Real-World Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, Dulaglutide, on Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients Studied
3.2. Changes in Metabolic Parameters during 12-Month Dulaglutide Parameters
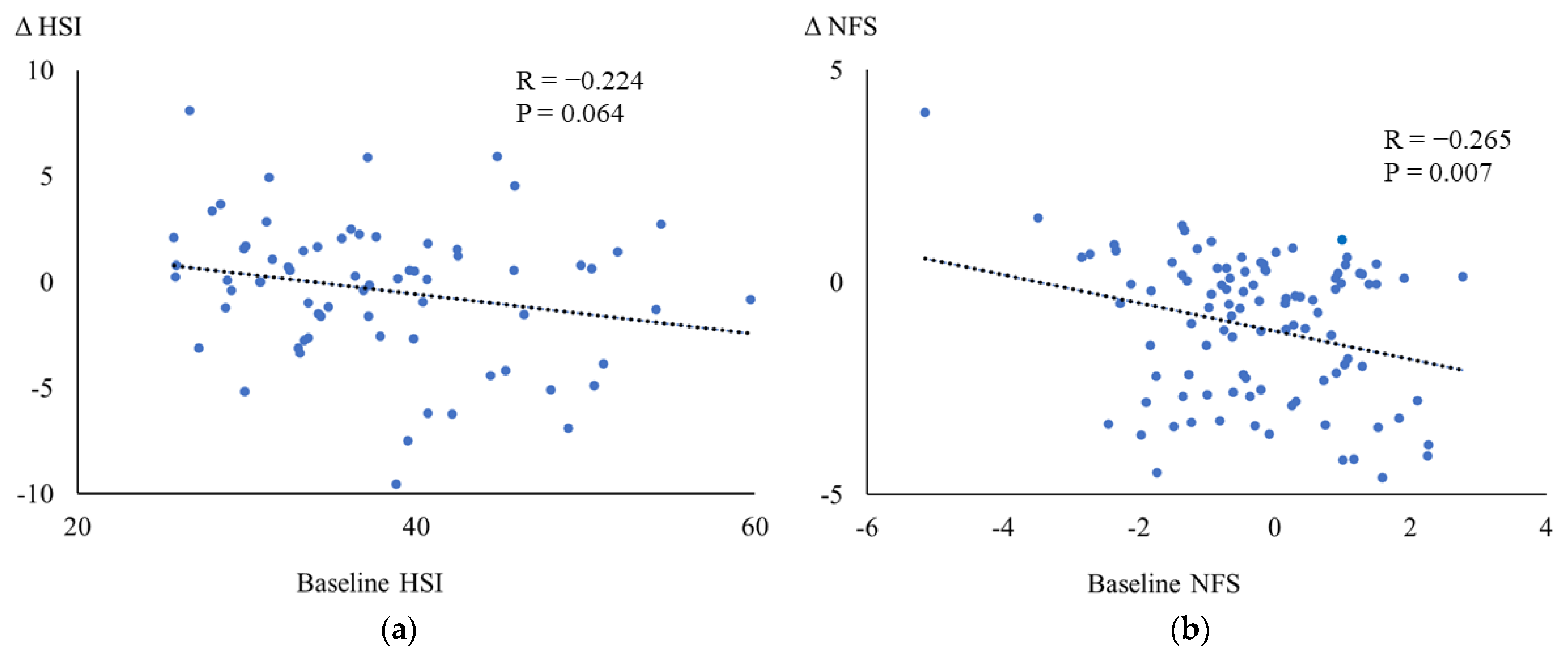
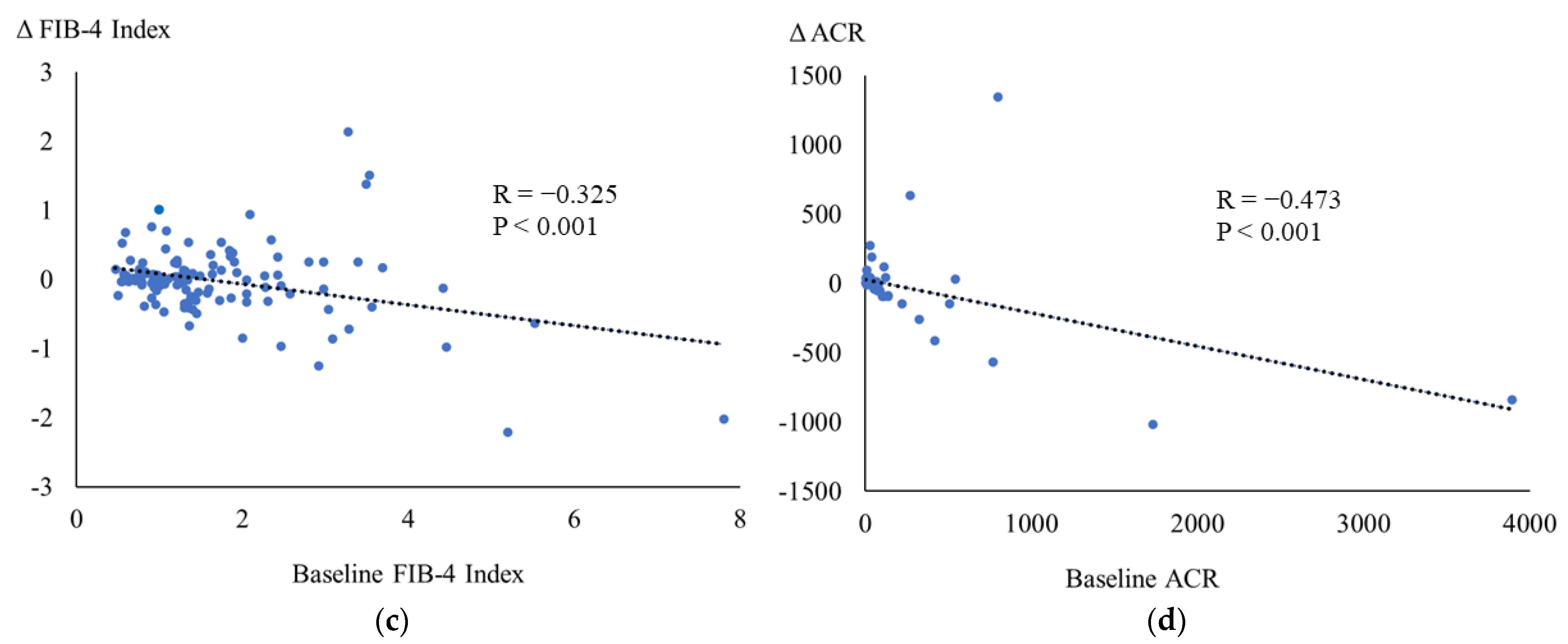
3.3. Correlations between the Baseline and the Changes in Metabolic Parameters
3.4. Correlations among the Changes in Metabolic Parameters
3.5. Subgroup Analysis in Patients with or without Insulin Treatment
3.6. Subgroup Analysis in Patients with or without SGLT2i Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Kamiya, H.; Haneda, M.; Inagaki, N.; Tanizawa, Y.; Araki, E.; Ueki, K.; Nakayama, T. Causes of death in Japanese patients with diabetes based on the results of a survey of 45,708 cases during 2001–2010: Report of the Committee on Causes of Death in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, K.; Sasako, T.; Okazaki, Y.; Kato, M.; Okahata, S.; Katsuyama, H.; Haraguchi, M.; Morita, A.; Ohashi, K.; Hara, K.; et al. Effect of an intensified multifactorial intervention on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in type 2 diabetes (J-DOIT3): An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendle, J.; Grunberger, G.; Blevins, T.; Giorgino, F.; Hietpas, R.T.; Botros, F.T. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A comprehensive review of the dulaglutide clinical data focusing on the AWARD phase 3 clinical trial program. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, N. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, M.; Terauchi, Y.; Ozeki, A.; Oura, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Imaoka, T. A 1-year safety study of dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes on a single oral hypoglycemic agent: An open-label, nonrandomized, phase 3 trial. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odawara, M.; Miyagawa, J.; Iwamoto, N.; Takita, Y.; Imaoka, T.; Takamura, T. Once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist dulaglutide significantly decreases glycated haemoglobin compared with once-daily liraglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: 52 weeks of treatment in a randomized phase III study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, Y.; Oura, T.; Matsui, A.; Matsuura, J.; Iwamoto, N. Analysis of efficacy and safety of dulaglutide 0.75 mg stratified by sex in patients with type 2 diabetes in 2 randomized, controlled phase 3 studies in Japan. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, S.; Imai, E.; Horio, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Nitta, K.; Yamagata, K.; Tomino, Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Hishida, A.; et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Sung, M.W.; et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Lydecker, A.; Murray, K.; Tetri, B.N.; Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A. Use of the Fib4 index for non-invasive evaluation of fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Itoh, Y.; Ono, M.; Fujii, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, N.; Kanemasa, K.; et al. Validation of the FIB4 index in a Japanese nonalcoholic fatty liver disease population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study Group. A 6-year, randomized, controlled trial comparing sulfonylurea, insulin, and metformin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes that could not be controlled with diet therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 128, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Sako, A.; Mishima, S.; Yanai, H. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes: A chart-based analysis. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Yoshikawa, R.; Sako, A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Possible Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects Beyond Glucose Lowering. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuyama, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Iijima, T.; Adachi, H.; Yanai, H. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Chart-Based Analysis. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.C.; Chan, J.C. Type 2 diabetes in East Asians: Similarities and differences with populations in Europe and the United States. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1281, 64–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lü, Q.; Tong, N. Glucagon-like peptide-1 mimetics, optimal for Asian type 2 diabetes patients with and without overweight/obesity: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Hahn, S.; Oh, T.J.; Park, K.S.; Cho, Y.M. Differences in the HbA1c-lowering efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues between Asians and non-Asians: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslanian, S.A.; Hannon, T.; Zeitler, P.; Chao, L.C.; Boucher-Berry, C.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Bismuth, E.; Dib, S.; Cho, J.I.; Cox, D. Once-Weekly Dulaglutide for the Treatment of Youths with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Cirrincione, A.; Casuccio, A.; Del Cuore, A.; Daidone, M.; Di Chiara, T.; Di Raimondo, D.; Corte, A.D.; Maida, C.; Simonetta, I.; et al. Efficacy of dulaglutide on vascular health indexes in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Wu, H.X.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.H.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.L.; Xu, S.N.; Huang, B.L.; et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight in adults with obesity without diabetes mellitus-a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Patti, A.M.; Giglio, R.V.; Chianetta, R.; Castellino, G.; Magán-Fernández, A.; Citarella, R.; Papanas, N.; Jenez, A.; Pantea Stoian, A.; et al. Liraglutide Improved Cardiometabolic Parameters More in Obese than in Non-obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Real-World 18-Month Prospective Study. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, A.M.; Nikolic, D.; Magan-Fernandez, A.; Vicenza Giglio, R.; Castellino, G.; Chianetta, R.; Citarella, R.; Corrado, E.; Provenzano, F.; Provenzano, V.; et al. Exenatide once-weekly improves metabolic parameters, endothelial dysfunction and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type-2 diabetes: An 8-month prospective study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 149, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, J.; Obata, A.; Obata, Y.; Fushimi, Y.; Shimoda, M.; Kohara, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; Kaku, K.; Kaneto, H. Dulaglutide exerts beneficial anti atherosclerotic effects in ApoE knockout mice with diabetes: The earlier, the better. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Hirowatari, Y.; Yoshida, H. Diabetic dyslipidemia: Evaluation and mechanism. Glob. Health Med. 2019, 1, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Gethmann, A.; Götze, O.; Gallwitz, B.; Holst, J.J.; Schmidt, W.E.; Nauck, M.A. Glucagon-like peptide 1 abolishes the postprandial rise in triglyceride concentrations and lowers levels of non-esterified fatty acids in humans. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholm, C.; Kumarathurai, P.; Samkani, A.; Pedersen, L.R.; Boston, R.C.; Nielsen, O.W.; Kristiansen, O.P.; Madsbad, S.; Sajadieh, A.; Haugaard, S.B. Effect of liraglutide on estimates of lipolysis and lipid oxidation in obese patients with stable coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 2012–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Deng, F.; Chen, F.; Zhu, D.; Hou, K. Pharmacoeconomic analysis (CER) of Dulaglutide and Liraglutide in the treatment of patients with type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1054946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Hirowatari, Y. Effects of liraglutide, a human glucagonlike peptide-1 analog, on glucose/lipid metabolism, and adipocytokines in patients with type 2 Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 1, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Taher, J.; Baker, C.L.; Cuizon, C.; Masoudpour, H.; Zhang, R.; Farr, S.; Naples, M.; Bourdon, C.; Pausova, Z.; Adeli, K. GLP-1 receptor agonism ameliorates hepatic VLDL overproduction and de novo lipogenesis in insulin resistance. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoar, S.; Ikram, W.; Shah, A.A.; Farooq, N.; Gouni, S.; Khavandi, S.; Tabibzadeh, E.; Khavandi, S. Non-high-density lipoprotein (non-HDL) cholesterol in adolescence as a predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases in adulthood. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Mori, K.; Taketani, H.; Ishiba, H.; Hara, T.; Okajima, A.; Umemura, A.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. Effect of 12-week dulaglutide therapy in Japanese patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Petracca, G.; Beatrice, G.; Csermely, A.; Lonardo, A.; Targher, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Botros, F.T.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: An exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.Q.; Xu, X.H.; Kong, X.-C.; Sun, R.; Jing, T.; Ye, L.; Su, X.-F.; Ma, J.-H. The Effects of Once-Weekly Dulaglutide and Insulin Glargine on Glucose Fluctuation in Poorly Oral-Antidiabetic Controlled Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2682657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balena, R.; Hensley, I.E.; Miller, S.; Barnett, A.H. Combination therapy with GLP-1 receptor agonists and basal insulin: A systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Adachi, H.; Katsuyama, H. Multi-Organ Protective Effects of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Rinaldi, L.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Di Salvo, J.; Epifani, R.; Marfella, R.; Docimo, G.; et al. An Overview of the Cardiorenal Protective Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.I.; Udell, J.A.; Drucker, D.J. Cardiorenal mechanisms of action of glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Medicine (N. Y.) 2021, 2, 1203–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Luo, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, K. The Efficacy and Safety of the Combination Therapy With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 838277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Combination therapy with GLP-1 receptor agonist and SGLT2 inhibitor. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, E.; Bell, D.S.H. Combination Treatment of SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Symbiotic Effects on Metabolism and Cardiorenal Risk. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age | 64.7 ± 15.6 |
| Gender (M/F) | 69/52 |
| Body height (cm) | 162 ± 10 |
| Body weight (kg) | 68.6 ± 19.2 |
| Body mass index (BMI) (kg/m2) | 26.8 ± 5.7 |
| Medications at baseline | |
| Insulin | 28 (23.1%) |
| Metformin | 58 (47.9%) |
| Sulfonylurea | 21 (17.3%) |
| Glinides | 10 (8.3%) |
| Thiazolidinedione | 36 (30.0%) |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | 14 (11.6%) |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 51 (42.1%) |
| ACE Inhibitors | 1 (0.8%) |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers | 50 (41.3%) |
| Calcium channel blockers | 58 (47.9%) |
| Diuretics | 14 (11.6%) |
| Alpha blockers | 1 (0.8%) |
| Beta Blockers | 10 (8.3%) |
| Statins | 66 (54.5%) |
| Ezetimibe | 15 (12.4) |
| Fibrates | 8 (6.6%) |
| Antiplatelet drugs | 18 (14.9%) |
| n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (kg) | 74 | 69.6 ± 21.0 | 67.9 ± 20.6 | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 74 | 26.9 ± 6.4 | 26.2 ± 6.5 | 0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 67 | 129 ± 22 | 117 ± 30 | 0.027 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 50 | 74 ± 12 | 75 ± 12 | 0.641 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 119 | 201 ± 88 | 174 ± 78 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 116 | 8.8 ± 1.6 | 7.7 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 108 | 4.04 ± 0.59 | 4.14 ± 0.50 | 0.017 |
| AST (IU/L) | 117 | 29 ± 19 | 28 ± 19 | 0.359 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 118 | 35 ± 31 | 32 ± 27 | 0.301 |
| γGTP (IU/L) | 105 | 67 ± 127 | 53 ± 74 | 0.001 |
| Total bilirubin | 53 | 0.66 ± 0.33 | 0.64 ± 0.34 | 0.628 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 104 | 183 ± 47 | 176 ± 41 | 0.075 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 114 | 49 ± 13 | 51 ± 15 | 0.011 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 58 | 101 ± 32 | 94 ± 30 | 0.086 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 115 | 199 ± 226 | 168 ± 155 | 0.026 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 103 | 135 ± 48 | 126 ± 39 | 0.017 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 121 | 0.85 ± 0.43 | 0.88 ± 0.43 | 0.373 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 121 | 73 ± 28 | 70 ± 25 | 0.170 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 102 | 5.3 ± 1.8 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 0.148 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 119 | 13.4 ± 2.0 | 13.5 ± 1.8 | 0.279 |
| Platelet (×104/μL) | 119 | 22.9 ± 7.2 | 22.7 ± 7.2 | 0.489 |
| HSI | 69 | 37.8 ± 7.9 | 37.4 ± 7.8 | 0.630 |
| NFS | 101 | −0.28 ± 1.35 | −1.34 ± 1.87 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 index | 112 | 1.72 ± 1.17 | 1.69 ± 1.11 | 0.591 |
| ACR (mg/g Cre) | 56 | 202 ± 569 | 183 ± 502 | 0.408 |
| Male (n = 69) | Female (n = 52) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | |
| Body weight (kg) | 42 | 74.2 ± 23.5 | 72.3 ± 23.2 | 0.005 | 32 | 63.6 ± 15.5 | 62.1 ± 14.7 | 0.055 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 42 | 26.6 ± 6.8 | 25.9 ± 6.9 | 0.006 | 32 | 27.2 ± 5.9 | 26.7 ± 6.1 | 0.059 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 39 | 130 ± 21 | 122 ± 31 | 0.302 | 28 | 128 ± 23 | 109 ± 28 | 0.033 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 31 | 74 ± 13 | 76 ± 12 | 0.428 | 19 | 73 ± 11 | 73 ± 10 | 0.879 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 69 | 201 ± 81 | 184 ± 85 | 0.012 | 50 | 200 ± 97 | 162 ± 64 | 0.004 |
| HbA1c (%) | 68 | 8.8 ± 1.5 | 7.8 ± 1.5 | <0.001 | 48 | 8.8 ± 1.7 | 7.6 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 61 | 4.10 ± 0.58 | 4.17 ± 0.54 | 0.135 | 47 | 3.95 ± 0.58 | 4.09 ± 0.44 | 0.057 |
| AST (IU/L) | 66 | 30 ± 20 | 27 ± 18 | 0.355 | 51 | 29 ± 17 | 29 ± 20 | 0.718 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 67 | 37 ± 31 | 31 ± 24 | 0.082 | 51 | 32 ± 30 | 33 ± 31 | 0.645 |
| γGTP (IU/L) | 61 | 80 ± 92 | 64 ± 92 | 0.044 | 44 | 47 ± 47 | 39 ± 33 | 0.007 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 34 | 0.74 ± 0.36 | 0.71 ± 0.37 | 0.504 | 52 | 0.72 ± 0.37 | 0.79 ± 0.39 | 0.968 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 61 | 184 ± 50 | 169 ± 43 | 0.003 | 43 | 182 ± 41 | 185 ± 36 | 0.579 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 66 | 47 ± 13 | 48 ± 12 | 0.397 | 48 | 52 ± 12 | 57 ± 17 | 0.007 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 34 | 101 ± 31 | 95 ± 27 | 0.452 | 24 | 102 ± 33 | 93 ± 34 | 0.113 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 67 | 213 ± 271 | 170 ± 182 | 0.019 | 48 | 180 ± 139 | 166 ± 108 | 0.427 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 60 | 139 ± 52 | 123 ± 42 | 0.004 | 43 | 130 ± 41 | 129 ± 34 | 0.772 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 69 | 0.95 ± 0.41 | 0.95 ± 0.44 | 0.504 | 52 | 0.72 ± 0.37 | 0.79 ± 0.39 | 0.026 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 69 | 73 ± 28 | 72 ± 24 | 0.875 | 52 | 73 ± 29 | 68 ± 27 | 0.052 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 56 | 5.6 ± 1.7 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | 0.352 | 46 | 5.0 ± 1.8 | 4.8 ± 1.3 | 0.260 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 68 | 13.8 ± 2.2 | 13.9 ± 2.2 | 0.505 | 51 | 12.9 ± 1.7 | 13.0 ± 1.5 | 0.435 |
| Platelet (×104/μL) | 68 | 22.1 ± 7.4 | 22.3 ± 7.7 | 0.673 | 52 | 23.9 ± 6.6 | 23.2 ± 6.5 | 0.110 |
| HSI | 39 | 37.2 ± 8.1 | 36.3 ± 8.2 | 0.063 | 30 | 38.6 ± 7.5 | 38.9 ± 7.0 | 0.131 |
| NFS | 56 | −0.34 ± 1.42 | −1.39 ± 1.87 | <0.001 | 45 | −0.20 ± 1.26 | −1.08 ± 1.66 | 0.001 |
| FIB-4 index | 63 | 1.78 ± 1.35 | 1.74 ± 1.25 | 0.859 | 49 | 1.66 ± 0.88 | 1.64 ± 0.91 | 0.547 |
| ACR (mg/g Cre) | 31 | 172 ± 352 | 145 ± 390 | 0.468 | 25 | 238 ± 755 | 229 ± 610 | 0.716 |
| ΔBMI | ΔHbA1c | ΔTG | ΔHDL-C | ΔLDL-C | ΔNon-HDL-C | ΔHSI | ΔNFS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔBMI | 1 | |||||||
| ΔHbA1c | 0.112 | 1 | ||||||
| ΔTG | −0.021 | 0.165 | 1 | |||||
| ΔHDL-C | 0.245 * | −0.236 * | −0.121 | 1 | ||||
| ΔLDL-C | 0.097 | 0.377 ** | −0.233 | 0.215 | 1 | |||
| ΔNon-HDL-C | 0.046 | 0.398 ** | 0.415 ** | −0.040 | 0.518 ** | 1 | ||
| ΔHSI | 0.586 ** | 0.037 | 0.064 | 0.141 | 0.208 | −0.026 | 1 | |
| ΔNFS | 0.201 | 0.067 | 0.268 ** | 0.013 | −0.083 | 0.149 | −0.212 | 1 |
| ΔFIB-4 index | 0.059 | −0.008 | −0.005 | 0.060 | −0.094 | 0.076 | −0.197 | −0.474 ** |
| With Insulin at Baseline (n = 28) | Without Insulin at Baseline (n = 93) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | |
| Body weight (kg) | 15 | 71.5 ± 21.3 | 71.0 ± 20.6 | 0.572 | 59 | 69.1 ± 21.0 | 67.1 ± 20.5 | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 15 | 26.9 ± 6.4 | 26.8 ± 6.5 | 0.638 | 59 | 26.9 ± 6.4 | 26.1 ± 6.5 | 0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 15 | 128 ± 23 | 134 ± 30 | 0.346 | 52 | 130 ± 22 | 112 ± 28 | 0.003 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 13 | 74 ± 10 | 82 ± 11 | 0.023 | 37 | 74 ± 13 | 72 ± 11 | 0.362 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 28 | 188 ± 75 | 172 ± 83 | 0.183 | 91 | 205 ± 92 | 175 ± 76 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 27 | 9.0 ± 1.7 | 8.1 ± 1.3 | 0.008 | 89 | 8.8 ± 1.6 | 7.6 ± 1.4 | <0.001 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 25 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 4.0 ± 0.7 | 0.695 | 83 | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 4.2 ± 0.4 | 0.010 |
| AST (IU/L) | 26 | 24 ± 10 | 23 ± 9 | 0.833 | 91 | 31 ± 20 | 29 ± 21 | 0.358 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 27 | 30 ± 20 | 29 ± 18 | 0.964 | 91 | 36 ± 33 | 33 ± 29 | 0.274 |
| γGTP (IU/L) | 23 | 77 ± 158 | 63 ± 86 | 0.135 | 82 | 63 ± 117 | 51 ± 71 | 0.005 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 15 | 0.68 ± 0.42 | 0.66 ± 0.35 | 0.893 | 38 | 0.66 ± 0.29 | 0.63 ± 0.33 | 0.593 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 23 | 183 ± 30 | 167 ± 24 | 0.032 | 81 | 183 ± 51 | 178 ± 44 | 0.440 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 23 | 50 ± 13 | 51 ± 22 | 0.696 | 91 | 49 ± 12 | 52 ± 13 | 0.002 |
| LDL-C(mg/dL) | 10 | 103 ± 33 | 97 ± 381 | 0.508 | 48 | 101 ± 32 | 93 ± 30 | 0.104 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 24 | 212 ± 219 | 147 ± 65 | 0.241 | 91 | 196 ± 228 | 174 ± 171 | 0.069 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 22 | 135 ± 36 | 119 ± 25 | 0.025 | 81 | 135 ± 51 | 127 ± 42 | 0.113 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 28 | 0.87 ± 0.24 | 0.92 ± 0.27 | 0.330 | 93 | 0.85 ± 0.45 | 0.87 ± 0.47 | 0.697 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 28 | 70 ± 26 | 63 ± 18 | 0.130 | 93 | 74 ± 29 | 73 ± 27 | 0.525 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 22 | 4.8 ± 1.8 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | 0.032 | 80 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | 5.0 ± 1.3 | 0.006 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 28 | 13.4 ± 2.1 | 13.3 ± 1.9 | 0.202 | 91 | 13.4 ± 2.0 | 13.6 ± 1.8 | 0.056 |
| Platelet (×104/μL) | 28 | 23.6 ± 7.0 | 24.9 ± 9.9 | 0.973 | 91 | 22.7 ± 7.2 | 22.0 ± 6.0 | 0.429 |
| HSI | 13 | 38.0 ± 7.3 | 38.5 ± 6.2 | 0.600 | 56 | 37.7 ± 8.0 | 37.2 ± 8.1 | 0.443 |
| NFS | 22 | −0.34 ± 1.29 | −1.70 ± 1.80 | 0.009 | 79 | −0.26 ± 1.37 | −1.24 ± 1.88 | <0.001 |
| FIB-4 index | 25 | 1.51 ± 1.05 | 1.50 ± 1.00 | 0.968 | 87 | 1.79 ± 1.19 | 1.75 ± 1.13 | 0.537 |
| ACR (mg/g Cre) | 9 | 74 ± 123 | 81 ± 103 | 0.953 | 47 | 226 ± 616 | 202 ± 544 | 0.302 |
| With SGLT2i at Baseline (n = 52) | Without SGLT2i at Baseline (n = 69) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | n | Baseline | 12 Months | p | |
| Body weight (kg) | 26 | 70.6 ± 17.7 | 69.7 ± 17.8 | <0.001 | 48 | 69.0 ± 22.6 | 66.9 ± 21.9 | 0.004 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 | 27.4 ± 5.3 | 27.1 ± 5.6 | 0.059 | 48 | 26.6 ± 6.9 | 25.8 ± 7.0 | 0.006 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 24 | 124 ± 19 | 118 ± 28 | 0.797 | 48 | 132 ± 23 | 116 ± 31 | 0.018 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 19 | 73 ± 15 | 74 ± 12 | 0.777 | 31 | 74 ± 11 | 75 ± 12 | 0.600 |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 51 | 200 ± 84 | 171 ± 66 | 0.009 | 68 | 202 ± 92 | 177 ± 85 | 0.007 |
| HbA1c (%) | 50 | 9.2 ± 1.6 | 7.9 ± 1.2 | <0.001 | 66 | 8.6 ± 1.6 | 7.6 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Alb (g/dL) | 48 | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 0.003 | 60 | 4.0 ± 0.6 | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 0.458 |
| AST (IU/L) | 51 | 30 ± 22 | 29 ± 21 | 0.490 | 66 | 29 ± 17 | 27 ± 17 | 0.484 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 52 | 36 ± 34 | 35 ± 33 | 0.813 | 66 | 33 ± 28 | 29 ± 21 | 0.250 |
| γGTP (IU/L) | 43 | 89 ± 187 | 59 ± 95 | 0.007 | 62 | 51 ± 51 | 49 ± 56 | 0.060 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 19 | 0.72 ± 0.35 | 0.68 ± 0.24 | 0.634 | 34 | 0.63 ± 0.32 | 0.62 ± 0.38 | 0.805 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 45 | 190 ± 56 | 180 ± 50 | 0.033 | 59 | 178 ± 37 | 173 ± 31 | 0.616 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 49 | 47 ± 11 | 52 ± 12 | <0.001 | 65 | 50 ± 13 | 51 ± 17 | 0.744 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 28 | 98 ± 26 | 93 ± 28 | 0.269 | 30 | 104 ± 37 | 94 ± 32 | 0.136 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 50 | 250 ± 316 | 188 ± 214 | 0.002 | 65 | 160 ± 100 | 153 ± 82 | 0.638 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 44 | 143 ± 59 | 130 ± 49 | 0.006 | 59 | 129 ± 37 | 123 ± 29 | 0.483 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 52 | 0.88 ± 0.47 | 0.86 ± 0.40 | 0.657 | 69 | 0.84 ± 0.35 | 0.89 ± 0.45 | 0.150 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 52 | 73 ± 26 | 72 ± 24 | 0.414 | 69 | 73 ± 30 | 69 ± 26 | 0.277 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 48 | 5.4 ± 1.8 | 5.1 ± 1.4 | 0.022 | 54 | 5.2 ± 1.7 | 5.1 ± 1.3 | 0.866 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 50 | 14.0 ± 1.9 | 14.3 ± 1.7 | 0.048 | 69 | 12.9 ± 2.0 | 13.0 ± 1.7 | 0.980 |
| Platelet (×104/μL) | 50 | 21.9 ± 6.6 | 22.1 ± 6.1 | 0.435 | 69 | 23.6 ± 7.5 | 23.1 ± 7.9 | 0.173 |
| HSI | 25 | 39.7 ± 7.5 | 39.6 ± 7.5 | 0.143 | 44 | 36.7 ± 7.9 | 39.2 ± 7.9 | 0.283 |
| NFS | 46 | −0.21 ± 1.21 | −1.63 ± 1.54 | <0.001 | 55 | −0.33 ± 1.46 | −1.10 ± 2.08 | 0.035 |
| FIB-4 index | 49 | 1.74 ± 1.33 | 1.62 ± 1.10 | 0.088 | 63 | 1.71 ± 1.02 | 1.75 ± 1.12 | 0.547 |
| ACR (mg/g Cre) | 29 | 124 ± 323 | 93 ± 163 | 0.983 | 27 | 285 ± 740 | 279 ± 690 | 0.313 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsuyama, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Umeyama, S.; Iida, S.; Adachi, H.; Yanai, H. Real-World Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, Dulaglutide, on Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030869
Katsuyama H, Hakoshima M, Umeyama S, Iida S, Adachi H, Yanai H. Real-World Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, Dulaglutide, on Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030869
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsuyama, Hisayuki, Mariko Hakoshima, Shohei Umeyama, Sakura Iida, Hiroki Adachi, and Hidekatsu Yanai. 2023. "Real-World Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, Dulaglutide, on Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030869
APA StyleKatsuyama, H., Hakoshima, M., Umeyama, S., Iida, S., Adachi, H., & Yanai, H. (2023). Real-World Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist, Dulaglutide, on Metabolic Parameters in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study. Biomedicines, 11(3), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030869






