Differential Regulation of Intracisternally Injected Angiotensin II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Intracisternal Catheterization
2.3. General Procedures for Behavioral Testing
2.4. Evaluation of Mechanical Allodynia
2.5. Evaluation of Orofacial Heat Hyperalgesia
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Chemicals
2.8. Experimental Protocols
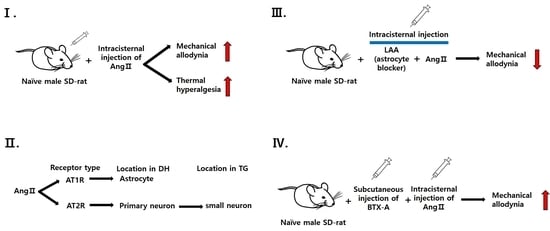
2.8.1. Pronociceptive Effects of Intracisternally Administered Ang II
2.8.2. Effects of Ang II Receptor Blockade on Ang II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia
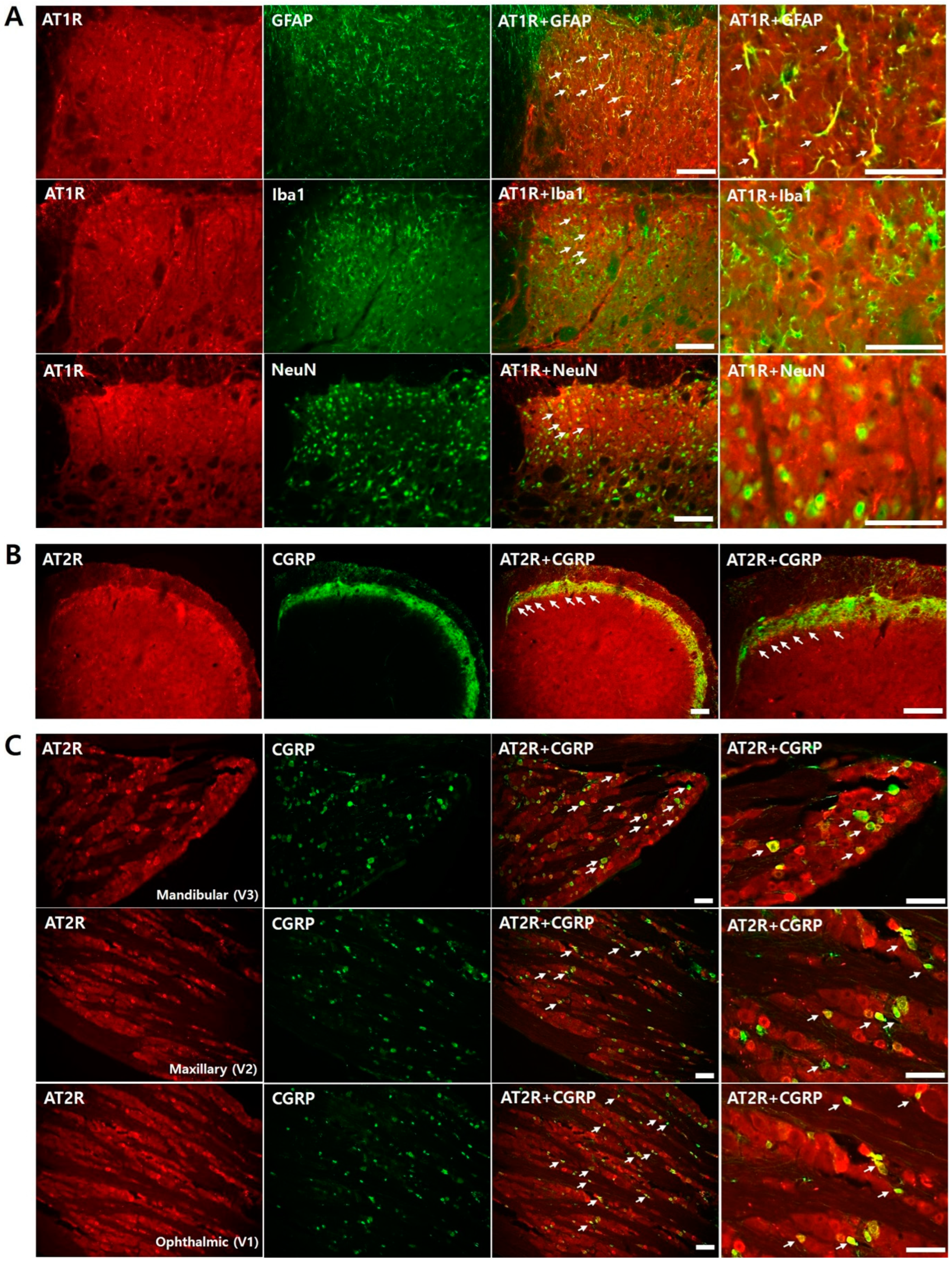
2.8.3. Colocalization of Ang II Receptors in Naïve Rats
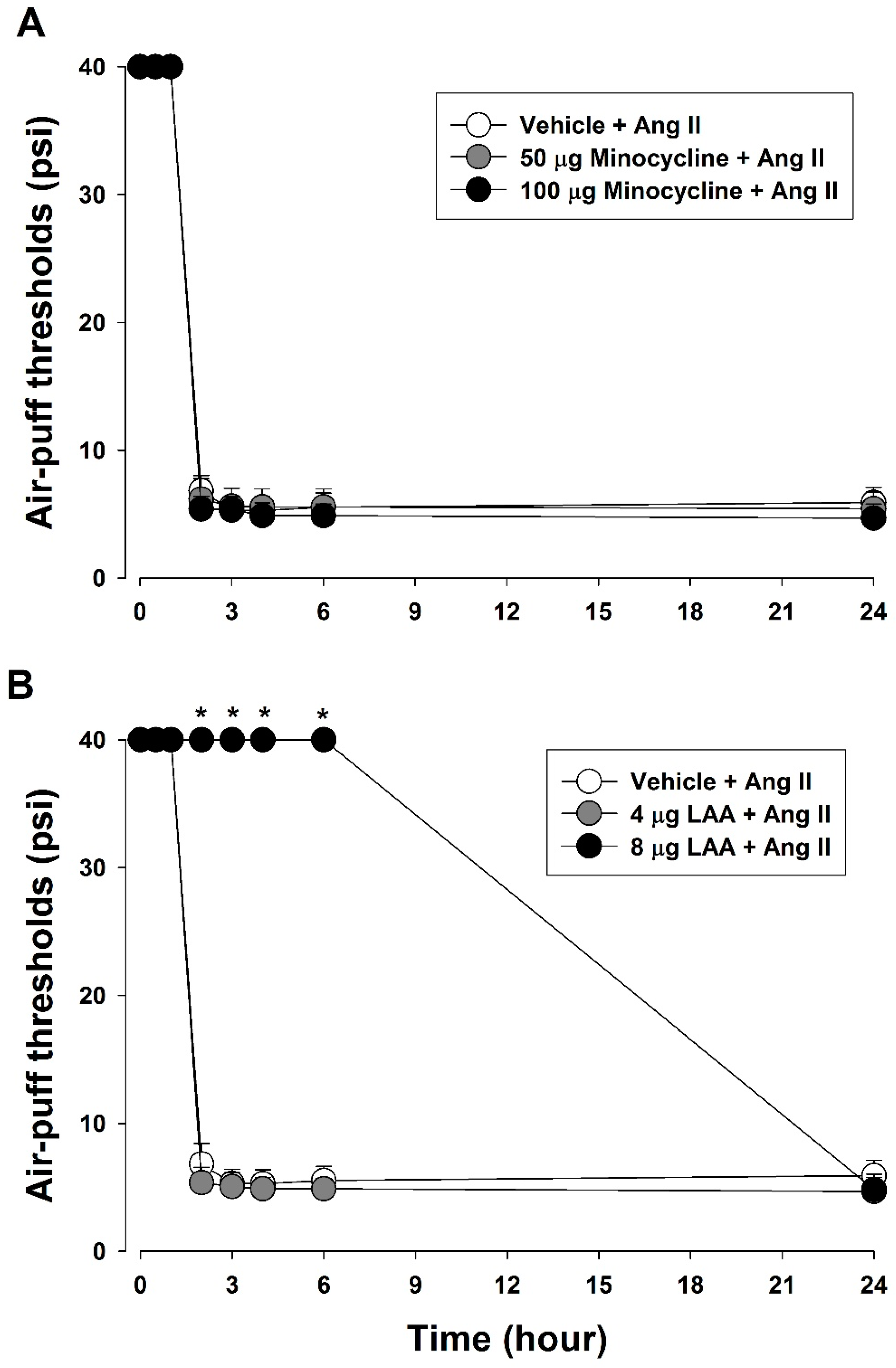
2.8.4. Role of Glial Cells in Ang II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
2.8.5. Effects of BTX-A on Ang II-Induced Thermal Hyperalgesia
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intracisternal Administration of Ang II Induces Nociceptive Behavior
3.2. Contribution of Ang II Receptors to Ang II-Induced Nociceptive Behavior
3.3. Colocalization of Ang Receptor in Naïve Rats
3.4. Role of Glial Cells in Ang II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia
3.5. Effects of BTX-A on Ang II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, M.; Poyan Mehr, A.; Kreutz, R. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gasparo, M.; Catt, K.J.; Inagami, T.; Wright, J.W.; Unger, T. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000, 52, 415–472. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schelling, P.; Ganten, U.; Sponer, G.; Unger, T.; Ganten, D. Components of the renin-angiotensin system in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and dogs with special consideration of the origin and the fate of angiotensin II. Neuroendocrinology 1980, 31, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sernia, C.; Mowchanuk, M.D. Brain angiotensinogen: In vitro synthesis and chromatographic characterization. Brain Res. 1983, 259, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.J.; Bouhnik, J.; Ménard, J.; Corvol, P. Identity of angiotensinogen precursors of rat brain and liver. Nature 1984, 308, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschepper, C.F.; Bouhnik, J.; Ganong, W.F. Colocalization of angiotensinogen and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes in rat brain. Brain Res. 1986, 374, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.; Moeller, I.; Jenkins, T.; Chai, S.Y.; Allen, A.M.; Ohishi, M.; Mendelsohn, F.A. Mapping tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin AT1, AT2 and AT4 receptors. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, W.; Nakagawasai, O.; Yaoita, F.; Kanno, S.; Yomogida, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Tadano, T.; Tan-No, K. Angiotensin II produces nociceptive behavior through spinal AT1 receptor-mediated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in mice. Mol. Pain. 2013, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, W.; Ogata, Y.; Nakagawasai, O.; Yaoita, F.; Tanado, T.; Tan-No, K. The intrathecal administration of losartan, an AT1 receptor antagonist, produces an antinociceptive effect through the inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation in the mouse formalin test. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 585, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.S.; Dworkin, R.H.; McCarthy, T.D.; Anand, P.; Bountra, C.; McCloud, P.I.; Hill, J.; Cutter, G.; Kitson, G.; Desem, N.; et al. EMA401-003 study group. EMA401, an orally administered highly selective angiotensin II type 2 receptor antagonist, as a novel treatment for postherpetic neuralgia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.S.C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Anand, P.; Freeman, R.; Piaia, A.; Callegari, F.; Doerr, C.; Mondal, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of EMA401 in peripheral neuropathic pain: Results of 2 randomised, double-blind, phase 2 studies in patients with postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 2021, 162, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, M.; Aguilar, C.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shepherd, A.J. Angiotensin receptors and neuropathic pain. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, H.; Patil, J.; Nussberger, J.; Nicoud, F.; Hess, B.; Ahmed, N.; Schaffner, T.; Wellner, M.; Müller, D.; Inagami, T.; et al. Endogenous angiotensinergic system in neurons of rat and human trigeminal ganglia. Regul. Pept. 2009, 154, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Bains, R.; Mokha, S.S. Effect of antisense knock-down of alpha(2a)- and alpha(2c)-adrenoceptors on the antinociceptive action of clonidine on trigeminal nociception in the rat. Pain 2002, 98, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaksh, T.L.; Rudy, T.A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol. Behav. 1976, 17, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hestehave, S.; Munro, G.; Christensen, R.; Brønnum Pedersen, T.; Arvastson, L.; Hougaard, P.; Abelson, K.S.P. Is there a reasonable excuse for not providing post-operative analgesia when using animal models of peripheral neuropathic pain for research purposes? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergova, S.; Hentall, I.D.; Gajavelli, S.; Varghese, M.S.; Sagen, J. Intraspinal transplantation of GABAergic neural progenitors attenuates neuropathic pain in rats: A pharmacologic and neurophysiological evaluation. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannampalli, P.; Pochiraju, S.; Bruckert, M.; Shaker, R.; Banerjee, B.; Sengupta, J.N. Analgesic effect of minocycline in rat model of inflammation-induced visceral pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 727, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, S.R.; Ju, J.S.; Yang, G.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Youn, D.H.; Bae, Y.C. Intratrigeminal ganglionic injection of LPA causes neuropathic pain-like behavior and demyelination in rats. Pain 2009, 146, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Ju, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Central VEGF-A pathway plays a key role in the development of trigeminal neuropathic pain in rats. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919872602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Son, J.Y.; Ju, J.S.; Ahn, D.K. Early Blockade of EphA4 Pathway Reduces Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.R.; Yang, G.Y.; Ahn, M.H.; Kim, M.J.; Ju, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Blockade of microglial activation reduces mechanical allodynia in rats with compression of the trigeminal ganglion. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 36, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Shin, H.J.; Won, K.A.; Yang, K.Y.; Ju, J.S.; Park, Y.Y.; Park, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Progesterone produces antinociceptive and neuroprotective effects in rats with microinjected lysophosphatidic acid in the trigeminal nerve root. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.K.; Kang, S.H.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Ju, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Co-administered low doses of Ibuprofen and Dexamethasone produce synergistic antinociceptive effects on neuropathic mechanical allodynia in rats. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.K.; Kim, K.; Jung, S.J.; Kim, M.J.; Ahn, D.K.; Hong, S.D.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.B. Molecular mechanism for local anesthetic action of eugenol in the rat trigeminal system. Pain 2009, 144, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P.; Pedersen, N.S.; Staahl, C.; Drewes, A.M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Subcutaneous Botulinum toxin type A reduces capsaicin-induced trigeminal pain and vasomotor reactions in human skin. Pain 2009, 141, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, M. Tissue renin-angiotensin-aldosterone systems: Targets for pharmacological therapy. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, W.; Ogata, Y.; Nakagawasai, O.; Yaoita, F.; Tadano, T.; Tan-No, K. Involvement of p38 MAPK activation mediated through AT1 receptors on spinal astrocytes and neurons in angiotensin II- and III-induced nociceptive behavior in mice. Neuropharmacology 2015, 99, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschina, E.; Unger, T. Angiotensin AT1/AT2 receptors: Regulation, signalling and function. Blood Press 2003, 12, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Siragy, H.M. Role of the angiotensin type 2 receptor in the regulation of blood pressure and renal function. Hypertension 2000, 35, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.T.; Anand, P.; Rice, A.S. Selective small molecule angiotensin II type 2 receptor antagonists for neuropathic pain: Preclinical and clinical studies. Pain 2016, 157 (Suppl. S1), S33–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulakat, L.; Sumners, C. Angiotensin Type 2 Receptors: Painful, or Not? Front Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 571994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, Y.; Nemoto, W.; Nakagawasai, O.; Yamagata, R.; Tadano, T.; Tan-No, K. Involvement of Spinal Angiotensin II System in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Neuropathic Pain in Mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Liao, Z.; Smith, P.G. Angiotensin II receptor type 2 activation is required for cutaneous sensory hyperinnervation and hypersensitivity in a rat hind paw model of inflammatory pain. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.T.; Woodruff, T.M.; Wyse, B.D.; Muralidharan, A.; Walther, T. A small molecule angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT₂R) antagonist produces analgesia in a rat model of neuropathic pain by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and p44/p42 MAPK activation in the dorsal root ganglia. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, A.; Wyse, B.D.; Smith, M.T. Analgesic efficacy and mode of action of a selective small molecule angiotensin II type 2 receptor antagonist in a rat model of prostate cancer-induced bone pain. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Mickle, A.D.; Golden, J.P.; Mack, M.R.; Halabi, C.M.; de Kloet, A.D.; Samineni, V.K.; Kim, B.S.; Krause, E.G.; Gereau, R.W., IV; et al. Macrophage angiotensin II type 2 receptor triggers neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8057–E8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Facer, P.; Yiangou, Y.; Sinisi, M.; Fox, M.; McCarthy, T.; Bountra, C.; Korchev, Y.E.; Anand, P. Angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) localization and antagonist-mediated inhibition of capsaicin responses and neurite outgrowth in human and rat sensory neurons. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.; Schwab, A.; Nussberger, J.; Schaffner, T.; Saavedra, J.M.; Imboden, H. Intraneuronal angiotensinergic system in rat and human dorsal root ganglia. Regul. Pept. 2010, 162, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.T.; Wyse, B.D.; Edwards, S.R. Small molecule angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT₂R) antagonists as novel analgesics for neuropathic pain: Comparative pharmacokinetics, radioligand binding, and efficacy in rats. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Lopes, J.; Pinto, M.; Pinho, D.; Morato, M.; Patinha, D.; Albino-Teixeira, A.; Tavares, I. Microinjection of angiotensin II in the caudal ventrolateral medulla induces hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, W.A.; Pelegrini-da-Silva, A.; Martins, A.R. Microinjection of renin-angiotensin system peptides in discrete sites within the rat periaqueductal gray matter elicits antinociception. Brain Res. 2003, 972, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelegrini-da-Silva, A.; Martins, A.R.; Prado, W.A. A new role for the renin-angiotensin system in the rat periaqueductal gray matter: Angiotensin receptor-mediated modulation of nociception. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yien, H.W.; Chan, J.Y.; Tsai, H.F.; Lee, T.Y.; Chan, S.H. Participation of nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis in the antinociceptive effect of angiotensin III in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 159, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, K.-D.; Son, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, Y.-M.; Ju, J.-S.; Jo, M.-J.; Park, M.-K.; Lee, M.-K.; Ahn, D.-K. Differential Regulation of Intracisternally Injected Angiotensin II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123279
Park K-D, Son J-Y, Kim H-K, Kim Y-M, Ju J-S, Jo M-J, Park M-K, Lee M-K, Ahn D-K. Differential Regulation of Intracisternally Injected Angiotensin II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(12):3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123279
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Ki-Don, Jo-Young Son, Hak-Kyun Kim, Yu-Mi Kim, Jin-Sook Ju, Min-Jeong Jo, Min-Kyoung Park, Min-Kyung Lee, and Dong-Kuk Ahn. 2023. "Differential Regulation of Intracisternally Injected Angiotensin II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats" Biomedicines 11, no. 12: 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123279
APA StylePark, K.-D., Son, J.-Y., Kim, H.-K., Kim, Y.-M., Ju, J.-S., Jo, M.-J., Park, M.-K., Lee, M.-K., & Ahn, D.-K. (2023). Differential Regulation of Intracisternally Injected Angiotensin II-Induced Mechanical Allodynia and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Rats. Biomedicines, 11(12), 3279. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11123279