p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition of Mesenchymal Transdifferentiated Tumor Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. p38-Signaling Inhibitors
2.3. Use of p38 Inhibitors and Cell Treatment
2.4. p38 Inhibitor Pre-Treatment before Cisplatin
2.5. Inhibition of Acquired p38 Activity in Cisplatin-Surviving Cells
2.6. Viability Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometric Assessment of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
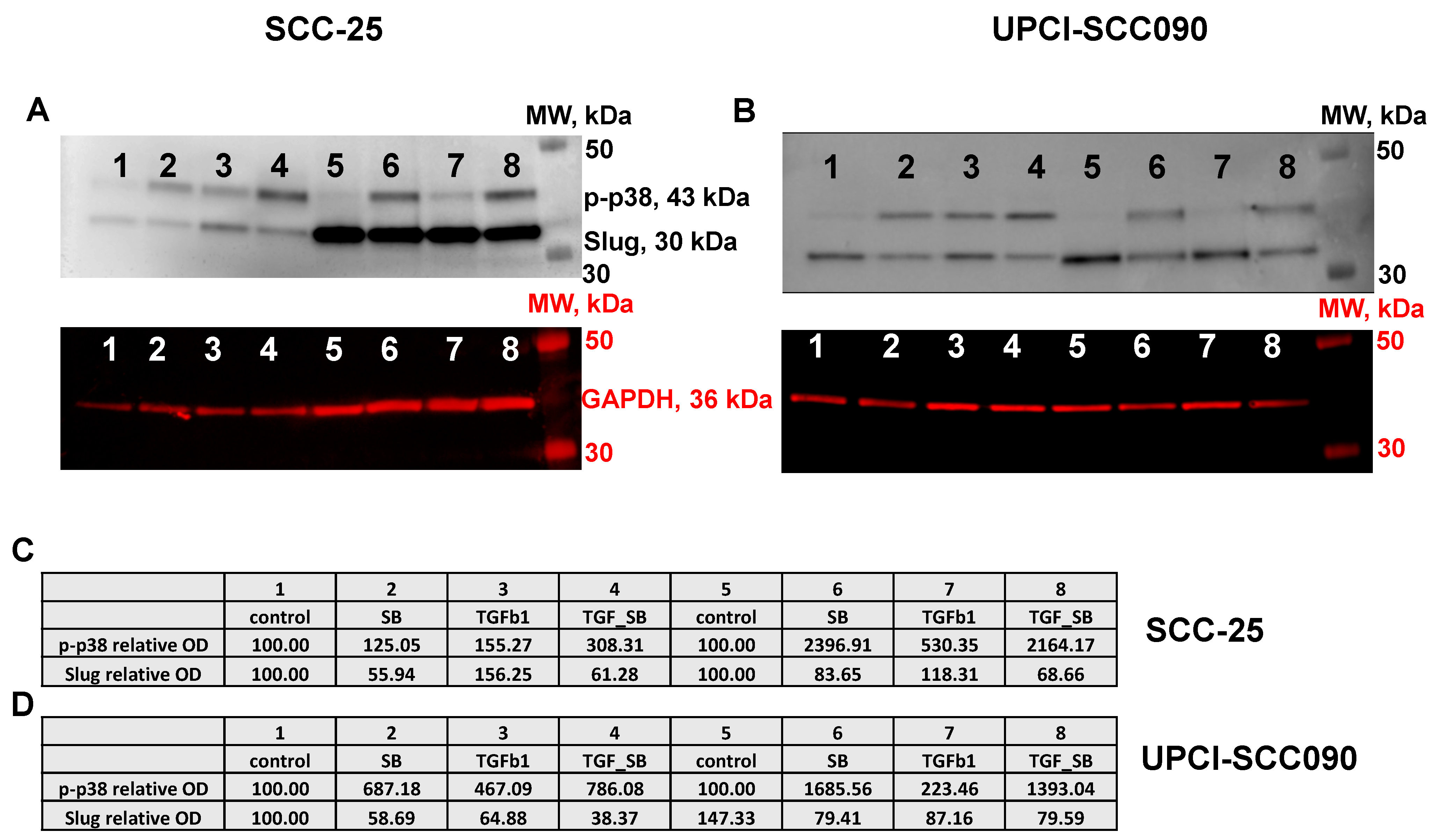
3.1. p38 MAPK Inhibitor SB202190 Downregulates Protein Levels of Slug in SCC-25 Cells
3.2. Inhibition of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Induces Growth Reduction in the RCT Resistant Cell Line SCC-25
3.3. p38 MAPK Inhibition Increases Apoptosis and Sensitizes HNSCC Cells to Cisplatin Treatment
3.4. p38 MAPK Inhibitor Targets Tumor Cells Surviving Cisplatin
3.5. Clinically Relevant p38 MAPK Inhibitor Ralimetinib Causes Apoptosis without Cisplatin Co-Treatment in HNSCC
3.6. Ralimetinib Targets the Downstream Protein ATF2 in HNSCC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greier, M.C.; Runge, A.; Dudas, J.; Pider, V.; Skvortsova, I.-I.; Savic, D.; Riechelmann, H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head neck cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingruber, J.; Dudas, J.; Sprung, S.; Lungu, B.; Mungenast, F. Interplay between Partial EMT and Cisplatin Resistance as the Drivers for Recurrence in HNSCC. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Alshaimaa, A.; Maria, M.V.; Daniel, D.; Herbert, R.; Jozsef, D.; Ira-Ida, S. Epithelial-mesenchymal crosstalk induces radioresistance in HNSCC cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3641–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerinck, J.; Berx, G. Partial EMT takes the lead in cancer metastasis. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 3174–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingruber, J.; Dudás, J.; Savic, D.; Schweigl, G.; Steinbichler, T.B.; do Carmo Greier, M.; Santer, M.; Carollo, S.; Trajanoski, Z.; Riechelmann, H. EMT-related transcription factors and protein stabilization mechanisms involvement in cadherin switch of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 414, 113084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingruber, J.; Savic, D.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Sprung, S.; Fleischer, F.; Glueckert, R.; Schweigl, G.; Skvortsova, I.-I.; Riechelmann, H.; Dudás, J. KLF4, Slug and EMT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells 2021, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechelmann, H.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Sprung, S.; Santer, M.; Runge, A.; Ganswindt, U.; Gamerith, G.; Dudas, J. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transcription Factor Slug Predicts Survival Benefit of Up-Front Surgery in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudas, J.; Ingruber, J.; Glueckert, R.; Sprung, S.; Fleischer, F.; Cidlinsky, N.; Dejaco, D.; Kofler, B.; Giotakis, A.I.; et al. Slug Is A Surrogate Marker of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puram, S.V.; Tirosh, I.; Parikh, A.S.; Patel, A.P.; Yizhak, K.; Gillespie, S.; Rodman, C.; Luo, C.L.; Mroz, E.A.; Emerick, K.S.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 1611–1624.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Barrett, T.F.; Paolini, R.; Parikh, A.; Puram, S.V. Partial EMT in head and neck cancer biology: A spectrum instead of a switch. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5049–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachat, C.; Peixoto, P.; Hervouet, E. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition History: From Embryonic Development to Cancers. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir, B.; Chiarella, A.M.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Rustgi, A.K. EMT, MET, plasticity and tumor metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, J.; Ladanyi, A.; Ingruber, J.; Steinbichler, T.B.; Riechelmann, H. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: A Mechanism that Fuels Cancer Radio/Chemoresistance. Cells 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudas, J.; Bitsche, M.; Schartinger, V.; Falkeis, C.; Sprinzl, G.M.; Riechelmann, H. Fibroblasts produce brain-derived neurotrophic factor and induce mesenchymal transition of oral tumor cells. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wei, J.; Sun, J. Roles of TGF-β signaling pathway in tumor microenvirionment and cancer therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, M.R.; Ala-Aho, R.; Jokilehto, T.; Peltonen, J.; Kallajoki, M.; Grenman, R.; Jaakkola, P.; Westermarck, J.; Kähäri, V.-M. p38α and p38δ mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms regulate invasion and growth of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5267–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leelahavanichkul, K.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Molinolo, A.A.; Basile, J.R.; Koontongkaew, S.; Gutkind, J.S. A role for p38 MAPK in head and neck cancer cell growth and tumor-induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Limón, A.; Joaquin, M.; Caballero, M.; Posas, F.; de Nadal, E. The p38 Pathway: From Biology to Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cano, J.; Roche, O.; Cimas, F.J.; Pascual-Serra, R.; Ortega-Muelas, M.; Fernández-Aroca, D.M.; Sánchez-Prieto, R. p38MAPK and Chemotherapy: We Always Need to Hear Both Sides of the Story. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Ming, X.; Deng, P.; Jiang, Y. Mechanisms regulating the nuclear translocation of p38 MAP kinase. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hernández, L.; García-Ortega, M.B.; Ruiz-Alcalá, G.; Carrillo, E.; Marchal, J.A.; García, M.Á. The p38 MAPK Components and Modulators as Biomarkers and Molecular Targets in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raingeaud, J.; Whitmarsh, A.J.; Barrett, T.; Dérijard, B.; Davis, R.J. MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, C.; Patel, G.; Jones, N. ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trempolec, N.; Dave-Coll, N.; Nebreda, A.R. SnapShot: p38 MAPK Substrates. Cell 2013, 152, 924.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Martinez, I.; Sirianni, N.; Wang, J.; López-Albaitero, A.; Gollin, S.M.; Johnson, J.T.; Khan, S. Human papillomavirus-16 associated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN): A natural disease model provides insights into viral carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.P.; Reddy, H.; Caivano, M.; Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, S.; Xiang, J.; Huang, S.; Lin, A. Induction of apoptosis by SB202190 through inhibition of p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16415–16420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neganova, I.; Chichagova, V.; Armstrong, L.; Lako, M. A critical role for p38MAPK signalling pathway during reprogramming of human fibroblasts to iPSCs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.D.; Mercante, A.M.D.C.; Louro, I.D.; Gonçalves, A.J.; Carvalho, M.B.D.; da Silva, E.H.T.; da Silva, A.M.Á. HIF1-α expression predicts survival of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.M.; Anderson, B.D.; Brooks, N.A.; Brooks, H.B.; Chan, E.M.; De Dios, A.; Gilmour, R.; Graff, J.R.; Jambrina, E.; Mader, M.; et al. Characterization of LY2228820 dimesylate, a potent and selective inhibitor of p38 MAPK with antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biau, J.; Thivat, E.; Chautard, E.; Stefan, D.; Boone, M.; Chauffert, B.; Bourgne, C.; Richard, D.; Molnar, I.; Levesque, S.; et al. Phase 1 trial of ralimetinib (LY2228820) with radiotherapy plus concomitant temozolomide in the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 154, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Jing, S.; He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, S.; Dai, W.; et al. IL-6/STAT3/TWIST inhibition reverses ionizing radiation-induced EMT and radioresistance in esophageal squamous carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11228–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.; Ridgway, L.D.; Korapati, A.L.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.; Siddik, Z.H.; Mills, G.B.; Claret, F.X. Sustained activation of JNK/p38 MAPK pathways in response to cisplatin leads to Fas ligand induction and cell death in ovarian carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19245–19256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.F.; Nebreda, A.R. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, E.; Safe, S. Transforming Growth Factor β/NR4A1-Inducible Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Is p38α (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14) Dependent. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00306-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.; Eustace, A.J.; Busschots, S.; Breen, L.; Crown, J.; Clynes, M.; O’Donovan, N.; Stordal, B. In Vitro Development of Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy Drug-Resistant Cancer Cell Lines: A Practical Guide with Case Studies. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Mallen-St Clair, J.; Wang, G.; Luo, J.; Palma-Diaz, F.; Lai, C.; Elashoff, D.A.; Sharma, S.; Dubinett, S.M.; St John, M. p38 MAPK mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating p38IP and Snail in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016, 60, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibi, A.M.; Basavaraj, V. Study of Podoplanin Expression in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Iran. J. Pathol. 2022, 17, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, W.-L.; Zhang, R.-N.; He, X.-S.; Wang, J.-R.; Liu, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Gan, W.-J. The Role of TGF-β Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 6675208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Haluska, P.; Tolcher, A.W.; Erlichman, C.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Lensing, J.L.; Beeram, M.; Molina, J.R.; Rasco, D.W.; Arcos, R.R.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase I Study of the Oral p38 MAPK Inhibitor, Ralimetinib (LY2228820 Dimesylate), in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarubin, T.; Han, J. Activation and signaling of the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Roy, S.; Anuja, K.; Thakur, S.; Akhter, Y.; Padhi, S.; Banerjee, B. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase modulates cisplatin resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma cells. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 122, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Raju, M.B.; Rahman, M.A. Current Insights of Inhibitors of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Inflammation. Med. Chem. 2021, 17, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodeller, F.; Schulze-Koops, H. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascade in CD4 T cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bergami, P.; Lau, E.; Ronai, Z. Emerging roles of ATF2 and the dynamic AP1 network in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, T.A.; Nguyen, A.N.; Hideshima, T.; Reddy, M.; Ma, J.Y.; Haghnazari, E.; Henson, M.; Stebbins, E.G.; Kerr, I.; O’Young, G.; et al. Inhibition of p38α MAPK enhances proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis of myeloma cells by modulating Hsp27, Bcl-X(L), Mcl-1 and p53 levels in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Leukemia 2006, 20, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, V.; Nahidino, P.; Forster, M.; Laufer, S.A. An updated patent review of p38 MAP kinase inhibitors (2014–2019). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Rosen, L.S.; Tolcher, A.W.; Papadopoulos, K.; Beeram, M.; Shi, P.; Pitou, C.; Bell, R.; Kulanthaivel, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Phase 1 and pharmacokinetic study of LY3007113, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, S.; Laskar, S.; Pandey, B.N. Role of ATF-2 in regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and radio-sensitivity of A549 cells mediated by secreted soluble factors. J. Radiat. Res. 2014, 55, i116–i117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Chen, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, B.; Gao, L.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Bao, Y.; Qu, L.; et al. ATF2 predicts poor prognosis and promotes malignant phenotypes in renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Su, X.; Lei, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J. Safety and efficacy of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors (MAPKIs) in COPD. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 950035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hideshima, T.; Podar, K.; Chauhan, D.; Ishitsuka, K.; Mitsiades, C.; Tai, Y.-T.; Hamasaki, M.; Raje, N.; Hideshima, H.; Schreiner, G.; et al. p38 MAPK inhibition enhances PS-341 (bortezomib)-induced cytotoxicity against multiple myeloma cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8766–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre Jean Perrin. Phase I/II Study of LY2228820 with Radiotherapy Plus Concomitant TMZ in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. 2019. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02364206 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Home|ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Sehgal, K.; Portell, A.; Ivanova, E.V.; Lizotte, P.H.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Greene, J.R.; Vajdi, A.; Gurjao, C.; Teceno, T.; Taus, L.J.; et al. Dynamic single-cell RNA sequencing identifies immunotherapy persister cells following PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e135038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakasugi, T. Treatment strategy after the discontinuation of immunotherapy for head and neck cancer: A review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2023, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Suzuki, H.I. TGF-β Signaling in Cellular Senescence and Aging-Related Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senturk, S.; Mumcuoglu, M.; Gursoy-Yuzugullu, O.; Cingoz, B.; Akcali, K.C.; Ozturk, M. Transforming growth factor-beta induces senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and inhibits tumor growth. Hepatology 2010, 52, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, A.; Patil, C.K.; Campisi, J. p38MAPK is a novel DNA damage response-independent regulator of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, M.A.; Peeper, D.S. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and senescence: Two cancer-related processes are crossing paths. Aging 2010, 2, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayess, H.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. Cellular senescence and tumor suppressor gene p16. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, H.; Passos, J.F. Cellular senescence: All roads lead to mitochondria. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Saluja, V.; Visser, J.; Moolenaar, F.; Meijer, D.K.F.; Poelstra, K.; Kok, R.J. Bioanalysis and pharmacokinetics of the p38 MAPkinase inhibitor SB202190 in rats. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 826, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Federspiel, J.; Greier, M.d.C.; Ladányi, A.; Dudas, J. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition of Mesenchymal Transdifferentiated Tumor Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123301
Federspiel J, Greier MdC, Ladányi A, Dudas J. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition of Mesenchymal Transdifferentiated Tumor Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123301
Chicago/Turabian StyleFederspiel, Julia, Maria do Carmo Greier, Andrea Ladányi, and Jozsef Dudas. 2023. "p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition of Mesenchymal Transdifferentiated Tumor Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123301
APA StyleFederspiel, J., Greier, M. d. C., Ladányi, A., & Dudas, J. (2023). p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibition of Mesenchymal Transdifferentiated Tumor Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3301. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123301






