The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice and Humans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model, Human Samples, and Tissue Processing
2.2. Immunofluorescence
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
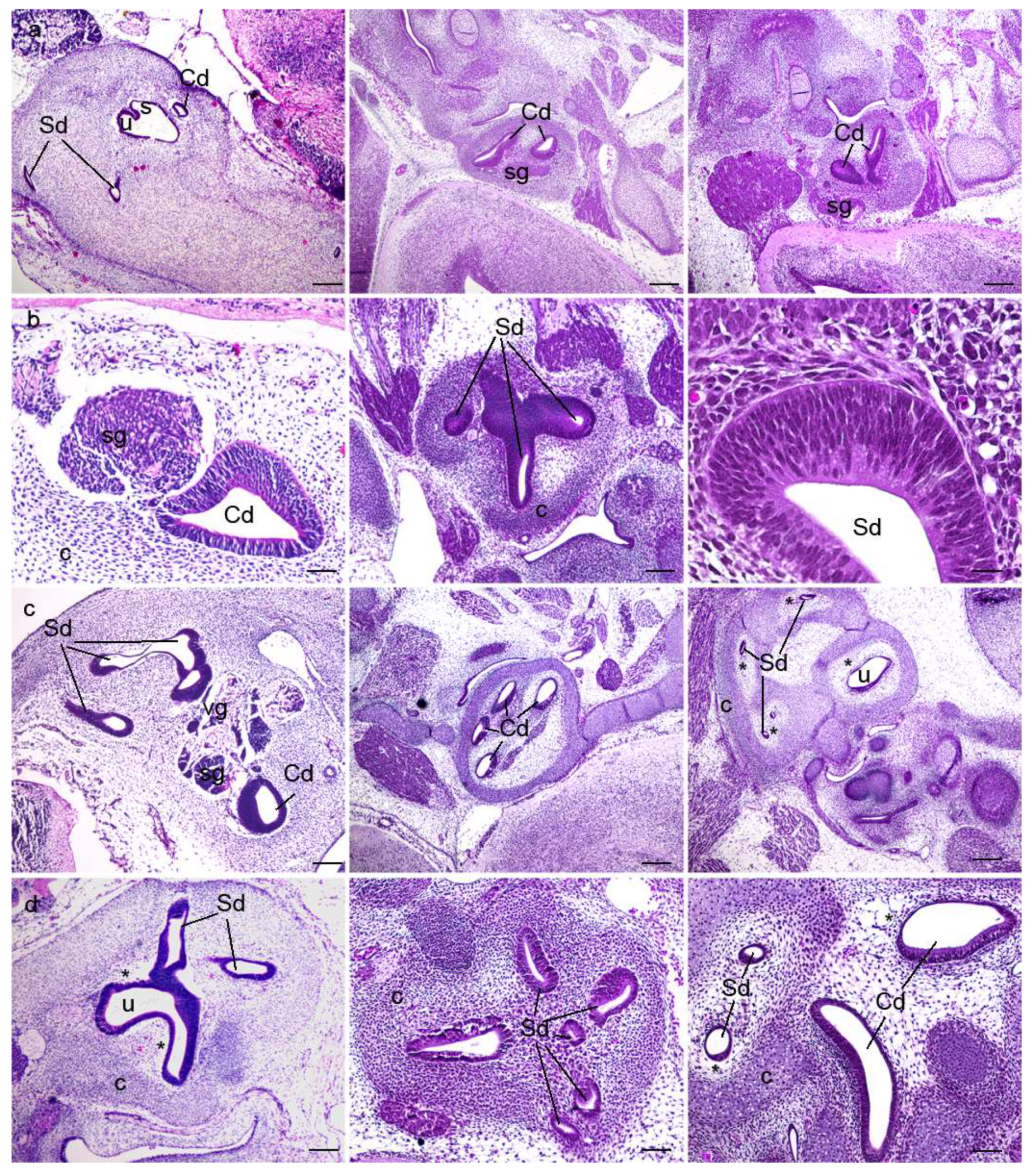
3.1. Mouse and Human Inner-Ear Development
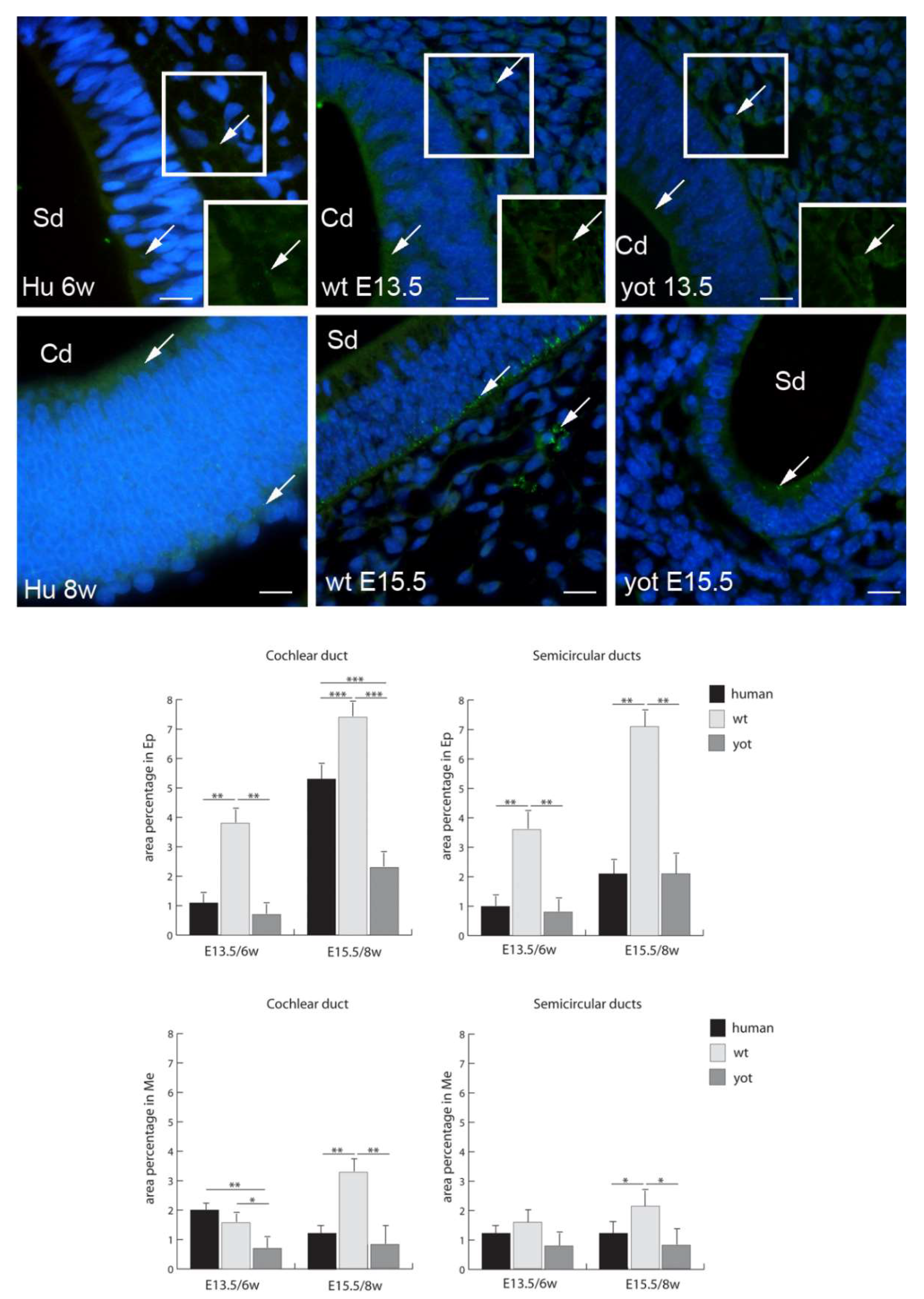
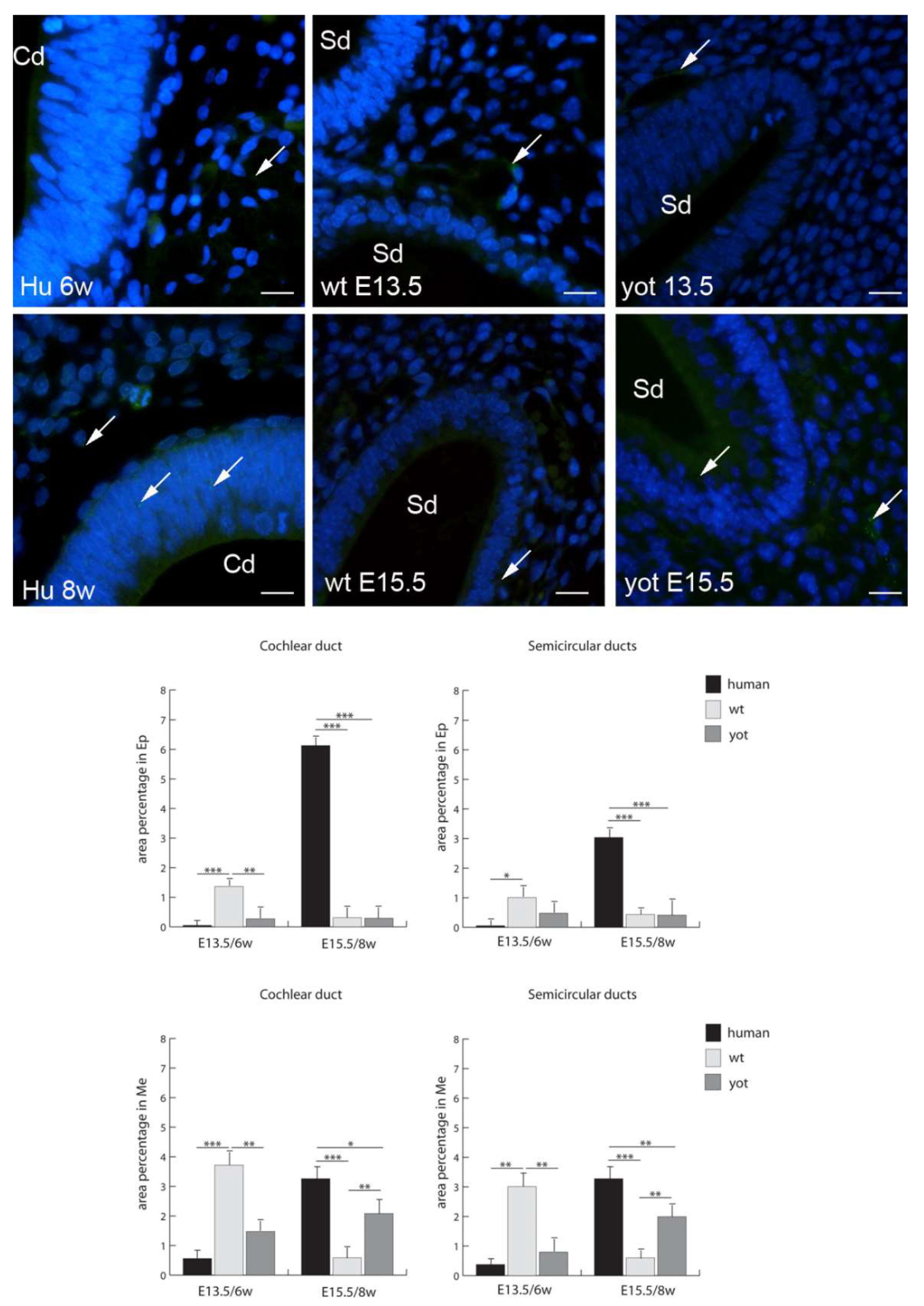
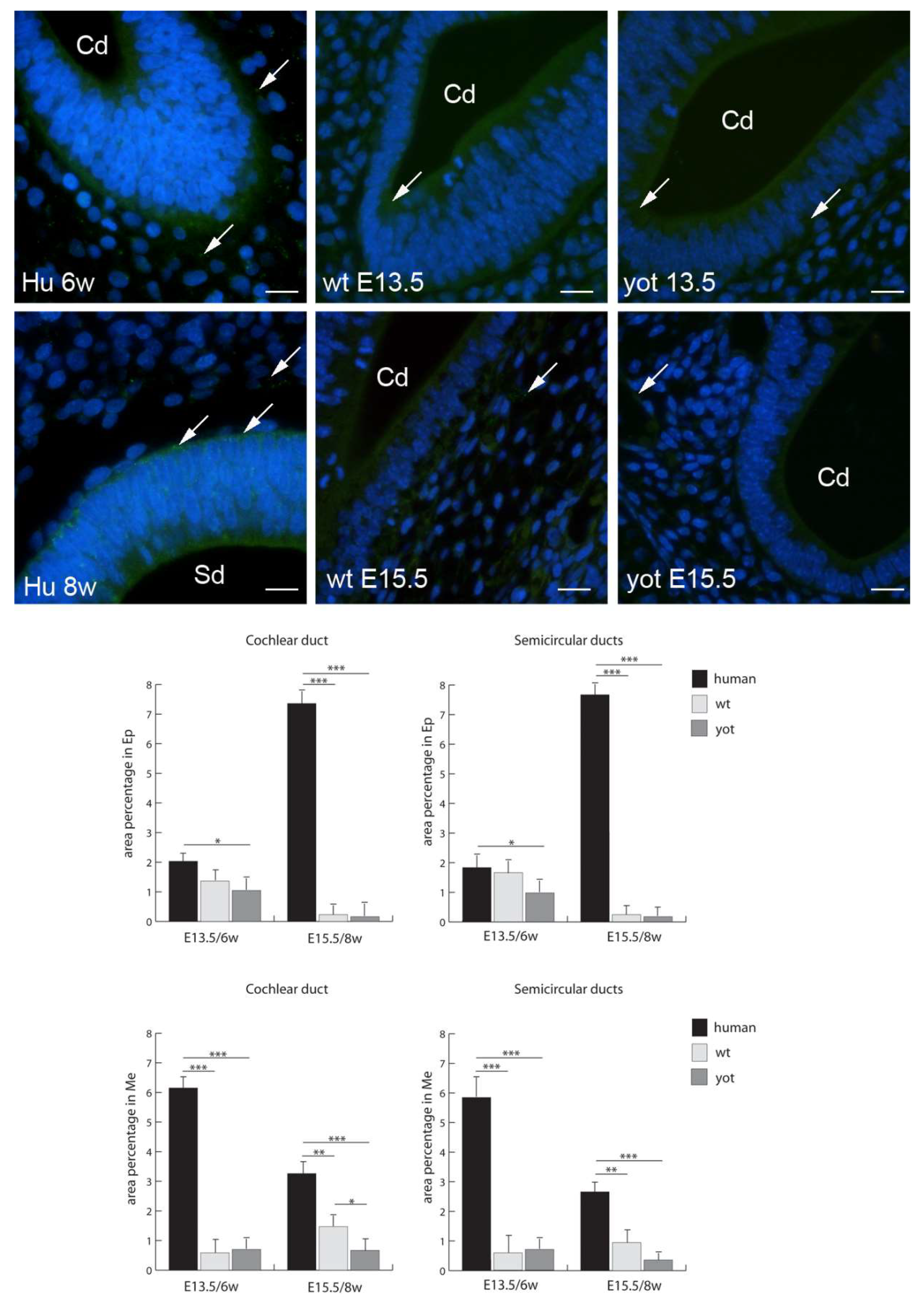
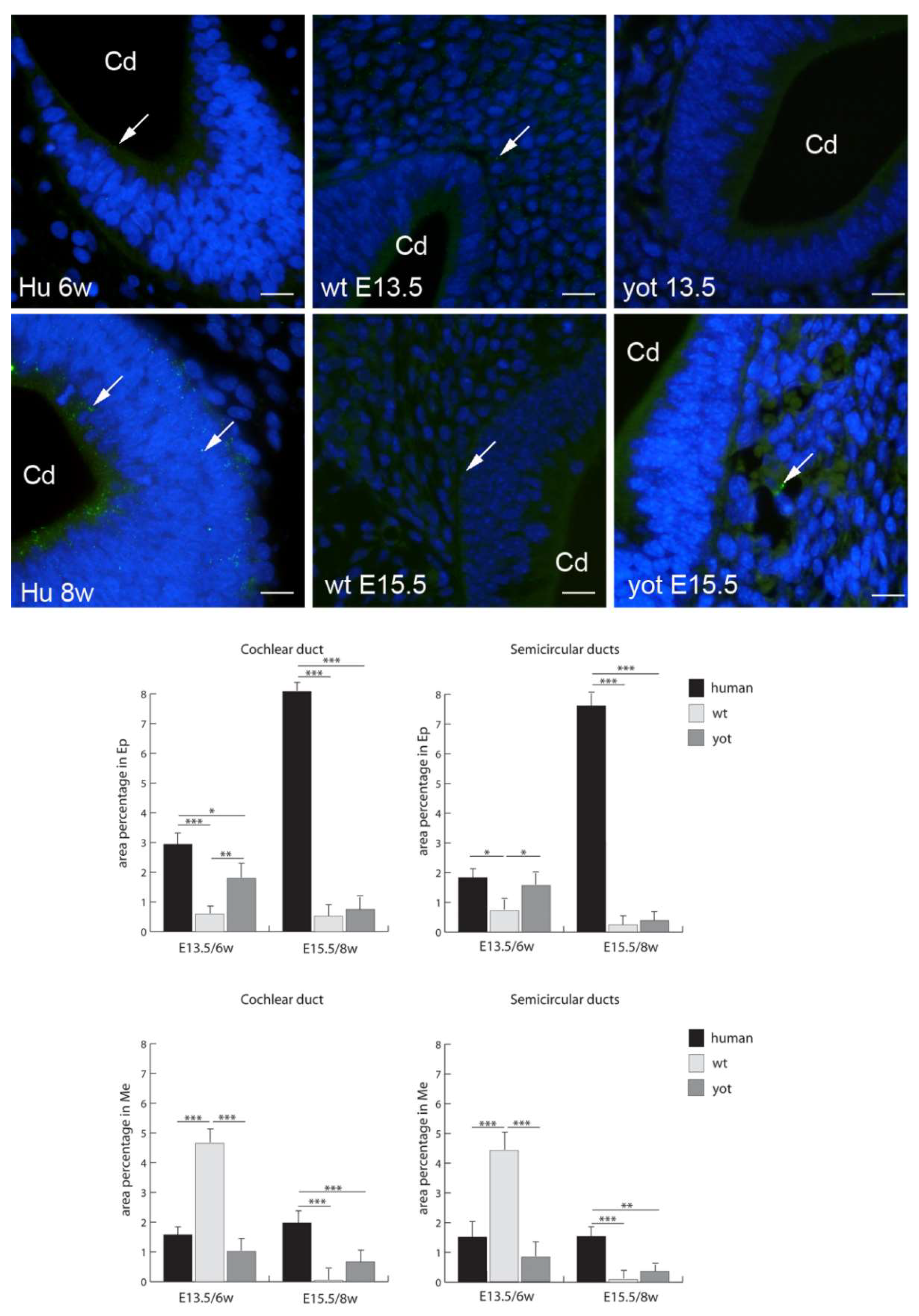
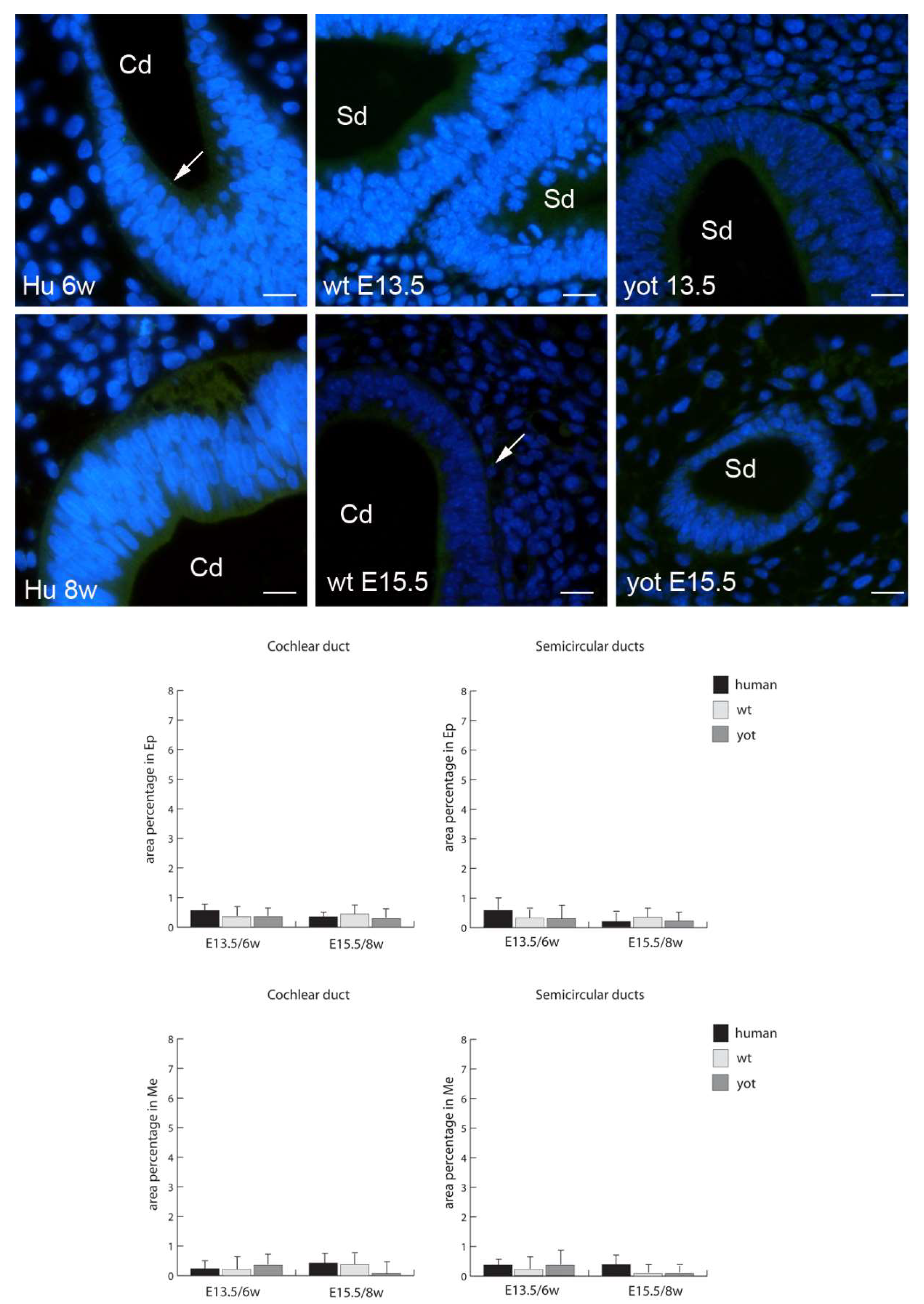
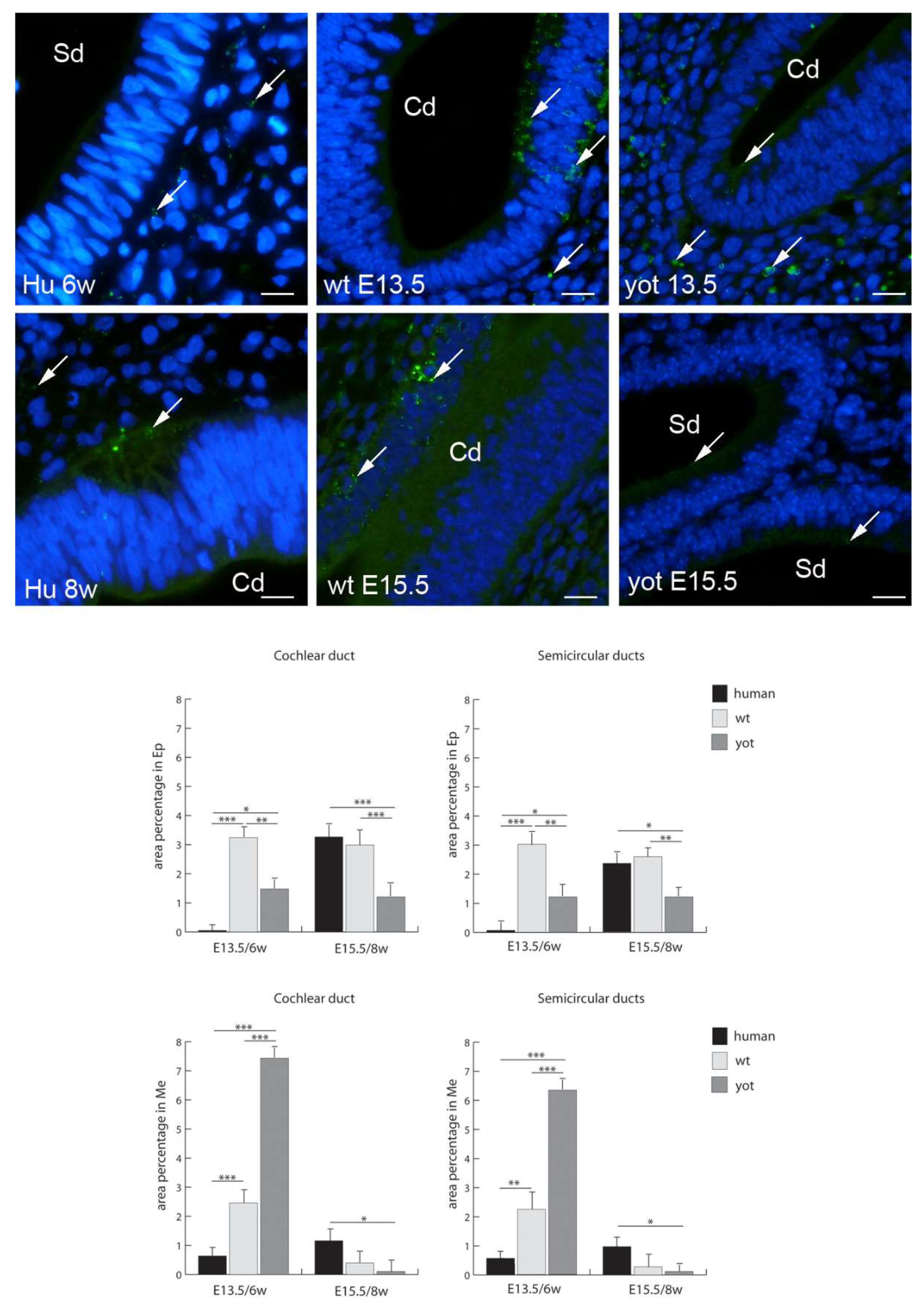
3.2. Connexins (Cxs) and Pannexin 1 (Panx1) Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morsli, H.; Choo, D.; Ryan, A.; Johnson, R.; Wu, D.K. Development of the mouse inner ear and origin of its sensory organs. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3327–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson Chacko, L.; Wertjanz, D.; Sergi, C.; Dudas, J.; Fischer, N.; Eberharter, T.; Hoermann, R.; Glueckert, R.; Fritsch, H.; Rask-Andersen, H.; et al. Growth and cellular patterning during fetal human inner ear development studied by a correlative imaging approach. BMC Dev. Biol. 2019, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freyer, L.; Aggarwal, V.; Morrow, B.E. Dual embryonic origin of the mammalian otic vesicle forming the inner ear. Development 2011, 138, 5403–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tafra, R.; Brakus, S.M.; Vukojevic, K.; Kablar, B.; Colovic, Z.; Saraga-Babic, M. Interplay of proliferation and proapoptotic and antiapoptotic factors is revealed in the early human inner ear development. Otol. Neurotol. Off. Publ. Am. Otol. Soc. Am. Neurotol. Soc. Eur. Acad. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.M. Connexins/connexons. Cell-free expression. Methods Mol. Biol. 2001, 154, 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Nickel, R.; Forge, A. Gap junctions and connexins in the inner ear: Their roles in homeostasis and deafness. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 16, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedner, P.; Steinhauser, C.; Theis, M. Functional redundancy and compensation among members of gap junction protein families? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingard, J.C.; Zhao, H.B. Cellular and Deafness Mechanisms Underlying Connexin Mutation-Induced Hearing Loss—A Common Hereditary Deafness. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.M.; Ren, T.Y.; Nuttall, A.L. Studies of inner ear blood flow in animals and human beings. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. Off. J. Am. Acad. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 1995, 112, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammano, F. Inner Ear Connexin Channels: Roles in Development and Maintenance of Cochlear Function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Huang, S.H.; Chou, K.H.; Liao, P.J.; Su, C.C.; Li, S.Y. Identification of mutations in members of the connexin gene family as a cause of nonsyndromic deafness in Taiwan. Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 2007, 12, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozic, M.; Filipovic, N.; Juric, M.; Kosovic, I.; Benzon, B.; Solic, I.; Kelam, N.; Racetin, A.; Watanabe, K.; Katsuyama, Y.; et al. Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1−/− (yotari) Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Salmon, M.; Maxeiner, S.; Kruger, O.; Theis, M.; Willecke, K.; Petit, C. Expression of the connexin43- and connexin45-encoding genes in the developing and mature mouse inner ear. Cell Tissue Res. 2004, 316, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordowitzki, P.; Sokolowska, G.; Wasielak-Politowska, M.; Skowronska, A.; Skowronski, M.T. Pannexins and Connexins: Their Relevance for Oocyte Developmental Competence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarian, N.; Houshangi-Tabrizi, S.; Zoidl, C.; Zoidl, G.R. Panx1b Modulates the Luminance Response and Direction of Locomotion in the Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Dalal, M.S.; Contreras, J.E. Pannexin-1 Channels as Mediators of Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Streeter, M.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhao, H.B. Identification and characterization of pannexin expression in the mammalian cochlea. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 512, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Mendoza, M.J.; Lorda-Diez, C.I.; Montero, J.A.; Garcia-Porrero, J.A.; Hurle, J.M. Reelin/DAB-1 signaling in the embryonic limb regulates the chondrogenic differentiation of digit mesodermal progenitors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, N.C.; Anderson, R.C.; McDermott, K.W. Reelin: Diverse roles in central nervous system development, health and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 112, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, V.; Lozic, M.; Kelam, N.; Filipovic, N.; Bernard, B.; Katsuyama, Y.; Vukojevic, K. Connexin Expression Is Altered in Liver Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racetin, A.; Filipovic, N.; Lozic, M.; Ogata, M.; Gudelj Ensor, L.; Kelam, N.; Kovacevic, P.; Watanabe, K.; Katsuyama, Y.; Saraga-Babic, M.; et al. A Homozygous Dab1(−/−) Is a Potential Novel Cause of Autosomal Recessive Congenital Anomalies of the Mice Kidney and Urinary Tract. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, Y.; Setsu, T.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kikkawa, S.; Terashima, T.; Maeda, K. Cortical layer V neurons in the auditory and visual cortices of normal, reeler, and yotari mice. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2010, 56, E50–E59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csomor, P.; Sziklai, I.; Karosi, T. Controversies in RELN/reelin expression in otosclerosis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, I.; Hennies, H.C.; Basta, D.; Ernst, A. Vestibular dysfunction of patients with mutations of Connexin 26. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhao, H.B. Pannexin1 channels dominate ATP release in the cochlea ensuring endocochlear potential and auditory receptor potential generation and hearing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.E.; Lopez, I.A.; Linthicum, F.H.; Ishiyama, A. Connexin 26 Immunohistochemistry in Temporal Bones with Cochlear Otosclerosis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2018, 127, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenz, C.M.; Van De Water, T.R. Immunolocalization of connexin 26 in the developing mouse cochlea. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 32, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forge, A.; Becker, D.; Casalotti, S.; Edwards, J.; Marziano, N.; Nevill, G. Gap junctions in the inner ear: Comparison of distribution patterns in different vertebrates and assessement of connexin composition in mammals. J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 467, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, M.; Fujioka, M.; Murayama, A.Y.; Ogawa, K.; Okano, H.; Ozawa, H. Dynamic Spatiotemporal Expression Changes in Connexins of the Developing Primate’s Cochlea. Genes 2021, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, J.; Schutz, M.; Dicke, N.; Strenzke, N.; Jokwitz, M.; Moser, T.; Willecke, K. Connexin32 can restore hearing in connexin26 deficient mice. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.M.; McWhorter, A.R. Vascular abnormalities in mice lacking the endothelial gap junction proteins connexin37 and connexin40. Dev. Biol. 2002, 251, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Thomas, L.; Dominguez Rieg, J.A.; Fenton, R.A.; Rieg, T. Genetic deletion of connexin 37 causes polyuria and polydipsia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Han, W.; Yamamoto, H.; Tang, W.; Lin, X.; Xiu, R.; Trune, D.R.; Nuttall, A.L. The cochlear pericytes. Microcirculation 2008, 15, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buniello, A.; Montanaro, D.; Volinia, S.; Gasparini, P.; Marigo, V. An expression atlas of connexin genes in the mouse. Genomics 2004, 83, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choung, Y.H.; Park, K.; Kang, S.O.; Markov Raynov, A.; Ho Kim, C.; Choung, P.H. Expression of the gap junction proteins connexin 26 and connexin 43 in human middle ear cholesteatoma. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibodies | Host | Dilution | Source | Catalogue No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Cx26, GJB2 | Rabbit | 1:50 | Cusabio (Wuhan, China) | CSBPA009452LA01HU |
| Cx32, GJB1 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Cusabio (Wuhan, China) | CSB-PA008853 | |
| Anti-Cx37/GJA4 | Rabbit | 1:300 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab181701 | |
| Anti-Cx40/GJA5 | Rabbit | 1:50 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab213688 | |
| Anti-Cx43/GJA1 | Goat | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab87645 | |
| Anti-Cx45/GJA7 | Rabbit | 1:50 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab135474 | |
| Anti-pannexin 1/PANX1 | Rabbit | 1:150 | Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany) | ABN242 | |
| Secondary | Donkey Anti-Goat IgG Alexa Fluor 488 | Donkey | 1:400 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab150129 |
| Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 488 | Donkey | 1:400 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | ab150073 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesko, J.; Rastović, P.; Mišković, J.; Šoljić, V.; Paštar, V.; Zovko, Z.; Filipović, N.; Katsuyama, Y.; Saraga-Babić, M.; Vukojević, K. The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice and Humans. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030589
Lesko J, Rastović P, Mišković J, Šoljić V, Paštar V, Zovko Z, Filipović N, Katsuyama Y, Saraga-Babić M, Vukojević K. The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice and Humans. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(3):589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030589
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesko, Josip, Pejana Rastović, Josip Mišković, Violeta Šoljić, Vlatka Paštar, Zdenka Zovko, Natalija Filipović, Yu Katsuyama, Mirna Saraga-Babić, and Katarina Vukojević. 2022. "The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice and Humans" Biomedicines 10, no. 3: 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030589
APA StyleLesko, J., Rastović, P., Mišković, J., Šoljić, V., Paštar, V., Zovko, Z., Filipović, N., Katsuyama, Y., Saraga-Babić, M., & Vukojević, K. (2022). The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1−/−) Mice and Humans. Biomedicines, 10(3), 589. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10030589







