Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Approval
2.2. Animals
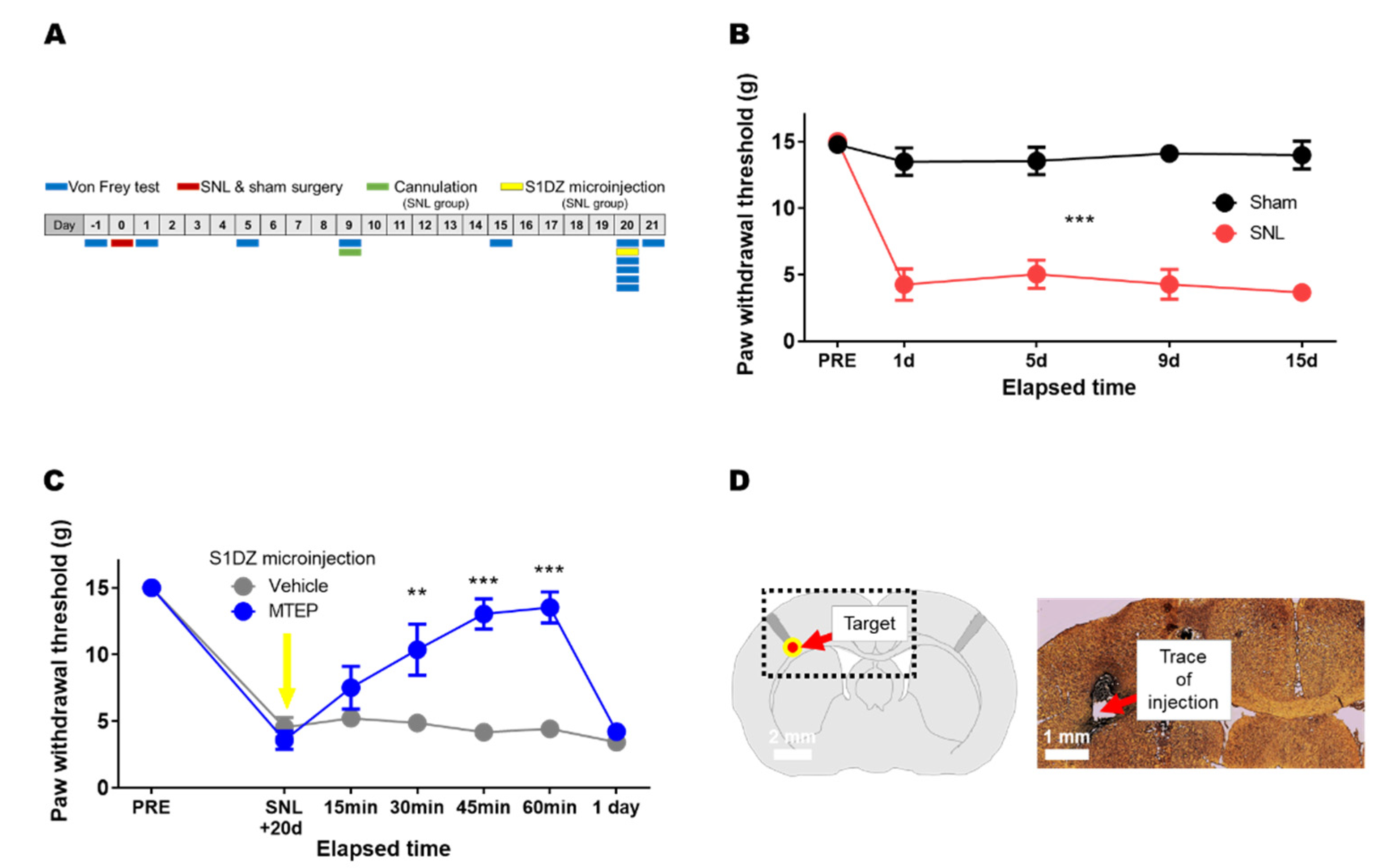
2.3. Neuropathic Pain Model
2.4. Cannula Implantation and Microinjection
2.5. Von Frey Test
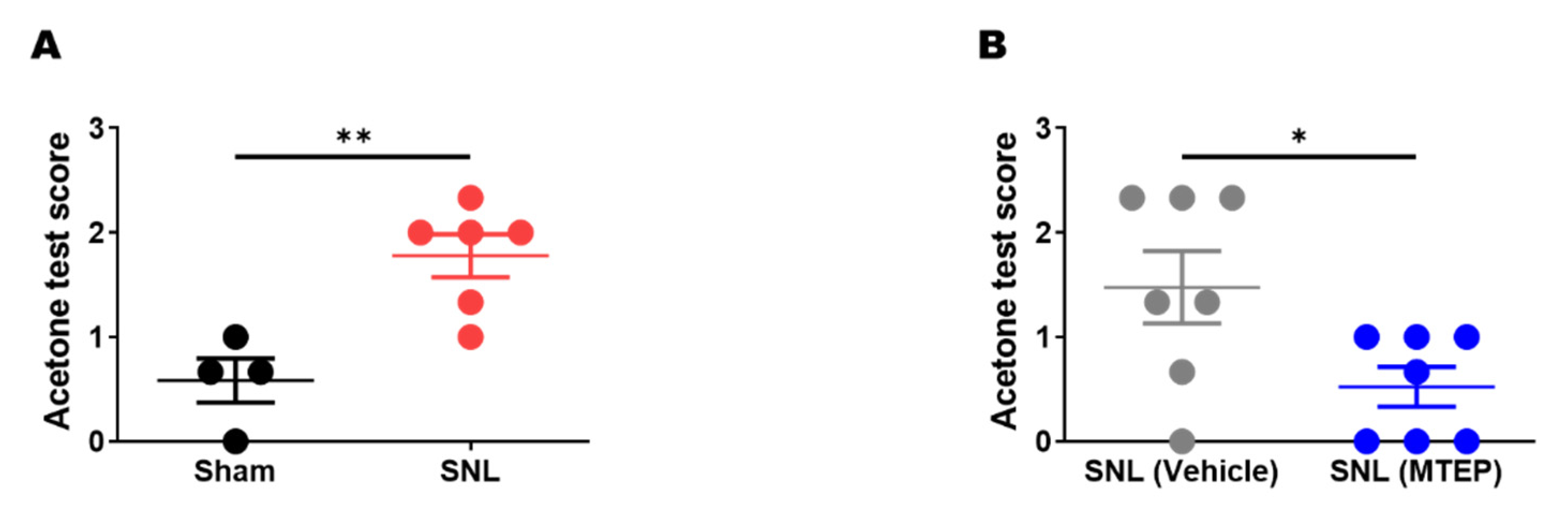
2.6. Acetone Test
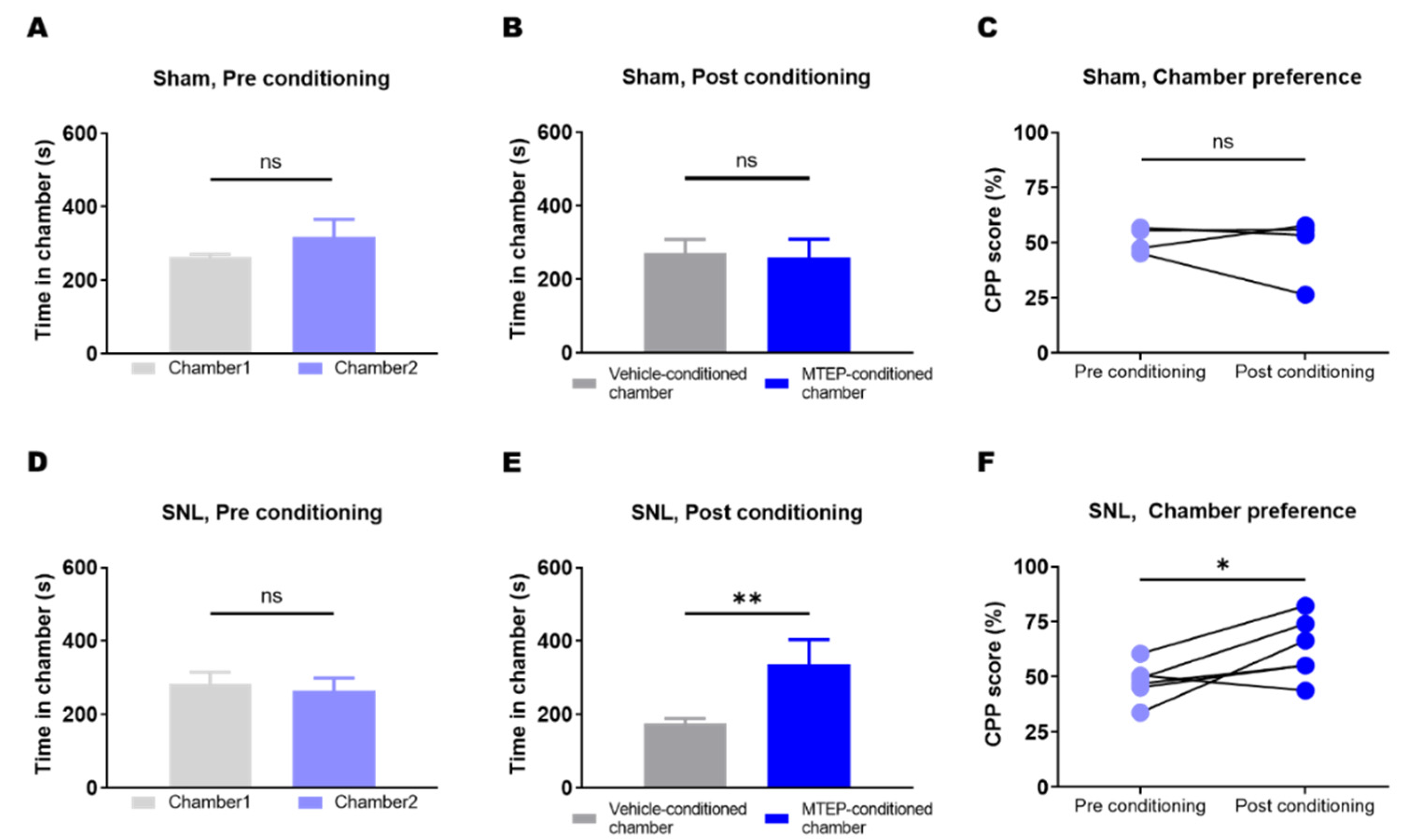
2.7. Conditioned Place Preference (CPP) Test
2.8. PET Analysis
2.9. Drugs
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. mGluR5 Availability Was Upregulated in the Left S1DZ of Animals with Right SNL Surgery
3.2. Pharmacological Blockade of mGluR5 in the S1DZ Ameliorated Mechanical Allodynia in Animals with Neuropathic Pain
3.3. Pharmacological Blockade of mGluR5 in the S1DZ Ameliorated Cold Allodynia in Neuropathic Pain Animals
3.4. Animals with Neuropathic Pain Showed a Preference for the Chamber Conditioned with Pharmacological Blockade of mGluR5 in the S1DZ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baron, R.; Binder, A.; Wasner, G. Neuropathic pain: Diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzcharles, M.A.; Cohen, S.P.; Clauw, D.J.; Littlejohn, G.; Usui, C.; Häuser, W. Nociplastic pain: Towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions. Lancet 2021, 397, 2098–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, M.S.; Park, H.; Kim, S.K. Neural plasticity in the brain during neuropathic pain. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Koga, K.; Chen, T.; Zhuo, M. Neuronal and microglial mechanisms for neuropathic pain in the spinal dorsal horn and anterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Song, Z.W.; Guo, S.W.; He, J.S.; Wang, S.Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Yang, H.L.; Liu, J.B. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling contributes to neuropathic pain via central sensitization mechanisms in a rat spinal nerve ligation model. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide and paracetamol, a new association to relieve hyperalgesia and pain in a sciatic nerve injury model in rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierck, C.J.; Whitsel, B.L.; Favorov, O.V.; Brown, A.W.; Tommerdahl, M. Role of primary somatosensory cortex in the coding of pain. Pain 2013, 154, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brecht, M. The body model theory of somatosensory cortex. Neuron 2017, 94, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Panchuelo, R.M.; Besle, J.; Mougin, O.; Gowland, P.; Bowtell, R.; Schluppeck, D.; Francis, S. Regional structural differences across functionally parcellated Brodmann areas of human primary somatosensory cortex. Neuroimage 2014, 93 Pt 2, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Panchuelo, R.M.; Francis, S.; Bowtell, R.; Schluppeck, D. Mapping human somatosensory cortex in individual subjects with 7T functional MRI. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 103, 2544–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akselrod, M.; Martuzzi, R.; Serino, A.; van der Zwaag, W.; Gassert, R.; Blanke, O. Anatomical and functional properties of the foot and leg representation in areas 3b, 1 and 2 of primary somatosensory cortex in humans: A 7T fMRI study. Neuroimage 2017, 159, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitsel, B.L.; Vierck, C.J.; Waters, R.S.; Tommerdahl, M.; Favorov, O.V. Contributions of nociresponsive area 3a to normal and abnormal somatosensory perception. J. Pain 2019, 20, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchuelo, R.M.S.; Eldeghaidy, S.; Marshall, A.; McGlone, F.; Francis, S.T.; Favorov, O. A nociresponsive specific area of human somatosensory cortex within BA3a: BA3c? Neuroimage 2020, 221, 1171887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favorov, O.V.; Pellicer-Morata, V.; DeJongh Curry, A.L.; Ramshur, J.T.; Brna, A.; Challener, T.D.; Waters, R.S. A newly identified nociresponsive region in the transitional zone (TZ) in rat sensorimotor cortex. Brain Res. 2019, 1717, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasabov, S.G.; Truong, H.; Rogness, V.M.; Alloway, K.D.; Simone, D.A.; Giesler, G.J. Responses of neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex to itch- and pain-producing stimuli in rats. J. Neurophysiol. 2020, 123, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, H.; Kanaya, M.; Ueta, Y.; Miyata, M. Distinct nociresponsive region in mouse primary somatosensory cortex. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Hsieh, G.; Ei-Kouhen, O.; Wilson, S.G.; Mikusa, J.P.; Hollingsworth, P.R.; Chang, R.; Moreland, R.B.; Brioni, J.; Decker, M.W.; et al. Role of central and peripheral mGluR5 receptors in post-operative pain in rats. Pain 2005, 114, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, M.O.; Hama, A.T.; Bradbury, M.; Anderson, J.; Varney, M.A.; Bristow, L. Role of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 (mGluR5) in the maintenance of cold hypersensitivity following a peripheral mononeuropathy in the rat. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Chen, S.R.; Chen, H.; Cai, Y.Q.; Pan, H.L. Regulation of increased glutamatergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons by mGluR5 in diabetic neuropathic pain. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, K.; Cornea, V.M.; Jong, Y.-J.J.I.; Laferrière, A.; Kumar, N.; Mickeviciute, A.; Fung, J.S.T.T.; Bandegi, P.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A.; O’Malley, K.L.; et al. Intracellular mGluR5 plays a critical role in neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Bai, H.H.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.L.; He, Y.T.; Duan, X.L.; Suo, Z.W.; Yang, X.; He, Y.X.; Hu, X.D. mGluR5/ERK signaling regulated the phosphorylation and function of glycine receptor α1ins subunit in spinal dorsal horn of mice. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.; Shim, H.G.; Kim, C.Y.; Ryu, H.H.; Jang, D.C.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.E.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Persistent activity of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in the periaqueductal gray constrains emergence of chronic neuropathic pain. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 4631–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danjo, Y.; Shigetomi, E.; Hirayama, Y.J.; Kobayashi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Fukazawa, Y.; Shibata, K.; Takanashi, K.; Parajuli, B.; Shinozaki, Y.; et al. Transient astrocytic mGluR5 expression drives synaptic plasticity and subsequent chronic pain in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20210989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.; Kim, C.Y.; Yun, Y.C.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.J. Upregulation of prefrontal metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 mediates neuropathic pain and negative mood symptoms after spinal nerve injury in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Chung, J.M. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992, 50, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, W.J. The up-and-down method for small samples. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1965, 60, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Chen, M.; Ling, J.; Tan, W.; Gu, J.G. TRPM8 mechanism of cold allodynia after chronic nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 13680–13690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, T.; Vera-Portocarrero, L.; Gutierrez, T.; Vanderah, T.W.; Dussor, G.; Lai, J.; Fields, H.L.; Porreca, F. Unmasking the tonic-aversive state in neuropathic pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1364–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweinhardt, P.; Fransson, P.; Olson, L.; Spenger, C.; Andersson, J.L.R. A template for spatial normalisation of MR images of the rat brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 129, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, M.; Anton, J.-L.L.; Valabregue, R.; Poline, J.-B. Region of interest analysis using an SPM toolbox—Abstract Presented at the 8th International Conference on Functional Mapping of the Human Brain, June 2–6, 2002, Sendai, Japan. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gadotti, V.M.; Chen, L.; Souza, I.A.; Stemkowski, P.L.; Zamponi, G.W. Role of prelimbic GABAergic circuits in sensory and emotional aspects of neuropathic pain. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gustin, S.M.; Peck, C.C.; Cheney, L.B.; Macey, P.M.; Murray, G.M.; Henderson, L.A. Pain and plasticity: Is chronic pain always associated with somatosensory cortex activity and reorganization? J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14874–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraga, S.; Itokazu, T.; Nishibe, M.; Yamashita, T. Neuroplasticity related to chronic pain and its modulation by microglia. Inflamm. Regen. 2022, 42, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, T.; Kato, D.; Nomura, Y.; Obata, N.; Quan, X.; Morinaga, A.; Yano, H.; Guo, Z.; Aoyama, Y.; Tachibana, Y.; et al. Pain induces stable, active microcircuits in the somatosensory cortex that provide a therapeutic target. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.H.; Kim, D.S.; Cho, Z.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Chung, M.A.; Lee, H.J.; Nam, T.S.; Lee, B.H. Modification of cortical excitability in neuropathic rats: A voltage-sensitive dye study. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 464, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-N.; Xing, X.-X.; Chen, L.; Dong, X.; Pan, H.-T.; Hua, X.-Y.; Wang, K. Brain Functional Alteration at Different Stages of Neuropathic Pain with Allodynia and Emotional Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 843815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, U.J.; Park, Y.G.; Won, R.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.H. Optical imaging of somatosensory evoked potentials in the rat cerebral cortex after spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolber, B.J. Mglurs Head to Toe in Pain, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Lax, N.C.; George, D.C.; Ignatz, C.; Kolber, B.J. The mGluR5 antagonist fenobam induces analgesic conditioned place preference in mice with spared nerve injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maione, S.; Oliva, P.; Marabese, I.; Palazzo, E.; Rossi, F.; Berrino, L.; Rossi, F.; Filippelli, A. Periaqueductal gray matter metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate formalin-induced nociception. Pain 2000, 85, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, G.M.; Mitchell, V.A.; Vaughan, C.W. Glutamate spillover modulates GABAergic synaptic transmission in the rat midbrain periaqueductal grey via metabotropic glutamate receptors and endocannabinoid signaling. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borich, M.R.; Brodie, S.M.; Gray, W.A.; Ionta, S.; Boyd, L.A. Understanding the role of the primary somatosensory cortex: Opportunities for rehabilitation. Neuropsychologia 2015, 79, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiechio, S. Modulation of Chronic Pain by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 75, ISBN 9780128038833. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.R.; Chuang, S.-C.; Zhao, W.; Wong, R.K.S.; Bianchi, R. Persistent receptor activity underlies group I mGluR-mediated cellular plasticity in CA3 neuron. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagni, L.; Ango, F.; Prezeau, L.; Worley, P.F.; Pin, J.-P.; Bockaert, J. Control of constitutive activity of metabotropic glutamate receptors by Homer proteins. Int. Congr. Ser. 2003, 1249, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ango, F.; Prézeau, L.; Muller, T.; Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Worley, P.F.; Pin, J.P.; Bockaert, J.; Fagni, L. Agonist-independent activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors by the intracellular protein Homer. Nature 2001, 411, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, G.; Yun, Y.-C.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071633
Chung G, Yun Y-C, Kim CY, Kim SK, Kim SJ. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(7):1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071633
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Geehoon, Yeong-Chan Yun, Chae Young Kim, Sun Kwang Kim, and Sang Jeong Kim. 2022. "Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats" Biomedicines 10, no. 7: 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071633
APA StyleChung, G., Yun, Y.-C., Kim, C. Y., Kim, S. K., & Kim, S. J. (2022). Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Dysgranular Zone of Primary Somatosensory Cortex Mediates Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Biomedicines, 10(7), 1633. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071633





