Histologic-Based Tumor-Associated Immune Cells Status in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Gene Signatures Related to Cancer Immunity and Clinical Outcomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
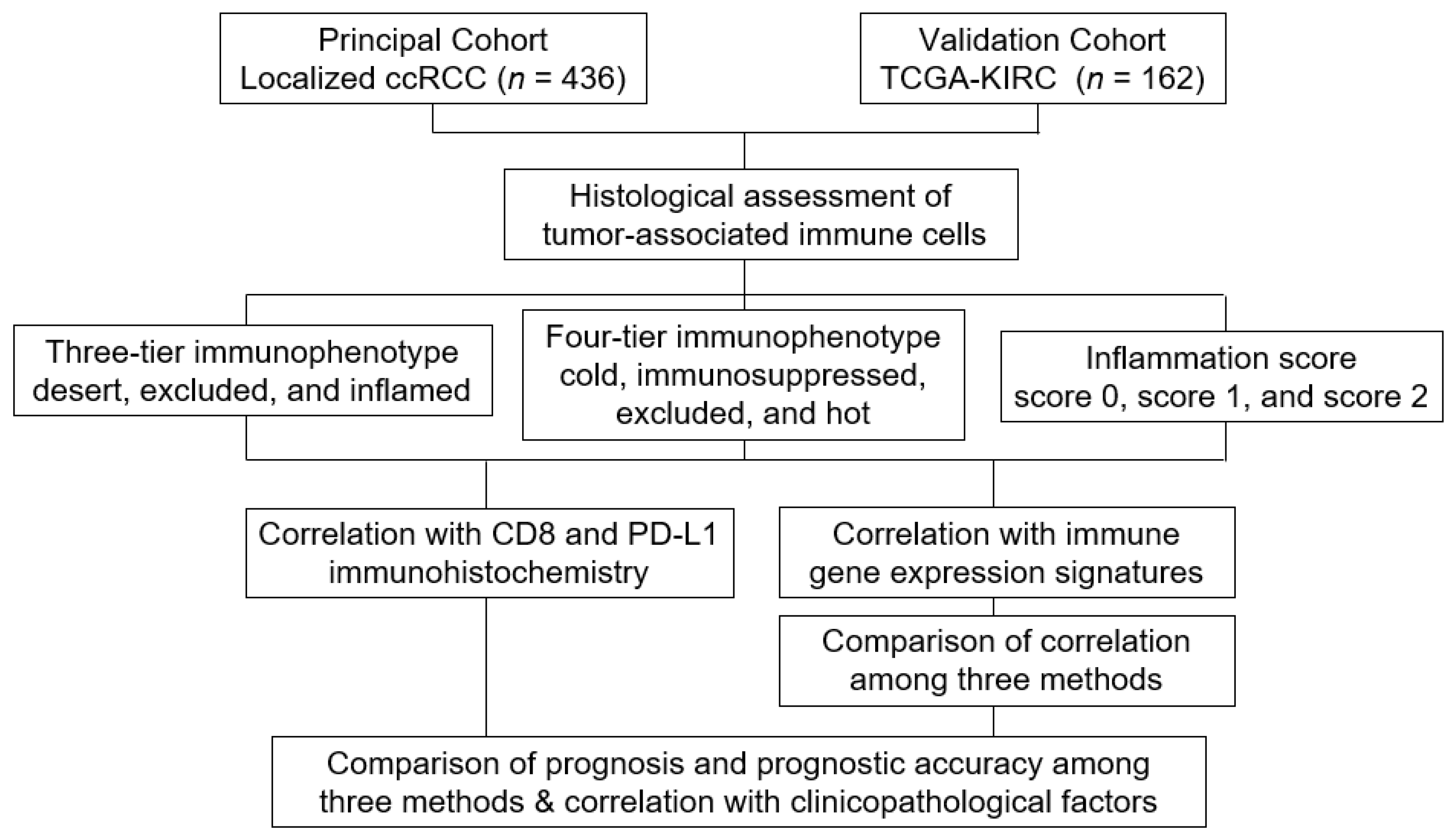
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Histological Evaluation of Tumor Immune Microenvironment
2.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics
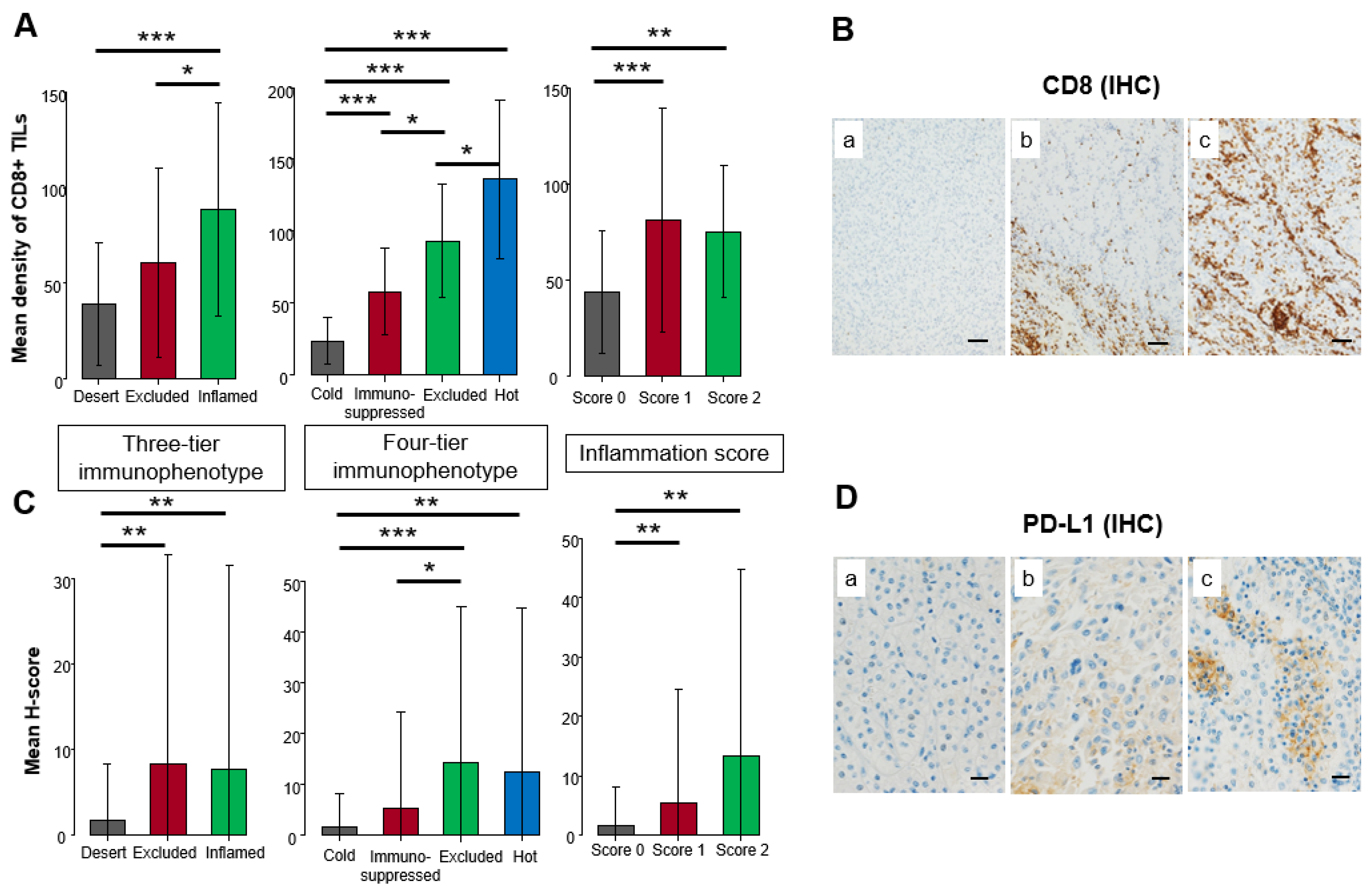
3.2. Comparison of Immunohistochemical Expression among Three-Tier and Four-Tier Immunophenotype and Inflammation Score
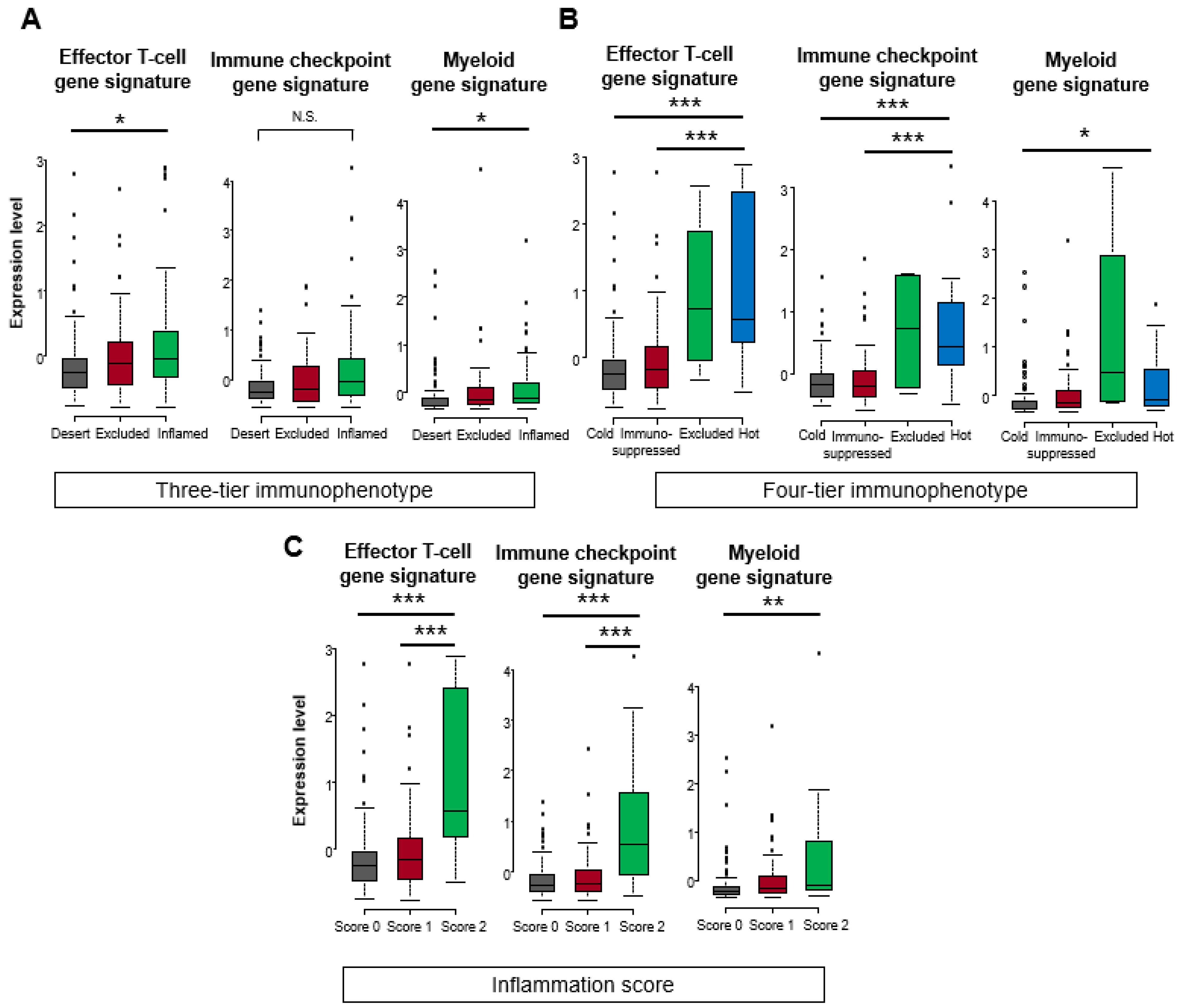
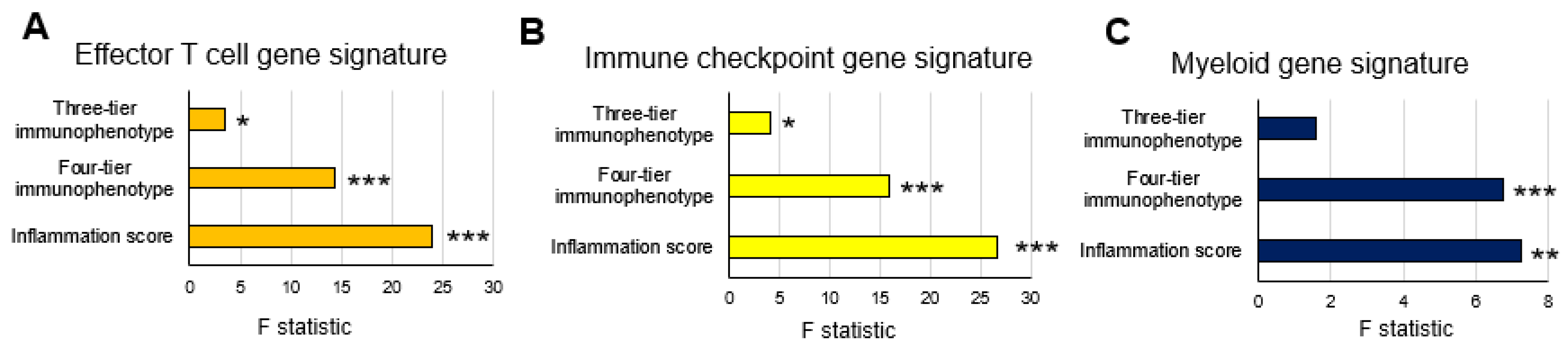
3.3. Comparison of Gene Expression Signatures among Three-Tier and Four-Tier Immunophenotypes and Inflammation Scores
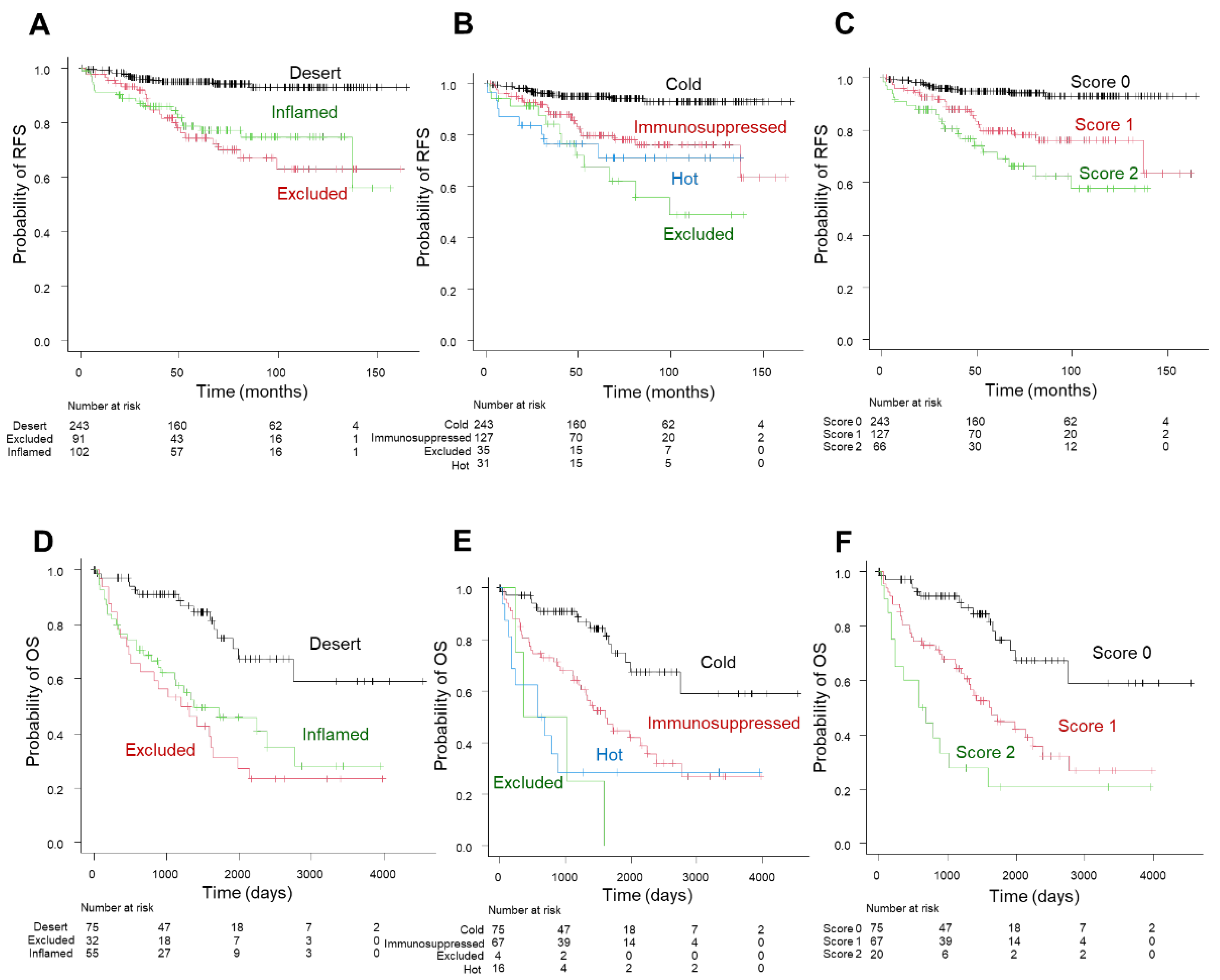
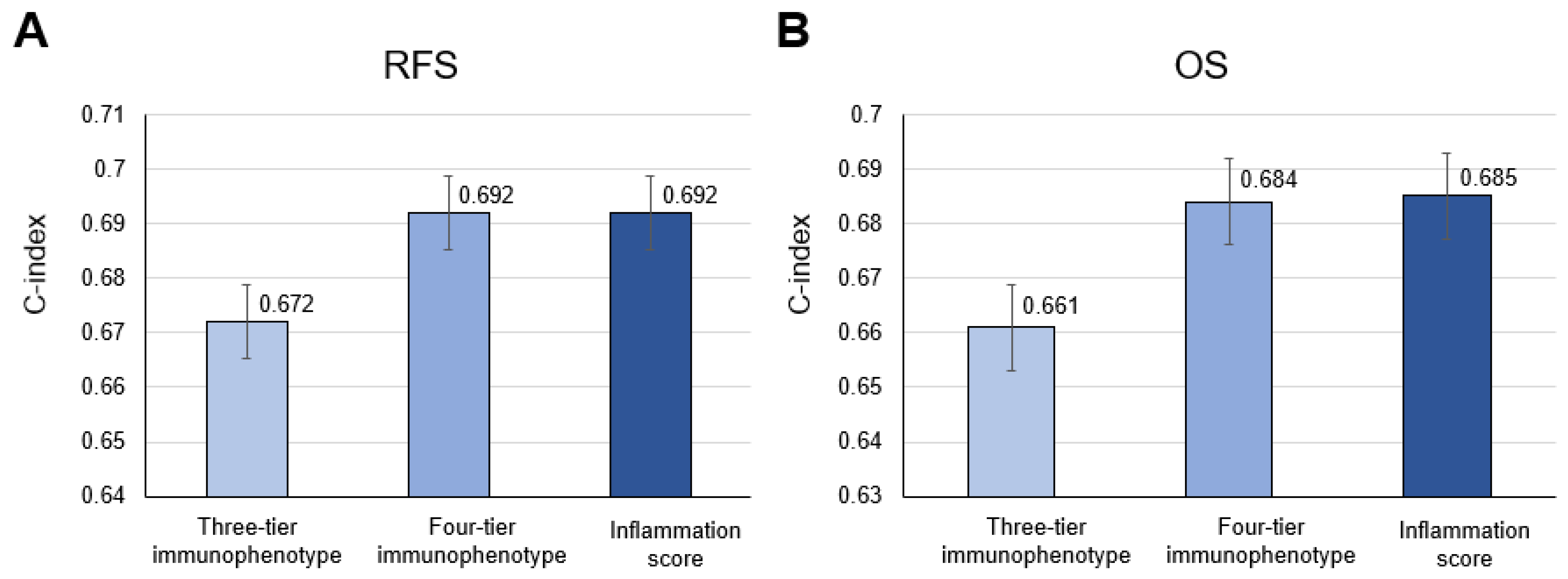
3.4. Comparison of Patient Outcome among Three-Tier and Four-Tier Immunophenotype and Inflammation Score
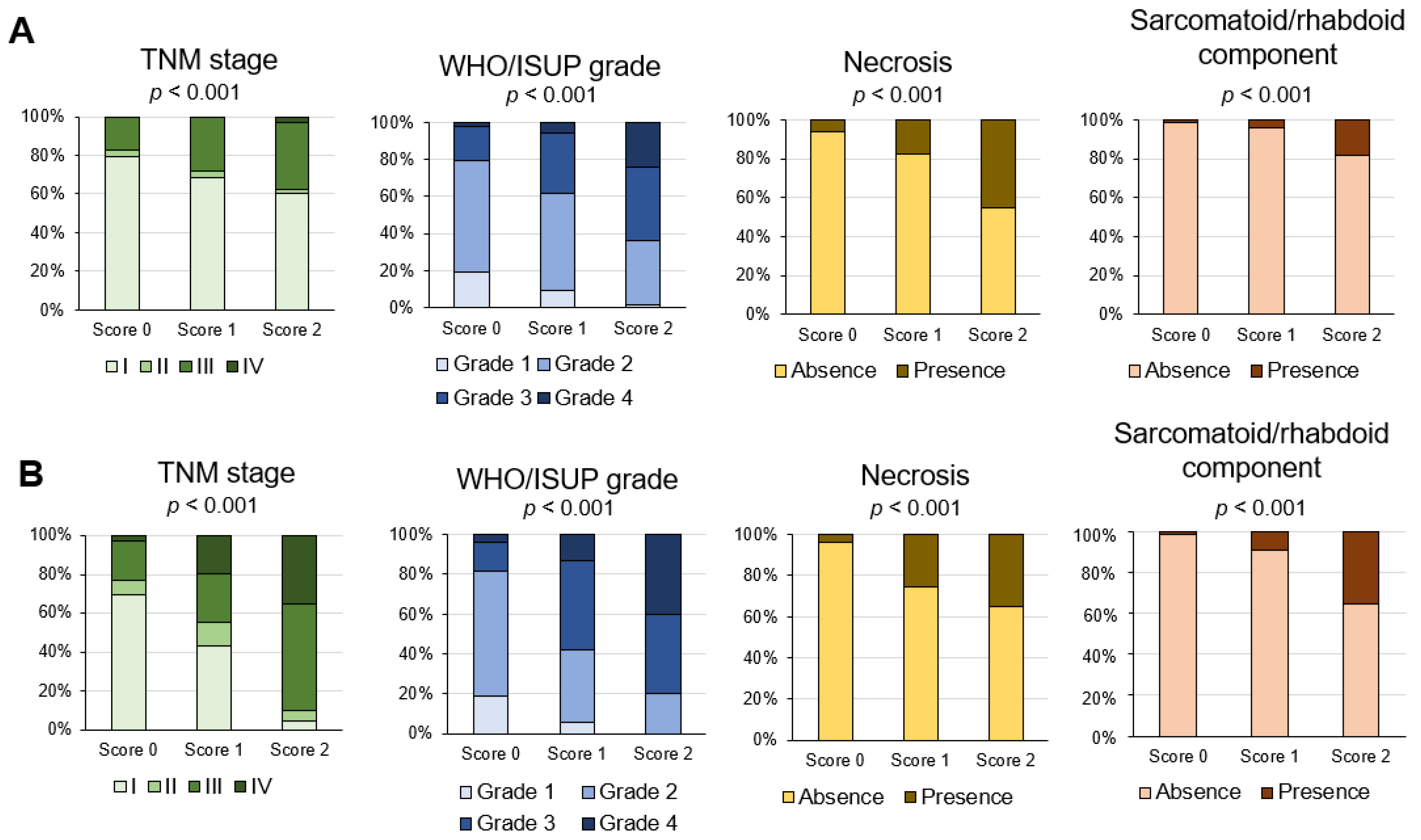
3.5. Association of Inflammation Score with Pathological Prognostic Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaddepally, R.K.; Kharel, P.; Pandey, R.; Garje, R.; Chandra, A.B. Review of Indications of FDA-Approved Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors per NCCN Guidelines with the Level of Evidence. Cancers 2020, 12, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shuch, B.; Amin, A.; Armstrong, A.J.; Eble, J.N.; Ficarra, V.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Martignoni, G.; Rini, B.I.; Kutikov, A. Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma: Distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casuscelli, J.; Vano, Y.A.; Fridman, W.H.; Hsieh, J.J. Molecular classification of renal cell carcinoma and its implication in future clinical practice. Kidney Cancer 2017, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şenbabaoğlu, Y.; Gejman, R.S.; Winer, A.G.; Liu, M.; Van Allen, E.M.; de Velasco, G.; Miao, D.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Drill, E.; Luna, A.; et al. Tumor immune microenvironment characterization in clear cell renal cell carcinoma identifies prognostic and immunotherapeutically relevant messenger RNA signatures. Genome. Biol. 2016, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghatalia, P.; Gordetsky, J.; Kuo, F.; Dulaimi, E.; Cai, K.Q.; Devarajan, K.; Bae, S.; Naik, G.; Chan, T.A.; Uzzo, R.; et al. Prognostic impact of immune gene expression signature and tumor infiltrating immune cells in localized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallin, J.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Funke, R.; Sznol, M.; Korski, K.; Jones, S.; Hernandez, G.; Mier, J.; He, X.; Hodi, F.S.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances antigen-specific T-cell migration in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, D.F.; Huseni, M.A.; Atkins, M.B.; Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Fong, L.; Joseph, R.W.; Pal, S.K.; Reeves, J.A.; et al. Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, L.; Hatipoglu, E.; Robert de Massy, M.; Litchfield, K.; Beattie, G.; Rowan, A.; Schnidrig, D.; Thompson, R.; Byrne, F.; Horswell, S.; et al. Determinants of anti-PD-1 response and resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1497–1518.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, S.; Salgado, R.; Gevaert, T.; Russell, P.A.; John, T.; Thapa, B.; Christie, M.; van de Vijver, K.; Estrada, M.V.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. Assessing Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Solid Tumors: A Practical Review for Pathologists and Proposal for a Standardized Method from the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 2: TILs in Melanoma, Gastrointestinal Tract Carcinomas, Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Mesothelioma, Endometrial and Ovarian Carcinomas, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Genitourinary Carcinomas, and Primary Brain Tumors. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 311–335. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, P.S.; Karanikas, V.; Evers, S. The where, then when, and the how of immune monitoring for cancer immunotherapies in the era of checkpoint inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegde, P.S.; Chen, D.S. Top 10 Challenges in Cancer Immunotherapy. Immunity 2020, 52, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verine, J.; Colin, D.; Nheb, M.; Prapotnich, D.; Ploussard, G.; Cathelineau, X.; Desgrandchamps, F.; Mongiat-Artus, P.; Feugeas, J.P. Architectural Patterns are a Relevant Morphologic Grading System for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis Assessment: Comparisons With WHO/ISUP Grade and Integrated Staging Systems. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Christie, A.; Rajaram, S.; Zhou, Q.; Araj, E.; Chintalapati, S.; Cadeddu, J.; Margulis, V.; Pedrosa, I.; Rakheja, D.; et al. Ontological analyses reveal clinically-significant clear cell renal cell carcinoma subtypes with convergent evolutionary trajectories into an aggressive type. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohe, C.; Yoshida, T.; Amin, M.B.; Atsumi, N.; Ikeda, J.; Saiga, K.; Noda, Y.; Yasukochi, Y.; Ohashi, R.; Ohsugi, H.; et al. Development and validation of a vascularity-based architectural classification for clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Correlation with conventional pathological prognostic factors, gene expression patterns, and clinical outcomes. Mod. Pathol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, J.; Bruni, D. Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold tumours with combination immunotherapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.J.; De Cubas, A.A.; Fan, H.; Smith, C.C.; Lang, M.; Reznik, E.; Bowlby, R.; Gibb, E.A.; Akbani, R.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. The Cancer Genome Atlas comprehensive molecular characterization of renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 313–326.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broad GDAC FIREHOSE-Broad Institute. Available online: http://gdac.broadinstitute.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Digital Slide Archive (DSA). Available online: https://cancer.digitalslidearchive.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Brierley, J.D.; Gospodarowics, M.K.; Wittekind, C. Union for International Cancer Control. In TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moch, H.; Humphrey, P.A.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsugi, H.; Yoshida, T.; Ohe, C.; Ikeda, J.; Sugi, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Tsuta, K.; Matsuda, T. The SSPN Score, a novel scoring system incorporating PBRM1 expression, predicts postoperative recurrence for patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2359–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, J.; Ohe, C.; Yoshida, T.; Ohsugi, H.; Sugi, M.; Tsuta, K.; Kinoshita, H. PD-L1 Expression and Clinicopathological Factors in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Comparison of Antibody Clone 73-10 With Clone 28-8. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 4577–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ohe, C.; Ikeda, J.; Atsumi, N.; Ohsugi, H.; Sugi, M.; Higasa, K.; Saito, R.; Tsuta, K.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Eosinophilic features in clear cell renal cell carcinoma correlate with outcomes of immune checkpoint and angiogenesis blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolen, C.R.; McCord, R.; Huet, S.; Frampton, G.M.; Bourgon, R.; Jardin, F.; Dartigues, P.; Punnoose, E.A.; Szafer-Glusman, E.; Xerri, L.; et al. Mutation load and an effector T-cell gene signature may distinguish immunologically distinct and clinically relevant lymphoma subsets. Blood Adv. 2017, 22, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, R.; Angori, S.; Batavia, A.A.; Rupp, N.J.; Ajioka, Y.; Schraml, P.; Moch, H. Loss of CDKN1A mRNA and protein expression are independent predictors of poor outcome in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancers 2020, 12, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; Wienert, S.; Poterie, A.; Loibl, S.; Budczies, J.; Badve, S.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Bane, A.; Bedri, S.; Brock, J.; et al. Standardized evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: Results of the ring studies of the international immuno-oncology biomarker working group. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, E.; Long, J.; Hu, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Tang, F.; Li, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Zeng, Z. Immune infiltration in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidegger, I.; Pircher, A.; Pichler, R. Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment in Renal Cell Cancer Biology and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brück, O.; Lee, M.H.; Turkki, R.; Uski, I.; Penttilä, P.; Paavolainen, L.; Kovanen, P.; Järvinen, P.; Bono, P.; Pellinen, T.; et al. Spatial immunoprofiling of the intratumoral and peritumoral tissue of renal cell carcinoma patients. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 2229–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, J.; Ohe, C.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroda, N.; Saito, R.; Kinoshita, H.; Tsuta, K.; Matsuda, T. Comprehensive pathological assessment of histological subtypes, molecular subtypes based on immunohistochemistry, and tumor-associated immune cell status in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Pathol. Int. 2021, 71, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.; Xu, B.; Satkunasivam, R.; Downes, M.R. Tumour front inflammation and necrosis are independent prognostic predictors in high-grade urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, O.; Sato, M.; Naito, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Orikasa, S.; Aizawa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Shintaku, I.; Nagura, H.; Ohtani, H. Proliferative activity of intratumoral CD8(+) T-lymphocytes as a prognostic factor in human renal cell carcinoma: Clinicopathologic demonstration of antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5132–5136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, N.A.; Becht, E.; Pagès, F.; Skliris, G.; Verkarre, V.; Vano, Y.; Mejean, A.; Saint-Aubert, N.; Lacroix, L.; Natario, I.; et al. Orchestration and Prognostic Significance of Immune Checkpoints in the Microenvironment of Primary and Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3031–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giraldo, N.A.; Becht, E.; Vano, Y.; Petitprez, F.; Lacroix, L.; Validire, P.; Sanchez-Salas, R.; Ingels, A.; Oudard, S.; Moatti, A.; et al. Tumor-Infiltrating and Peripheral Blood T-cell Immunophenotypes Predict Early Relapse in Localized Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4416–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbois, M.; Udyavar, A.R.; Ryner, L.; Kozlowski, C.; Guan, Y.; Dürrbaum, M.; Lu, S.; Fortin, J.P.; Koeppen, H.; Ziai, J.; et al. Integrated digital pathology and transcriptome analysis identifies molecular mediators of T-cell exclusion in ovarian cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuselinck, B.; Job, S.; Becht, E.; Karadimou, A.; Verkarre, V.; Couchy, G.; Giraldo, N.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Molinié, V.; Sibony, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of clear cell renal cell carcinoma are associated with sunitinib response in the metastatic setting. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakouny, Z.; Braun, D.A.; Shukla, S.A.; Pan, W.; Gao, X.; Hou, Y.; Flaifel, A.; Tang, S.; Bosma-Moody, A.; He, M.X.; et al. Integrative molecular characterization of sarcomatoid and rhabdoid renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Three-tier immunophenotype | Based on the location of TAICs, regardless of the TAICs degree | |||
| Desert | Excluded | Inflamed | ||
| No TAICs | Peritumoral TAICs | Intratumoral TAICs | ||
| Four-tier immunophenotype | Considering both the location and degree of TAICs | |||
| Cold | Immunosuppressed | Excluded | Hot | |
| No TAICs | Focal or low TAICs, regardless of the TAICs location | Diffuse or high peritumoral TAICs | Diffuse or high intratumoral TAICs | |
| Inflammation score | Based on the degree of TAICs, regardless of the TAICs location | |||
| Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 | ||
| No TAICs | Focal or low TAICs | Diffuse or high TAICs | ||
| Variables | Principal Cohort n = 436 | TCGA Cohort n = 162 | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three-tier immunophenotype, n (%) | 0.029 | ||
| Desert | 243 (55.7) | 75 (46.3) | |
| Excluded | 91 (20.9) | 32 (19.8) | |
| Inflamed | 102 (23.4) | 55 (34.0) | |
| Four-tier immunophenotype, n (%) | 0.003 | ||
| Cold | 243 (55.7) | 75 (46.3) | |
| Immunosuppressed | 127 (29.1) | 67 (41.4) | |
| Excluded | 35 (8.0) | 4 (2.5) | |
| Hot | 31 (7.1) | 16 (9.9) | |
| Inflammation score, n (%) | 0.018 | ||
| Score 0 | 243 (55.7) | 75 (46.3) | |
| Score 1 | 127 (29.1) | 67 (41.4) | |
| Score 2 | 66 (15.1) | 20 (12.3) |
| Cohort | Principal Cohort | TCGA Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Three-tier immunophenotype | Desert | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | ||
| Excluded | 5.23 (2.63–10.39) | <0.001 | 3.93 (2.05–7.54) | <0.001 | |
| Inflamed | 4.44 (2.23–8.81) | <0.001 | 3.10 (1.66–5.79) | <0.001 | |
| Four-tier immunophenotype | Cold | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | ||
| Immunosuppressed | 3.87 (1.97–7.59) | <0.001 | 2.94 (1.62–5.36) | <0.001 | |
| Excluded | 7.60 (3.47–16.7) | <0.001 | 8.49 (2.79–25.9) | <0.001 | |
| Hot | 5.82 (2.41–14.1) | <0.001 | 5.20 (2.38–11.4) | <0.001 | |
| Inflammation score | Score 0 | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | ||
| Score 1 | 3.87 (1.97–7.59) | <0.001 | 2.94 (1.62–5.36) | <0.001 | |
| Score 2 | 6.77 (3.37–13.6) | <0.001 | 5.79 (2.82–11.9) | <0.001 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohe, C.; Yoshida, T.; Ikeda, J.; Tsuzuki, T.; Ohashi, R.; Ohsugi, H.; Atsumi, N.; Yamaka, R.; Saito, R.; Yasukochi, Y.; et al. Histologic-Based Tumor-Associated Immune Cells Status in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Gene Signatures Related to Cancer Immunity and Clinical Outcomes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020323
Ohe C, Yoshida T, Ikeda J, Tsuzuki T, Ohashi R, Ohsugi H, Atsumi N, Yamaka R, Saito R, Yasukochi Y, et al. Histologic-Based Tumor-Associated Immune Cells Status in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Gene Signatures Related to Cancer Immunity and Clinical Outcomes. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020323
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhe, Chisato, Takashi Yoshida, Junichi Ikeda, Toyonori Tsuzuki, Riuko Ohashi, Haruyuki Ohsugi, Naho Atsumi, Ryosuke Yamaka, Ryoichi Saito, Yoshiki Yasukochi, and et al. 2022. "Histologic-Based Tumor-Associated Immune Cells Status in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Gene Signatures Related to Cancer Immunity and Clinical Outcomes" Biomedicines 10, no. 2: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020323
APA StyleOhe, C., Yoshida, T., Ikeda, J., Tsuzuki, T., Ohashi, R., Ohsugi, H., Atsumi, N., Yamaka, R., Saito, R., Yasukochi, Y., Higasa, K., Kinoshita, H., & Tsuta, K. (2022). Histologic-Based Tumor-Associated Immune Cells Status in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Correlates with Gene Signatures Related to Cancer Immunity and Clinical Outcomes. Biomedicines, 10(2), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020323







