Identification of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 as New Relapse Predictors in Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient and Healthy Volunteer Recruitment
2.2. Ethics Approval
2.3. ELISA Assay
2.4. Soluble Immune Checkpoint Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
| Characteristic | Healthy Volunteers n = 67 | All Patients n = 83 | Stage I n = 55 | Stage II n = 16 | Stage III n = 12 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.9680 | |||||
| Male | 29 (43) | 54 (65) | 36 (67) | 10 (19) | 8 (14) | |
| Female | 38 (56) | 29 (35) | 19 (66) | 6 (21) | 4 (13) | |
| Age | 0.9695 | |||||
| Median Range | 59 (50–75) | 67 (38–86) | 67 (38–86) | 67 (61–77) | 65 (58–83) | |
| Relapse | 13 (15) | 6 (47) | 5 (38) | 2 (15) | 0.1428 | |
| Perineural Invasion | 3 (3) | 1 (33.3) | 1 (33.3) | 1 (33.3) | 0.4504 | |
| Linfovascular Invasion | 11 (13) | 2 (18) | 5 (46) | 4 (36) | 0.0014 | |
| Tumour Histology | ||||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 58 (69) | 43 (74) | 8 (13) | 7 (12) | 0.0619 | |
| Epidermoid | 21 (25) | 12 (57) | 6 (29) | 3 (14) | 0.4463 | |
| Large Cell Neuroendrocrine Carcinoma | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | 0.0137 | |
| Others | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | 0.0023 | |
| Adjuvant Treatment | ||||||
| Chemotherapy | 18 (22) | 0 (0) | 8 (44) | 10 (56) | 0.0001 | |
| Radiotherapy | 7 (8) | 2 (29) | 1 (14) | 4 (57) | 0.0034 | |
| Immunotherapy | 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) | 0.0501 | |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Smoker | 67 (80) | 47 (70) | 13 (20) | 7 (10) | 0.0973 | |
| Exitus | 5 (6) | 2 (40) | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 0.3961 |
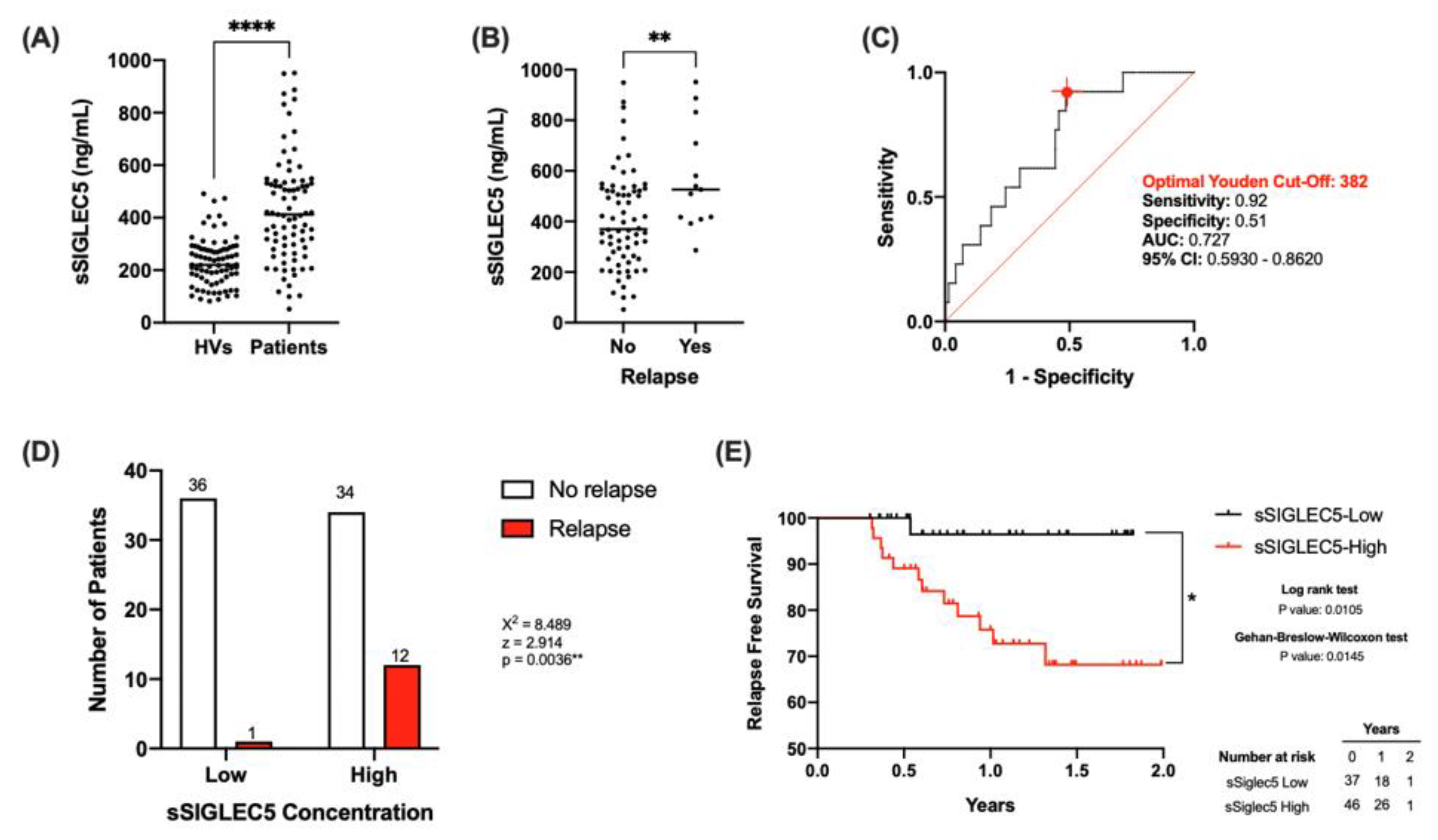
3.2. sSIGLEC5 Is a Relapse Predictor in Lung Cancer Patients
3.3. sLAG3 Is Increased in Relapse Lung Cancer Patients
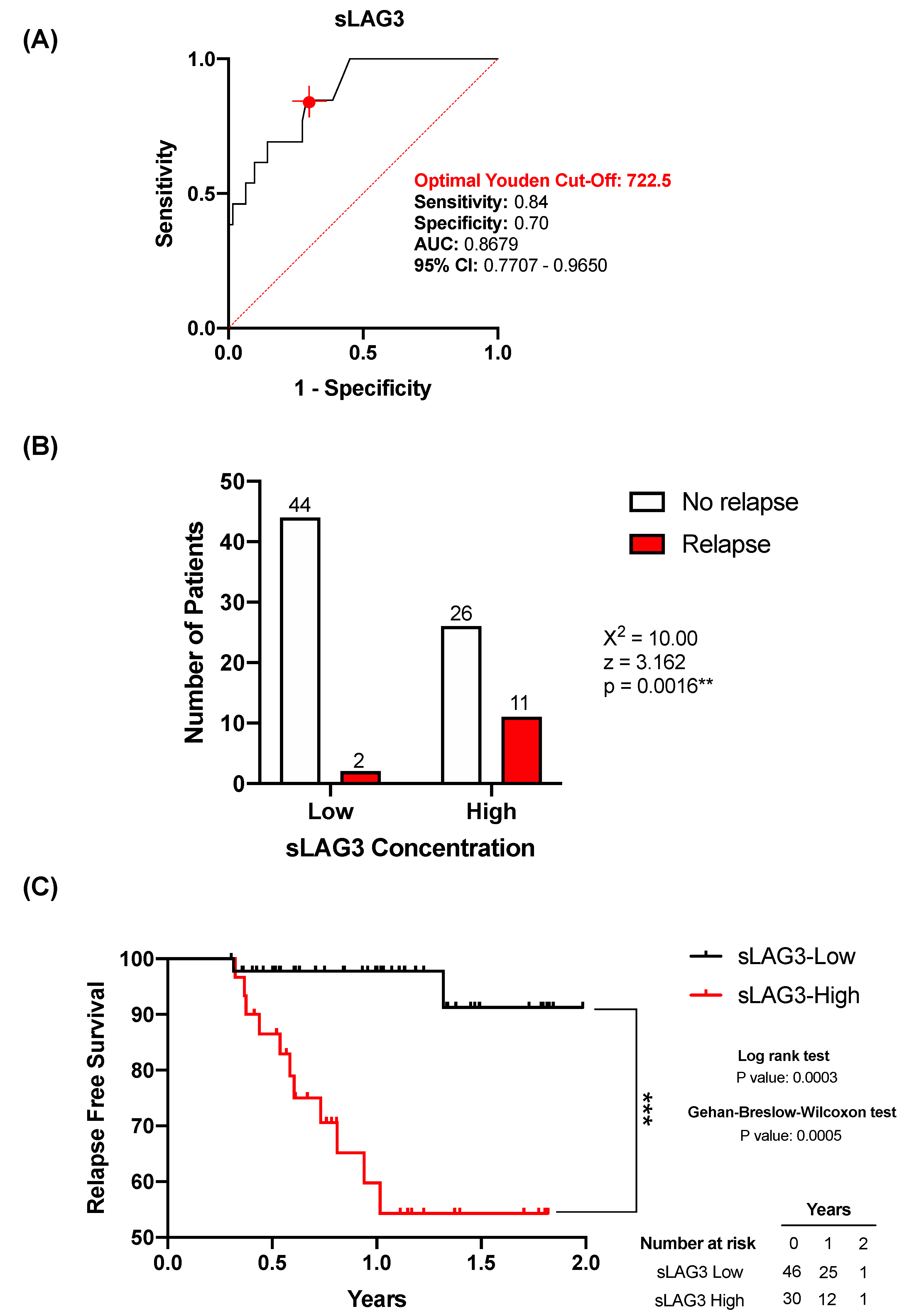
3.4. sLAG3 Can Act as a Relapse Predictor in Lung Cancer Patients
3.5. Combination of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 Increases Robustness of the Predictive Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, G.; Etxeberria, J.; Hao, Y. Global Patterns and Trends in Lung Cancer Incidence: A Population-Based Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu-Aljabar, R.D.; Awad, O.A. A Comparative Analysis Study of Lung Cancer Detection and Relapse Prediction Using XGBoost Classifier. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1076, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Akerley, W.; Borghaei, H.; Chang, A.C.; Cheney, R.T.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; Demmy, T.L.; Ganti, A.K.P.; Govindan, R.; et al. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2012, 10, 1236–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Xin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Shi, R.; Bao, X. A Novel 4-Gene Signature for Overall Survival Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with Lymph Node Metastasis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstraw, P.; Crowley, J.; Chansky, K.; Giroux, D.J.; Groome, P.A.; Rami-Porta, R.; Postmus, P.E.; Rusch, V.; Sobin, L. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Seventh) Edition of the TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastorino, U. Lung Cancer Screening. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodgame, B.; Viswanathan, A.; Miller, C.R.; Gao, F.; Meyers, B.; Battafarano, R.J.; Patterson, A.; Cooper, J.; Guthrie, T.J.; Bradley, J.; et al. A Clinical Model to Estimate Recurrence Risk in Resected Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 31, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T. Therapeutic Strategy for Postoperative Recurrence in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. WJCO 2014, 5, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, A.; Myles, J.P.; van Tongeren, M.; Page, R.D.; Liloglou, T.; Duffy, S.W.; Field, J.K. The LLP Risk Model: An Individual Risk Prediction Model for Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoggart, C.; Brennan, P.; Tjonneland, A.; Vogel, U.; Overvad, K.; Østergaard, J.N.; Kaaks, R.; Canzian, F.; Boeing, H.; Steffen, A.; et al. A Risk Model for Lung Cancer Incidence. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, J.; Simon, R. Gene Expression-Based Prognostic Signatures in Lung Cancer: Ready for Clinical Use? JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, C.G.; Lipson, E.J.; Brahmer, J.R. Breathing New Life into Immunotherapy: Review of Melanoma, Lung and Kidney Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Boyle, T.A.; Zhou, C.; Rimm, D.L.; Hirsch, F.R. PD-L1 Expression in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haragan, A.; Field, J.K.; Davies, M.P.A.; Escriu, C.; Gruver, A.; Gosney, J.R. Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Specimen Sampling in Predicting Treatment Response. Lung Cancer 2019, 134, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovanović, D.; Roksandić-Milenković, M.; Kotur-Stevuljević, J.; Ćeriman, V.; Vukanić, I.; Samardžić, N.; Popević, S.; Ilić, B.; Gajić, M.; Simon, M.; et al. Soluble SPD-L1 and Serum Amyloid A1 as Potential Biomarkers for Lung Cancer. J. Med. Biochem. 2019, 38, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Läubli, H.; Alisson-Silva, F.; Stanczak, M.A.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Deng, L.; Verhagen, A.; Varki, N.; Varki, A. Lectin Galactoside-Binding Soluble 3 Binding Protein (LGALS3BP) Is a Tumor-Associated Immunomodulatory Ligand for CD33-Related Siglecs. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 33481–33491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crocker, P.R.; Paulson, J.C.; Varki, A. Siglecs and Their Roles in the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdicchio, M.; Ilarregui, J.M.; Verstege, M.I.; Cornelissen, L.A.M.; Schetters, S.T.T.; Engels, S.; Ambrosini, M.; Kalay, H.; Veninga, H.; den Haan, J.M.M.; et al. Sialic Acid-Modified Antigens Impose Tolerance via Inhibition of T-Cell Proliferation and de Novo Induction of Regulatory T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3329–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuster, M.M.; Esko, J.D. The Sweet and Sour of Cancer: Glycans as Novel Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 526–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, M.; Mezouar, S.; Pegon, J.; Muczynski, V.; Adam, F.; Bianchini, E.P.; Bazaa, A.; Proulle, V.; Rupin, A.; Paysant, J.; et al. Soluble Siglec-5 Associates to PSGL-1 and Displays Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tinoco, R.; Carrette, F.; Barraza, M.L.; Otero, D.C.; Magaña, J.; Bosenberg, M.W.; Swain, S.L.; Bradley, L.M. PSGL-1 Is an Immune Checkpoint Regulator That Promotes T Cell Exhaustion. Immunity 2016, 44, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Roh, S.A.; Cho, D.-H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, J.C. A Nineteen Gene-Based Risk Score Classifier Predicts Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Li, Y.; Mo, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Cai, G. A Robust Gene Signature for the Prediction of Early Relapse in Stage I-III Colon Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, D.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X. Soluble Immune Checkpoints in Cancer: Production, Function and Biological Significance. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hock, B.D.; Drayson, M.; Patton, W.N.; Taylor, K.; Kerr, L.; McKenzie, J.L.; the Working Party on Leukaemia in adults (part of the NCRI Haematological Oncology Clinical Studies Group). Circulating Levels and Clinical Significance of Soluble CD86 in Myeloma Patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 133, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Cantero-Cid, R.; Lozano-Rodríguez, R.; Pascual-Iglesias, A.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; Casalvilla-Dueñas, J.C.; Bonel Pérez, G.C.; Guevara, J.; Marcano, C.; Barragán, C.; et al. Soluble SIGLEC5: A New Prognosis Marker in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fresno, C.; García-Rio, F.; Gómez-Piña, V.; Soares-Schanoski, A.; Fernández-Ruíz, I.; Jurado, T.; Kajiji, T.; Shu, C.; Marín, E.; Gutierrez del Arroyo, A.; et al. Potent Phagocytic Activity with Impaired Antigen Presentation Identifying Lipopolysaccharide-Tolerant Human Monocytes: Demonstration in Isolated Monocytes from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6494–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshow, D.B.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Hastings, K.; Politi, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Chen, L.; Melero, I.; Schalper, K.A.; Herbst, R.S. Immunotherapy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Facts and Hopes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4592–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.; Yang, Y.-W.; Buchanan, P. Lung Cancer: Biology and Treatment Options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixidó, C.; Vilariño, N.; Reyes, R.; Reguart, N. PD-L1 Expression Testing in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 175883591876349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarogoulidis, K.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Darwiche, K.; Boutsikou, E.; Machairiotis, N.; Tsakiridis, K.; Katsikogiannis, N.; Kougioumtzi, I.; Karapantzos, I.; Huang, H.; et al. Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 4), S389–S396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Ansari, R.; Bustin, F.; Flynn, P.; Hart, L.; Otterson, G.A.; Vlahovic, G.; Soh, C.-H.; O’Connor, P.; Hainsworth, J. Efficacy of Bevacizumab plus Erlotinib versus Erlotinib Alone in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer after Failure of Standard First-Line Chemotherapy (BeTa): A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunn, P.A.; Kelly, K. New Chemotherapeutic Agents Prolong Survival and Improve Quality of Life in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review of the Literature and Future Directions. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Salgia, R. Managing Patients with Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JOP 2018, 14, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Rodriguez, R.; Avendano-Ortiz, J.; Montalban-Hernandez, K.; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R.; Martin-Quiros, A.; Maroun-Eid, C.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.J.; Fabrega, A.; Terron, V.; et al. SIGLEC5: An Immune Checkpoint Ligand in Sepsis. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.-P.; Tang, X.-Y.; Xiong, Y.-L.; Zheng, K.-F.; Liu, Y.-J.; Shi, X.-G.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, T.; Ma, N.; Zhao, J.-B. Immune Checkpoint LAG3 and Its Ligand FGL1 in Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 785091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecocq, Q.; Keyaerts, M.; Devoogdt, N.; Breckpot, K. The Next-Generation Immune Checkpoint LAG-3 and Its Therapeutic Potential in Oncology: Third Time’s a Charm. IJMS 2020, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, H.; Rozeboom, L.; Rivard, C.J.; Ellison, K.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Suda, K.; Ren, S.; Wu, C.; Hou, L.; et al. LAG-3 Protein Expression in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datar, I.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Wang, J.; Henick, B.S.; Choi, J.; Badri, T.; Dong, W.; Mani, N.; Toki, M.; Mejías, L.D.; et al. Expression Analysis and Significance of PD-1, LAG-3, and TIM-3 in Human Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Spatially Resolved and Multiparametric Single-Cell Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montalbán-Hernández, K.; Casalvilla-Dueñas, J.C.; Cruz-Castellanos, P.; Gutierrez-Sainz, L.; Lozano-Rodríguez, R.; Avendaño-Ortiz, J.; del Fresno, C.; de Castro-Carpeño, J.; López-Collazo, E. Identification of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 as New Relapse Predictors in Lung Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051047
Montalbán-Hernández K, Casalvilla-Dueñas JC, Cruz-Castellanos P, Gutierrez-Sainz L, Lozano-Rodríguez R, Avendaño-Ortiz J, del Fresno C, de Castro-Carpeño J, López-Collazo E. Identification of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 as New Relapse Predictors in Lung Cancer. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051047
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontalbán-Hernández, Karla, José Carlos Casalvilla-Dueñas, Patricia Cruz-Castellanos, Laura Gutierrez-Sainz, Roberto Lozano-Rodríguez, José Avendaño-Ortiz, Carlos del Fresno, Javier de Castro-Carpeño, and Eduardo López-Collazo. 2022. "Identification of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 as New Relapse Predictors in Lung Cancer" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051047
APA StyleMontalbán-Hernández, K., Casalvilla-Dueñas, J. C., Cruz-Castellanos, P., Gutierrez-Sainz, L., Lozano-Rodríguez, R., Avendaño-Ortiz, J., del Fresno, C., de Castro-Carpeño, J., & López-Collazo, E. (2022). Identification of sSIGLEC5 and sLAG3 as New Relapse Predictors in Lung Cancer. Biomedicines, 10(5), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051047






