Identification of Novel Targeting Sites of Calcineurin and CaMKII in Human CaV3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid cDNA Construction and Mutagenesis
2.2. Cell Culture and Transient Expression
2.3. Cell Lysis and Immunoprecipitation
2.4. In Vitro Calcineurin and CaMKII reactions
2.5. Gel-Assisted Digestion, In-Gel Digestion, and Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography
2.6. Mass Spectrometry (MS), Database Searching, and Phosphopeptide Quantification
2.7. Generation of Phospho-S2137 Cav3.2 Antibody and Immunoblotting
2.8. Electrophysiological Recording
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Amino Acid Residues on Cav3.2 Dephosphorylated by Calcineurin
3.2. CaMKII Kinase Phosphorylates S2137 of Cav3.2
3.3. Effect of S2137 Phosphorylation on the Functional Properties of Cav3.2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catterall, W.A. Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels. CSH Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiaen, L.; Callewaert, G.; Parys, J.B.; Wuytack, F.; Raeymaekers, L.; Droogmans, G.; Nilius, B.; Eggermont, J.; De Smedt, H. Intracellular calcium: Physiology and physiopathology. Verh. K Acad. Geneeskd. Belg. 2000, 62, 471–499. [Google Scholar]
- Catterall, W.A.; Lenaeus, M.J.; El-Din, T.M.G. Structure and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 2020, 60, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgari, D.; Frosio, A.; Calamaio, S.; Marzi, G.A.; Pappone, C.; Rivolta, I. T-Type Calcium Channels: A Mixed Blessing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, N.; Zamponi, G.W. Genetic T-type calcium channelopathies. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourinet, E.; Alloui, A.; Monteil, A.; Barrere, C.; Couette, B.; Poirot, O.; Pages, A.; McRory, J.; Snutch, T.P.; Eschalier, A.; et al. Silencing of the Ca(v)3.2 T-type calcium channel gene in sensory neurons demonstrates its major role in nociception. Embo J. 2005, 24, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Caballero, A.; Gadotti, V.M.; Stemkowski, P.; Weiss, N.; Souza, I.A.; Hodgkinson, V.; Bladen, C.; Chen, L.; Hamid, J.; Pizzoccaro, A.; et al. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP5 modulates neuropathic and inflammatory pain by enhancing Cav3.2 channel activity. Neuron 2014, 83, 1144–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.T.; Zamponi, G.W. Regulation of voltage gated calcium channels by GPCRs and post-translational modification. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rahman, G.; Gorelik, J.; Bhargava, A. Voltage-Gated T-Type Calcium Channel Modulation by Kinases and Phosphatases: The Old Ones, the New Ones, and the Missing Ones. Cells 2023, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Depuy, S.D.; Yao, J.; McIntire, W.E.; Barrett, P.Q. Protein kinase A activity controls the regulation of T-type CaV3.2 channels by Gbetagamma dimers. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 7465–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Davies, L.A.; Howard, J.D.; Adney, S.K.; Welsby, P.J.; Howell, N.; Carey, R.M.; Colbran, R.J.; Barrett, P.Q. Molecular basis for the modulation of native T-type Ca2+ channels in vivo by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsby, P.J.; Wang, H.; Wolfe, J.T.; Colbran, R.J.; Johnson, M.L.; Barrett, P.Q. A mechanism for the direct regulation of T-type calcium channels by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10116–10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, K.; Calderon-Rivera, A.; Sandoval, A.; Gonzalez-Ramirez, R.; Vargas-Parada, A.; Ojeda-Alonso, J.; Granados-Soto, V.; Delgado-Lezama, R.; Felix, R. Cdk5-Dependent Phosphorylation of Ca(v)3.2 T-Type Channels: Possible Role in Nerve Ligation-Induced Neuropathic Allodynia and the Compound Action Potential in Primary Afferent C Fibers. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftinca, M.; Hamid, J.; Chen, L.; Varela, D.; Tadayonnejad, R.; Altier, C.; Turner, R.W.; Zamponi, G.W. Regulation of T-type calcium channels by Rho-associated kinase. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Perez-Reyes, E.; Lee, J.H. Modulation of Ca(v)3.2 T-type Ca2+ channels by protein kinase C. Febs Lett. 2003, 547, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Hameed, S.; Fernandez-Fernandez, J.M.; Fablet, K.; Karmazinova, M.; Poillot, C.; Proft, J.; Chen, L.N.; Bidaud, I.; Monteil, A.; et al. A Ca(v)3.2/Syntaxin-1A Signaling Complex Controls T-type Channel Activity and Low-threshold Exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2810–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.C. Physical interaction between calcineurin and Cav3.2 T-type Ca2+ channel modulates their functions. Febs Lett. 2013, 587, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, M.; Yao, C.Y. Calcineurin in development and disease. Genes Dis. 2022, 9, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molkentin, J.D.; Lu, J.R.; Antos, C.L.; Markham, B.; Richardson, J.; Robbins, J.; Grant, S.R.; Olson, E.N. A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 1998, 93, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, B.J.; Dai, Y.S.; Bueno, O.F.; Parsons, S.A.; Xu, J.; Plank, D.M.; Jones, F.; Kimball, T.R.; Molkentin, J.D. Calcineurin/NFAT coupling participates in pathological, but not physiological, cardiac hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.S.; Huang, C.H.; Chieng, H.L.; Chang, Y.T.; Chang, D.R.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Shin, H.S.; Campbell, K.P.; et al. The Ca(v)3.2 T-Type Ca2+ Channel Is Required for Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy in Mice. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.L.; Chien, C.W.; Chen, W.C.; Chen, Y.R.; Wu, C.P.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.J. A Multiplexed Quantitative Strategy for Membrane Proteomics: Opportunities for Mining Therapeutic Targets for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2008, 7, 1983–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.W.; Chang, Y.T.; Wang, Q.C.; Lin, J.J.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, C.C. Quantitative Phosphoproteomic Study of Pressure-Overloaded Mouse Heart Reveals Dynamin-Related Protein 1 as a Modulator of Cardiac Hypertrophy. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2013, 12, 3094–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitski, M.M.; Lemeer, S.; Boesche, M.; Lang, M.; Mathieson, T.; Bantscheff, M.; Kuster, B. Confident Phosphorylation Site Localization Using the Mascot Delta Score. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, C.C.; Tsai, C.F.; Tsui, Y.H.; Sudhir, P.R.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Sung, T.Y.; Hsu, W.L. IDEAL-Q, an Automated Tool for Label-free Quantitation Analysis Using an Efficient Peptide Alignment Approach and Spectral Data Validation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesneac, I.; Chemin, J.; Bidaud, I.; Huc-Brandt, S.; Vandermoere, F.; Lory, P. Phosphorylation of the Cav3.2 T-type calcium channel directly regulates its gating properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13705–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Zhang, B.; Murray, B.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Skrzypek, E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: Mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, D512–D520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnad, F.; Gunawardena, J.; Mann, M. PHOSIDA 2011: The posttranslational modification database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D253–D260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Caballero, A.; Gandini, M.A.; Huang, S.; Chen, L.; Souza, I.A.; Dang, Y.L.; Stutts, M.J.; Zamponi, G.W. Cav3.2 calcium channel interactions with the epithelial sodium channel ENaC. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.; Green, S.H. CaMKII and CaMKIV mediate distinct prosurvival signaling pathways in response to depolarization in neurons. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2007, 36, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Rao, A.; Hogan, P.G. Interaction of calcineurin with substrates and targeting proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelladeana, A.; Krinks, M.H.; Ruzzene, M.; Klee, C.; Pinna, L.A. Dephosphorylation of Phosphopeptides by Calcineurin (Protein Phosphatase 2b). Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 219, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagur, R.; Hajnoczky, G. Intracellular Ca2+ Sensing: Its Role in Calcium Homeostasis and Signaling. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dephoure, N.; Gould, K.L.; Gygi, S.P.; Kellogg, D.R. Mapping and analysis of phosphorylation sites: A quick guide for cell biologists. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecky, B.J.; Liang, R.Q.; Bao, J.X. T-type calcium channel blockers as neuroprotective agents. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Phys. 2014, 466, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, E.K.; Zamponi, G.W. Central and peripheral contributions of T-type calcium channels in pain. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, V.; Chen, Y.C.; Chin, Y.K.; Dekan, Z.; Chang, Y.W.; Yu, H.M.; Alewood, P.F.; Chen, C.C.; King, G.F. The Tarantula Toxin omega-Avsp1a Specifically Inhibits Human Ca(V)3.1 and Ca(V)3.3 via the Extracellular S3-S4 Loop of the Domain 1 Voltage-Sensor. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunican, D.J.; Doherty, P. Designing cell-permeant phosphopeptides to modulate intracellular signaling pathways. Biopolymers 2001, 60, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


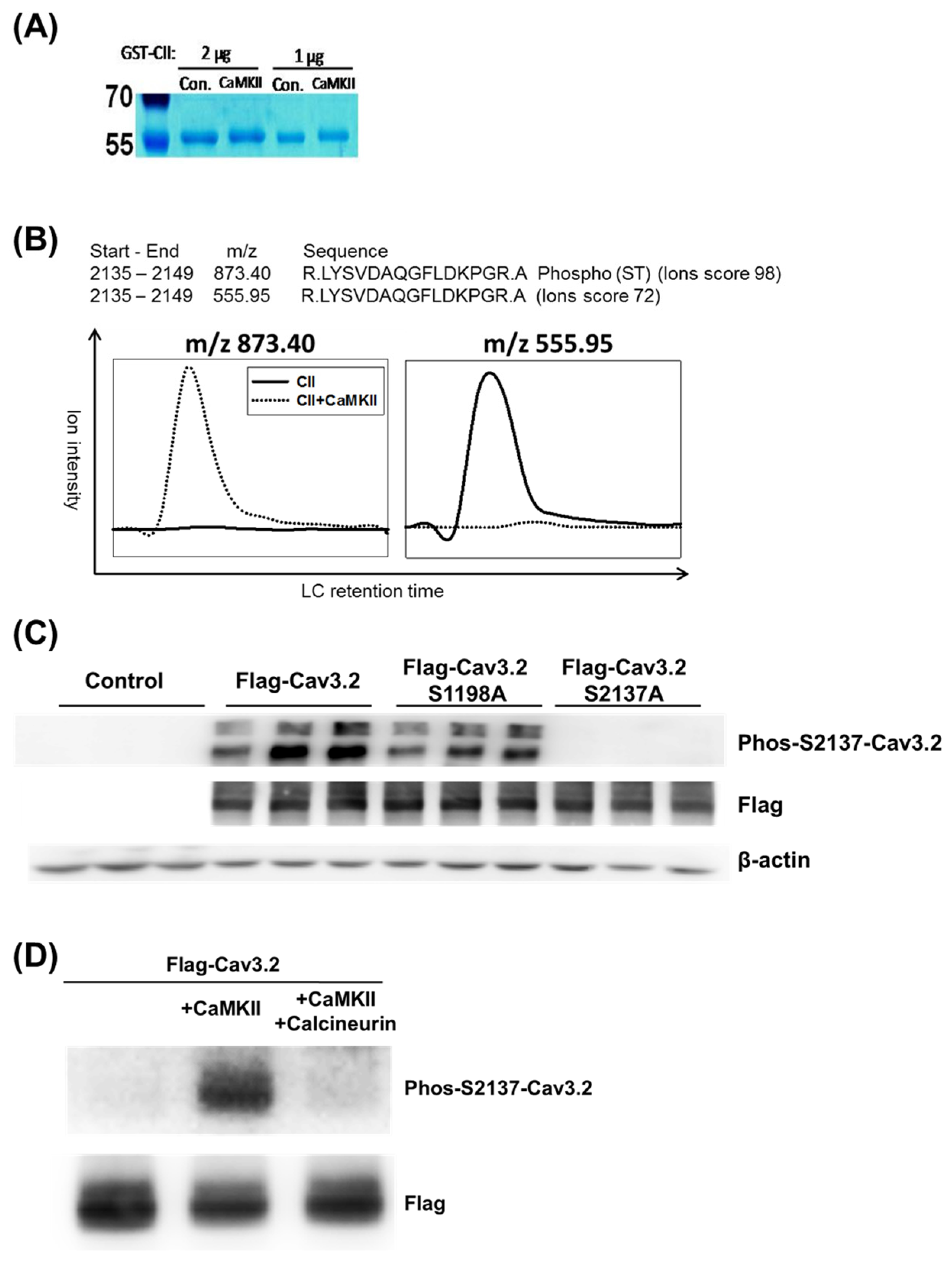


| Spectra_No. a | Exp_mz b | Phosphopeptide_Matched c | Start d | End d | Site e | Score f | Delta_Score g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 800.40 | VPLGAPPPGPAALVGASPEpSPGAPGR | 13 | 38 | S32 | 70 | 20 |
| 2 | 827.07 | VPLGAPPPGPAALVGApSPEpSPGAPGR | 13 | 38 | S29, S32 | 48 | 39 |
| 3 | 1069.48 | EAERGpSELGVSPSESPAAER | 39 | 58 | S44 | 133 | 50 |
| 4 | 826.87 | GSELGVpSPSESPAAER | 43 | 58 | S49 | 86 | 19 |
| 5 | 866.85 | GSELGVpSPSEpSPAAER | 43 | 58 | S49, S53 | 75 | 11 |
| 6 | 766.64 | EAERGpSELGVpSPSEpSPAAER | 39 | 58 | S44, S49, S53 | 36 | 6 |
| 7 | 1327.08 | HLpSNDSTLASFSEPGSCYEELLK | 440 | 462 | S442 | 84 | 7 |
| 8 | 585.77 | AGAPPpSPPSPGR | 553 | 564 | S558 | 37 | 16 |
| 9 | 585.77 | AGAPPSPPpSPGR | 553 | 564 | S561 | 31 | 21 |
| 10 | 625.75 | AGAPPpSPPpSPGR | 553 | 564 | S558, S561 | 35 | 26 |
| 11 | 824.38 | WAGGPPGTGGHGPLSLNpSPDPYEK | 636 | 659 | S653 | 40 | 8 |
| 12 | 1043.92 | ALEDPEGELpSGSESGDSDGR | 706 | 725 | S715 | 128 | 29 |
| 13 | 1083.90 | ALEDPEGELpSGpSESGDSDGR | 706 | 725 | S715, S717 | 93 | 25 |
| 14 | 1177.44 | ALEDPEGELpSGpSEpSGDpSDGRGVYEFTQDVR | 706 | 735 | S715, S717, S719, S722 | 54 | 10 |
| 15 | 709.30 | ATDTPGPGPGpSPQR | 748 | 761 | S758 | 47 | 24 |
| 16 | 1123.46 | SDTDEDKTpSVHFEEDFHK | 1027 | 1044 | S1035 | 69 | 7 |
| 17 | 820.38 | SSPFLDAAPpSLPDSR | 1090 | 1104 | S1099 | 74 | 14 |
| 18 | 860.37 | SSPFLDAAPpSLPDpSR | 1090 | 1104 | S1099, S1103 | 36 | 13 |
| 19 | 898.43 | SSPFLDAAPSLPDpSRR | 1090 | 1105 | S1103 | 41 | 21 |
| 20 | 730.35 | RGpSSSSGDPPLGDQKPPASLR | 1105 | 1125 | S1107 | 77 | 6 |
| 21 | 1135.00 | RGpSSpSSGDPPLGDQKPPASLR | 1105 | 1125 | S1107, S1109 | 43 | 6 |
| 22 | 558.26 | SpSWSSLGR | 1143 | 1150 | S1144 | 43 | 10 |
| 23 | 711.29 | EpSLLSGEGKGSTDDEAEDGR | 1164 | 1183 | S1165 | 49 | 7 |
| 24 | 500.23 | ESLLpSGEGK | 1164 | 1172 | S1168 | 55 | 30 |
| 25 | 711.29 | ESLLSGEGKGpSTDDEAEDGR | 1164 | 1183 | S1174 | 75 | 6 |
| 26 | 616.21 | GSpTDDEAEDGR | 1173 | 1183 | T1175 | 36 | 9 |
| 27 | 1106.43 | ESLLSGEGKGpSpTDDEAEDGR | 1164 | 1183 | S1174, T1175 | 113 | 35 |
| 28 | 670.35 | AEpSLDPRPLRPAALPPTK | 1196 | 1213 | S1198 | 30 | 23 |
| 29 | 504.58 | RRpSTFPSPEAQR | 1585 | 1596 | S1587 | 47 | 12 |
| 30 | 531.23 | RRpSpTFPSPEAQR | 1585 | 1596 | S1587, T1588 | 32 | 8 |
| 31 | 600.26 | STFPpSPEAQR | 1587 | 1596 | S1591 | 34 | 18 |
| 32 | 542.25 | RPYYADYpSPTRR | 1597 | 1608 | S1604 | 46 | 11 |
| 33 | 892.92 | VDADRPPLPQEpSPGAR | 1894 | 1909 | S1905 | 50 | 31 |
| 34 | 622.30 | SGEPLHALpSPR | 1991 | 2001 | S1999 | 62 | 38 |
| 35 | 910.42 | IDpSPRDTLDPAEPGEK | 2028 | 2043 | S2030 | 55 | 22 |
| 36 | 619.65 | TPVRPVTQGGSLQpSPPR | 2044 | 2060 | S2057 | 91 | 36 |
| 37 | 873.42 | LYpSVDAQGFLDKPGR | 2135 | 2149 | S2137 | 92 | 33 |
| 38 | 839.13 | KMpSPPCISVEPPAEDEGSARPSAAEGGSTTLR | 2186 | 2217 | S2188 | 42 | 12 |
| 39 | 460.86 | RTPpSCEATPHR | 2219 | 2229 | S2222 | 46 | 14 |
| Site | Domain | Predicted Kinase Motif a |
|---|---|---|
| S32 | N-terminal | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) ERK (P-X-S/T-P, P-E-S/T-P) |
| S44 | N-terminal | PKA (R-X-S/T) |
| S49 | N-terminal | CK2 (S/T-X-X-E) GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) NEK6 (L-X-X-S/T) |
| S53 | N-terminal | CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) |
| S442 | I–II loop | CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) AKT (R-X-R-X-X-S/T) |
| S558 | I–II loop | ERK (P-X-S/T-P) |
| S561 | I–II loop | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) CDK2 (S/T-P-X-K/R) ERK (P-X-S/T-P) CDK1 (S/T-P-X-K/R) |
| S653 | I–II loop | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) |
| S715 | I–II loop | CK2 (S/T-X-X-E) GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) |
| S717 | I–II loop | NEK6 (L-X-X-S/T) |
| S719 | I–II loop | CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) |
| S722 | I–II loop | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) |
| S758 | I–II loop | CDK2 (S/T-P-X-K/R) ERK (P-X-S/T-P) CDK1 (S/T-P-X-K/R) |
| S1035 | II–III loop | Aurora (R/K-X-S/T-I/L/V) |
| S1099 | II–III loop | GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) |
| S1103 | II–III loop | CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) NEK6 (L-X-X-S/T) |
| S1107 | II–III loop | PKA (R-X-S/T, R-R/K-X-S/T) CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) AKT (R-R/S/T-X-S/T-X-S/T) |
| S1109 | II–III loop | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) |
| S1144 | II–III loop | PKA (R-X-S/T, R-R/K-X-S/T) CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) AKT (R-R/S/T-X-S/T-X-S/T) |
| S1165 | II–III loop | PKA (R-X-S/T) Aurora (R/K-X-S/T-I/L/V) |
| S1168 | II–III loop | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) |
| T1175 | II–III loop | CK2 (S/T-X-X-E) |
| S1198 | II–III loop | CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) PKD (L/V/I-X-R/K-X-X-S/T) CHK1/2 (L-X-R-X-X-S/T) CHK1 (M/I/L/V-X-R/K-X-X-S/T) |
| S1587 | III–IV loop | PKA (R-X-S/T, R-R/K-X-S/T) GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) |
| T1588 | III–IV loop | PKA (R-X-S/T, R-R/K-X-S/T) CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) AKT (R-X-R-X-X-S/T) |
| S1591 | III–IV loop | CK1 (S/T-X-X-X-S) |
| S1604 | III–IV loop | CDK2 (S/T-P-X-K/R) CDK1 (S/T-P-X-K/R) |
| S1999 | C-terminal | CDK1 (S/T-P-K/R) |
| S2030 | C-terminal | CDK1 (S/T-P-K/R) |
| S2057 | C-terminal | CK1 (S-X-X-S/T) GSK3 (S-X-X-X-S) CDK2 (S/T-P-X-K/R) CDK1 (S/T-P-X-K/R) |
| S2137 | C-terminal | CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T, R-X-X-S/T-V) PKD (L/V/I-X-R/K-X-X-S/T) CHK1/2 (L-X-R-X-X-S/T) CHK1 (M/I/L/V-X-R/K-X-X-S/T) |
| S2222 | C-terminal | CaMKII (R-X-X-S/T) AKT (R-X-R-X-X-S/T) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Identification of Novel Targeting Sites of Calcineurin and CaMKII in Human CaV3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112891
Chang Y-W, Chen Y-C, Chen C-C. Identification of Novel Targeting Sites of Calcineurin and CaMKII in Human CaV3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112891
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yu-Wang, Yong-Cyuan Chen, and Chien-Chang Chen. 2023. "Identification of Novel Targeting Sites of Calcineurin and CaMKII in Human CaV3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112891
APA StyleChang, Y.-W., Chen, Y.-C., & Chen, C.-C. (2023). Identification of Novel Targeting Sites of Calcineurin and CaMKII in Human CaV3.2 T-Type Calcium Channel. Biomedicines, 11(11), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112891







