Delphi-Based Consensus on Interstitial Lung Disease Screening in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases (Croatian National-Based Study)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dahani, A.; Arain, S.-R.; Riaz, A.; Khan, F.; Jabeen, R. Prevalence and Pattern of Pulmonary Manifestation in Patients with Connective Tissue Disorder. Cureus 2020, 12, e7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lauretis, A.; Veeraraghavan, S.; Renzoni, E. Review series: Aspects of interstitial lung disease: Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: How does it differ from IPF? How should the clinical approach differ? Chron. Respir. Dis. 2011, 8, 53–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graney, B.A.; Fischer, A. Advocating for early interstitial lung disease detection in mixed connective tissue disease. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyldgaard, C.; Hilberg, O.; Pedersen, A.-B.; Ulrichsen, S.-P.; Løkke, A.; Bendstrup, E.; Ellingsen, T. A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Comorbidity and mortality. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, K.; Solomon, J.-J.; Olson, A.; Kong, A.-M.; Cole, A.-L.; Fischer, A.; Swigris, J.-J. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease in the United States: Prevalence, Incidence, and Healthcare Costs and Mortality. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadura, S.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease: Manifestations and current concepts in pathogenesis and management. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhong, Y.-J.; Wang, G.-F. Prevalence of interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis: A meta-analysis from 2000 to 2020. Semin. Arthritis. Rheum. 2021, 51, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N.; Cavazza, A.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Interstitial lung disease in Sjögren’s syndrome: A clinical review. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S126), 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, T.; Shi, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Shu, J.; Alqalyoobi, S.; Zeki, A.A.; Leung, P.S.; Shuai, Z. Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease: A Common Lesion With Heterogeneous Mechanisms and Treatment Considerations. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.-A.; Lee, J.S.; Ebstein, E.; Furukawa, H.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Gazal, S.; Kannengiesser, C.; Ottaviani, S.; Oka, S.; Tohma, S.; et al. Promoter Variant and Rheumatoid Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juge, P.; Borie, R.; Kannengiesser, C.; Gazal, S.; Revy, P.; Wemeau-Stervinou, L.; Debray, M.; Ottaviani, S.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Nathan, N.; et al. Shared Genetic Predisposition in Rheumatoid Arthritis–Interstitial Lung Disease and Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis. In Proceedings of the Abstracts Accepted for Publication; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. and European League Against Rheumatism: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Migita, K.; Nakamura, T.; Koga, T.; Eguchi, K. HLA-DRB1 Alleles and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Related Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Furukawa, H.; Oka, S.; Shimada, K.; Sugii, S.; Ohashi, J.; Matsui, T.; Ikenaka, T.; Nakayama, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Takaoka, H.; et al. Association of Human Leukocyte Antigen with Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Protective Role for Shared Epitope. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mori, S.; Koga, Y.; Sugimoto, M. Different Risk Factors between Interstitial Lung Disease and Airway Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Res. Med. 2012, 106, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorlova, O.; Martin, J.-E.; Rueda, B.; Koeleman, B.P.C.; Ying, J.; Teruel, M.; Diaz-Gallo, L.-M.; Broen, J.C.; Vonk, M.C.; Simeon, C.P.; et al. Identification of Novel Genetic Markers Associated with Clinical Phenotypes of Systemic Sclerosis through a Genome-Wide Association Strategy. PLoS Genet 2011, 7, e1002178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, D.D.; Kung, T.N.; Siannis, F.; Pellett, F.; Farewell, V.T.; Lee, P. HLA Markers for Susceptibility and Expression in Scleroderma. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simeón, C.P.; Fonollosa, V.; Tolosa, C.; Palou, E.; Selva, A.; Solans, R.; Armadans, L.; Moreno, E.; Marsal, S.; Vilardell, M. Association of HLA Class II Genes with Systemic Sclerosis in Spanish Patients. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2733–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikly, M.; Rands, A.; McHugh, N.; Wordsworth, P.; Welsh, K. Human Leukocyte Antigen Class II Associations with Systemic Sclerosis in South Africans. Tissue Antigens 2004, 63, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Yi, L.; Guo, G.; Tu, W.; Wu, W.; Yang, L.; Xiao, R.; Li, Y.; Chu, H.; et al. Association of HLA-DPB1 with Scleroderma and Its Clinical Features in Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odani, T.; Yasuda, S.; Ota, Y.; Fujieda, Y.; Kon, Y.; Horita, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Atsumi, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Koike, T. Up-Regulated Expression of HLA-DRB5 Transcripts and High Frequency of the HLA-DRB5*01:05 Allele in Scleroderma Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossini-Castillo, L.; Simeon, C.P.; Beretta, L.; Broen, J.C.; Vonk, M.C.; Ríos-Fernández, R.; Espinosa, G.; Carreira, P.; Camps, M.T.; Castillo, M.J.; et al. A Multicenter Study Confirms CD226 Gene Association with Systemic Sclerosis-Related Pulmonary Fibrosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, M.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Fatini, C.; Guiducci, S.; Cuomo, G.; Bonino, C.; Bazzichi, L.; Liakouli, V.; Giacomelli, R.; Abbate, R.; et al. Association of a Functional Polymorphism in the Matrix Metalloproteinase-12 Promoter Region with Systemic Sclerosis in an Italian Population. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sumita, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Baba, S.; Soejima, M.; Murakawa, Y.; Hara, M.; Kamatani, N. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Surfactant Proteins in Systemic Sclerosis in Japanese: T/T Genotype at 1580 C/T (Thr131Ile) in the SP-B Gene Reduces the Risk of Interstitial Lung Disease. Rheumatology 2007, 47, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoshino, K.; Satoh, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kuwana, M. Association of Hepatocyte Growth Factor Promoter Polymorphism with Severity of Interstitial Lung Disease in Japanese Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieudé, P.; Bouaziz, M.; Guedj, M.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Müller, M.; Cusi, D.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Melchers, I.; Koenig, W.; et al. Evidence of the Contribution of the X Chromosome to Systemic Sclerosis Susceptibility: Association with the Functional IRAK1 196Phe/532Ser Haplotype. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3979–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredemeier, M.; Artur Bogo Chies, J.; Wieck, A.; Gatz Capobianco, K.; Hennemann Pitrez, E.; Eduardo Paim Rohde, L.; Fernando Furlan Pinotti, A.; Carlos Tavares Brenol, J.; Machado Xavier, R. TCRBV20S1 and TCRBV3S1 Gene Segment in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, R.; Mayes, M.D.; Tan, F.K.; Gorlova, O.Y.; Hummers, L.K.; Shah, A.A.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Martin, J.; Bossini-Castillo, L.; et al. IRF5 Polymorphism Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinoy, H.; Salway, F.; Fertig, N.; Shephard, N.; Tait, B.D.; Thomson, W.; Isenberg, D.A.; Oddis, C.V.; Silman, A.J.; Ollier, W.E.; et al. In Adult Onset Myositis, the Presence of Interstitial Lung Disease and Myositis Specific/Associated Antibodies Are Governed by HLA Class II Haplotype, Rather Than by Myositis Subtype. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gono, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kuwana, M.; Sugiura, T.; Furuya, T.; Takagi, K.; Ichida, H.; Katsumata, Y.; Hanaoka, M.; Ota, Y.; et al. Brief Report: Association of HLA-DRB1*0101/*0405 with Susceptibility to Anti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Gene 5 Antibody-Positive Dermatomyositis in the Japanese Population. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3736–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegunsoye, A.; Vij, R.; Noth, I. Integrating Genomics Into Management of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest 2019, 155, 1026–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarnani, R.; Yeoh, S.-A.; Denneny, E.K.; Wincup, C. Lupus and the Lungs: The Assessment and Management of Pulmonary Manifestations of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 610257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchi, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Therapeutic Options for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Connective Tissue Diseases. A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Hino, T.; Hwang, J.; Franks, T.-J.; Han, J.; Im, Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Chung, M.-P.; Hatabu, H.; Chung, M.P.; et al. Connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD) and interstitial lung abnormality (ILA): Evolving concept of CT findings, pathology and management. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2022, 9, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansey, D.; Wells, A.-U.; Colby, T.-V.; Ip, S.; Nikolakoupolou, A.; du Bois, R.-M.; Hansell, D.-M.; Nicholson, A.-G. Variations in histological patterns of interstitial pneumonia between connective tissue disorders and their relationship to prognosis. Histopathology 2004, 44, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, J.J.; Fischer, A. Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Focused Review. J. Intensive. Care. Med. 2015, 30, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez, J.; Aburto, M.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Bonilla, G.; Acosta, O.; Candelas, G.; Cano-Jiménez, E.; Castellví, I.; González-Ruiz, J.M.; Corominas, H.; et al. Screening criteria for interstitial lung disease associated to rheumatoid arthritis: Expert proposal based on Delphi methodology. Reumatol. Clin. 2022, S2173-5743(22)00095-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Gruden, J.; Tazelaar, H.-D.; Leslie, K.-O. Pleuropulmonary pathology in patients with rheumatic disease. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, N.; Sathananthan, M. Connective Tissue Disease-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: Prevalence, Patterns, Predictors, Prognosis, and Treatment. Lung 2020, 198, 735–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira-Avendano, I.; Abril, A.; Burger, C.-D.; Dellaripa, P.-F.; Fischer, A.; Gotway, M.-B.; Lee, A.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Matteson, E.-L.; Yi, E.S.; et al. Interstitial Lung Disease and Other Pulmonary Manifestations in Connective Tissue Diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote-Corral, S.; Silva-Fernández, L.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Guerra-Rodríguez, M.; Aburto, M.; Castañeda, S.; Valenzuela, C.; Narváez, J. Screening of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Reumatol. Clin. 2021, 18, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargani, L.; Romei, C.; Bruni, C.; Lepri, G.; El-Aoufy, K.; Orlandi, M.; D’Errico, L.; Bandini, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Guiducci, S.; et al. Lung ultrasound B-lines in systemic sclerosis: Cut-off values and methodological indications for interstitial lung disease screening. Rheumatology 2022, 61, SI56–SI64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
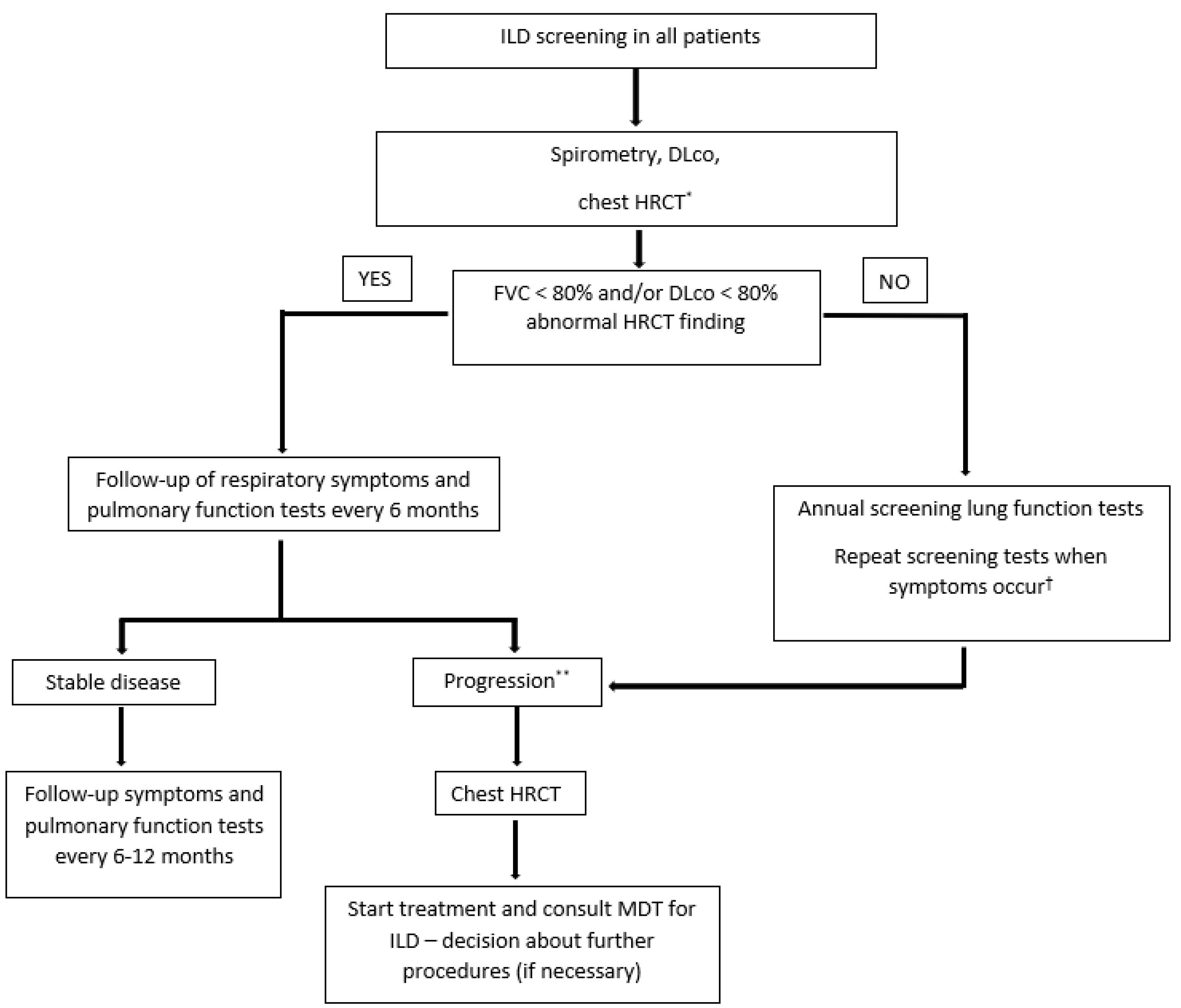
| Question | Consensus (n = 14) |
|---|---|
| 1. Should patients with newly diagnosed MCTD/SSc be referred to initial consultations for ILD screening (HRCT)? | Patients should be referred for ILD screening (n = 14) |
| 2. If you answered the previous question with yes, based on clinical judgment which of the following is important/essential in deciding on HRCT? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 13) Symptoms, i.e., exertional dyspnea (n = 11) |
| 3. If the patient does not have ILD (or other pulmonary pathology) on HRCT, how should possible ILD development be monitored in the patient? | Disease progression should be monitored by HRCT based on clinical judgment (n = 12) |
| 4. If you answered HRCT should be repeated based on clinical judgment, which of the following parameters should be taken into consideration when deciding? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 10) Symptoms, i.e., new onset of exertional dyspnea (n = 10) |
| 5. In a patient with MCTD/SSc and confirmed ILD, should HRCT be repeated during follow-up? | Disease progression should be monitored by HRCT based on clinical judgment (n = 12) |
| 6. If you answered HRCT should be repeated based on clinical judgment, which of the following parameters should be taken into consideration when deciding? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 11) Symptoms, i.e., new onset of exertional dyspnea (n = 9) |
| Question | Consensus (n = 14) |
|---|---|
| 1. Should patients with newly diagnosed pSS/SLE be referred to initial consultations for ILD screening (HRCT)? | Patients should be referred for ILD screening (n = 13) |
| 2. If you answered the previous question with yes, based on clinical judgment which of the following is important/essential in deciding on HRCT? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 13) Symptoms, i.e., exertional dyspnea or dry cough (n = 12) |
| 3. If the patient does not have ILD (or other pulmonary pathology) on HRCT, how should possible ILD development be monitored in the patient? | Disease progression should be monitored by HRCT based on clinical judgment (n = 13) |
| 4. If you answered HRCT should be repeated based on clinical judgment, which of the following parameters should be taken into consideration when deciding? | Symptoms, i.e., new onset of dry cough (n = 12) Pulmonary function tests (n = 10) |
| 5. In a patient with pSS/SLE and confirmed ILD, should HRCT be repeated during follow-up? | Disease progression should be monitored by HRCT based on clinical judgment (n = 14) |
| 6. If you answered HRCT should be repeated based on clinical judgment, which of the following parameters should be taken into consideration when deciding? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 13) Symptoms, i.e., new onset of exertional dyspnea or dry cough (n = 11) |
| Question | Consensus (n = 14) |
|---|---|
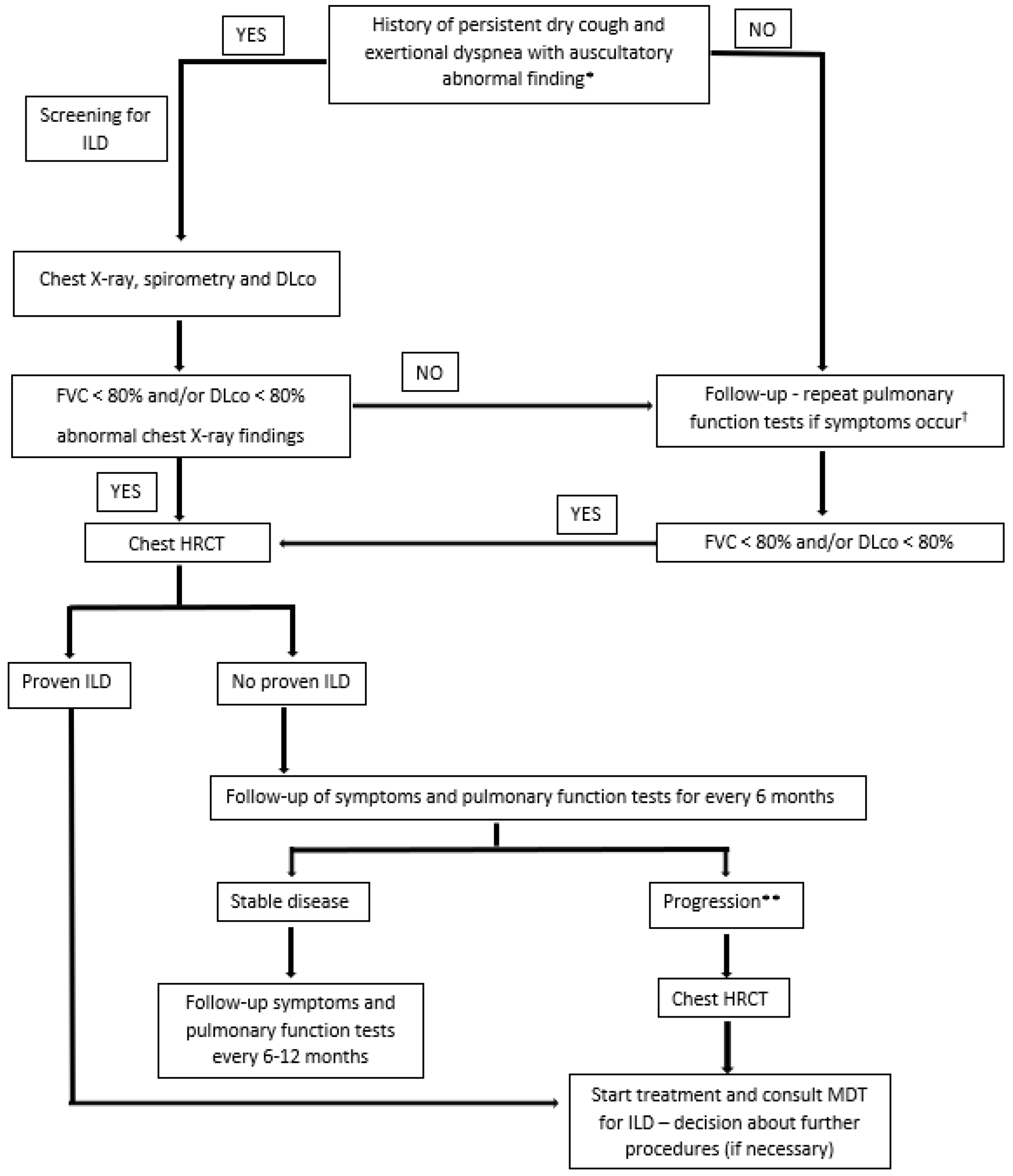
| 1. Should patients with newly diagnosed RA be referred for mandatory ILD screening? | Patients should be referred for screening (n = 14) |
| 2. What is the most important clinical symptom in newly diagnosed RA patients indicating to ILD? | Exertional dyspnea (n = 13) Persistent dry cough (n = 12) |
| 3. What is the most important screening test for ILD in newly diagnosed RA patients? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 14) |
| 4. What are the most relevant pulmonary function test results for ILD screening? | DLco < 80% of predictive value (n = 14) FVC < 80% of predictive value (n = 13) |
| 5. What test should be considered crucial for follow-up in RA patients with confirmed ILD? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 14) Clinical examination (n = 10) HRCT (n = 8) |
| 6. What should be considered crucial for follow-up in RA patients without confirmed ILD? | Clinical monitoring (n = 13) |
| 7. How often should chest X-ray be repeated in stable RA-ILD patients? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 9) |
| 8. How often should pulmonary function tests be repeated in stable RA-ILD patients? | Every 6–12 months (n = 12) |
| 9. How often should HRCT be repeated in stable RA-ILD patients? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 13) |
| 10. How often should chest X-ray be repeated in stable RA patients without confirmed ILD? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 13) |
| 11. How often should pulmonary function tests be repeated in stable RA patients without confirmed ILD? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 9) Every 12 months (n = 5) |
| 12. How often should HRCT be repeated in stable RA patients without confirmed ILD? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 12) |
| Question | Consensus (n = 14) |
|---|---|
| 1. Should patients with newly diagnosed IIM be referred for mandatory ILD screening? | Patients should be referred for screening (n = 13) |
| 2. What is the most important clinical symptom in newly diagnosed IIM patients indicating to ILD? | Persistent dry cough (n = 12) Exertional dyspnea (n = 11) |
| 3. What is the most important screening test for ILD in newly diagnosed IIM patients? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 14) Serological test (n = 13) Clinical examination (n = 11) |
| 4. What are the most relevant pulmonary function test results for ILD screening? | DLco < 80% of predictive value (n = 14) FVC < 80% of predictive value (n = 13) |
| 5. What test should be considered crucial for follow-up in IIM patients with confirmed ILD? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 14) Clinical examination (n = 10) HRCT (n = 8) |
| 6. What should be considered crucial for follow-up in IIM patients without confirmed ILD? | Pulmonary function tests (n = 13) Clinical monitoring (n = 11) |
| 7. How often should chest X-ray be repeated in stable IIM-ILD patients? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 9) |
| 8. How often should pulmonary function tests be repeated in stable IIM-ILD patients? | Every 6–12 months (n = 14) |
| 9. How often should HRCT be repeated in stable IIM-ILD patients? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 13) |
| 10. How often should chest X-ray be repeated in stable IIM patients without confirmed ILD? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 13) Every 12 months (n = 3) |
| 11. How often should pulmonary function tests be repeated in stable IIM patients without confirmed ILD? | Every 12 months (n = 10) In case of symptom worsening (n = 3) |
| 12. How often should HRCT be repeated in stable IIM patients without confirmed ILD? | In case of symptom worsening (n = 13) |
| Disease | Susceptibility Genes | Autoantibodies and Serological Immune Markers |
|---|---|---|
| RA-ILD [10,11,12,13,14,15,16] | DRB1 * 16:02, DRB1 * 15:02 TERT, RTEL1, PARN or SFTPC MUC5B | RF anti-CCP |
| SSc-ILD [10,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] | HLA-B * 62, HLA-C * 06, DRB1 * 11 DPB1 * 03:01, DR51 CD226, MMP12, SFTPB, CTGF, HGF, IRAK1, TCRBV, IRF5 CD247 | anti-Scl-70 anti-U3RNP anti-U11/U12RNP anti-RuvBL1/2 anti-EIF2B anti-PM-Scl anti-U1RNP anti-cardiolipin anti-Th/To anti-Ro52 anti-NOR90 nucleolar ANA ANCA |
| PM/DM-ILD [10,30,31] | DRB1 * 03, DRB1 * 01:01, DRB1 * 04:05 DQB1 * 06:02 | MSAs anti-Jo-1 anti-PL-12 anti-PL-7 anti-KS anti-OJ anti-EJ anti-Zo anti-Ku anti-MDA5 MAAs anti-Ro52/60 anti-U1RNP |
| MCTD-ILD [10,32] | TERC, TERT | Anti-U1RNP CIC C3 CH50 |
| pSS-ILD [10] | anti-SSA/Ro anti-SSB/La | |
| SLE-ILD [33] | anti-La anti-Scl-70 anti-U1RNP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radić, M.; Novak, S.; Barešić, M.; Hećimović, A.; Perković, D.; Tekavec-Trkanjec, J.; Mayer, M.; Prus, V.; Morović-Vergles, J.; Marasović Krstulović, D.; et al. Delphi-Based Consensus on Interstitial Lung Disease Screening in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases (Croatian National-Based Study). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123291
Radić M, Novak S, Barešić M, Hećimović A, Perković D, Tekavec-Trkanjec J, Mayer M, Prus V, Morović-Vergles J, Marasović Krstulović D, et al. Delphi-Based Consensus on Interstitial Lung Disease Screening in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases (Croatian National-Based Study). Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123291
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadić, Mislav, Srđan Novak, Marko Barešić, Ana Hećimović, Dijana Perković, Jasna Tekavec-Trkanjec, Miroslav Mayer, Višnja Prus, Jadranka Morović-Vergles, Daniela Marasović Krstulović, and et al. 2022. "Delphi-Based Consensus on Interstitial Lung Disease Screening in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases (Croatian National-Based Study)" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123291
APA StyleRadić, M., Novak, S., Barešić, M., Hećimović, A., Perković, D., Tekavec-Trkanjec, J., Mayer, M., Prus, V., Morović-Vergles, J., Marasović Krstulović, D., Cerovec, M., Bulat Kardum, L., Samaržija, M., & Anić, B. (2022). Delphi-Based Consensus on Interstitial Lung Disease Screening in Patients with Connective Tissue Diseases (Croatian National-Based Study). Biomedicines, 10(12), 3291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123291








