Effect of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on Infarct Growth Rate and Stroke Outcomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Receiving Endovascular Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
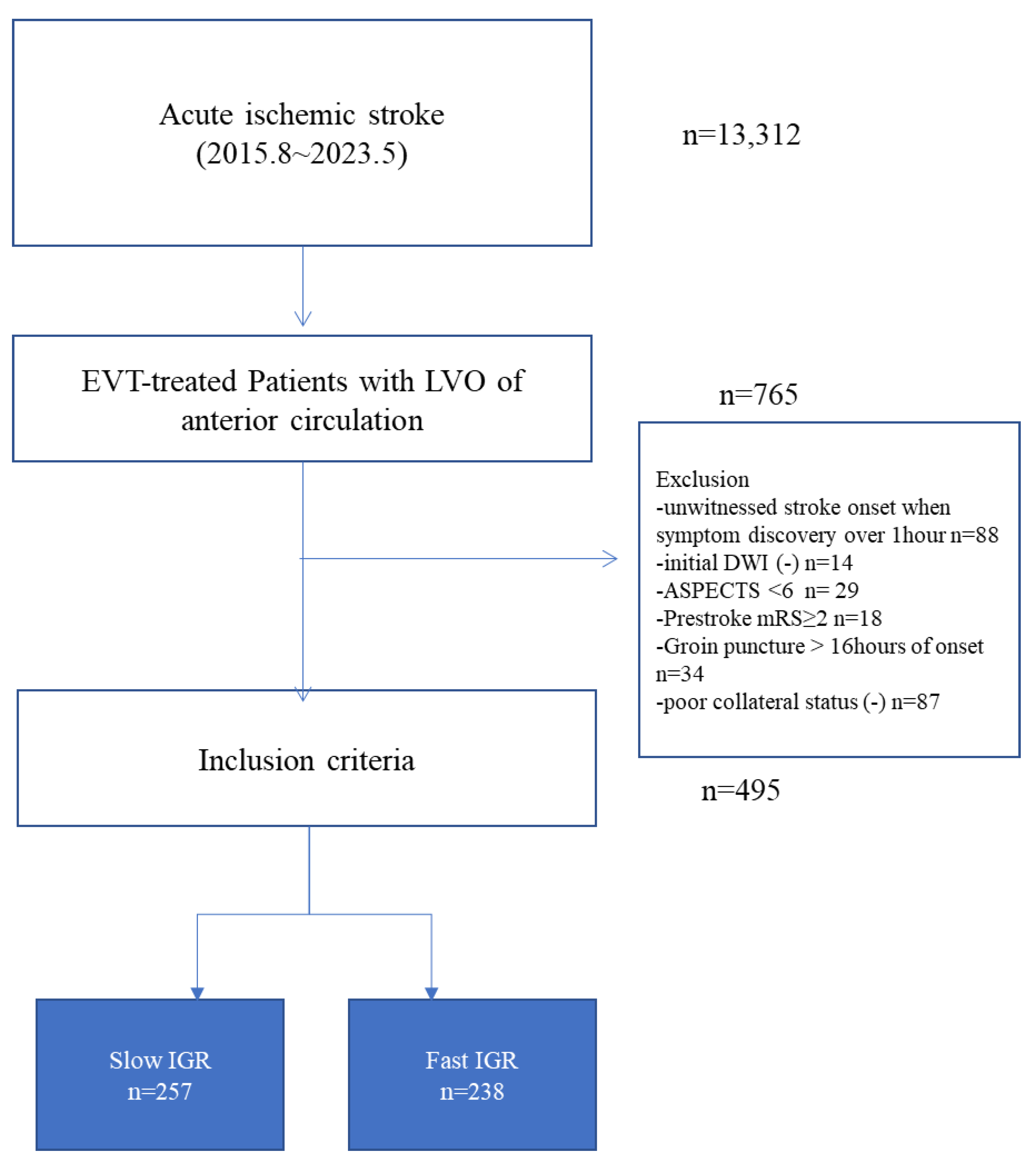
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Clinical Data and Definition of Parameters
2.3. Assessment of CSVD Burden
2.4. Definitions of Imaging Biomarkers
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consents Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Mechanisms of sporadic cerebral small vessel disease: Insights from neuroimaging. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forestier, G.; Agbonon, R.; Bricout, N.; Benhassen, W.; Turc, G.; Bretzner, M.; Pasi, M.; Benzakoun, J.; Seners, P.; Personnic, T.; et al. Small vessel disease and collaterals in ischemic stroke patients treated with thrombectomy. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 4708–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Gan, J.; Chen, F.; Le, C.; Chen, Y. Overall cerebral small vessel disease burden is associated with outcome of acute ischemic stroke after mechanical thrombectomy. Interv. Neuroradiol. 2022, 15910199221138140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ning, Y.; Lei, L.; Yuan, H.; Liu, H.; Luo, G.; Wei, M.; Li, Y. Cerebral Small Vessel Diseases and Outcomes for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients after Endovascular Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, H. Small Vessel Disease Burden and Outcomes of Mechanical Thrombectomy in Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 602037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Thijs, V.N.; Wechsler, L.; Kemp, S.; Schlaug, G.; Skalabrin, E.; Bammer, R.; Kakuda, W.; Lansberg, M.G.; Shuaib, A.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging profiles predict clinical response to early reperfusion: The diffusion and perfusion imaging evaluation for understanding stroke evolution (DEFUSE) study. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansberg, M.G.; Straka, M.; Kemp, S.; Mlynash, M.; Wechsler, L.R.; Jovin, T.G.; Wilder, M.J.; Lutsep, H.L.; Czartoski, T.J.; Bernstein, R.A.; et al. MRI profile and response to endovascular reperfusion after stroke (DEFUSE 2): A prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.W.; Christensen, S.; McElduff, P.; Levi, C.R.; Butcher, K.S.; De Silva, D.A.; Ebinger, M.; Barber, P.A.; Bladin, C.; Donnan, G.A.; et al. Pretreatment diffusion- and perfusion-MR lesion volumes have a crucial influence on clinical response to stroke thrombolysis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2010, 30, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, H.M.; Mlynash, M.; Inoue, M.; Tipirnini, A.; Liggins, J.; Bammer, R.; Lansberg, M.G.; Kemp, S.; Zaharchuk, G.; Straka, M.; et al. The growth rate of early DWI lesions is highly variable and associated with penumbral salvage and clinical outcomes following endovascular reperfusion. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litak, J.; Mazurek, M.; Kulesza, B.; Szmygin, P.; Litak, J.; Kamieniak, P.; Grochowski, C. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.L.; Sweet, J.G.; Bishop, N.; Cipolla, M.J. Pial Collateral Reactivity During Hypertension and Aging: Understanding the Function of Collaterals for Stroke Therapy. Stroke 2016, 47, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federau, C.; Christensen, S.; Mlynash, M.; Tsai, J.; Kim, S.; Zaharchuk, G.; Inoue, M.; Straka, M.; Mishra, N.K.; Kemp, S.; et al. Comparison of stroke volume evolution on diffusion-weighted imaging and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery following endovascular thrombectomy. Int. J. Stroke 2017, 12, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.; Christensen, S.; Tress, B.M.; Churilov, L.; Desmond, P.M.; Parsons, M.W.; Barber, P.A.; Levi, C.R.; Bladin, C.; Donnan, G.A.; et al. Failure of collateral blood flow is associated with infarct growth in ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2013, 33, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe-Orozco, D.; Sequeiros, J.M.; Farooqui, M.; Zevallos, C.B.; Mendez-Ruiz, A.; Dajles, A.; Kobsa, J.; Prasad, A.; Petersen, N.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S. Stroke Severity and Early Ischemic Changes Predict Infarct Growth Rate and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Large-Vessel Occlusion. Stroke: Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2022, 2, e000182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Lee, S.; Chung, J.W.; Han, M.K.; Park, J.M.; Kang, K.; Park, T.H.; Park, S.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Hong, K.S.; et al. MRI-based Algorithm for Acute Ischemic Stroke Subtype Classification. J. Stroke 2014, 16, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duering, M.; Biessels, G.J.; Brodtmann, A.; Chen, C.; Cordonnier, C.; de Leeuw, F.E.; Debette, S.; Frayne, R.; Jouvent, E.; Rost, N.S.; et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease-advances since 2013. Lancet Neurol 2023, 22, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staals, J.; Makin, S.D.; Doubal, F.N.; Dennis, M.S.; Wardlaw, J.M. Stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and total MRI brain small-vessel disease burden. Neurology 2014, 83, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazin, P.L.; Cuzzocreo, J.L.; Yassa, M.A.; Gandler, W.; McAuliffe, M.J.; Bassett, S.S.; Pham, D.L. Volumetric neuroimage analysis extensions for the MIPAV software package. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 165, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.K.; d’Esterre, C.D.; Qazi, E.M.; Almekhlafi, M.; Hahn, L.; Demchuk, A.M.; Goyal, M. Multiphase CT Angiography: A New Tool for the Imaging Triage of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Radiology 2015, 275, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.H.; Lee, J.K.; Park, M.S.; Park, S.S.; Hong, K.S.; Ryu, W.S.; Kim, D.E.; Park, M.S.; Choi, K.H.; Kim, J.T.; et al. Neurologic deterioration in patients with acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. Neurology 2020, 95, e2178–e2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Shue, F.; Bu, G.; Kanekiyo, T. Pathophysiology and probable etiology of cerebral small vessel disease in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Thrippleton, M.J.; Makin, S.D.; Marshall, I.; Geerlings, M.I.; de Craen, A.J.M.; van Buchem, M.A.; Wardlaw, J.M. Cerebral blood flow in small vessel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2016, 36, 1653–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, H.S.; de Leeuw, F.E. Cerebral small vessel disease: Recent advances and future directions. Int. J. Stroke 2023, 18, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Tan, L.; Song, Y.; Li, D.; Xue, B.; Lai, X.; Gao, Y. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Neuroimaging Features, Biochemical Markers, Influencing Factors, Pathological Mechanism and Treatment. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 843953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.S.; Ovbiagele, B. Association of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis with severity of white matter hyperintensities. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 44-e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, M.S.; Simpson, J.E.; Matthews, F.; Brayne, C.; Lewis, C.E.; Barber, R.; Kalaria, R.N.; Forster, G.; Esteves, F.; Wharton, S.B.; et al. White matter lesions in an unselected cohort of the elderly: Molecular pathology suggests origin from chronic hypoperfusion injury. Stroke 2006, 37, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, R.O.; Djuanda, E.; Yow, H.Y.; Carare, R.O. Lymphatic drainage of the brain and the pathophysiology of neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Lee, S.H. Cerebral microbleeds: Their associated factors, radiologic findings, and clinical implications. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Leng, X.; Nie, X.; Yan, H.; Tian, X.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wen, M.; Pu, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Small vessel disease burden may not portend unfavorable outcome after thrombectomy for acute large vessel occlusion. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 7824–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Yu, H.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Liu, S.H.; Xu, G.Q. The relationship between severe extracranial artery stenosis or occlusion and cerebral small vessel disease in patients with large artery atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1008319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, N.R.; Tarkin, J.M.; Walsh, J.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Patterson, A.J.; Graves, M.J.; Rudd, J.H.F.; Warburton, E.A. Carotid Atheroinflammation Is Associated With Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Severity. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 690935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Slow IGR (n = 257) | Fast IGR (n = 238) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year (SD) | 69.6 (13.6) | 70.0 (12.3) | 0.38 |
| Male, n (%) | 153 (59.5) | 134 (56.3) | 0.52 |
| Initial NIHSS, score (IQR) | 13 (9–18) | 16 (13–18) | <0.001 |
| Time from stroke onset to arrival, h (IQR) | 2.7 (0.8–8.7) | 1.1 (0.6–2.5) | <0.001 |
| Time from stroke onset to imaging, h (IQR) | 3.4 (1.3–7.0) | 1.6 (1.0–2.9) | <0.001 |
| Stroke subtypes, n (%) | 0.07 | ||
| LAA | 66 (25.7) | 50 (21.0) | |
| CE | 138 (53.7) | 152 (63.9) | |
| others | 53 (20.6) | 36 (15.1) | |
| Prior stroke, n (%) | 54 (21.0) | 51 (21.4) | 0.91 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 164 (63.8) | 146 (61.3) | 0.58 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 70 (27.2) | 60 (25.2) | 0.61 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | 50 (19.5) | 38 (16.0) | 0.35 |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 43 (16.7) | 32 (13.4) | 0.32 |
| Prior antithrombotics, n (%)) | 91 (35.4) | 89 (37.4) | 0.71 |
| Prior statin, n (%) | 50 (19.5) | 42 (17.6) | 0.65 |
| Prior IVT, n (%) | 105 (40.9) | 143 (60.1) | <0.001 |
| Occlusion site, n (%) | 0.003 | ||
| M1 | 192 (74.7) | 203 (85.3) | |
| distal M1/M2 | 52 (20.2) | 22 (9.2) | |
| ICA | 13 (5.1) | 13 (5.5) | |
| Successful reperfusion, n (%) | 206 (80.2) | 182 (76.5) | 0.33 |
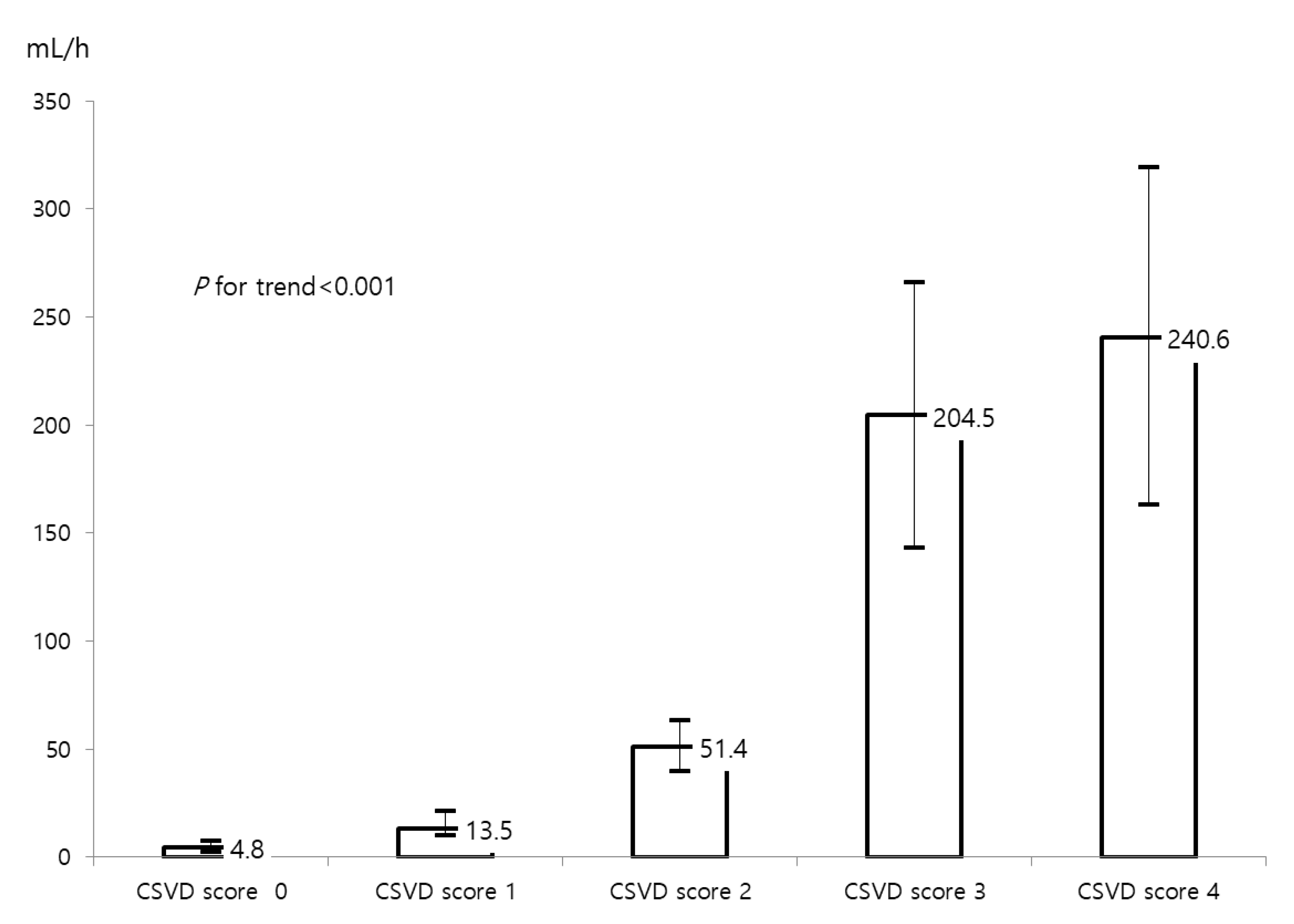
| CSVD score, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 179 (69.6) | 44 918.5) | |
| 1 | 56 (21.8) | 61 (25.6) | |
| 2 | 22 (8.6) | 76 (31.9) | |
| 3 | 0 (0.0) | 46 (19.3) | |
| 4 | 0 (0.0) | 11 (4.6) |
| Fast IGR | Stroke Progression | 3-Month mRS > 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | OR | 95%CI | OR | 95%CI | |
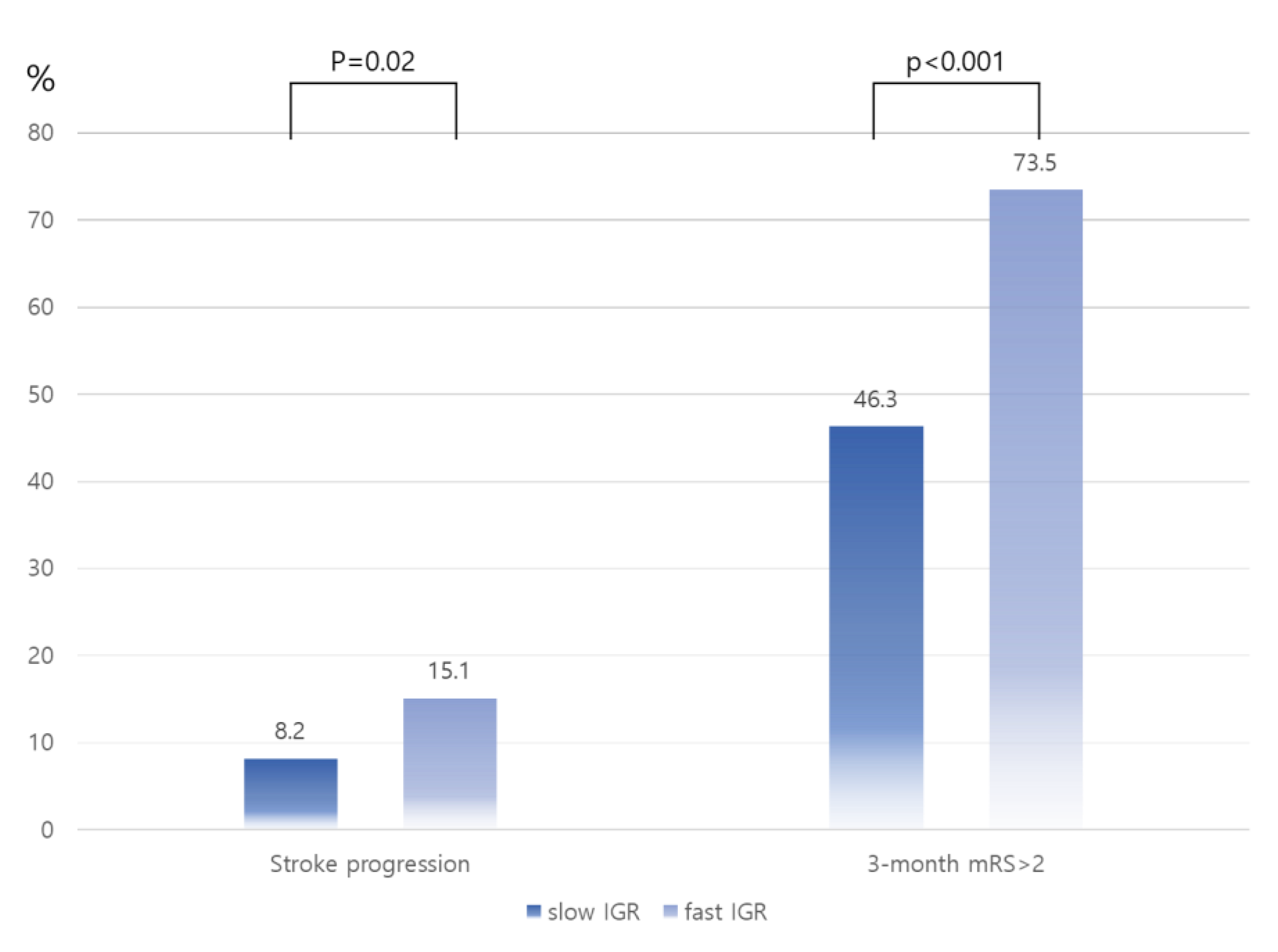
| High CSVD | 26.26 | 6.26–110.14 | 5.83 | 2.75–12.36 | 4.07 | 1.85–8.95 |
| Age | 0.998 | 0.98–1.02 | 0.99 | 0.97–1.02 | 1.05 | 1.03–1.07 |
| Male | 0.97 | 0.63–1.49 | 0.45 | 0.23–0.87 | 0.74 | 0.48–1.16 |
| Time from stroke onset to imaging time | 0.68 | 0.27–1.70 | 0.88 | 0.23–3.45 | 0.56 | 0.22–1.46 |
| Time from stroke onset to arrival time | 1.29 | 0.52–3.24 | 1.15 | 0.30–4.50 | 1.85 | 0.72–4.80 |
| Initial NIHSS | 1.05 | 1.01–1.08 | 0.94 | 0.89–0.996 | 1.11 | 1.07–1.16 |
| Stroke subtypes | ||||||
| Others | reference | reference | reference | |||
| LAA | 1.24 | 0.65–2.36 | 1.76 | 0.64–4.86 | 1.13 | 0.59–2.18 |
| CE | 1.48 | 0.83–2.63 | 1.82 | 0.71–4.66 | 0.73 | 0.41–1.30 |
| Prior IVT | 1.41 | 0.87–2.27 | 0.76 | 0.39–1.51 | 0.83 | 0.52–1.35 |
| Occlusion site | 0.70 | 0.47–1.05 | 1.63 | 1.04–2.58 | 1.16 | 0.78–1.72 |
| Successful reperfusion | 0.79 | 0.48–1.30 | 0.30 | 0.16–0.56 | 0.25 | 0.14–0.44 |
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.004 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.65 |
| Male | 0.65 | 0.59–1.52 | 0.82 |
| Time from stroke onset to imaging time | 0.60 | 0.22–1.66 | 0.33 |
| Time from stroke onset to arrival time | 1.52 | 0.55–4.21 | 0.42 |
| Initial NIHSS | 1.01 | 0.97–1.05 | 0.75 |
| Stroke subtypes | 0.93 | 0.66–1.32 | 0.69 |
| Prior IVT | 1.42 | 0.83–2.41 | 0.20 |
| Occlusion site | 0.70 | 0.45–1.10 | 0.12 |
| CSVD markers | |||
| DWMH Fazekas 2–3 | 3.24 | 2.05–5.13 | <0.001 |
| PWMH Fazekas 3 | 1.15 | 1.08–1.23 | <0.001 |
| EPVS (Score 2–4) | 3.47 | 1.21–9.94 | 0.02 |
| CMB(s) ≥ 1 | 13.74 | 3.14–60.15 | 0.001 |
| Lacune(s) ≥ 1 | 1.54 | 0.88–2.67 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohn, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.; Sung, J.H.; Han, S.-W.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, M.; Yu, K.-H.; Lee, J.J.; et al. Effect of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on Infarct Growth Rate and Stroke Outcomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Receiving Endovascular Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113102
Sohn J-H, Kim Y, Kim C, Sung JH, Han S-W, Kim Y, Park S-H, Lee M, Yu K-H, Lee JJ, et al. Effect of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on Infarct Growth Rate and Stroke Outcomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Receiving Endovascular Treatment. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113102
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohn, Jong-Hee, Yejin Kim, Chulho Kim, Joo Hye Sung, Sang-Won Han, Yerim Kim, Soo-Hyun Park, Minwoo Lee, Kyung-Ho Yu, Jae Jun Lee, and et al. 2023. "Effect of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on Infarct Growth Rate and Stroke Outcomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Receiving Endovascular Treatment" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113102
APA StyleSohn, J.-H., Kim, Y., Kim, C., Sung, J. H., Han, S.-W., Kim, Y., Park, S.-H., Lee, M., Yu, K.-H., Lee, J. J., & Lee, S.-H. (2023). Effect of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Burden on Infarct Growth Rate and Stroke Outcomes in Large Vessel Occlusion Stroke Receiving Endovascular Treatment. Biomedicines, 11(11), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113102





