A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose a Siamese network architecture and implement Siamese convolutional neural networks (Siamese CNNs) and Siamese autoencoders (Siamese AEs). The Siamese network architecture is used to extract features of similarity between two different epochs of EEG.
- (2)
- To train sleep staging models with a Siamese network, we developed a new loss function. The new loss function incorporates metrics for traditional sleep staging models such as cross entropy loss and distance metrics for measuring the distance between two distributions.
- (3)
- We evaluated our model on two public datasets, SleepEDF and MASS-SS3, and compared our results with baseline sleep staging models and some SOTA sleep staging methods. The results show that our encoder can greatly improve the accuracy of the baseline model and outperform the state-of-the-art models in sleep staging.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
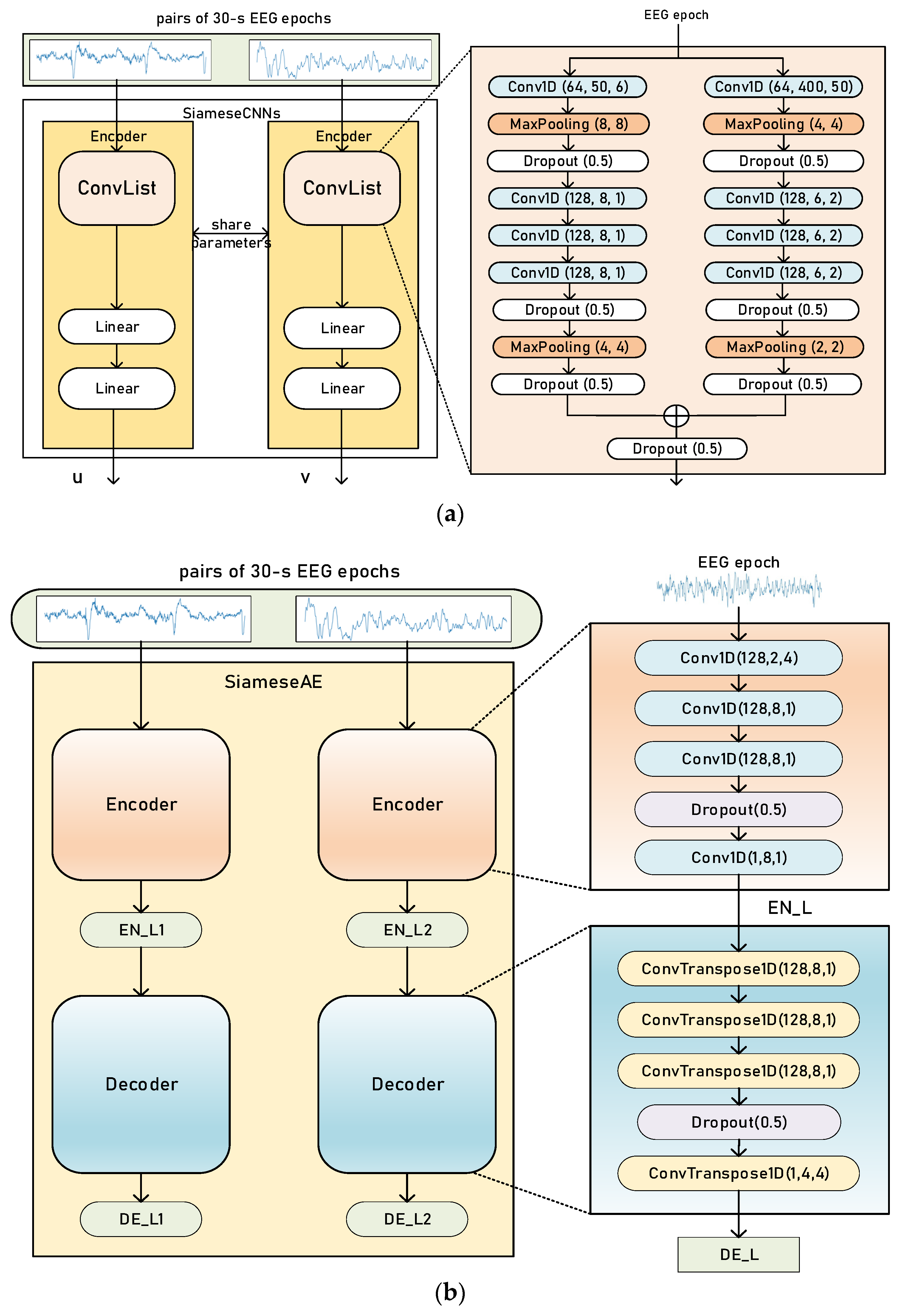
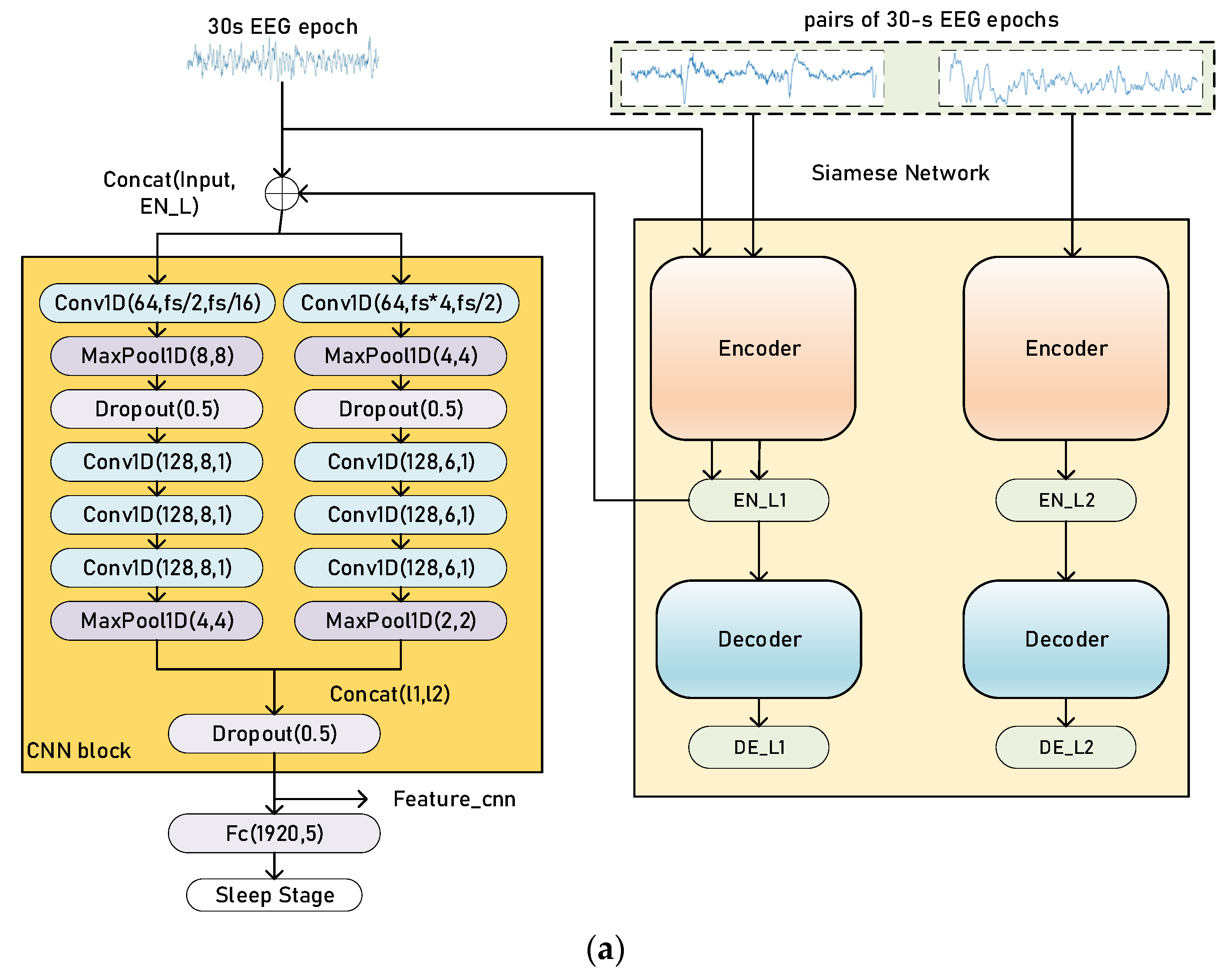
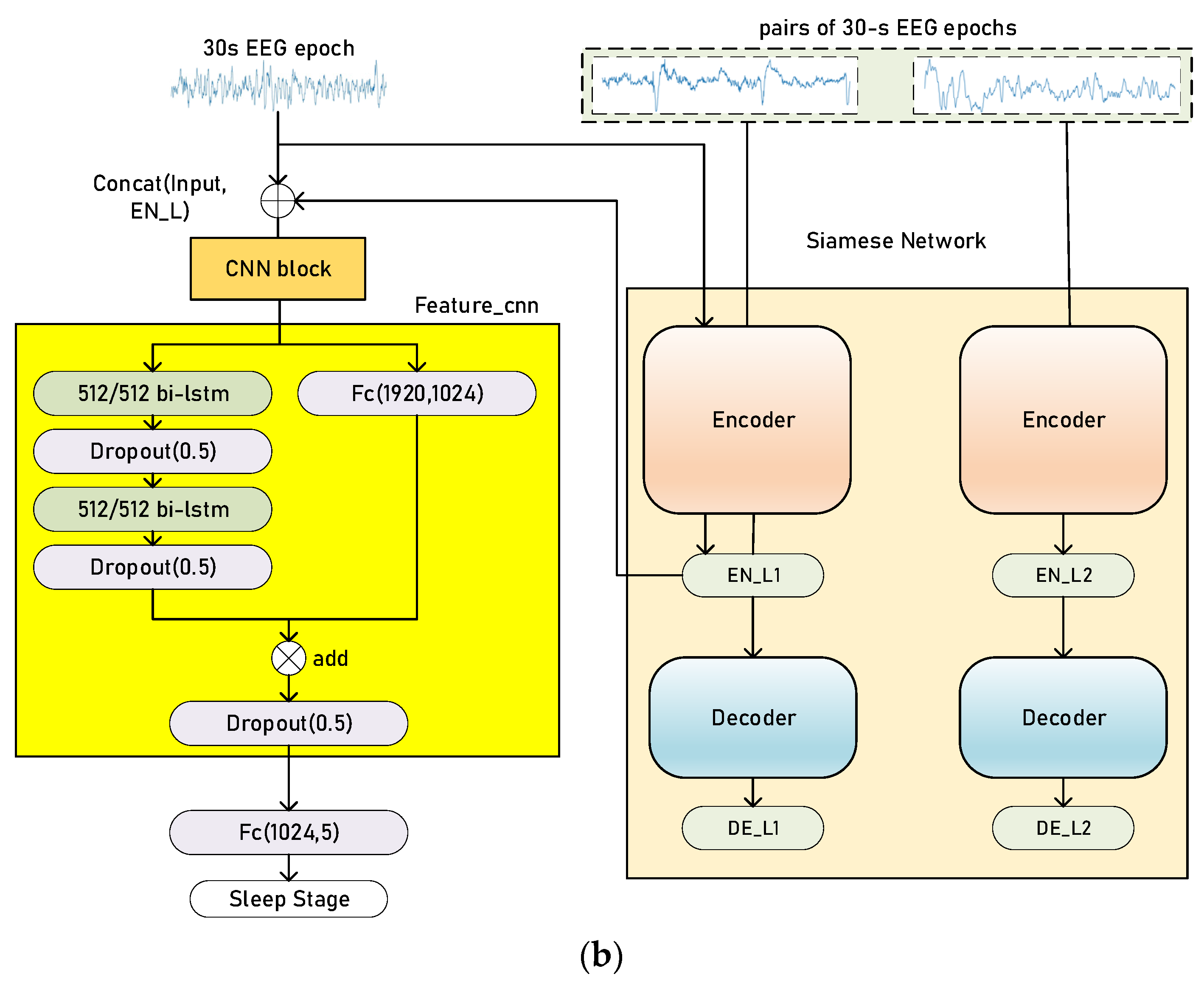
2.2. Siamese Networks
2.3. Loss Functions for Measuring Similarity
2.4. Training and Evaluation Process
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Classification Performance
3.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zoubek, L.; Charbonnier, S.; Lecocq, S.; Buguet, A.; Chapotot, F. Feature selection for sleep/wake stages classification using data-driven methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2007, 2, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattu, V.K.; Manzar, D.; Kumary, D.S.; Burman, D.; Spence, D.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. The Global Problem of Insufficient Sleep and Its Serious Public Health Implications. Healthcare 2018, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, Y.; Banville, H.; Albuquerque, I.; Gramfort, A.; Falk, T.H.; Faubert, J. Deep Learning-Based Electroencephalography Analysis: A Systematic Review. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iber, C.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Chesson, A.L., Jr.; Quan, S.F. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, IL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, J.A. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1969, 26, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; Vos, M.D. Automatic Sleep Stage Classification Using Single-Channel EEG: Learning Sequential Features with Attention-Based Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 1452–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Alickovic, E.; Subasi, A. Ensemble SVM Method for Automatic Sleep Stage Classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira TL, T.; Kozakevicius, A.J.; Rodrigues, C.R. Single-channel EEG sleep stage classification based on a streamlined set of statistical features in the wavelet domain. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.R.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H. Computer-aided sleep staging using complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and bootstrap aggregating. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2016, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Automatic sleep stages classification using optimise flexible analytic wavelet transform. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 19215, 10536.
- Phan, H.; Mikkelsen, K. Automatic Sleep Staging of EEG Signals: Recent Development, Challenges, and Future Directions. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 04TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supratak, A.; Dong, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, Y. DeepSleepNet: A Model for Automatic Sleep Stage Scoring Based on Raw Single-Channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldele, E.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Kwoh, C.-K.; Li, X.; Guan, C. An Attention-Based Deep Learning Approach for Sleep Stage Classification With Single-Channel EEG. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conneau, A.; Kiela, D.; Schwenk, H.; Barrault, L.; Bordes, A. Supervised Learning of Universal Sentence Representations from Natural Language Inference Data. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02364. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, M.; Bilge, H.Ş. Deep Metric Learning: A Survey. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, I.; Hu, Y.-T.; Sun, R.; Pyrros, A.; Siddiqui, N.; Koyejo, S.; Zhao, Z.; Forsyth, D.; Schwing, A. Max-Sliced Wasserstein Distance and Its Use for GANs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kolouri, S.; Nadjahi, K.; Simsekli, U.; Badeau, R.; Rohde, G.K. Generalized Sliced Wasserstein Distances 2019. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- O’Reilly, C.; Gosselin, N.; Carrier, J.; Nielsen, T. Montreal Archive of Sleep Studies: An Open-Access Resource for Instrument Benchmarking and Exploratory Research. J. Sleep Res. 2014, 23, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinalis, O.; Matthews, P.M.; Guo, Y. Automatic Sleep Stage Scoring Using Time-Frequency Analysis and Stacked Sparse Autoencoders. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinalis, O.; Matthews, P.M.; Guo, Y.; Zafeiriou, S. Automatic Sleep Stage Scoring with Single-Channel EEG Using Convolutional Neural Networks 2016. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.01683. [Google Scholar]
- Perslev, M.; Jensen, M.H.; Darkner, S.; Jennum, P.J.; Igel, C. U-Time: A Fully Convolutional Network for Time Series Segmentation Applied to Sleep Staging. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chen, O.Y.; De Vos, M. Joint Classification and Prediction CNN Framework for Automatic Sleep Stage Classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, G. An Improved Deep Convolutional Neural Network with Multi-Scale Information for Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Neurocomputing 2019, 359, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer normalization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S.; Hadsell, R.; LeCun, Y. Learning a Similarity Metric Discriminatively, with Application to Face Verification. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05); IEEE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter; Sepp; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolova, M.; Lapalme, G. A Systematic Analysis of Performance Measures for Classification Tasks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Afghah, F.; Acharya, U.R. SleepEEGNet: Automated Sleep Stage Scoring with Sequence to Sequence Deep Learning Approach. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Jin, J.; Wang, X. Deep Convolutional Network Method for Automatic Sleep Stage Classification Based on Neurophysiological Signals. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI); IEEE: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mixed Neural Network Approach for Temporal Sleep Stage Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 324–333. [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chen, O.Y.; De Vos, M. SeqSleepNet: End-to-End Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Sequence-to-Sequence Automatic Sleep Staging. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset | W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SleepEDF | 7927 | 2804 | 17,799 | 5703 | 7717 | 41,950 |
| MASS-SS3 | 6056 | 4598 | 28,311 | 7398 | 10,205 | 56,568 |
| Predicted | Per-Class | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | NEM | PR(%) | RE(%) | F1(%) | |
| W | 7103 | 394 | 225 | 49 | 156 | 87.5 | 89.6 | 88.5 |
| N1 | 488 | 928 | 889 | 14 | 487 | 55.3 | 33.1 | 41.4 |
| N2 | 330 | 234 | 15751 | 722 | 762 | 87 | 88.4 | 87.7 |
| N3 | 26 | 2 | 706 | 4952 | 17 | 85.8 | 86.8 | 86.3 |
| REM | 170 | 120 | 536 | 35 | 6856 | 82.8 | 88.8 | 85.7 |
| Predicted | Per-Class | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | NEM | PR(%) | RE(%) | F1(%) | |
| W | 7245 | 370 | 166 | 39 | 107 | 85.8 | 91.4 | 88.5 |
| N1 | 534 | 929 | 884 | 20 | 437 | 55.6 | 33.1 | 41.5 |
| N2 | 435 | 257 | 15,778 | 718 | 611 | 87.2 | 88.7 | 87.9 |
| N3 | 32 | 1 | 635 | 5021 | 14 | 86.5 | 88 | 87.2 |
| REM | 200 | 113 | 642 | 10 | 6752 | 85.2 | 87.5 | 86.4 |
| Predicted | Per-Class | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | NEM | PR(%) | RE(%) | F1(%) | |
| W | 5501 | 328 | 92 | 11 | 124 | 87.1 | 90.8 | 88.9 |
| N1 | 563 | 2344 | 808 | 8 | 875 | 64.5 | 50.9 | 56.9 |
| N2 | 163 | 650 | 25,906 | 786 | 806 | 91.1 | 91.5 | 91.3 |
| N3 | 6 | 3 | 1326 | 6062 | 1 | 88.2 | 81.9 | 85.0 |
| REM | 85 | 311 | 308 | 3 | 9498 | 84.0 | 93.1 | 88.3 |
| Dataset | Method | Per-Class F1-Score | Overall Metrics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | N1 | N2 | N3 | REM | Accuracy | MF1 | κ | ||
| SleepEDF-20 | DeepSleepNet [12] | 86.7 | 45.5 | 85.1 | 83.3 | 82.6 | 81.9 | 76.6 | 0.76 |
| SleepEEGNet [32] | 89.4 | 44.4 | 84.7 | 84.6 | 79.6 | 81.5 | 76.6 | 0.75 | |
| ResnetLSTM [33] | 86.5 | 28.4 | 87.7 | 89.8 | 76.2 | 82.5 | 73.7 | 0.76 | |
| MultitaskCNN [23] | 87.9 | 33.5 | 87.5 | 85.8 | 80.3 | 83.1 | 75.0 | 0.77 | |
| AttnSleep [13] | 89.7 | 42.6 | 88.8 | 90.2 | 79.0 | 84.4 | 78.1 | 0.79 | |
| Siamese CNNs (Ours) | 88.5 | 41.4 | 87.7 | 86.3 | 85.7 | 84.9 | 78.0 | 0.79 | |
| Siamese AEs (Ours) | 91.4 | 33.1 | 88.7 | 88.0 | 87.5 | 85.2 | 78.3 | 0.79 | |
| MASS-SS3 | DeepSleepNet [12] | 87.3 | 59.8 | 90.3 | 81.5 | 89.3 | 86.2 | 81.7 | 0.80 |
| MixedNet [34] | 84.6 | 56.3 | 90.7 | 84.8 | 86.1 | 85.9 | 80.5 | - | |
| SeqSleepNet [35] | - | - | - | - | - | 86.5 | 82.4 | 0.80 | |
| Siamese AEs (Ours) | 90.8 | 50.9 | 91.5 | 81.9 | 93.1 | 87.2 | 82.1 | 0.81 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Shan, W. A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020327
You Y, Guo X, Yang Z, Shan W. A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Yuyang, Xiaoyu Guo, Zhihong Yang, and Wenjing Shan. 2023. "A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020327
APA StyleYou, Y., Guo, X., Yang, Z., & Shan, W. (2023). A Siamese Network-Based Method for Improving the Performance of Sleep Staging with Single-Channel EEG. Biomedicines, 11(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020327





