; Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, G.; Cilibrasi, C.; Bazzoni, R.; Cadamuro, M.; Negroni, C.; Butta, V.; Strazzabosco, M.; Dalprà, L.; Lavitrano, M.; Bentivegna, A. Valproic acid inhibits proliferation and reduces invasiveness in glioma stem cells through Wnt/β catenin signalling activation. Genes 2018, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Casey, S.C.; Felsher, D.W. Inactivation of MYC reverses tumorigenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 276, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, M.; Annibali, D.; Carucci, N.; Favuzzi, E.; Cole, M.D.; Evan, G.I.; Soucek, L.; Nasi, S. The action mechanism of the Myc inhibitor termed Omomyc may give clues on how to target Myc for cancer therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; O’Grady, S.; Tang, M.; Crown, J. MYC as a target for cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 94, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niland, S.; Riscanevo, A.X.; Eble, J.A. Matrix metalloproteinases shape the tumor microenvironment in cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.L.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, Y.T.; Wang, G.H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.H.; Zhou, H.H. Low expression of microRNA-320b correlates with tumorigenesis and unfavorable prognosis in glioma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yin, C.Y.; Jiang, J.; Kong, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-153 suppresses cell invasion by targeting SNAI1 and predicts patient prognosis in glioma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Y.; Jin, T.; Liang, H.; Cui, G.; He, S.; Gao, G. Correlation of microrna-372 upregulation with poor prognosis in human glioma. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z. Plasma microRNA-720 may predict prognosis and diagnosis in glioma patients. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, M.S.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, C.; Shrivastava, A. Elucidating the mechanisms of Temozolomide resistance in gliomas and the strategies to overcome the resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Shim, J.S. Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to overcome drug resistance in cancer. Molecules 2016, 21, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Pan, M.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; Liu, N.; You, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. MiR-181b modulates chemosensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme cells to temozolomide by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, R.; Guan, F.; Ma, S.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Yang, B. MicroRNA-128-3p Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Temozolomide in Glioblastoma by Targeting c-Met and EMT. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Tu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C. Downregulation of miR-186 promotes the proliferation and drug resistance of glioblastoma cells by targeting Twist1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 5301–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, F. Molecular functions and biological roles of long non-coding RNAs in human physiology and disease. J. Gene Med. 2019, 21, e3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dong, B.; Cao, J.; Mao, Y.; Guan, W.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S. Long non-coding RNA in glioma: Signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27582–27592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, T.; Wu, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. The miR155HG/miR-185/ANXA2 loop contributes to glioblastoma growth and progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, L. LncRNA HOXA-AS3 promotes the malignancy of glioblastoma through regulating miR-455-5p/USP3 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11755–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Deng, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, B.; Jin, Z.; Lin, F.; et al. LncRNA SNHG5 Promotes Proliferation of Glioma by Regulating miR-205-5p/ZEB2 Axis. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 11487–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.H.; Guo, L.; Yan, F.; Dou, Z.-Q.Q.; Yu, Q.; Chen, G. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIRM1 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of glioma cells by regulating the miR-873-5p/ZEB2 axis. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yang, Y.; Guan, J.; Lv, T.; Qu, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, H. LncRNA UCA1 sponges miR-204-5p to promote migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells via upregulation of ZEB1. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, X.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, W.; Tian, B.; Ma, T.; Lu, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Long Non-coding RNA MALAT1 Upregulates ZEB2 Expression to Promote Malignant Progression of Glioma by Attenuating miR-124. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, X.; Yan, D.; Li, D.; Guan, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, B. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 Decreases the Sensitivity of Resistant Glioblastoma Cell Lines to Temozolomide. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Guo, J.; Han, S.; Bao, L.; Diao, Y.; Lin, Z. Positive feedback loop of lncRNA HOXC-AS2/ miR-876-5p/ZEB1 to regulate EMT in glioma. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 7601–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Bao, Z.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Pan, M.; Ji, J. LINC00511 contributes to glioblastoma tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via LINC00511/miR-524-5p/YB1/ZEB1 positive feedback loop. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Xie, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z. Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of malignant glioma by regulating the miR-101/ZEB1 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, M.; Xia, P.; Lu, Z. HOTTIP Mediated Therapy Resistance in Glioma Cells Involves Regulation of EMT-Related miR-10b. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 873561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Du, P.; Peng, R.; Peng, G.; Yuan, J.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Mo, X.; Liao, Y. Long Noncoding RNA OR7E156P/miR-143/HIF1A Axis Modulates the Malignant Behaviors of Glioma Cell and Tumor Growth in Mice. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 690213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, L. Effect of lncrna zeb1-as1 on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of glioma u87 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 5120–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.-L.; Hu, L.; Chen, S.-H.; Sun, B.; Fu, M.-L.; Qin, C.-Z.; Qu, Q.; Wang, G.-H.; He, C.-J.; Zhou, H.-H. A Long Noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Long non-coding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating miR-577. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, H.; Hou, W.; Bao, H.; Xiong, J.; Che, W.; Gu, Y.; Sun, H.; Liang, P. Long non-coding RNA linc00645 promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by regulating miR-205-3p-ZEB1 axis in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Z.; Ji, W.; Xu, B.; Huo, Z.; Huang, H.; Huang, J.; Jiao, J.; Shao, J.; Zhang, X. Noncoding RNAs involved in the STAT3 pathway in glioma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. EMT: A new vision of hypoxia promoting cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yao, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Dou, C.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X. Hypoxia Accelerates Aggressiveness of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Involving Oxidative Stress, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Non-Canonical Hedgehog Signaling. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1856–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oeck, S.; Zhang, G.J.; Schramm, A.; Glazer, P.M. Hypoxia induces resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer cells via upregulation of FGFR1 and the MAPK pathway. Cancer Res. 2021, 80, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, N.; Ashok, C.; Natua, S.; Pant, D.; Cherian, A.; Pandkar, M.R.; Yadav, P.; Narayanan, V.S.S.; Mishra, J.; Samaiya, A.; et al. Hypoxia-induced TGF-β–RBFOX2–ESRP1 axis regulates human MENA alternative splicing and promotes EMT in breast cancer. NAR Cancer 2020, 2, zcaa021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Ma, H.; Fu, Z.; Li, L. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 predicts unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 26, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.C.; Han, N.; Wu, N.; Zhao, K.L.; Han, C.; Wang, H.X.; Ping, G.F.; Zheng, P.F.; Feng, H.; Qin, L.; et al. Interplay between long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 and miR-101/ZEB1 axis regulates proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 605–617. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C. LncRNA ZEB1-AS1/miR-409–3p/ZEB1 feedback loop is involved in the progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 507, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, M.; Novitskiy, S.; Moses, H.L. The roles of TGFβ in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, J.; Tang, Z. LncRNA UCA1 is necessary for TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and stemness via acting as a ceRNA for Slug in glioma cells. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.V.; Conroy, S.; Tomar, T.; Eggens-Meijer, E.; Bhat, K.; Copray, S.; Walenkamp, A.M.E.; Boddeke, E.; Balasubramanyian, V.; Wagemakers, M.; et al. TGF-β is an inducer of ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruna, A.; Darken, R.S.; Rojo, F.; Ocaña, A.; Peñuelas, S.; Arias, A.; Paris, R.; Tortosa, A.; Mora, J.; Baselga, J.; et al. High TGFβ-Smad Activity Confers Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients and Promotes Cell Proliferation Depending on the Methylation of the PDGF-B Gene. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallini, P.; Lennard, T.; Kirby, J.; Meeson, A. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: What is the impact on breast cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; He, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. EMT and Cancer Cell Stemness Associated With Chemotherapeutic Resistance in Esophageal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 672222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, A.; You, Y. Exosomal transfer of long non-coding RNA SBF2-AS1 enhances chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R435–R444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asti, E.; Garnier, D.; Lee, T.H.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J. Oncogenic extracellular vesicles in brain tumor progression. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, F.; Kosaka, N.; Ito, K.; Kimura, T.; Egawa, S.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C29–C39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Fang, J. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4493–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhou, B. Epigenetic Regulation of EMT: The Snail Story. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1698–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, P.; et al. CircMYO10 promotes osteosarcoma progression by regulating miR-370-3p/RUVBL1 axis to enhance the transcriptional activity of β-catenin/LEF1 complex via effects on chromatin remodeling. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; You, J.H.; Kim, M.-S.; Roh, J.-L. Epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes ferroptosis of head and neck cancer. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, K.-J. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focusing on hypoxia and TGF-β signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.N.; Ahn, D.H.; Kang, N.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, M.S.; Yim, H.W.; et al. TGF-β induced EMT and stemness characteristics are associated with epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, J.M.; Yan, X.L.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, J.K.; Huang, H.Q. Formononetin sensitizes glioma cells to doxorubicin through preventing EMT via inhibition of histone deacetylase 5. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6434–6441. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.Y.; Park, S.J.; Shim, J.W.; Song, Y.J.; Yang, K.; Park, S.-J.J.; Heo, K. Accumulation of low-dose BIX01294 promotes metastatic potential of U251 glioblastoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chu, L.; Li, X.; Kan, P.; Xin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, P. The Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of MiR-106a in Multidrug Resistance Reversal in Human Glioma U87/DDP and U251/G Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.-J.J.; He, H.-Y.Y.; Wu, J.-C.C.; Ding, X.-Q.Q.; Yang, L.; Jia, N.; Li, Z.-J.J.; Zheng, H.-C.C. The roles of ING5 in gliomas: A good marker for tumorigenesis and a potential target for gene therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56558–56568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Plch, J.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T. KDM5 demethylases and their role in cancer cell chemoresistance. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Huang, H.; Guan, F.; Zhu, G.; Xiao, Z.; Mao, B.; Su, H.; Hu, Z. Histone demethylase KDM5A inhibits glioma cells migration and invasion by down regulating ZEB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madany, M.; Thoma, T.; Edwards, L.A. The Curious Case of ZEB1. Discoveries 2018, 6, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, H.; Hou, A.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Niu, J.; Hu, L. Prognostic Significance of Zinc Finger E-Box-Binding Homeobox Family in Glioblastoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouédraogo, Z.G.; Biau, J.; Kemeny, J.L.; Morel, L.; Verrelle, P.; Chautard, E. Role of STAT3 in Genesis and Progression of Human Malignant Gliomas. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5780–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, C.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Qu, J. MicroRNA-361-5p inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of glioma cells through targeting Twist1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yidayitula, Y.; Zhao, H.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X.; Xu, M. LncRNA LINC00152 promoted glioblastoma progression through targeting the miR-107 expression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17674–17681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Li, X.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.C.; Liu, W.; Cui, G.; Xu, J. Upregulation of HOTAIRM1 increases migration and invasion by glioblastoma cells. Aging 2021, 13, 2348–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Long, J.; Yang, C.; Gong, B.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J. LncRNA DGCR5 plays a tumor-suppressive role in glioma via the miR-21/Smad7 and miR-23a/PTEN axes. Aging 2020, 12, 20285–20307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Sang, M.; Ju, Y.; Fan, X.; Gu, L.; Li, Z.; Geng, C.; Sang, M. ZEB1-Mediated Transcriptional Upregulation of circWWC3 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression through Activating Ras Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Circular RNA circVAPA contributes to non-small-cell lung cancer progression via miR-342-3p-dependent regulation of ZEB2. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Guan, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. CircCRIM1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by working as ceRNAs of CRIM1 and targeting miR-383-5p/ZEB2 axis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mao, P.; Feng, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, C.; Xu, M.; Gao, K. Blocking hsa_circ_0006168 suppresses cell proliferation and motility of human glioblastoma cells by regulating hsa_circ_0006168/miR-628-5p/IGF1R ceRNA axis. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, Y. Circular RNA HIPK3 promotes glioma progression by binding to miR-124-3p. Gene 2019, 690, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNA | Expression in Glioma * | Role in Gliomagenesis | Downstream Targets | Upstream Regulators | Biological Function in Glioma Cells | Reported Prognostic Value ** | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-590-3p | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1, ZEB2, N-cadherin, Vimentin, E-cadherin | - | Inhibit migration, invasion | - | [35] |
| miR-940 | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB2, N-cadherin, Vimentin, Fibronectin, α-SMA, MMP2, E-cadherin | - | Inhibit migration, invasion | - | [36] |
| miR-205 | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1/Akt/mTOR, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin | - | Inhibit migration, invasion | YES | [37,38] |
| miR-200a | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1/TF | MYC, H19 | Inhibit proliferation, migration | - | [39,40,41] |
| miR-200c | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1/E-cadherin, EGFR, ZEB2 | EGFR, MeCP2 /SUV39H1, ZEB1-AS1, LINC00115 | Inhibit migration, proliferation, promote apoptosis | - | [42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| miR-141 | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1 | ZEB1-AS1 | Inhibit migration, proliferation, promote apoptosis | - | [42,46] |
| miR-203 | - | Tumour suppressor | ADAMDEC1 | ADAMDEC1/FGF2/FGFR1/ERK1/2/ZEB1 | - | - | [48] |
| miR-622 | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB2 | - | Inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion, promote apoptosis | YES | [49] |
| miR-769-3p | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB2/Wnt /β-catenin | - | Inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion | YES | [50] |
| miR-139 | Down | Tumour suppressor | ZEB1 | - | Inhibit migration, invasion | - | [51] |
| lnRNA | Expression in Glioma * | Role in Gliomagenesis | Downstream Targets | Upstream Regulators | Biological Function in Glioma Cells | Reported Prognostic Value ** | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNHG5 | Up | Oncogene | miR-205-5p/ZEB2 | - | Promote proliferation | - | [88] |
| HOTAIRM1 | - | Oncogene | miR-873-5p/ZEB2 | - | Promote proliferation, inhibit apoptosis | YES | [89] |
| UCA1 | - | Oncogene | miR-204-5p/ZEB1, Fibronectin, COL5 A1 | - | Promote migration, invasion | - | [90] |
| MALAT1 | Up | Oncogene | miR-124/ZEB2, ZEB1, MDR1, MRP5, LRP1, E-cadherin, ZO-1, α-SMA, Fibronectin | - | Promote proliferation, inhibit cell cycle arrest, inhibit apoptosis | YES | [91,92] |
| HOXC-AS2 | Up | Oncogene | miR-876-5p/ZEB1, Vimentin, N-cadherin | ZEB1 | Promote migration, invasion | YES | [93] |
| LINC00511 | Up | Oncogene | miR-524-5p/YB1/ZEB1, Cyclin D1, CDK4, Vimentin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin | ZEB1 | Promote proliferation, migration, invasion, inhibit cell cycle arrest | YES | [94] |
| H19 | Up | Oncogene | miR-200a/CDK6/ZEB1 | - | Promote proliferation, invasion, migration | - | [41] |
| HOTTIP | - | Oncogene | miR-10b/ZEB1/ZEB2 /E-cadherin, VEGF, MMP-9, Vimentin, miR-101/ZEB1 | HIF-1α | Promote chemoresistance, proliferation, migration, invasion angiogenesis, metastasis | YES | [95,96] |
| OR7E156P | Up | Oncogene | miR-143/HIF-1α/ZEB1 /VEGF, Snail, Vimentin | - | Promote invasion, proliferation | YES | [97] |
| ZEB1-AS1 | Up | Oncogene | ZEB1, Snail, MMP2, MMP9, N-cadherin, Integrin-β1, Vimentin, E-cadherin, Cyclin D1, CDK2, Rb, Bax, Bcl-2, miR-200c/miR-141 /ZEB1, miR-577 | - | Promote proliferation, invasion, migration, inhibit cell cycle arrest inhibit apoptosis | YES | [46,98,99,100] |
| LINC00115 | Up | Oncogene | miR-200s/ZEB1, Vimentin, E-cadherin miR-200s/ZNF596 /EZH2/STAT3 | TGF-β | Promote proliferation | YES | [47] |
| LINC00645 | Up | Oncogene | miR-205-3p/ZEB1, Snail, Vimentin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin, Bcl-2, Bax | TGF-β | Promote proliferation, migration, invasion, inhibit apoptosis | YES | [101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenda, B.; Żebrowska-Nawrocka, M.; Turek, G.; Balcerczak, E. Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox Family: Non-Coding RNA and Epigenetic Regulation in Gliomas. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051364
Lenda B, Żebrowska-Nawrocka M, Turek G, Balcerczak E. Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox Family: Non-Coding RNA and Epigenetic Regulation in Gliomas. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051364
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenda, Bartosz, Marta Żebrowska-Nawrocka, Grzegorz Turek, and Ewa Balcerczak. 2023. "Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox Family: Non-Coding RNA and Epigenetic Regulation in Gliomas" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051364
APA StyleLenda, B., Żebrowska-Nawrocka, M., Turek, G., & Balcerczak, E. (2023). Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox Family: Non-Coding RNA and Epigenetic Regulation in Gliomas. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051364






