Platelets and Escherichia coli: A Complex Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
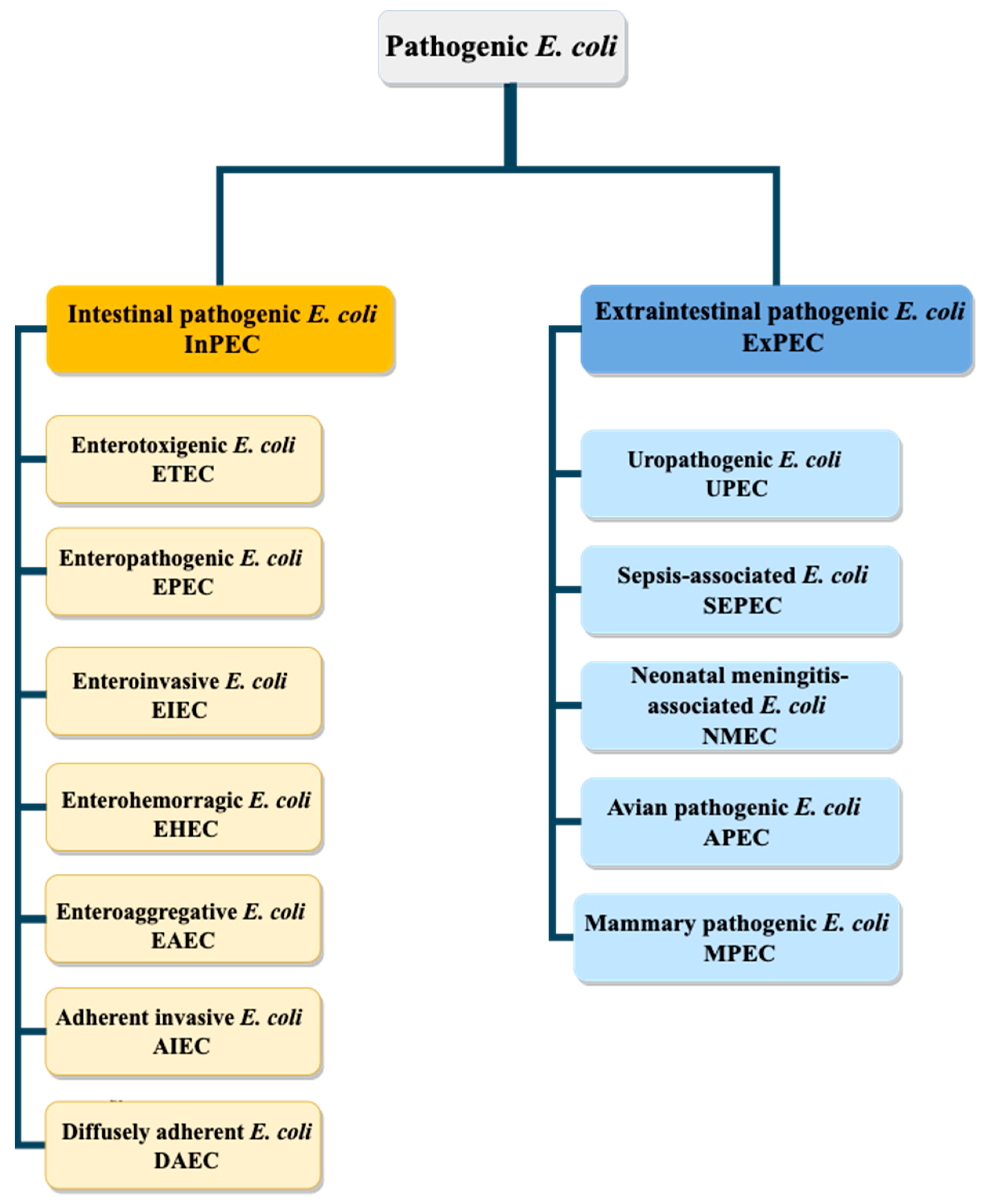
2. Escherichia coli Pathovars
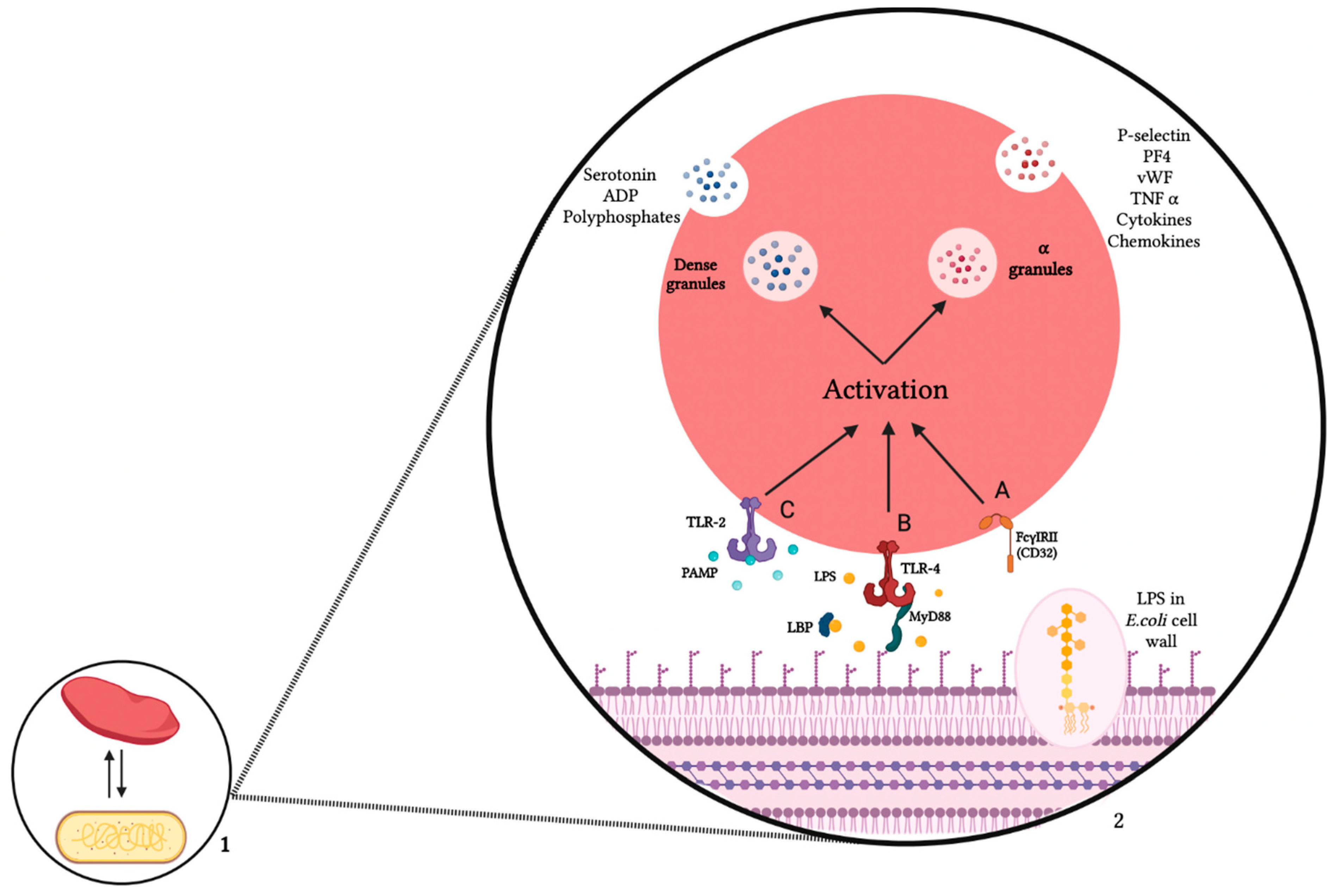
3. Mechanism of Interaction between Platelets and E. coli
3.1. Platelet Receptors
3.2. E. coli Products
3.3. Platelets—E. coli Interaction Consequences
| (A) E. coli Strain Effect on Platelet Activation and Aggregation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPS/E. coli Strain | Strain Origin | Platelet Form | Reported Interaction Result | Platelet Receptor Involved | Reference |
| CFT073 RS218 | Pyelonephritis and bacteremia Neonatal meningitis | PRP | Activation and aggregation | FcγRIIA and αIIbβ3 | [56] |
| K12 | Non pathogen | PRP | Activation and dense granule release | GPIIb/IIIa | [53] |
| O18:K1 | Pathogen | PRP | - | - | [53] |
| O111 | EHEC | PRP | Activation | TLR4 | [54] |
| O157:H7 | EHEC | PRP | Aggregation | αIIbβ3/ Fc | [55] |
| (B) E. coli LPS Effect on Platelet Activation and Aggregation | |||||
| O111:B4 | EHEC | PRP | - | - | [57] |
| O111:B4, O55:B5 and O127:B8 | EHEC | PRP | Activation Alpha and dense granule secretion | CD14, TLR4/MD2 and MyD88 | [31] |
| O157:H7 | EHEC | PRP, WP | No aggregation | - | [55] |
| O103, O111, O121, O157O111:B4 | EHEC Non-EHEC | PRP, WP | Activation and fibrinogen binding | GPIIb/III | [39] |
| LPS | Not mentioned | PRP WP | - | - | [58] |
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.R.; Storey, R.F. The Role of Platelets in Inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannachi, N.; Fournier, P.-E.; Martel, H.; Habib, G.; Camoin-Jau, L. Statins Potentiate the Antibacterial Effect of Platelets on Staphylococcus Aureus. Platelets 2021, 32, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeaman, M.R. Bacterial-Platelet Interactions: Virulence Meets Host Defense. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeaman, M.R. Platelets: At the Nexus of Antimicrobial Defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Watson, S.P. Platelets and the Innate Immune System: Mechanisms of Bacterial-Induced Platelet Activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Damien, P.; Chabert, A.; Pozzetto, B.; Cognasse, F.; Garraud, O. Platelets and Infections-Complex Interactions with Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Seaghdha, M.; van Schooten, C.J.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Emsley, J.; Silverman, G.J.; Cox, D.; Lenting, P.J.; Foster, T.J. Staphylococcus Aureus Protein A Binding to von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain Is Mediated by Conserved IgG Binding Regions. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarowska, J.; Futoma-Koloch, B.; Jama-Kmiecik, A.; Frej-Madrzak, M.; Ksiazczyk, M.; Bugla-Ploskonska, G.; Choroszy-Krol, I. Virulence Factors, Prevalence and Potential Transmission of Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Isolated from Different Sources: Recent Reports. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U.E. Coli as an All-Rounder: The Thin Line between Commensalism and Pathogenicity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 358, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Russo, T.A. Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli: “The Other Bad E. Coli”. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2002, 139, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, C.-D.; Dobrindt, U. What Defines Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila, J.; Sáez-López, E.; Johnson, J.R.; Römling, U.; Dobrindt, U.; Cantón, R.; Giske, C.G.; Naas, T.; Carattoli, A.; Martínez-Medina, M.; et al. Escherichia Coli: An Old Friend with New Tidings. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 437–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzhenry, R.J. Intimin Type Influences the Site of Human Intestinal Mucosal Colonisation by Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Gut 2002, 50, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kaper, J.B. Cloning and Characterization of the Eae Gene of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandes, R.T.; Elias, W.P.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Gomes, T.A.T. An Overview of Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia Coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 297, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafari, A.; Aslani, M.M.; Bouzari, S. Escherichia Coli: A Brief Review of Diarrheagenic Pathotypes and Their Role in Diarrheal Diseases in Iran. Iran J. Microbiol. 2012, 4, 102–117. [Google Scholar]
- Gouali, M.; Weill, F.-X. Enterohemorragic Escherichia coli (EHEC): Topical enterobacteriaceae. Presse Med. 2013, 42, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botos, I.; Segal, D.M.; Davies, D.R. The Structural Biology of Toll-like Receptors. Structure 2011, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sameer, A.S.; Nissar, S. Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Structure, Functions, Signaling, and Role of Their Polymorphisms in Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1157023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hally, K.; Fauteux-Daniel, S.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Larsen, P.; Cognasse, F. Revisiting Platelets and Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): At the Interface of Vascular Immunity and Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, E6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.; Ma, Y.; Hong, L.; Gao, D.; West, X.Z.; Salomon, R.G.; Byzova, T.V.; Podrez, E.A. Engagement of Platelet Toll-like Receptor 9 by Novel Endogenous Ligands Promotes Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiraki, R.; Inoue, N.; Kawasaki, S.; Takei, A.; Kadotani, M.; Ohnishi, Y.; Ejiri, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Hirata, K.; Kawashima, S.; et al. Expression of Toll-like Receptors on Human Platelets. Thromb. Res. 2004, 113, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Stoppelaar, S.F.; Claushuis, T.A.M.; Schaap, M.C.L.; Hou, B.; van der Poll, T.; Nieuwland, R.; van ’t Veer, C. Toll-like Receptor Signalling Is Not Involved in Platelet Response to Streptococcus Pneumoniae In Vitro or In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, C.; Tilley, D.; Cunningham, A.; Smolenski, A.; Kadioglu, A.; Cox, D.; Jenkinson, H.F.; Kerrigan, S.W. Invasive Streptococcus Pneumoniae Trigger Platelet Activation via Toll-like Receptor 2. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anabel, A.-S.; Eduardo, P.-C.; Pedro Antonio, H.-C.; Carlos, S.-M.; Juana, N.-M.; Honorio, T.-A.; Nicolás, V.-S.; Sergio Roberto, A.-R. Human Platelets Express Toll-like Receptor 3 and Respond to Poly I:C. Hum. Immunol. 2014, 75, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’ Atri, L.P.; Schattner, M. Platelet Toll-like Receptors in Thromboinflammation. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 1867–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koupenova, M.; Mick, E.; Mikhalev, E.; Benjamin, E.J.; Tanriverdi, K.; Freedman, J.E. Sex Differences in Platelet Toll-like Receptors and Their Association With Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andonegui, G.; Kerfoot, S.M.; McNagny, K.; Ebbert, K.V.J.; Patel, K.D.; Kubes, P. Platelets Express Functional Toll-like Receptor-4. Blood 2005, 106, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklaus, M.; Klingler, P.; Weber, K.; Koessler, A.; Boeck, M.; Kobsar, A.; Koessler, J. The Involvement of Toll-like Receptors 2 and 4 in Human Platelet Signalling Pathways. Cell. Signal. 2020, 76, 109817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Han, J.; Welch, E.J.; Ye, R.D.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A.; Malik, A.B.; Du, X.; Li, Z. Lipopolysaccharide Stimulates Platelet Secretion and Potentiates Platelet Aggregation via TLR4/MyD88 and the CGMP-Dependent Protein Kinase Pathway. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 7997–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stark, R.J.; Aghakasiri, N.; Rumbaut, R.E. Platelet-Derived Toll-like Receptor 4 (Tlr-4) Is sufficient to promote microvascular thrombosis in endotoxemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stegner, D.; Nieswandt, B. Platelet Receptor Signaling in Thrombus Formation. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Al-Tamimi, M.; Baker, R.I.; Andrews, R.K.; Gardiner, E.E. The Platelet Fc Receptor, FcγRIIa. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 268, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, S.P.; Rosse, W.F.; Kurlander, R.J. Characterization of the IgG-Fc Receptor on Human Platelets. Blood 1982, 60, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arman, M.; Krauel, K.; Tilley, D.O.; Weber, C.; Cox, D.; Greinacher, A.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Watson, S.P. Amplification of Bacteria-Induced Platelet Activation Is Triggered by FcγRIIA, Integrin AIIbβ3, and Platelet Factor 4. Blood 2014, 123, 3166–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide Endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Yeh, W.-C.; Ohashi, P.S. LPS/TLR4 Signal Transduction Pathway. Cytokine 2008, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, A.; Svensson, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Svanborg, C.; Tarr, P.I.; Mooney, J.C.; Watkins, S.L.; Johnson, R.; Karpman, D. Lipopolysaccharide from Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli Binds to Platelets through TLR4 and CD62 and Is Detected on Circulating Platelets in Patients with Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Blood 2006, 108, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konowalchuk, J.; Speirs, J.I.; Stavric, S. Vero Response to a Cytotoxin of Escherichia Coli. Infect. Immun. 1977, 18, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eklund, M.; Leino, K.; Siitonen, A. Clinical Escherichia Coli Strains Carrying Stx Genes: Stx Variants and Stx-Positive Virulence Profiles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4585–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strockbine, N.A.; Marques, L.R.; Newland, J.W.; Smith, H.W.; Holmes, R.K.; O’Brien, A.D. Two Toxin-Converting Phages from Escherichia Coli O157:H7 Strain 933 Encode Antigenically Distinct Toxins with Similar Biologic Activities. Infect. Immun. 1986, 53, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, D.L.; Jackson, M.P.; Samuel, J.E.; Holmes, R.K.; O’Brien, A.D. Cloning and Sequencing of a Shiga-like Toxin Type II Variant from Escherichia Coli Strain Responsible for Edema Disease of Swine. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraser, M.E.; Chernaia, M.M.; Kozlov, Y.V.; James, M.N.G. Crystal Structure of the Holotoxino from Shigella Dysenteriae at 2.5 Å Resolution. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1994, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Ohta, Y.; Noda, M. Shiga Toxin 2 Is Specifically Released from Bacterial Cells by Two Different Mechanisms. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesh, V.L.; Burris, J.A.; Owens, J.W.; Gordon, V.M.; Wadolkowski, E.A.; O’Brien, A.D.; Samuel, J.E. Comparison of the Relative Toxicities of Shiga-like Toxins Type I and Type II for Mice. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, J.T.; Sowers, E.G.; Wells, J.G.; Greene, K.D.; Griffin, P.M.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Strockbine, N.A. Non-O157 Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia Coli Infections in the United States, 1983–2002. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, D.; Li, X.-P.; Kahn, J.N.; May, K.L.; Kahn, P.C.; Tumer, N.E. The A1 Subunit of Shiga Toxin 2 Has Higher Affinity for Ribosomes and Higher Catalytic Activity than the A1 Subunit of Shiga Toxin 1. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarr, P.I. Shiga Toxin-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Distinct Mechanisms of Pathogenesis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2009, 75, S29–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose, P.E.; Armour, J.A.; Williams, C.E.; Hill, F.G. Verotoxin and Neuraminidase Induced Platelet Aggregating Activity in Plasma: Their Possible Role in the Pathogenesis of the Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. J. Clin. Pathol. 1985, 38, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpman, D.; Papadopoulou, D.; Nilsson, K.; Sjögren, A.C.; Mikaelsson, C.; Lethagen, S. Platelet Activation by Shiga Toxin and Circulatory Factors as a Pathogenetic Mechanism in the Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Blood 2001, 97, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.A.; Polanowska-Grabowska, R.K.; Fujii, J.; Obrig, T.; Gear, A.R.L. Shiga Toxin Binds to Activated Platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 2, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejes, A.V.; Best, M.G.; van der Heijden, W.A.; Vancura, A.; Verschueren, H.; de Mast, Q.; Wurdinger, T.; Mannhalter, C. Impact of Escherichia Coli K12 and O18:K1 on Human Platelets: Differential Effects on Platelet Activation, RNAs and Proteins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matus, V.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Hidalgo, P.; Pozo, L.M.; Panes, O.; Wozniak, A.; Mezzano, D.; Pereira, J.; Sáez, C.G. Human Platelet Interaction with E. Coli O111 Promotes Tissue-Factor-Dependent Procoagulant Activity, Involving Toll like Receptor 4. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriarty, R.D.; Cox, A.; McCall, M.; Smith, S.G.J.; Cox, D. Escherichia Coli Induces Platelet Aggregation in an FcγRIIa-Dependent Manner. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, C.N.; Kerrigan, S.W.; Cox, D.; Henderson, I.R.; Watson, S.P.; Arman, M. Human Platelet Activation by Escherichia Coli: Roles for FcγRIIA and Integrin AIIbβ3. Platelets 2016, 27, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallance, T.M.; Ravishankar, D.; Albadawi, D.A.I.; Layfield, H.; Sheard, J.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Dash, P.; Patel, K.; Widera, D.; Vaiyapuri, S. Effect of Ultrapure Lipopolysaccharides Derived from Diverse Bacterial Species on the Modulation of Platelet Activation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claushuis, T.A.M.; Van Der Veen, A.I.P.; Horn, J.; Schultz, M.J.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Van ’T Veer, C.; Van Der Poll, T. Platelet Toll-like Receptor Expression and Activation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis. Platelets 2019, 30, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orth-Höller, D.; Würzner, R. Role of Complement in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli-Induced Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 40, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würzner, R.; Riedl, M.; Rosales, A.; Orth-Höller, D. Treatment of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli-Induced Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (EHUS). Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 40, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauel, K.; Pötschke, C.; Weber, C.; Kessler, W.; Fürll, B.; Ittermann, T.; Maier, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Bröker, B.M.; Greinacher, A. Platelet Factor 4 Binds to Bacteria, [Corrected] Inducing Antibodies Cross-Reacting with the Major Antigen in Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Blood 2011, 117, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palankar, R.; Kohler, T.P.; Krauel, K.; Wesche, J.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Greinacher, A. Platelets Kill Bacteria by Bridging Innate and Adaptive Immunity via Platelet Factor 4 and FcγRIIA. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Ni, H. Crosstalk Between Platelets and Microbial Pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquino-Domínguez, A.S.; Romero-Tlalolini, M.d.L.A.; Torres-Aguilar, H.; Aguilar-Ruiz, S.R. Recent Advances in the Discovery and Function of Antimicrobial Molecules in Platelets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijgsveld, J.; Zaat, S.A.; Meeldijk, J.; van Veelen, P.A.; Fang, G.; Poolman, B.; Brandt, E.; Ehlert, J.E.; Kuijpers, A.J.; Engbers, G.H.; et al. Thrombocidins, Microbicidal Proteins from Human Blood Platelets, Are C-Terminal Deletion Products of CXC Chemokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20374–20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasupuleti, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Antimicrobial Peptides: Key Components of the Innate Immune System. Crit. Re.v Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannachi, N.; Grac, L.; Baudoin, J.-P.; Fournier, P.-E.; Habib, G.; Camoin-Jau, L. Effect of Antiplatelet Agents on Platelet Antistaphylococcal Capacity: An in Vitro Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrigan, S.W.; Cox, D. Platelet-Bacterial Interactions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik-Bielecka, A.; Bold, T.; Ziółkowski, G.; Pierchała, M.; Królikowska, A.; Reichert, P. Antibacterial Activity of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Plasma: An In Vitro Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9471723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohidnezhad, M.; Varoga, D.; Wruck, C.J.; Podschun, R.; Sachweh, B.H.; Bornemann, J.; Bovi, M.; Sönmez, T.T.; Slowik, A.; Houben, A.; et al. Platelets Display Potent Antimicrobial Activity and Release Human Beta-Defensin 2. Platelets 2012, 23, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-Q.; Yeaman, M.R.; Selsted, M.E. Antimicrobial Peptides from Human Platelets. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 6524–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappelmayer, J.; Beke Debreceni, I.; Vida, A.; Antal-Szalmás, P.; Clemetson, K.J.; Nagy, B. Distinct Effects of Re- and S-Forms of LPS on Modulating Platelet Activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketter, P.M.; Kamucheka, R.; Arulanandam, B.; Akers, K.; Cap, A.P. Platelet Enhancement of Bacterial Growth during Room Temperature Storage: Mitigation through Refrigeration. Transfusion 2019, 59, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plainvert, C.; Bidet, P.; Peigne, C.; Barbe, V.; Médigue, C.; Denamur, E.; Bingen, E.; Bonacorsi, S. A New O-Antigen Gene Cluster Has a Key Role in the Virulence of the Escherichia Coli Meningitis Clone O45:K1:H7. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8528–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K.; Li, G. O-Specific Polysaccharide Confers Lysozyme Resistance to Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Virulence 2018, 9, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D.; Kubicek-Sutherland, J.Z. Mechanisms and Consequences of Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobial Peptides. Drug Resis. Updat. 2016, 26, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Diamond, G. The Role of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides in Innate Host Defences. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, M.; Rolain, J.-M.; Baron, S.A. The History of Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria: Progress and Challenges. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, S.; Hadjadj, L.; Rolain, J.-M.; Olaitan, A.O. Molecular Mechanisms of Polymyxin Resistance: Knowns and Unknowns. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, L.; Riziki, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Diene, S.M.; Rolain, J.-M. Study of Mcr-1 Gene-Mediated Colistin Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Humans and Animals in Different Countries. Genes 2017, 8, E394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napier, B.A.; Burd, E.M.; Satola, S.W.; Cagle, S.M.; Ray, S.M.; McGann, P.; Pohl, J.; Lesho, E.P.; Weiss, D.S. Clinical Use of Colistin Induces Cross-Resistance to Host Antimicrobials in Acinetobacter Baumannii. mBio 2013, 4, e00021-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| E. coli Strain | Strain Origin | Platelet Form | Growth Inhibition Result | Factor Involved | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC 11303 | Laboratory | PRP | + | hBD-2 | [70] |
| ATCC 35218 ATCC 25922 | Laboratory | L-PRP | − | - | [69] |
| ML35 | Laboratory | Purified peptides from WP | + | pH = 5.5 Peptides concentration | [71] |
| K-12 WT | Laboratory | WP | − | - | [62] |
| KPM53 KPM121 | Laboratory | WP | + | FcγRIIA and chemokine PF4 | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ezzeroug Ezzraimi, A.; Hannachi, N.; Mariotti, A.; Rolain, J.-M.; Camoin-Jau, L. Platelets and Escherichia coli: A Complex Interaction. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071636
Ezzeroug Ezzraimi A, Hannachi N, Mariotti A, Rolain J-M, Camoin-Jau L. Platelets and Escherichia coli: A Complex Interaction. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(7):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071636
Chicago/Turabian StyleEzzeroug Ezzraimi, Amina, Nadji Hannachi, Antoine Mariotti, Jean-Marc Rolain, and Laurence Camoin-Jau. 2022. "Platelets and Escherichia coli: A Complex Interaction" Biomedicines 10, no. 7: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071636
APA StyleEzzeroug Ezzraimi, A., Hannachi, N., Mariotti, A., Rolain, J.-M., & Camoin-Jau, L. (2022). Platelets and Escherichia coli: A Complex Interaction. Biomedicines, 10(7), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071636







