Plasma Gel Made of Platelet-Poor Plasma: In Vitro Verification as a Carrier of Polyphosphate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Collection
2.2. Platelet-Poor Plasma Preparation
2.3. Heating Protocol
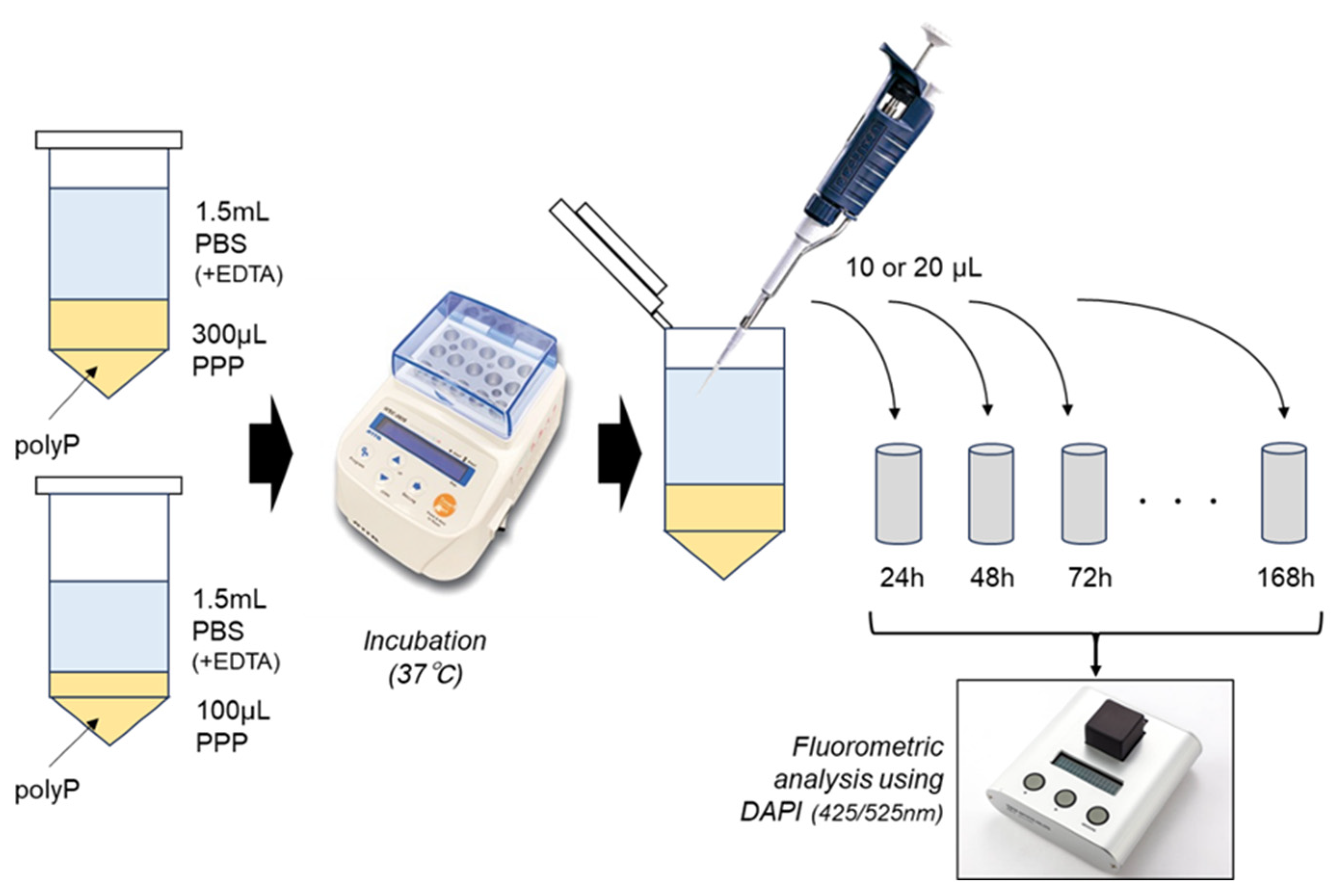
2.4. polyP-Releasing Test
2.5. Determination of Water Content in PPP Gels
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopic Examination of Plasma Gel
2.7. Statistical Analysis
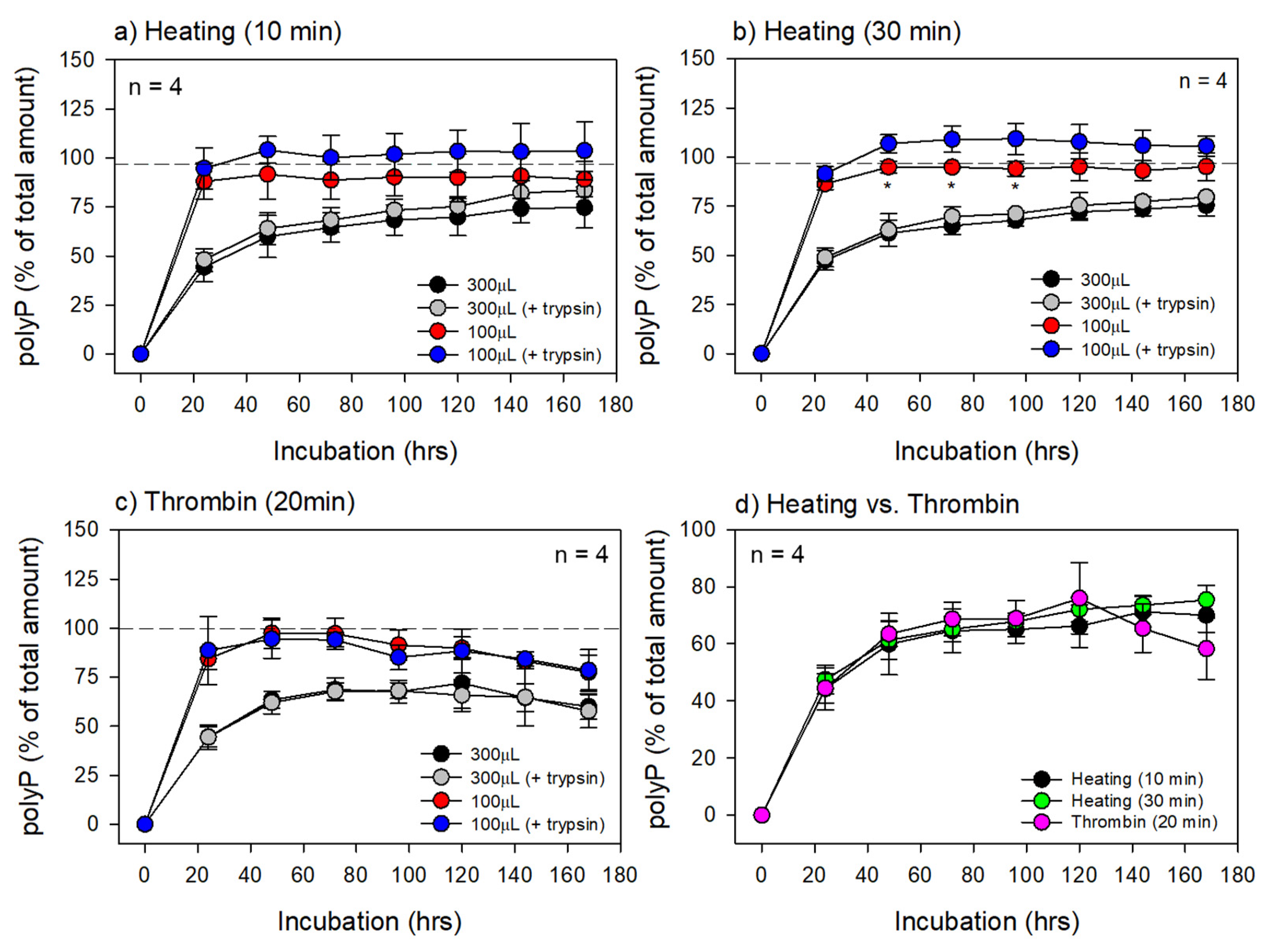
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Heating Temperature and Time and Insoluble Components
4.2. Structural Characteristics and Water Content
4.3. Degradation of the PG Matrices
4.4. Advantages of the Thermally-Prepared PG Matrices over Thrombin-Prepared Methods
4.5. Immunogenicity of the PG Matrix
4.6. Candidate polyP-Binding Proteins and Other Molecules
4.7. Technical Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Pinto, N.R.; Pereda, A.; Jimenez, P.; Corso, M.D.; Kang, B.S.; Nally, M.; Lanata, N.; Wang, H.L.; Quirynen, M. The impact of the centrifuge characteristics and centrifugation protocols on the cells, growth factors, and fibrin architecture of a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) clot and membrane. Platelets 2018, 29, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratajczak, J.; Vangansewinkel, T.; Gervois, P.; Merckx, G.; Hilkens, P.; Quirynen, M.; Lambrichts, I.; Bronckaers, A. Angiogenic Properties of ‘Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin’. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Y. Autologous liquid platelet rich fibrin: A novel drug delivery system. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheno, E.; Mourão, C.; Mello-Machado, R.C.; Stellet Lourenço, E.; Miron, R.J.; Catarino, K.F.F.; Alves, A.T.; Alves, G.G.; Calasans-Maia, M.D. In vivo evaluation of the biocompatibility and biodegradation of a new denatured plasma membrane combined with liquid PRF (Alb-PRF). Platelets 2021, 32, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.; Zhao, J.; Justin, A.W.; Markaki, A.E. Albumin-based hydrogels for regenerative engineering and cell transplantation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 3457–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doghaim, N.N.; El-Tatawy, R.A.; Neinaa, Y.M.E. Assessment of the efficacy and safety of platelet poor plasma gel as autologous dermal filler for facial rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewska, L. Autologous Plasma Gel as an Effective Method of Facial Volume Restoration and Skin Rejuvenation. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 2023, 9989544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, C.F.; Lowenstein, A. The Use of Alb-PRF as a Drug Delivery System for Malignant Lesion Treatment. Rev. Bras. Cancerol. 2023, 69, e-013762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, A.; Abbina, S.; Kalathottukaren, M.T.; Morrissey, J.H.; Haynes, C.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Pfaendtner, J.; Chou, K.C. Design of Polyphosphate Inhibitors: A Molecular Dynamics Investigation on Polyethylene Glycol-Linked Cationic Binding Groups. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyo-Fourtine, J.; Juillé, M.; Hénin, J.; Clavaguéra, C.; Duboué-Dijon, E. Consistent Picture of Phosphate–Divalent Cation Binding from Models with Implicit and Explicit Electronic Polarization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Smith, S.A. Polyphosphate: An ancient molecule that links platelets, coagulation, and inflammation. Blood 2012, 119, 5972–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, C.F.; Gheno, E.; Lourenço, E.; Barbosa, R.; Kurtzman, G.; Javid, K.; Mavropoulos, E.; Benedicenti, S.; Calasans-Maia, M.; de Mello Machado, R.; et al. Characterization of a new membrane from concentrated growth factors associated with denaturized Albumin (Alb-CGF) for clinical applications: A preliminary study. Int. J. Growth Factors Stem. Cells Dent. 2018, 1, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushiki, T.; Mochizuki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kamimura, M.; Ishiguro, H.; Suwabe, T.; Kawase, T. Modulation of ATP Production Influences Inorganic Polyphosphate Levels in Non-Athletes' Platelets at the Resting State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Aizawa, H.; Masuki, H.; Tsujino, T.; Sato, A.; Kawabata, H.; Isobe, K.; Nakata, K.; Kawase, T. Fluorometric Quantification of Human Platelet Polyphosphate Using 4',6-Diamidine-2-phenylindole Dihydrochloride: Applications in the Japanese Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.C.; Thomas, V.; Schmidt, G.; Vohra, Y.K.; Chu, T.M.; Kowolik, M.J.; Janowski, G.M. Recent advances in the development of GTR/GBR membranes for periodontal regeneration—A materials perspective. Dent. Mater. Off. Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukioka, T.; Hiratsuka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Isobe, K.; Okudera, T.; Okudera, H.; Azuma, A.; Uematsu, K.; et al. An on-site preparable, novel bone-grafting complex consisting of human platelet-rich fibrin and porous particles made of a recombinant collagen-like protein. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2019, 107, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, G.; Mou, X.; Hotovely-Salomon, A.; Levdansky, L.; Gaberman, E.; Belenky, D.; Gorodetsky, R. Heat denaturation of fibrinogen to develop a biomedical matrix. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 84B, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarja, G.A.; Brash, J.L.; Bishop, P.; Woodhouse, K.A. Protein and platelet interactions with thermally denatured fibrinogen and cross-linked fibrin coated surfaces. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonidakis, K.A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Patterson, J.; Vos, B.E.; Koenderink, G.H.; Vermant, J.; Lambrechts, D.; Roeffaers, M.; Van Oosterwyck, H. Fibrin structural and diffusional analysis suggests that fibers are permeable to solute transport. Acta Biomater. 2017, 47, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühsel, S.; Brückner, A.; Schmelzle, S.; Heethoff, M.; Blüthgen, N. Surface area-volume ratios in insects. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.E. Biophysical Mechanisms Mediating Fibrin Fiber Lysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2748340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstaff, C.; Kolev, K. Basic mechanisms and regulation of fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13 (Suppl. S1), S98–S105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risman, R.A.; Kirby, N.C.; Bannish, B.E.; Hudson, N.E.; Tutwiler, V. Fibrinolysis: An illustrated review. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 7, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, M.; Isobe, K.; Kawabata, H.; Uematsu, K.; Okuda, K.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kawase, T. Platelet Counts in Insoluble Platelet-Rich Fibrin Clots: A Direct Method for Accurate Determination. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaide, H.; Shainoff, J.R. Cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin by fibrin-stablizing factor (factor XIIIa). J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1975, 85, 574–597. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, H.O.; Sheu, M.T.; Sokoloski, T.D.; Chen, C.Y. Drug release from glutaraldehyde-treated fibrin gels. Drug Des. Deliv. 1990, 7, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Dare, E.V.; Griffith, M.; Poitras, P.; Kaupp, J.A.; Waldman, S.D.; Carlsson, D.J.; Dervin, G.; Mayoux, C.; Hincke, M.T. Genipin Cross-Linked Fibrin Hydrogels for in vitro Human Articular Cartilage Tissue-Engineered Regeneration. Cells Tissues Organs 2009, 190, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawa, V.; Terry, F.; Gokemeijer, J.; Mitra-Kaushik, S.; Roberts, B.J.; Tourdot, S.; De Groot, A.S. T-Cell Dependent Immunogenicity of Protein Therapeutics Pre-clinical Assessment and Mitigation–Updated Consensus and Review 2020. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER); Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Immunogenicity Assessment for Therapeutic Protein Products. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/85017/download (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Bogahawaththa, D.; Ashraf, R.; Chandrapala, J.; Donkor, O.; Vasiljevic, T. In vitro immunogenicity of various native and thermally processed bovine milk proteins and their mixtures. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8726–8736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, E.A. Screening for Good Batches of Fetal Bovine Serum for Myeloma and Hybridoma Growth. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Jensen, S.S.; Øster, A.; Houen, G. A comparison of the immunogenicity of the native and denatured forms of a protein. APMIS 1996, 104, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenzlin, V.; Roewe, J.; Strueve, M.; Martínez-Negro, M.; Sharma, A.; Reinhardt, C.; Morsbach, S.; Bosmann, M. Bacterial-Type Long-Chain Polyphosphates Bind Human Proteins in the Phosphatidylinositol Signaling Pathway. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Collins, J.N.; Choi, S.H.; Morrissey, J.H. Novel Polyphosphate-Binding Proteins in Human Plasma and Platelet Releasates. Blood 2011, 118, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Wholey, W.Y.; Wagner, N.O.; Cremers, C.M.; Mueller-Schickert, A.; Hock, N.T.; Krieger, A.G.; Smith, E.M.; Bender, R.A.; Bardwell, J.C.; et al. Polyphosphate is a primordial chaperone. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.L.; Lionikiene, A.S.; Georgiev, G.; Klemmer, A.; Brain, C.; Kim, P.Y.; Mutch, N.J. Polyphosphate colocalizes with factor XII on platelet-bound fibrin and augments its plasminogen activator activity. Blood 2016, 128, 2834–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, J.J.; Willbold, S.; Blank, L.M. Methods for the Analysis of Polyphosphate in the Life Sciences. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Heating (10 min) | Heating (30 min) | Thrombin (20 min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (mg) | (Percentage) | Weight (mg) | (Percentage) | Weight (mg) | (Percentage) | |
| Liquid | 288.8 ± 9.8 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 272.0 ± 7.1 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 327.2 ± 2.4 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Gel | 276.0 ± 9.0 | 95.6 ± 1.7 | 254.6 ± 8.8 | 88.4 ± 2.5 | 327.2 ± 2.4 | 100.0 ± 0.0 |
| Dried | 225.2 ± 7.1 | 78.0 ± 2.3 | 226.6 ± 14.2 | 78.6 ± 3.3 | 150.8 ± 10.3 | 46.1 ± 2.9 |
| Water content in PG or FG | 52.8 in 300 (μL) | 29.4 in 300 (μL) | 177.9 in 330 (μL) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, M.; Masuki, H.; Kawabata, H.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, T.; Tsujino, T.; Isobe, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Mourão, C.F.; Kawase, T. Plasma Gel Made of Platelet-Poor Plasma: In Vitro Verification as a Carrier of Polyphosphate. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112871
Nakamura M, Masuki H, Kawabata H, Watanabe T, Watanabe T, Tsujino T, Isobe K, Kitamura Y, Mourão CF, Kawase T. Plasma Gel Made of Platelet-Poor Plasma: In Vitro Verification as a Carrier of Polyphosphate. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112871
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Masayuki, Hideo Masuki, Hideo Kawabata, Taisuke Watanabe, Takao Watanabe, Tetsuhiro Tsujino, Kazushige Isobe, Yutaka Kitamura, Carlos Fernando Mourão, and Tomoyuki Kawase. 2023. "Plasma Gel Made of Platelet-Poor Plasma: In Vitro Verification as a Carrier of Polyphosphate" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112871
APA StyleNakamura, M., Masuki, H., Kawabata, H., Watanabe, T., Watanabe, T., Tsujino, T., Isobe, K., Kitamura, Y., Mourão, C. F., & Kawase, T. (2023). Plasma Gel Made of Platelet-Poor Plasma: In Vitro Verification as a Carrier of Polyphosphate. Biomedicines, 11(11), 2871. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11112871









