Effects of Human RelA Transgene on Murine Macrophage Inflammatory Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
Ethics Statement
2.2. Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophage Isolation and Culture
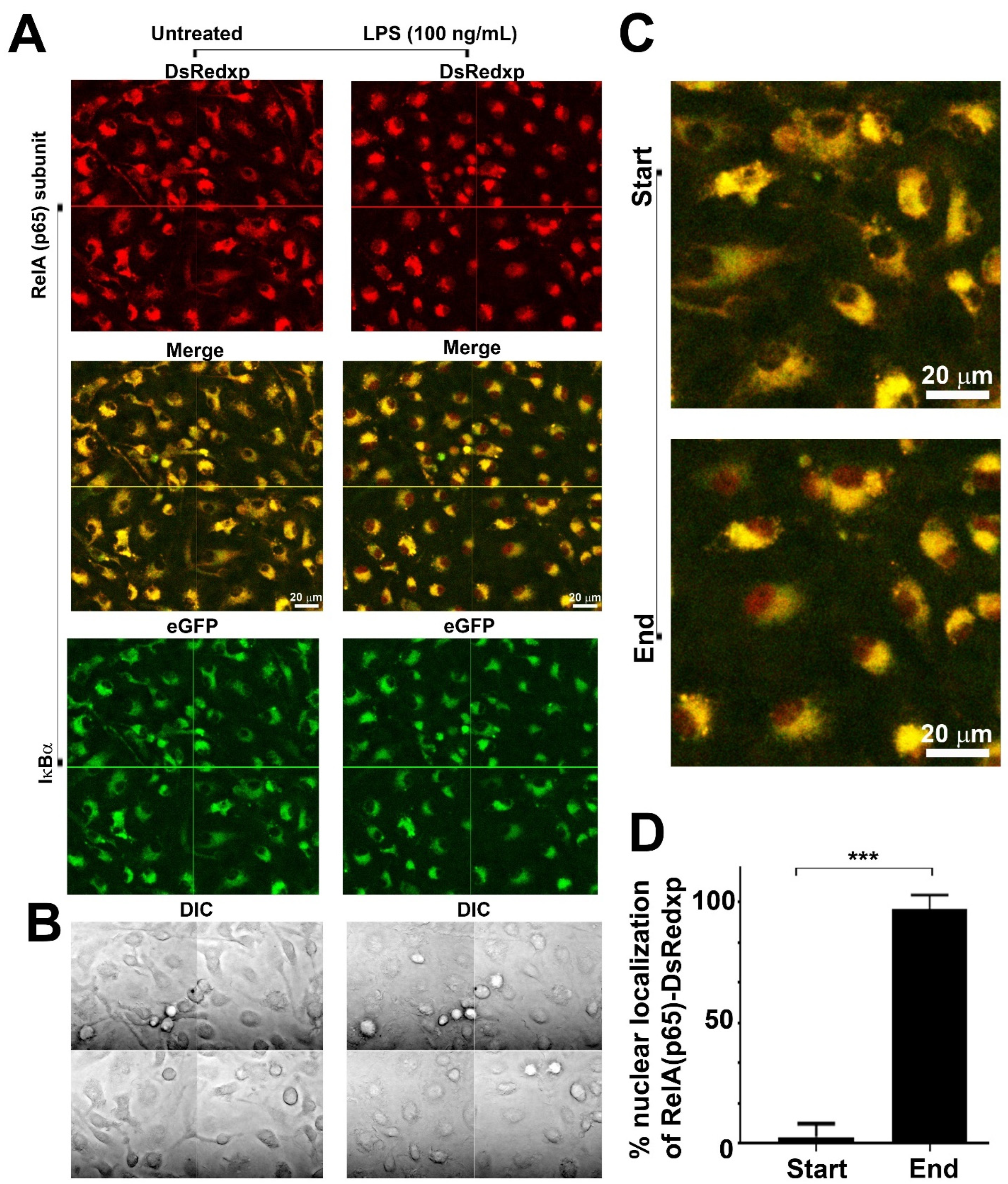
2.3. Confocal Microscopy
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.4.1. Read Mapping and Analysis of Differential Expression
2.4.2. Network and Pathway Analyses
2.5. RNA Extraction and qPCR
2.6. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Datasets
3. Results
3.1. Confocal Imaging of RelA(p65) Translocation in LPS-Stimulated Murine BMDMs
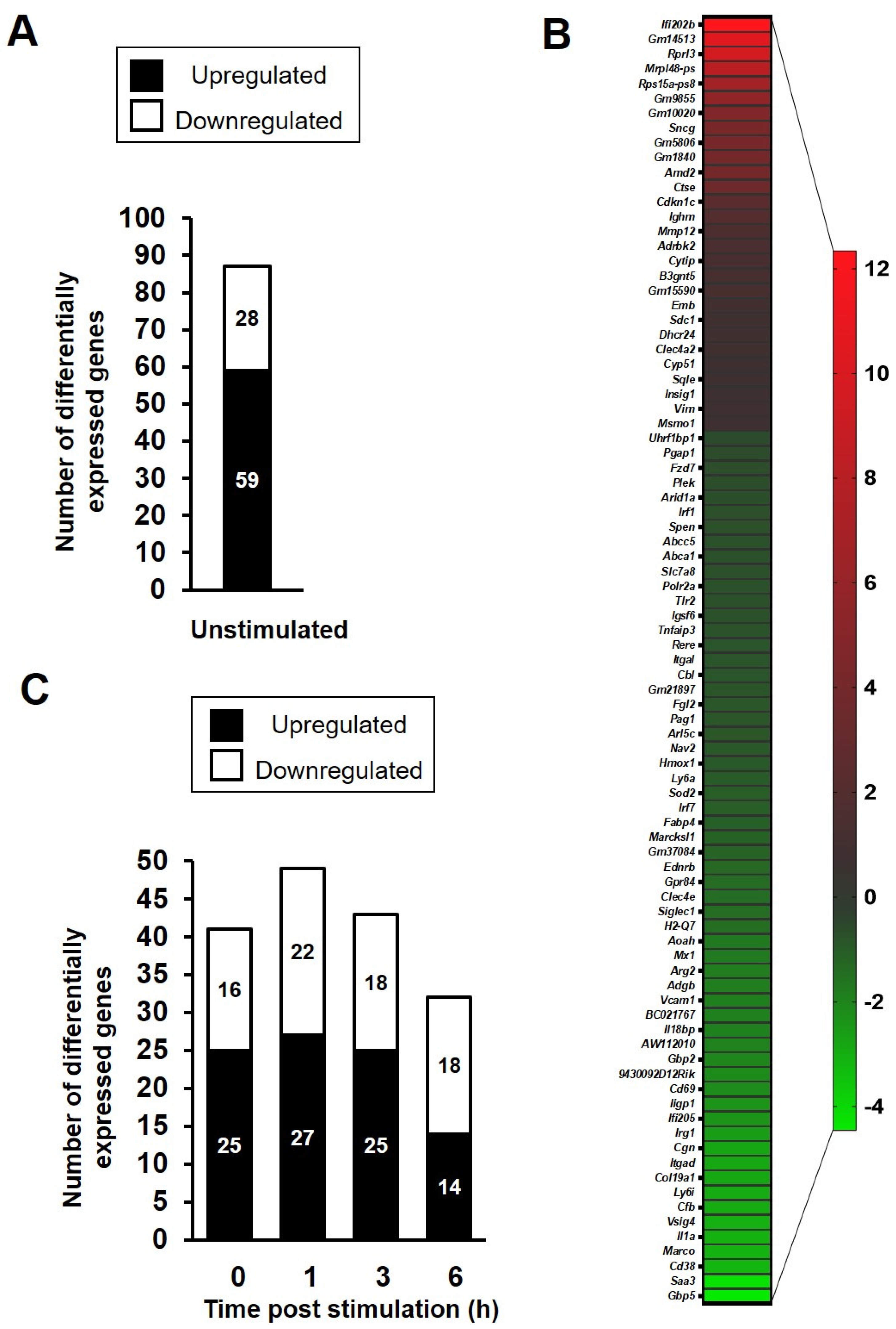
3.2. RNA Sequencing of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Following TLR4 Activation
3.3. NFκB Target and Non-Target Genes Are Differentially Expressed in LPS-Stimulated BMDMs
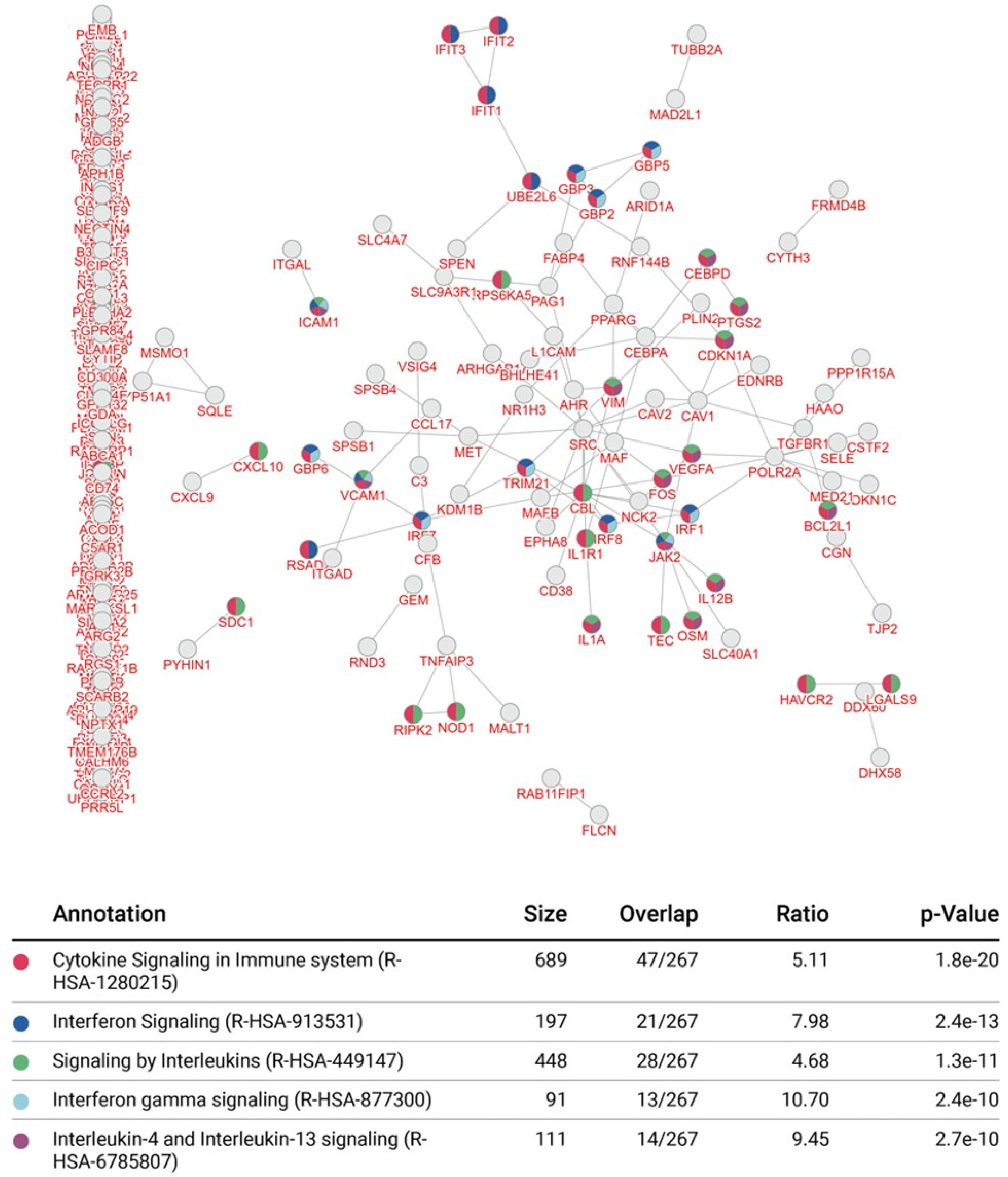
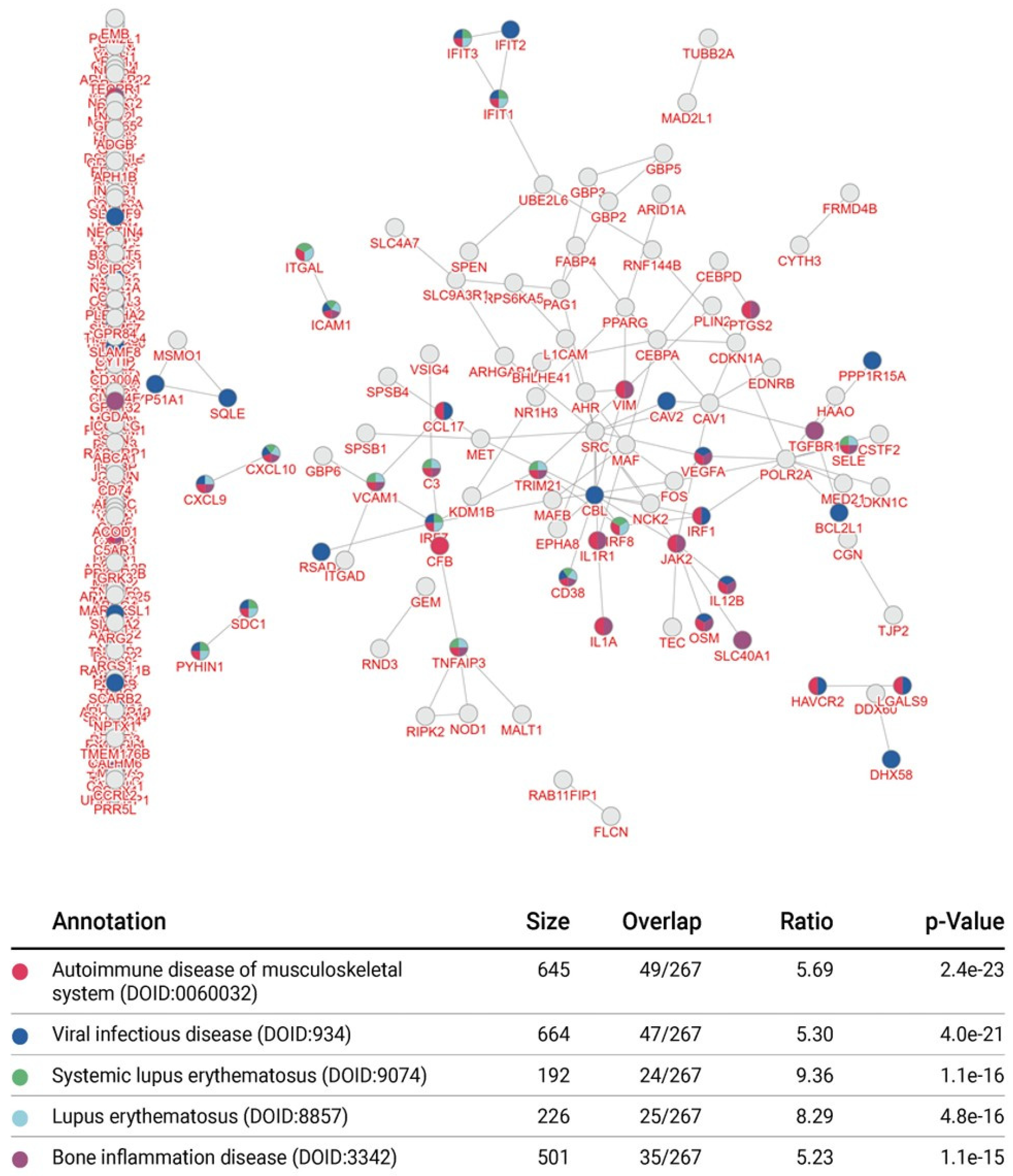
3.4. Integrative Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in p65-DsRed/IκBα-eGFP BMDMs
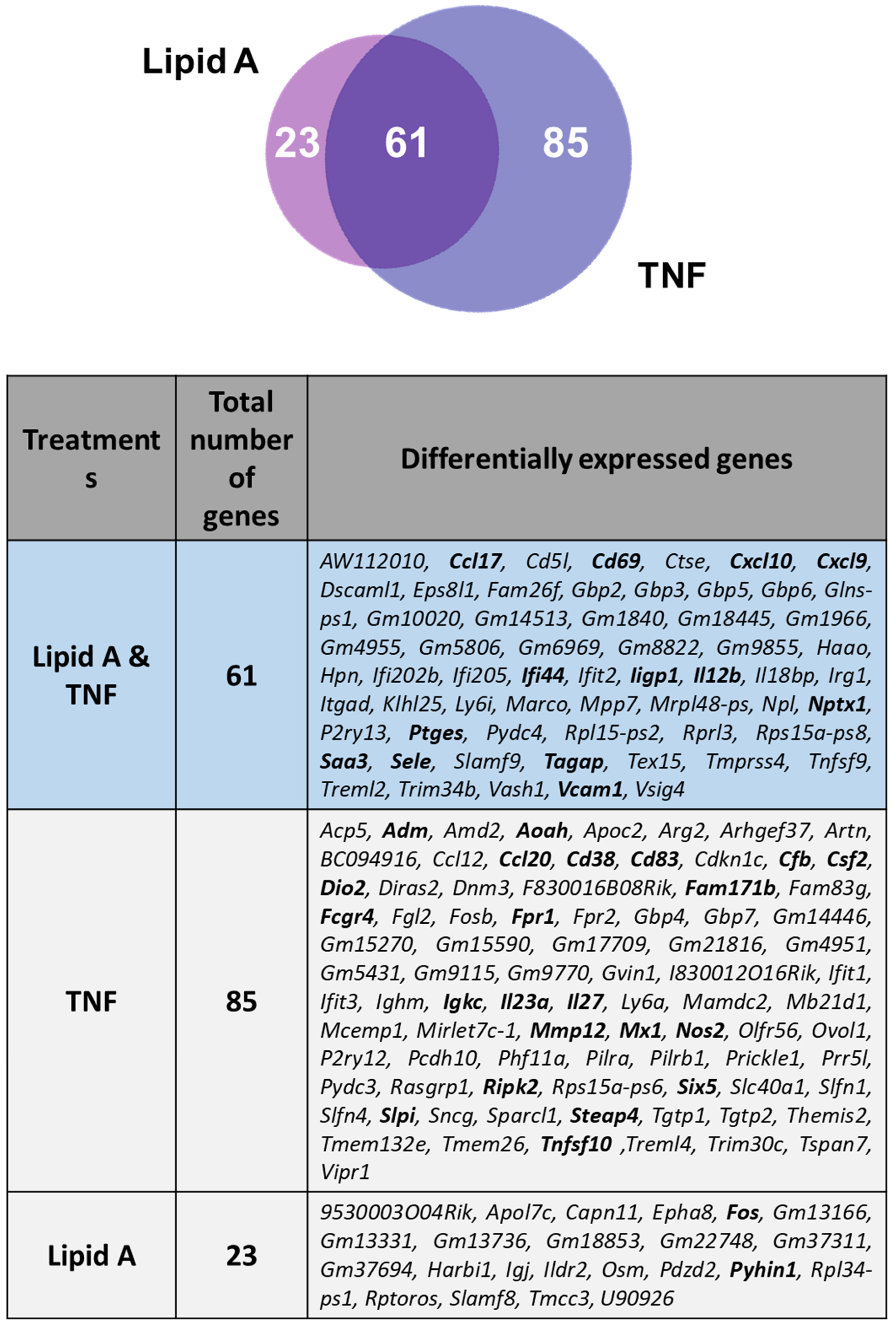
3.5. Comparison of BMDM Transcriptional Responses to TNFR1 and TLR4 Activation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, J.P.; Carmody, R.J. NF-kappaB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 335, 41–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, V.N.; Schon, M.P.; Seitz, C.S. c-Rel in Epidermal Homeostasis: A Spotlight on c-Rel in Cell Cycle Regulation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, A.A.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The I kappa B proteins: Multifunctional regulators of Rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, H.; Karin, M. Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases. Sci. STKE 2006, 2006, re13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.D. The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, M.; Scheidereit, C. The IkappaB kinase complex in NF-kappaB regulation and beyond. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.L.; Krappmann, D. Controlling NF-kappaB activation in T cells by costimulatory receptors. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnall, J.; Boddington, C.; England, H.; Brignall, R.; Downton, P.; Alsoufi, Z.; Boyd, J.; Rowe, W.; Bennett, A.; Walker, C.; et al. Quantitative analysis of competitive cytokine signaling predicts tissue thresholds for the propagation of macrophage activation. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaaf3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legembre, P.; Barnhart, B.C.; Zheng, L.; Vijayan, S.; Straus, S.E.; Puck, J.; Dale, J.K.; Lenardo, M.; Peter, M.E. Induction of apoptosis and activation of NF-kappaB by CD95 require different signalling thresholds. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, C.A.; Brown, C.D.; Freiman, A.; Isherwood, J.; Wen, X.; Pique-Regi, R.; Luca, F. High-throughput characterization of genetic effects on DNA-protein binding and gene transcription. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1701–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neueder, A.; Bates, G.P. RNA Related Pathology in Huntington’s Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1049, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andersen, V.; Christensen, J.; Ernst, A.; Jacobsen, B.A.; Tjonneland, A.; Krarup, H.B.; Vogel, U. Polymorphisms in NF-kappaB, PXR, LXR, PPARgamma and risk of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Burisch, J.; Pedersen, N.; Roug, S.; Galsgaard, J.; Turino, S.Y.; Brodersen, J.B.; Rashid, S.; Rasmussen, B.K.; et al. Polymorphisms in the inflammatory pathway genes TLR2, TLR4, TLR9, LY96, NFKBIA, NFKB1, TNFA, TNFRSF1A, IL6R, IL10, IL23R, PTPN22, and PPARG are associated with susceptibility of inflammatory bowel disease in a Danish cohort. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhuo, Z.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jia, W.; Hu, J.-H.; Fu, K.; Zhu, S.-B.; He, J.; et al. NFKB1 -94insertion/deletion ATTG polymorphism and cancer risk: Evidence from 50 case-control studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9806–9822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, Y.R.; Dedeoglu, F.; Leyva Castillo, J.M.; Bainter, W.; Ohsumi, T.K.; Bousvaros, A.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Geha, R.S.; Chou, J. Human RELA haploinsufficiency results in autosomal-dominant chronic mucocutaneous ulceration. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Demissie, E.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Mambole, A.; O’Garra, A.; Tomczak, M.F.; Erdman, S.E.; Fox, J.G.; et al. NF-kappaB1 inhibits TLR-induced IFN-beta production in macrophages through TPL-2-dependent ERK activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacque, E.; Schweighoffer, E.; Visekruna, A.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Janzen, J.; Zillwood, R.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Tybulewicz, V.L.; Ley, S.C. IKK-induced NF-kappaB1 p105 proteolysis is critical for B cell antibody responses to T cell-dependent antigen. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Yang, N.; Ruckshanthi, J.P.; Williams, J.; Borysiewicz, E.; Wang, P.; Adamson, A.; Li, J.; Bateman, J.F.; White, M.R.; et al. The intervertebral disc contains intrinsic circadian clocks that are regulated by age and cytokines and linked to degeneration. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Smith, E.; Stegmaier, P.; Bergey, F.; Morris, L.; Kittner, M.; England, H.; Spiller, D.; White, M.H.; et al. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis. Model Mech. 2020, 13, dmm044040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanos, C. Physical state and biological activity of lipopolysaccharides. Toxicity and immunogenicity of the lipid A component. Z. Immun. Exp. Klin. Immunol. 1975, 149, 214–229. [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, S.; Warren, H.S.; Lowry, S.F.; Calvano, S.E.; Remick, D. Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury Investigators. Acute inflammatory response to endotoxin in mice and humans. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ankers, J.M.; Awais, R.; Jones, N.A.; Boyd, J.; Ryan, S.; Adamson, A.D.; Harper, C.; Bridge, L.; Spiller, D.; A Jackson, D.; et al. Dynamic NF-κB and E2F interactions control the priority and timing of inflammatory signalling and cell proliferation. eLife 2016, 5, e10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, A.; Boddington, C.; Downton, P.; Rowe, W.; Bagnall, J.; Lam, C.; Maya-Mendoza, A.; Schmidt, L.; Harper, C.; Spiller, D.; et al. Signal transduction controls heterogeneous NF-κB dynamics and target gene expression through cytokine-specific refractory states. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.K.; Vogel, S.N. Bone marrow-derived macrophages: Development and regulation of differentiation markers by colony-stimulating factor and interferons. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Apicella, M.A.; Griffiss, J.M.; Schneider, H. Isolation and characterization of lipopolysaccharides, lipooligosaccharides, and lipid A. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 235, 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Boudeau, J.; Glasser, A.L.; Masseret, E.; Joly, B.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A. Invasive ability of an Escherichia coli strain isolated from the ileal mucosa of a patient with Crohn’s disease. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4499–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelest, E.; Kel, A.E.; Goessling, E.; Wingender, E. Prediction of potential C/EBP/NF-kappaB composite elements using matrix-based search methods. Silico Biol. 2003, 3, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bunting, K.; Rao, S.; Hardy, K.; Woltring, D.; Denyer, G.S.; Wang, J.; Gerondakis, S.; Shannon, M.F. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression in T cells to identify targets of the NF-kappa B transcription factor c-Rel. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7097–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. A Database and Functional Annotation of NF-kB Target Genes. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 7986–7995. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ke, S.; Denison, M.S.; Rabson, A.B.; Gallo, M.A. Ah receptor and NF-kappaB interactions, a potential mechanism for dioxin toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, W.; Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Lv, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Long non coding RNA SLC26A4-AS1 exerts antiangiogenic effects in human glioma by upregulating NPTX1 via NFKB1 transcriptional factor. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Koide, N.; Odkhuu, E.; Tsolmongyn, B.; Naiki, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yokochi, T. Mouse pyrin and HIN domain family member 1 (pyhin1) protein positively regulates LPS-induced IFN-beta and NO production in macrophages. Innate Immun. 2014, 20, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.P.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Jung, Y.H.; Ryu, J.M.; Suh, H.N.; Kim, M.O.; Oh, K.B.; Han, H.J. Reactive oxygen species induce MMP12-dependent degradation of collagen 5 and fibronectin to promote the motility of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3283–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, S.; Yun, A.; Kim, H.; Bae, D.; Yang, S.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, E.; et al. TRRUST v2: An expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D380–D386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wernersson, R.; Hansen, R.B.; Horn, H.; Mercer, J.; Slodkowicz, G.; Workman, C.T.; Rigina, O.; Rapacki, K.; Stærfeldt, H.H.; et al. A scored human protein-protein interaction network to catalyze genomic interpretation. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Kale, A.; Perrone, R.; Lopez-Dominguez, J.A.; Pisco, A.O.; Kasler, H.G.; Schmidt, M.S.; Heckenbach, I.; Kwok, R.; Wiley, C.D.; et al. Senescent cells promote tissue NAD(+) decline during ageing via the activation of CD38(+) macrophages. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1265–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xue, W.; Li, M.; Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; et al. VCAM-1(+) macrophages guide the homing of HSPCs to a vascular niche. Nature 2018, 564, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, B.; Jiang, W.; Han, H.; Li, J.; Mao, W.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Qian, G.; Qian, J.; Zeng, W.; et al. Acyloxyacyl hydrolase promotes the resolution of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsen, T.; de Vlieg, J.; Alkema, W. BioVenn—A web application for the comparison and visualization of biological list using area-proportional Venn diagrams. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrington, M.G.; Fraser, I.D.C. NF-kappaB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lernbecher, T.; Muller, U.; Wirth, T. Distinct NF-kappa B/Rel transcription factors are responsible for tissue-specific and inducible gene activation. Nature 1993, 365, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Ullrich, R.; Memet, S.; Lilienbaum, A.; Feuillard, J.; Raphael, M.; Israel, A. NF-kappaB activity in transgenic mice: Developmental regulation and tissue specificity. Development 1996, 122, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, L.V.; Ley, S.C.; Seddon, B. TNF activation of NF-kappaB is essential for development of single-positive thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Jimi, E.; Zhong, H.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Repression of gene expression by unphosphorylated NF-kappaB p65 through epigenetic mechanisms. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsopoulou, S.; Burkitt, M.D.; Bergey, F.; England, H.; Hough, R.; Schmidt, L.; Spiller, D.G.; White, M.H.; Paszek, P.; Jackson, D.A.; et al. Macrophage-Specific NF-kappaB Activation Dynamics Can Segregate Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'shea, J.M.; Perkins, N.D. Regulation of the RelA (p65) transactivation domain. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzi, R.; Gareus, R.; Fengler, S.; Pasparakis, M. GFP-p65 knock-in mice as a tool to study NF-kappaB dynamics in vivo. Genesis 2009, 47, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, G.; Paraoan, L.; Spiller, D.G.; Wilde, G.J.; Browne, M.A.; Djali, P.K.; Unitt, J.F.; Sullivan, E.; Floettmann, E.; White, M.R. Multi-parameter analysis of the kinetics of NF-kappaB signalling transcription in single living cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Mat, N.F.C.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The IL-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Lee, Z.H.; Song, Y.W. CXCL10 and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, S.A.; Young, N.A.; Narvaez-Miranda, J.; Jablonski, K.A.; Arcos, J.; Rosas, L.; Papenfuss, T.L.; Torrelles, J.B.; Jarjour, W.N.; Guerau-De-Arellano, M. CD38 Is Robustly Induced in Human Macrophages and Monocytes in Inflammatory Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, M.R.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, S. Emerging Roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in Immunological Disorders and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.C.; Ganchi, P.A.; Ballard, D.W.; Greene, W.C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: Evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science 1993, 259, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malynn, B.A.; Ma, A. A20: A multifunctional tool for regulating immunity and preventing disease. Cell. Immunol. 2019, 340, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstrepen, L.; Verhelst, K.; van Loo, G.; Carpentier, I.; Ley, S.C.; Beyaert, R. Expression, biological activities and mechanisms of action of A20 (TNFAIP3). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, M.J.; Mitchell, O.; Flynn, H.R.; Chen, C.S.; Yang, H.T.; Ben-Addi, H.; Boeing, S.; Snijders, A.P.; Ley, S.C. TLR and TNF-R1 activation of the MKK3/MKK6-p38alpha axis in macrophages is mediated by TPL-2 kinase. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2845–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TRRUST 1 v.2 Database Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transcription Factor | Description | Number of Genes | p-Value | FDR 2 |
| Nfkb1 | Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 1, p105 | 9 | 7.9 × 10−9 | 8.74 × 10−8 |
| Irf1 | Interferon regulatory factor 1 | 4 | 8.8 × 10−7 | 4.85 × 10−6 |
| Stat1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 | 4 | 3.2 × 10−6 | 1.16 × 10−5 |
| RelA(p65) | v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian) | 5 | 3.1 × 10−5 | 8.58 × 10−5 |
| Mafb | v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family, protein B (avian) | 2 | 8.8 × 10−5 | 1.61 × 10−4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papoutsopoulou, S.; Morris, L.; Bayliff, A.; Mair, T.; England, H.; Stagi, M.; Bergey, F.; Alam, M.T.; Sheibani-Tezerji, R.; Rosenstiel, P.; et al. Effects of Human RelA Transgene on Murine Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040757
Papoutsopoulou S, Morris L, Bayliff A, Mair T, England H, Stagi M, Bergey F, Alam MT, Sheibani-Tezerji R, Rosenstiel P, et al. Effects of Human RelA Transgene on Murine Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):757. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040757
Chicago/Turabian StylePapoutsopoulou, Stamatia, Lorna Morris, Andrew Bayliff, Thomas Mair, Hazel England, Massimiliano Stagi, François Bergey, Mohammad Tauqeer Alam, Raheleh Sheibani-Tezerji, Philip Rosenstiel, and et al. 2022. "Effects of Human RelA Transgene on Murine Macrophage Inflammatory Responses" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040757
APA StylePapoutsopoulou, S., Morris, L., Bayliff, A., Mair, T., England, H., Stagi, M., Bergey, F., Alam, M. T., Sheibani-Tezerji, R., Rosenstiel, P., Müller, W., Martins Dos Santos, V. A. P., & Campbell, B. J. (2022). Effects of Human RelA Transgene on Murine Macrophage Inflammatory Responses. Biomedicines, 10(4), 757. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040757







