Oxaliplatin-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Single Institution Series and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, Y.-Y.; Hu, F.-C.; Liang, J.-T.; Chiu, W.-T.; Cheng, A.-L.; Yang, C.-H. Characteristics and risk factors of oxaliplatin-related hypersensitivity reactions. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2010, 109, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, B.B.; Cuddahy, T.; Briscella, C.; Ross, N.; Olszanski, A.; Denlinger, C.S. Oxaliplatin: Detection and Management of Hypersensitivity Reactions. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 23, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Bradley, T.; Tai, J.; Budman, D.R. Hypersensitivity to oxaliplatin: An investigation of incidence and risk factors and literature review. Oncology 2009, 76, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Huang, R.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Shangguan, X.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Yin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D. Safety Profile of Oxaliplatin in 3,687 Patients With Cancer in China: A Post-Marketing Surveillance Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 757196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, M.R.; Sun, W. Oxaliplatin-associated hypersensitivity reactions: Clinical presentation and management. Clin. Color. Cancer 2006, 6, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palapinyo, S.; Klaewsongkram, J.; Sriuranpong, V.; Areepium, N. Incidence of oxaliplatin hypersensitivity reaction among colorectal cancer patients: A 5-year retrospective study. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 20, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, T.; Iwasa, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Kato, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Yamada, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Successful Rechallenge for Oxaliplatin Hypersensitivity Reactions in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, M.W. Hypersensitivity reactions associated with oxaliplatin. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2006, 5, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrigou, E.; Makrilia, N.; Koti, I.; Saif, M.W.; Syrigos, K.N. Hypersensitivity reactions to antineoplastic agents: An overview. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, M.; Sancho-Serra, M.D.C.; Simarro, M. Hypersensitivity to antineoplastic agents: Mechanisms and treatment with rapid desensitization. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, B.; Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Efficacy and safety of oxaliplatin-based regimen versus cisplatin-based regimen in the treatment of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 24, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroldi, F.; Prochilo, T.; Bertocchi, P.; Zaniboni, A. Oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity reaction: Underlying mechanisms and management. J. Chemother. 2015, 27, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syrigou, E.; Syrigos, K.; Saif, M.W. Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin and other antineoplastic agents. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008, 8, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, N.; Najam, R.; Qazi, F.; Mateen, A. Clinical Features of Oxaliplatin Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions and Therapeutic Approaches. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parel, M.; Ranchon, F.; Nosbaum, A.; You, B.; Vantard, N.; Schwiertz, V.; Gourc, C.; Gauthier, N.; Guedat, M.-G.; He, S.; et al. Hypersensitivity to oxaliplatin: Clinical features and risk factors. BMC Pharmacol. Toxic. 2014, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maindrault-Goebel, F.; André, T.; Tournigand, C.; Louvet, C.; Perez-Staub, N.; Zeghib, N.; De Gramont, A. Allergic-type reactions to oxaliplatin: Retrospective analysis of 42 patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2262–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, A.; Tsavaris, N.; Gogas, H.; Souglakos, J.; Vambakas, L.; Vardakas, N.; Polyzos, K.; Tsigris, C.; Mantas, D.; Papachristodoulou, A.; et al. Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: A 10-year experience. Oncology. 2009, 76, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.A.; Segal, N.H.; Cercek, A.; Yaeger, R.; Stadler, Z.; Kemeny, N.E.; Nusrat, M.; Shahrokni, A.; Connell, L.; Saltz, L.B. Simplified Graded Infusion Strategy for Mitigation of Oxaliplatin Hypersensitivity. Clin. Color. Cancer 2022, 21, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Park, K.H.; Lee, C.; Kang, B.; Beom, S.-H.; Shin, S.J.; Jung, M.; et al. A New Practical Desensitization Protocol for Oxaliplatin-Induced Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Necessary and Useful Approach. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 26, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 5.0. Published 27 November 2017. 2020. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcae_v5_quick_reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Thomas, R.R.; Quinn, M.G.; Schuler, B.; Grem, J.L. Hypersensitivity and idiosyncratic reactions to oxaliplatin. Cancer 2003, 97, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, S.W.K.; Chan, R.T.T.; Au, G.K.H. Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: Experience in a single institute. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 17, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bautista, M.; Stevens, W.T.; Chen, C.-S.; Curtis, B.R.; Aster, R.H.; Hsueh, C.-T. Hypersensitivity reaction and acute immune-mediated thrombocytopenia from oxaliplatin: Two case reports and a review of the literature. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 26, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandi, G.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Galli, C.; Falcone, A.; Antonuzzo, A.; Mordenti, P.; Di Marco, M.C.; Biasco, G. Hypersensitivity reactions related to oxaliplatin (OHP). Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, K.-H.; Kang, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-H.; Han, S.-W.; Kang, H.-R. Incidence and Risk of Oxaliplatin-Induced Hypersensitivity in Patients with Asymptomatic Prior Exposure: A Prospective Observational Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1642–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Kitano, T.; Yoshimura, K.-I.; Matsumoto, S.; Kanai, M.; Hazama, M.; Ishiguro, H.; Nagayama, S.; Yanagihara, K.; et al. Oxaliplatin-free interval as a risk factor for hypersensitivity reaction among colorectal cancer patients treated with FOLFOX. Oncology 2010, 79, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couraud, S.; Planus, C.; Rioufol, C.; Mornex, F. Hypersensibilité aux sels de platine. Rev. De Pneumol. Clin. 2008, 64, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Hacker, U.T.; Kern, W.; Schalhorn, A.; Hiddemann, W. Adverse reactions to oxaliplatin: A retrospective study of 25 patients treated in one institution. Anticancer Drugs 2003, 14, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Sugatani, K.; Yoshida, N.; Kokura, S.; Matsuda, K.; Tsukamoto, S.; Ihara, N.; Kuriu, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: Identifying the risk factors and judging the efficacy of a desensitization protocol. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Aravind, S.; Nalysnyk, L.; Ranganathan, M.G. Dose Delay Amongst Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy. Blood 2008, 112, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló, S.; Blasco, I.; Fabregat, L.G.; Cervantes, A.; Jordan, K. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of infusion reactions to systemic anticancer therapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S4), 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, A.; Goel, R.; Berdzik, J.; Leichman, C.G.; Javle, M. Hypersensitivity Reactions to oxaliplatin: Incidence and management. Oncology 2004, 18, 1671–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg, S.; Disler, C.; Perego, P. The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.J. The complexity of drug hypersensitivity reactions. Allergy 2021, 76, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rébé, C.; Demontoux, L.; Pilot, T.; Ghiringhelli, F. Platinum Derivatives Effects on Anticancer Immune Response. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.Y.Q.; Yeo, C.H.F.; Ang, W.H. Immuno-chemotherapeutic platinum(IV) prodrugs of cisplatin as multimodal anticancer agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 6752–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, W.J. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantari, C.; Pederzoli-Ribeil, M.; Witko-Sarsat, V. The role of neutrophils and monocytes in innate immunity. Contrib. Microbiol. 2008, 15, 118–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Krempski, J.W.; Nadeau, K. Advances and novel developments in mechanisms of allergic inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Tsuduki, Y.; Ioroi, T.; Yamane, M.; Yamauchi, H.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Nakata, I.; Nishiguchi, K.; Matsubayashi, T.; et al. Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels as a predictive marker of oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions in Japanese patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Study Population | Pts with HSRs | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 153 1 | n = 17 | |
| (100%) | (11%) | |
| Female | 83 (54.3) | 10 (58.8) |
| Male | 70 (45.7) | 7 (41.2) |
| Age, years | 70 (27–87) | 69 (51–82) |
| (median, range) | ||
| Diagnosis | ||
| Colorectal cancer | 108 (70.6) | 14 (82.4) |
| Pancreatic cancer | 12 (7.8) | 1 (5.9) |
| Biliary tract cancer | 6 (3.9) | 2 (11.7) |
| Stomach cancer | 26 (17.0) | 0 (0) |
| Esophagus cancer | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) |
| Chemotherapy regimen | ||
| FOLFOX | 21 (13.7) | 2 (11.7) |
| XELOX | 71 (46.4) | 6 (35.3) |
| FOLFOX + bevacizumab | 17 (11.0) | 1 (5.9) |
| FOLFOX + cetuximab | 2 (1.3) | 2 (11.7) |
| FOLFOX + panitumumab | 13 (8.5) | 2 (11.7) |
| FOLFOX + trastuzumab | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0) |
| FLOT | 6 (3.9) | 0 (0) |
| FOLFIRINOX | 3 (2.0) | 0 (0) |
| FOLFOXIRI + bevacizumab | 4 (2.6) | 2 (11.7) |
| XELOX + bevacizumab | 13 (8.5) | 2 (11.7) |
| XELOX + trastuzumab | 2 (1.3) | 0 (0) |
| Purpose of treatment | ||
| Adjuvant | 65 (42.5) | 3 (17.6) |
| Palliative | 88 (57.5) | 14 (82.4) |
| Prior exposure to platinum salts 2 | ||
| Yes | 30 (19.6) | 8 (47.1) |
| No | 123 (80.4) | 9 (52.9) |
| Number of infusions | ||
| Median (range) | 5 (1–12) | 6 (1–11) |
| Premedication 3 | ||
| Steroids (8 mg) | 13 (8.5) | 2 (11.7) |
| Steroids (12 mg) | 137 (89.5) | 13 (76.5) |
| Steroids (18.8 mg) | 0 (0) | 1 (5.9) |
| Antihistamines (10 mg) | 37 (24.2) | 5 (29.4) |
| Antiemetics | 153 (100) | 17 (100) |
| History of allergic diseases | ||
| Yes | 22 (14.4) | 3 (17.6) |
| No | 131 (85.6) | 14 (82.4) |
| Total Reactions | n = 17 (%) |
|---|---|
| Severity 1 | |
| Grade 1 | 1 (5.9) |
| Grade 2 | 3 (17.6) |
| Grade 3 | 12 (70.6) |
| Grade 4 | 1 (5.9) |
| Grade 5 | 0 (0) |
| Cycle number of event (median, range) | 2 (1–11) |
| Premedication | |
| Steroids | 17 (100) |
| Antihistamines | 5 (29.4) |
| Antiemetics | 17 (100) |
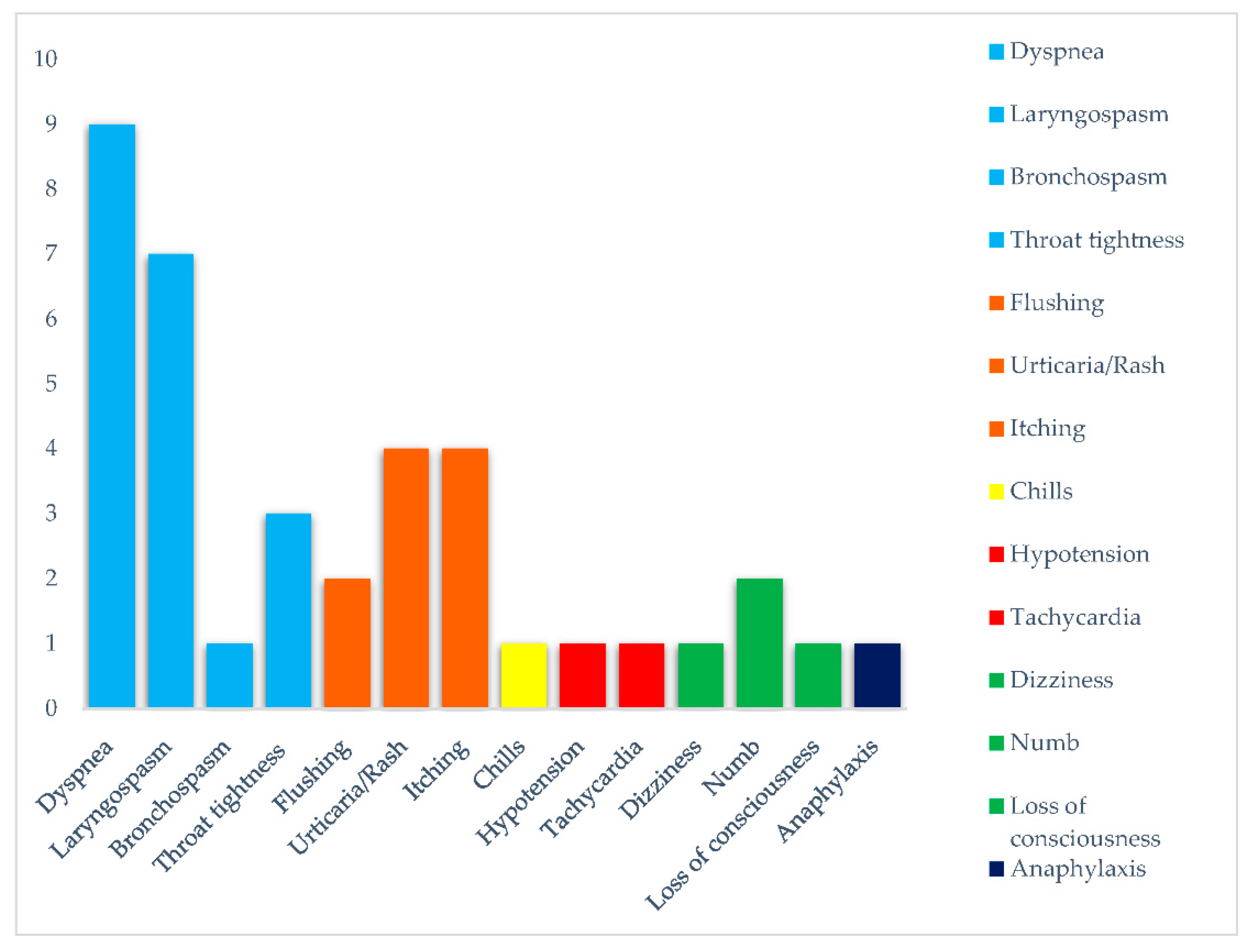
| Symptoms | |
| Respiratory | |
| Dyspnea | 9 (52.9) |
| Laryngospasm | 7 (41.2) |
| Bronchospasm | 1 (5.9) |
| Throat tightness | 3 (17.6) |
| Cutaneous | |
| Flushing | 2 (11.7) |
| Urticaria/rash | 4 (23.5) |
| Itching | 4 (23.5) |
| General | |
| Chills | 1 (5.9) |
| Cardiovascular | |
| Hypotension | 1 (5.9) |
| Tachycardia | 1 (5.9) |
| Neurological | |
| Dizziness | 1 (5.9) |
| Numb | 2 (11.7) |
| Loss of consciousness | 1 (5.9) |
| Anaphylaxis | 1 (5.9) |
| Management of reaction | |
| Infusion interruption | 17 (100) |
| Steroids administration | 14 (82.4) |
| Antihistamines administration | 5 (29.4) |
| Oxygen administration | 3 (17.6) |
| Saline solution administration | 3 (17.6) |
| Epinephrine administration | 1 (5.9) |
| Rechallenge | |
| Yes | 13 (76.5) |
| No | 4 (23.5) |
| Subsequent Reaction | |
| Yes | 6 (46.2) |
| No | 7 (53.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbin, F.; Ghidini, M.; Panichi, A.; Tomasello, G.; Bareggi, C.; Galassi, B.; Denaro, N.; Ruatta, F.; Cauchi, C.; Rossino, M.G.; et al. Oxaliplatin-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Single Institution Series and Literature Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123275
Barbin F, Ghidini M, Panichi A, Tomasello G, Bareggi C, Galassi B, Denaro N, Ruatta F, Cauchi C, Rossino MG, et al. Oxaliplatin-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Single Institution Series and Literature Review. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123275
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbin, Francesca, Michele Ghidini, Alessandra Panichi, Gianluca Tomasello, Claudia Bareggi, Barbara Galassi, Nerina Denaro, Fiorella Ruatta, Carolina Cauchi, Maria Grazia Rossino, and et al. 2022. "Oxaliplatin-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Single Institution Series and Literature Review" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123275
APA StyleBarbin, F., Ghidini, M., Panichi, A., Tomasello, G., Bareggi, C., Galassi, B., Denaro, N., Ruatta, F., Cauchi, C., Rossino, M. G., & Garrone, O. (2022). Oxaliplatin-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Single Institution Series and Literature Review. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3275. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123275








