Effective Perturbations by Phenobarbital on INa, IK(erg), IK(M) and IK(DR) during Pulse Train Stimulation in Neuroblastoma Neuro-2a Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Drugs, and Solutions
2.2. Cell Preparation
2.3. Electrophysiological Measurements
2.4. Data Recordings
2.5. Whole-Cell Data Analyses
2.6. Curve-Fitting Approximations and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
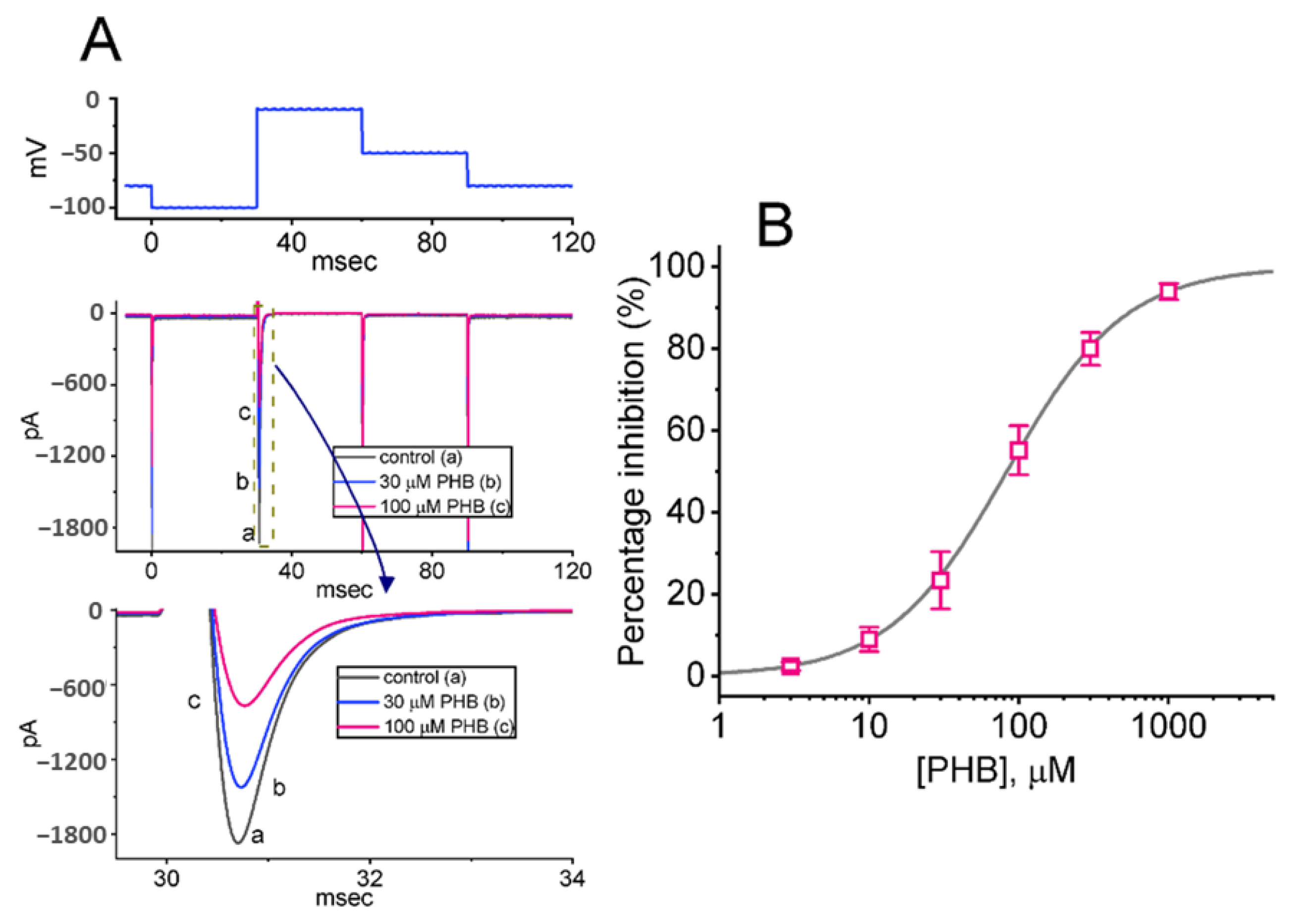
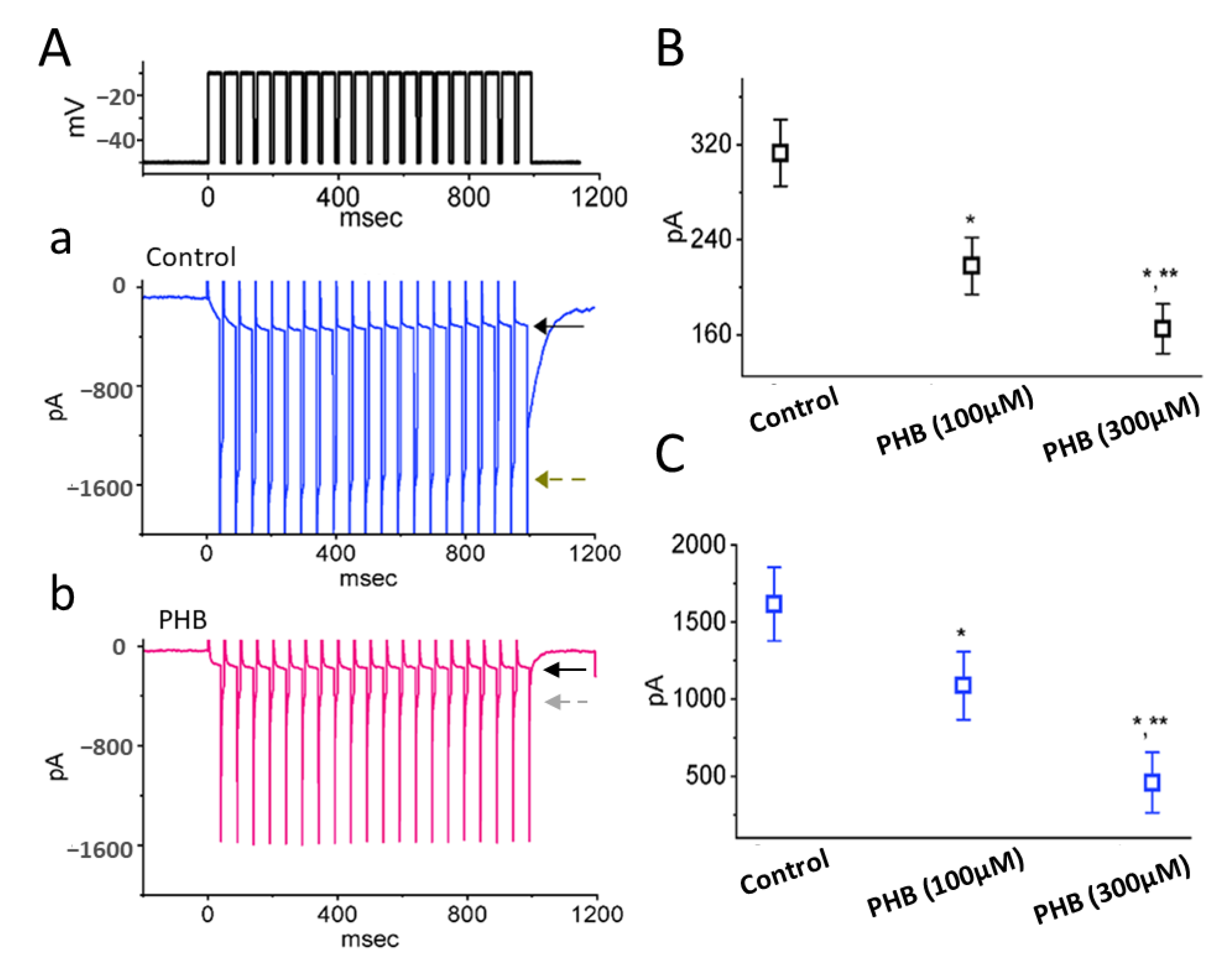
3.1. Effects of PHB on the Amplitude of Voltage-Gated Na+ Current (INa) in Neuro-2a Cells
3.2. PHB-Induced Increase in Cumulative Inhibition of INa Inactivation
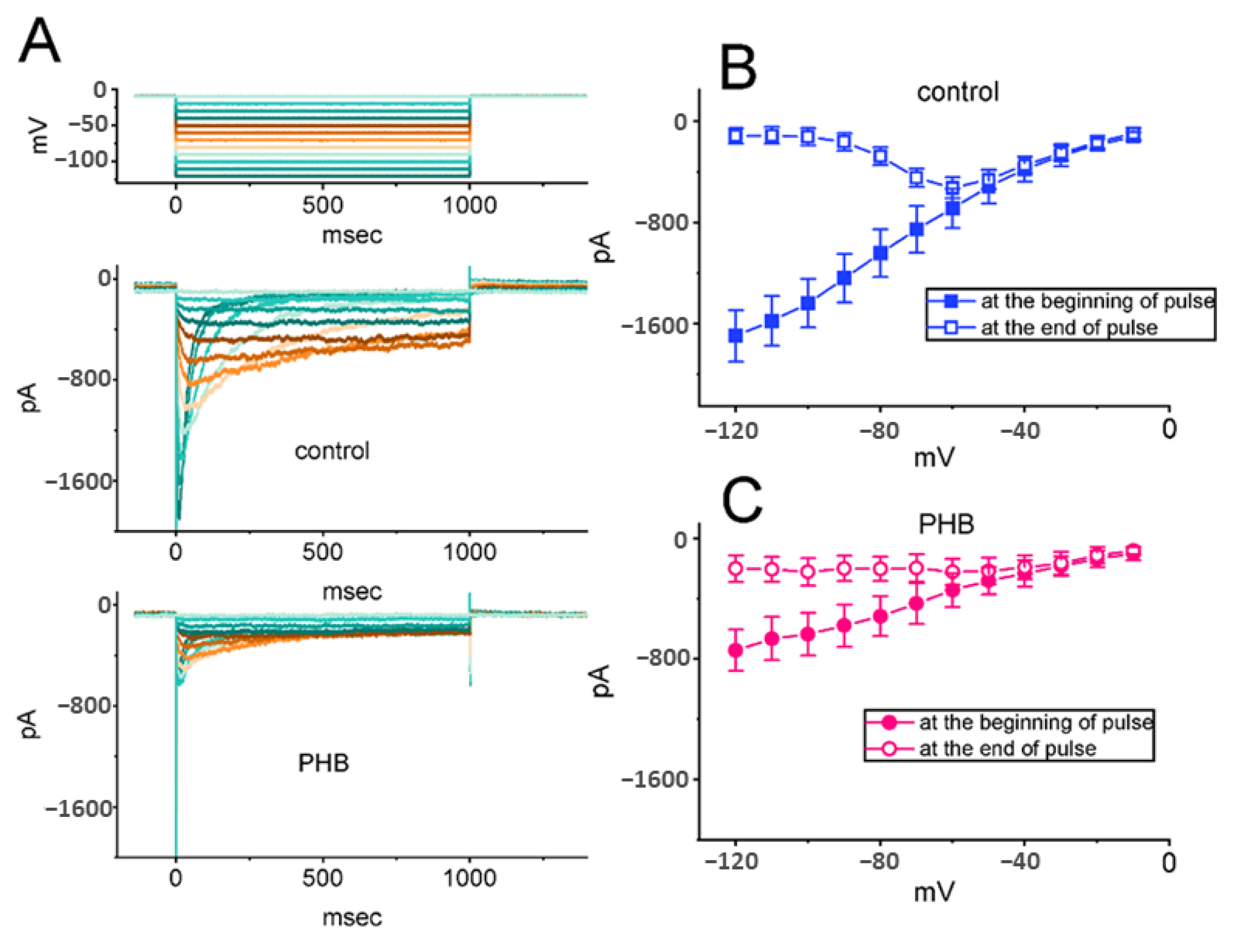
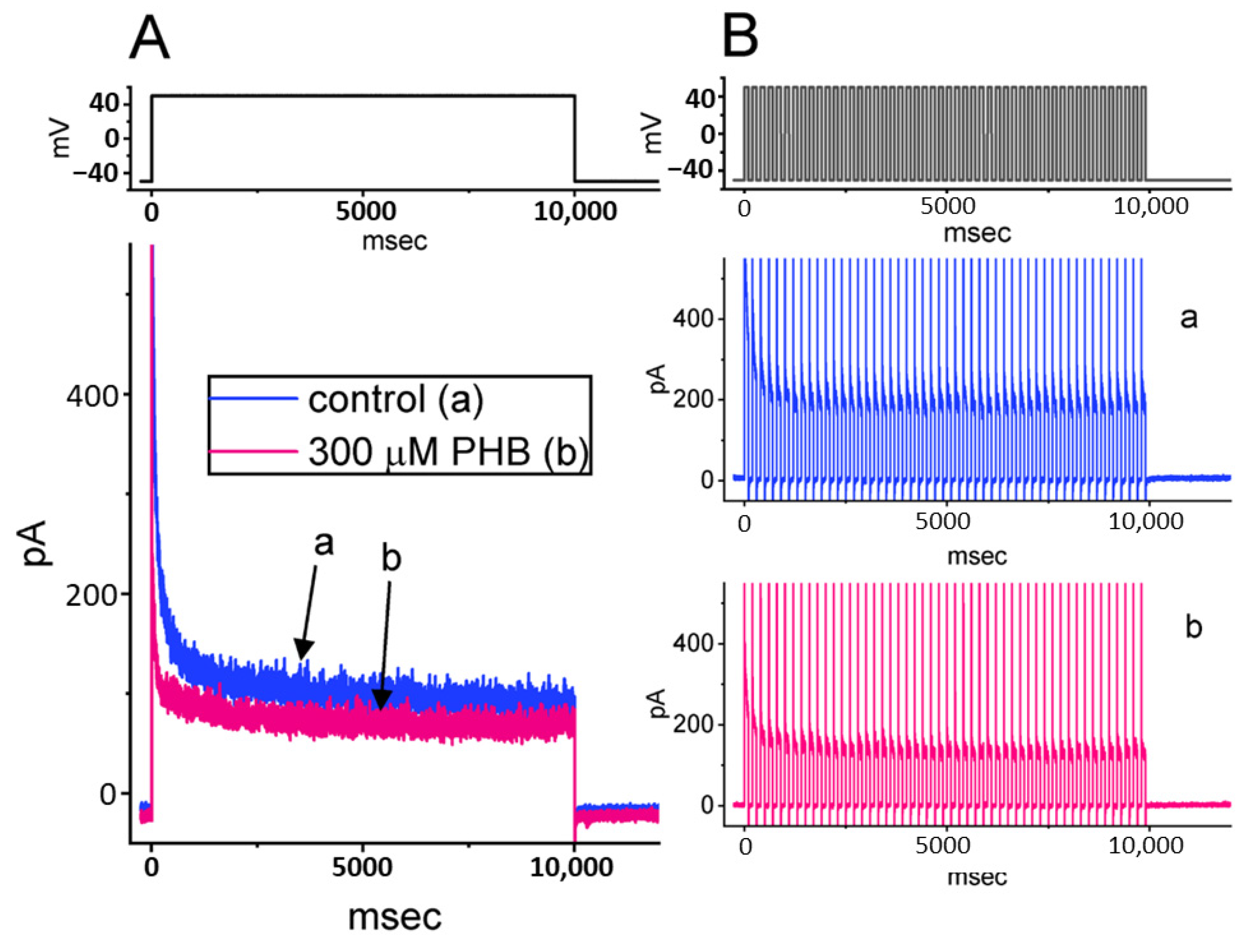
3.3. Effects of PHB on erg-Mediated K+ Current (IK(erg)) Residing in Neuro-2a Cells
3.4. Modification by PHB on the Magnitude of IK(erg) Activated by PT Stimulation
3.5. Slowing in Recovery from IK(erg) Block Caused by PHB in Neuro-2a Cells
Modification by PHB of the Time Course of IK(erg) Evoked by the Envelope-of-Tail Test
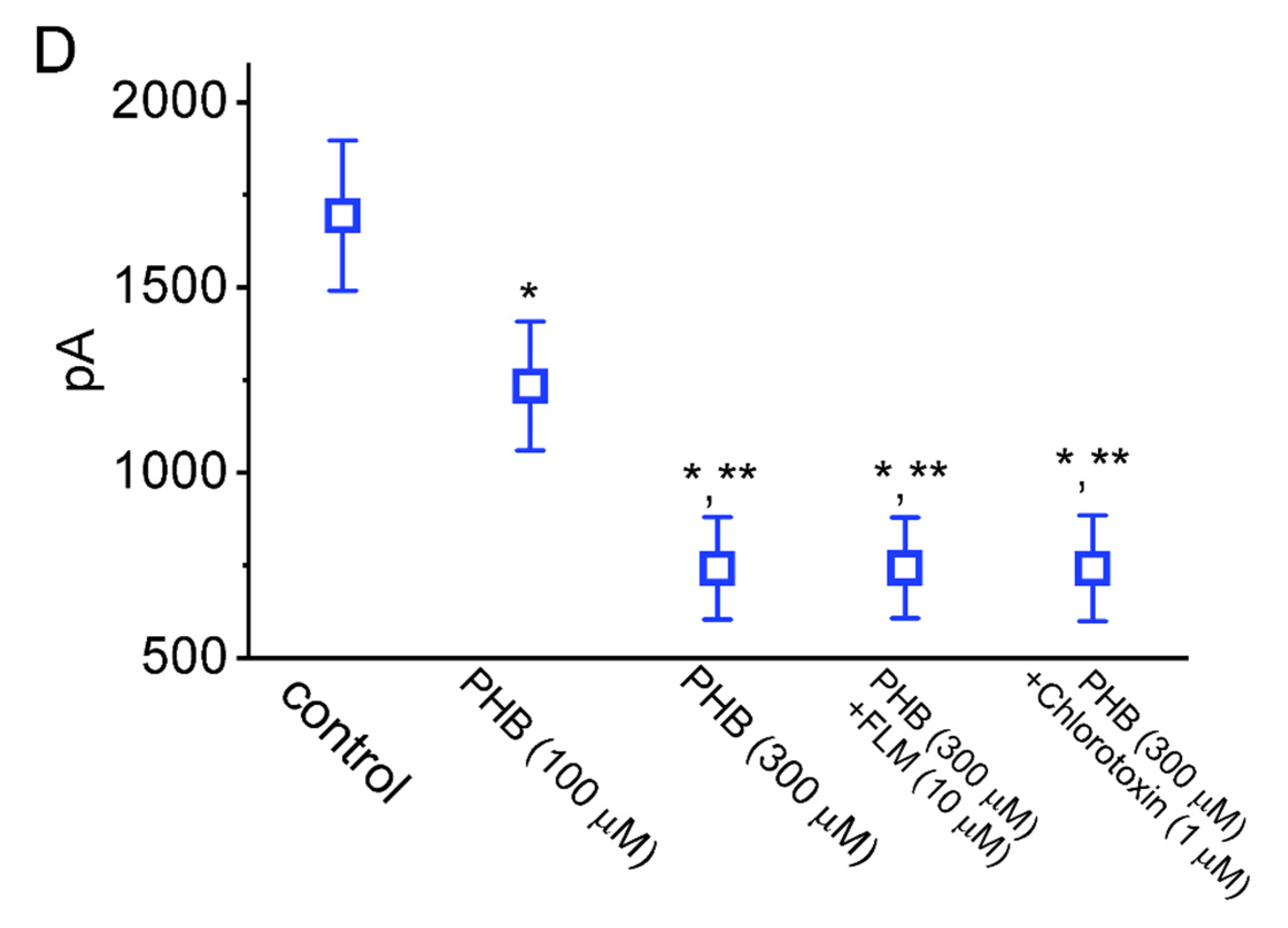
3.6. Modification by PHB of M-Type K+ Current (IK(M)) in Neuro-2a Cells
3.7. Modification by PHB on IK(M) Inactivation during PT Stimulation
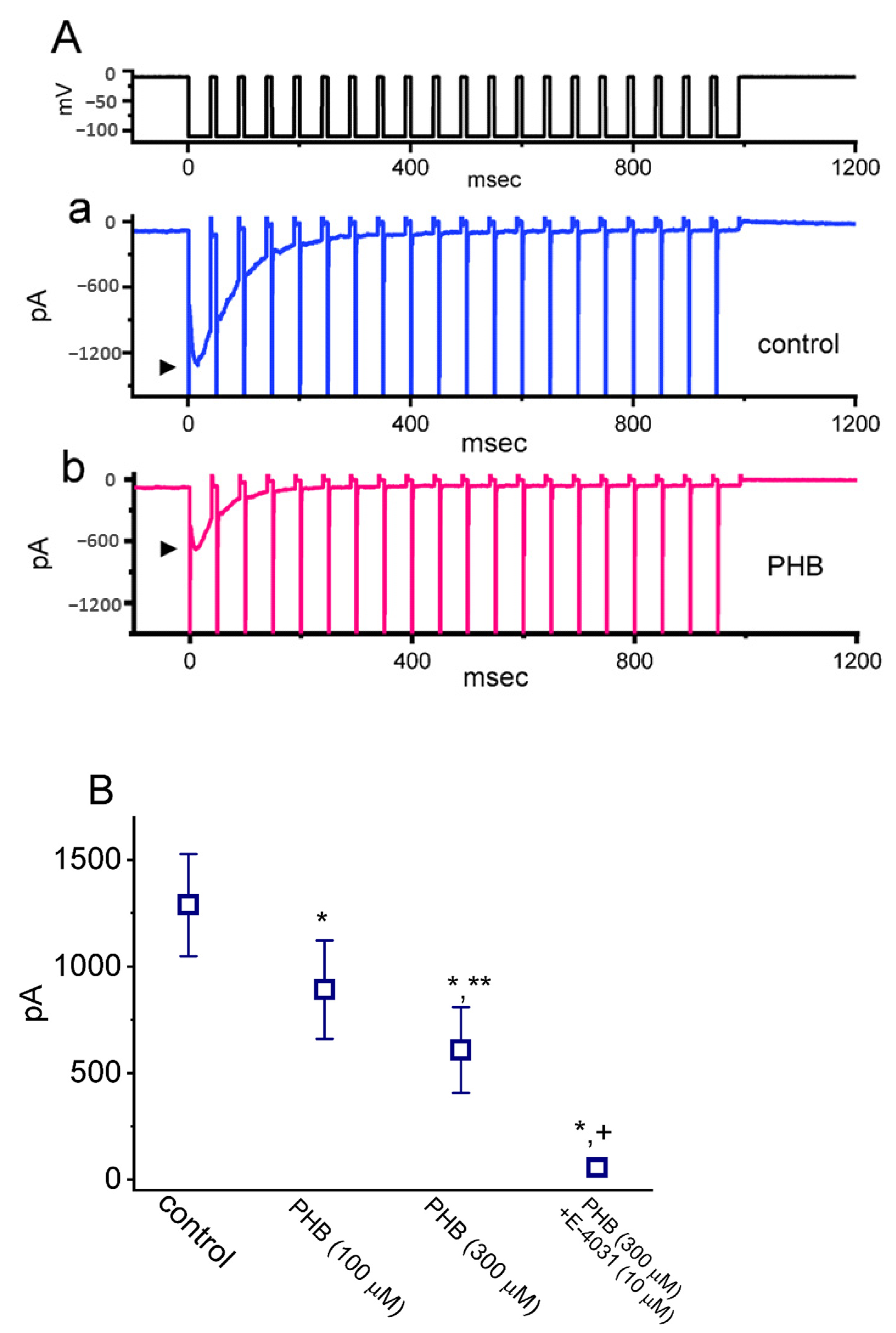
3.8. Inhibitory Effect of PHB on Delayed-Rectifier K+ Current (IK(DR)) Residing in Neuro-2a Cells
3.9. PHB-Induced Increase in Cumulative Inhibition of IK(DR) Inactivation in Neuro-2a Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | action potential |
| erg | ether-à-go-go related gene |
| FLM | flumazenil |
| GABAA receptor | γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor |
| I-V | current versus voltage |
| IC50 | the concentration required for 50% inhibition |
| IK(DR) | delayed-rectifier K+ current |
| IK(erg) | erg-mediated K+ current |
| IK(M) | M-type K+ current |
| INa | voltage-gated Na+ current |
| Kerg channel | erg-mediated K+ channel |
| KV channel | voltage-gated K+ channel |
| NaV channel | voltage-gated Na+ channel |
| PHB | phenobarbital (phenobarbitone, phenobarb, Luminal Sodium®) |
| PT stimulation | pulse train stimulation |
| SEM | standard error of mean |
| τ | time constant |
| TEA | tetraethylammonium chloride |
| Tef | tefluthrin |
| TTX | tetrodotoxin |
References
- Armijo, J.A.; Shushtarian, M.; Valdizan, E.M.; Cuadrado, A.; de las Cuevas, I.; Adín, J. Ion channels and epilepsy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1975–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, A.; Semnanian, S.; Atapour, N.; Shojaei, A.; Moradi-Chameh, H.; Ghafouri, S.; Sheibani, V.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J. Low-frequency electrical stimulation enhances the effectiveness of phenobarbital on GABAergic currents in hippocampal slices of kindled rats. Neuroscience 2016, 330, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodie, M.J.; Dichter, M.A. Antiepileptic drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Li, N.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, D.; Lin, W. Efficacy of Phenobarbital and Prognosis Predictors in Women with Epilepsy from Rural Northeast China: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 838098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farwell, J.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Hirtz, D.G.; Sulzbacher, S.I.; Ellenberg, J.H.; Nelson, K.B. Phenobarbital for febrile seizures—Effects on intelligence and on seizure recurrence. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, M.; Pan, S.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhuang, X. Phenobarbital versus valproate for generalized convulsive status epilepticus in adults (2): A multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial in China (China 2-P vs. V). Epilepsy Res. 2021, 177, 106755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, A.; Arras, M.; Jurd, R.; Rudolph, U. Identification of a molecular target mediating the general anesthetic actions of pentobarbital. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onizuka, C.; Irifune, M.; Mukai, A.; Shimizu, Y.; Doi, M.; Oue, K.; Yoshida, M.; Kochi, T.; Imado, E.; Kanematsu, T.; et al. Pentobarbital may protect against neurogenic inflammation after surgery via inhibition of substance P release from peripheral nerves of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 771, 136467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Lu, W.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Han, J. Sodium Pentobarbital Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Growth Partly via Normalizing Microcirculatory Hemodynamics and Oxygenation in Tumors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2022, 382, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagaja, M.; Zagaja, A.; Szala-Rycaj, J.; Szewczyk, A.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Raszewski, G.; Andres-Mach, M. Influence of Umbelliferone on the Anticonvulsant and Neuroprotective Activity of Selected Antiepileptic Drugs: An In Vivo and In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, R.G.; Sikorska, M.; Sandhu, J.K.; Lanthier, P.; Ribecco-Lutkiewicz, M.; Bani-Yaghoub, M. Differentiation of mouse Neuro 2A cells into dopamine neurons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 186, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, T.H.; Cho, H.Y.; Wu, S.N. The Evidence for Sparsentan-Mediated Inhibition of I(Na) and I(K(erg)): Possibly Unlinked to Its Antagonism of Angiotensin II or Endothelin Type a Receptor. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Goldin, A.L.; Waxman, S.G. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddese, A.; Bean, B.P. Subthreshold sodium current from rapidly inactivating sodium channels drives spontaneous firing of tuberomammillary neurons. Neuron 2002, 33, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.A.; Salari, A.; Lin, J.L.; Cowan, L.M.; Penington, N.J.; Milescu, M.; Milescu, L.S. Sodium channels implement a molecular leaky integrator that detects action potentials and regulates neuronal firing. eLife 2020, 9, e54940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.R.; Bauer, C.K. Functions of erg K+ channels in excitable cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2004, 8, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, F.; Taccola, G.; Grandolfo, M.; Guasti, L.; Arcangeli, A.; Nistri, A.; Ballerini, L. ERG conductance expression modulates the excitability of ventral horn GABAergic interneurons that control rhythmic oscillations in the developing mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Chang, W.T.; Wu, S.N. Characterization of the Synergistic Inhibition of I(K(erg)) and I(K(DR)) by Ribociclib, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Wu, S.N. Effective Perturbations on the Amplitude and Hysteresis of Erg-Mediated Potassium Current Caused by 1-Octylnonyl 8-[(2-hydroxyethyl)[6-oxo-6(undecyloxy)hexyl]amino]-octanoate (SM-102), a Cationic Lipid. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yamasaki, M.; Abe, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Morino, H.; Kawakami, H.; Sakimura, K.; Watanabe, M.; Hashimoto, K. Kv11 (ether-à-go-go-related gene) voltage-dependent K+ channels promote resonance and oscillation of subthreshold membrane potentials. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cho, H.Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Ke, T.L.; Wu, S.N. The Effectiveness of Isoplumbagin and Plumbagin in Regulating Amplitude, Gating Kinetics, and Voltage-Dependent Hysteresis of erg-mediated K+ Currents. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, A.E.; Eigenberger, B.; Jurkiewicz, N.K.; Salata, J.J.; Pica, A.; Suessbrich, H.; Lang, F. Blockade of HERG channels by the class III antiarrhythmic azimilide: Mode of action. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katchman, A.N.; McGroary, K.A.; Kilborn, M.J.; Kornick, C.A.; Manfredi, P.L.; Woosley, R.L.; Ebert, S.N. Influence of opioid agonists on cardiac human ether-a-go-go-related gene K+ currents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Cheng, H.; Incardona, J.; Reynolds, W.; Viviani, F.; Tabart, M.; Rampe, D. Discovery of a small molecule activator of the human ether-a-go-go-related gene (HERG) cardiac K+ channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.A.; Passmore, G.M. Neural KCNQ (Kv7) channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Liu, P.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, W.K.; Wu, S.N. Evidence for the Effectiveness of Remdesivir (GS-5734), a Nucleoside-Analog Antiviral Drug in the Inhibition of I (K(M)) or I (K(DR)) and in the Stimulation of I (MEP). Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Darwish, Y.; Fu, X.; Trussell, L.O.; Huang, H. KCNQ Channels Enable Reliable Presynaptic Spiking and Synaptic Transmission at High Frequency. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, J.A.; Möller, M.; Zaydman, M.; Zhao, L.; Beller, Z.; Becker, S.; Ritter, N.; Hou, P.; Shi, J.; Silva, J.; et al. A benzodiazepine activator locks K(v)7.1 channels open by electro-mechanical uncoupling. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Heckman, L.; Niday, Z.; Jo, S.; Fujita, A.; Shim, J.; Pandey, R.; Al Jandal, H.; Jayakar, S.; Barrett, L.B.; et al. Cannabidiol activates neuronal Kv7 channels. eLife 2022, 11, e73246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.T.; Lu, G.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Wu, S.N. Effective Perturbations of the Amplitude, Gating, and Hysteresis of I(K(DR)) Caused by PT-2385, an HIF-2α Inhibitor. Membranes 2021, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labro, A.J.; Priest, M.F.; Lacroix, J.J.; Snyders, D.J.; Bezanilla, F. Kv3.1 uses a timely resurgent K+ current to secure action potential repolarization. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraldi, M.; Guidotti, A.; Schwartz, J.P.; Costa, E. GABA receptors in clonal cell lines: A model for study of benzodiazepine action at molecular level. Science 1979, 205, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, A.M.; O’Beirne, G.B.; Regan, C.M.; Williams, D.C. Antiproliferative action of benzodiazepines in cultured brain cells is not mediated through the peripheral-type benzodiazepine acceptor. J. Neurochem. 1989, 53, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Bovee, T.F.; Kamelia, L.; Rietjens, I.M.; Hendriksen, P.J. Exploration of new functional endpoints in neuro-2a cells for the detection of the marine biotoxins saxitoxin, palytoxin and tetrodotoxin. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 30, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.N.; Tang, H.L.; Lin, G.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, P.; Li, H.J.; Gao, M.M.; Zhao, Q.H.; Yi, Y.H.; Liao, W.P.; et al. Epigenetic Downregulation of Scn3a Expression by Valproate: A Possible Role in Its Anticonvulsant Activity. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Saify, Z.S.; Jamali, K.S.; Naz, S.; Hassan, S.; Siddiqui, S. Vitex negundo induces an anticonvulsant effect by inhibiting voltage gated sodium channels in murine Neuro 2A cell line. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted, J.B.; Carlson, K.; Klebe, R.; Ruddle, F.; Rosenbaum, J. Isolation of microtubule protein from cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 65, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, D.; Wei, Z.; Zhong, W.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z. Method for electric parametric characterization and optimization of electroporation on a chip. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4483–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.M.; Cho, H.Y.; Chiang, C.W.; Chuang, T.H.; Wu, S.N.; Tu, Y.F. Characterization in Inhibitory Effectiveness of Carbamazepine in Voltage-Gated Na+ and Erg-Mediated K+ Currents in a Mouse Neural Crest-Derived (Neuro-2a) Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Chuang, T.H.; Yu, M.C.; Wu, S.N. Activation of Voltage-Gated Na+ Current by GV-58, a Known Activator of Ca(V) Channels. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.N.; Shen, A.Y.; Hwang, T.L. Analysis of mechanical restitution and post-rest potentiation in isolated rat atrium. Chin. J. Physiol. 1996, 39, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.L.; Chuang, C.W.; Cho, H.Y.; Chuang, T.H.; Wu, S.N. The Evidence for Effective Inhibition of I(Na) Produced by Mirogabalin ((1R,5S,6S)-6-(aminomethyl)-3-ethyl-bicyclo [3.2.0] hept-3-ene-6-acetic acid), a Known Blocker of Ca(V) Channels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oortgiesen, M.; van Kleef, R.G.; Vijverberg, H.P. Block of deltamethrin-modified sodium current in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells: Local anesthetics as potential antidotes. Brain Res. 1990, 518, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, B.S.; Lo, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C. Underlying mechanism of actions of tefluthrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, on voltage-gated ion currents and on action currents in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells and GnRH-secreting (GT1-7) neurons. Toxicology 2009, 258, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCavera, S.J.; Soderlund, D.M. Differential state-dependent modification of inactivation-deficient Nav1.6 sodium channels by the pyrethroid insecticides S-bioallethrin, tefluthrin and deltamethrin. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meves, H. Inactivation of the ERG current in NG108-15 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 263, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.G.; Willets, J.M.; Atcheson, R.; Frost, C.; Smart, D.; Rowbotham, D.J.; Smith, G. Effects of propofol and thiopentone on potassium- and carbachol-evoked [3H]noradrenaline release and increased [Ca2+]i from SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.X.; Zhang, X.B.; Gong, N.; Wang, M.Y.; Xu, T.L. Differential effects of thiopental and pentobarbital on spinal GABA(A) receptors. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, E.C.; Wu, K.C.; Kao, F.C.; Wu, S.N. Effects of midazolam on ion currents and membrane potential in differentiated motor neuron-like NSC-34 and NG108-15 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 724, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, N.P.; Liu, Y.F.; Wu, P.C.; Hsing, C.H.; Huang, B.M.; So, E.C. Midazolam’s Effects on Delayed-Rectifier K+ Current and Intermediate-Conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Lu, J.Y.; Wu, B.W. Class III anti-arrhythmia drug E-4031 potentiates Na+/Ca2+ exchange current in rat ventricular myocytes. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2000, 21, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kodirov, S.A. Tale of tail current. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2020, 150, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, A.; Mueller, S.; Kopp, K.; Brueggemann, A.; Suessbrich, H.; Gerlach, U.; Busch, A.E. Inhibition of cardiac potassium currents by pentobarbital. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 365, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendig, J.J. Barbiturates: Active form and site of action at node of Ranvier sodium channels. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1981, 218, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prokic, E.J.; Weston, C.; Yamawaki, N.; Hall, S.D.; Jones, R.S.; Stanford, I.M.; Ladds, G.; Woodhall, G.L. Cortical oscillatory dynamics and benzodiazepine-site modulation of tonic inhibition in fast spiking interneurons. Neuropharmacology 2015, 95, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Rudolph, U.; Knutson, D.E.; Li, G.; Cook, J.M.; Hentschke, H.; Antkowiak, B.; Drexler, B. Zolpidem Activation of Alpha 1-Containing GABA(A) Receptors Selectively Inhibits High Frequency Action Potential Firing of Cortical Neurons. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.T.; Lo, Y.C.; Huang, Y.M.; Tseng, Y.T.; Wu, S.N. Important modifications by sugammadex, a modified γ-cyclodextrin, of ion currents in differentiated NSC-34 neuronal cells. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methaneethorn, J.; Leelakanok, N. Pharmacokinetic variability of phenobarbital: A systematic review of population pharmacokinetic analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.-M.; Lai, P.-C.; Cho, H.-Y.; Chuang, T.-H.; Wu, S.-N.; Tu, Y.-F. Effective Perturbations by Phenobarbital on INa, IK(erg), IK(M) and IK(DR) during Pulse Train Stimulation in Neuroblastoma Neuro-2a Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081968
Wu P-M, Lai P-C, Cho H-Y, Chuang T-H, Wu S-N, Tu Y-F. Effective Perturbations by Phenobarbital on INa, IK(erg), IK(M) and IK(DR) during Pulse Train Stimulation in Neuroblastoma Neuro-2a Cells. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081968
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Po-Ming, Pei-Chun Lai, Hsin-Yen Cho, Tzu-Hsien Chuang, Sheng-Nan Wu, and Yi-Fang Tu. 2022. "Effective Perturbations by Phenobarbital on INa, IK(erg), IK(M) and IK(DR) during Pulse Train Stimulation in Neuroblastoma Neuro-2a Cells" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081968
APA StyleWu, P.-M., Lai, P.-C., Cho, H.-Y., Chuang, T.-H., Wu, S.-N., & Tu, Y.-F. (2022). Effective Perturbations by Phenobarbital on INa, IK(erg), IK(M) and IK(DR) during Pulse Train Stimulation in Neuroblastoma Neuro-2a Cells. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081968





