Blood Neutrophil Counts Define Specific Clusters of Bronchiectasis Patients: A Hint to Differential Clinical Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
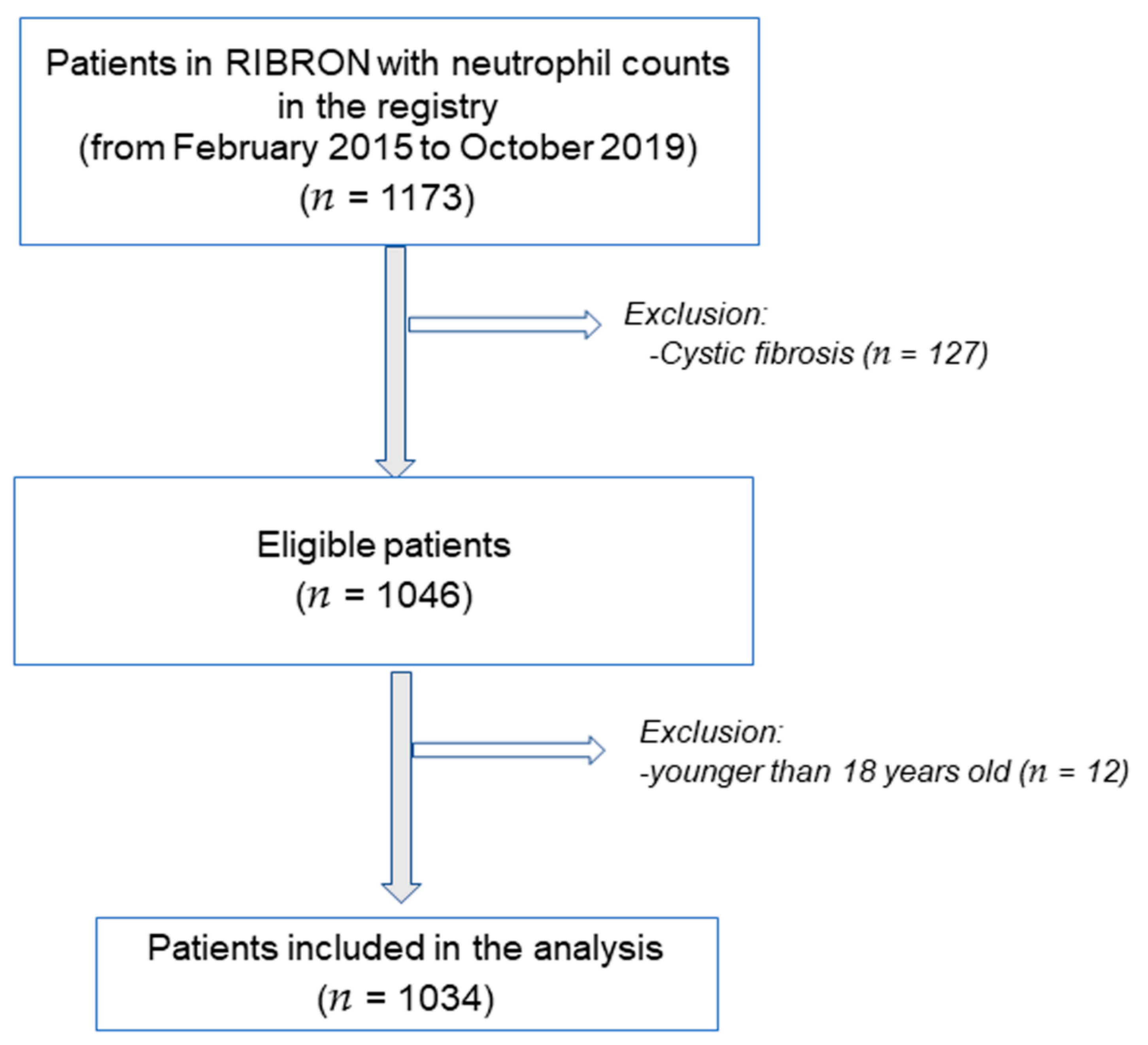
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Clinical Variables and Scores
2.4. Clusters of Patients
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
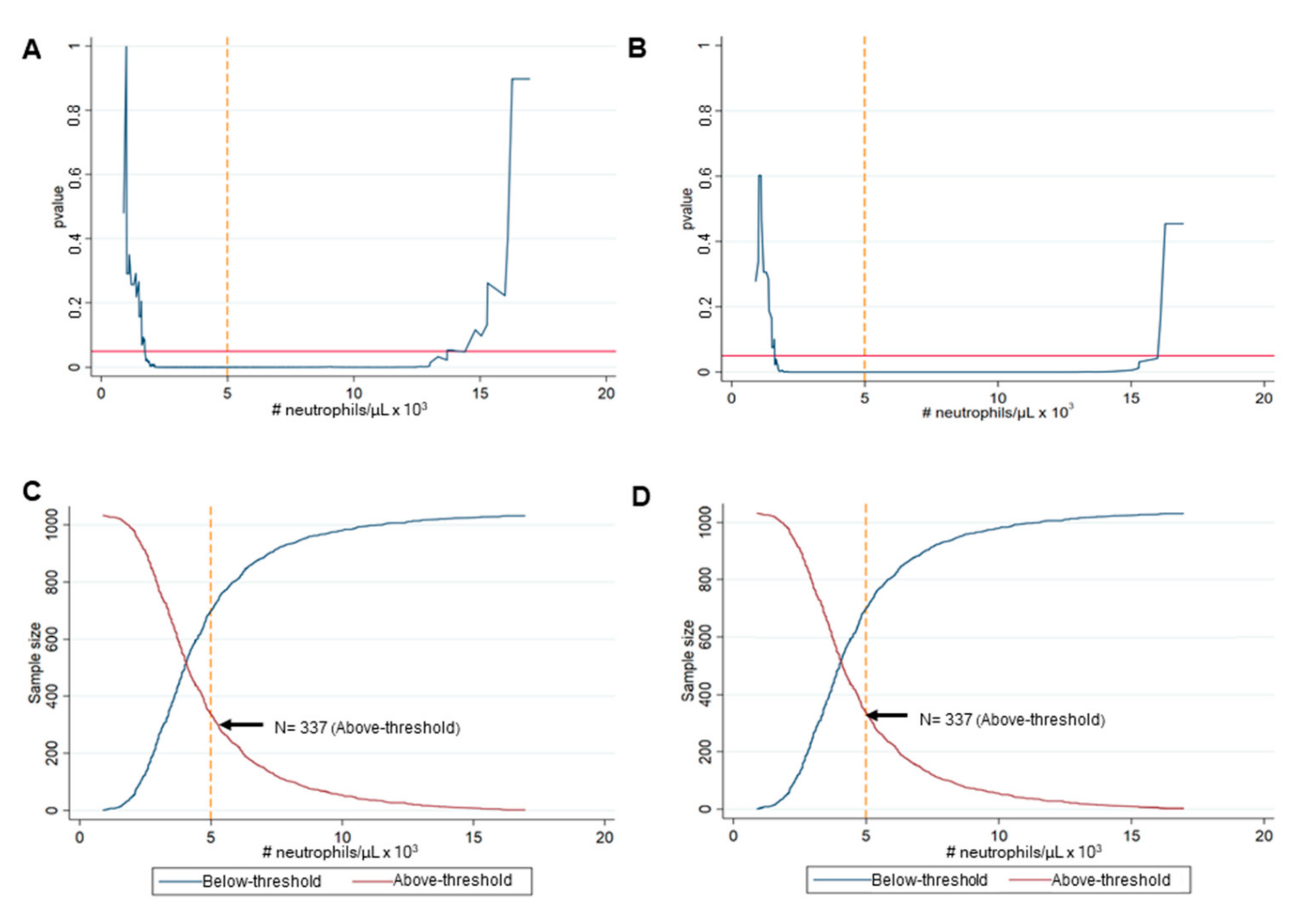
3.1. Identification of the Best Cut-Off Value of Neutrophils
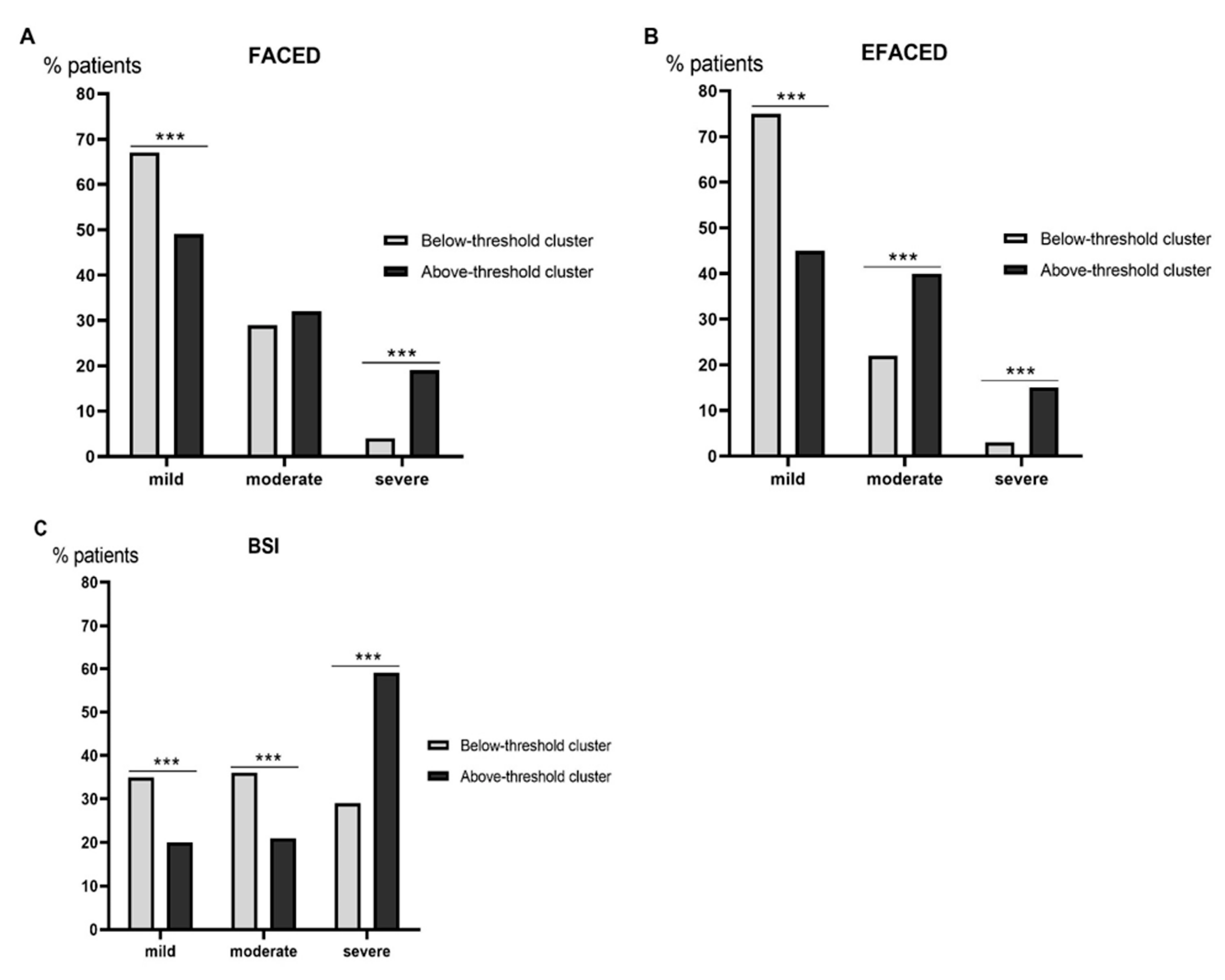
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
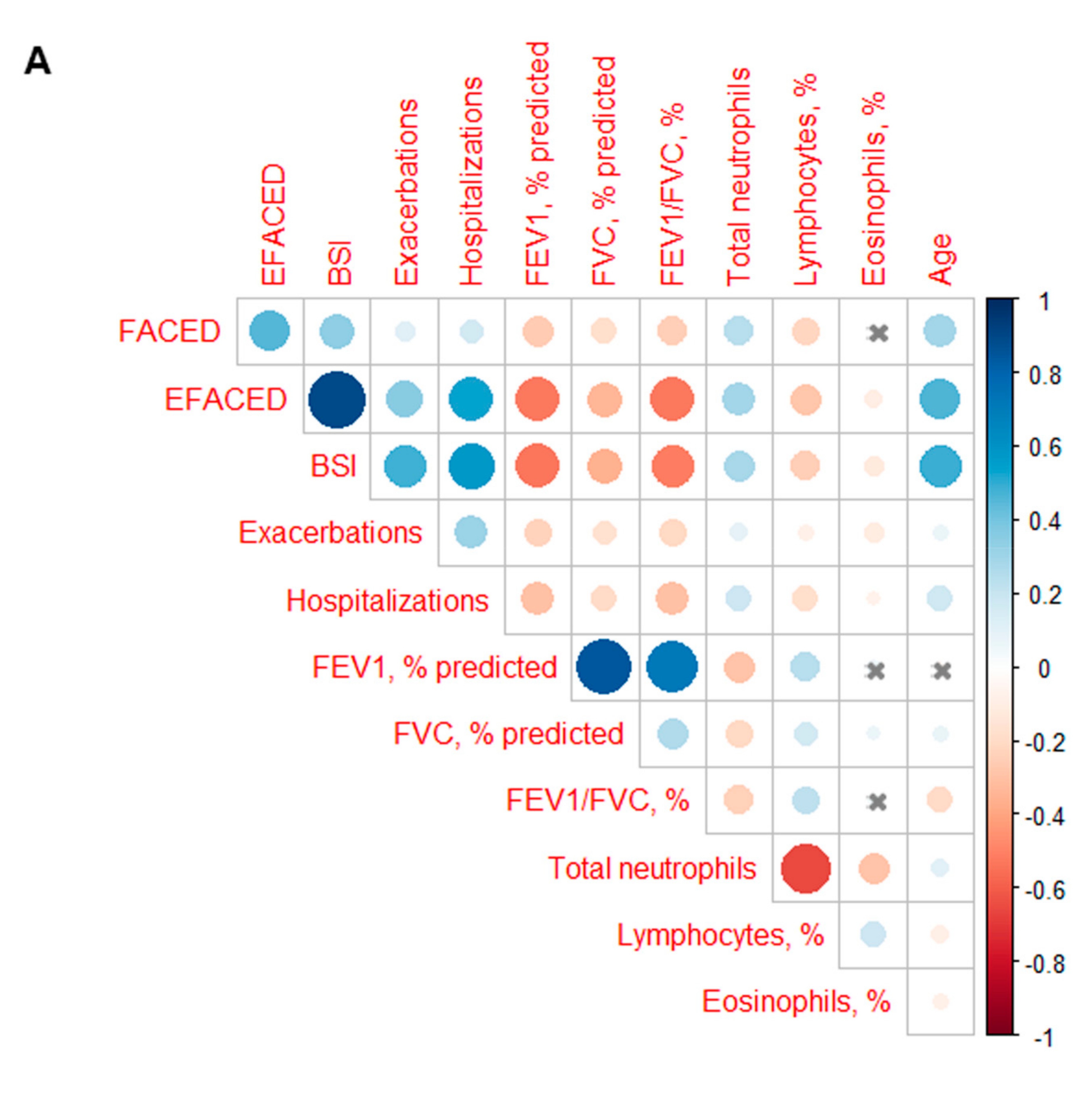
3.3. Profile of the Systemic Parameters in the Two Patient Clusters
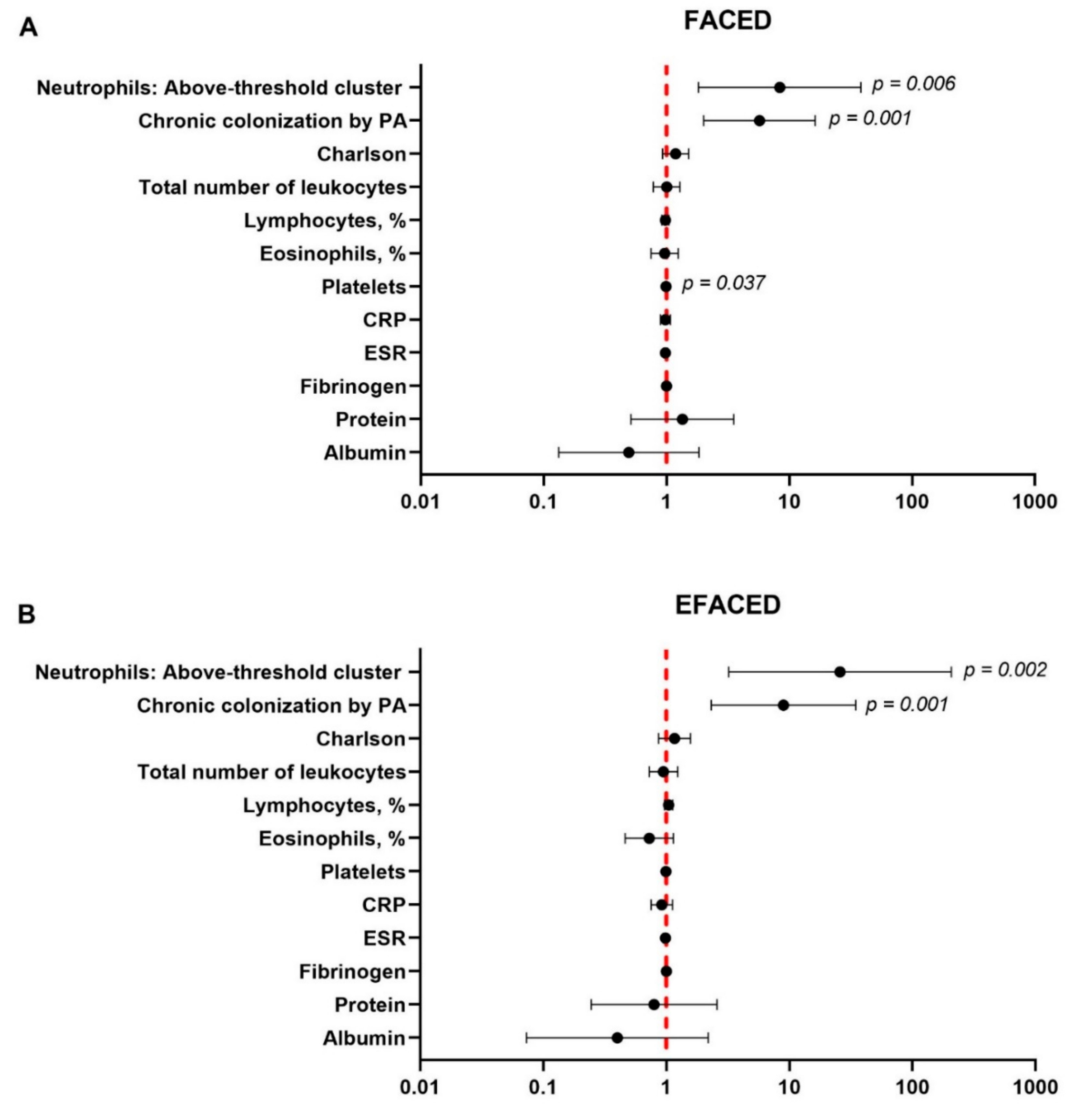
3.4. Multivariate Analyses
4. Discussion
Study Critique
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mincham, K.T.; Bruno, N.; Singanayagam, A.; Snelgrove, R.J. Our evolving view of neutrophils in defining the pathology of chronic lung disease. Immunology 2021, 164, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, J.-J.; Li, H.-M.; Han, X.-R.; Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; de la Rosa-Carrillo, D.; Chen, R.; Guan, W.-J.; Zhong, N.-S. The Roles of Bacteria and Viruses in Bronchiectasis Exacerbation: A Prospective Study. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Rosa Carrillo, D.; López-Campos, J.L.; Navarrete, B.A.; Rubio, M.C.; Moreno, R.C.; García-Rivero, J.L.; Carro, L.M.; Fuster, C.O.; Martínez-García, M.Á. Consensus document on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic bronchial infection in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, M.Á.; Máiz, L.; Olveira, C.; Girón, R.M.; de la Rosa, D.; Blanco, M.; Cantón, R.; Vendrell, M.; Polverino, E.; de Gracia, J.; et al. Spanish Guidelines on the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Bronchiectasis in Adults. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2018, 54, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polverino, E.; Goeminne, P.C.; McDonnell, M.J.; Aliberti, S.; Marshall, S.E.; Loebinger, M.R.; Murris, M.; Cantón, R.; Torres, A.; Dimakou, K.; et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the management of adult bronchiectasis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasteur, M.C.; Bilton, D.; Hill, A.T. British thoracic society guideline for non-CF bronchiectasis. Thorax 2010, 65, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keir, H.R.; Chalmers, J.D. Neutrophil extracellular traps in chronic lung disease: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsó, E. Look at the wood and not at the tree: The Microbiome in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease and Cystic Fibrosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, P.; Davidson, D.J.; McHugh, B.J.; Rossi, A.G.; Hill, A.T. Blood Neutrophils Are Reprogrammed in Bronchiectasis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, A.P.; Brown, V.; Courtney, J.; Kelly, M.; Garske, L.; Elborn, J.S.; Ennis, M. Neutrophil apoptosis, proinflammatory mediators and cell counts in bronchiectasis. Thorax 2004, 59, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keir, H.R.; Shoemark, A.; Dicker, A.J.; Perea, L.; Pollock, J.; Giam, Y.H.; Suarez-Cuartin, G.; Crichton, M.L.; Lonergan, M.; Oriano, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps, disease severity, and antibiotic response in bronchiectasis: An international, observational, multicohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Villa, C.; Dobarganes, Y.; Olveira, C.; Girón, R.; García-Clemente, M.; Máiz, L.; Sibila, O.; Golpe, R.; Menéndez, R.; et al. Phenotypic Clustering in Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis Patients: The Role of Eosinophils in Disease Severity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Villa, C.; Dobarganes, Y.; Olveira, C.; Girón, R.; García-Clemente, M.; Máiz, L.; Sibila, O.; Golpe, R.; Menéndez, R.; et al. Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers Define Specific Clusters in Patients with Bronchiectasis: A Large-Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalmers, J.D.; Chang, A.B.; Chotirmall, S.H.; Dhar, R.; McShane, P.J. Bronchiectasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-García, M.A.; Villa, C.; Dobarganes, Y.; Girón, R.; Maíz, L.; García-Clemente, M.; Sibila, O.; Golpe, R.; Rodríguez, J.; Barreiro, E.; et al. RIBRON: The spanish Online Bronchiectasis Registry. Characterization of the First 1912 Patients. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, T.; Oscullo, G.; Zaldivar, E.; Villa, C.; Dobarganes, Y.; Girón, R.; Olveira, C.; Maíz, L.; García-Clemente, M.; Sibila, O.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Concentration in Steady-State Bronchiectasis: Prognostic Value of Future Severe Exacerbations. Data from the Spanish Registry of Bronchiectasis (RIBRON). Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.; Masefield, S.; Polverino, E.; De Soyza, A.; Loebinger, M.R.; Menendez, R.; Ringshausen, F.C.; Vendrell, M.; Powell, P.; Chalmers, J.D. Research priorities in bronchiectasis: A consensus statement from the EMBARC Clinical Research Collaboration. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, B.; Dunn, L. The Declaration of Helsinki on Medical Research involving Human Subjects: A Review of Seventh Revision. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2020, 17, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; de Gracia, J.; Vendrell Relat, M.; Giron, R.-M.; Maiz Carro, L.; de la Rosa Carrillo, D.; Olveira, C. Multidimensional approach to non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: The FACED score. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Athanazio, R.A.; Girón, R.M.; Máiz-Carro, L.; de la Rosa, D.; Olveira, C.; de Gracia, J.; Vendrell, M.; Prados-Sánchez, C.; Gramblicka, G.; et al. Predicting high risk of exacerbations in bronchiectasis: The E-FACED score. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chalmers, J.D.; Goeminne, P.; Aliberti, S.; McDonnell, M.J.; Lonni, S.; Davidson, J.; Poppelwell, L.; Salih, W.; Pesci, A.; Dupont, L.J.; et al. The bronchiectasis severity index an international derivation and validation study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokwani, R.; Wark, P.A.B.; Baines, K.J.; Fricker, M.; Barker, D.; Simpson, J.L. Blood neutrophils in copd but not asthma exhibit a primed phenotype with downregulated cd62l expression. Int. J. COPD 2019, 14, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, M.J.; Sapey, E.; Stockley, R. Neutrophil phenotypes in chronic lung disease. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2019, 13, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre-Roig, C.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Glogauer, M.; Scapini, P. Neutrophil Diversity in Health and Disease. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonergan, M.; Dicker, A.J.; Crichton, M.L.; Keir, H.R.; Van Dyke, M.K.; Mullerova, H.; Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Chalmers, J.D. Blood neutrophil counts are associated with exacerbation frequency and mortality in COPD. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giam, Y.H.; Shoemark, A.; Chalmers, J.D. Neutrophil dysfunction in bronchiectasis: An emerging role for immunometabolism. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 2003157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerpin, E.; Jacinto, T.; Fonseca, J.A.; Alving, K.; Janson, C.; Malinovschi, A. Systemic inflammatory markers in relation to lung function in NHANES. 2007–2010. Respir. Med. 2018, 142, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, M.A.; Posadas, T.; Sotgiu, G.; Blasi, F.; Saderi, L.; Aliberti, S. Repeteability of Circulating Eosinophil Measures and Inhaled Corticosteroids Effect in Bronchiectasis. A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaya, M.; Usami, O.; Nakayama, S.; Tode, N.; Yamada, A.; Ito, S.; Omata, F.; Momma, H.; Funakubo, M.; Ichinose, M. Malnutrition, Airflow Limitation and Severe Emphysema are Risks for Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Japanese Subjects: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2020, 15, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
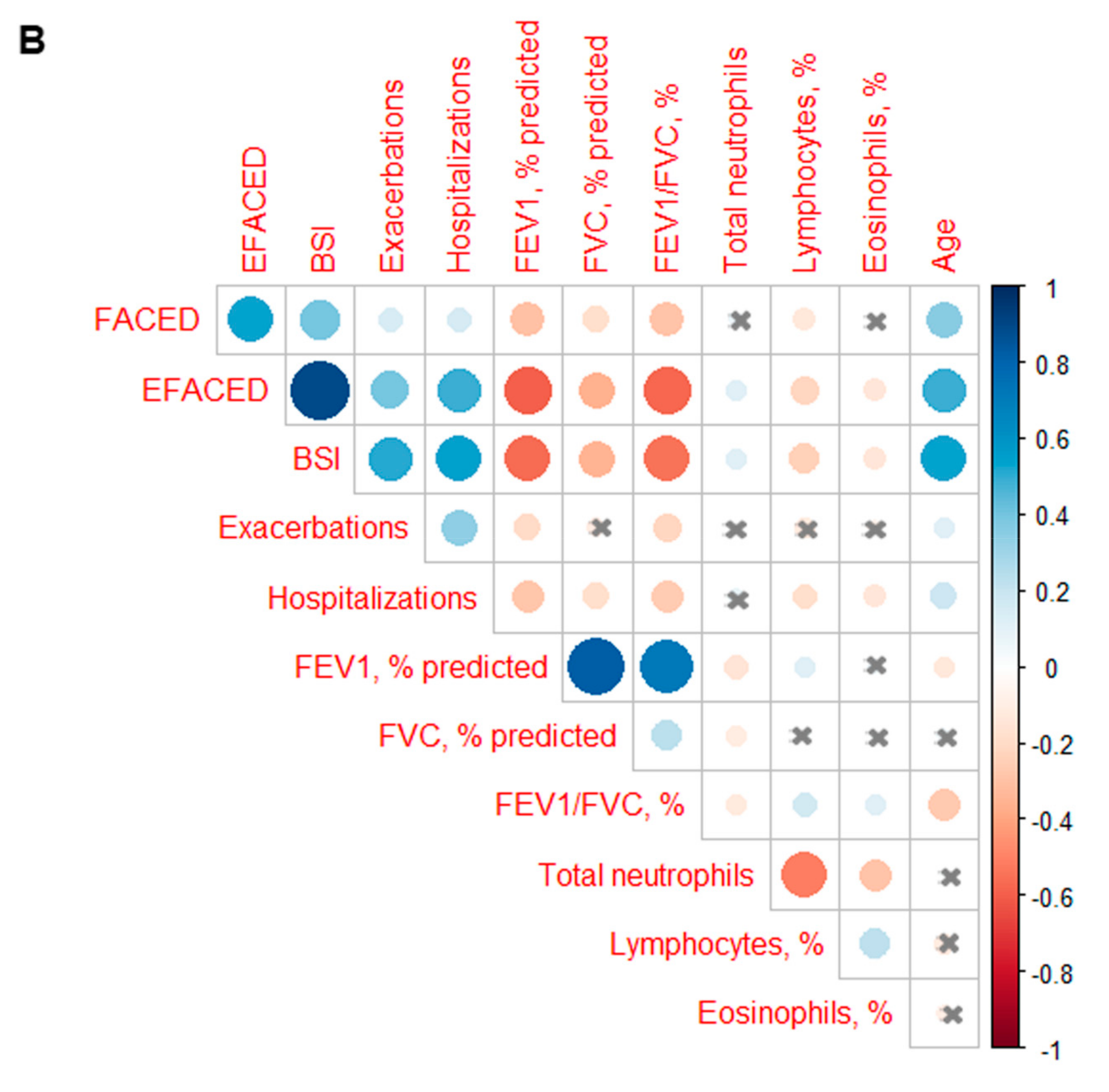
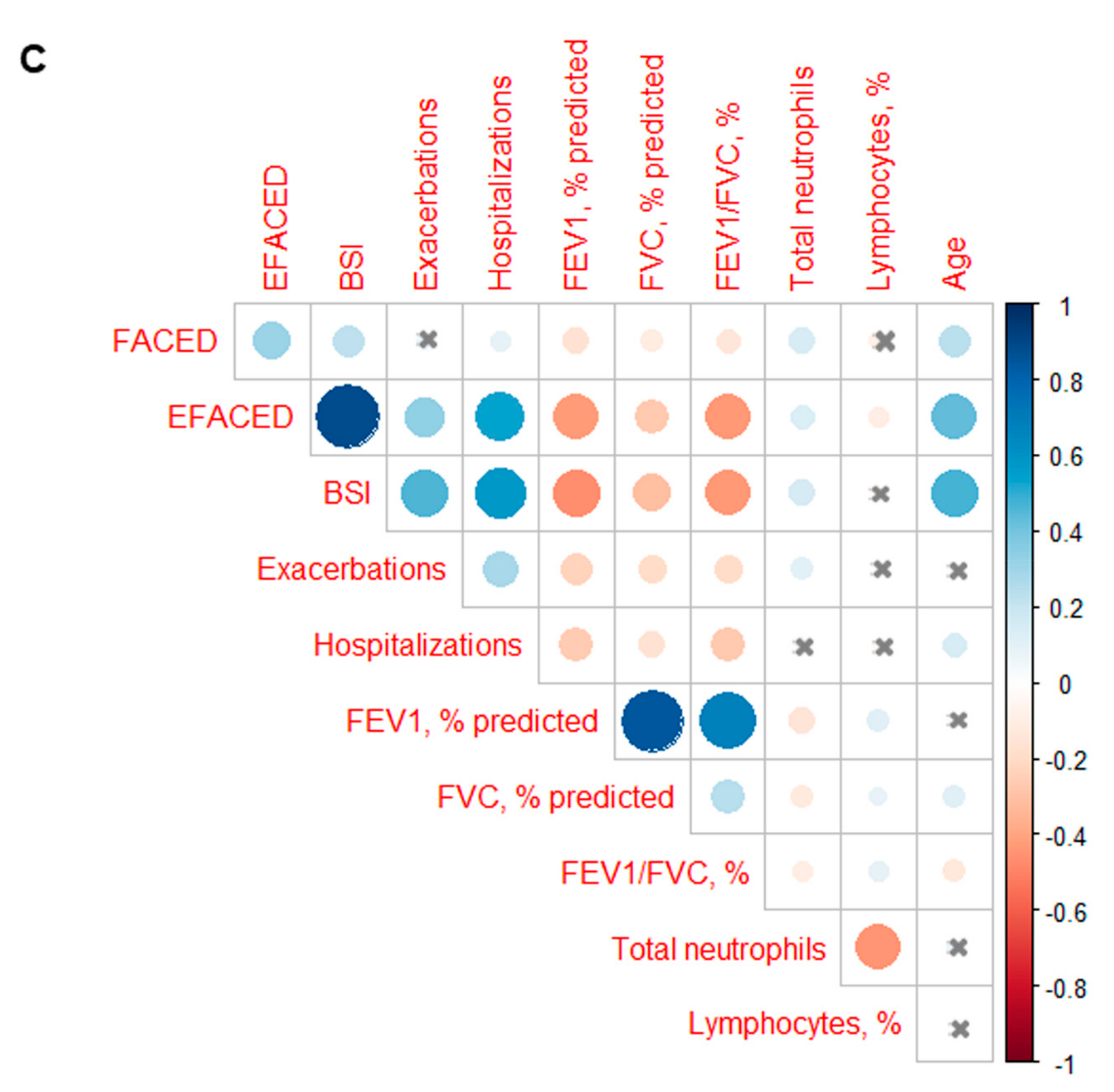
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| <4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 697) | (N = 337) | |
| Anthropometric variables, (SD) | ||
| Age, years | 67.1 (14.6) | 70.3 (15.6) ** |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.7 (4.9) | 26.2 (5.2) |
| Disease severity, (SD) | ||
| FACED score | 1.9 (1.5) | 2.8 (1.9) *** |
| EFACED score | 2.4 (1.9) | 3.8 (2.4) *** |
| BSI | 6.9 (4.3) | 9.6 (5.1) *** |
| Exacerbations | 1.5 (1.6) | 1.7 (1.6) * |
| Hospitalization | 0.5 (1.2) | 1.1 (1.7) *** |
| Charlson Index | 1.8 (1.4) | 2.2 (1.9) *** |
| Radiological extension | 2.88 (1.41) | 2.83 (1.39) |
| Chronic colonization by PA, N (%) | 150 (21.5) | 113 (33.5) *** |
| Asthma, N (%) | 70 (10) | 36 (10.7) |
| COPD, N (%) | 57 (8.2) | 62 (18.4) *** |
| Smoking history | ||
| Never smokers, N (%) | 443 (64) | 162 (48) *** |
| Current smokers, N (%) | 51 (7) | 40 (12) * |
| Ex-smokers, N (%) | 203 (29) | 135 (40) ** |
| Packs-year, (SD) | 28.2 (24.8) | 35.4 (27.2) ** |
| Lung function,(SD) | ||
| FEV1, % predicted | 78 (24) | 64 (25) *** |
| FVC, % predicted | 88 (21) | 79 (23) *** |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 70 (12) | 64 (14) *** |
| DLCO, % predicted | 86 (22) | 73 (25) *** |
| KCO, % predicted | 80 (36) | 69 (41) * |
| RV, % predicted | 137 (45) | 147 (58) |
| TLC, % predicted | 102 (18) | 102 (24) |
| RV/TLC, % | 50 (11) | 52 (13) |
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| <4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 640) | (N = 275) | |
| Anthropometric variables, (SD) | ||
| Age, years | 66.4 (14.7) | 68.6 (16.2) * |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.6 (4.9) | 26.1 (5.3) |
| Disease severity, (SD) | ||
| FACED score | 1.8 (1.5) | 2.5 (1.8) *** |
| EFACED score | 2.3 (1.9) | 3.4 (2.3) *** |
| BSI | 6.7 (4.2) | 8.8 (4.8) *** |
| Exacerbations | 1.5 (1.6) | 1.6 (1.5) |
| Hospitalization | 0.5 (1.2) | 1 (1.6) *** |
| Charlson Index | 1.7 (1.3) | 2.1 (2) ** |
| Radiological extension | 2.9 (1.4) | 2.8 (1.4) |
| Chronic colonization by PA, N (%) | 143 (22.3) | 90 (32.7) ** |
| Smoking history | ||
| Never smokers, N (%) | 438 (68) | 161 (59) ** |
| Current smokers, N (%) | 38 (6) | 30 (11) * |
| Ex-smokers, N (%) | 164 (26) | 84 (30) |
| Packs-year, (SD) | 22.3 (19.7) | 28.4 (23.3) * |
| Lung function,(SD) | ||
| FEV1, % predicted | 80 (23) | 68 (25) *** |
| FVC, % predicted | 88 (21) | 81 (24) *** |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 71 (11) | 67 (13) *** |
| DLCO, % predicted | 87 (22) | 78 (23) ** |
| KCO, % predicted | 80 (37) | 72 (39) |
| RV, % predicted | 133 (43) | 143 (55) |
| TLC, % predicted | 101 (18) | 99 (22) |
| RV/TLC, % | 49 (11) | 52 (13) |
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| <4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 547) | (N = 224) | |
| Anthropometric variables, (SD) | ||
| Age, years | 67.4 (14.1) | 69.6 (15.3) * |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.9 (4.9) | 26.2 (5.0) |
| Disease severity, (SD) | ||
| FACED score | 1.5 (1.3) | 2.2 (1.7) *** |
| EFACED score | 2 (1.7) | 3.1 (2.2) *** |
| BSI | 5.8 (3.6) | 7.9 (4.4) *** |
| Exacerbations | 1.3 (1.6) | 1.4 (1.5) |
| Hospitalization | 0.4 (1) | 0.9 (1.3) *** |
| Charlson Index | 1.8 (1.4) | 2 (1.9), p = 0.065 |
| Radiological extension | 2.76 (1.38) | 2.67 (1.43) |
| Smoking history | ||
| Never smokers, N (%) | 323 (59) | 97 (43) *** |
| Current smokers, N (%) | 47 (9) | 35 (16) ** |
| Ex-smokers, N (%) | 177 (32) | 92 (41) * |
| Packs-year, (SD) | 27.8 (24.3) | 33.2 (22.1) * |
| Lung function, (SD) | ||
| FEV1, % predicted | 82 (23) | 68 (25) *** |
| FVC, % predicted | 90 (20) | 82 (23) *** |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 71 (11) | 65 (15) *** |
| DLCO, % predicted | 87 (22) | 74 (27) *** |
| KCO, % predicted | 79 (37) | 67 (41) * |
| RV, % predicted | 135 (44) | 145 (55) |
| TLC, % predicted | 103 (17) | 102 (24) |
| RV/TLC, % | 49 (11) | 52 (13) |
| Comorbidities, N (%) | Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| Myocardial infarction | 22 (3.2%) | 20 (5.9%) * |
| Heart failure | 42 (6%) | 44 (13.1%) *** |
| Peripheral arterial disease | 16 (2.3%) | 15 (4.5%) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 24 (3.4%) | 20 (5.9%) |
| Dementia | 3 (0.4%) | 6 (1.8%) * |
| Connective tissue disease | 39 (5.6%) | 24 (7.1%) |
| Gastroduodenal ulcer | 53 (7.6%) | 15 (4.5%) |
| Mild chronic liver disease | 27 (3.9%) | 11 (3.3%) |
| Diabetes | 71 (10.2%) | 51 (15.1) * |
| Diabetes with target organ damage | 8 (1.1%) | 12 (3.6%) * |
| Hemiplegia | 0 | 2 (0.6%) |
| Moderate– severe chronic kidney failure | 16 (2.3%) | 20 (5.9%) ** |
| Solid tumor or neoplasm | 44 (6.3%) | 30 (8.9%) |
| Leukemia | 13 (1.9%) | 6 (1.8%) |
| Lymphoma | 9 (1.3%) | 0 |
| Moderate–severe chronic liver disease | 9 (1.3%) | 3 (0.9%) |
| Solid tumor or neoplasm with metastasis | 6 (0.9%) | 3 (0.9%) |
| Definite AIDS | 1 (0.1%) | 3 (0.9%) |
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| <4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 697) | (N = 337) | |
| Blood parameters, (SD) | ||
| Total leukocytes, cells/µL | 6.28 (2.61) × 103 | 10.62 (4.16) × 103 *** |
| Total neutrophils, cells/µL | 3.37 (0.91) × 103 | 7.53 (2.58) × 103 *** |
| Neutrophils, % | 54.79 (9.61) | 71.01 (10.98) *** |
| Total lymphocytes, cells/µL | 2.13 (2.27) × 103 | 2.07 (3.15) × 103 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 32.58 (9.43) | 18.92 (9.03) *** |
| Total eosinophils, cells/µL | 0.21 (0.20) × 103 | 0.18 (0.19) × 103 |
| Eosinophils, % | 3.27 (2.8) | 1.8 (1.8) *** |
| Platelets, cells/µL | 239 (67) × 103 | 277 (85) × 103 *** |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin, mg/dL | 133.23 (35.73) | 137.62 (42.09) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 2.89 (8.54) | 5.31 (10.44) *** |
| ESR, mm/h | 16.03 (14.62) | 22.27 (19.98) *** |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 396.5 (109.5) | 500.5 (162.9) *** |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.61 (1.46) | 13.5 (1.74) |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.39 (4.12) | 41.22 (5.02) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.81 (0.43) | 0.87 (0.46) |
| Total proteins, g/dL | 7.04 (0.59) | 6.89 (0.7) ** |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.23 (0.41) | 4.08 (0.51) *** |
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| < 4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥ 4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 640) | (N = 275) | |
| Blood parameters, (SD) | ||
| Total leukocytes, cells/µL | 6.19 (1.72) × 103 | 10.61 (4.35) × 103 *** |
| Total neutrophils, cells/µL | 3.36 (0.91) × 103 | 7.48 (2.49) × 103 *** |
| Neutrophils, % | 54.85 (9.31) | 70.95 (11.1) *** |
| Total lymphocytes, cells/µL | 2.06 (1.23) × 103 | 2.11 (3.46) × 103 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 32.64 (9.15) | 19.0 (9.0) *** |
| Total eosinophils, cells/µL | 0.20 (0.20) × 103 | 0.19 (0.19) × 103 |
| Eosinophils, % | 3.22 (2.68) | 1.90 (1.88) *** |
| Platelets, cells/µL | 240 (66) × 103 | 284 (86) × 103 *** |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin, mg/dL | 132.87 (35.71) | 135.65 (44.16) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 2.64 (7.72) | 5.09 (9.75) *** |
| ESR, mm/h | 16.01 (14.32) | 23.2 (20.35) *** |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 394.9 (108.1) | 496.1 (167.2) *** |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.58 (1.42) | 13.35 (1.65) * |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.31 (4.02) | 40.76 (4.7) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.43) | 0.87 (0.5) |
| Total proteins, g/dL | 7.05 (0.58) | 6.97 (0.67) |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.25 (0.39) | 4.14 (0.48) * |
| Below-Threshold Cluster | Above-Threshold Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| < 4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | ≥ 4.99 × 103 Cells/µL | |
| (N = 547) | (N = 224) | |
| Blood parameters, (SD) | ||
| Total leukocytes, cells/µL | 6.29 (2.87) × 103 | 10.78 (4.68) × 103 *** |
| Total neutrophils, cells/µL | 3.33 (0.94) × 103 | 7.56 (2.52) × 103 *** |
| Neutrophils, % | 54.08 (9.69) | 70.7 (11.98) *** |
| Total lymphocytes, cells/µL | 2.18 (2.53) | 2.21 (3.82) × 103 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 33.15 (9.69) | 19.26 (9.64) *** |
| Total eosinophils, cells/µL | 0.21 (0.21) | 0.17 (0.18) × 103 * |
| Eosinophils, % | 3.29 (2.88) | 1.67 (1.7) *** |
| Platelets, cells/µL | 238 (67) | 280 (84) × 103 *** |
| Alpha-1 antitrypsin, mg/dL | 132.64 (36.22) | 137.98 (44.09) |
| CRP, mg/dL | 2.32 (7.09) | 4.66 (9.84) ** |
| ESR, mm/h | 15.07 (13.86) | 20.03 (17.65) ** |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 398.1 (106.2) | 505.7 (160.1) *** |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 13.69 (1.4) | 13.6 (1.68) |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.5 (4.05) | 41.47 (4.9) |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.39) | 0.85 (0.29) |
| Total proteins, g/dL | 7.02 (0.57) | 6.86 (0.64) * |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.23 (0.42) | 4.13 (0.46) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Olveira, C.; Girón, R.; García-Clemente, M.; Máiz, L.; Sibila, O.; Golpe, R.; Menéndez, R.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Prados, C.; et al. Blood Neutrophil Counts Define Specific Clusters of Bronchiectasis Patients: A Hint to Differential Clinical Phenotypes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051044
Wang X, Olveira C, Girón R, García-Clemente M, Máiz L, Sibila O, Golpe R, Menéndez R, Rodríguez-López J, Prados C, et al. Blood Neutrophil Counts Define Specific Clusters of Bronchiectasis Patients: A Hint to Differential Clinical Phenotypes. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051044
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuejie, Casilda Olveira, Rosa Girón, Marta García-Clemente, Luis Máiz, Oriol Sibila, Rafael Golpe, Rosario Menéndez, Juan Rodríguez-López, Concepción Prados, and et al. 2022. "Blood Neutrophil Counts Define Specific Clusters of Bronchiectasis Patients: A Hint to Differential Clinical Phenotypes" Biomedicines 10, no. 5: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051044
APA StyleWang, X., Olveira, C., Girón, R., García-Clemente, M., Máiz, L., Sibila, O., Golpe, R., Menéndez, R., Rodríguez-López, J., Prados, C., Martinez-García, M. A., Rodriguez, J. L., de la Rosa, D., Qin, L., Duran, X., Garcia-Ojalvo, J., & Barreiro, E. (2022). Blood Neutrophil Counts Define Specific Clusters of Bronchiectasis Patients: A Hint to Differential Clinical Phenotypes. Biomedicines, 10(5), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10051044







