Diagnosis of Endometriosis Based on Comorbidities: A Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
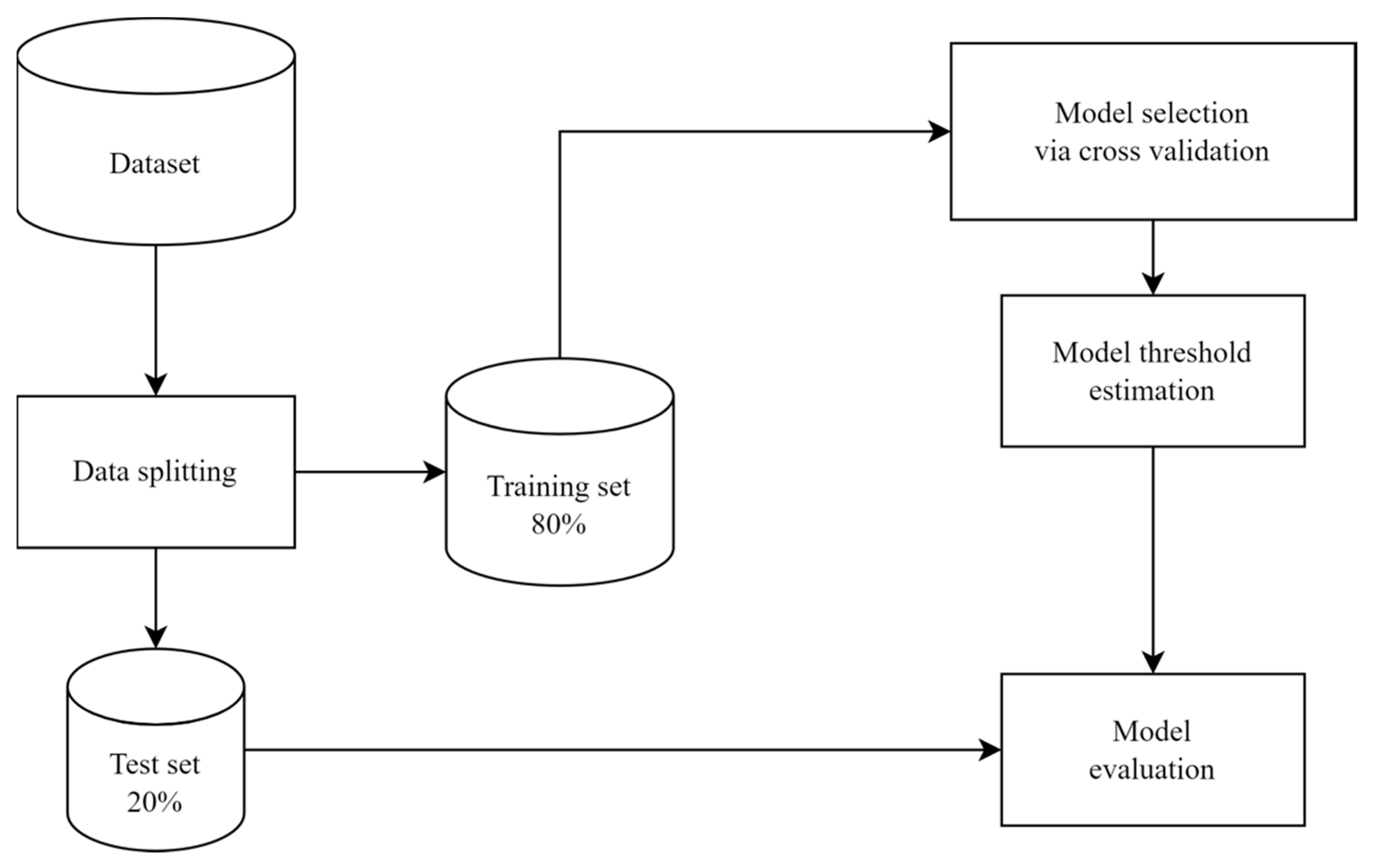
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Preprocessing
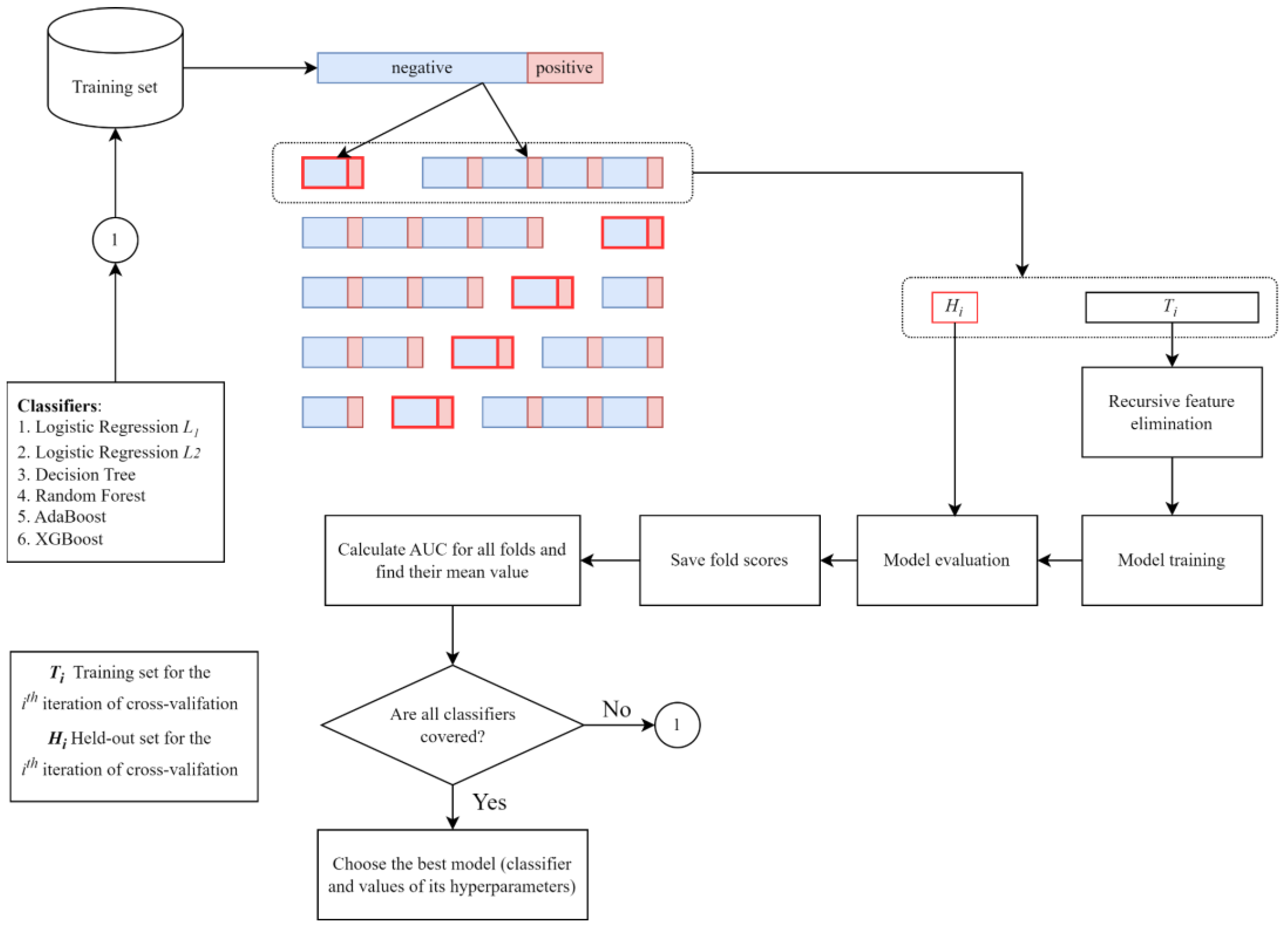
2.3. Initial Model Selection
2.4. Machine Learning Platform: A General Review
2.5. Model and Feature Selection
2.6. Model Threshold Estimation
2.7. Model Evaluation
2.8. Software and Packages
3. Results
3.1. Data Description
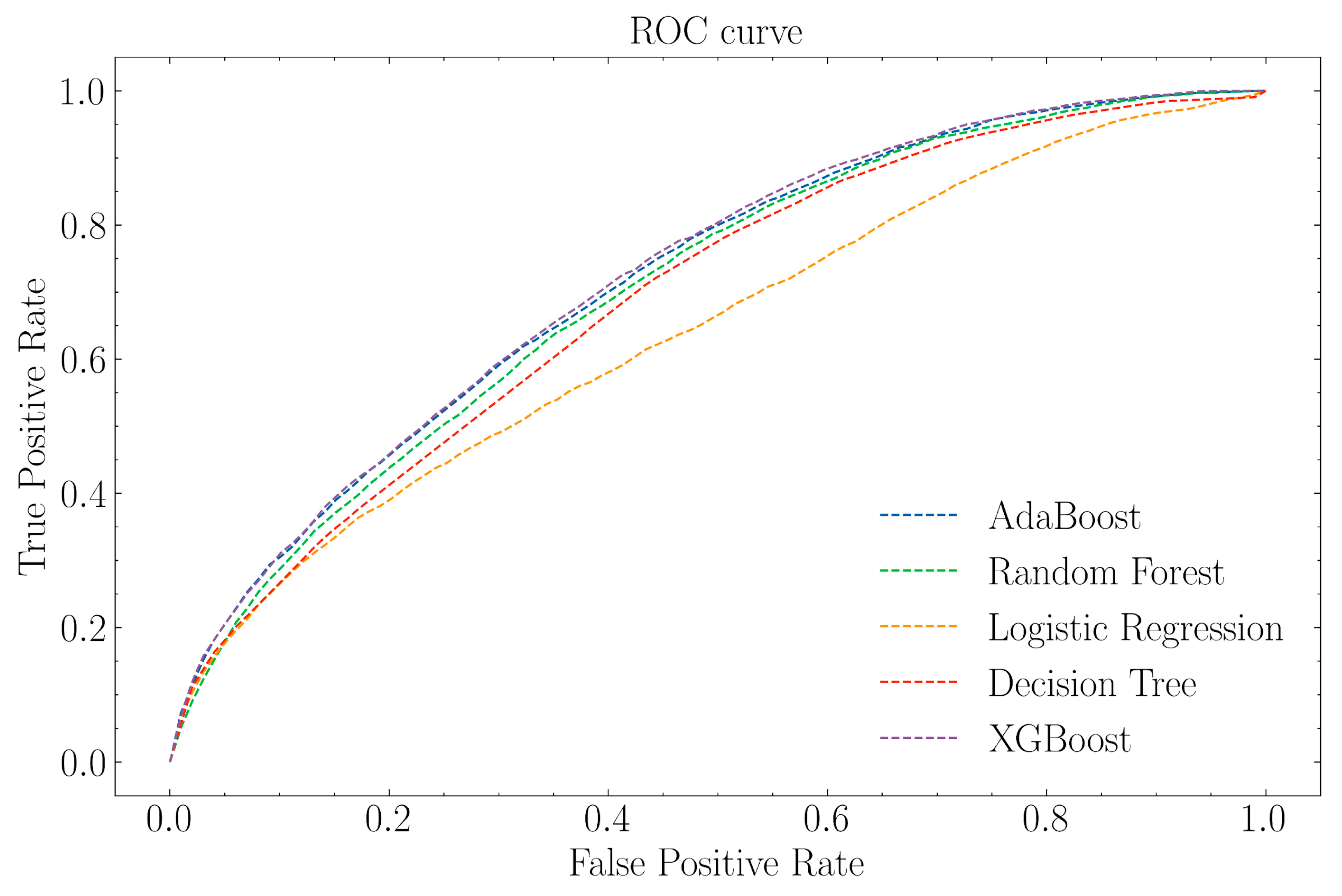
3.2. Prediction Performance
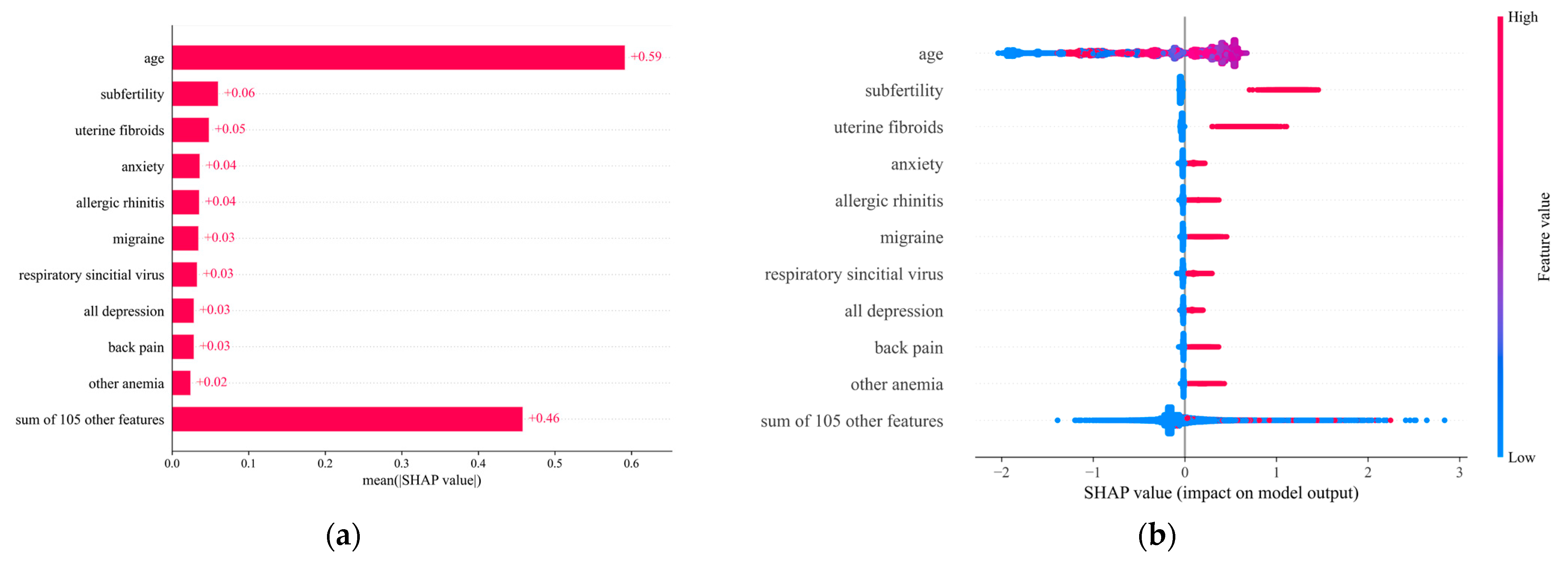
3.3. Impact Direction and Importance of Each Feature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zondervan, K.T.; Becker, C.M.; Missmer, S.A. Endometriosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.M.; Yang, H.; Du, E.X.; Kelley, C.; Winkel, C. The direct and indirect costs associated with endometriosis: A systematic literature review. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzic, M.; Aimagambetova, G.; Garzon, S.; Bapayeva, G.; Ukybassova, T.; Terzic, S.; Norton, M.; Laganà, A.S. Ovulation induction in infertile women with endometriotic ovarian cysts: Current evidence and potential pitfalls. Minerva Medica 2020, 111, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.S.; Kotlyar, A.M.; Flores, V.A. Endometriosis is a chronic systemic disease: Clinical challenges and novel innovations. Lancet 2021, 397, 839–852. [Google Scholar]
- Mechsner, S. Endometriosis, an ongoing pain—Step-by-step treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciullo, L.; Viscardi, M.F.; Piacenti, I.; Scaramuzzino, S.; Cavalli, A.; Piccioni, M.G.; Porpora, M.G. A deep insight into pelvic pain and endometriosis: A review of the literature from pathophysiology to clinical expressions. Minerva Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 73, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.G.; La Rosa, V.L.; Vitagliano, A.; Noventa, M.; Laganà, F.M.; Ardizzone, A.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; Terzic, M.M.; Terzic, S.; Laganà, A.S. Sexual function and quality of life in patients affected by deep infiltrating endometriosis: Current evidence and future perspectives. J. Endometr. Pelvic Pain Disord. 2017, 9, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, M.; Behboodi Moghadam, Z.; Zareiyan, A.; Jafarabadi, M. Impact of endometriosis on Reproductive Health: An Integrative Review. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 41, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, W.; Cao, L. Miscarriage on endometriosis and adenomyosis in women by assisted reproductive technology or with spontaneous conception: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4381346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimagambetova, G.; Terzic, S.; Bapayeva, G.; Micic, J.; Kongrtay, K.; Laganà, A.S.; Terzic, M. Endometriotic cyst and infertility. In Advances in Health and Disease; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 38, pp. 31–65. ISBN 978-1-53619-723-5. [Google Scholar]
- Filip, L.; Duică, F.; Prădatu, A.; Crețoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Crețoiu, S.M.; Predescu, D.-V.; Varlas, V.N.; Voinea, S.-C. Endometriosis associated infertility: A critical review and analysis on ETIOPATHOGENESIS and therapeutic approaches. Medicina 2020, 56, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzkowsky, K. Rethinking endometriosis and Pelvic Pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e154876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Koo, Y.-J.; Lee, D.-H. Classification of endometriosis. J. Med. 2021, 38, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.M.; Bokor, A.; Heikinheimo, O.; Horne, A.; Jansen, F.; Kiesel, L.; King, K.; Kvaskoff, M.; Nap, A.; Petersen, K.; et al. Eshre guideline: Endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. Open 2022, 2022, hoac009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eskenazi, B.; Warner, M.L. Epidemiology of endometriosis. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 24, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarria-Santamera, A.; Orazumbekova, B.; Terzic, M.; Issanov, A.; Chaowen, C.; Asúnsolo-Del-Barco, A. Systematic Review and meta-analysis of incidence and prevalence of endometriosis. Healthcare 2020, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendifallah, S.; Puchar, A.; Suisse, S.; Delbos, L.; Poilblanc, M.; Descamps, P.; Golfier, F.; Touboul, C.; Dabi, Y.; Daraï, E. Machine learning algorithms as new screening approach for patients with endometriosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blass, I.; Sahar, T.; Shraibman, A.; Ofer, D.; Rappoport, N.; Linial, M. Revisiting the risk factors for endometriosis: A machine learning approach. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surrey, E.S.; Soliman, A.M.; Johnson, S.J.; Davis, M.; Castelli-Haley, J.; Snabes, M.C. Risk of developing comorbidities among women with endometriosis: A retrospective matched Cohort Study. J. Women’s Health 2018, 27, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.-W.; Horng, H.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Yen, M.-S.; Chao, H.-T.; Wang, P.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.; Chao, K.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; et al. Women with endometriosis have higher comorbidities: Analysis of domestic data in Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, S.; Lazzeroni, M.; Peccatori, F.; Bendinelli, B.; Saieva, C.; Palli, D.; Masala, G.; Caini, S. The risk of extra-ovarian malignancies among women with endometriosis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2019, 134, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Friedman, J.; Tisbshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Su-In, L. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sarría-Santamera, A.; Khamitova, Z.; Gusmanov, A.; Terzic, M.; Polo-Santos, M.; Ortega, M.A.; Asúnsolo, A. History of endometriosis is independently associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Additive logistic regression: A statistical view of boosting (with discussion and a rejoinder by the authors). Ann. Stat. 2000, 28, 337–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, J. XGBoost with Python: Gradient Boosted Trees with XGBoost and Scikit-Learn; Machine Learning Mastery: Victoria, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene Selection for Cancer Classification using Support Vector Machines. Mach. Learn. 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abibullaev, B.; Zollanvari, A. Learning discriminative spatial spectral features of ERPs for accurate brain–computer interfaces. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2019, 23, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Cohen, S. Self-report symptom-based endometriosis prediction using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivajohan, B.; Elgendi, M.; Menon, C.; Allaire, C.; Yong, P.; Bedaiwy, M.A. Clinical use of artificial intelligence in endometriosis: A scoping review. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth-Carson, S.J.; Ng, C.H.M.; Dior, U.P. Editorial: Comorbidities in women with endometriosis: Risks and implications. Front. Reprod. Health 2022, 4, 875277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, K.D.; Seaman, H.E.; de Vries, C.S.; Wright, J.T. Can symptomatology help in the diagnosis of endometriosis? Findings from a national case–control study—Part 1. BJLOG 2008, 115, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cea Soriano, L.; López-Garcia, E.; Schulze-Rath, R.; Garcia Rodríguez, L.A. Incidence, treatment and recurrence of endometriosis in a UK-based population analysis using data from The Health Improvement Network and the Hospital Episode Statistics database. Health Care 2017, 22, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, V.H.; Weil, C.; Chodick, G.; Shalev, V. Epidemiology of endometriosis: A large population-based database study from a healthcare provider with 2 million members. BJOG 2018, 125, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Ihle, P.; Köster, I.; Schubert, I. Prevalence and incidence of diagnosed endometriosis and risk of endometriosis in patients with endometriosis-related symptoms: Findings from a statutory health insurance-based cohort in Germany. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2012, 160, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signorile, P.G.; Viceconte, R.; Baldi, A. New insights in pathogenesis of endometriosis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 879015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Endometriosis and infertility: A committee opinion. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 98, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uimari, O.; Nazri, H.; Tapmeier, T. Endometriosis and Uterine Fibroids (Leiomyomata): Comorbidity, Risks and Implications. Front. Reprod. Health 2021, 3, 750018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, A.S.; La Rosa, V.L.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; Valenti, G.; Sapia, F.; Chiofalo, B.; Rossetti, D.; Frangez, H.B.; Bokal, E.V.; Vitale, S.G. Anxiety and depression in patients with endometriosis: Impact and management challenges. Int. J. Women’s Health 2017, 9, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalliotakis, I.; Cakmak, H.; Matalliotakis, M.; Kappou, D.; Arici, A. High Rate of Allergies among Women with Endometriosis. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2012, 32, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classifier | Hyperparameter | Hyperparameter Space |
|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | Penalty | L1, L2 |
| Regularization parameter C | 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 1000, 10,000, 20,000, 30,000, 40,000, 50,000, 60,000, 70,000, 80,000, 90,000, 100,000 | |
| Decision Tree | Maximum depth | 1, 2, 10 |
| Criterion | ‘gini’, ‘entropy’ | |
| Minimum samples per leaf | 1, 2, 10 | |
| Splitter | ‘random’, ‘best’ | |
| Random Forest | Maximum Features | ‘auto’, ‘log2′ |
| Maximum depth | 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 | |
| Number of estimators | 10, 100, 1000, 10,000 | |
| Ada Boost | Number of estimators | 10, 100, 1000 |
| Learning rate | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1 | |
| XGBoost | Number of estimators | 10, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, 1000,1250 |
| Learning rate | 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100 | |
| Maximum depth | 5, 8, 10 | |
| Sampling method | ‘uniform’ | |
| Gamma | 0, 1, 3, 5 | |
| Subsample ratio of columns by tree | 0.3, 0.5, 0.7 | |
| Subsample | 0.7, 0.8, 0.9 |
| Classifier | AUC | Number of Selected Features | Hyperparameter Space |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.646 | 115 | Penalty: L2, |
| Regularization parameter C: 8000 | |||
| Decision Tree | 0.693 | 100 | Criterion: ‘gini’, |
| Maximum depth: 10, Minimum samples per leaf: 1, | |||
| Splitter: ‘best’ | |||
| Random Forest | 0.705 | 100 | Maximum features: ‘auto’ |
| Maximum depth: 20, Number of estimators: 1000 | |||
| Ada Boost | 0.718 | 115 | Learning rate: 0.1, |
| Number of estimators: 1000 | |||
| XGBoost | 0.721 | 115 | Number of estimators: 1225, |
| Maximum depth: 8, Subsample ratio of columns: 0.3, | |||
| Gamma: 1, | |||
| Learning rate: 0.01, | |||
| Sampling method: ‘uniform’, | |||
| Subsample: 0.8 |
| AUC | Balanced acc. | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.725 | 0.658 | 0.686 | 0.629 | 0.015 |
| Predicted Label | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| True label | Positive | 706 | 323 |
| Negative | 45,054 | 76,473 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tore, U.; Abilgazym, A.; Asunsolo-del-Barco, A.; Terzic, M.; Yemenkhan, Y.; Zollanvari, A.; Sarria-Santamera, A. Diagnosis of Endometriosis Based on Comorbidities: A Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113015
Tore U, Abilgazym A, Asunsolo-del-Barco A, Terzic M, Yemenkhan Y, Zollanvari A, Sarria-Santamera A. Diagnosis of Endometriosis Based on Comorbidities: A Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113015
Chicago/Turabian StyleTore, Ulan, Aibek Abilgazym, Angel Asunsolo-del-Barco, Milan Terzic, Yerden Yemenkhan, Amin Zollanvari, and Antonio Sarria-Santamera. 2023. "Diagnosis of Endometriosis Based on Comorbidities: A Machine Learning Approach" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113015
APA StyleTore, U., Abilgazym, A., Asunsolo-del-Barco, A., Terzic, M., Yemenkhan, Y., Zollanvari, A., & Sarria-Santamera, A. (2023). Diagnosis of Endometriosis Based on Comorbidities: A Machine Learning Approach. Biomedicines, 11(11), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113015







