The Unmet Needs for Studying Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Using Animal Models
Abstract
1. The Implications of the Definitions and Terminologies of Chronic Pelvic and Visceral Pain
| IASP/EAU | ICS/ESSIC | |
|---|---|---|
| Endometriosis | Chronic secondary visceral pain syndrome | Chronic visceral pain |
| EPS | Chronic primary visceral pain—chronic primary pelvic pain syndrome | - |
| CPBPS/BPS | Chronic primary visceral pain | Chronic pelvic pain |
| Interstitial cystitis | - | Chronic pelvic pain |
2. The Implications of Symptom Identification in the Study of Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain
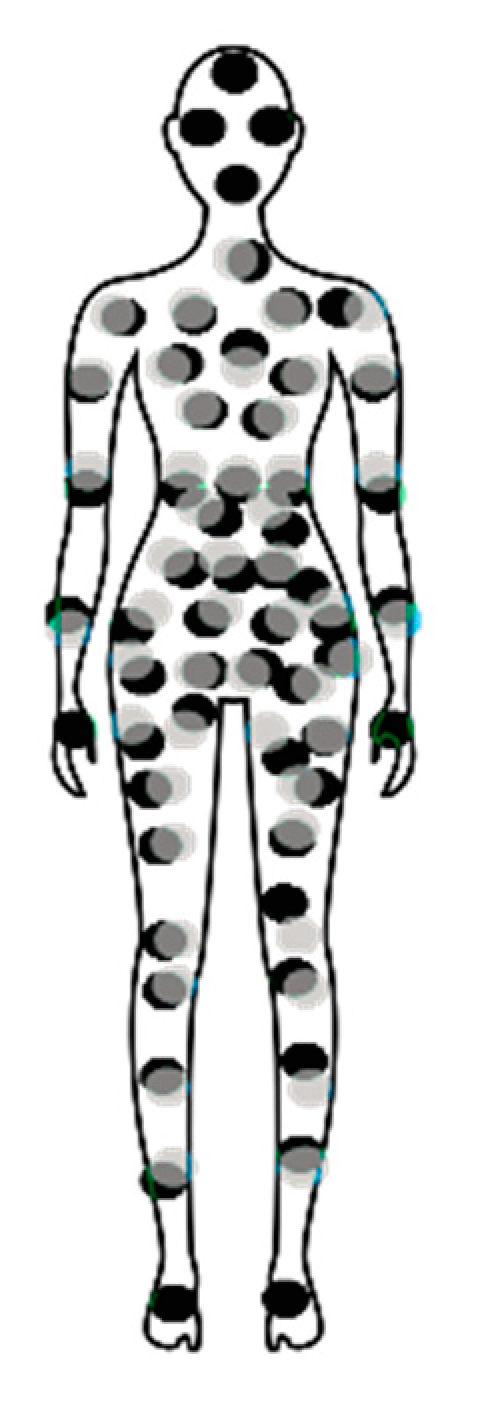
3. Back-translation of Patient Symptoms According to Their Associations with Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain
4. Systemic Symptoms Prompt Systemic Models for the Study of Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain
| Model | U | P | O | I | N | T | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrograde menstruation | + | [38] | |||||
| Autologous transplantation | + | + | + | + | + | [39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] | |
| Allogenic transplantation | + | [39] | |||||
| Autologous transplantation to the sciatic nerve | + | + | [64,65,66,67,68,69,70] | ||||
| Autologous transplantation to muscle | + | [71,72,73,74,75] | |||||
| Syngeneic transplantation | + | + | + | + | [76,77] | ||
| Xenograft transplantation | + | [78] | |||||
| Intraperitoneal injection of endometrial tissue | + | [79,80,81] | |||||
| Peritonitis | + | + | [82,83] | ||||
| Colonic instillation of TNBS | + | + | + | + | [84,85,86,87,88,89] | ||
| Uterine pain | + | [90] | |||||
| Autoimmune | + | + | + | + | [91,92,93,94,95,96] | ||
| Prostatic inflammation | + | + | + | [97,98,99,100] | |||
| Pseudorabies virus | + | + | + | + | [101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108] | ||
| Systemic administration of molecules | + | + | + | [109,110,111] | |||
| Restraint stress | + | + | + | [112,113,114,115] | |||
| Water avoidance stress | + | + | + | + | + | [116,117,118,119,120,121] | |
| Chronic variable stress | + | + | [122] | ||||
| Cold stress | + | [123,124] | |||||
| Social stress | + | + | + | [125,126,127] | |||
| Foot shock stress | + | + | + | [128,129] | |||
| Early-life stress by odor–shock conditioning | + | + | + | [130,131] | |||
| Early-life stress by neonatal maternal deprivation | + | + | + | + | [132,133,134] |
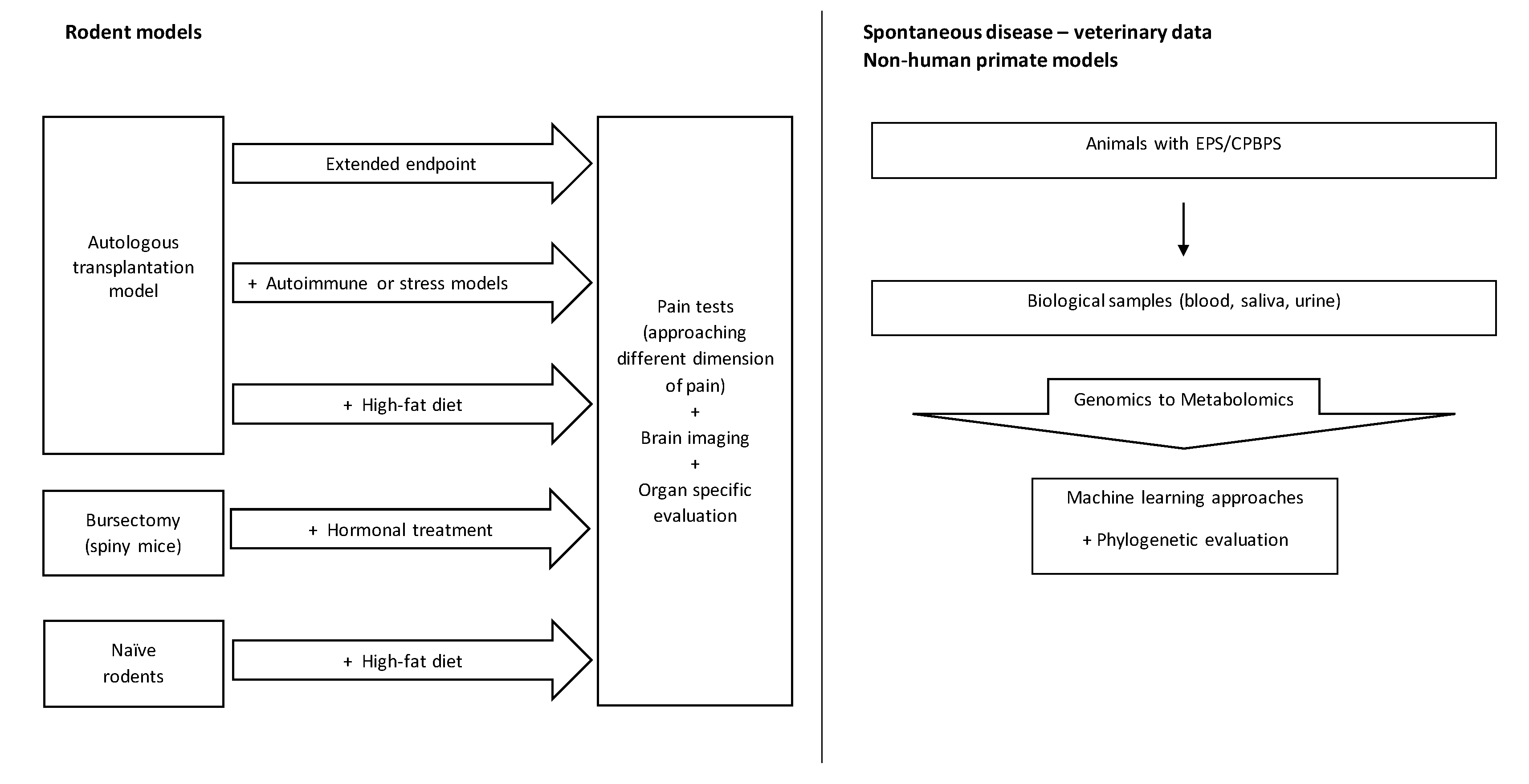
5. Going beyond the Existing Models to Study the Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Associated with EPS and CPBPS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholas, M.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Goebel, A.; et al. The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11: Chronic Primary Pain. Pain 2019, 160, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, Q.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Barke, A.; Korwisi, B.; Baranowski, A.P.; Wesselmann, U.; Rief, W.; Treede, R.D. The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11: Chronic Secondary Visceral Pain. Pain 2019, 160, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association for the Study of Pain. Classification of Chronic Pain, Second Edition (Revised); Merskey, H., Bogduk, N., Eds.; IASP Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, C.M.; Bokor, A.; Heikinheimo, O.; Horne, A.; Jansen, F.; Kiesel, L.; King, K.; Kvaskoff, M.; Nap, A.; Petersen, K.; et al. ESHRE Guideline: Endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Open 2022, 2022, hoac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Working Group of AAGL, ESGE, ESHRE and WES; Tomassetti, C.; Johnson, N.P.; Petrozza, J.; Abrao, M.S.; Einarsson, J.I.; Horne, A.W.; Lee, T.T.M.; Missmer, S.; Vermeulen, N.; et al. An International Terminology for Endometriosis, 2021. Hum. Reprod. Open 2021, 2021, hoab029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fall, M.; Baranowski, A.; Elneil, S.; Engeler, D.; Hughes, J.; Messelink, E.; Oberpenning, F.; de C Williams, A.; European Association of Urology. EAU Guidelines on Chronic Pelvic Pain. Eur. Urol. 2010, 57, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentin Clemens, J.; Erickson, D.R.; Varela, N.P.; Henry Lai, H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doggweiler, R.; Whitmore, K.E.; Meijlink, J.M.; Drake, M.J.; Frawley, H.; Nordling, J.; Hanno, P.; Fraser, M.O.; Homma, Y.; Garrido, G.; et al. A Standard for Terminology in Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndromes: A Report from the Chronic Pelvic Pain Working Group of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 984–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocjancic, E.; Chung, E.; Garzon, J.A.; Haylen, B.; Iacovelli, V.; Jaunarena, J.; Locke, J.; Millman, A.; Nahon, I.; Ohlander, S.; et al. International Continence Society (ICS) Report on the Terminology for Sexual Health in Men with Lower Urinary Tract (LUT) and Pelvic Floor (PF) Dysfunction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2022, 41, 140–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria, Classification, and Nomenclature for Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: An ESSIC Proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripp, D.A.; Nickel, J.C.; Wong, J.; Pontari, M.; Moldwin, R.; Mayer, R.; Carr, L.K.; Doggweiler, R.; Yang, C.C.; Mishra, N.; et al. Mapping of Pain Phenotypes in Female Patients with Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis and Controls. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schliep, K.C.; Mumford, S.L.; Peterson, C.M.; Chen, Z.; Johnstone, E.B.; Sharp, H.T.; Stanford, J.B.; Hammoud, A.O.; Sun, L.; Buck Louis, G.M. Pain Typology and Incident Endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Hsu, J.-W.; Huang, K.-L.; Bai, Y.-M.; Su, T.-P.; Li, C.-T.; Yang, A.C.; Chang, W.-H.; Chen, T.-J.; Tsai, S.-J.; et al. Risk of Developing Major Depression and Anxiety Disorders among Women with Endometriosis: A Longitudinal Follow-up Study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 190, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.J.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lin, H.-C. Comorbidities of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Population-BasedStudy. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E903–E909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.J.; Liu, S.P.; Lin, H.C. A Case-Control Study on the Association between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2013, 32, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, H.C.; Frawley, H.C.; Donoghue, J.F.; Readman, E.; Healey, M.; Ellett, L.; Reddington, C.; Hicks, L.J.; Harlow, K.; Rogers, P.A.W.; et al. Peripheral, Central, and Cross Sensitization in Endometriosis-Associated Pain and Comorbid Pain Syndromes. Front. Reprod. Health 2021, 3, 729642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As-Sanie, S.; Harris, R.E.; Napadow, V.; Kim, J.; Neshewat, G.; Kairys, A.; Williams, D.; Clauw, D.J.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T. Changes in Regional Gray Matter Volume in Women with Chronic Pelvic Pain: AVoxel-Based Morphometry Study. Pain 2012, 153, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As-Sanie, S.; Kim, J.; Schmidt-Wilcke, T.; Sundgren, P.C.; Clauw, D.J.; Napadow, V.; Harris, R.E. Functional Connectivity Is Associated With Altered Brain Chemistry in Women with Endometriosis-Associated Chronic Pelvic Pain. J. Pain 2016, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinhans, N.M.; Yang, C.C.; Strachan, E.D.; Buchwald, D.S.; Maravilla, K.R. Alterations in Connectivity on Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Provocation of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A MAPP Research Network Feasibility Study of Urological Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndromes. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, L.A.; Kutch, J.J.; Tillisch, K.; Naliboff, B.D.; Labus, J.S.; Jiang, Z.; Farmer, M.A.; Apkarian, A.V.; Mackey, S.; Martucci, K.T.; et al. Alterations in Resting State Oscillations and Connectivity in Sensory and Motor Networks in Women with Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twiss, C.; Kilpatrick, L.; Craske, M.; Buffington, C.A.T.; Ornitz, E.; Rodríguez, L.V.; Mayer, E.A.; Naliboff, B.D. Increased Startle Responses in Interstitial Cystitis: Evidence for Central Hyperresponsiveness to Visceral Related Threat. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgendorf, S.K.; Kreder, K.J.; Rothrock, N.E.; Hoffman, A.; Kirschbaum, C.; Sternberg, E.M.; Bridget Zimmerman, M.; Ratliff, T.L. Diurnal Cortisol Variations and Symptoms in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, K.; Warnaby, C.; Stagg, C.J.; Moore, J.; Kennedy, S.; Tracey, I. Dysmenorrhoea Is Associated with Central Changes in Otherwise Healthy Women. Pain 2011, 152, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de França Moreira, M.; Gamboa, O.L.; Pinho Oliveira, M.A. Association between Severity of Pain, Perceived Stress and Vagally-Mediated Heart Rate Variability in Women with Endometriosis. Women Health 2021, 61, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrua, A.; Pinto, R.; Taylor, A.; Canelas, A.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; Cruz, C.D.; Birder, L.A.; Cruz, F. Can the Adrenergic System Be Implicated in the Pathophysiology of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis? A Clinical and Experimental Study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2015, 34, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.C.; Shoskes, D.; Irvine-Bird, K. Clinical Phenotyping of Women with Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome: AKey to Classification and Potentially Improved Management. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, M.B.; Irvine-Bird, K.; Curtis Nickel, J. Multiple Sensitivity Phenotype in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2014, 8, E758–E761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Su, M.; Zhan, H.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, X. Adding a Sexual Dysfunction Domain to UPOINT System Improves Association withSymptoms in Women with Interstitial Cystitis and Bladder Pain Syndrome. Urology 2014, 84, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartha, G.K.; Kerr, H.; Shoskes, D.A. Clinical Phenotyping of Urologic Pain Patients. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2013, 23, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.H.; Thu, J.H.L.; Moh, F.V.; Paradis, A.; Vetter, J. Clustering of Patients with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome and ChronicProstatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhat, C.; Vang, N.; Tanaka, P.P.; Nezhat, C. Optimal Management of Endometriosis and Pain. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 134, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, P.; Berkley, K.J. Chronic Pelvic Pain and Endometriosis: Translational Evidence of the Relationship and Implications. Hum. Reprod. Update 2011, 17, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, J.; Hawe, J.; Hunter, D.; Holmes, M.; Finn, P.; Garry, R. Laparoscopic Excision of Endometriosis: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Fertil. Steril. 2004, 82, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urothelial Dysfunction and Chronic Inflammation Are Associated With Increased Bladder Sensation in Patients With Chronic Renal Insufficiency. Int. Neurourol. J. 2018, 22, S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birder, L.; Andersson, K.E. Urothelial Signaling. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 653–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez-Badinez, P.; de Leo, B.; Laux-Biehlmann, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Zollner, T.M.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Simitsidellis, I.; Charrua, A.; Cruz, F.; Gomez, R.; et al. Preclinical Models of Endometriosis and Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: An Innovative Medicines Initiative-PainCare Initiative to Improve Their Value for Translational Research in Pelvic Pain. Pain 2021, 162, 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoons, E.; de Clercq, K.; van den Eynde, C.; Pinto, S.J.P.C.; Luyten, K.; van Bree, R.; Tomassetti, C.; Voets, T.; Vriens, J. Mimicking Sampson’s Retrograde Menstrual Theory in Rats: A New Rat Model forOngoing Endometriosis-Associated Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aken, M.A.; Groothuis, P.G.; Panagiotou, M.; van Duin, M.; Nap, A.W.; van Rijn, T.C.; Kozicz, T.; Braat, D.D.; Peeters, A.B. An Objective and Automated Method for Evaluating Abdominal Hyperalgesia in a RatModel for Endometriosis. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.-H.; Zou, G.; Ding, S.-J.; Li, T.-T.; Zhu, L.-B.; Wang, J.-Z.; Yao, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.-M. Mast Cell Stabilizer Ketotifen Reduces Hyperalgesia in a Rodent Model ofSurgically Induced Endometriosis. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.E.X.G.; Medeiros, F.d.C.; Rocha, H.A.L.; Silva, K.S.D. Effects of Omega-6/3 and Omega-9/6 Nutraceuticals on Pain and Fertility inPeritoneal Endometriosis in Rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2019, 34, e201900405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.J.; Neagoe, I.; Bräuer, N.; Koch, M.; Rotgeri, A.; Nagel, J.; Laux-Biehlmann, A.; Machet, F.; Coelho, A.-M.; Boyce, S.; et al. Eliapixant Is a Selective P2X3 Receptor Antagonist for the Treatmentof Disorders Associated with Hypersensitive Nerve Fibers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, Z.K.; Taherianfard, M.; Naderi, M.M.; Ferrero, H. Possible Therapeutic Effect of Royal Jelly on Endometriotic Lesion Size, PainSensitivity, and Neurotrophic Factors in a Rat Model of Endometriosis. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.; Maddern, J.; Grundy, L.; Manavis, J.; Harrington, A.M.; Schober, G.; Brierley, S.M. A Mouse Model of Endometriosis That Displays Vaginal, Colon, Cutaneous, andBladder Sensory Comorbidities. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, S.; Cruz, M.L.; Torres-Reveron, A.; Appleyard, C.B. Impact of Physical Activity on Pain Perception in an Animal Model ofEndometriosis. J. Endometr. Pelvic. Pain Disord. 2015, 7, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, M.L.; Bonocher, C.M.; Meola, J.; Portella, R.L.; Ribeiro-Silva, A.; Brunaldi, M.O.; Ferriani, R.A.; Rosa-E-Silva, J.C. Effect of Physical Exercise on Endometriosis Experimentally Induced in Rats. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, S.; Cruz, M.L.; Seguinot, I.I.; Torres-Reveron, A.; Appleyard, C.B. Impact of Psychological Stress on Pain Perception in an Animal Model ofEndometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingwei, C.; Huilan, D.; Ruixiao, T.; Hua, Y.; Huirong, M. Effect of Bushenwenyanghuayu Decoction on Nerve Growth Factor andBradykinin/Bradykinin B1 Receptor in a Endometriosis Dysmenorrhea Mouse Model. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 35, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuvone, T.; Affaitati, G.; de Filippis, D.; Lopopolo, M.; Grassia, G.; Lapenna, D.; Negro, L.; Costantini, R.; Vaia, M.; Cipollone, F.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide Reduces Viscerovisceral Hyperalgesia in aRat Model of Endometriosis plus Ureteral Calculosis: Role of Mast Cells. Pain 2016, 157, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, F.; Li, X.; Bao, M.; Yang, N.; Shi, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Guan, Y.; et al. Upregulation of A2δ-1 Calcium Channel Subunit in the Spinal Cord Contributes toPelvic Organ Cross-Sensitization in a Rat Model of Experimentally-Induced Endometriosis. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, F.; Bao, M.; Li, X.; Chao, Y.; Lin, C.; Guo, R.; Zhang, C.; Wu, A.; Yue, Y.; et al. Activation of P38 MAPK in the Rostral Ventromedial Medulla by Visceral NoxiousInputs Transmitted via the Dorsal Columns May Contribute to Pelvic Organ Cross-Sensitization in Rats with Endometriosis. Neuroscience 2015, 291, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, N.; Suess, G.; Shirley, R. Resolvins RvD1 and 17(R)-RvD1 Alleviate Signs of Inflammation in a Rat Model ofEndometriosis. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, H.G.; Erbas, O.; Pala, E.E.; Artunc Ulkumen, B.; Akman, L.; Akman, T.; Oltulu, F.; Yavasoglu, A. The Effects of Sunitinib on Endometriosis. J. Obs. Gynaecol. 2015, 35, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsek, Y.; Gul, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Ozerol, I.H.; Ozerol, E.; Parlakpinar, H. Atorvastatin Exerts Anti-Nociceptive Activity and Decreases Serum Levels ofHigh-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in a Rat Endometriosis Model. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2014, 290, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopopolo, M.; Affaitati, G.; Fabrizio, A.; Massimini, F.; Lapenna, D.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Costantini, R. Effects of Tramadol on Viscero-Visceral Hyperalgesia in a Rat Model ofEndometriosis plus Ureteral Calculosis. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2014, 28, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, S.L.; McGinty, K.A.; Resuehr, D.; Berkley, K.J. Endometriosis-Induced Vaginal Hyperalgesia in the Rat: Role of the EctopicGrowths and Their Innervation. Pain 2009, 147, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, X.; Zhen, X.; Guo, S.-W. Levo-Tetrahydropalmatine Retards the Growth of Ectopic Endometrial Implants andAlleviates Generalized Hyperalgesia in Experimentally Induced Endometriosis in Rats. Reprod. Sci 2011, 18, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, S.-W. Trichostatin A, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Reduces Lesion Growth andHyperalgesia in Experimentally Induced Endometriosis in Mice. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagabukuro, H.; Berkley, K.J. Influence of Endometriosis on Visceromotor and Cardiovascular Responses Inducedby Vaginal Distention in the Rat. Pain 2007, 132 (Suppl. S1), S96–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cason, A.M.; Samuelsen, C.L.; Berkley, K.J. Estrous Changes in Vaginal Nociception in a Rat Model of Endometriosis. Horm. Behav. 2003, 44, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamberardino, M.A.; Berkley, K.J.; Affaitati, G.; Lerza, R.; Centurione, L.; Lapenna, D.; Vecchiet, L. Influence of Endometriosis on Pain Behaviors and Muscle Hyperalgesia Induced by aUreteral Calculosis in Female Rats. Pain 2002, 95, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, P.W.L.L.; Chaves Filho, A.J.M.; Vieira, C.F.X.; Oliveira, T.d.Q.; Soares, M.V.R.; Jucá, P.M.; Quevedo, J.; Barichello, T.; Macedo, D.; das Chagas Medeiros, F. Peritoneal Endometriosis Induces Time-Related Depressive- and Anxiety-likeAlterations in Female Rats: Involvement of Hippoca.ampal pro-Oxidative and BDNF Alterations. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, S.L.; Dmitrieva, N.; Berkley, K.J. Sprouted Innervation into Uterine Transplants Contributes to the Development ofHyperalgesia in a Rat Model of Endometriosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Qiu, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.-M. Fractalkine/CX3CR1 Contributes to Endometriosis-Induced Neuropathic Pain andMechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Lu, X.; Jiang, J. Effects of Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway on the Pain of SciaticEndometriosis in a Rat Model. Can. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2019, 97, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.-W. Valproic Acid and Progestin Inhibit Lesion Growth and Reduce Hyperalgesia inExperimentally Induced Endometriosis in Rats. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 19, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Meng, J.; Qin, X.; Jiang, J. Anti-Nociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Sulforaphane on SciaticEndometriosis in a Rat Model. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 723, 134858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Franklin, N.S.; Gonzalez-Cano, R.; Peterse, D.; Ghalali, A.; Madrian, E.; Verri, W.A.J.; Andrews, N.; Woolf, C.J.; Rogers, M.S. Nonsurgical Mouse Model of Endometriosis-Associated Pain That Responds toClinically Active Drugs. Pain 2020, 161, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, G.M. A Model for Radiating Leg Pain of Endometriosis. J. Bodyw. Mov. 2016, 20, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, W.; Strong, J.A.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.-M. Sciatic Endometriosis Induces Mechanical Hypersensitivity, Segmental NerveDamage, and Robust Local Inflammation in Rats. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Cui, H.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C. Suppression of TLR4-MyD88 Signaling Pathway Attenuated Chronic Mechanical Pain ina Rat Model of Endometriosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. Screening the Role of Pronociceptive Molecules in a Rodent Model of EndometriosisPain. J. Pain 2014, 15, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Giudice, L.C.; Levine, J.D. Impact of Surgical Excision of Lesions on Pain in a Rat Model of Endometriosis. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Bogen, O.; Chen, X.; Giudice, L.C.; Levine, J.D. Ectopic Endometrium-Derived Leptin Produces Estrogen-Dependent Chronic Pain in aRat Model of Endometriosis. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Chen, X.; Hendrich, J.; Irwin, J.C.; Green, P.G.; Giudice, L.C.; Levine, J.D. Ectopic Uterine Tissue as a Chronic Pain Generator. Neuroscience 2012, 225, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddern, J.; Grundy, L.; Harrington, A.; Schober, G.; Castro, J.; Brierley, S.M. A Syngeneic Inoculation Mouse Model of Endometriosis That Develops MultipleComorbid Visceral and Cutaneous Pain like Behaviours. Pain 2021, 163, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, E.; Horne, A.W.; Jerina, H.; Mikolajczak, M.; Hilferty, L.; Mitchell, R.; Fleetwood-Walker, S.M.; Saunders, P.T.K. EP2 Receptor Antagonism Reduces Peripheral and Central Hyperalgesia in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Endometriosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosh, J.A.; Lee, J.; Balasubbramanian, D.; Stanley, J.A.; Long, C.R.; Meagher, M.W.; Osteen, K.G.; Bruner-Tran, K.L.; Burghardt, R.C.; Starzinski-Powitz, A.; et al. Molecular and Preclinical Basis to Inhibit PGE2 Receptors EP2 and EP4 as a NovelNonsteroidal Therapy for Endometriosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9716–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.N.; Beckett, E.A.H.; Evans, S.F.; Hutchinson, M.R. Spinal Glial Adaptations Occur in a Minimally Invasive Mouse Model ofEndometriosis: Potential Implications for Lesion Etiology and Persistent Pelvic Pain. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shao, X. Nobiletin Alleviates Endometriosis via Down-Regulating NF-ΚB Activity inEndometriosis Mouse Model. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Xuan, Y.; Luo, Z.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ren, N.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, X. Increased Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 in Endometriosis andIts Correlation with Endometriosis-Related Dysmenorrhea and Recurrence. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2015, 184, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laux-Biehlmann, A.; Boyken, J.; Dahllöf, H.; Schmidt, N.; Zollner, T.M.; Nagel, J. Dynamic Weight Bearing as a Non-Reflexive Method for the Measurement of AbdominalPain in Mice. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruen, M.; Laux-Biehlmann, A.; Zollner, T.M.; Nagel, J. Use of Dynamic Weight Bearing as a Novel End-Point for the Assessment ofAbdominal Pain in the LPS-Induced Peritonitis Model in the Rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 232, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Ustinova, E.E.; Patnam, R.; Fraser, M.O.; Gutkin, D.W.; Pezzone, M.A. Enhanced Expression of Mast Cell Growth Factor and Mast Cell Activation in the Bladder Following the Resolution of Trinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid (TNBS) Colitis in Female Rats. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2007, 26, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamorita, N.; Yoshikawa, S.; Kashyap, M.; Tyagi, P.; Arai, Y.; Chancellor, M.B.; Yoshimura, N. Liposome Based Intravesical Therapy Targeting Nerve Growth Factor Ameliorates Bladder Hypersensitivity in Rats with Experimental Colitis. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustinova, E.E.; Gutkin, D.W.; Pezzone, M.A. Sensitization of Pelvic Nerve Afferents and Mast Cell Infiltration in the Urinary Bladder Following Chronic Colonic Irritation Is Mediated by Neuropeptides. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F123–F130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Yi, S.; Xu, J. Inhibition of CXCR4 in Spinal Cord and DRG with AMD3100 Attenuates Colon-Bladder Cross-Organ Sensitization. Drug. Des. Devel. 2022, 16, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzone, M.A.; Liang, R.; Fraser, M.O. A Model of Neural Cross-Talk and Irritation in the Pelvis: Implications for the Overlap of Chronic Pelvic Pain Disorders. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, L.; Harrington, A.M.; Castro, J.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Deiteren, A.; Maddern, J.; Rychkov, G.Y.; Ge, P.; Peters, S.; Feil, R.; et al. Chronic Linaclotide Treatment Reduces Colitis-Induced Neuroplasticity and Reverses Persistent Bladder Dysfunction. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Micevych, P.; McDonald, J.; Rapkin, A.; Chaban, V. Inflammation in the Uterus Induces Phosphorylated Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase and Substance P Immunoreactivity in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Innervating Both Uterus and Colon in Rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.W.; Liu, B.K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Shao, Y. Establishment of a Novel Autoimmune Experimental Model of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis in C57BL/6 Mice. Inflammation 2017, 40, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, Y.; Yao, J.R.; Kreder, K.J.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Lyu, D.; Maeda, D.; Kume, H.; Homma, Y.; Luo, Y. Autoimmunity to Urothelial Antigen Causes Bladder Inflammation, Pelvic Pain, and Voiding Dysfunction: A Novel Animal Model for Hunner-Type Interstitial Cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2021, 320, F174–F182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.K.; Jin, X.W.; Lu, H.Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Shao, Y. The Effects of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist in an Experimental Autoimmune Cystitis Model Resembling Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. Inflammation 2019, 42, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izgi, K.; Altuntas, C.Z.; Bicer, F.; Ozer, A.; Sakalar, C.; Li, X.; Tuohy, V.K.; Daneshgari, F. Uroplakin Peptide-Specific Autoimmunity Initiates Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.; Becich, M.J.; Klutke, C.G.; Ratliff, T.L. Experimental Autoimmune Cystitis: A Potential Murine Model for Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis. J. Urol. 1992, 148, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, W.; O’Donnell, M.; Lutgendorf, S.; Bradley, C.; Schrepf, A.; Liu, L.; Kreder, K.; Luo, Y. Evidence for the Role of Mast Cells in Cystitis-Associated Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Study of Chronic Pelvic Pain Research Network Animal Model Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, O.; Gocun, P.U.; Aronsson, P.; Carlsson, T.; Winder, M. Cross-Organ Sensitization between the Prostate and Bladder in an Experimental Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, E.S.; La, J.H.; Young, E.E.; Feng, B.; Joyce, S.; Gebhart, G.F. Chronic Prostatitis Induces Bladder Hypersensitivity and Sensitizes Bladder Afferents in the Mouse. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Mizoguchi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takaoka, E.; Ni, J.; Wang, Z.; DeFranco, D.B.; de Groat, W.C.; Tyagi, P.; et al. Bladder Overactivity and Afferent Hyperexcitability Induced by Prostate-to-Bladder Cross-Sensitization in Rats with Prostatic Inflammation. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2063–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, S.; Wolf-Johnson, A.S.; Suzuki, T.; Takaoka, E.; DeFranco, D.B.; Wang, Z.; A. Birder, L.; Yoshimura, N. MP45-06 Bladder Urothelial and Afferent Dysfunctions Underlying Bladder Overactivity in Rats with Chemically Induced Prostatic Inflammation. J. Urol. 2018, 199, e599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin, L.; Janni, G.; Manz, H.J.; Rabkin, S.D. Activation of CNS Circuits Producing a Neurogenic Cystitis: Evidence for Centrally Induced Peripheral Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 10016–10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Mudge, C.S.; Klumpp, D.J. Urothelial Lesion Formation Is Mediated by TNFR1 during Neurogenic Cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2006, 291, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Keshavan, P.; Gregory, G.D.; Klumpp, D.J. RANTES Mediates TNF-Dependent Lamina Propria Mast Cell Accumulation and Barrier Dysfunction in Neurogenic Cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasmin, L.; Janni, G.; Ohara, P.T.; Rabkin, S.D. CNS Induced Neurogenic Cystitis Is Associated with Bladder Mast Cell Degranulation in the Rat. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Rudick, C.N.; Hoxha, E.; Allsop, S.A.; Dimitrakoff, J.D.; Klumpp, D.J. Ca 2 /Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II Is Associated with Pelvic Pain of Neurogenic Cystitis. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yaggie, R.E.; Jiang, M.C.; Rudick, C.N.; Done, J.; Heckman, C.J.; Rosen, J.M.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Klumpp, D.J. Acyloxyacyl Hydrolase Modulates Pelvic Pain Severity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 314, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, C.N.; Bryce, P.J.; Guichelaar, L.A.; Berry, R.E.; Klumpp, D.J. Mast Cell-Derived Histamine Mediates Cystitis Pain. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudick, C.N.; Chen, M.C.; Mongiu, A.K.; Klumpp, D.J. Organ Cross Talk Modulates Pelvic Pain. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R1191–R1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, R.; Füllhase, C.; Santos, C.; Andersson, K.E. Development of Bladder Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Dopaminergic Brain Lesion. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, N.; Kuno, S.; Chancellor, M.B.; de Groat, W.C.; Seki, S. Dopaminergic Mechanisms Underlying Bladder Hyperactivity in Rats with a Unilateral 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) Lesion of the Nigrostriatal Pathway. Br. J. Pharm. 2003, 139, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, R.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Coelho, A.; Ferreira, S.; Silva, C.; Igawa, Y.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. Bladder Pain Induced by Prolonged Peripheral Alpha 1A Adrenoceptor Stimulation Involves the Enhancement of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Activity and an Increase of Urothelial Adenosine Triphosphate Release. Acta Physiol. 2016, 218, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Mitsui, T.; Tsuchiya, S.; Kanda, M.; Kira, S.; Nakagomi, H.; Sawada, N.; Kamiyama, M.; Shigetomi, E.; et al. Intermittent Restraint Stress Induces Circadian Misalignment in the Mouse Bladder, Leading to Nocturia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercan, F.; Şan, T.; Çavdar, S. The Effects of Cold-Restraint Stress on Urinary Bladder Wall Compared with Interstitial Cystitis Morphology. Urol. Res. 1999, 27, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, F.; Çetinel, Ş.; Erin, N.; Aydin, H.; Hürdaǧ, C.; Parker, T.; Parker, K.; Mayhew, T. Volume of Nerve Fibers in the Stress-Induced Bladder of Adult Rats Following Capsaicin Treatment. Urol. Int. 2003, 71, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Boucher, W.; Kempuraj, D.; Donelan, J.M.; Theoharides, T.C. Acute Stress and Intravesical Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Induces Mast Cell Dependent Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Release From Mouse Bladder Explants. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.; Serrão, P.; Rodriguez, L.; Birder, L.A.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. The Water Avoidance Stress Induces Bladder Pain Due to a Prolonged Alpha1A Adrenoceptor Stimulation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharm. 2017, 390, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinel, Ş.; Ercan, F.; Çikler, E.; Contuk, G.; Şener, G. Protective Effect of Melatonin on Water Avoidance Stress Induced Degeneration of the Bladder. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.L.; Leung, J.; Kun, S.; Zhang, R.; Karagiannides, I.; Raz, S.; Lee, U.; Glovatscka, V.; Pothoulakis, C.; Bradesi, S.; et al. The Effects of Acute and Chronic Psychological Stress on Bladder Function in a Rodent Model. Urology 2011, 78, 967.e1-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.; Serrão, P.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. Effect of Water Avoidance Stress on Serum and Urinary NGF Levels in Rats: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications for BPS/IC Patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.J.; Ackerman, A.L.; Wu, A.; Zhang, R.; Leung, J.; Bradesi, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Rodríguez, L.V. Chronic Psychological Stress in High-Anxiety Rats Induces Sustained Bladder Hyperalgesia. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlam, B.; Çikler, E.; Zeybek, A.; Çetinel, Ş.; Şener, G.; Ercan, F. An Aqueous Garlic Extract Alleviates Water Avoidance Stress-Induced Degeneration of the Urinary Bladder. BJU Int. 2006, 98, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, M.Y. Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Chronic Variable Stress in Rats. LUTS Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2015, 7, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Ishizuka, O.; Nishizawa, O. Cold Stress Induces Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, T.; Ishizuka, O.; Aizawa, N.; Zhong, C.; Ogawa, T.; Nakayama, T.; Tanabe, T.; Nishizawa, O. Cold Environmental Stress Induces Detrusor Overactivity via Resiniferatoxin-Sensitive Nerves in Conscious Rats. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2008, 27, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingin, G.C.; Peterson, A.; Erickson, C.S.; Nelson, M.T.; Vizzard, M.A. Social Stress Induces Changes in Urinary Bladder Function, Bladder NGF Content, and Generalized Bladder Inflammation in Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R893–R900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingin, G.C.; Heppner, T.J.; Tykocki, N.R.; Erickson, C.S.; Vizzard, M.A.; Nelson, M.T. Social Stress in Mice Induces Urinary Bladder Overactivity and Increases TRPV 1 Channel-Dependent Afferent Nerve Activity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol 2015, 309, R629–R638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.K.; Baez, M.A.; Bhatnagar, S.; Valentino, R.J. Social Stress-Induced Bladder Dysfunction: Potential Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor. Am. J. Physiol Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.Y.; Yang, X.; Wright, D.E.; Christianson, J.A.; Christianson, J. Foot Shock Stress Generates Persistent Widespread Hypersensitivity and Anhedonic Behavior in an Anxiety-Prone Strain of Mice. Pain 2020, 161, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, M.T.; Ness, T.J. Footshock-Induced Urinary Bladder Hypersensitivity: Role of Spinal Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptors. J. Pain 2008, 9, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligon, C.; Mohammadi, E.; Ge, P.; Hannig, G.; Higgins, C.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. Linaclotide Inhibits Colonic and Urinary Bladder Hypersensitivity in Adult Female Rats Following Unpredictable Neonatal Stress. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloner, A.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. Sexually Dimorphic Effects of Unpredictable Early Life Adversity on Visceral Pain Behavior in a Rodent Model. J. Pain 2013, 14, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, R.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. MP29-03 Childhood Stressful Events Induce Chronic Bladder Pain in Adulthood through a TRPV1 Dependent Mechanism. J. Urol. 2017, 197, e380–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, I.M.; Pierce, A.N.; di Silvestro, E.R.; Maloney, M.O.; Christianson, J.A. Differential Influence of Early Life and Adult Stress on Urogenital Sensitivity and Function in Male Mice. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.N.; Eller-Smith, O.C.; Christianson, J.A. Voluntary Wheel Running Attenuates Urinary Bladder Hypersensitivity and Dysfunction Following Neonatal Maternal Separation in Female Mice. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.A.; Pearson, A.M.; Slack, J.L.; Por, E.D.; Scribner, A.N.; Eti, N.A.; Burney, R.O. Endometriosis in the Mouse: Challenges and Progress Toward a ‘Best Fit’ Murine Model. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 806574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Nakamura, T.; Motooka, Y.; Ito, F.; Jiang, L.; Akatsuka, S.; Iwase, A.; Kajiyama, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Toyokuni, S. Novel Ovarian Endometriosis Model Causes Infertility via Iron-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Mice. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Jia, S.; Guo, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, A.; Xie, W.; Sun, G.; Leng, J.; Lang, J. Central Sensitization-Related Changes in Brain Function Activity in a Rat Endometriosis-Associated Pain Model. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Mamillapalli, R.; Ding, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, Z.W.; Gao, X.B.; Taylor, H.S. Endometriosis Alters Brain Electrophysiology, Gene Expression and Increases Pain Sensitization, Anxiety, and Depression in Female Mice. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogil, J.S. The History of Pain Measurement in Humans and Animals. Front. Pain Res. 2022, 3, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Antúnez Muñoz, C.; Nunez-Badinez, P.; de Leo, B.; Saunders, P.; Vincent, K.; Cano, A.; Nagel, J.; Gómez, R. Rodent Animal Models of Endometriosis-Associated Pain: Unmet Needs and Resources Available for Improving Translational Research in Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Chaloner, A.; Sawalha, A.H.; Greenwood Van-Meerveld, B. Importance of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Visceral Pain Induced by Chronic Water Avoidance Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, S.V.; Plotsky, P.M.; Sablad, M.; Miller, J.C.; Zhou, H.; Bayati, A.I.; McRoberts, J.A.; Mayer, E.A. Neonatal Maternal Separation Alters Stress-Induced Responses to Viscerosomatic Nociceptive Stimuli in Rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G307–G316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.-W. Early Maternal Separation Accelerates the Progression of Endometriosis in AdultMice. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2020, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, I.M.; Pierce, A.N.; O’neil, P.T.; Christianson, J.A. Assessment of Perigenital Sensitivity and Prostatic Mast Cell Activation in a Mouse Model of Neonatal Maternal Separation. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 2015, e53181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, I.M.; Jones, B.M.; Brake, A.D.; Pierce, A.N.; Eller, O.C.; Supple, R.M.; Wright, D.E.; Christianson, J.A. Voluntary Wheel Running Improves Outcomes in an Early Life Stress-Induced Model of Urologic Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome in Male Mice. Pain 2021, 162, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, K.N.; Beckett, E.A.H.; Evans, S.F.; Grace, P.M.; Watkins, L.R.; Hutchinson, M.R. Glial Contributions to Visceral Pain: Implications for Disease Etiology and the Female Predominance of Persistent Pain. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, H.M.; Lombardini, E.D.; Caudell, D.L.; Appt, S.E.; Dubois, A.; Cline, J.M. Decidualization of Endometriosis in Macaques. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto-Kakiuchi, A.; Netsu, S.; Matsuo, S.; Hayashi, S.; Ito, T.; Okabayashi, S.; Yasmin, L.; Yuzawa, K.; Kondoh, O.; Kato, A.; et al. Characteristics of Histologically Confirmed Endometriosis in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 2352–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakayama, M.; Iwatani, C.; Tsuchiya, H.; Nakamura, S.; Nonoguchi, K.; Itoh, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Ishigaki, H.; Mori, T.; et al. The Natural History of Spontaneously Occurred Endometriosis in Cynomolgus Monkeysby Monthly Follow-Up Laparoscopy for Two Years. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2020, 251, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westropp, J.L.; Delgado, M.; Buffington, C.A.T. Chronic Lower Urinary Tract Signs in Cats: Current Understanding of Pathophysiologyand Management. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pr. 2019, 49, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Busch, C. Endometriosis in Rhesus Monkeys. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 1984, 89, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto-Kakiuchi, A.; Netsu, S.; Okabayashi, S.; Taniguchi, K.; Tanimura, H.; Kato, A.; Suzuki, M.; Sankai, T.; Konno, R. Spontaneous Endometriosis in Cynomolgus Monkeys as a Clinically Relevant Experimental Model. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornillie, F.J.; D’Hooghe, T.M.; Bambra, C.S.; Lauweryns, J.M.; Isahakia, M.; Koninckx, P.R. Morphological Characteristics of Spontaneous Endometriosis in the Baboon (Papio Anubis and Papio Cynocephalus). Gynecol. Obs. Investig. 1992, 34, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, M.; Matsuda, A.; Natsume, T.; Ogawa, S.; Awaga, Y.; Hayashi, I.; Hama, A.; Takamatsu, H. Pain-Related Behavior and Brain Activation in Cynomolgus Macaques with NaturallyOccurring Endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2019, 34, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, H.M.; Bharadwaj, M.S.; O’Brien Cox, A.; Furdui, C.M.; Appt, S.E.; Caudell, D.L. Endometrium and Endometriosis Tissue Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism in aNonhuman Primate Model. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, H.M.; Appt, S.E.; Taylor, R.N.; Torres-Mendoza, Y.; Lenk, E.E.; Rosenthal, N.S.; Caudell, D.L. Systemic Iron Deficiency in a Nonhuman Primate Model of Endometriosis. Comp. Med. 2018, 68, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, A.; Lanza, A.; Menicagli, F.; Signorile, P.G.; Spugnini, E.P. Histological and Immunohistochemical Characterization of a Case of Endometriosis in a Guinea Pig (Cavia tschudii). Case Rep. Vet. Med. 2017, 2017, 4594510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalini, L.; Fedder, J. Characteristics of the Endometrium in Menstruating Species: Lessons Learned from the Animal Kingdom. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 102, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doré, M.; Lagacé, A. Spontaneous External Endometriosis in a Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla). Can. Vet. J. 1985, 26, 347. [Google Scholar]
- Westropp, J.L.; Buffington, C.A.T. In Vivo Models of Interstitial Cystitis. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birder, L.; Andersson, K.-E. Animal Modelling of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Int. Neurourol. J. 2018, 22, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, M. Effects of Early-Life Stress on the Brain and Behaviors: Implications of Early Maternal Separation in Rodents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacagnina, M.J.; Heijnen, C.J.; Watkins, L.R.; Grace, P.M. Autoimmune Regulation of Chronic Pain. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasieńska, G.; Ziomkiewicz, A.; Ellison, P.T.; Lipson, S.F.; Thune, I. Large Breasts and Narrow Waists Indicate High Reproductive Potential in Women. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 1213–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, C.J.; Lees, B.; Stevenson, J.C. Sex- and Menopause-Associated Changes in Body-Fat Distribution. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 55, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, Y.; Osuga, Y.; Harada, M.; Hirata, T.; Koga, K.; Yoshino, O.; Hirota, Y.; Morimoto, C.; Yano, T.; Taketani, Y. Concentration of Adiponectin in Peritoneal Fluid Is Decreased in Women with Endometriosis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2005, 54, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alviggi, C.; Clarizia, R.; Castaldo, G.; Matarese, G.; Colucci, C.C.; Conforti, S.; Pagano, T.; Revelli, A.; de Placido, G. Leptin Concentrations in the Peritoneal Fluid of Women with Ovarian Endometriosis Are Different According to the Presence of a “deep” or “Superficial” Ovarian Disease. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2009, 25, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.W.; Shin, J.H.; Park, H.T.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.H.; Hur, J.Y. Resistin Concentration Is Increased in the Peritoneal Fluid of Women with Endometriosis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 64, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolbin, M.M.; Mamillapalli, R.; Nematian, S.E.; Goetz, L.; Taylor, H.S. Adipocyte Alterations in Endometriosis: Reduced Numbers of Stem Cells and MicroRNA Induced Alterations in Adipocyte Metabolic Gene Expression. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2019, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Schwartz, A.V.; LaValley, M.P.; Wang, N.; Desai, N.; Sun, X.; Neogi, T.; Nevitt, M.; Lewis, C.E.; Guermazi, A.; et al. Visceral Adiposity Is Associated with Pain, but Not Structural Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrand, S.; de Mutsert, R.; Christen, T.; Maan, A.C.; Jukema, J.W.; Lamb, H.J.; de Roos, A.; Rosendaal, F.R.; den Heijer, M.; Swenne, C.A. Body Fat, Especially Visceral Fat, Is Associated with Electrocardiographic Measures of Sympathetic Activation. Obesity 2014, 22, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.; Klein Wolterink, R.G.J.; Godinho-Silva, C.; Domingues, R.G.; Ribeiro, H.; da Silva, J.A.; Mahú, I.; Domingos, A.I.; Veiga-Fernandes, H. Neuro-Mesenchymal Units Control ILC2 and Obesity via a Brain–Adipose Circuit. Nature 2021, 597, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Filaretova, L.; Bharti, J.; Roy, K.K.; Sharma, J.B.; Sengupta, J. Pathophysiological Basis of Endometriosis-Linked Stress Associated with Pain and Infertility: A Conceptual Review. Reprod. Med. 2020, 1, 32–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, M.E.; Melnyk, S.B.; Simmen, F.A.; Yang, Y.; Pabona, J.M.P.; Simmen, R.C.M. High-Fat Diet Promotion of Endometriosis in an Immunocompetent Mouse Model Is Associated With Altered Peripheral and Ectopic Lesion Redox and Inflammatory Status. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 2870–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Birder, L.A.; Jiang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Dysregulation of Bladder Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Human Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neto, A.C.; Santos-Pereira, M.; Abreu-Mendes, P.; Neves, D.; Almeida, H.; Cruz, F.; Charrua, A. The Unmet Needs for Studying Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Using Animal Models. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030696
Neto AC, Santos-Pereira M, Abreu-Mendes P, Neves D, Almeida H, Cruz F, Charrua A. The Unmet Needs for Studying Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Using Animal Models. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030696
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeto, Ana Catarina, Mariana Santos-Pereira, Pedro Abreu-Mendes, Delminda Neves, Henrique Almeida, Francisco Cruz, and Ana Charrua. 2023. "The Unmet Needs for Studying Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Using Animal Models" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030696
APA StyleNeto, A. C., Santos-Pereira, M., Abreu-Mendes, P., Neves, D., Almeida, H., Cruz, F., & Charrua, A. (2023). The Unmet Needs for Studying Chronic Pelvic/Visceral Pain Using Animal Models. Biomedicines, 11(3), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030696







