Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Patients with Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Single-Institution Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
Statistical Analyses
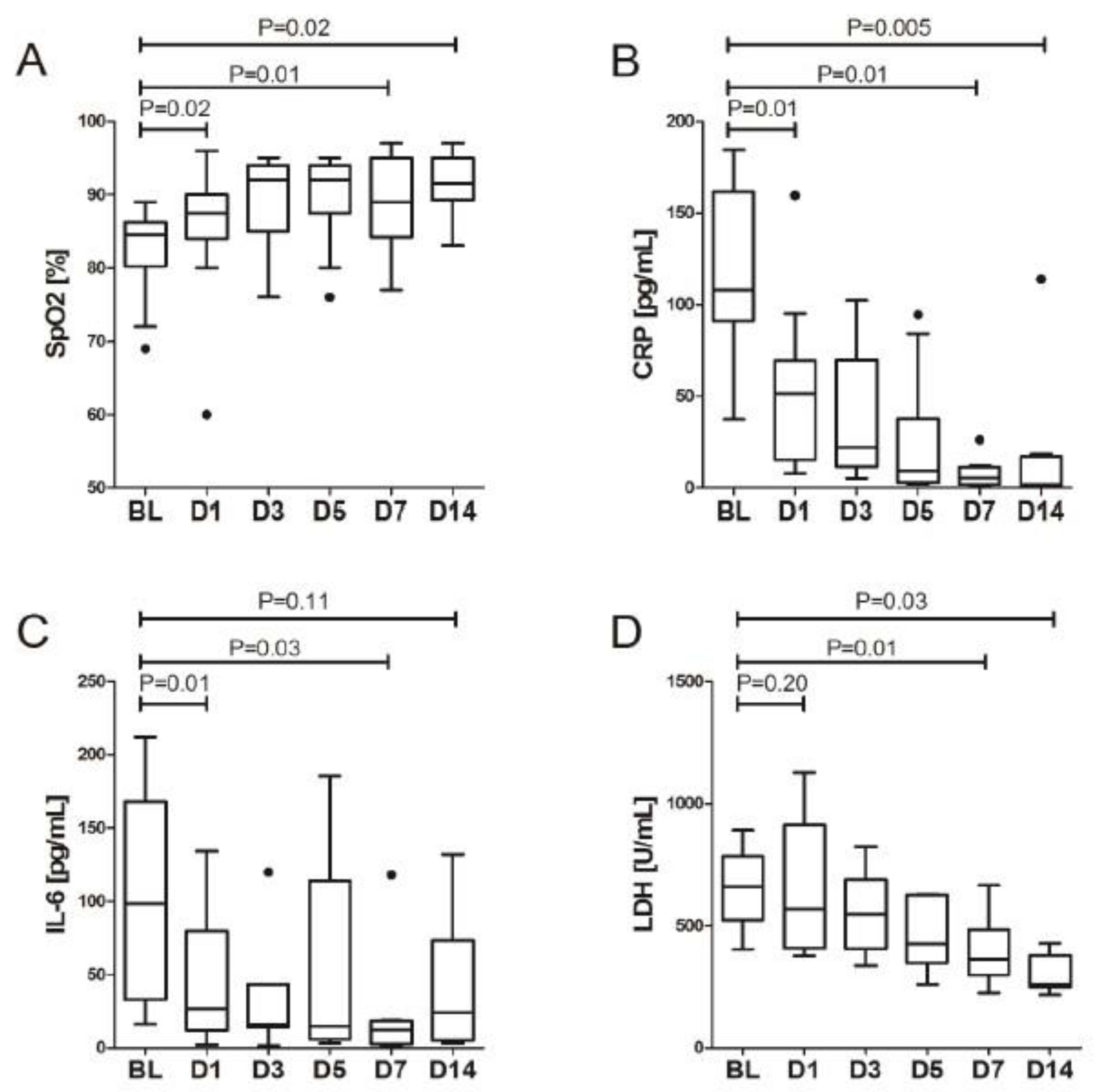
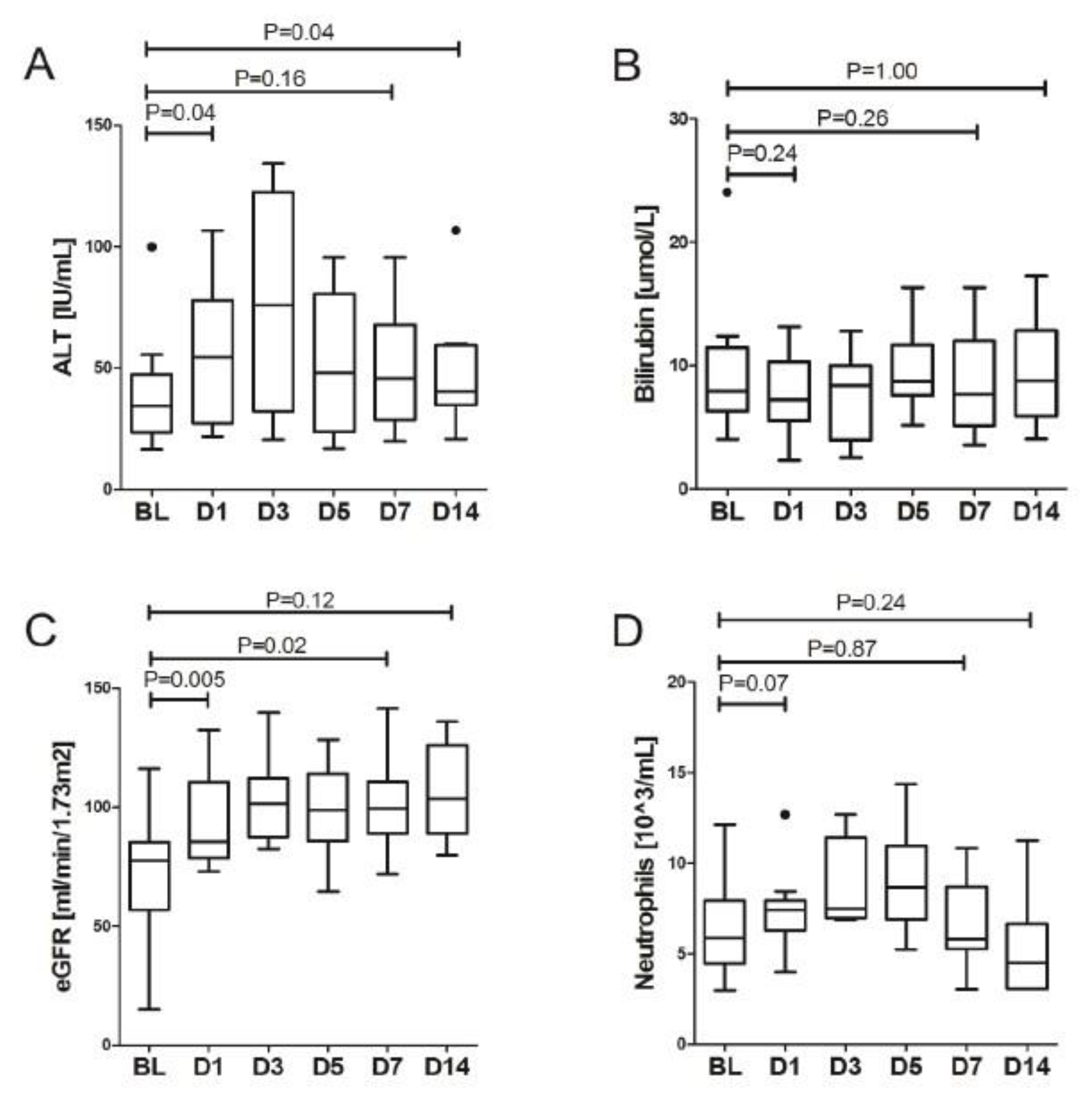
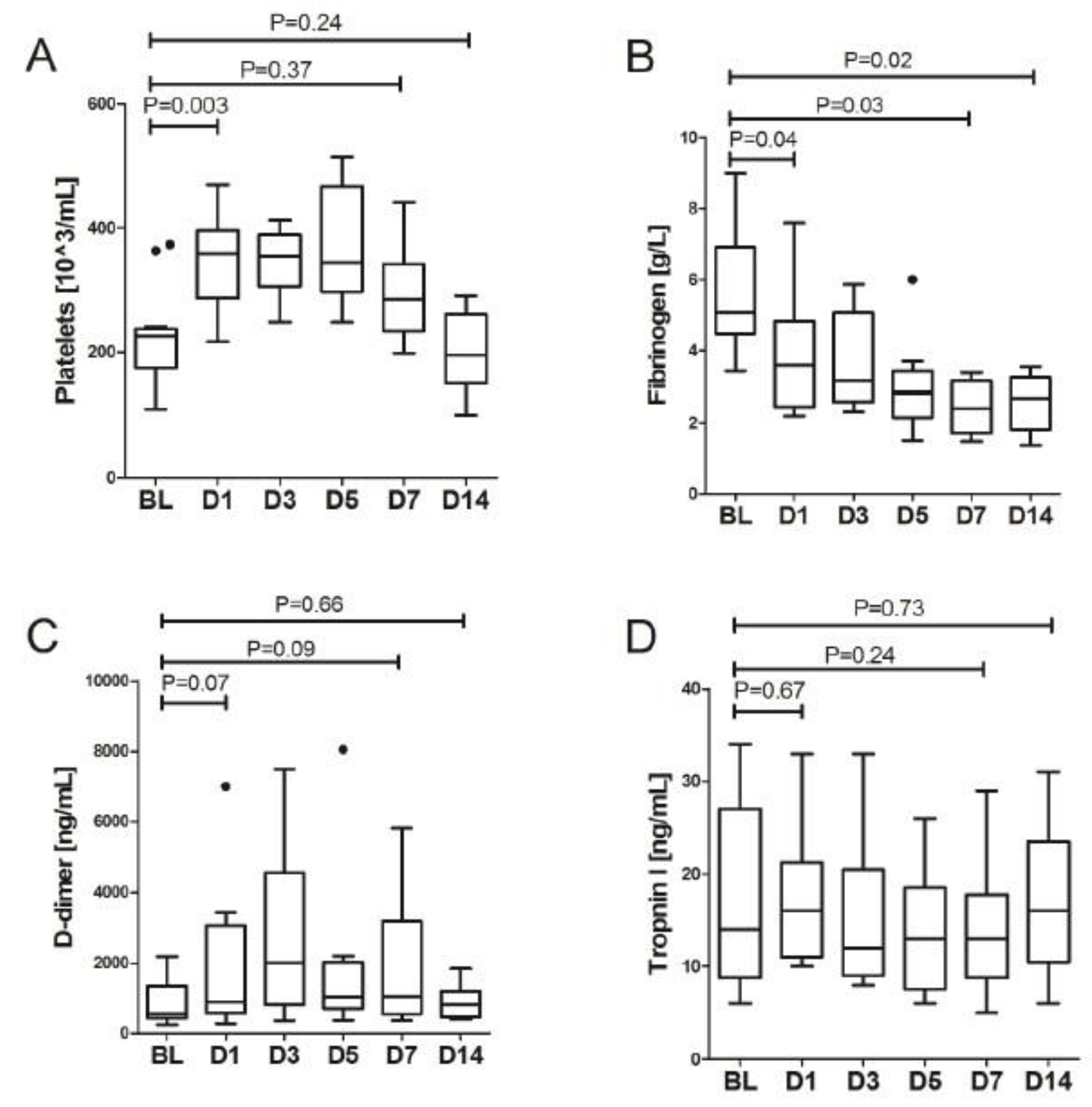
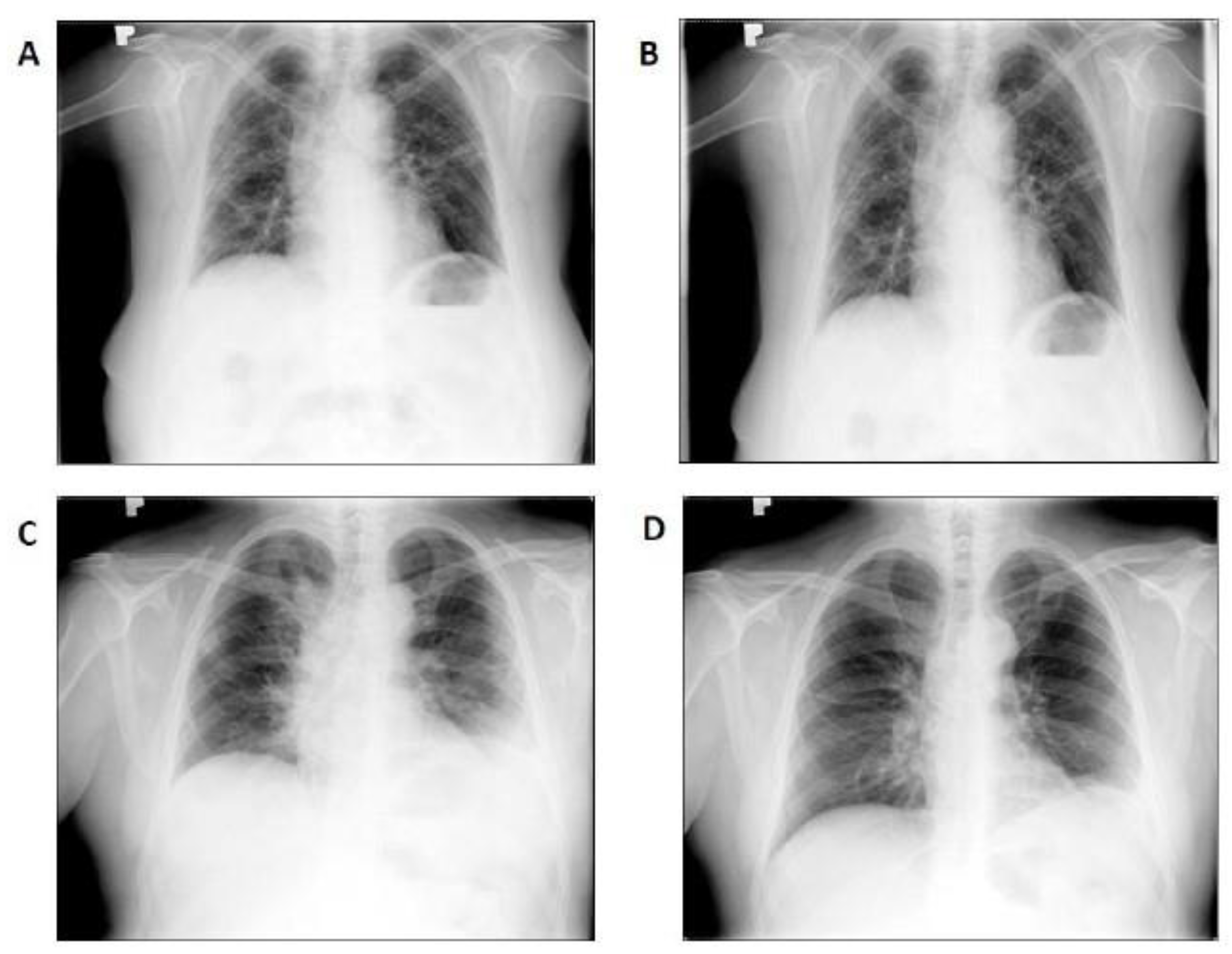
3. Results
LDRT Efficacy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Research Result. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.; Fang, M.; Yu, T.; et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ñamendys-Silva, S. Respiratory support for patients with COVID-19 infection. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, C.; Han, J.; Yau, L.; Reiss, W.G.; Kramer, B.; Neidhart, J.D.; Criner, G.J.; Kaplan-Lewis, E.; Baden, R.; Pandit, L.; et al. Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rödel, F.; Keilholz, L.; Herrmann, M.; Sauer, R.; Hildebrandt, G. Radiobiological mechanisms in inflammatory diseases of low-dose radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, F.; Frey, B.; Gaipl, U.; Keilholz, L.; Fournier, C.; Manda, K.; Schollnberger, H.; Hildebrandt, G.; Rodel, C. Modulation of inflammatory immune reactions by low-dose ionizing radiation: Molecular mechanisms and clinical application. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, M.; Sabater, S.; Hernández, V.; Rovirosa, A.; Lara, P.C.; Biete, A.; Panés, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of low-dose radiotherapy. Indications, dose, and radiobiological mechanisms involved. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2012, 188, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Dhawanet, G. How radiotherapy was historically used to treat pneumonia: Could it be useful today? J. Biol. Med. 2013, 86, 555–570. [Google Scholar]
- Micke, O.; Seegenschmied, M.H. German Working Group on Radiotherapy in Germany. Consensus guidelines for radiation therapy of benign diseases: A multicenter approach in Germany. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 52, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seegenschmiedt, M.H.; Katalinic, A.; Makoski, H.; Haase, W.; Gademann, G.; Hassenstein, E. Radiation therapy for benign diseases: Patterns of care study in Germany. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Horban, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Kozielewicz, D.; Pawłowska, M.; Parczewski, M.; Piekarska, A.; Simon, K.; Tomasiewicz, K.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D. Management of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Recommendations of the Polish Association of Epidemiologists and Infectiologists as of March 31, 2020. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Ślosarek, K.; Gądek, A.; Sroka, Ł.; Dolla, Ł.; Biały, A.; Radwan, M.; Bodusz, D.; Nachlik, M.; Rutkowski, T.; Jaroszewicz, J. Lung volume irradiation procedures in patients with pneumonia during COVID-19 infection—Physical aspects of treatment planning and dosimetry. Nowotwory J. Oncol. 2021, 71, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W.K.; Wu, A.K.L.; Ip, W.K.; Lee, N.L.S.; Chan, I.H.S.; Lit, L.C.W.; Hui, D.S.C.; Chan, M.H.M.; Chung, S.S.C.; et al. Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flisiak, R.; Rzymski, P.; Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Rogalska, M.; Rorat, M.; Czupryna, P.; Lorenc, B.; Ciechanowski, P.; Kozielewicz, D.; Piekarska, A.; et al. Demographic and Clinical Overview of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients during the First 17 Months of the Pandemic in Poland. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarębska-Michaluk, D.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Rogalska, M.; Martonik, D.; Pabjan, P.; Berkan-Kawińska, A.; Bolewska, B.; Oczko-Grzesik, B.; Kozielewicz, D.; Tudrujek-Zdunek, M.; et al. Effectiveness of Tocilizumab with and without Dexamethasone in Patients with Severe COVID-19: A Retrospective Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3359–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, R.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Rogalska, M.; Łapiński, T.; Berkan-Kawińska, A.; Bolewska, B.; Tudrujek-Zdunek, M.; Kozielewicz, D.; Rorat, M.; Leszczyński, P.; et al. Tocilizumab Improves the Prognosis of COVID-19 in Patients with High IL-6. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.; Kriesen, S.; Paape, D.; Hildebrandt, G.; Manda, K. Modulation of Inflammatory Reactions by Low-Dose Ionizing Radiation: Cytokine Release of Murine Endothelial Cells Is Dependent on Culture Conditions. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, N.E.; van Berkel, V.; Cai, L. COVID-19 and low-dose radiation therapy. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2021, 2, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.B.; Nasti, T.H.; Dhere, V.R.; Kleber, T.J.; Switchenko, J.M.; Buchwald, Z.S.; Stokes, W.A.; Weinberg, B.D.; Rouphael, N.; Steinberg, J.P.; et al. Immunomodulatory Low-Dose Whole-Lung Radiation for Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019-Related Pneumonia. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 15, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameri, A.; Ameri, P.; Rahnama, N.; Mokhtari, M.; Sedaghat, M.; Hadavand, F.; Bozorgmehr, R.; Haghighi, M.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Low-Dose Whole-Lung Irradiation for COVID-19 Pneumonia: Final Results of a Pilot Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmamed, N.; Alcantara, P.; Cerezo, E.; Gaztañaga, M.; Cabello, N.; Gómez, S.; Bustos, A.; Doval, A.; Corona, J.; Rodriguez, G.; et al. Low-Dose Radiation Therapy in the Management of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia (LOWRAD-Cov19): Preliminary Report. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.N.; Guleria, R.; Wig, N.; Mohan, A.; Rath, G.; Subramani, V.; Bhatnagar, S.; Mallick, S.; Sharma, A.; Patil, P.; et al. Low-dose radiation therapy for COVID-19 pneumonia: A pilot study. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, G.; Ponniah, S.; Sundaram, V.; Marimuthu, P.K.; Pitchaikannu, V.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Thangarasu, J.; Kannupaiyan, G.; Ramamoorthy, P.; Thangaraj, B.; et al. Whole lung irradiation as a novel treatment for COVID-19: Interim results of an ongoing phase 2 trial in India. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 163, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, M.; Vázquez, S.; García, E.; Visus, M.; Jové, D.; Ripol, O.; Solé, C.; Gutiérrez, L.; Morales-Rull, J.L.; Montero, Á.; et al. Saving time in the radiotherapy procedures for COVID-19 pneumonia treatment. A single-institution experience. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 2344–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristofilou, A.; Finazzi, T.; Blum, A.; Zehnder, T.; Zellweger, N.; Lustenberger, J.; Bauer, T.; Dott, C.; Avcu, Y.; Kohler, G.; et al. Low-Dose Radiation Therapy for Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized Double-Blind Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, H.; Shiri, I.; Bevelacqua, J.J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Rahmim, A.; Zaidi, H.; Mortazavi, S.A.R.; Mortazavi, S.M.J. Low Dose Radiation Therapy and Convalescent Plasma: How a Hybrid Method May Maximize Benefits for COVID-19 Patients. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2020, 10, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, A.; Adhikary, A.; Woloschak, G.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Papineni, R.V. A combinatorial approach of a polypharmacological adjuvant 2-deoxy-D-glucose with low dose radiation therapy to quell the cytokine storm in COVID-19 management. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Kong, Q.; Wang, G.; Jin, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, D.; Niu, C.; Han, W.; Li, W.; Cui, J. Low-dose ionizing radiation induces direct activation of natural killer cells and provides a novel approach for adoptive cellular immunotherapy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2014, 29, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevelacqua, J.J.; Mortazavi, S.A.R.; Mortazavi, S.M.J. Re: Low dose radiation therapy for COVID-19 pneumonia: Is there any supportive evidence? Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.P. Radiation and circulatory disease. Mutat. Res. Rev. 2016, 770, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.S.; Salotti, J.A.; Little, M.P.; McHugh, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.P.; Howe, N.L.; Ronckers, C.M.; Rajaraman, P.; Craft, A.W.; et al. Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumours: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2012, 380, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmacher, V. Less Can Be More: The Hormesis Theory of Stress Adaptation in the Global Biosphere and Its Implications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuttler, J.M. Remedy for radiation fear—Discard the politicized science. Dose Respons. 2014, 12, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworowski, Z. Radiation hormesis—A remedy for fear. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubiana, M.; Feinendegen, L.E.; Yang, C.; Kaminski, J.M. The linear no-threshold relationship is inconsistent with radiation biologic and experimental data. Radiology 2009, 251, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, K.R.; Kamprad, F. Estimation of cancer risks from radiotherapy of benign diseases. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2006, 182, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi-Moghadam, A.; Haghani, M.; Bevelacqua, J.J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Kaveh-Ahangar, A.; Mortazavi, S.M.J.; Mortazavi, S.A.R. SAR COVID-19 Tragic Pandemic: Concerns over Unintentional “Directed Accelerated Evolution” of Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and Introducing a Modified Treatment Method for ARDS. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2020, 10, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Gorman, E.; Millar, J.; McAuley, D.; O’Kane, C. Mesenchymal stromal cells for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and COVID-19 infection: Optimizing the therapeutic potential. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.J.; Cai, L. Induction of cell-proliferation hormesis and cell-survival adaptive response in mouse hematopoietic cells by whole-body low-dose radiation. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 53, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.J.; Harman, R.J.; Bunnell, B.A.; Schreiber, M.A.; Xiang, C.; Wang, F.S.; Santidrian, A.F.; Minev, B.R. Rationale for the clinical use of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for COVID-19 patients. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No | Age [yrs] | Gender (M/F) | BMI | Co-Morbidities | Symptoms Duration before LDRT | Co-Medications for COVID-19 | Baseline MEWS [Points] | The Lowest Sp02 [%], Days after LDRT. *—Oxygen Support | Duration of Hospitalization [Days] | Outcome, Day 28 | Outcome, Long-term Follow-Up | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | 1 | 3 | 7 | 14 | |||||||||||
| 1 | 49 | M | n/a | AH, DM | 10 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 88 * | 90 * | 94 * | 97 * | 92 | 20 | Released | Resolved |
| 2 | 62 | F | 26 | AH | 6 days | DEX, LMWH, RDV, FFP | 1 | 86 * | 89 * | 92 * | 95 * | 97 | 24 | Released | Resolved |
| 3 | 67 | M | 28 | AH, DM | 3 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 69 * | 87 * | 85 * | 84 * | 90 * | 28 | Released | Resolved |
| 4 | 70 | F | n/a | AH, dyslipidemia, stroke | 7 days | FFP, LMWH, DEX, RDV | 1 | 82 * | 84 * | 76 * | 85 * | 89 * | 28 | Released | Resolved |
| 5 | 78 | M | n/a | AH emphysema | 8 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 3 | 85 * | 86 * | 11 | Died | Died | |||
| 6 | 68 | M | 31 | AH | 8 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 78 * | 84 * | 6 | Died | Died | |||
| 7 | 69 | F | 39 | AH, DM | 9 days | LMWH | 1 | 85 * | 96 * | 95 * | 95 * | 95 | 24 | Released | Resolved |
| 8 | 61 | M | 31 | Acute kidney injury | 5 days | LMWH, DEX | 3 | 83 * | 88 * | 83 * | 83 * | 14 | Mechanical ventilation | Died | |
| 9 | 66 | F | 26 | AH, DM atrial fibrillation | 8 days | DEX, LMWH | 1 | 86 * | 90 * | 94 * | 86 | 15 | Released | Resolved | |
| 10 | 68 | M | 34 | AH, dyslipidemia, | 7 days | LMWH, DEX | 1 | 84 * | 60 * | 85 * | 85 * | 20 | Released | Resolved | |
| 11 | 65 | M | 35 | Hypothyroidism, CKD | 7 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 72 * | 80 * | 80 * | 7 | High flow | Lost to follow-up | ||
| 12 | 53 | F | 30 | AH, DM | 5 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 76 * | 80 * | 82 * | 77 * | 83 * | 23 | Released | Resolved |
| 13 | 56 | F | 31 | AH, DM, CKD, cardiomyopathy, pulmonary embolism | 5 days | RDV, LMWH, DEX | 1 | 81 * | 86 * | 95 * | 95 | 14 | Released | Resolved | |
| 14 | 53 | M | 35 | AH, DM, liver damage | 14 days | LMWH, DEX | 1 | 89 * | 96 * | 82 * | 95 * | 95 | 10 | Released | Resolved |
| 15 | 74 | M | 31 | AH, DM, UTI E. faecium VRE+ | 1 day | RDV, TCZ, DEX, LMWH | 1 | 87 * | 88 * | 92 * | 92 * | 91 * | 28 | Released | Resolved |
| Baseline | Day 1 | p | Day 3 | p | Day 5 | p | Day 7 | p | Day 14 | p | Friedman ANOVA P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp02 [%] | 84.5 (81.0–86.0) | 87.5 (84.0–90.0) | 0.016 | 92.0 (85.0–94.0) | 0.308 | 92.0 (90.0–94.0) | 0.463 | 89.0 (84.5–95.0) | 0.575 | 91.5 (89.5–95.0) | 0.249 | 0.007 |
| WBC [103/uL] | 7.3 (5.4–9.2) | 8.7 (8.1–9.4) | 0.028 | 8.4 (8.3–9.6) | 0.345 | 10.1 (8.1–13.0) | 0.463 | 7.8 (7.3–11.2) | 0.575 | 7.6 (5.8–9.9) | 0.036 | 0.702 |
| Neutrophils [103/uL] | 5.9 (4.6–7.9) | 7.4 (6.5–7.5) | 0.069 | 7.5 (7.1–10.2) | 0.180 | 8.6 (7.0–10.9) | n/a | 5.8 (5.3–8.7) | 0.285 | 4.5 (3.1–6.6) | 0.080 | n/a |
| Platelets [103/uL] | 225 (175–237) | 359 (290–288) | 0.003 | 354 (310–387) | 0.753 | 344 (297–467) | 0.465 | 285 (251–339) | 0.025 | 196 (163–257) | 0.017 | 0.214 |
| CRP [ng/mL] | 107.9 (91.2–161.5) | 51.4 (16.8–67.0) | 0.007 | 22.1 (13.3–68.2) | 0.017 | 9.3 (3.5–33.4) | 0.110 | 5.5 (2.2–10.7) | 0.018 | 1.9 (0.6–16.7) | 0.237 | <0.001 |
| IL-6 [pg/mL] | 98.7 (32.8–168.3) | 26.9 (14.4–63.0) | 0.006 | 15.8 (14.1–43.5) | 0.138 | 14.7 (5.8–113.0) | 0.500 | 12.2 (3.4–18.5) | 0.674 | 24.2 (5.6–53.9) | 0.080 | 0.119 |
| Fibrinogen [g/L] | 5.1 (4.6–5.8) | 3.6 (2.5–4.7) | 0.037 | 3.2 (2.7–4.7) | 0.018 | 2.8 (2.2–3.4) | 0.075 | 2.4 (1.8–3.0) | 0.028 | 2.7 (1.9–3.1) | 0.600 | 0.233 |
| D-dimer [ng/mL] | 561 (434–1351) | 890 (577–3054) | 0.075 | 2012 (819–3628) | 0.401 | 1028 (700–2027) | 0.093 | 1044 (596–2325) | 0.161 | 809 (470–1195) | 0.021 | 0.625 |
| LDH [U/L] | 660 (523–785) | 570 (419–875) | 0.203 | 547 (421-679) | 0.028 | 425 (349–626) | 0.028 | 364 (307–480) | 0.008 | 262 (247–378) | 0.028 | 0.017 |
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 2453 (912–2717) | 1128 (686–2456) | 0.249 | 1607 (390–2125) | 0.080 | 1106 (534–2251) | 1.000 | 797 (453–1992) | 0.267 | 720 (370–992) | 0.068 | n/a |
| ALT [IU/mL] | 34.3 (25.7–45.3) | 54.4 (27.6–76.2) | 0.041 | 75.9 (32.8–114.9) | 0.327 | 48.0 (25.0–76.9) | 0.889 | 45.7 (28.8–66.0) | 1.000 | 40.4 (36.1–59.0) | 0.674 | 0.924 |
| Bilirubin [umol/L] | 7.9 (6.5–10.6) | 7.2 (5.6–10.1) | 0.241 | 8.4 (4.4–9.9) | 0.600 | 8.7 (7.6–11.6) | 0.753 | 7.6 (5.3–11.4) | 0.735 | 8.8 (6.1–12.5) | 0.779 | 0.490 |
| Troponin T [ng/L] | 14 (9–26) | 16 (11–19) | 0.675 | 12 (9–16) | 0.345 | 13 (9–14) | 0.273 | 13 (9–16) | 0.059 | 16 (11–22) | 0.012 | 0.428 |
| eGFR [ml/min/1.73 m2] | 77.4 (63.8–84.8) | 85.6 (79.1–107.9) | 0.005 | 101.6 (89.0–110.8) | 0.018 | 98.7 (86.9–113.1) | 0.249 | 99.4 (89.1–110.5) | 0.173 | 103.4 (89.0–125.5) | 0.674 | 0.119 |
| Baseline | Day 7 | p | Day 14 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp02 [%] | 84.5 (81.0–86.0) | 89.0 (84.5–95.0) | 0.008 | 91.5 (89.5–95.0) | 0.018 |
| WBC [103/uL] | 7.3 (5.4–9.2) | 7.8 (7.3–11.2) | 0.214 | 7.61 (5.79–9.93) | 0.799 |
| Neutrophils [103/uL] | 5.9 (4.6–7.9) | 5.8 (5.3–8.7) | 0.866 | 4.49 (3.07–6.63) | 0.237 |
| Platelets [103/uL] | 225 (175–237) | 285 (251–339) | 0.374 | 195.5 (163.0–257.0) | 0.241 |
| CRP [ng/mL] | 107.9 (91.2–161.5) | 5.5 (2.2–10.7) | 0.008 | 1.91 (0.60–16.70) | 0.005 |
| IL-6 [pg/mL] | 98.7 (32.8–168.3) | 12.2 (3.4–18.5) | 0.028 | 24.2 (5.6–53.9) | 0.116 |
| Fibrinogen [g/L] | 5.1 (4.6–5.8) | 2.4 (1.8–3.0) | 0.028 | 2.7 (1.9–3.1) | 0.018 |
| D-dimer [ng/mL] | 561 (434–1351) | 1044 (596–2325) | 0.093 | 809.0 (469.7–1194.9) | 0.657 |
| LDH [U/L] | 660 (523–785) | 364 (307–480) | 0.008 | 262 (247–378) | 0.028 |
| Ferritin [ng/mL] | 2453 (912–2717) | 797 (453–1992) | 0.173 | 720.2 (369.7–992.1) | 0.043 |
| ALT [IU/mL] | 34.3 (25.7–45.3) | 45.7 (28.8–66.0) | 0.161 | 40.4 (36.1–59.0) | 0.037 |
| Bilirubin [umol/L] | 7.9 (6.5–10.6) | 7.6 (5.3–11.4) | 0.263 | 8.8 (6.1–12.5) | 1.000 |
| Tropnin T [ng/L] | 14 (9–26) | 13 (9–16) | 0.249 | 16.0 (11.0–22.0) | 0.753 |
| eGFR [mL/min/1.73 m2] | 77.4 (63.8–84.8) | 99.4 (89.1–110.5) | 0.005 | 103.4 (89.0–125.5) | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rutkowski, T.W.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Piotrowski, D.; Ślosarek, K.; Sobala-Szczygieł, B.; Słonina, D.; Włostowska, B.; Bodusz, D.; Piasecki, M.; Nachlik, M.; et al. Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Patients with Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Single-Institution Prospective Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030858
Rutkowski TW, Jaroszewicz J, Piotrowski D, Ślosarek K, Sobala-Szczygieł B, Słonina D, Włostowska B, Bodusz D, Piasecki M, Nachlik M, et al. Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Patients with Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Single-Institution Prospective Study. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030858
Chicago/Turabian StyleRutkowski, Tomasz Wojciech, Jerzy Jaroszewicz, Damian Piotrowski, Krzysztof Ślosarek, Barbara Sobala-Szczygieł, Dorota Słonina, Bożena Włostowska, Dawid Bodusz, Maciej Piasecki, Michał Nachlik, and et al. 2023. "Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Patients with Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Single-Institution Prospective Study" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030858
APA StyleRutkowski, T. W., Jaroszewicz, J., Piotrowski, D., Ślosarek, K., Sobala-Szczygieł, B., Słonina, D., Włostowska, B., Bodusz, D., Piasecki, M., Nachlik, M., Oczko-Grzesik, B., Gądek, A., Kowal, D., Rutkowski, R., Wojarska-Tręda, E., & Składowski, K. (2023). Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Patients with Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Single-Institution Prospective Study. Biomedicines, 11(3), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030858





